Abstract
Background: Early diagnosis in pancreatic cancer is key for improving prognosis. Hypoxia plays a critical role in tumor progression. Thus, an evaluation of associations between pancreatic tumor progression and markers of hypoxia is needed. Methods: We assessed the expression of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIF-1α and HIF-2α) by immuno-histochemical staining from 29 subjects with the following: pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), neuroendocrine tumor (NET), and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and compared it to the expression in non-tumor samples. Results: Expression of HIF-1α increased significantly from PanIN (3.01 ± 0.17) to IPMN (7.63 ± 0.18), NET (9.10 ± 0.23) and PDAC samples (11.06 ± 0.15, p < 0.0001). Similar findings were observed for HIF-2α (p < 0.0001)}. A strong correlation between HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression was demonstrated (R2 = 0.8408, p < 0.0001). Conclusions: This data suggest that HIF-1α and HIF-2α may play a role in the progression from PanIN through PDAC. Further studies are necessary to confirm these findings and determine the effect of HIFs abrogation on tumor progression that can lead to novel therapies.
1. Introduction
The diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cancer is perhaps the most vexing of all carcinomas. We do not currently have a reliable means of screening, or early biomarkers and as a result, most are found on a CT/MRI scan at an advanced stage. Pancreatic cancer is highly aggressive and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related death in the United States. In contrast to the steady increase in survival for most cancers, advances have been slow for lung and pancreatic cancers. More than half of these pancreatic cancers are ductal adenocarcinomas that grow rapidly and are diagnosed at a late stage, for which the 5-year survival is 3% [1]. Prognosis is mainly influenced by early diagnosis. Conventional treatments with chemotherapy and radiotherapy have little impact on patients’ survival. Treatment by surgical resection is the only remote chance of a cure but is not available for late stage disease. Future hopes may rest in a better understanding of the molecular biology of pancreatic tumor progression that can be applied to enable early diagnosis and treatment [2].
Hypoxia is a common phenomenon in human solid tumors and plays a critical role in tumor progression. Most tumor cells are dependent upon glycolysis for survival and concomitantly overexpress hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), an essential transcriptional regulator of glycolysis and the hypoxic response [3]. HIFs are overexpressed in a majority of primary tumors, cancer cell lines, and metastases, making it a critical regulator of the malignant phenotype [4,5,6,7]. HIF-1 and HIF-2 are heterodimeric transcription factors consisting of an oxygen-sensitive alpha subunit (HIF-α) and constitutively expressed beta subunit (HIF-β) that facilitates both oxygen delivery and adaptation to hypoxia by regulating the expression of genes that control glucose uptake, metabolism, angiogenesis, erythropoiesis, cell proliferation, and apoptosis [8,9]. HIF-1α and HIF-2α are both labile under normoxic conditions due to VHL-dependent proteasomal degradation, but stabilization occurs under hypoxia due to inactivation of HIF prolyl hydroxylase (HPH), which prevents HIF hydroxylation and VHL recognition [3,10,11]. Although both HIF-1α and HIF-2α have high homology and are induced similarly in hypoxia, they have differences in transcriptional targets as well as impact on multiple physiological pathways and tumorigenesis [6,12,13,14].
Increased evidence has revealed that HIF-1α overexpression is well correlated with carcinogenesis and tumor progression in many kinds of cancer. In most malignancies, HIF-1α overexpression was associated with unfavorable prognosis [7,15,16,17]. Studies about the correlation between HIF-2α overexpression and clinical outcome in cancer patients yielded inconsistent results [18,19,20,21]. There are some contradicting results of HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression in cancer cell growth and patient outcome according to types of tumors [12,20,22]. Despite these differences and contradictions, both HIF-1α and HIF-2α have roles in tumor growth, creating a good option for tumor treatment target [21].
Pancreatic tumors are characterized by desmoplastic, hypo-vascularity and ineffective drug delivery. Constitutive expression of HIF-1α contributes to the survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells in hypoxia and glucose deprivation through the activation of anaerobic metabolism and the Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway [23,24,25]. Increasing evidence has revealed that HIF-1α overexpression in pancreatic cancers was a predictor of greater invasion, recurrence and shorter survival time [12,15,16,17,26,27,28]. SIAH (Seven-In-Absentia Homolog) is the most downstream component of oncogenic K-RAS pathway and associated with expression of HIF-1 α in carcinoma [29]. Its expression is upregulated as human pancreatic cancer progresses to advanced stages [24].
