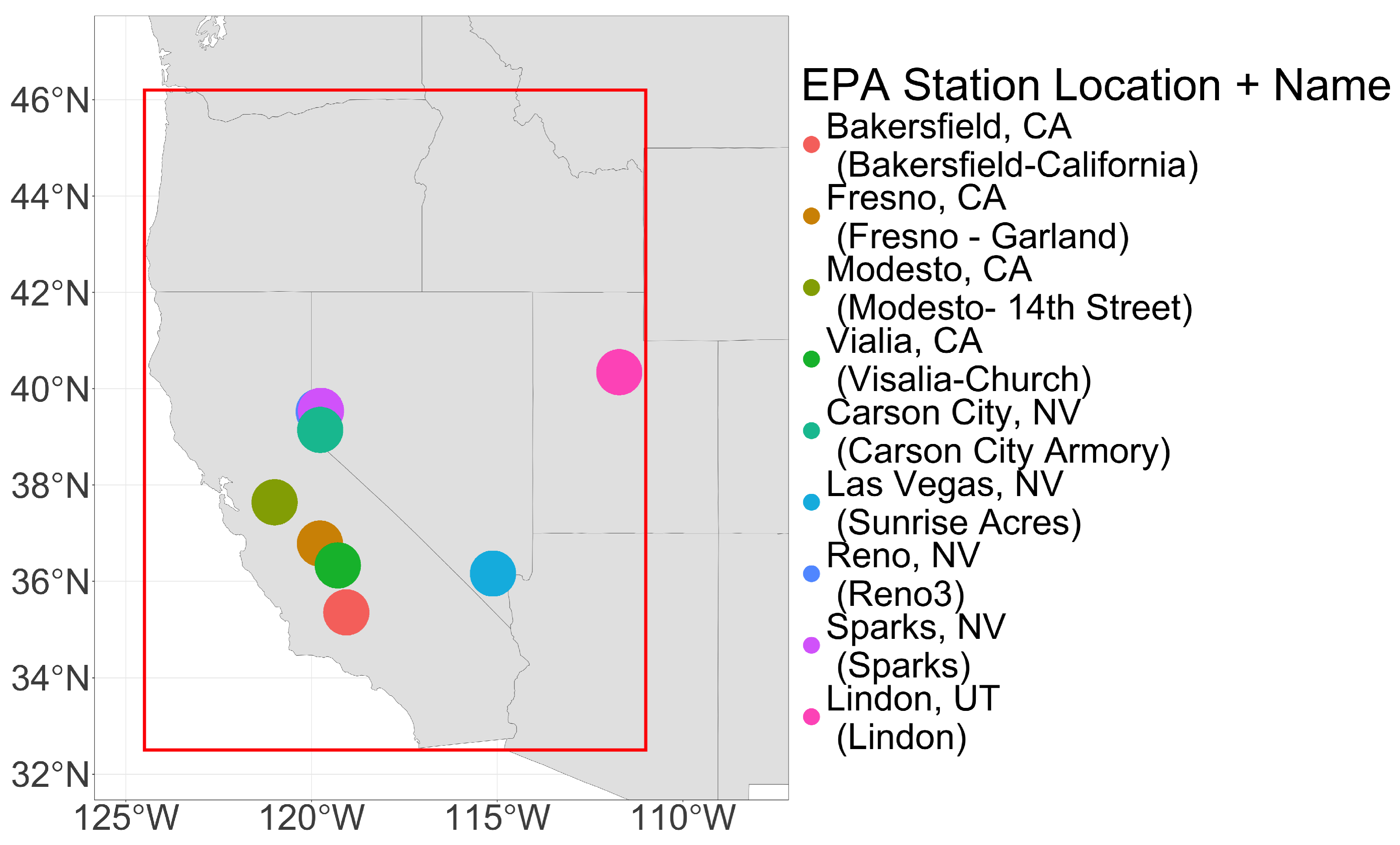
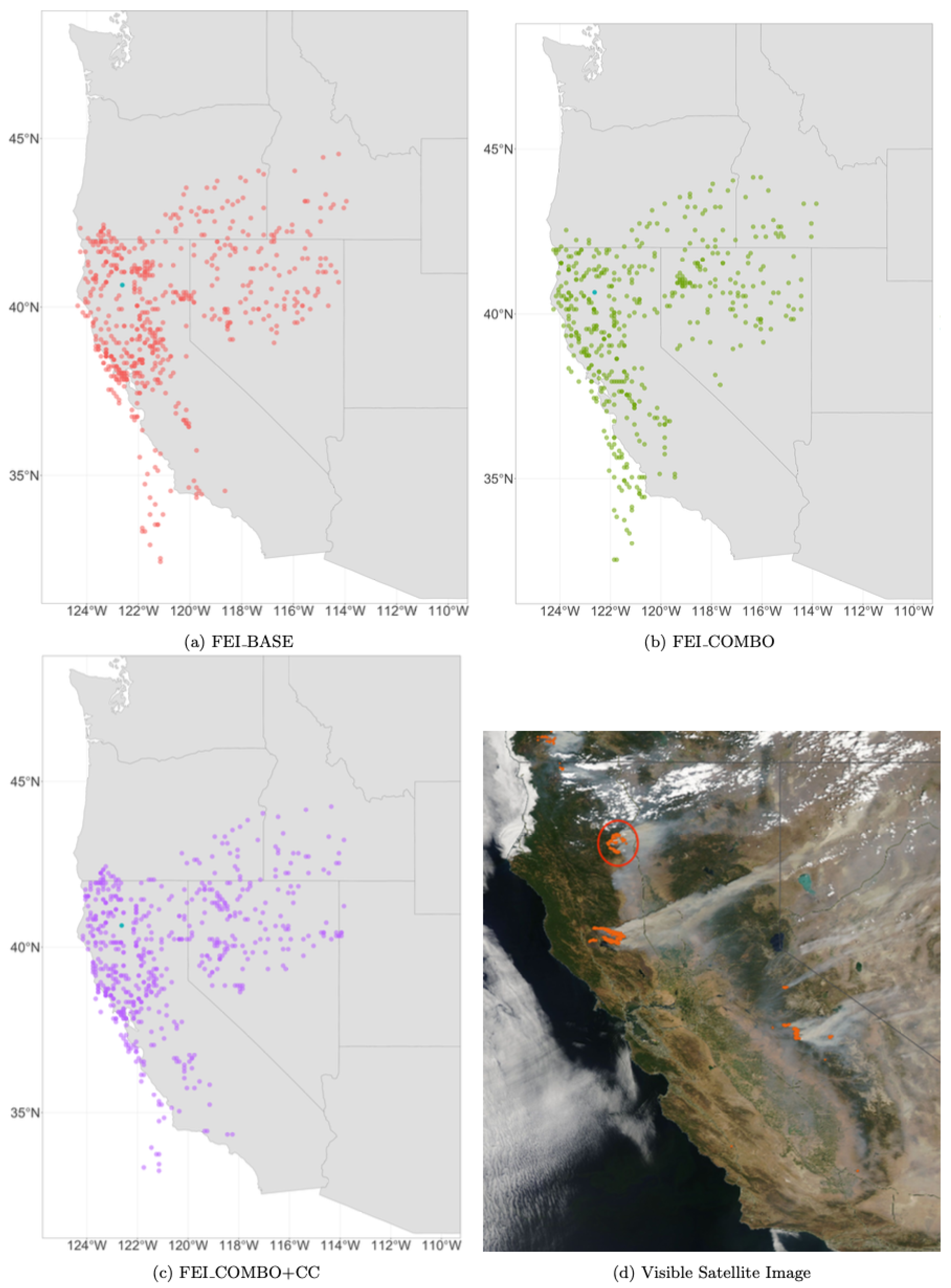
Figure 1.
A map of the spatial domain and the EPA monitor locations used in this study. The red box represents the spatial domain. Reno and Sparks are geographically close and appear overlapping at this scale.
