A Case of Sarcoid-Lymphoma Syndrome with Various Etiological Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
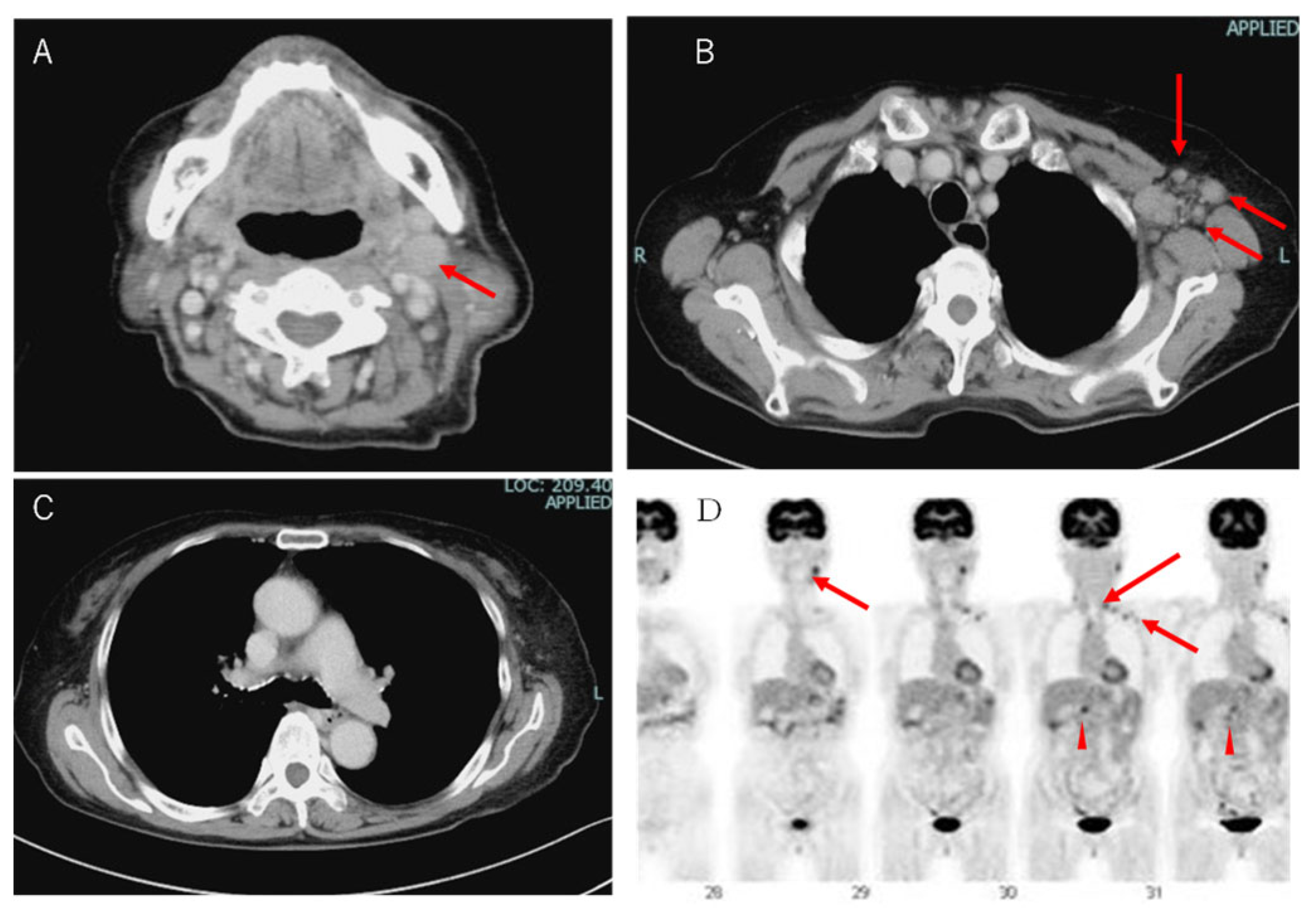
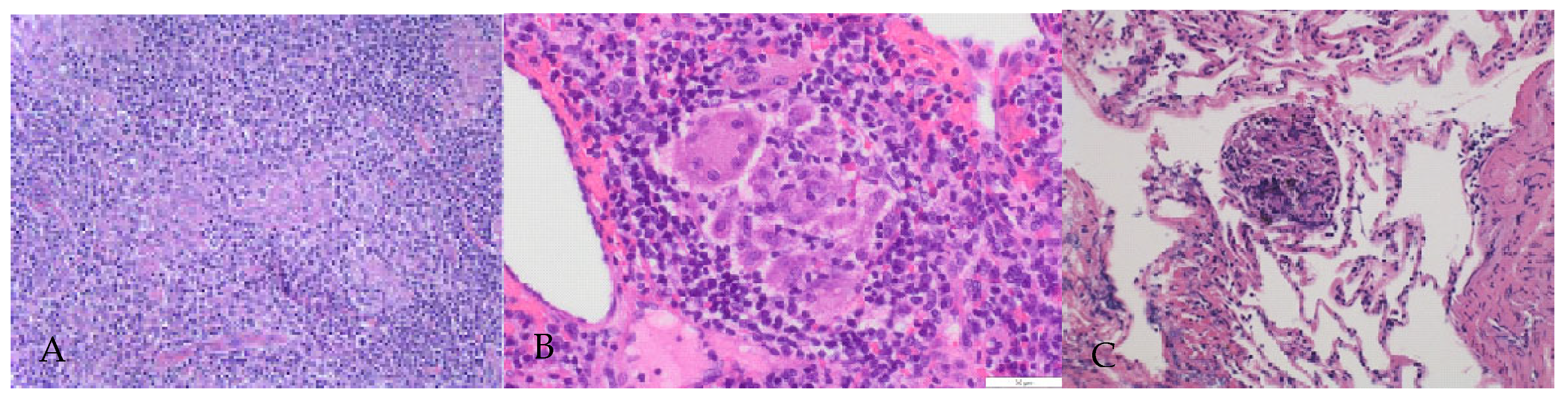
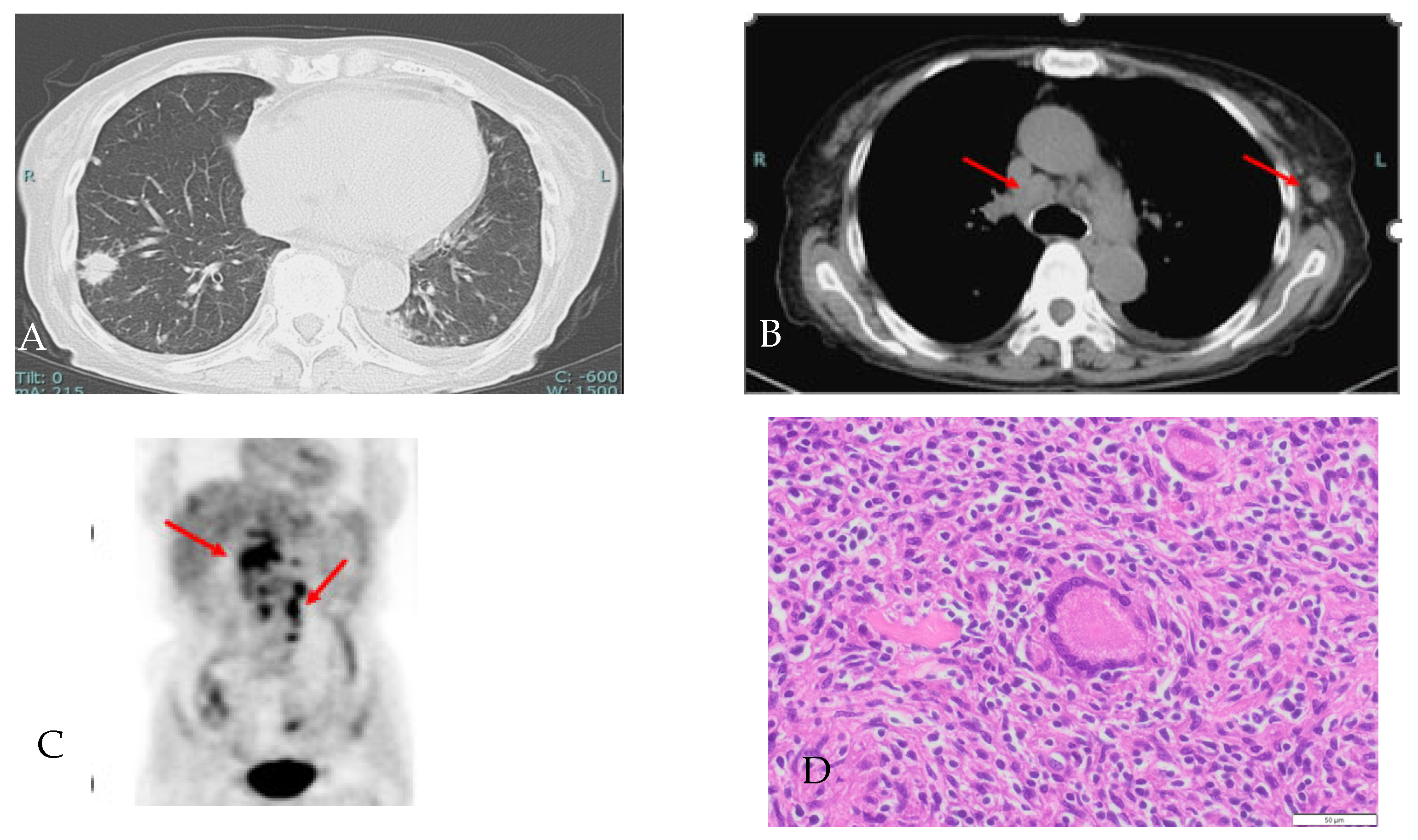
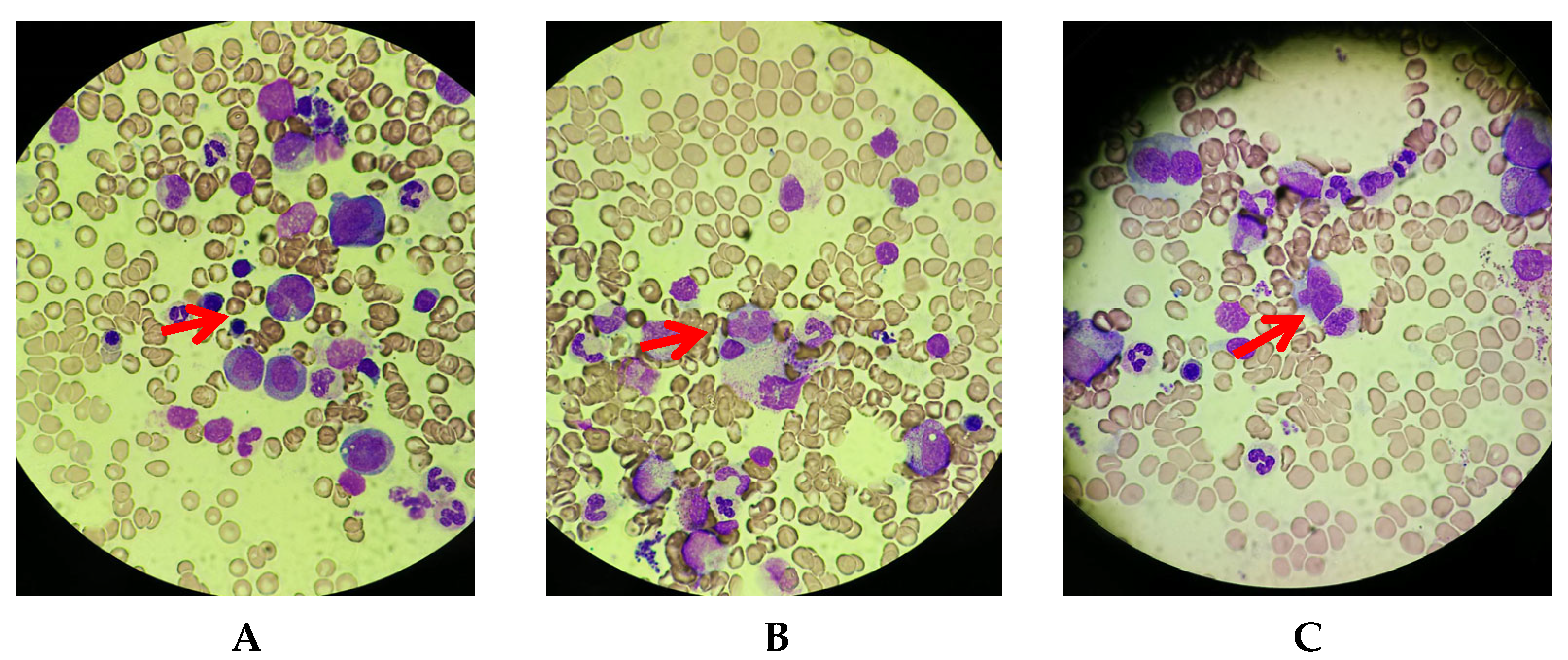
2. Case Presentation Section
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Gal, A.; Koss, M. Reprint of: The pathology of pulmonary sarcoidosis: Update. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 35, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, A.; Knox, K.S. Immunopathogenesis of sarcoidosis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsen, D.; Spilianakis, C.G.; Flavell, R.A. How are TH1 and TH2 effector cells made? Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2009, 21, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, C.; Jäger, B.; Wieczorek, G.; Engelhard, P.; Oliver, S.J.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Littlewood-Evans, A.; Welte, T.; Hornung, V.; Prasse, A. The NLRP3 inflammasome pathway is activated in sarcoidosis and involved in granuloma formation. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagavant, H.; Cizio, K.; Araszkiewicz, A.M.; Papinska, J.A.; Garman, L.; Li, C.; Pezant, N.; Drake, W.P.; Montgomery, C.G.; Deshmukh, U.S. Systemic immune response to vimentin and granuloma formation in a model of pulmonary sarcoidosis. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022, 5, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.X.; Weichhart, T. A fungal antigenic driver for Löfgren’s syndrome sarcoidosis. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20211572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabufetti, A.; Borradori, L.; Heidemeyer, K.; Feldmeyer, L.; Hunger, R.E.; Yawalkar, N.; Seyed Jafari, S.M. New onset of sarcoidosis after COVID-19 infection. J. Eur. Acad. Derm. Venereol. 