Although HIF-1α expression is suggested as a prognostic factor and molecular biomarker of pancreatic cancer [24,26,27,28], there is little known about the role of HIF-2α and the comparison of HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression in various pancreatic precancerous lesions and tumors.
The aim of this study was to investigate the potential role of hypoxia-inducible factors on the progression of premalignant lesions to adenocarcinomas of pancreas. We measure the expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α by applying immunohistochemistry in the following samples: pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), neuroendocrine tumor (NET), and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). As controls, non-tumor samples from the same patients were analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Specimens
Surgical specimens of pancreatic lesions and adjacent normal pancreatic tissues were obtained from 29 patients undergoing pancreatic surgical resection between December 2009 and November 2016 at the Sentara Norfolk General Hospital in Norfolk, VA. These patients underwent partial pancreatectomy, distal pancreatectomy or Whipple surgery. Patients’ age ranged from 34 to 79 years (mean, 62.6 years) and 46.0% were males. Histologic diagnoses were confirmed by the Pathology Department at Sentara Norfolk General Hospital. The following samples were studied: PDAC (15 cases), NET (7 cases), IPMN (4 cases), and PanIN (3 cases).
2.2. Ethical Statement
This study was approved by the institutional review board of the Eastern Virginia Medical School (EVMS), Norfolk, VA (IRB # 05-09-EX-0298. Initial approval on 07-FEB -2007, current Continuing Review approved on 04-JUN-2020). Written informed consent was obtained from the patients before their surgeries.
2.3. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining for HIF-1α and -2α
HIF-1α and HIF 2α staining was performed using the protocol from Novus Biologicals (NB100–105) with minor modifications. The Ultra Vision Quanto Detection System HRP DAB Quanto Thermofisher, Kalamazoo, MI was applied for the entire staining process. Paraffin embedding and sample cutting was performed at the Biorepository Lab, Department of Pathology & Anatomy, EVMS. In brief, sections (4 μm thick) were baked at 60 °C for 1 h, deparafinized and rehydrated in xylene and descending ethanol concentration. Next, sections were subjected to heat-based antigen retrieval in sodium citrate buffer pH 6.0 (Sigma-Aldrich) in a microwave oven at 20 min. After inactivation of endogenous peroxidase with BIO SB peroxidase blocker, sections were blocked with Ultravision Protein block. Tissue sections were incubated overnight at 4 °C with antibody anti-HIF-1α (1:100 dilution; mouse monoclonal antibody; cat. No. NB 100–105; Novus Biologicals, Littleton, CO, USA) or anti-HIF-2α (1:100 dilution; rabbit polyclonal antibody; cat. No. NB 100–122; Novus Biologicals). Then, sections were washed with Tris Buffered Saline (TBS) and treated with either goat anti-mouse or goat anti-rabbit antibody-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) for 20 min at room temperature, followed by additional washing with TBS. After that, tissue staining was visualized by diaminobenzidine (DAB) as the chromogen substrate for 5 min at room temperature. Nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin (American MasterTech Scientific, Inc, Lodi, CA, USA), dehydrated and mounted using Permount Mounting Medium (Fisher Chemical, Fair lawn, NJ, USA). Negative controls, in which the primary antibody was replaced with TBS, were run with all of the samples. Normal pancreatic tissues (non-tumor, NT) removed from the same patient served as a matched negative control.
Stained samples were visualized under light microscopy (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and digital images were captured using the Infiniti-2 Digital CCD Microscopy Camera attached to the light microscope (Lumenera Corporation, Ottawa, Canada). Both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α were evaluated. The samples were initially scanned at low power and at least four high-power fields (magnification: ×400) were chosen randomly. Proportion and intensity of staining was evaluated and scored for HIF-1α and -2α using the Immunoreactivity Scoring System.