Figure 1.
A map of the spatial domain and the EPA monitor locations used in this study. The red box represents the spatial domain. Reno and Sparks are geographically close and appear overlapping at this scale.
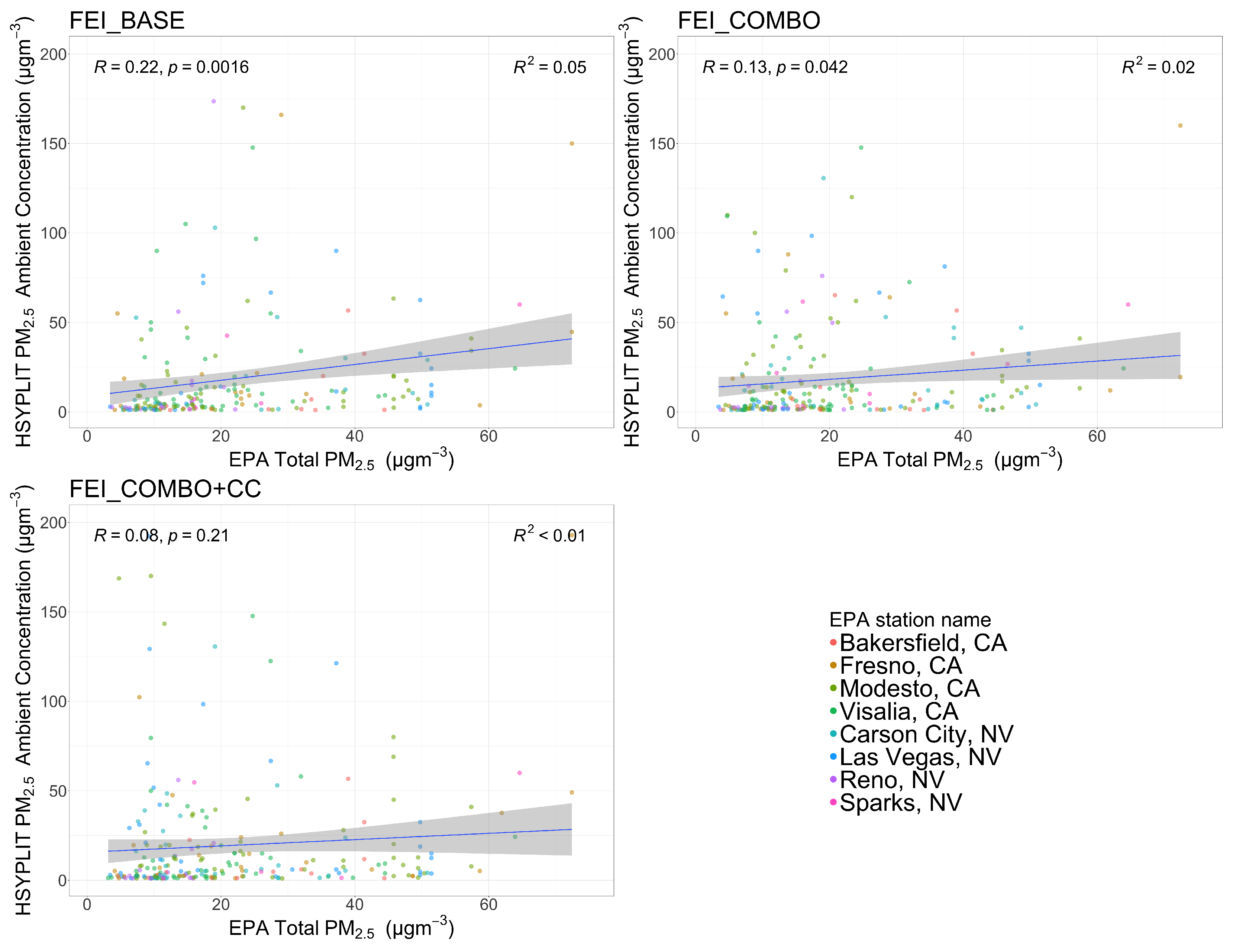
Figure 2.
