Abstract
Background: This study investigated the impact of serum cytokeratin 19 fragment (CYFRA21-1) level on the clinical outcomes of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) treated with sorafenib (SOR) or lenvatinib (LEN). Methods: A total of 71 cases with unresectable HCC taking SOR or LEN were included. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify the prognostic factors in patients taking SOR or LEN. Results: Among the 71 patients taking SOR or LEN, the frequency of cases showing high CYFRA21-1 levels after administration increased compared to before the administration. There was no association between the CYFRA21-1 level and the result of treatment response using modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) 12 weeks after the administration. Univariate analysis identified a maximum intrahepatic tumor diameter of 70 mm or more, extrahepatic metastasis, baseline alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) ≥ 2000 ng/mL, baseline AFP-L3 index ≥ 15%, baseline des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) ≥ 1000 mAU/mL, baseline CYFRA21-1 > 3.5 ng/mL, 12-week mRECIST progressive disease (PD), 12-week DCP ratio ≥ 4, 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2, administration period less than 12 weeks, ALBI grade 3 at PD, and no additional treatment after discontinuation of SOR/LEN as prognostic factors. Multivariate analysis revealed that AFP-L3 index ≥ 15%, 12-week mRECIST PD, 12-week DCP ratio ≥ 4, 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2, administration period less than 12 weeks, and no additional treatment after discontinuation of SOR/LEN were independent factors. Conclusions: Patients with a high CYFRA21-1 level at baseline tend to have poor prognosis, and patients with a high CYFRA21-1 ratio 12 weeks after administration have poor prognosis. Serum CYFRA21-1 measurement may have additional effects on prognostic prediction, and it may be necessary to pay close attention to the transition to the next HCC treatment in cases whose CYFRA21-1 level is high.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [1]. Treatments for HCC include surgical resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), radiotherapy (RT), and systemic chemotherapy [2,3]. In particular, the recent development of systemic chemotherapy has been remarkable. After sorafenib (SOR) was approved in Japan in 2009 as the first molecular-targeted agent (MTA) for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage B/C unresectable HCC, lenvatinib (LEN), regorafenib, ramucirumab, cabozantinib, and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab were approved and have come to be widely used for unresectable HCC [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. In order to achieve a favorable prognosis, it is important to provide appropriate treatment at appropriate times, and we should be aware of the treatment effects on tumor markers and prognosis in cases taking MTAs in the real world.
Serum cytokeratin 19 fragment (CYFRA21-1) is known to be a biomarker in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and esophageal cancer; additionally, it is a surrogate marker for cancer stem cells [12,13]. CYFRA21-1 in HCC patients reflects Keratin 19 (K19) expression, and many patients with tumor thrombus of the portal vein (Vp) and extrahepatic metastasis have been reported in HCC cases with high CYFRA21-1 levels [14,15]. However, there are no reports regarding the relationship between CYFRA21-1 and clinical outcome in patients taking SOR or LEN for unresectable HCC.
We previously experienced a case in whose CYFRA21-1 level was high after repeated TACE before MTA administration, and the case had a poor prognosis. In the present study, based on that experience, we analyzed the relationship between serum CYFRA21-1 level and prognosis in patients taking SOR or LEN as their initial MTA treatment, and we considered its clinical significance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
We carried out a retrospective cohort study to observe the tumor markers, including alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), AFP L3 index, Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin (DCP), and CYFRA21-1 before and after administration of SOR and LEN, which were administered as the initial MTA in 36 and 35 cases between July 2009 and July 2020, respectively. Inclusion criteria were BCLC stage B/C unresectable HCC, the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS) 0–1, and Child–Pugh grade A/B. All patients included in the study underwent CYFRA21-1 measurement before and after administration. The definition of HCC in this study is a pathological diagnosis of HCC, classical HCC findings (contrast enhancement in arterial phase and washout in portal vein phase) on dynamic computed tomography (CT), Gd-EOB-GTPA magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, and intrahepatic tumors with elevated AFP/AFP-L3 index/DCP level. Cases with no intrahepatic nodules, a follow-up period within 4 weeks, administration period within 4 weeks, other organ cancers, or without CYFRA21-1 measurement before and after administration were excluded from this study. We analyzed the relationship between the laboratory findings and prognosis following the SOR/LEN administration. We received the informed consent of all cases involved in this study. This study was carried out in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration and with the approval of the ethics committee of our hospital (Human Ethics Review Committee of University of Yamanashi) [16].
