Isolated Central Nervous System Vasculitides in COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
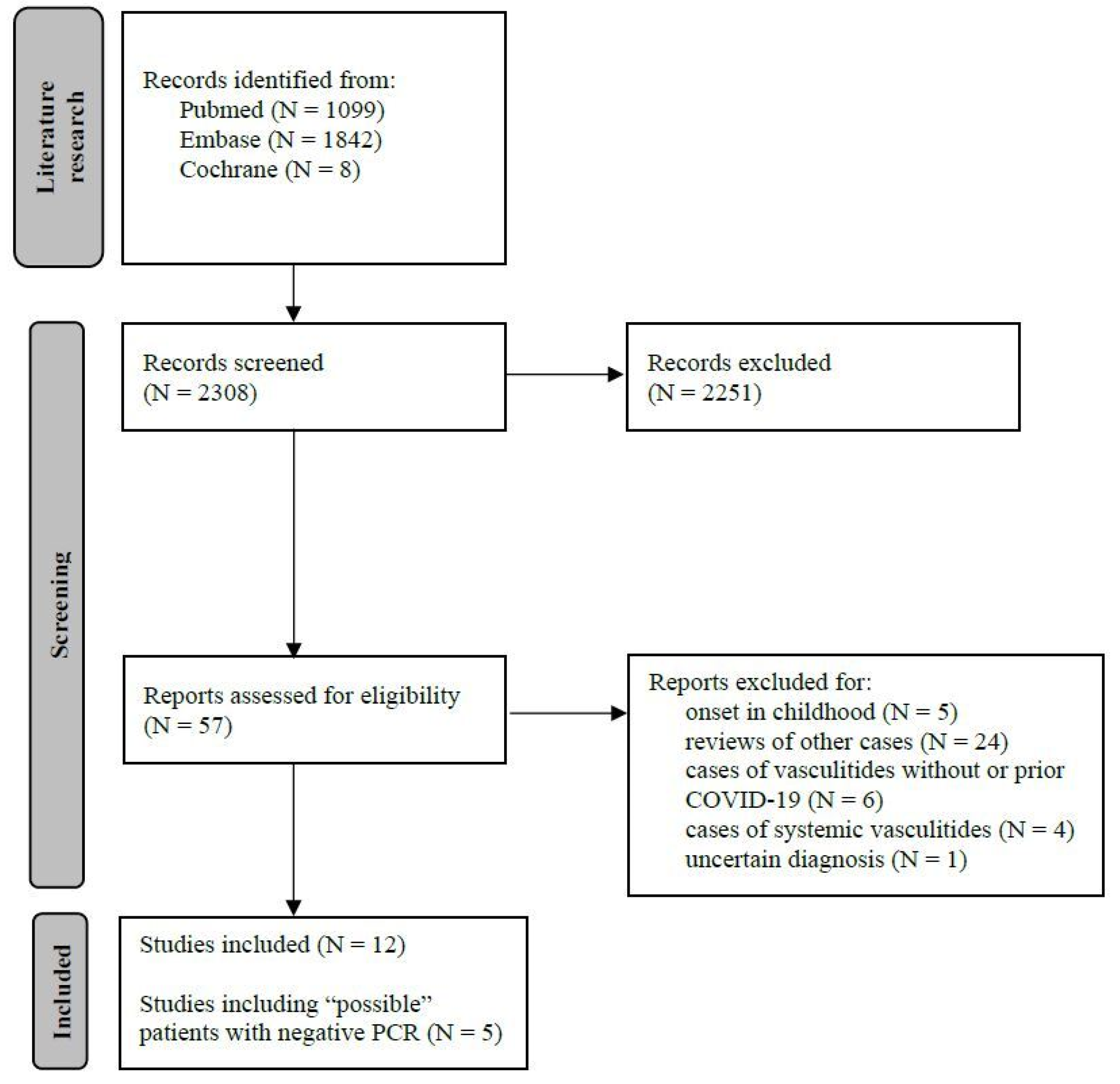
3.1. Literature Research (Figure 1)
3.2. Patient Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.J.; Calamia, K.T.; Christianson, T.J.H.; Weigand, S.D.; Miller, D.V.; Giannini, C.; Meschia, J.F.; Huston, J., 3rd; Hunder, G.G. Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis: Analysis of 101 Patients. Ann. Neurol. 2007, 62, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvarani, C.; Brown, R.D.J.; Christianson, T.J.H.; Huston, J., 3rd; Giannini, C.; Miller, D.V.; Hunder, G.G. Adult Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis Treatment and Course: Analysis of One Hundred Sixty-Three Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueras, C.; Sala, M.; Sasal, M.; Viñas, J.; Garcia, N.; Bella, M.-R.; Cervantes, M.; Segura, F. Recurrent Stroke as a Manifestation of Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System in a Patient Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Giannini, C.; Salvarani, C.; Hunder, G.; Brown, R.D. Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis: Pathology and Mechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outteryck, O.; Sénéchal, O.; Berteloot, D.; Delalande, I.; Mounier-Vehier, F. Cerebral vasculitis secondary to Varicella-Zoster virus infection. Rev. Neurol. 2005, 161, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.J.; Lasky, A.S.; Graf, W.D. Stroke Associated with Central Nervous System Vasculitis after West Nile Virus Infection. J. Child Neurol. 2006, 21, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, G.G.; Chatham, W.W. Vasculitis Related to Viral and Other Microbial Agents. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 29, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.; Menshawy, K.; Gonzalez, M.; Goldman, J.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Marshall, R.; Morgello, S. Brain Large Artery Inflammation Associated with HIV and Large Artery Remodeling. AIDS 2016, 30, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer, L.; Pikija, S.; Schulte, E.C.; Sztriha, L.K.; Nardone, R.; Sellner, J. Cerebrovascular Manifestations of Herpes Simplex Virus Infection of the Central Nervous System: A Systematic Review. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabi, Y.M.; Harthi, A.; Hussein, J.; Bouchama, A.; Johani, S.; Hajeer, A.H.; Saeed, B.T.; Wahbi, A.; Saedy, A.; AlDabbagh, T.; et al. Severe Neurologic Syndrome Associated with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Corona Virus (MERS-CoV). Infection 2015, 43, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umapathi, T.; Kor, A.C.; Venketasubramanian, N.; Lim, C.C.T.; Pang, B.C.; Yeo, T.T.; Lee, C.C.; Lim, P.L.; Ponnudurai, K.; Chuah, K.L.; et al. Large Artery Ischaemic Stroke in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). J. Neurol. 2004, 251, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, J.; Kremer, S.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Kummerlen, C.; Collange, O.; Boulay, C.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Ohana, M.; et al. