Antineoplastic Effect of Metformin Against Glioblastoma Multiforme In Vitro and In Vivo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy and Information Sources
2.3. Bias and Quality Assessments
2.4. Data Extraction and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
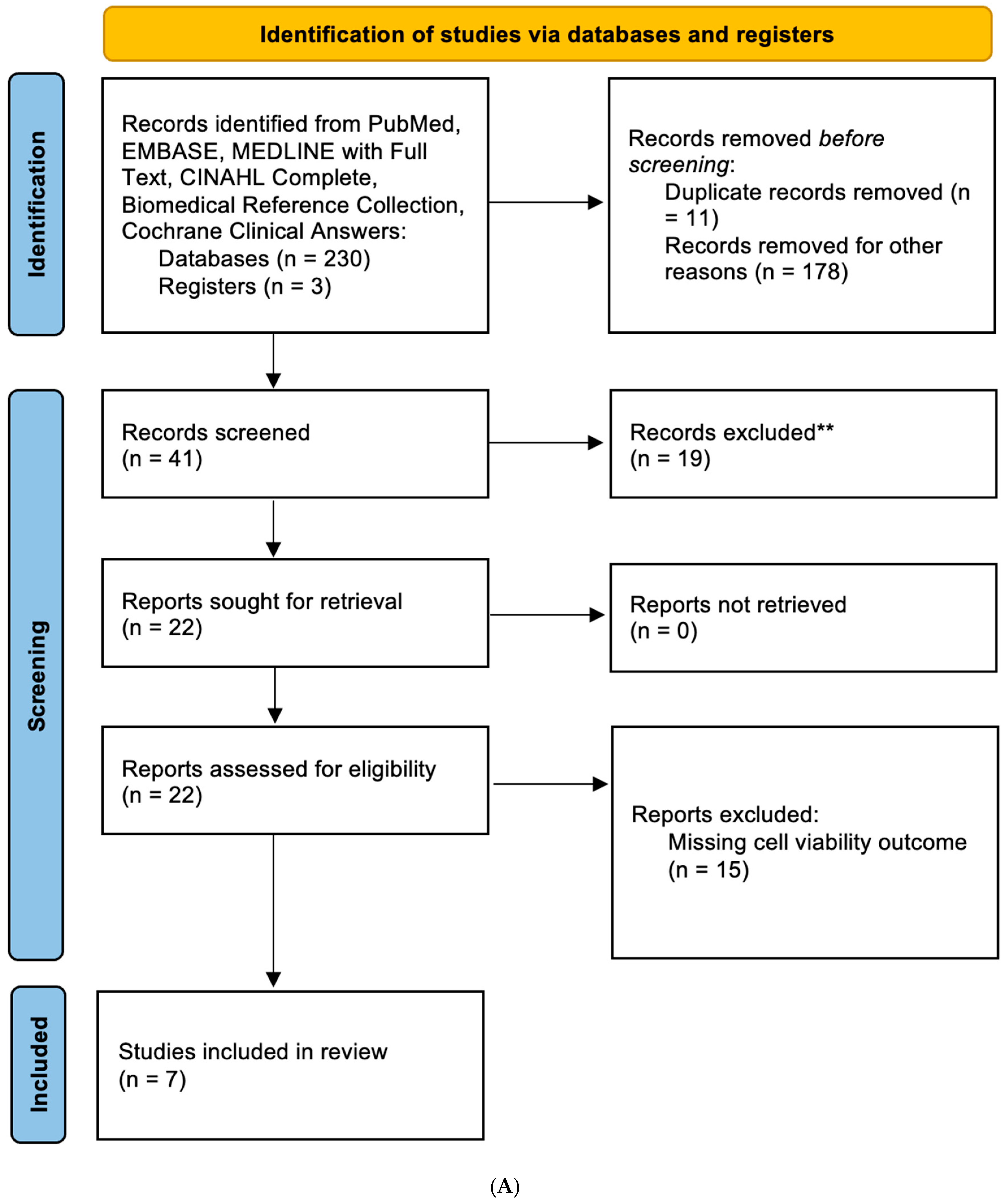
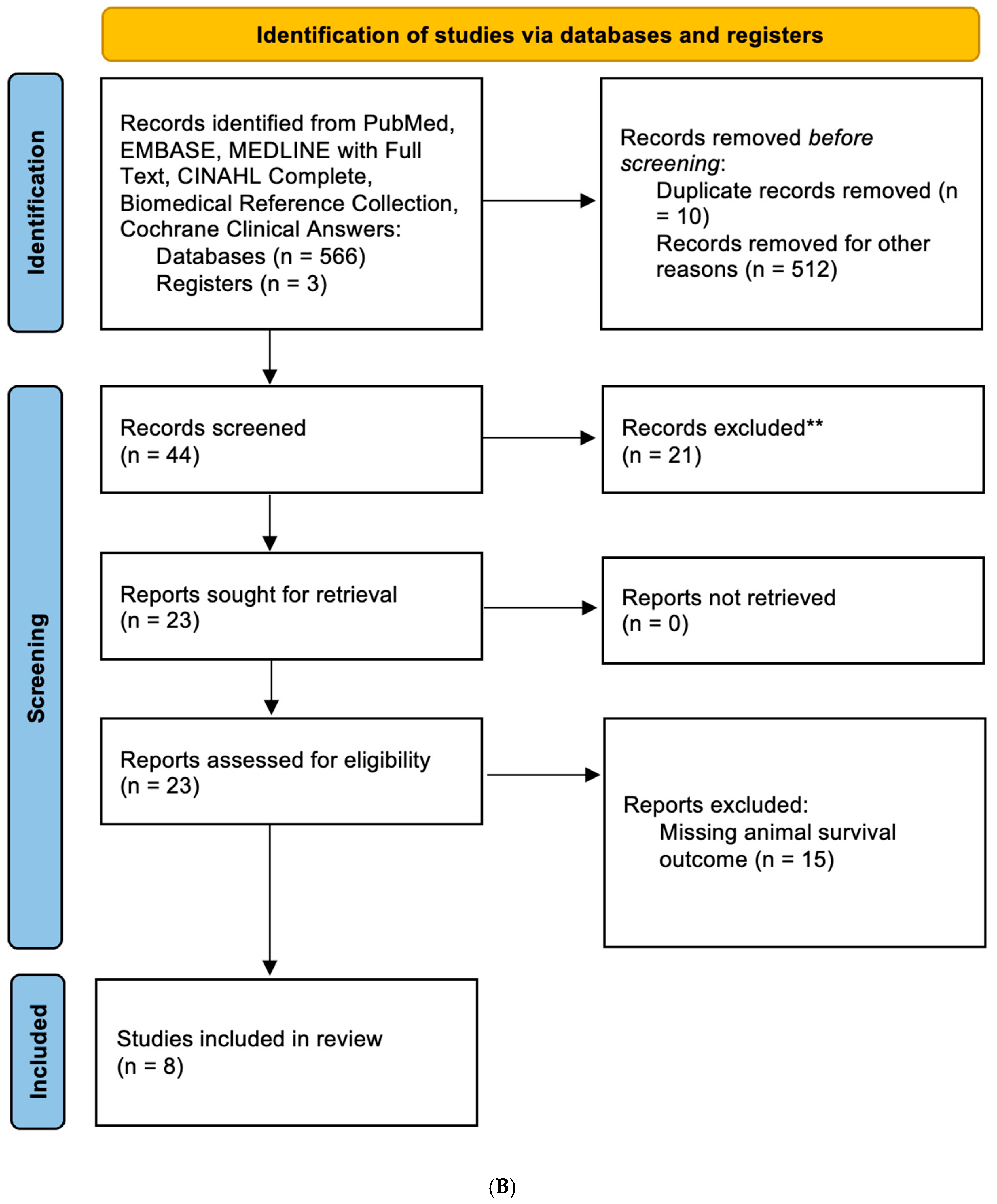
3.1. Characteristics of the Studies for Analysis
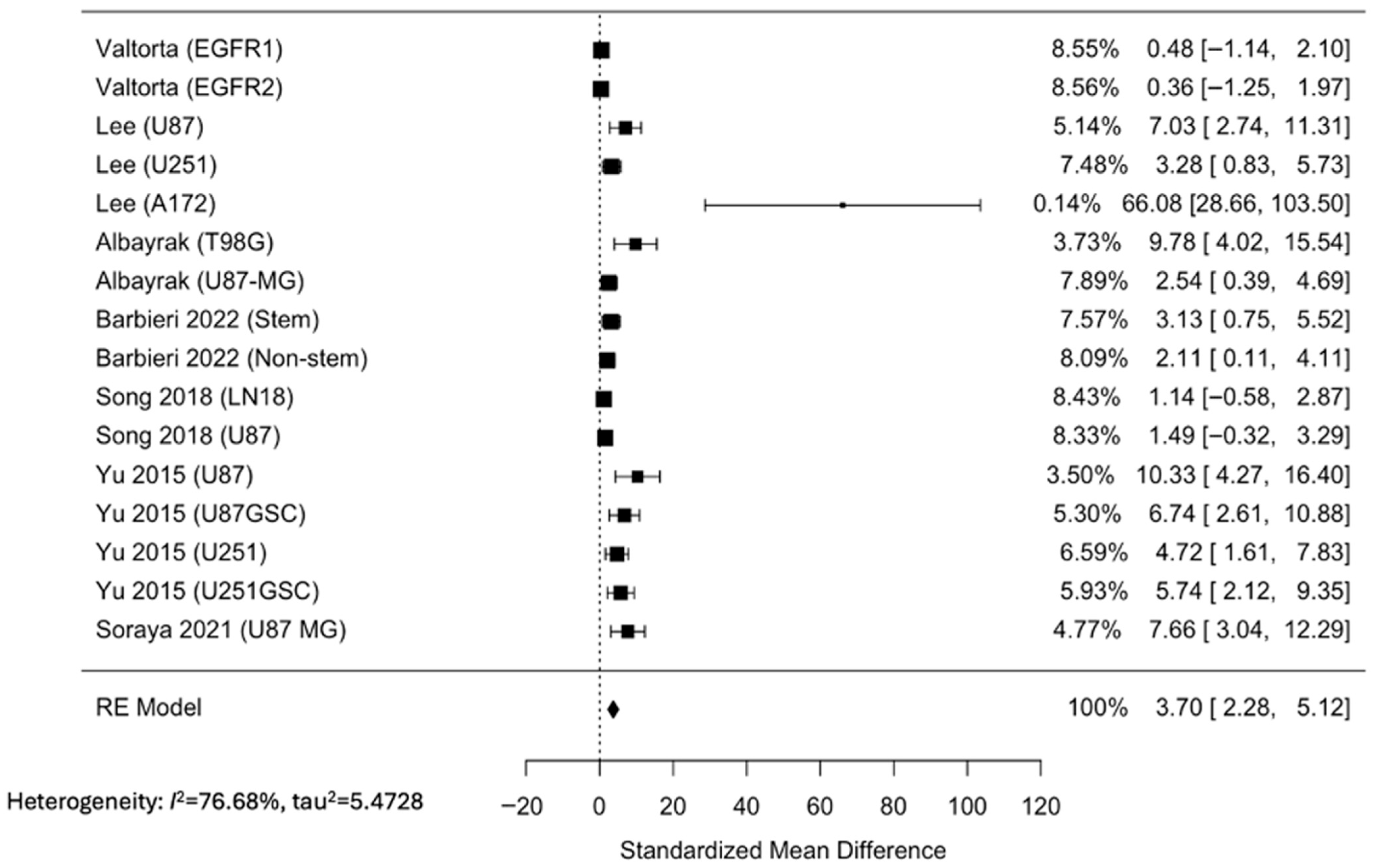
3.2. Metformin Reduced Cell Viability of GBM Cell Lines
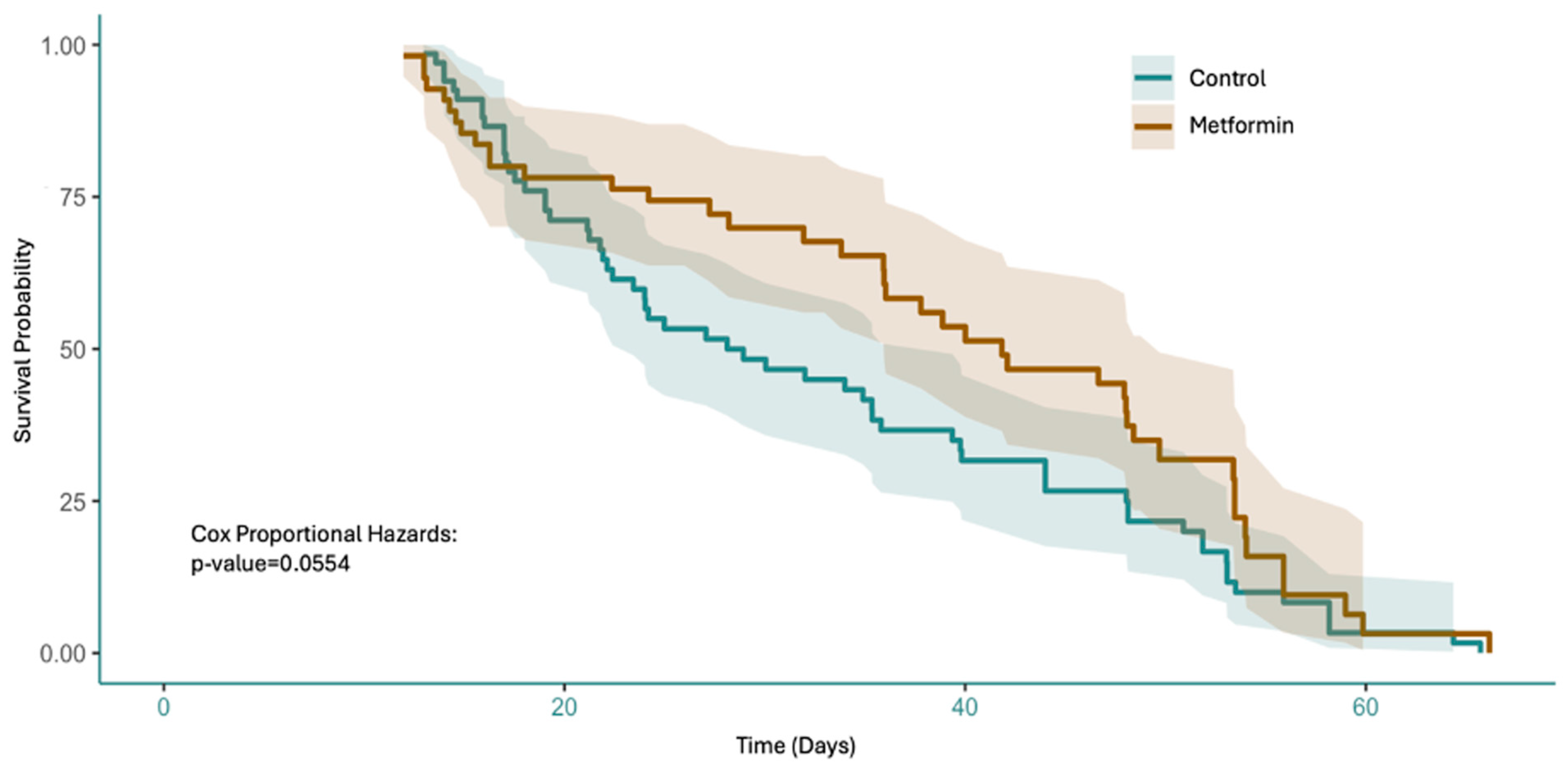
3.3. Metformin Increases Survival of GBM In Vivo
3.4. Bias and Quality Assessments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Caverzan, M.D.; Beauge, L.; Oliveda, P.M.; Cesca Gonzalez, B.; Buhler, E.M.; Ibarra, L.E. Exploring Monocytes-Macrophages in Immune Microenvironment of Glioblastoma for the Design of Novel Therapeutic Strategies. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, L.R.; Mellinghoff, I.K. Glioblastoma and Other Primary Brain Malignancies in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2023, 329, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, M.; Chen, R.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y. Analysis of epidemiology and nomogram construction for prediction and clinical decision-making in gliomas. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1624142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Sage, J.C.; Miller, M.R.; Verhaak, R.G.; Hippenmeyer, S.; Vogel, H.; Foreman, O.; Bronson, R.T.; Nishiyama, A.; Luo, L.; et al. Mosaic analysis with double markers reveals tumor cell of origin in glioma. Cell 2011, 146, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esemen, Y.; Awan, M.; Parwez, R.; Baig, A.; Rahman, S.; Masala, I.; Franchini, S.; Giakoumettis, D. Molecular Pathogenesis of Glioblastoma in Adults and Future Perspectives: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Benjamin, L.E. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyan, A.; Ghorbanlo, M.; Eslami, M.; Jahanshahi, M.; Ziaei, E.; Salami, A.; Mokhtari, K.; Shahpasand, K.; Farahani, N.; Meybodi, T.E.; et al. Glioblastoma multiforme: Insights into pathogenesis, key signaling pathways, and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Odia, Y.; Khosla, A.A.; Ahluwalia, M.S. Key Clinical Principles in the Management of Glioblastoma. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poon, M.T.C.; Sudlow, C.L.M.; Figueroa, J.D.; Brennan, P.M. Longer-term (≥2 years) survival in patients with glioblastoma in population-based studies pre- and post-2005: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, V.; De Jesus, K.; Mailankody, S. The high price of anticancer drugs: Origins, implications, barriers, solutions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Mansour, H.M.; Aguilar, T.M.; Lucke-Wold, B. Advances in Anti-Cancer Drug Development: Metformin as Anti-Angiogenic Supplemental Treatment for Glioblastoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Guo, Y. Metformin and Its Benefits for Various Diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yao, Y.; Jia, R.; Ge, S.; Zhuang, A. Metformin and cancer hallmarks: Shedding new lights on therapeutic repurposing. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielecka-Wajdman, A.M.; Ludyga, T.; Smyk, D.; Smyk, W.; Mularska, M.; Świderek, P.; Majewski, W.; Mullins, C.S.; Linnebacher, M.; Obuchowicz, E. Glucose Influences the Response of Glioblastoma Cells to Temozolomide and Dexamethasone. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748221075468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panwar, V.; Singh, A.; Bhatt, M.; Tonk, R.K.; Azizov, S.; Raza, A.S.; Sengupta, S.; Kumar, D.; Garg, M. Multifaceted role of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway in human health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Cho, S.; Blenis, J. mTORC1, the maestro of cell metabolism and growth. Genes Dev. 2025, 39, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzer, A.; German, N.J.; Gonzalez-Herrera, K.N.; Asara, J.M.; Haigis, M.C.; Struhl, K. Metformin and phenformin deplete tricarboxylic acid cycle and glycolytic intermediates during cell transformation and NTPs in cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10574–10579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, R.S.; Jawaid, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Verma, R.; Patra, P.K.; Vijaypal, S.V.; Pal, Y.; Upadhyay, R. Metformin’s anticancer odyssey: Revealing multifaceted mechanisms across diverse neoplastic terrains- a critical review. Biochimie 2025, 233, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Mechanisms of metformin inhibiting cancer invasion and migration. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 4885–4901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gonda, T.A.; Tu, S.; Wang, T.C. Chronic inflammation, the tumor microenvironment and carcinogenesis. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 2005–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtorta, S.; Lo Dico, A.; Raccagni, I.; Martelli, C.; Pieri, V.; Rainone, P.; Todde, S.; Zinnhardt, B.; De Bernardi, E.; Coliva, A.; et al. Imaging Metformin Efficacy as Add-On Therapy in Cells and Mouse Models of Human EGFR Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 664149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.E.; Lim, J.H.; Hong, Y.K.; Yang, S.H. High-Dose Metformin Plus Temozolomide Shows Increased Anti-tumor Effects in Glioblastoma In Vitro and In Vivo Compared with Monotherapy. Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 50, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albayrak, G.; Konac, E.; Dere, U.A.; Emmez, H. Targeting Cancer Cell Metabolism with Metformin, Dichloroacetate and Memantine in Glioblastoma (GBM). Turk. Neurosurg. 2021, 31, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, F.; Bosio, A.G.; Pattarozzi, A.; Tonelli, M.; Bajetto, A.; Verduci, I.; Cianci, F.; Cannavale, G.; Palloni, L.M.G.; Francesconi, V.; et al. Chloride intracellular channel 1 activity is not required for glioblastoma development but its inhibition dictates glioma stem cell responsivity to novel biguanide derivatives. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Lyu, X.; Cui, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, G. Metformin inhibits TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-like process and stem-like properties in GBM via AKT/mTOR/ZEB1 pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7023–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhao, G.; Xie, G.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Li, Y. Metformin and temozolomide act synergistically to inhibit growth of glioma cells and glioma stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 32930–32943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soraya, H.; Sani, N.A.; Jabbari, N.; Rezaie, J. Metformin Increases Exosome Biogenesis and Secretion in U87 MG Human Glioblastoma Cells: A Possible Mechanism of Therapeutic Resistance. Arch. Med. Res. 2021, 52, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Cai, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, W.; Sun, T. Metformin-induced reduction of CCR8 enhances the anti-tumor immune response of PD-1 immunotherapy in glioblastoma. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 964, 176274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Q.; Yi, K.; Cui, X.