2.2. Administration of SOR/LEN
The initial dose of SOR (Nexavar; Bayer, Tokyo, Japan) was 800 mg/day, in general, and was reduced to 400 mg/day for patients with Child–Pugh class B, low body weight (<50 kg) or with pleural effusion/ascites. The initial dose of SOR was reduced by the judgement of the primary physicians. LEN (Lenvima; Eisai, Tokyo, Japan) administration was commenced with 12 mg/day and 8 mg/day for cases with a weight of ≥60 kg and of <60 kg, respectively. The initial dose for cases classified as Child–Pugh class B was reduced to 8 mg/day by the judgement of the primary physician.
In all cases, no other treatment was administered while MTA was being administered. Monitoring for adverse events (AEs) was carried out once every 1–2 weeks in accordance with the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 4.0. MTA treatment was continued until severe AEs occurred, progressive disease (PD) on imaging, or clinical PD was observed.
2.3. Measurement of Serum CYFRA21-1
Serum CYFRA21-1 level was determined on the automated chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay (CLEIA) system, Lumipulse G600 II (Fujirebio, Tokyo, Japan). The detection limit of CYFRA21-1 was 0.5 ng/mL [14].
2.4. Follow-Up after Administration
Blood tests were performed before administration, every 1–2 weeks for three months after the start of administration, and every 4 weeks thereafter. Liver function was evaluated using the Child–Pugh classification and albumin–bilirubin (ALBI) grade [17]. Serum AFP, AFP L3 index, and DCP were measured before administration and at 12 and 24 weeks after administration. The serum CYFRA21-1 level was measured before administration and at 12 and 24 weeks after administration. For each patient, the baseline tumor marker level was assigned a value of 1, and the ratios for the level at 12 and 24 weeks relative to baseline level after the start of administration were calculated. Imaging analysis used dynamic CT, or Gd-EOB-GTPA MRI were performed before administration and at 12 weeks after administration. Treatment response was evaluated using modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (mRECIST) and discussed by two hepatologists and one radiologist [18,19].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as median and range and were compared using the Mann–Whitney test, Friedman test, and Kruskal–Wallis test. Categorical variables were expressed as counts and percentages and were compared using the chi-square test. The best cut-off values in receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis were determined by Youden index. In this study, survival time after administration was defined as overall survival (OS). The Kaplan–Meier curves were used for overall survival, and the Cox proportional hazards model was used for the assessment of the prognostic factors. A p-value less than 0.05 was statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan), a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). More precisely, it is a modified version of the R commander designed to include statistical functions frequently used in biostatistics [20].
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. There were 71 cases, 62 of which were male, and the mean age was 70 (52–91) years. At the time of the start of administration, 20, 48, and 3 cases had an ALBI grade 1, 2, and 3, respectively. The median intrahepatic tumor diameter was 27 (8.4–180) mm, and the median number of intrahepatic tumors was 6 (1–10). Portal vein tumor thrombosis and extrahepatic metastasis were observed in 16 and 29 cases, respectively. Thirty-nine cases were BCLC stage C. The median duration of SOR/LEN administration was 17 (4–95) weeks, and additional treatments after SOR/LEN discontinuation were TACE (28 cases), other MTA administration (23 cases), hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy (HAIC) (7 cases), RT (6 cases), surgery (1 case), and RFA (1 case).

Table 1.
Patient characteristics.
