GABAA-ρ Receptors in the CNS: Their Functional, Pharmacological, and Structural Properties in Neurons and Astroglia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
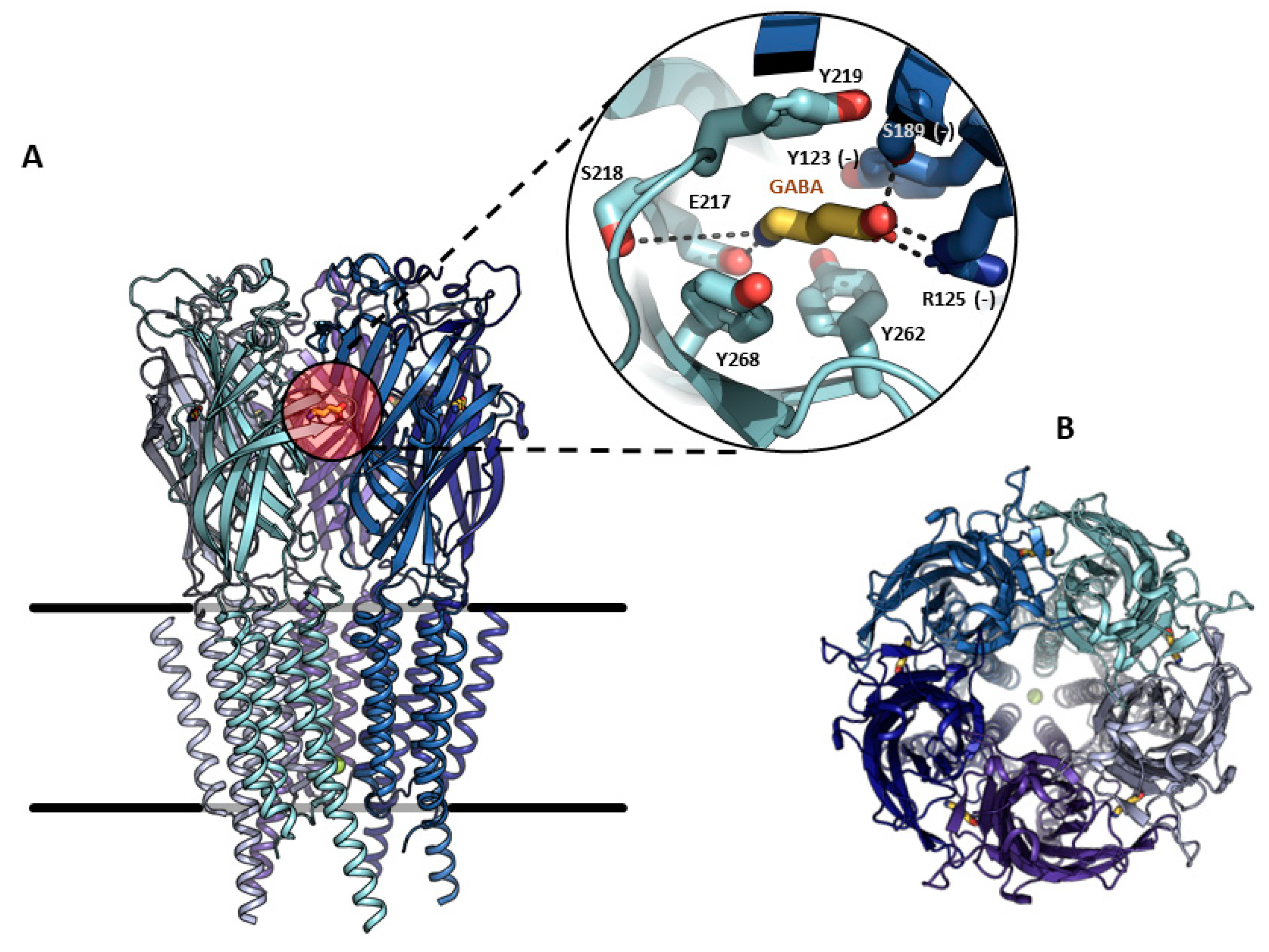
2. Structural Properties, Characterization, and Functions of GABAA-ρ Receptors
3. Trafficking and Scaffold Proteins of GABAA-ρ Receptors
4. GABAA-ρ Receptors in Astroglia
5. GABAA Receptors and Extrasynaptic Communication in Brain Diseases
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, E.; Frankel, S. gamma-Aminobutyric acid in brain: Its formation from glutamic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1950, 187, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krnjevic, K.; Phillis, J.W. Iontophoretic studies of neurones in the mammalian cerebral cortex. J. Physiol. 1963, 165, 274–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, I.; Gundersen, C.B.; Miledi, R. Actions of pentobarbital on rat brain receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurosci. 1986, 6, 2290–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polenzani, L.; Woodward, R.M.; Miledi, R. Expression of mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors with distinct pharmacology in Xenopus oocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 4318–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Arellano, A.; Machuca-Parra, A.I.; Reyes-Haro, D.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. Expression of GABAρ receptors in the neostriatum: Localization in aspiny, medium spiny neurons and GFAP-positive cells. J. Neurochem. 2012, 122, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Haro, D.; González-González, M.A.; Pétriz, A.; Rosas-Arellano, A.; Kettenmann, H.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. γ-Aminobutyric acid-ρ expression in ependymal glial cells of the mouse cerebellum. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 4, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Haro, D.; Rosas-Arellano, A.; González-González, M.A.; Mora-Loyola, E.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. GABAρ expression in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 532, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétriz, A.; Reyes-Haro, D.; González-González, M.A.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. GABAρ subunits confer a bicuculline-insensitive component to GFAP+ cells of cerebellum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 17522–17527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Haro, D.; Hernández-Santos, J.A.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. GABAρ selective antagonist TPMPA partially inhibits GABA-mediated currents recorded from neurones and astrocytes in mouse striatum. Neuropharmacology 2017, 113, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varman, D.R.; Soria-Ortíz, M.B.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Reyes-Haro, D. GABAρ3 expression in lobule X of the cerebellum is reduced in the valproate model of autism. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 687, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Nieuwenhuijzen, P.S.; Parker, K.; Liao, V.; Houlton, J.; Kim, H.L.; Johnston, G.A.R.; Hanrahan, J.R.; Chebib, M.; Clarkson, A.N. Targeting GABAC Receptors Improves Post-Stroke Motor Recovery. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.A. Receptor classes and the transmitter-gated ion channels. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1992, 17, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.R.; Bowery, N.G. 3H-baclofen and 3H-GABA bind to bicuculline-insensitive GABA B sites in rat brain. Nature 1981, 290, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.W.; Sieghart, W. International Union of Pharmacology. LXX. Subtypes of gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) receptors: Classification on the basis of subunit composition, pharmacology, and function. Update. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Olsen, R.W.; Peters, J.; Spedding, M. A nomenclature for ligand-gated ion channels. Neuropharmacology 2009, 56, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Arellano, A.; Estrada-Mondragón, A.; Mantellero, C.A.; Tejeda-Guzmán, C.; Castro, M.A. The adjustment of γ-aminobutyric acidA tonic subunits in Huntington’s disease: From transcription to translation to synaptic levels into the neostriatum. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowgill, J.; Fan, C.; Haloi, N.; Tobiasson, V.; Zhuang, Y.; Howard, R.J.; Lindahl, E. Structure and dynamics of dif-ferential ligand binding in the human ρ-type GABAA receptor. Neuron 2023, S0896-6273(23)00587-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, G.R.; Lu, L.; O’Hara, B.F.; Kasch, L.M.; Montrose-Rafizadeh, C.; Donovan, D.M.; Shimada, S.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Guggino, W.B.; Uhl, G.R.; et al. Cloning of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) rho 1 cDNA: A GABA receptor subunit highly expressed in the retina. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2673–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L.; Guggino, W.B.; Cutting, G.R. A novel gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit (rho 2) cloned from human retina forms bicuculline-insensitive homooligomeric receptors in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 6524–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogurusu, T.; Shingai, R. Cloning of a putative gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor subunit rho 3 cDNA. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1305, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Torres, A.; Vazquez, A.E.; Panicker, M.M.; Miledi, R. Cloning and functional expression of alternative spliced variants of the rho1 gamma-aminobutyrate receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4019–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miledi, R.; Parker, I.; Sumikawa, K. Properties of acetylcholine receptors translated by cat muscle mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackam, A.S.; Wang, T.L.; Guggino, W.B.; Cutting, G.R. The N-terminal domain of human GABA receptor rho1 subunits contains signals for homooligomeric and heterooligomeric interaction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 13750–13757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Ripps, H.; Qian, H. Random assembly of GABA rho1 and rho2 subunits in the formation of heteromeric GABA(C) receptors. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 26, 289–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ripps, H. Response kinetics and pharmacological properties of heteromeric receptors formed by coassembly of GABA rho- and gamma 2-subunits. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1999, 266, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, C.J.; Buckley, N.J.; Garret, M.; Deuchars, J.; Deuchars, S.A. Evidence for inhibition mediated by coassembly of GABAA and GABAC receptor subunits in native central neurons. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7241–7250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Qian, H. Interactions between rho and gamma2 subunits of the GABA receptor. J. Neurochem. 2005, 94, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X.; Lipton, S.A. Evidence for coassembly of mutant GABAC rho1 with GABAA gamma2S, glycine alpha1 and glycine alpha2 receptor subunits in vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3137–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, R.M.; Polenzani, L.; Miledi, R. Characterization of bicuculline/baclofen-insensitive (rho-like) gamma-aminobutyric acid receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. II. Pharmacology of gamma-aminobutyric acidA and gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptor agonists and antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 43, 609–625. [Google Scholar]
- Enz, R.; Cutting, G.R. Molecular composition of GABAC receptors. Vision Res. 1998, 38, 1431–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xue, F.; Chang, Y. Structural determinants for antagonist pharmacology that distinguish the rho1 GABAC receptor from GABAA receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, G.A.; Curtis, D.R.; Beart, P.M.; Game, C.J.; McCulloch, R.M.; Twitchin, B. Cis- and trans-4-aminocrotonic acid as GABA analogues of restricted conformation. J. Neurochem. 