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Fang, C.; Tan, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; et al. Blood exosomes-based targeted delivery of cPLA2 siRNA and metformin to modulate glioblastoma energy metabolism for tailoring personalized therapy. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsakova, L.; Krasko, J.A.; Stankevicius, E. Metabolic-targeted Combination Therapy with Dichloroacetate and Metformin Suppresses Glioblastoma Cell Line Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. In Vivo 2021, 35, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, Y.; Koh, I.; Shim, J.K.; Park, J.; Choi, J.; Yun, M.; Jeon, J.Y.; Huh, Y.M.; et al. Inhibition of glioblastoma tumorspheres by combined treatment with 2-deoxyglucose and metformin. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, A.; Sunayama, J.; Okada, M.; Watanabe, E.; Seino, S.; Shibuya, K.; Suzuki, K.; Narita, Y.; Shibui, S.; Kayama, T.; et al. Glioma-initiating cell elimination by metformin activation of FOXO3 via AMPK. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Ambe, R.; Barragan, J.; Reyes, K.M.; Cervantes, J. Metformin Reduces Viability and Inhibits the Immunoinflammatory Profile of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells. Neuroglia 2024, 5, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, T.S.; McKay, R.M.; Burns, D.K.; Kernie, S.G.; Parada, L.F. A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 2012, 488, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H.; Kettenmann, H. The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and progression. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, N.J.; Bird, C.E.; Hicks, W.H.; Abdullah, K.G. Economic implications of the modern treatment paradigm of glioblastoma: An analysis of global cost estimates and their utility for cost assessment. J. Med. Econ. 2021, 24, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