3.2. Transition of Tumor Markers Including Serum CYFRA21-1 Level
In cases taking SOR or LEN, AFP ratios at 12 and 24 weeks after administration were 0.91 (0.5–12) and 1.5 (0.5–60), and DCP ratios at 12 and 24 weeks after administration were 1.9 (0.01–82) and 2.7 (0.01–927). AFP ratios at 12 and 24 weeks after administration in cases with mRECIST PD (n = 36) were higher than cases with non-PD (n = 35) (p < 0.001, 0.057) (Figure 1A). DCP ratios at 12 and 24 weeks after administration in cases with PD were higher than cases with non-PD (p = 0.087, 0.049) (Figure 1B).
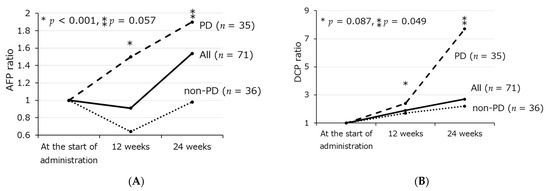
Figure 1.
Transition of AFP ratio (A) and DCP ratio (B) from the start of administration to 24 weeks after administration according to treatment response using mRECIST. * Comparison of PD group and non-PD group at 12 weeks, ** Comparison of PD group and non-PD group at 24 weeks.
The serum CYFRA21–1 level was 2.2 (1.1–16) ng/mL prior to the previous HCC treatment before administration, 2.6 (0.76–11) ng/mL at the start of administration, 3.3 (1.0–14) ng/mL (p < 0.001) at 12 weeks after the administration, and 3.7 (1.0–14) ng/mL at 24 weeks after the administration. In the ROC analysis performed to estimate shorter survival, the AUROC values of CYFRA21-1 and CYFRA21-1 ratio were 0.70 and 0.76, the following study was examined using the cut-off values 3.5 and 2.0 for baseline CYFRA21-1 level and CYFRA21-1 ratio. The frequency of cases with a CYFRA21-1 level ≥ 3.5 ng/mL were 8.8, 21, 44, and 55% prior to the previous HCC treatment, the start of administration, 12 weeks after the administration, and 24 weeks after the administration, respectively (p < 0.001) (Figure 2A). There was no association between the CYFRA21-1 level and the result of treatment response using mRECIST 12 weeks after the administration (Figure 2B).
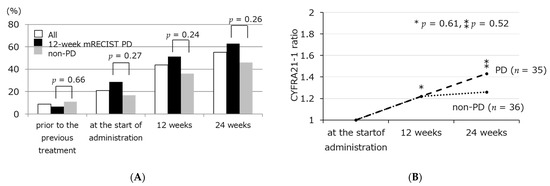
Figure 2.
Frequency of CYFRA21-1 ≥ 3.5 ng/mL (A), and transition of CYFRA21-1 ratio (B) from the start of administration to 24 weeks after administration according to treatment response using mRECIST. * Comparison of PD group and non-PD group at 12 weeks, ** Comparison of PD group and non-PD group at 24 weeks.
3.3. Factors Relating to Survival after SOR/LEN Administration
The median overall survival after SOR/LEN administration was shorter in patients with baseline CYFRA21-1 ≥ 3.5 ng/mL than patients with <3.5 ng/mL. The median overall survival was shorter in patients with 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2 than patients with <2 (Figure 3A,B). Univariate analysis of factors relating to survival after SOR/LEN administration revealed that intrahepatic tumor diameter ≥ 70 mm, extrahepatic metastasis, AFP ≥ 2000 ng/mL, AFP L3 index ≥ 15%, DCP ≥ 1000 mAU/mL, and CYFRA21-1 ≥ 3.5 ng/mL were significant as pre-administration factors, and that mRECIST PD at 12 weeks, 12-week DCP ratio ≥ 4, 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2, administration period less than 12 weeks, ALBI grade 3 at the time of PD, and no additional treatment after SOR/LEN discontinuation were significant post-administration factors. Multivariate analysis identified AFP L3 index ≥15% as a pre-administration independent factor. Post-administration independent factors were mRECIST PD at 12 weeks, 12-week DCP ratio ≥ 4, 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2, administration period less than 12 weeks, and no additional treatment after discontinuation. The patients with a intrahepatic tumor diameter ≥ 70 mm, baseline AFP ≥ 2000 ng/mL, or baseline CYFRA21-1 ≥ 3.5 ng/mL tend to have poor prognosis (Table 2, Figure 3C).