2.4. Immunoreactivity Scoring System (IRS)
Three sequential slides were obtained for each subject. For morphometric comparison of tissue biopsies from tumor positive and negative cases, four separated images per slide were captured first at 100× for the general view and after at ×400 magnification. To ensure that the analysis was unprejudiced, each image captured at ×400 was analyzed four times for intensity score (IS) and for proportional score (PS) using the Image J software. The average of these was calculated for each slide. All tested material was analyzed in the same way. Immunoreactivity score was calculated based on a previously defined scoring system incorporating intensity and percent of cells staining [30,31]. The proportional score (PS) was graded as follows: 0 = less than 10% of cells staining positive, 1 = 10–29% of cells staining positive, 2 = 30–49% of cells staining positive, 3 = 50–80% of cells staining positive, 4 = greater than 80% of cells staining positive. Intensity score (IS) was graded as 0 = negative, 1 = low positive, 2 = positive, 3 = high positive using IHC profiler [32,33]. These two scores were multiplied to obtain a ‘final score (FS)’ for immunoreactivity. The FS rated the samples for immunoreactivity as follows: negative (FS I) = 0–1, mild (FS II) = 2–3, moderate (FS III = 4–8 and strongly positive (FS IV) = 9–12 [30]. All samples were independently evaluated by two investigators (JHJ and DS) and the scores of each one was averaged to obtain a final score for each slide. Both investigators were blinded for pathological diagnosis of each case.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Parametric (analysis of variance ANOVA) and non-parametric tests (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) were used to compare mean differences between groups, depending on sample size and distribution. If significance was observed, post hoc analysis was performed (Tukey–Kramer; Wilcoxon) between each group. Fisher’s Exact Test was used for categorical variables. Simple linear regression analysis was used to assess associations between variables. All statistical analyses were performed using JMP Pro 12 statistical software (SAS Institute Inc., Calgary, NC, USA), with the risk of Type I error set at α = 0.05.
3. Results
Slides from 29 patients were analyzed in this study. Their clinical characteristics are shown in Table 1. Comorbidities including diabetes mellitus (DM), hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia and cancer were present mainly in patients with PDAC and NET (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Different Pancreatic Lesions.
Both HIF-1α and HIF-2α proteins were uniformly overexpressed in tumor tissue and representative IHC staining microphotographs are shown in Figure 1. HIF-1α and HIF-2α proteins were detected in the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The other lesions show greater stromal collagen contents with weak immunoreactivity of both HIF-1α and HIF-2α compared to control (NT).
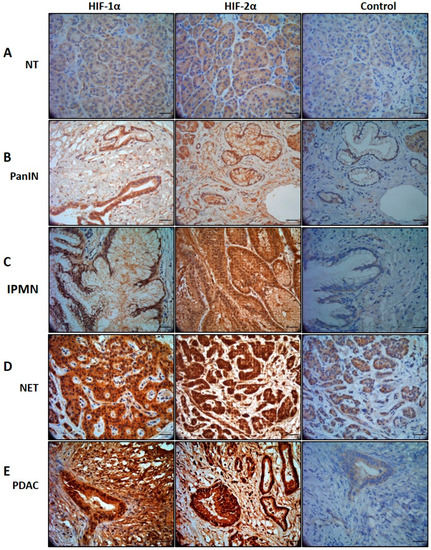
Figure 1.
HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression in different type of pancreatic pathology. (A) In Non-tumor (NT) biopsies, expression is very weak. (B) Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) showed mild cytoplasm and nuclear expression. (C) Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), showed moderate cytoplasmic and nuclear expression. (D) Neuroendocrine tumor (NET), demonstrated moderate cytoplasmic and from moderate to strong nuclear expression. (E) Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), showed moderate cytoplasmic and strong nuclear expression. The characteristic atypical cells form irregular and incomplete structures, i.e., tubular or glandular structures with strong expression embedded in a dense desmoplastic tumor stroma. Control images from non-tumor (NT) stained with the same antibody showing negative or very weak immunostaining. Scale bar, 100 μm.
Nuclear immunoreactivities of HIF-1α and HIF-2α for the five different groups are shown as FS in Table 2 and Figure 2 (Supplementary Figure S1). The expression of HIF-1α increased significantly from PanIN (3.01 ± 0.17) through IPMN (7.63 ± 0.18) and NET (9.10 ± 0.23) to PDAC samples (11.06 ± 0.15, p < 0.001). The expression of HIF-2α also increased significantly from PanIN (2.79 ± 0.22) through IPMN (6.19 ± 0.17), and NET (8.56 ± 0.14) to PDAC samples (11.88 ± 0.04, p < 0.001).

Table 2.
FS of HIF-1α and HIF -2α for each group.