2022, 36, e756–e759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eishi, Y. Etiologic link between sarcoidosis and Propionibacterium acnes. Respir. Investig. 2013, 51, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starshinova, A.A.; Malkova, A.M.; Basantsova, N.Y.; Zinchenko, Y.S.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Ershov, G.A.; Soprun, L.A.; Mayevskaya, V.A.; Churilov, L.P.; Yablonskiy, P.K. Sarcoidosis as an Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2020, 10, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, H. Sarcoid reaction malignant tumor. Cancer Trat. Rev. 1986, 13, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baster, R.; Birkr, F. Histology of tumour associated sarcoid-like stromal reaction in breast cancer. An analysis of 5 cases with immunohistochemical investigation. Viechows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. Histopathol. 1988, 412, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, P.R.; Kurzrock, R. Sarcoidosis and malignancy. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brincker, H. The sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndrome. Br. J. Cancer 1986, 54, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brincker, H. Sarcoidosis and malignanc. Chest 1995, 108, 1472–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Bella, C.; Soluri, M.F.; Puccio, S.; Benagiano, M.; Grassi, A.; Bitetti, J.; Cianchi, F.; Sblattero, D.; Peano, C.; D’Elios, M.M. The Helicobacter pylori CagY Protein Drives Gastric Th1 and Th17 Inflammation and B Cell Proliferation in Gastric MALT Lymphoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durazzo, M.; Adriani, A.; Fagoonee, S.; Saracco, G.M.; Pellicano, R. Helicobacter pylori and Respiratory Diseases: 2021 Update. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, A.; Brähler, E.; Möde, R.; Wirtz, H.; Bosse-Henck, A. Anxiety and depression in sarcoidosis: The influence of age, gender, affected organs, concomitant diseases and dyspnea. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2012, 29, 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Fan, S.; et al. Meta-analysis of infectious agents and depression. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Alberti, L.; Piattelli, A.; Artese, L.; Favia, G.; Patel, S.; Saunders, N.; Porter, S.R.; Scully, C.M.; Ngui, S.L.; Teo, C.G. Human herpesvirus 8 variants in sarcoid tissues. Lancet 1997, 350, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouser, E.D.; Maier, L.A.; Wilson, K.C.; Bonham, C.A.; Morgenthau, A.S.; Patterson, K.C.; Abston, E.; Bernstein, R.C.; Blankstein, R.; Chen, E.S.; et al. Diagnosis and Detection of Sarcoidosis. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, e26–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalayer, É.; Bachy, E.; Occelli, P.; Weiler, L.; Faurie, P.; Ghesquieres, H.; Pavic, M.; Broussolle, C.; Sève, P. Sarcoidosis and lymphoma: A comparative study. QJM Int. J. Med. 2015, 108, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzghoul, B.N.; Zayed, Y.; Obeidat, A.; Alzghoul, B.; Naser, A.; Shilbayeh, A.R.; Innabi, A.; Al-Hakim, T.; Buchanan, M.; Mehrad, B.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Sarcoidosis Patients with Self-Reported Lymphoma: A US Nationwide Registry Study. Lung 2021, 199, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasazuki, S.; Inoue, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Otani, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ikeda, S.; Hanaoka, T.; Tsugane, S.; Japan Public Health Center Study Group. Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection combined with CagA and pepsinogen status on gastric cancer development among Japanese men and women: A nested case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunninghake, G.W.; Costabel, U.; Ando, M.; Baughman, R.; Cordier, J.F.; du Bois, R.; Eklund, A.; Kitaichi, M.; Lynch, J.; Rizzato, G.; et al. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society/World Association of Sarcoidosis and other Granulomatous Disorders. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 1999, 16, 149–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.S.; Rose, C.S.; Maier, L.A. Sarcoidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchernev, G.; Tana, C.; Schiavone, C.; Cardoso, J.C.; Ananiev, J.; Wollina, U. Sarcoidosis vs. Sarcoid-like reactions: The Two Sides of the same Coin? Wien Med. Wochenschr. 2014, 164, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupp, J.C.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bargagli, E.; Mihailović-Vučinić, V.; Rottoli, P.; Grubanovic, A.; Müller, A.; Jochens, A.; Tittmann, L.; Schnerch, J.; et al. Phenotypes of organ involvement in sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, P.; Bruder, D. Mechanism of granuloma formation in sarcoidosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2017, 24, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Laboratory Data | Reference Range | First Visit | After 2 Years | Laboratory Data | Reference Range | First Visit | After 2 Years |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | Electrolyte | ||||||
| Hematocrit (%) | 42.0–53 | 39.1 * | 34.1 * | Na (mmol/L) | 138–145 | 140 | 136 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 13.5–17.5 | 12.2 | 10.5 * | K (mmol/L) | 3.6–4.8 | 4.9 | 3.9 |
| White-cell count (per mm3) | 3700–8500 | 8100 | 27,000 * | Cl (mmol/L) | 101–108 | 103 | 100 * |
| Differential (%) | Ca (mmol/L) | 8.8–10.1 | 8.8 | 8.9 | |||
| Neutrophils | 44.0–68.0 | 67.5 | 90 * | P (mmol/L) | 2.7–4.6 | 2.4 | 2.0 * |
| Bands | 0.0–10.0 | 0 | 5.5 | Coagulation system | |||
| Metamyelocytes | 0 | 0 | 0 | PT (s) | 10–13.5 | 11.0 | 12.6 |
| Lymphocytes | 27.0–44.0 | 24.7 * | 2.5 * | PT-INR | 0.8–1.2 | 0.96 | 1.1 |
| Monocytes | 3.0–12.0 | 4.4 | 1.5 * | ATPP (s) | 23.0–38.0 | 31.3 | 51 * |
| Eosinophils | 0.0–10.0 | 2.2 | 0.5 | d-Dimer (µg/mL) | 0.00–1.00 | 0.67 | 2.37 * |
| Basophils | 0.0–3.0 | 1.2 | 0 | Fibrinogen (mg/dL) | 200–400 | 387 | 482 * |
| Platelet count (×103 per mm3) | 150–355 | 312 | 362 * | ||||
| Red-cell count (×106 per mm3) | 3.90–5.30 | 4.12 | 4.27 | ||||
| Biochemical test | Urine | ||||||
| Urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 2–80 | 12 | 22 | Color | Yellow | Yellow | Yellow |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.65–1.07 | 0.62 * | 0.78 | Clarity | Clear | Clear | Clear |
| ALT (U/L) | 3–40 | 20 | 20 | Specific gravity | 1.009~1.025 | 1.036 * | 1.016 |
| AST (U/L) | 8–35 | 17 | 32 | pH | 4.8~7.5 | 7.5 | 6.5 |
| LDH (U/L) | 124–222 | 143 | 211 | Protein | - | - | - |
| ALP (U/L) | 106–322 | 355 * | 1102 * | sugar | - | - | - |
| Ferritin (ng/mL) | 14–304 | 76 | 185 | White cells per high-power field | - | - | 4 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.00–0.3 | 0.27 * | 17.73 * | Red cells per high-power field | - | - | - |
| sIL-2R (U/mL) | 122–496 | 1249 * | 14,477 * | Virus Serological diagnosis | |||