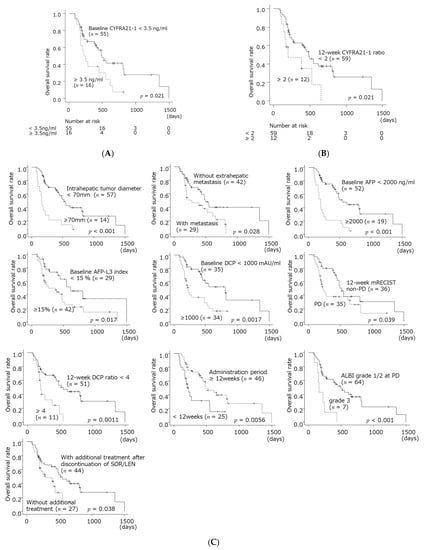
Figure 3.
Overall survival after starting SOR/LEN according to baseline CYFRA21-1 level (A), 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio (B), and other prognostic factors (C).

Table 2.
Univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazard model of overall survival in patients taking SOR/LEN.
3.4. Characteristics in Patients with High CYFRA 21-1 Level
The cases showing high CYFRA21-1 levels (baseline CYFRA21-1 ≥ 3.5 ng/mL, or 12-week CYFRA21-1 ratio ≥ 2) (n = 25) were more likely to show AFP ≥ 2000 ng/mL than the cases with low CYFRA21-1 levels (n = 46) (48% vs. 15%, p = 0.005). Among the cases showing high CYFRA21-1 levels, there were many cases showing TACE unsuitable pattern such as confluent multinodular type, simple nodular type with extra-nodular growth, and intrahepatic multiple disseminated nodules, proposed by Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert (APPLE) Consensus Statement (76% vs. 41%, p = 0.006) [21] (Table 3).

Table 3.
Patient characteristics according to serum CYFRA21-1 level.
4. Discussion
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is predicted to be the sixth most commonly diagnosed cancer and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [22]. HCC is increasingly found in a resectable stage with the development of surveillance, but recurrence after curative therapy is repeated. SOR was approved in 2009 as a first-line systemic chemotherapy for unresectable HCC, and treatment options for patients with unresectable HCC were limited at that time [4]. After that, in 2017, REG was approved as a second-line therapy after SOR [6]. LEN was reported as not being inferior to SOR in a phase III randomized trial (REFLECT study) and has come to be widely used since 2018 [5]. Since 2019, many drugs have become available, such as ramucirumab, cabozantinib, and atezolizumab plus bevacizumab [7,10,11]. On the other hand, it is still difficult to determine which treatment is appropriate prior to administration. In this study, by analyzing the relationship between the tumor markers and prognosis, we considered the significance of serum CYFRA21-1 level in patients with unresectable HCC.
In this study, we found that the survival in patients whose 12-week CYFRA21-1 level did not decrease was shorter than that of the low CYFRA21-1 group, and patients with high baseline CYFRA21-1 levels tend to have shorter survival. There was no association between the CYFRA21-1 level and the result of treatment response using mRECIST 12 weeks after the administration. The values of the AFP and DCP levels were reported to be prognostic factors associated with survival [23,24]. Furthermore, the AFP ratio after SOR administration is useful for predicting antitumor response [25]. In this study, high baseline CYFRA21-1 level and high CYFRA21-1 ratio were important markers similar to other markers by multivariate analysis. It is also the first report in which many patients with a high CYFRA21-1 level or high CYFRA21-1 ratio showed a high AFP level and TACE-unsuitable pattern. Serum CYFRA21-1 may be a marker of malignancy that cannot be adequately determined by mRECIST criteria or other blood tests alone.