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomari, S.O.; Abou-Mrad, Z.; Bydon, A. COVID-19 and the Central Nervous System. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2020, 198, 106116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; Williams, E.P.; Zalduondo, L.; Samir, P.; Zheng, M.; Sundaram, B.; Banoth, B.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; et al. Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes. Cell 2021, 184, 149–168.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGonagle, D.; Bridgewood, C.; Ramanan, A.V.; Meaney, J.F.M.; Watad, A. COVID-19 Vasculitis and Novel Vasculitis Mimics. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e224–e233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.M.; Scolding, N.J. The Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis. Pract. Neurol. 2020, 20, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, J.L.; Rutgers, D.R.; Spliet, W.G.; Frijns, C.J. Vessel Wall Enhancement on MRI in the Diagnosis of Primary Central Nervous System Vasculitis. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, NP24–NP27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, G.; Hak, J.-F.; Coze, S.; Kaphan, E.; Carvelli, J.; Girard, N.; Stellmann, J.-P. COVID-19-White Matter and Globus Pallidum Lesions: Demyelination or Small-Vessel Vasculitis? Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benguerfi, S.; Reizine, F.; Eugène, F.; Tattevin, P.; Maamar, A. Remarkable Resolution of COVID-19-Associated Cerebral Vasculitis with Methylprednisolone. Infect. Dis. Now. 2022, 52, 181–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, A.M.U.; Jamora, R.D.G.; Jose, A.C.E.; Anlacan, V.M.M. Cerebral Vasculitis in a COVID-19 Confirmed Postpartum Patient: A Case Report. Case Rep. Neurol. 2021, 13, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, R.d.M.C.; Santos, D.H.; Olivetti, B.C.; Takahashi, J.T. Bilateral Trochlear Nerve Palsy Due to Cerebral Vasculitis Related to COVID-19 Infection. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2020, 78, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.; Coughlan, C.; Karunaratne, K.; Gorgoraptis, N.; Varley, J.; Husselbee, J.; Mallon, D.; Carroll, R.; Jones, B.; Boynton, C.; et al. Immunosuppression for Intracranial Vasculitis Associated with SARS-CoV-2: Therapeutic Implications for COVID-19 Cerebrovascular Pathology. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2020, 92, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafi, R.; Roger, P.-A.; Perin, B.; Kuchcinski, G.; Deleval, N.; Dallery, F.; Michel, D.; Hacein-Bey, L.; Pruvo, J.-P.; Outteryck, O.; et al. COVID-19 Neurologic Complication with CNS Vasculitis-Like Pattern. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschenbaum, D.; Imbach, L.L.; Rushing, E.J.; Frauenknecht, K.B.M.; Gascho, D.; Ineichen, B.V.; Keller, E.; Kohler, S.; Lichtblau, M.; Reimann, R.R.; et al. Intracerebral Endotheliitis and Microbleeds Are Neuropathological Features of COVID-19. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2021, 47, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lersy, F.; Anheim, M.; Willaume, T.; Chammas, A.; Brisset, J.