| ACE | 7.0–25.0 | 14.9 | 23.0 | EBV anti-EBNA (FA) | <10 | 20 * | 10 * |
| lysozyme | 5.0–10.2 | 6.9 | 14.5 * | EBV anti-VCA IgG (FA) EBV anti-EA-DRIgG (FA) | <10 <10 | 160 * <10 | 80 * <10 |
| Total protein (g/dL) | 6.6–8.4 | 6.9 | 5.2 * | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8–5.2 | 4.0 | 2.7 * | HTLV-I anti-PA | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Serum proteins | EBV DNA Copy/mL | 7 × 103 | |||||
| A/G | 1.55–2.55 | 1.71 | 1.33 * | IGRA (T spot) | |||
| Albumin (%) | 60.8–71.8% | 63.1 | 57.0 * | NIL | 0 | ||
| α1 | 1.7–2.9% | 2.7 | 4.3 * | ESAT6 | 0 | ||
| α2 | 5.7–9.5% | 7.6 | 9.0 | CFP10 | 0 | ||
| β | 7.2–11.1% | 9.4 | 9.7 | Positive control: | 760 | ||
| γ | 10.2–20.4% | 17.2 | 20.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Furuyama, K.; Tsukita, M.; Shirato, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Ashino, Y.; Hattori, T. A Case of Sarcoid-Lymphoma Syndrome with Various Etiological Factors. Reports 2023, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6020019
Furuyama K, Tsukita M, Shirato Y, Sasaki Y, Ashino Y, Hattori T. A Case of Sarcoid-Lymphoma Syndrome with Various Etiological Factors. Reports. 2023; 6(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleFuruyama, Kazuki, Makiko Tsukita, Yoichi Shirato, Yusaku Sasaki, Yugo Ashino, and Toshio Hattori. 2023. "A Case of Sarcoid-Lymphoma Syndrome with Various Etiological Factors" Reports 6, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6020019
APA StyleFuruyama, K., Tsukita, M., Shirato, Y., Sasaki, Y., Ashino, Y., & Hattori, T. (2023). A Case of Sarcoid-Lymphoma Syndrome with Various Etiological Factors. Reports, 6(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports6020019