Serum CYFRA21-1 is a surrogate marker for cancer stem cells (CSCs), and CSCs have the ability to differentiate into hepatocytes or bile duct cells [26,27,28,29]. CSCs were reported to be associated with tumor growth, resistance to systemic chemotherapy and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and are related to the prognosis of solid cancer patients [30]. There are a few reports that high CYFRA21-1 level is related to increased tumor size, metastasis and microvascular invasion [31]. Furthermore, high CYFRA21-1 level in HCC patients is reported to reflect Keratin 19 (K19) expression. In previous studies, K19 expression is related to increased tumor size, decreased tumor differentiation, metastasis, microvascular invasion, and recurrence [32,33,34]. However, there is still much controversy concerning why high CYFRA21-1 level and K19 expression are related to tumor activity [35] [36,37,38].
This study is the first report on the transition of CYFRA21-1 level in patients with unresectable HCC; as such, it may be useful in solving current problems. Molecular classification of HCC may have a key role as a prognostic marker in unresectable HCC, and serum CYFRA21-1 could be a simple marker of the molecular classification. Therefore, measurement of the serum CYFRA21-1 level may have a clinical impact when making a decision on which therapies to employ for advanced stage of HCC. Some cases with a transition from classical HCC to combined HCC or poor differentiation can be observed after repetitive TACE in the real world [39,40,41]. There may be some cases that have transformed from classical HCC into combined HCC in patients with a high CYFRA21-1 level in this study. Further studies are required because the pathological evaluation in this study was insufficient.
According to the multivariable analysis in this study, additional treatment after SOR/LEN discontinuation is another independent prognostic factor for patients with unresectable HCC. The survival of the group that received additional treatment was longer than the group without additional treatment. The content of additional treatments in this study was diverse, including TACE, other chemotherapy, HAIC, RT, operation, and RFA. Recent studies have shown that post-progression survival is important in patients with systemic chemotherapy for unresectable HCC [42,43]. REG and RAM following SOR therapy are useful in extending survival after PD [44,45]. TACE for advanced HCC after stopping SOR therapy was found to be associated with a decreased mortality risk [46]. However, as yet, there are insufficient reports presenting the clinical significance of additional treatments after stopping LEN therapy. Detailed reports regarding additional treatments after MTA discontinuation that involve larger numbers of cases will be needed.
This study has several limitations. First, it was a retrospective, single-center study involving a small number of cases. This study targeted patients whose CYFRA21-1 levels were measured before and after administration, and the results may be biased by patient selection. Second, the present study includes many patients who have started with a reduction dose of SOR/LEN. Third, tumor biopsy was not carried out, and neither was a pathological evaluation. Finally, no stratified analysis was performed by content of additional treatments. Therefore, further additional research is needed in the future.
High serum level of CYFRA21-1 is a prognostic factor for unresectable HCC patients receiving SOR or LEN therapy. Patients with high levels of baseline or 12-week CYFRA21-1 levels should be carefully followed up. Additional evaluation of serum CYFRA21-1 level may be more useful than only a mRECIST evaluation and other tumor markers in assessment following the start of SOR/LEN therapy.