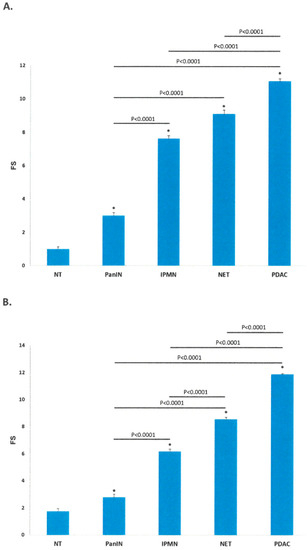
Figure 2.
Final Score of Immunoreactivity for HIF-1α (A) and HIF-2α (B). (A,B) Bar diagrams correspond to Final Scores (FS) for HIF-1 α and HIF-2 α in the 5 groups. FS of both HIF-1α and HIF-2α increased progressively from PanIN through IPMN, NET to PDAC. Data are mean ± SEM; * p < 0.0001 PanIN, IPMN, NET and PDAC versus NT. Analysis of variance with post hoc analysis (Tukey-Kramer). HIF = hypoxia inducible factor, IPMN = intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, NET = neuroendocrine tumor, NT = non-tumor, PanIN = pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia, PDAC = pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
Three slides were obtained for each of the 29 subjects and four pictures were taken from each slide. Some slides were not suitable and were excluded from the analysis. Percent strength immunoreactivity for HIF-1α and HIF-2α were calculated for each group and is shown in Table 3 (Supplementary Figure S2).

Table 3.
Immunohistochemical analysis of HIF-1α and HIF-2α.
Simple linear regression analysis showed a strong correlation between HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression (R2 = 0.841, p < 0.001) (Figure 3).
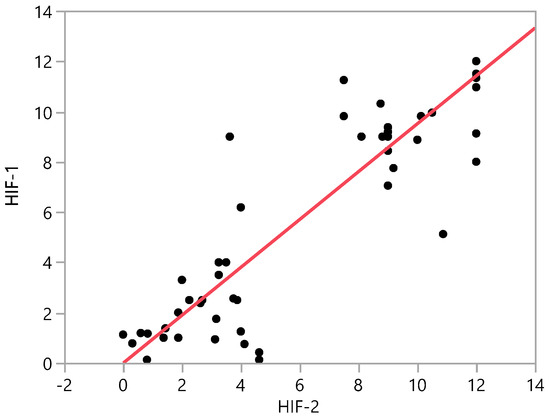
Figure 3.
Correlation between HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression for all samples. R calculated with Simple linear regression analysis. HIF = hypoxia inducible factor, IPMN = intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, NET = neuroendocrine tumor, NT = non-tumor, PanIN = pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia, PDAC = pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
4. Discussion
In this study, we found that significantly higher expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in PDAC, NETs, IPMN and precancerous lesions such as PanINs when compared with non-tumor samples. Furthermore, we observed a significant stepwise increase in nuclear expression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α from non-tumor tissue to PanINs, IPMNs, NETs and PDACs.
HIF indirectly regulates cellular processes such as proliferation and differentiation through interactions with other signaling proteins such as c-Myc and Notch. There are multiple mechanisms by which HIF can become activated and promote tumor progression [22]. HIF is an attractive target for anti-tumor therapy because it has low activity in normal, well oxygenated tissues, so it can be hypothesized that side effects caused by inhibition will be minimal [34]. Hypoxic tumors were more sensitive to tirapazamine (the lead compound in the benzotriazine-di-N-oxide class of hypoxic cytotoxins that selectively act in hypoxic tumor cells through bioreductive mechanisms)—containing therapies in xeno-grafted mouse tumors and in clinical trials in non-small-cell lung cancer and head and neck cancer. [35,36]. Although it appears that transcription factors like HIF1 can be targeted such that metabolic effects have anticancer application, it is important to note that targeting the downstream genes themselves may be a more controlled and/or specific approach [34].
We focused on the pathogenesis of progression from precancerous lesions through pancreatic adenocarcinoma with the increased expression of the HIF-1α and HIF-2α. We can postulate that both HIF-1α and HIF-2α are playing a role in this progression. Furthermore, the potential abrogation of expression of HIFs will lead to a potential target for antineoplastic therapies for NETs and PDACs.