-C.; Cotton, F.; Kremer, S. Cerebral Vasculitis of Medium-Sized Vessels as a Possible Mechanism of Brain Damage in COVID-19 Patients. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 48, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raban, D.; Barhaghi, K.; Timpone, V.; Jones, W.; Sauer, B.; Pollard, R.; Callen, A. COVID-19 Associated Intracranial Vasculopathy-MRI Vessel Wall Imaging as Adjunct to Emergent CT Angiography-a Case Report. Emerg. Radiol. 2021, 28, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rettenmaier, L.A.; Abdel-Wahed, L.; Abdelmotilib, H.; Conway, K.S.; Narayanan, N.; Groth, C.L. COVID-19-Associated Necrotizing Encephalopathy Presenting without Active Respiratory Symptoms: A Case Report with Histopathology. J. Neurovirol. 2022, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strause, J.; Atsina, K.-B.; Bialo, D.; Orwitz, J.; Wolf, R.L.; Cucchiara, B. Ischemic Stroke Associated with Aneurysmal Lenticulostriate Vasculopathy and Symmetric Reversible Basal Ganglia Lesions in COVID-19. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 426, 117484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uginet, M.; Breville, G.; Assal, F.; Lövblad, K.-O.; Vargas, M.I.; Pugin, J.; Serratrice, J.; Herrmann, F.R.; Lalive, P.H.; Allali, G. COVID-19 Encephalopathy: Clinical and Neurobiological Features. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 4374–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaschetto, R.; Cena, T.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Meneghetti, G.; Bazzano, S.; Vecchio, D.; Pirisi, M.; Brustia, D.; Barini, M.; Cammarota, G.; et al. Cerebral Nervous System Vasculitis in a COVID-19 Patient with Pneumonia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 79, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, G.C.; de Sousa, T.C.; Sakiyama, M.A.K.; da Silva, J.S.N.L.; de Sousa, E.d.J.S. Vasculitis-Related Stroke in Young as a Presenting Feature of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID19)—Case Report. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 79, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermilov, V.V.; Barkanov, V.B.; Barkanova, O.N.; Dorofeev, N.A.; Filatov, V.E. Clinical and anatomical features of SARS-CoV-2 with acute hemorrhagic necrotizing encephalopathy. Arkh. Patol. 2021, 83, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lersy, F.; Kremer, S. Meningeal Inflammation and Cerebral Vasculitis during Acute COVID-19 with Spontaneous Regression. Intensive Care Med. 2022, 48, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugin, D.; Vargas, M.-I.; Thieffry, C.; Schibler, M.; Grosgurin, O.; Pugin, J.; Lalive, P.H. COVID-19-Related Encephalopathy Responsive to High-Dose Glucocorticoids. Neurology 2020, 95, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmons, G.M.; Rempe, T.; Bevins, E.A.; Goodwill, V.; Miner, A.; Kavanaugh, A.; Ritter, M.; Graves, J.S. CNS Lymphocytic Vasculitis in a Young Woman With COVID-19 Infection. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Barra, L.J.; Sposato, L.A.; Mandzia, J.L. Primary CNS Vasculitis: A Systematic Review on Clinical Characteristics Associated with Abnormal Biopsy and Angiography. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.A.; Roy, D.; Mondal, G.P.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Ghosh, K.C.; Das, S.; Krishna, H.; Patra, C.; Kiran, J.; Benito-León, J. Primary Angiitis of Central Nervous System—A Challenging Diagnosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 366, 577844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboix, A.; Jiménez, C.; Massons, J.; Parra, O.; Besses, C. Hematological disorders: A commonly unrecognized cause of acute stroke. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2016, 9, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Korteweg, C. Pathology and Pathogenesis of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuker, C.; Schmidt, A.; Strunk, D.; Sporns, P.B.; Wiendl, H.; Meuth, S.G.; Minnerup, J. Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: Diagnosis and Treatment. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418785071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boysson, H.; Boulouis, G.; Aouba, A.; Bienvenu, B.; Guillevin, L.; Zuber, M.; Touzé, E.; Naggara, O.; Pagnoux, C. Adult Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: Isolated Small-Vessel Vasculitis Represents Distinct Disease Pattern. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| First Author | Diagnosis | Gender Age | COVID-19 Testing | COVID-19 Onset | COVID-19 Pneumonia/ ICU | Neurologic Features | MRI | CSF | Pathology | Treatments | Outcome: COVID/Neurological |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benguerfi | P | M 74 | PCR (NF) + | Fever, cough | +/+ | Coma | Micro and subarachnoid haemorrhages, multiple ischemic lesions | Normal with SARS-CoV-2 RNA − | No | Steroids * | Recovery |
| Chua | P | F 39 | Respiratory tract + | Fever | −/− | Postpartum headache | Micro and subarachnoid haemorrhages with intracranial arterial narrowing | NA | No | No | Recovery |
| De Oliveira | P | M 69 | PCR (NF) + | Fever, abdominal and chest pain | −/− | Headache, bilateral 4th cranial nerve | Basilar and vertebral arteries (walls GAD+) | Normal cells, mildly increased proteins | No | Steroids * | Recovery |
| Dixon | P | M 64 | PCR (NF) + | Cough, fever | +/+ | Impaired consciousness | Multi-infarcts in bilateral MCA and PCA territories (wall GAD+) | NA | No | Steroids * | Recovery |
| Hanafi | P | M 65 | PCR (NF) + | Cough, fever | +/+ | Coma | Deep white matter vasculopathy with patchy GAD+ | NA | No | NA | NA |
| Kirschenbaum | D | 2 M 70–79 | Respiratory tract + | Respiratory symptoms | +/+ (N = 1) +/− (N = 1) | Coma (N = 1) None (N = 1) | Multiple microbleeds (N = 1) NA (N = 1) | NA | Autopsy: petechial haemorrhages with endotheliitis | NA | Death |
| Lersy | D§/P | 11 (10 M) 61–79 | PCR (NF) or respiratory tract + | Respiratory symptoms | +/+ (N = 9) | Coma (N = 11), pyramidal syndrome (N = 3) | Micro and subarachnoid haemorrhages, ischemic strokes (wall GAD+) §2: intracranial arterial narrowing | 6: normal cells, proteins mildly increased or not, SARS-CoV-2 RNA − | No | NA | NA |
| Raban | P | F 51 | Respiratory tract + | Sore throat, cough | +/− | Hemiparesis | Unilateral ischemic stroke (wall GAD+) | Normal with SARS-CoV-2 RNA − | No | No | Recovery |