Correlation between 2013 HYSPLIT modeled smoke PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Figure 2.
Correlation between 2013 HYSPLIT modeled smoke PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Figure 3.
Correlation between 2016 HYSPLIT modeled PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Figure 3.
Correlation between 2016 HYSPLIT modeled PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Figure 4.
Correlation between 2018 HYSPLIT modeled smoke PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Figure 4.
Correlation between 2018 HYSPLIT modeled smoke PM2.5 concentration using each FEI and the EPA measured PM2.5 concentration. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
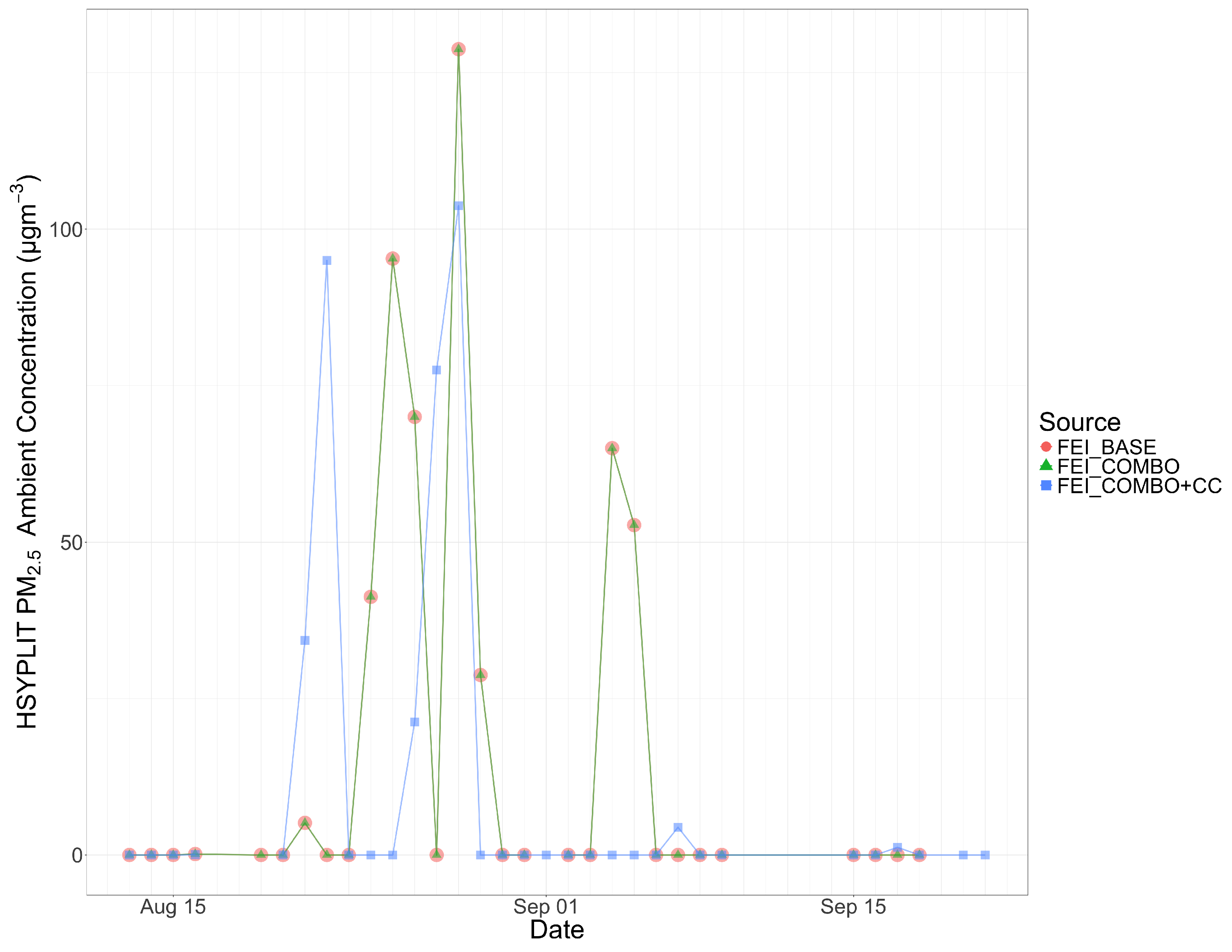
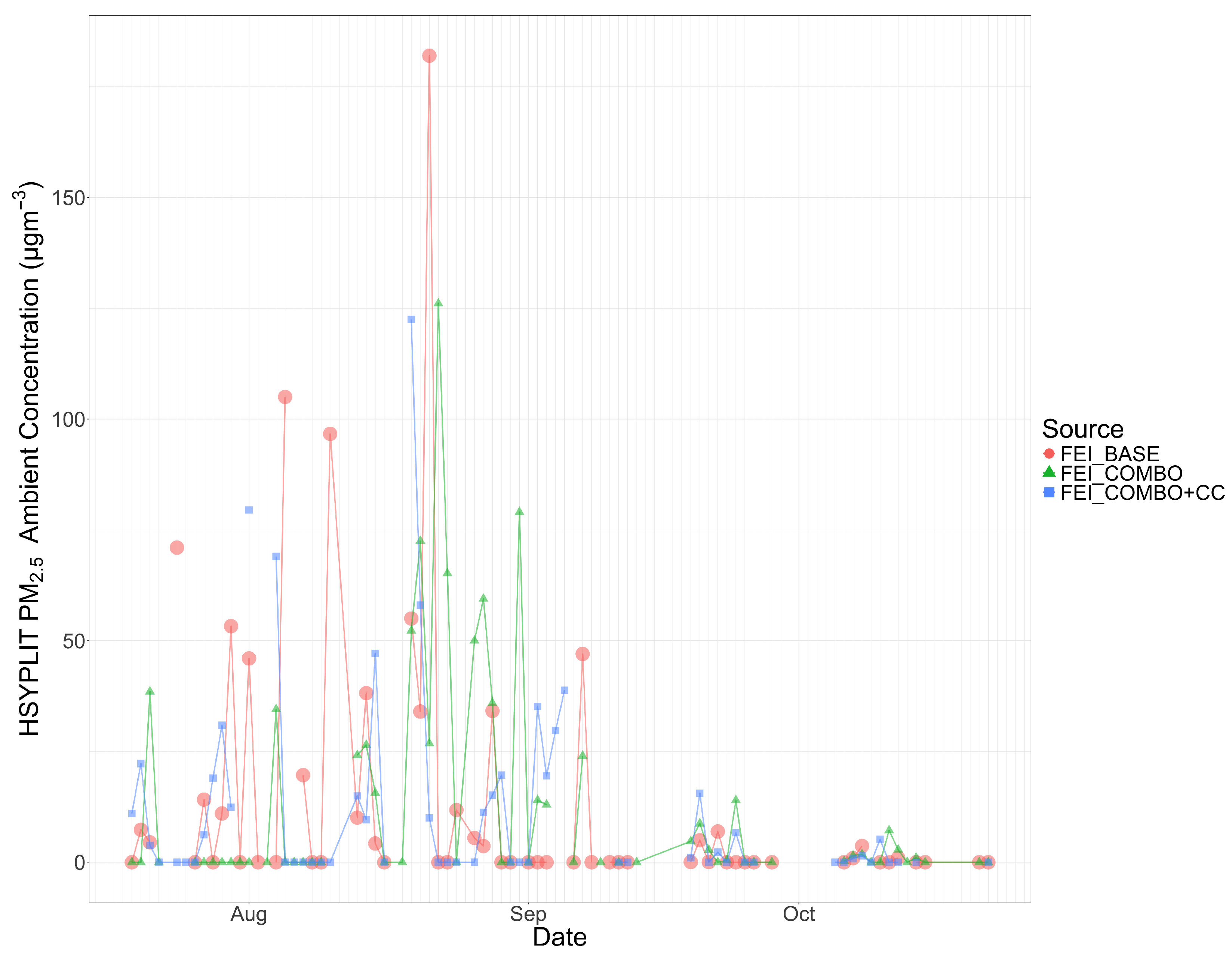
Figure 5.
The 2013 Rim Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
Figure 5.
The 2013 Rim Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
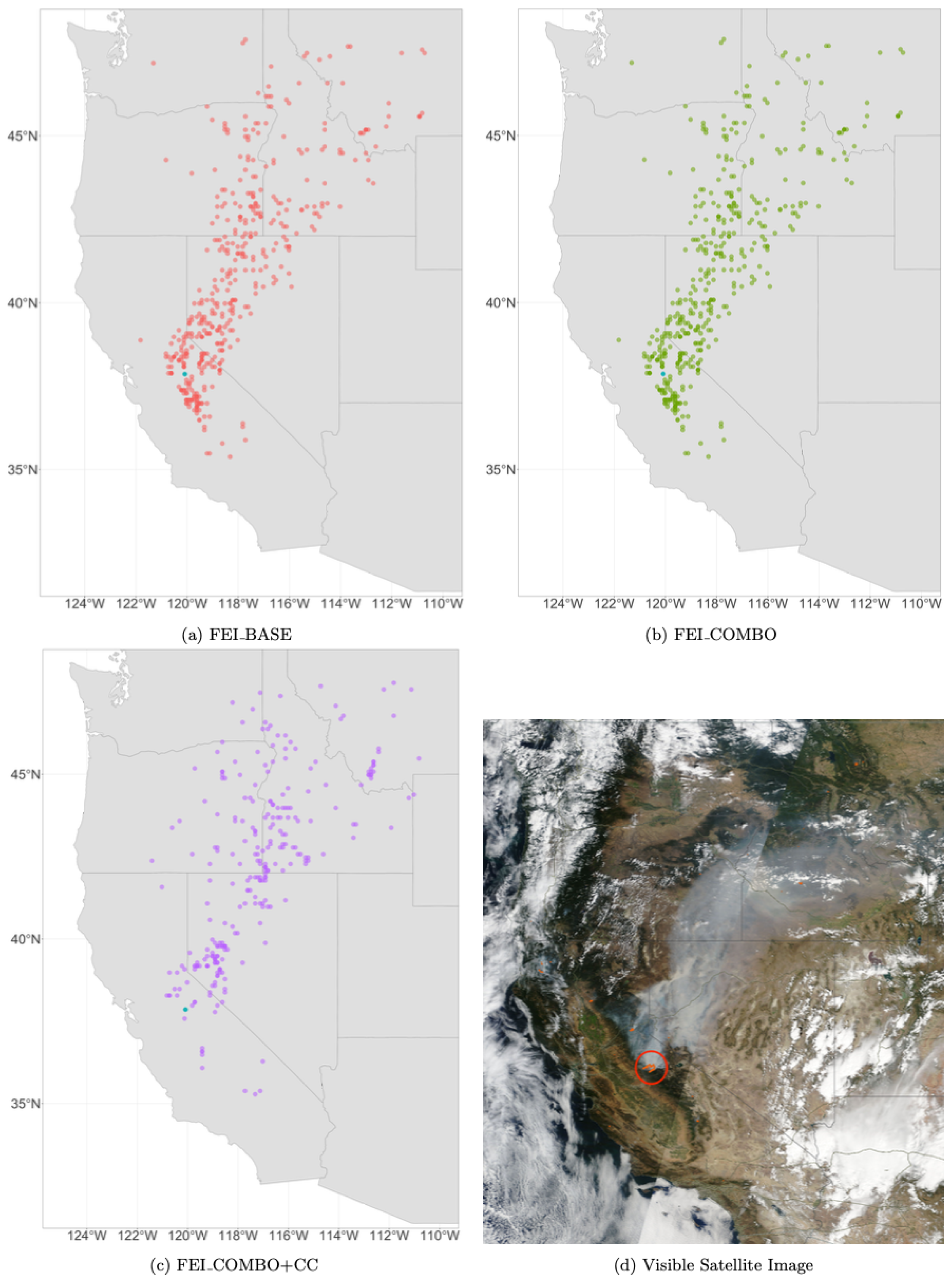
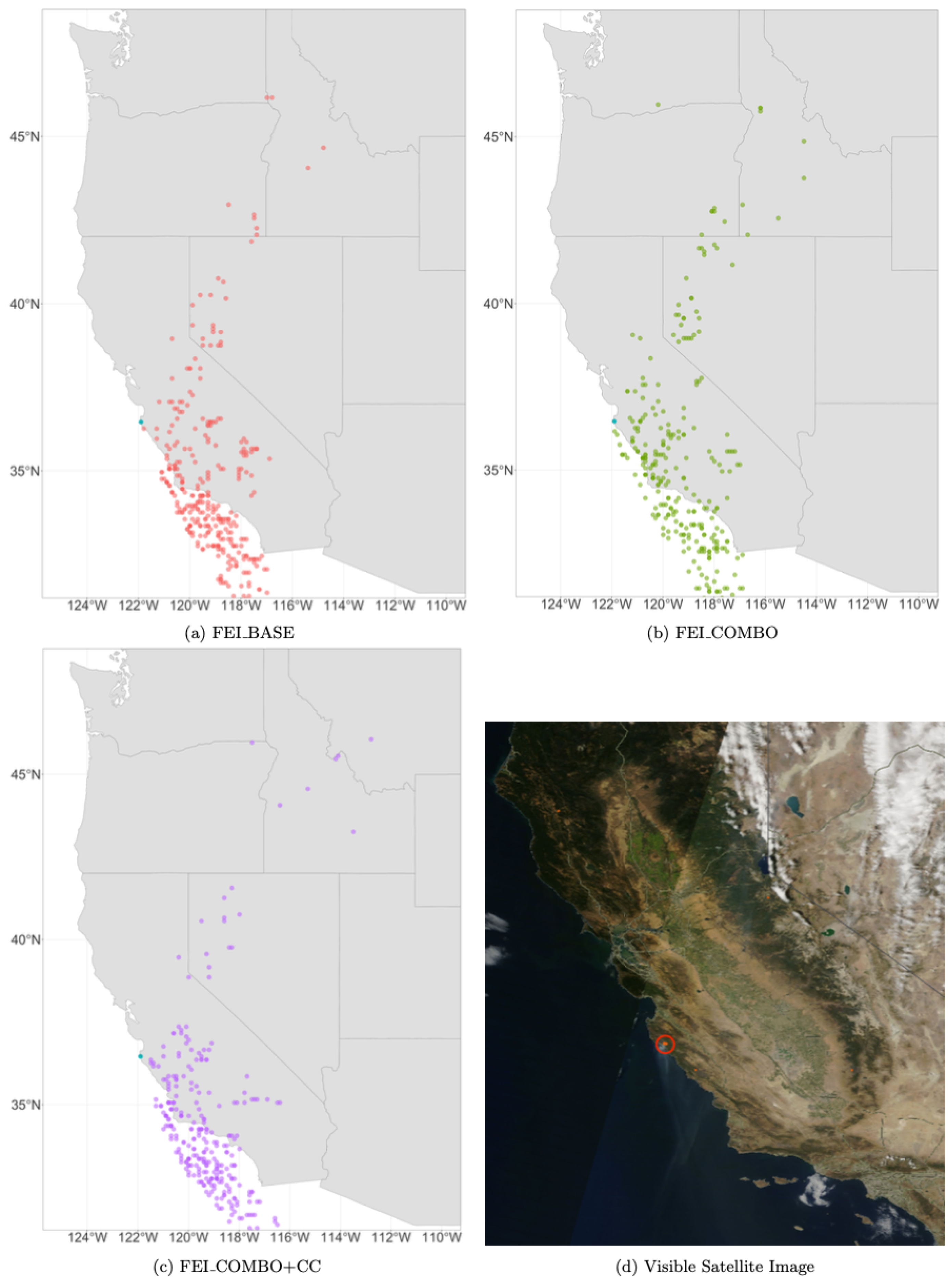