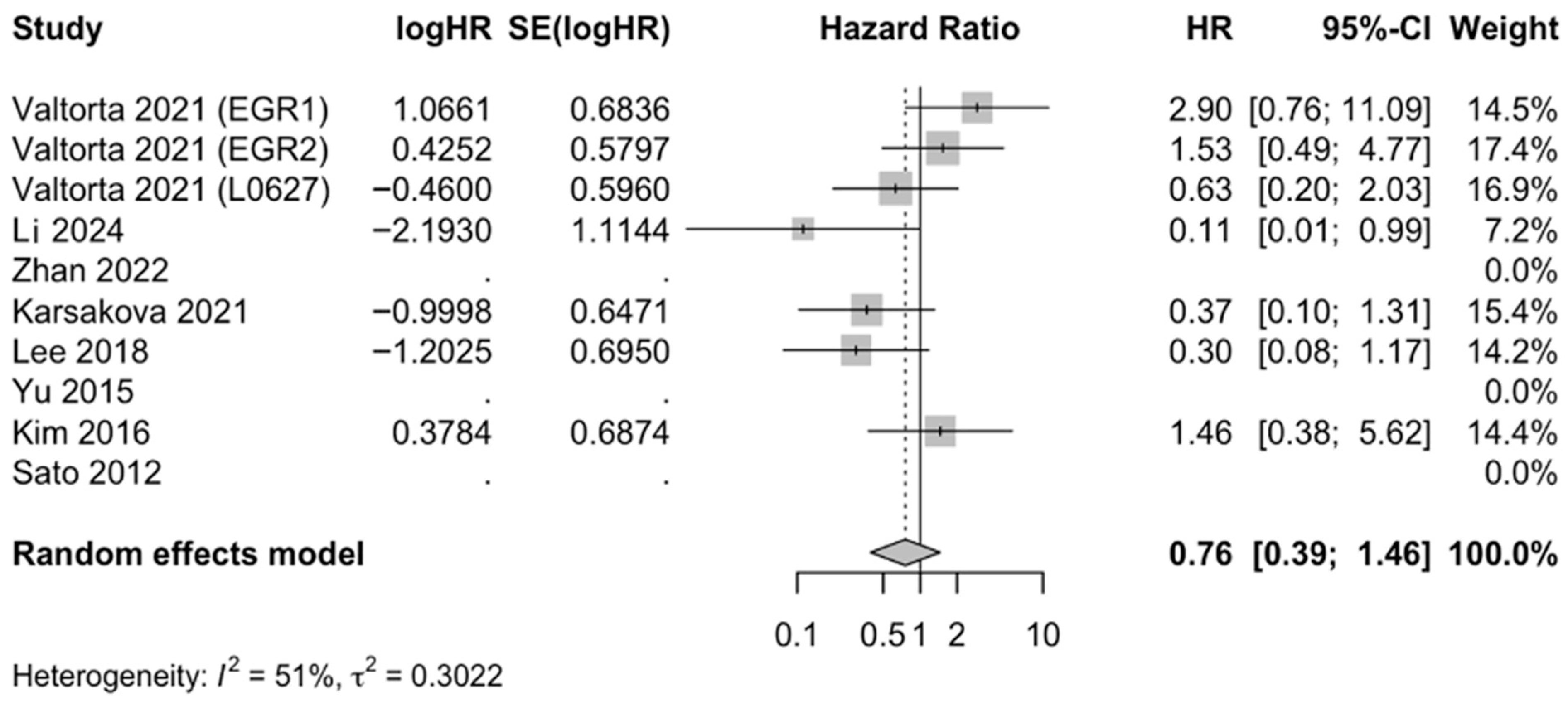


| Source | Type of Study | Cell Line(s) | Metformin Used as an Adjuvant Therapy? | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valtorta 2021 [21] | In vitro, in vivo | EGFR1, EGFR2, L0627 | Yes | Metformin addition improved TMZ efficacy in GBM preclinical models representative of classical molecular subtype, increasing survival time and reducing tumor relapsing rate. |
| Lee 2018 [22] | In vitro, in vivo | U87, U251, A172 | Yes | Metformin combined with TMZ enhanced apoptosis in GBM cell lines and prolonged survival in mouse models. |
| Albayrak 2021 [23] | In vitro | T98G, U87-MG | No | Metformin reduced cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. |
| Barbieri 2022 [24] | In vitro | Patient-derived GBM cultures | No | Metformin inhibited chloride intracellular channel 1 (CLIC1) activity, inhibiting GSC proliferation, although novel biguanide derivatives may demonstrate higher efficacy. |
| Song 2018 [25] | In vitro | LN18, U87 | No | Metformin suppressed transforming growth factor beta-1-induced (TGF-β1-induced) epithelial–mesenchymal transition-like processes, migration, and invasion in GBM cells by inhibiting the AKT/mTOR/ZEB1 pathway. |
| Yu 2015 [26] | In vitro, in vivo | U87, U87GSC, U251, U251GSC | Yes | Metformin used with TMZ inhibited proliferation, self-renewal, and tumor growth of GBM cells in vitro and in vivo by suppressing AKT/mTOR signaling. |
| Soraya 2021 [27] | In vitro | U87-MG | No | Metformin reduced cell survival while downregulating oncogenic microRNAs (miRNAs). |
| Li 2024 [28] | In vivo | GL261 | Yes | Metformin enhanced anti-programmed cell death protein-1 (anti-PD-1) immunotherapy in GBM mouse models by promoting T cell-mediated antitumor responses. |