1975, 24, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusama, T.; Spivak, C.E.; Whiting, P.; Dawson, V.L.; Schaeffer, J.C.; Uhl, G.R. Pharmacology of GABA rho 1 and GABA alpha/beta receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes and COS cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 109, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, D.I.; Ong, J. GABAB receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 67, 187–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomet, U.; Baur, R.; Dodd, R.H.; Sigel, E. Loreclezole as a simple functional marker for homomeric rho type GABA(C) receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 408, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Kim, H.L.; Gavande, N.; Yamamoto, I.; Kumar, R.J.; Mewett, K.N.; Johnston, G.A.; Hanrahan, J.R.; Chebib, M. Medicinal chemistry of ρ GABAC receptors. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Gauthier, P.; Gottesmann, C. Study of a GABAC receptor antagonist on sleep-waking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 2001, 154, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naffaa, M.M.; Hung, S.; Chebib, M.; Johnston, G.A.R.; Hanrahan, J.R. GABAρ receptors: Distinctive functions and molecular pharmacology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1881–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, R.; Brandstätter, J.H.; W‚àö¬ßssle, H.; Bormann, J. Immunocytochemical localization of the GABAc receptor rho subunits in the mammalian retina. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 4479–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulen, P.; Brandstätter, J.H.; Enz, R.; Bormann, J.; Wässle, H. Synaptic clustering of GABA(C) receptor rho-subunits in the rat retina. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Picaud, S.A.; Werblin, F.S. GABA transporters and GABAC-like receptors on catfish cone- but not rod-driven horizontal cells. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14, 2648–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.L.; Yang, X.L. Subcellular localization and complements of GABA(A) and GABA(C) receptors on bullfrog retinal bipolar cells. J. Neurophysiol. 2000, 84, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Dowling, J.E. GABAA and GABAC receptors on hybrid bass retinal bipolar cells. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Slaughter, M.M. Preferential suppression of the ON pathway by GABAC receptors in the amphibian retina. J. Neurophysiol. 1995, 74, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, E.L.; Koulen, P.; Wässle, H. GABAA and GABAC receptors on mammalian rod bipolar cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1998, 396, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, A.J.; Sah, P. GABA receptors inhibited by benzodiazepines mediate fast inhibitory transmission in the central amygdala. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 9698–9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, J.; Nagano, M.; Suzuki, H. Differential expression of GABA(A) receptor subunits in the distinct nuclei of the rat amygdala. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2005, 138, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Gracia, C.; Nuche-Bricaire, A.; Crespo-Ramírez, M.; Miledi, R.; Fuxe, K.; Pérez de la Mora, M. GABA(A) ρ receptor mechanisms in the rat amygdala and its role in the modulation of fear and anxiety. Psychopharmacology 2010, 212, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Arellano, A.; Parodi, J.; Machuca-Parra, A.I.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, A.; Inestrosa, N.C.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. The GABA(A)ρ receptors in hippocampal spontaneous activity and their distribution in hippocampus, amygdala and visual cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 500, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Heer, M.; Somvanshi, R.K. Regional and subcellular distribution of GABAC ρ3 receptor in brain of R6/2 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 640, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegelius, K.; Pasternack, M.; Hiltunen, J.O.; Rivera, C.; Kaila, K.; Saarma, M.; Reeben, M. Distribution of GABA receptor rho subunit transcripts in the rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Chávez, A.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. Cloning and functional expression of the bovine GABA(C) rho2 subunit. Molecular evidence of a widespread distribution in the CNS. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazao, R.; Nogueira, M.I.; Wässle, H. Colocalization of synaptic GABA(C)-receptors with GABA (A)-receptors and glycine-receptors in the rodent central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 330, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas-Arellano, A.; Ochoa-de la Paz, L.D.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. Brain distribution and molecular cloning of the bovine GABA rho1 receptor. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 57, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesnoy-Marchais, D. Persistent GABAA/C responses to gabazine, taurine and beta-alanine in rat hypoglossal motoneurons. Neuroscience 2016, 330, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, B.E.; Breitenbach, U.; Stühmer, T.; Harvey, R.J.; Darlison, M.G. In situ hybridization and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction studies on the expression of the GABA(C) receptor rho1- and rho2-subunit genes in avian and rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1997, 9, 2414–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boue-Grabot, E.; Roudbaraki, M.; Bascles, L.; Tramu, G.; Bloch, B.; Garret, M. Expression of GABA receptor rho subunits in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1998, 70, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, V.L.; Duguid, I.C.; Krasel, C.; Stephens, G.J. Evidence that GABA rho subunits contribute to functional ionotropic GABA receptors in mouse cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Physiol. 2006, 577, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, C.; García-Alcocer, G.; Berumen, L.C.; Rosas-Arellano, A.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. Expression of GABArho subunits during rat cerebellum development. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 432, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Delgado, G.; Reyes-Haro, D.; Espino-Saldaña, A.E.; Rosas-Arellano, A.; Pétriz, A.; Juárez-Mercado, P.; Miledi, R.; Martínez-Torres, A. Dynamics of GABAρ2 receptors in retinal bipolar neurons and cerebellar astrocytes. Neuroreport 2011, 22, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denter, D.G.; Heck, N.; Riedemann, T.; White, R.; Kilb, W.; Luhmann, H.J. GABAC receptors are functionally expressed in the intermediate zone and regulate radial migration in the embryonic mouse neocortex. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limon, A.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Miledi, R. Loss of functional GABA(A) receptors in the Alzheimer diseased brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 10071–10076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, S.H.; Reutiman, T.J.; Folsom, T.D.; Rustan, O.G.; Rooney, R.J.; Thuras, P.D. Downregulation of GABAA receptor protein subunits α6, β2, δ, ε, γ2, τ, and ρ2 in superior frontal cortex of subjects with autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, E.; Shamsizadeh, A.; Salari, E.; Fatemi, I.; Allahtavakoli, M.; Roohbakhsh, A. Effect of TPMPA (GABAC receptor antagonist) on neuronal response properties in rat barrel cortex. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2017, 34, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Chebib, M.; Schmid, K.L. Identification of GABA receptors in chick cornea. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Didelon, F.; Sciancalepore, M.; Savic’, N.; Mladinic’, M.; Bradbury, A.; Cherubini, E. gamma-Aminobutyric acidA rho receptor subunits in the developing rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 67, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozzo, A.; Armellin, M.; Franzot, J.; Chiaruttini, C.; Nistri, A.; Tongiorgi, E. Expression and dendritic mRNA localization of GABAC receptor rho1 and rho2 subunits in developing rat brain and spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 15, 1747–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, K.; Stief, F.; Draguhn, A.; Frahm, C. Ionotropic GABA receptors with mixed pharmacological properties of GABAA and GABAC receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 497, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hattori, N.; Jiang, B.; Nakayama, Y.; Zhang, N.Y.; Wu, B.; Kitagawa, K.; Taketo, M.; Matsuda, H.; Inagaki, C. Single cell RT-PCR demonstrates differential expression of GABAC receptor rho subunits in rat hippocampal pyramidal and granule cells. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 123, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakuijala, A.; Palgi, M.; Wegelius, K.; Schmidt, M.; Enz, R.; Paulin, L.; Saarma, M.; Pasternack, M. GABA receptor rho subunit expression in the developing rat brain. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2005, 154, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandage, A.K.; Jin, Z.; Bazov, I.; Kononenko, O.; Bakalkin, G.; Korpi, E.R.; Birnir, B. GABA-A and NMDA receptor subunit mRNA expression is altered in the caudate but not the putamen of the postmortem brains of alcoholics. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, K.; Ren, Y.; Dai, W.; Xu, M.; Lu, L.; Lu, Z. Study on olfactory function in GABAC receptor/channel rho1 subunit knockout mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 427, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivilotti, L.; Nistri, A. Pharmacology of a novel effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid on the frog optic tectum in vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 164, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Schmid, K.L.; Liu, L. Identification of GABA receptors in chick retinal pigment epithelium. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 539, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekema, G.M.; Zheng, W.; Lu, L. Interaction of GABA receptor/channel rho(1) and gamma(2) subunit. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 2326–2333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Strong, J.A.; Wang, L.; Yu, L.; Xu, M.; Lu, L. Function of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor/channel rho 1 subunits in spinal cord. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48321–48329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabert, J.; Jost, B.; Patz, S.; Wahle, P. GABA(C) receptors are expressed in GABAergic and non-GABAergic neurons of the rat superior colliculus and visual cortex. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 199, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasternack, M.; Boller, M.; Pau, B.; Schmidt, M. GABA(A) and GABA(C) receptors have contrasting effects on excitability in superior colliculus. J. Neurophysiol. 1999, 82, 2020–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlicker, K.; McCall, M.A.; Schmidt, M. GABAC receptor-mediated inhibition is altered but not eliminated in the superior colliculus of GABAC rho1 knockout mice. J. Neurophysiol. 2009, 101, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.W.; Tae, H.S.; Cromer, B.A. Role of the ρ GABA(C) receptor N-terminus in assembly, trafficking and function. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.G.; Koulen, P.; Bedford, F.; Gordon-Weeks, P.R.; Moss, S.J. The protein MAP-1B links GABA(C) receptors to the cytoskeleton at retinal synapses. Nature 1999, 397, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billups, D.; Hanley, J.G.; Orme, M.; Attwell, D.; Moss, S.J. GABAC receptor sensitivity is modulated by interaction with MAP1B. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 8643–8650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, J.G.; Jones, E.M.; Moss, S.J. GABA receptor rho1 subunit interacts with a novel splice variant of the glycine transporter, GLYT-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Vicini, S.; Olsen, R.W. The gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) promotes GABAA receptor clustering and modulates the channel kinetics. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11557–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, J.T.; Rostaing, P.; Schiavo, G.; Fritschy, J.M.; Olsen, R.; Triller, A.; Moss, S.J. The subcellular distribution of GABARAP and its ability to interact with NSF suggest a role for this protein in the intracellular transport of GABA(A) receptors. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2001, 18, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Bedford, F.K.; Brandon, N.J.; Moss, S.J.; Olsen, R.W. GABA(A)-receptor-associated protein links GABA(A) receptors and the cytoskeleton. Nature 1999, 397, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boué-Grabot, E.; Emerit, M.B.; Toulmé; Séguéla, P.; Garret, M. Cross-talk and co-trafficking between rho1/GABA receptors and ATP-gated channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 6967–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, L.; Binder, J.; Haynl, C.; Enz, R. Endocytosis of GABA(C) receptors depends on subunit composition and is regulated by protein kinase C-ζ and protein phosphatase 1. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croci, C.; Brändstatter, J.H.; Enz, R. ZIP3, a new splice variant of the PKC-zeta-interacting protein family, binds to GABAC receptors, PKC-zeta, and Kv beta 2. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6128–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Haro, D.; Bulavina, L.; Pivneva, T. Glia, el pegamento de las ideas [Glia, the glue of ideas]. Ciencia 2014, 65, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Barres, B.A. The mystery and magic of glia: A perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron 2008, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez-Fort, M.; Audinat, E.; Angulo, M.C. Central role of GABA in neuron-glia interactions. Neuroscientist 2012, 18, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormann, J.; Kettenmann, H. Patch-clamp study of gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor Cl- channels in cultured astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 1988, 85, 9336–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, H.; Backus, K.H.; Schachner, M. Aspartate, glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid depolarize cultured astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 23, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bovolin, P.; Santi, M.R.; Puia, G.; Costa, E.; Grayson, D. Expression patterns of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit mRNAs in primary cultures of granule neurons and astrocytes from neonatal rat cerebella. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 1992, 89, 9344–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höft, S.; Griemsmann, S.; Seifert, G.; Steinhäuser, C. Heterogeneity in expression of functional ionotropic glutamate and GABA receptors in astrocytes across brain regions: Insights from the thalamus. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.; Fritschy, J.M.; Grosche, J.; Pratt, G.D.; Möhler, H.; Kettenmann, H. Developmental regulation of voltage-gated K+ channel and GABAA receptor expression in Bergmann glial cells. J. Neurosci. 1994, 14 Pt 1, 2503–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Arellano, A.; Tejeda-Guzmán, C.; Lorca-Ponce, E.; Palma-Tirado, L.; Mantellero, C.A.; Rojas, P.; Missirlis, F.; Castro, M.A. Huntington’s disease leads to decrease of GABA-A tonic subunits in the D2 neostriatal pathway and their relocalization into the synaptic cleft. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 110, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Yoon, B.E. Altered GABAergic Signaling in Brain Disease at Various Stages of Life. Exp. Neurobiol. 2017, 26, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghit, A.; Assal, D.; Al-Shami, A.S.; Hussein, D.E.E. GABAA receptors: Structure, function, pharmacology, and related disorders. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mederos, S.; Perea, G. GABAergic-astrocyte signaling: A refinement of inhibitory brain networks. Glia 2019, 67, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Xia, X.; Zheng, J.C. Astrocytes: GABAceptive and GABAergic Cells in the Brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 892497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, B.E.; Lee, C.J. GABA as a rising gliotransmitter. Front. Neural. Circuits 2014, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolteus, A.J.; Bordey, A. GABA release and uptake regulate neuronal precursor migration in the postnatal subventricular zone. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7623–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Ceglia, R.; Ledonne, A.; Litvin, D.G.; Lind, B.L.; Carriero, G.; Latagliata, E.C.; Bindocci, E.; Di Castro, M.A.; Savtchouk, I.; Vitali, I.; et al. Specialized astrocytes mediate glutamatergic gliotransmission in the CNS. Nature, 2023; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| CNS Region or Cell Type | GABAA-ρ1 | GABAA-ρ2 | GABAA-ρ3 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Retina | [20,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] | |||