5. Conclusions
The serum CYFRA21-1 level of baseline and 12 weeks after administration are prognostic factors in unresectable HCC patients taking SOR or LEN. They may be useful as additional markers to determine the direction of treatment for unresectable HCC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.T.; methodology, H.T. and S.M.; software, H.T.; validation, H.T.; formal analysis, H.T.; data curation, H.T., L.O., Y.K., R.K., N.N., M.M., Y.S., A.T., M.S., E.T., S.T., M.F., T.Y., T.I., S.M. and N.E.; writing—original draft preparation, H.T.; writing—review and editing, L.O., Y.K., R.K., N.N., M.M., Y.S., A.T., M.S., E.T., S.T., M.F., T.Y., T.I., S.M. and N.E.; visualization, H.T.; supervision, S.M. and N.E.; project administration, H.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Human Ethics Review Committee of Yamanashi University Hospital.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Research data obtained in this study are not shared.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bray, F.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.-K.; Yen, C.-J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Okusaka, T.; Motomura, K.; Ohno, I.; Morimoto, M.; Seo, S.; Wada, Y.; Sato, S.; Yamashita, T.; Furukawa, M.; et al. Ramucirumab after prior sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and elevated alpha-fetoprotein: Japanese subgroup analysis of the REACH-2 trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, A.X.; Park, J.O.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Poon, R.; Pastorelli, D.; Blanc, J.-F.; Chung, H.; Baron, A.D.; Pfiffer, T.E.F.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib (REACH): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Yasuchika, K.; Ishii, T.; Katayama, H.; Yoshitoshi, E.Y.; Ogiso, S.; Minami, T.; Miyauchi, Y.; Kojima, H.; Yamaoka, R.; et al. Identification of keratin 19-positive cancer stem cells associating human hepatocellular carcinoma using CYFRA 21-1. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2531–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Yasuchika, K.; Ishii, T.; Katayama, H.; Yoshitoshi, E.Y.; Ogiso, S.; Kita, S.; Yasuda, K.; Fukumitsu, K.; Mizumoto, M.; et al. Keratin 19, a Cancer Stem Cell Marker in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3081–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Medical Association. Declaration of Helsinki. Law Med. Health Care 1991, 19, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of Liver Function in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A New Evidence-Based Approach—The ALBI Grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) Assessment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, M.; Han, K.-H.; Ye, S.-L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-M.; Wang, C.-K.; Ikeda, M.; Chan, S.L.; Choo, S.P.; et al. A Changing Paradigm for the Treatment of Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Consensus Statements. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatocellular carcinoma in developing countries: Prevention, diagnosis and treatment. World J. Hepatol. 2012, 4, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueshima, K.; Kudo, M.; Takita, M.; Nagai, T.; Tatsumi, C.; Ueda, T.; Kitai, S.; Ishikawa, E.; Yada, N.; Inoue, T.; et al. Des-γ-Carboxyprothrombin May Be a Promising Biomarker to Determine the Therapeutic Efficacy of Sorafenib for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. 2011, 29, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, K.; Nouso, K.; Morimoto, Y.; Tomoda, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Hagihara, H.; Kuwaki, K.; Ohnishi, H.; Ikeda, F.; et al. Evaluation of the effect of sorafenib using serum NX-des-γ-carboxyprothrombin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 43, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzuya, T.; Asahina, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Tanaka, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Hoshioka, T.; Tamaki, S.; Kato, T.; Yasui, Y.; Hosokawa, T.; et al. Early Decrease in α-Fetoprotein, but Not Des-γ-Carboxy Prothrombin, Predicts Sorafenib Efficacy in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology 2011, 81, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, H.; Ohno, S.; Miyazaki, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Egashira, A.; Saeki, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sugimachi, K. CYFRA 21-1 determination in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfuso, B.; El-Khobar, K.E.; Sukowati, C.; Tiribelli, C. The multiple origin of cancer stem cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2015, 39, S92–S97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komuta, M.; Spee, B.; Borght, S.V.; De Vos, R.; Verslype, C.; Aerts, R.; Yano, H.; Suzuki, T.; Matsuda, M.; Fujii, H.; et al. Clinicopathological study on cholangiolocellular carcinoma suggesting hepatic progenitor cell origin. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1544–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-S.; Heo, J.; Libbrecht, L.; Chu, I.