| Zhan 2022 [29] | In vivo | Patient-derived GBM cultures | No | Exosome-mediated delivery of metformin disrupted GBM energy metabolism and significantly reduced tumor growth, prolonging survival in xenograft models. |
| Korsakova 2021 [30] | In vivo | GL261 | Yes | Metformin and DCA synergistically impaired GBM metabolism, reduced proliferation, and inhibited tumor growth in allograft models. |
| Kim 2017 [31] | In vivo | GSC11 | No | Metformin suppressed stemness and invasiveness, showing survival benefit in mouse xenograft models. |
| Sato 2012 [32] | In vivo | Patient-derived GBM cultures | No | Metformin activated AMPK-FOXO3 signaling to promote differentiation of stem-like cells, depleting tumorigenic potential and inhibiting tumor formation to extend survival. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vashi, B.; Gonzales-Portillo, D.; Cervantes, J. Antineoplastic Effect of Metformin Against Glioblastoma Multiforme In Vitro and In Vivo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroglia 2025, 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia6040040
Vashi B, Gonzales-Portillo D, Cervantes J. Antineoplastic Effect of Metformin Against Glioblastoma Multiforme In Vitro and In Vivo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroglia. 2025; 6(4):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia6040040
Chicago/Turabian StyleVashi, Bhavya, Daniel Gonzales-Portillo, and Jorge Cervantes. 2025. "Antineoplastic Effect of Metformin Against Glioblastoma Multiforme In Vitro and In Vivo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Neuroglia 6, no. 4: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia6040040
APA StyleVashi, B., Gonzales-Portillo, D., & Cervantes, J. (2025). Antineoplastic Effect of Metformin Against Glioblastoma Multiforme In Vitro and In Vivo: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neuroglia, 6(4), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia6040040