| Outer nuclear layer | X | X | X | |
| Retinal rod bipolar cells | ||||
| Outer plexiform layer | X | X | ||
| Dendritic tree of bipolar cells | ||||
| Inner nuclear layer | X | X | ||
| Bodies of horizontal cells | X | X | ||
| Bodies of bipolar cells | ||||
| Inner plexiform layer | X | X | ||
| Axons of bipolar cells | ||||
| Amygdala | X | X | [46,47,48,49,50,51] | |
| Basolateral | x | x | x | |
| Central | X | X | ||
| Cortical basomedial | x | x | x | |
| Intercalated paracapsular islands | X | X | ||
| Lateral | X | X | ||
| Postmortem nuclei | ||||
| Brainstem | X | [7,26,52,53,54,55,56] | ||
| Hypoglosal motoneurons | X | |||
| Dorsal vagal nucleus | X | |||
| Lateral parabrachial nucleus | X | X | X | |
| Medial nucleus of trapezoid body | X | |||
| Motoneurons | ||||
| Rachidian bulb | X | X | ||
| Olivar | X | X | ||
| Cuneiform | X | X | ||
| Cuneiform accessory | X | X | ||
| Reticular nuclei | X | |||
| Solitary tract nucleus | X | X | ||
| Varolio’s pons | [6,53,57,58,59,60] | |||
| Cerebellum | X | |||
| Astrocytes | X | X | ||
| Basket cells | X | X | ||
| Ependymal cells | X | |||
| (paraventricular zone) | X | X | ||
| Purkinje cell layer | X | |||
| Cerebral cortex | X | [49,50,51,61,62,63,64] | ||
| Entorhinal | X | |||
| Frontal | X | |||
| Layer II (pyramidal-parvalbumin neurons | ||||
| Lateral | X | |||
| Medial | X | X | ||
| Mediolateral | X | X | X | |
| Layer VI (pyramidal-parvalbumin neurons | ||||
| Mediolateral | X | |||
| Parietal | X | X | X | |
| Somatosensory | X | |||
| Barrel (principal and adjacent whisker) | ||||
| Temporal | ||||
| Visual | x | x | ||
| Cornea | X | x | ||
| Corpus callosum | X | X | ||
| Hippocampus | X | X | X | [49] |
| CA1 | X | X | X | [65] |
| CA2 | [52] | |||
| CA3 | X | X | [50,51,52,66,67,68,69,70] | |
| Dendate gyrus | X | X | X | |
| Granular | X | X | X | |
| Polymorph | X | |||
| Molecular | X | X | ||
| Stratum oriens | X | X | ||
| Subiculum | X | X | ||
| Stratum radiatum | X | X | X | |
| Isthmo-optic | X | X | ||
| Neostriatum | X | X | ||
| Polygonal and fusiform cells | X | X | ||
| Calbindin interneurons | [56] | |||
| Calretinin interneurons | X | X | [5,9,51,52,54,71] | |
| D2 projection neurons | X | X | ||
| Astrocytes | X | X | ||
| Olfactory bulb | X | |||
| Mitral cells | X | X | ||
| Optic tectum | X | |||
| Optic nerve and tract | X | [72] | ||
| Pituitary gland | X | X | ||
| Retinal pigment epithelium | X | X | [73] | |
| Spinal cord | X | X | X | [52] |
| Dorsal root ganglion | X | X | [52] | |
| Laminae I | X | [74] | ||
| Laminae II | X | [51,52,53,67,75,76] | ||
| Motoneurons | X | X | ||
| Interneurons | X | |||
| Ventral horn | X | X | ||
| Superior colliculus | X | X | [51,53,57,77,78,79] | |
| Dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus | X | |||
| Superficial gray layer | ||||
| Calbindin neurons | X | X | ||
| Thalamus | X | X | X | |
| Dorsal | X | |||
| X | ||||
| x Only determined by functionality | [51,56] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosas-Arellano, A.; Estrada-Mondragón, A.; Martínez-Torres, A.; Reyes-Haro, D. GABAA-ρ Receptors in the CNS: Their Functional, Pharmacological, and Structural Properties in Neurons and Astroglia. Neuroglia 2023, 4, 239-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia4040017
Rosas-Arellano A, Estrada-Mondragón A, Martínez-Torres A, Reyes-Haro D. GABAA-ρ Receptors in the CNS: Their Functional, Pharmacological, and Structural Properties in Neurons and Astroglia. Neuroglia. 2023; 4(4):239-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia4040017
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosas-Arellano, Abraham, Argel Estrada-Mondragón, Ataúlfo Martínez-Torres, and Daniel Reyes-Haro. 2023. "GABAA-ρ Receptors in the CNS: Their Functional, Pharmacological, and Structural Properties in Neurons and Astroglia" Neuroglia 4, no. 4: 239-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia4040017
APA StyleRosas-Arellano, A., Estrada-Mondragón, A., Martínez-Torres, A., & Reyes-Haro, D. (2023). GABAA-ρ Receptors in the CNS: Their Functional, Pharmacological, and Structural Properties in Neurons and Astroglia. Neuroglia, 4(4), 239-252. https://doi.org/10.3390/neuroglia4040017