-S.; Kaposi-Novak, P.; Calvisi, D.F.; Mikaelyan, A.; Roberts, L.; Demetris, A.J.; Sun, Z.; et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglia, G.P.; Ciruolo, M.; Olivero, A.; Carucci, P.; Rolle, E.; Rosso, C.; Abate, M.L.; Risso, A.; Ribaldone, D.G.; Tandoi, F.; et al. Prognostic Role of Serum Cytokeratin-19 Fragment (CYFRA 21-1) in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Fujita, J.; Murota, M.; Li, J.-Q.; Ishida, T.; Nishioka, M.; Imaida, Y.; Kuriyama, S. CYFRA 21-1 is released in TNF-α-induced apoptosis in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HuH-7. Int. J. Oncol. 2002, 21, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.-J.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.-X.; Jiang, M.-R.; Tian, B.; Liu, Y.-K.; Shao, X.-X.; Ye, S.-L.; Wu, J.-R.; Zeng, R.; et al. From proteomic analysis to clinical significance: Overexpression of cytokeratin 19 correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Komuta, M.; Yasui, Y.; Tamaki, N.; Hosokawa, T.; Ueda, K.; Kuzuya, T.; Itakura, J.; Nakanishi, H.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Expression of Keratin 19 Is Related to High Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Radiofrequency Ablation. Oncology 2011, 80, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uenishi, T.; Kubo, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Shuto, T.; Ogawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Tanaka, S.; Kaneda, K.; Hirohashi, K. Cytokeratin 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts early postoperative recurrence. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uenishi, T.; Yamazaki, O.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirohashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Tanaka, S.; Hai, S.; Ono, K.; Kubo, S. Clinical significance of serum cytokeratin-19 fragment (CYFRA 21-1) in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat. Surg. 2006, 13, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaere, O.; Komuta, M.; Berkers, J.; Spee, B.; Janssen, C.; De Luca, F.; Katoonizadeh, A.; Wouters, J.; van Kempen, L.; Durnez, A.; et al. Keratin 19: A key role player in the invasion of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2013, 63, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durnez, A.; Verslype, C.; Nevens, F.; Fevery, J.; Aerts, R.; Pirenne, J.; Lesaffre, E.; Libbrecht, L.; Desmet, V.; Roskams, T. The clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of cytokeratin 7 and 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. A possible progenitor cell origin. Histopathology 2006, 49, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, N.-O.; Strnad, P.; Bantel, H.; Omary, B. Keratins: Biomarkers and modulators of apoptotic and necrotic cell death in the liver. Hepatology 2016, 64, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zen, C.; Zen, Y.; Mitry, R.R.; Corbeil, D.; Karbanova, J.; O’Grady, J.; Karani, J.; Kane, P.; Heaton, N.; Portmann, B.C.; et al. Mixed phenotype hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization and liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Ren, J.; O’Neil, M.; Zhao, J.; Bridges, B.; Cox, J.; Abdulkarim, B.; Schmitt, T.M.; Kumer, S.C.; Weinman, S.A. Impact of stem cell marker expression on recurrence of TACE-treated hepatocellular carcinoma post liver transplantation. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Terashima, T.; Yamashita, T.; Takata, N.; Nakagawa, H.; Toyama, T.; Arai, K.; Kitamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; Mizukoshi, E.; et al. Post-progression survival and progression-free survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by sorafenib. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 46, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Kariyama, K.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Shimada, N.; Tajiri, K.; Tsuji, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Ochi, H.; et al. Therapeutic potential of lenvatinib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in clinical practice: Multicenter analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomonari, T.; Sato, Y.; Tani, J.; Hirose, A.; Ogawa, C.; Morishita, A.; Tanaka, H.; Tanaka, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Okamoto, K.; et al. Comparison of therapeutic outcomes of sorafenib and lenvatinib as primary treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma with a focus on molecular-targeted agent sequential therapy: A propensity score-matched analysis. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 51, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, H.; Kurosaki, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Komiyama, Y.; Itakura, J.; Takahashi, Y.; Nakanishi, H.; Yasui, Y.; Tamaki, N.; Maeyashiki, C.; et al. Baseline and Early Predictors of Good Patient Candidates for Second-Line after Sorafenib Treatment in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.-K.; Yen, C.-L.; Shiu, S.-I.; Lee, S.-W.; Chang, P.-Y.; Yeh, H.-Z.; Lee, T.-Y. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization after stopping sorafenib therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).