This study has limitations. First, it is retrospective and single center, so extrapolating our findings to overall pancreatic tumors population seems challenging. Second, evaluation of HIF-1α and HIF-2α expression was based on immunohistochemical analysis, not confirmed by another method like western blotting. Third, there is lack of long-term follow up and survival data, and the number of samples is limited to be able to draw solid conclusions. Despite these limitations, our findings illuminate viable avenues for further research on HIF-associated therapeutics development.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our findings revealed stepwise increase of HIF-1α and -2α immunoreactivity with progression of disease in pancreatic tissues. To our knowledge, this is the first study describing HIF expression patterns in a broad range of pancreatic lesions. Our data suggest that HIF-1α and HIF-2α may play a role in pancreatic tumor progression but further large-scale studies will be necessary to confirm these findings and to define the effect of HIFs abrogation on tumor progression that can lead to novel therapies for this aggressive disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2571-841X/3/4/30/s1.
Author Contributions
J.H.J. and D.S. were involved in data acquisition, data analysis and interpretation, drafting of the article and approval of final version. J.W. was involved in data acquisition, data analysis and interpretation, critical review of the final draft for important intellectual content and approval of final version. H.K.P., C.M.C. and A.I.V. were involved in study conception and design, data analysis and interpretation, critical review of the final draft for important intellectual content and approval of final version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Gyeongsang National University Fund for Professors on Sabbatical Leave, 2017.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Abbreviations
| HIF | hypoxia inducible factor |
| PDAC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| NET | neuroendocrine tumor |
| IPMN | intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| PanIN | pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia |
| NT | non-tumor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Han, G.; Zhai, H.; Zhang, F.-M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, X.; Fan, D. Expression and Clinical Significance of CacyBP/SIP in Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreatology 2008, 8, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacs, J.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Mole, D.R.; Lee, S.; Torres-Cabala, C.; Chung, Y.-L.; Merino, M.; Trepel, J.; Zbar, B.; Toro, J.; et al. HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: Novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenza, G.L. Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birner, P.; Schindl, M.; Obermair, A.; Plank, C.; Breitenecker, G.; Oberhuber, G. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a marker for an unfavorable prognosis in early-stage invasive cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4693–4696. [Google Scholar]
- Talks, K.L.; Turley, H.; Gatter, K.C.; Maxwell, P.H.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Harris, A.L. The Expression and Distribution of the Hypoxia-Inducible Factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α in Normal Human Tissues, Cancers, and Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; De Marzo, A.M.; Laughner, E.; Lim, M.; Hilton, D.A.; Zagzag, D.; Buechler, P.; Isaacs, W.B.; Semenza, G.L.; Simons, J.W. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5830–5835. [Google Scholar]
- Forsythe, J.A.; Jiang, B.H.; Iyer, N.V.; Agani, F.; Leung, S.W.; Koos, R.D.; Semenza, G.L. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Wolf, P.L.; Escudero, R.; Deutsch, R.; Jamieson, S.W.; Thistlethwaite, P.A. Early Expression of Angiogenesis Factors in Acute Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 342, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wiesener, M.S.; Chang, G.-W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruick, R.K. A Conserved Family of Prolyl-4-Hydroxylases That Modify HIF. Science 2001, 294, 1337–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, M.; Guo, X.; Jian, J. Expression and significance of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in pancreatic cancer. Acta Acad. Med. Wuhan 2015, 35, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Du, F.; Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Xu, B. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 in digestive system cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; De Cubas, A.A.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Richter, S.; Peitzsch, M.; Menschikowski, M.; Lenders, J.W.; Timmers, H.J.L.M.; Mannelli, M.; Opocher, G.; et al. Opposing effects of HIF1α and HIF2α on chromaffin cell phenotypic features and tumor cell proliferation: Insights from MYC-associated factor X. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-S.; Chen, X.-H.; Yin, X.; Zhang, B.-H. Prognostic Significance of HIF-1α Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Kitadai, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kuwai, T.; Hihara, J.; Yoshida, K.; Toge, T.; Chayama, K. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α is associated with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour angiogenesis in human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.-G.; Xing, C.-G.; Feng, Y.