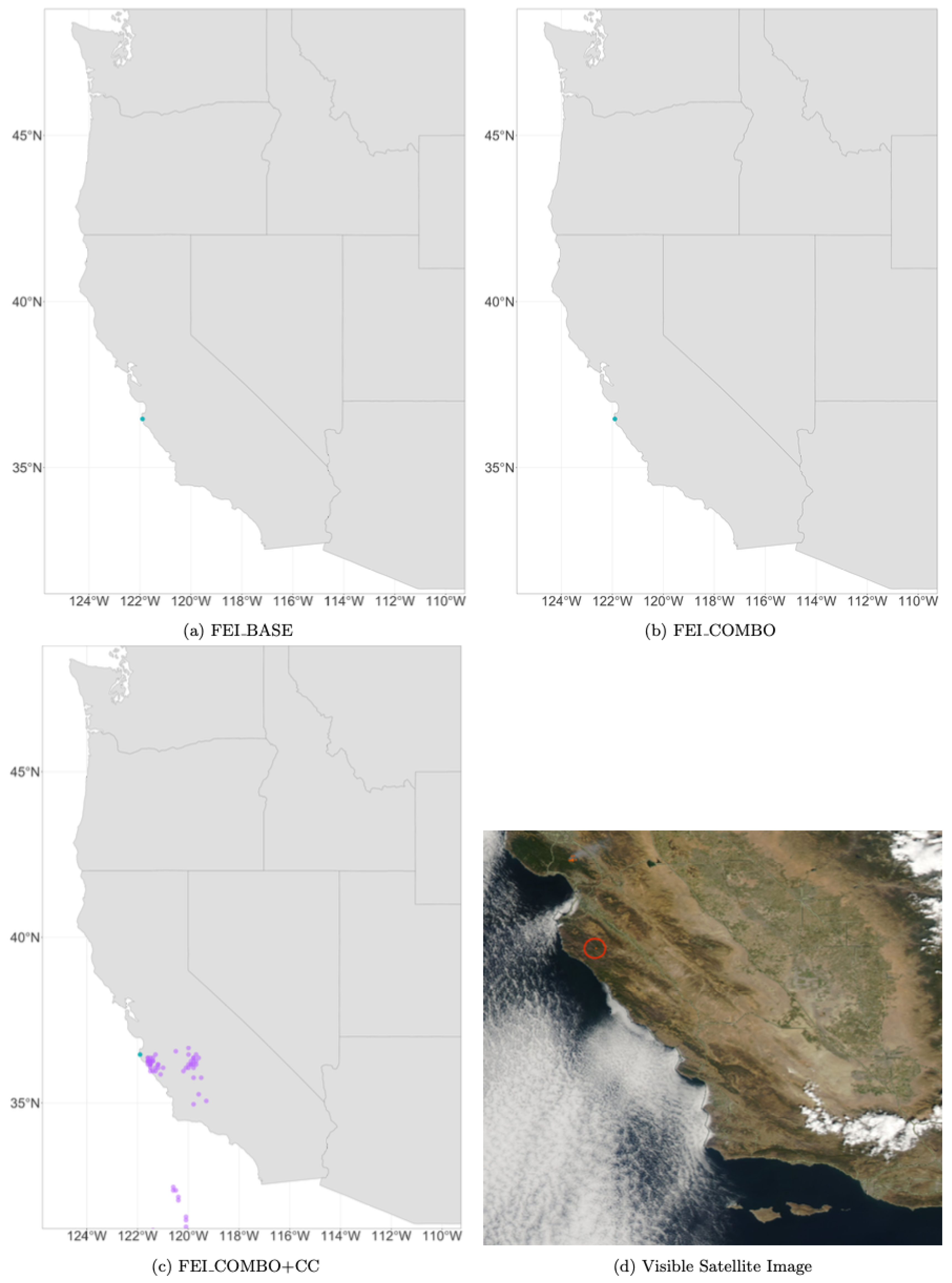
Figure 6.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points at 10 m for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 24 August 2013, during the Rim Fire and a visual satellite image of the Rim fire on 24 August 2013, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Terra). The Rim Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 6.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points at 10 m for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 24 August 2013, during the Rim Fire and a visual satellite image of the Rim fire on 24 August 2013, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Terra). The Rim Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 7.
The 2016 Soberanes Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
Figure 7.
The 2016 Soberanes Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
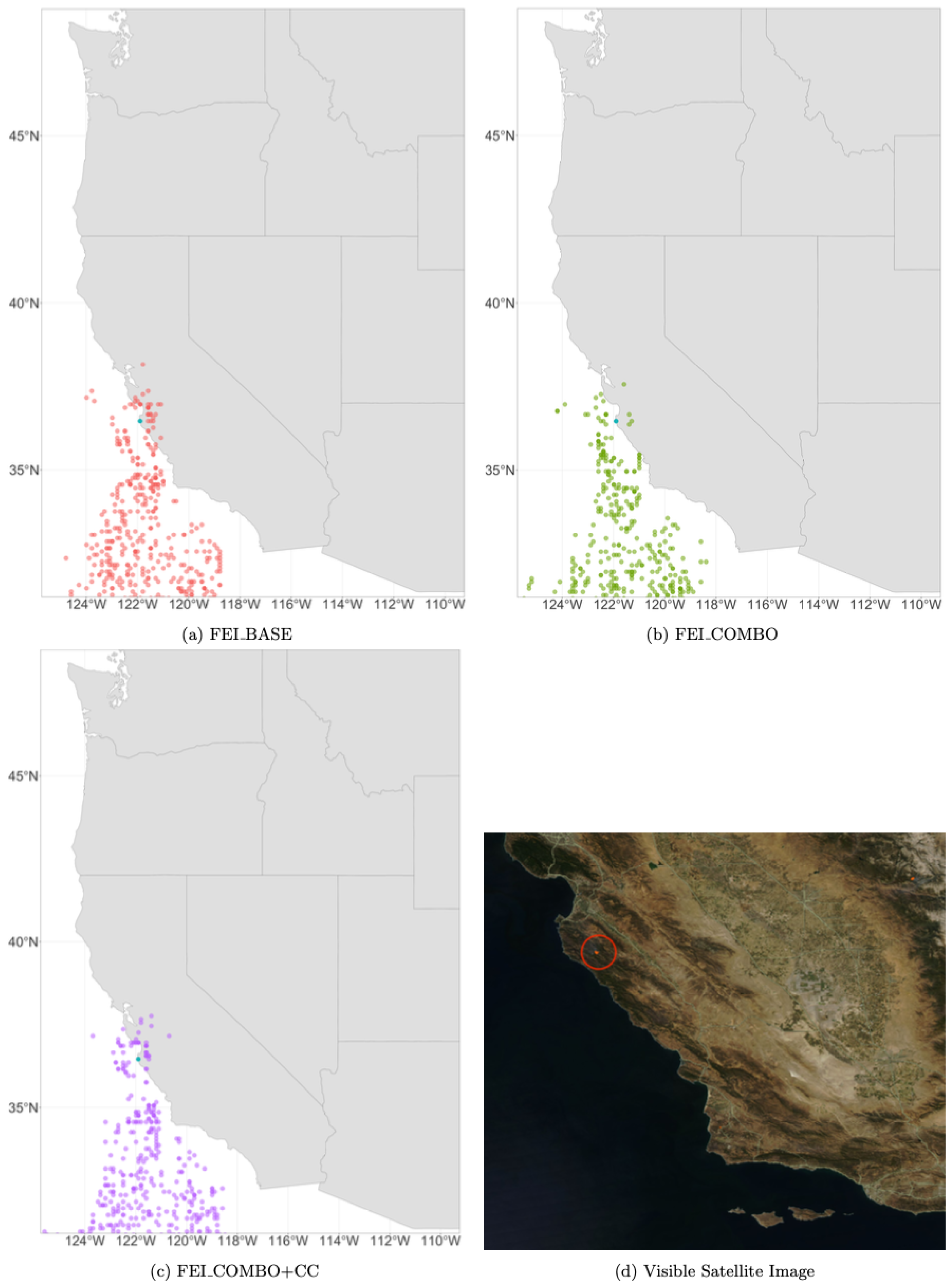