| Rettenmaier | D | F 48 | PCR (NF) + | None | −/− | Aphasia | Bithalamic lesion GAD+ | Mildly increased cells, increased proteins | Biopsy: small vessel vasculitides | Steroids * | Improved |
| Strause | P | M 24 | PCR (NF) + | Sore throat, loss of taste and smell | −/− | Hemiparesis, dysarthria, | Multi-infarcts basal ganglia (wall GAD+) | Normal | No | Steroids * | Recovery |
| Uginet | P | 17/31 cases (2 F/31) 53–77 | PCR (NF) + | Dyspnoea | +/+ | Headache, inattention | Cerebral microbleeds (wall GAD+) | 7 CSF: normal cells, proteins mildly increased or not, SARS-CoV-2 RNA − | No | No | Recovery |
| Vaschetto | P | M 64 | PCR (NF) + | Cough, fever | +/+ | Coma, tetraplegia | Multi-infarcts parietal-occipital and pons, leptomeningeal GAD+ | Normal cells, increased proteins | No | IVIG, steroids * | Recovery |
| First Author | Diagnosis | Gender Age | COVID-19 Testing | COVID-19 Onset | COVID-19 Pneumonia/ ICU | Neurologic Features | MRI | CSF | Pathology | Treatments | Outcome: COVID/Neurological |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| De Sousa | P | M 28 | IgM + | Neurological | −/− | Headache, dysarthria, left hemiparesis | Unilateral parietal and frontal lesions DWI+ | NA | No | NA | NA |
| Ermilov | D | M 20 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Autopsy: widespread vasculitides, thrombosis, haemorrhagic necrosis | NA | Death |
| Lersy | P | M 46 | NA | Respiratory symptoms | +/+ | Delirium | Meningeal and diffuse leptomeningeal inflammation (wall GAD+) | Normal | No | No | Recovery |
| Pugin | P | 3 M, 2 F 69–78 | NA | Fever, dyspnoea | +/+ | Coma | (Wall GAD+) | Normal | No | Steroids * | Recovery |
| Timmons | D | F 26 | NA | Sore throat, taste/smell loss | −/− | Foot drop | Unilateral frontoparietal white matter lesions GAD+ | Normal | Biopsy: lymphocytic vasculitides | Steroids *, mycophenolate mofetil | Improved |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vecchio, D.; Moretto, F.; Padelli, S.; Grossi, F.; Cantello, R.; Vaschetto, R. Isolated Central Nervous System Vasculitides in COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series. Reports 2022, 5, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports5030036
Vecchio D, Moretto F, Padelli S, Grossi F, Cantello R, Vaschetto R. Isolated Central Nervous System Vasculitides in COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series. Reports. 2022; 5(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports5030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleVecchio, Domizia, Francesca Moretto, Samuel Padelli, Francesca Grossi, Roberto Cantello, and Rosanna Vaschetto. 2022. "Isolated Central Nervous System Vasculitides in COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series" Reports 5, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports5030036
APA StyleVecchio, D., Moretto, F., Padelli, S., Grossi, F., Cantello, R., & Vaschetto, R. (2022). Isolated Central Nervous System Vasculitides in COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series. Reports, 5(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/reports5030036