-Z.; Chen, J.; Deng, C. Clinical Significance of Immunohistochemical Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor–1α as a Prognostic Marker in Rectal Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Color. Cancer 2006, 5, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, E.M.; Yaromina, A.; Houben, R.; Groot, A.J.; Dubois, L.; Vooijs, M. Prognostic Role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α Tumor Cell Expression in Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Huang, T.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, W.; Shi, Q.; Li, H.; Ren, J.; Hou, F. Association Between Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α (HIF-2α) Expression and Colorectal Cancer and Its Prognostic Role: A Systematic Analysis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, T.; Kikuchi, H.; Herraiz, M.-T.; Park, D.-Y.; Mizukami, Y.; Mino-Kenduson, M.; Lynch, M.P.; Rueda, B.R.; Benita, Y.; Xavier, R.J.; et al. HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha have divergent roles in colon cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, M.; Jiang, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Chen, S.-X.; Liang, X.-H. Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1 and Hypoxia Inducible Factor 2 Play Distinct and Functionally Overlapping Roles in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4732–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, E.B.; Giaccia, A.J. The role of hypoxia-inducible factors in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akakura, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Horiuchi, I.; Suzuki, A.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Niizeki, H.; Ki, K.; Hosokawa, M.; Asaka, M. Constitutive expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha renders pancreatic cancer cells resistant to apoptosis induced by hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6548–6554. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, R.; Smyrk, T.C.; Reed, N.R.; Schmidt, R.L.; Schnelldorfer, T.; Chari, S.T.; Petersen, G.M.; Tang, A.H. Combining clinicopathological predictors and molecular biomarkers in the oncogenic K-RAS/Ki67/HIF-1alpha pathway to predict survival in resectable pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Morinibu, A.; Itasaka, S.; Hiraoka, M.; Harada, H. HIF-1 maintains a functional relationship between pancreatic cancer cells and stromal fibroblasts by upregulating expression and secretion of Sonic hedgehog. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 10525–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbert, L.E.; Fisher, S.B.; Balci, S.; Saka, B.; Chen, Z.; Kim, S.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Adsay, N.V.; Maithel, S.K.; Landry, J.C.; et al. High nuclear hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha expression is a predictor of distant recurrence in patients with resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 91, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, X.-L.; Pankaj, P.; Hu, Q.-D.; Liang, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α expression and its clinical significance in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Pancreatology 2014, 14, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.-C.; Mori, R.; Vallbohmer, D.; Brabender, J.; Klein, E.; Drebber, U.; Baldus, S.E.; Cooc, J.; Azuma, M.; Metzger, R.; et al. High Expression of HIF1a Is a Predictor of Clinical Outcome in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinomas and Correlated to PDGFA, VEGF, and bFGF. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aga, M.; Kondo, S.; Wakisaka, N.; Moriyama-Kita, M.; Endo, K.; Nakanishi, Y.; Murono, S.; Sugimoto, H.; Ueno, T.; Yoshizaki, T. Siah-1 is associated with expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 2017, 44, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedchenko, N.; Reifenrath, J. Different approaches for interpretation and reporting of immunohistochemistry analysis results in the bone tissue—A review. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cases, A.I.; Ohtsuka, T.; Kimura, H.; Zheng, B.; Shindo, K.; Oda, Y.; Mizumoto, K.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, M. Significance of expression of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.; Bukhari, A.B.; Malhotra, R.; De, A. IHC Profiler: An Open Source Plugin for the Quantitative Evaluation and Automated Scoring of Immunohistochemistry Images of Human Tissue Samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mane, D.R.; Kale, A.D.; Belaldavar, C. Validation of immunoexpression of tenascin-C in oral precancerous and cancerous tissues using ImageJ analysis with novel immunohistochemistry profiler plugin: An immunohistochemical quantitative analysis. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2017, 21, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denko, N.C. Hypoxia, HIF1 and glucose metabolism in the solid tumour. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, R.; Röper, B.; Carlsen, J.M.; Huisman, M.C.; Lebschi, J.A.; Andratschke, N.; Picchio, M.; Souvatzoglou, M.; Machulla, H.-J.; Piert, M. Pretreatment 18F-FAZA PET Predicts Success of Hypoxia-Directed Radiochemotherapy Using Tirapazamine. J. Nucl. Med. 2007, 48, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischin, D.; Hicks, R.J.; Fisher, R.; Binns, D.; Corry, J.; Porceddu, S.; Peters, L.J. Prognostic Significance of [18F]-Misonidazole Positron Emission Tomography–Detected Tumor Hypoxia in Patients With Advanced Head and Neck Cancer Randomly Assigned to Chemoradiation With or Without Tirapazamine: A Substudy of Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group Study 98.02. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2098–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).