Figure 8.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points at 10 m for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 30 August 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes fire on 30 August 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Terra). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 8.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points at 10 m for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 30 August 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes fire on 30 August 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Terra). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 9.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 26 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 26 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The visible satellite image shows a faint smoke plume. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 9.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 26 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 26 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The visible satellite image shows a faint smoke plume. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 10.
HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient concentration locations for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 27 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 27 September 2016, from NASA WorldView. The Sobeanes fire is not captured in the visible imagery of this day.
Figure 10.
HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient concentration locations for each of the three FEIs (represented in red, green, and purple) on 27 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 27 September 2016, from NASA WorldView. The Sobeanes fire is not captured in the visible imagery of this day.
Figure 11.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on (represented in red, green, and purple) 28 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 28 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). Thermal anomalies from the Soberanes fire are not captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua on this day.
Figure 11.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on (represented in red, green, and purple) 28 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 28 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). Thermal anomalies from the Soberanes fire are not captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua on this day.
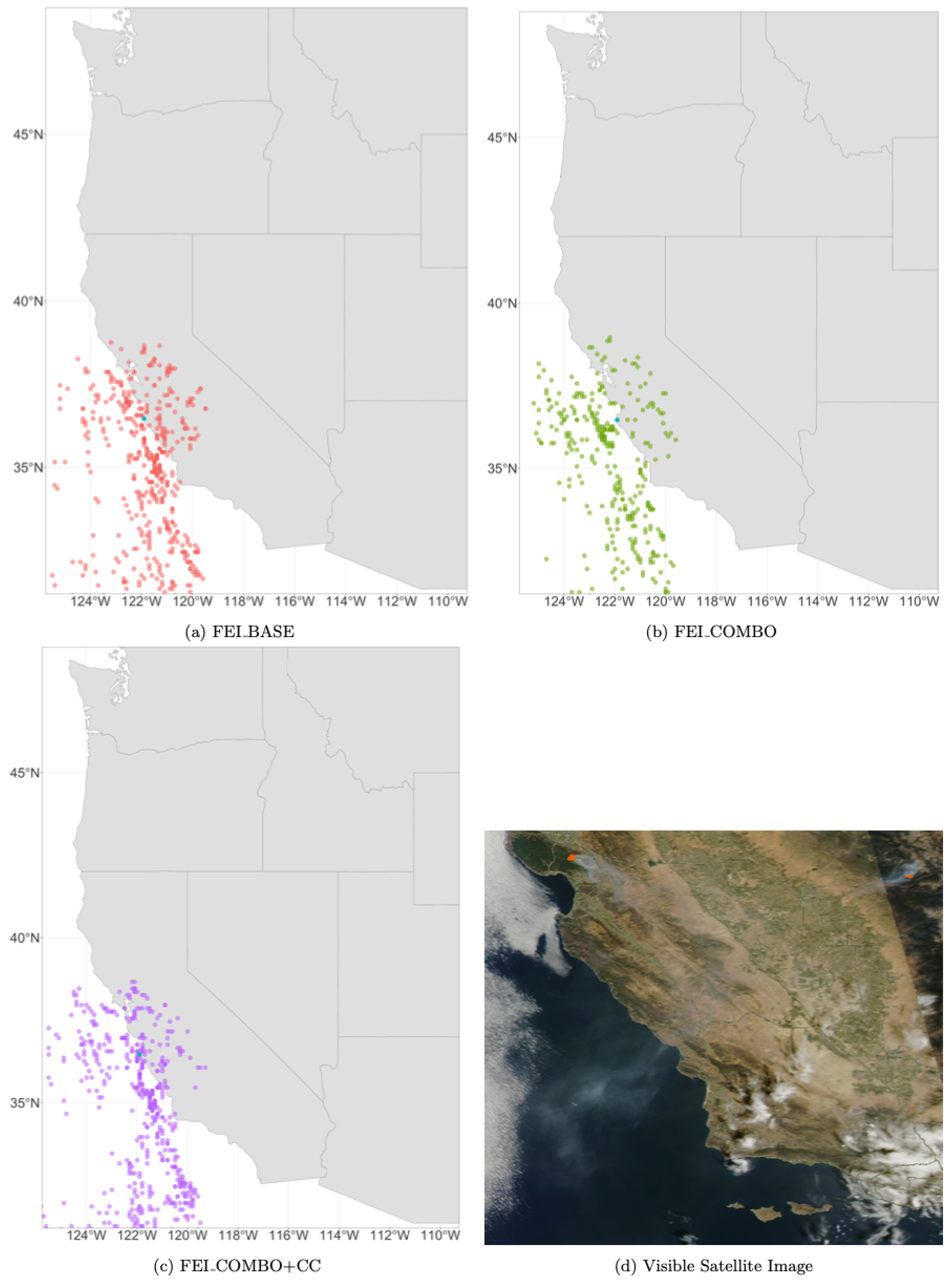
Figure 12.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on (represented in red, green, and purple) 29 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 29 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 12.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on (represented in red, green, and purple) 29 September 2016, during the Soberanes Fire and a visual satellite image of the Soberanes Fire on 29 September 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Soberanes Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire.
Figure 13.
The 2018 Carr Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
Figure 13.
The 2018 Carr Fire daily PM2.5 concentrations in Reno, NV, from HYSPLIT using all three FEIs.
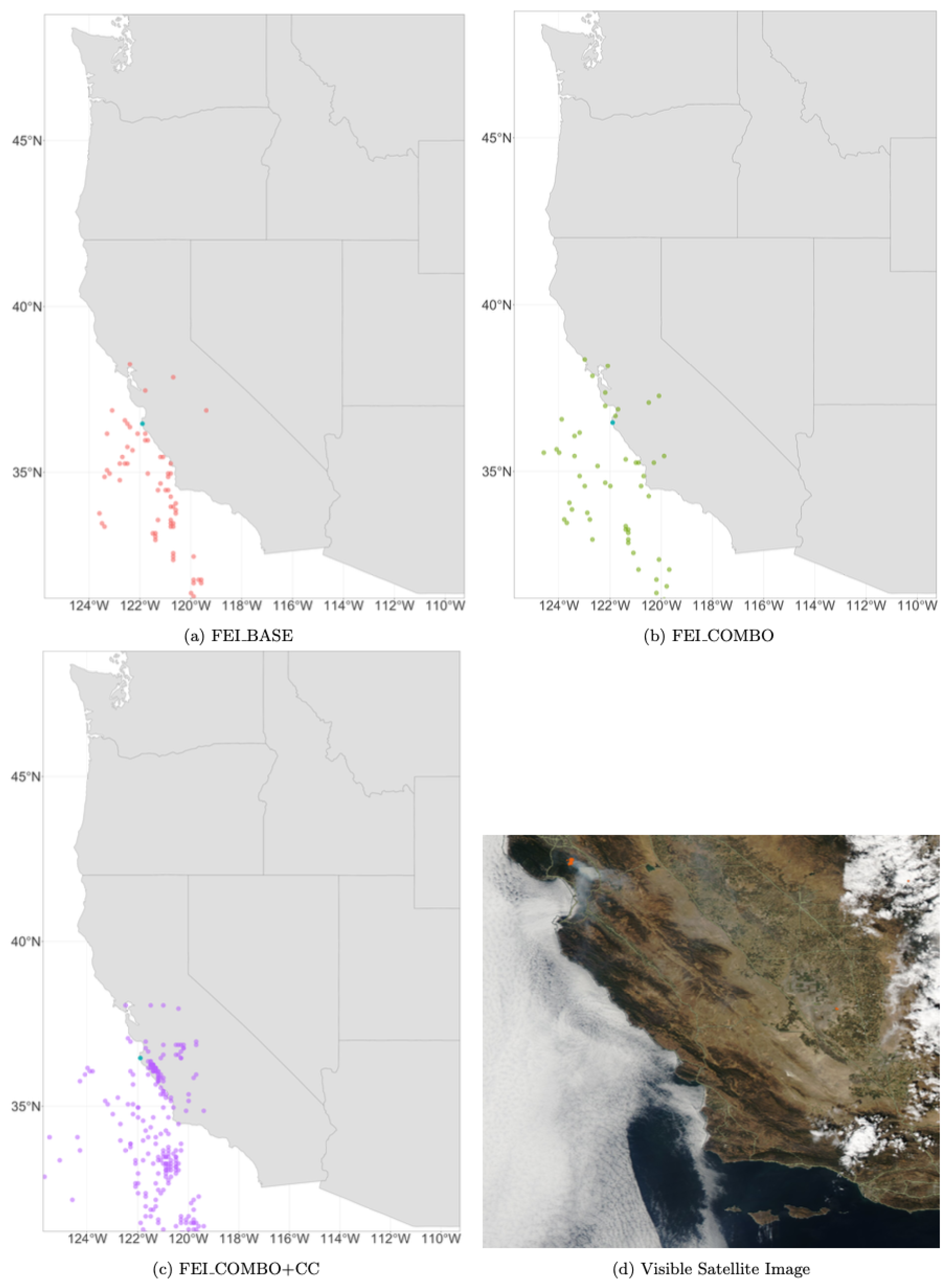
Figure 14.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on 4 August 2018, during the Carr Fire and a visual satellite image of the Carr Fire on 4 August 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Carr Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire. This is an example of a day with numerous smoke plumes that mix in the atmosphere.
Figure 14.
Daily HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient smoke concentration grid points for each of the three FEIs on 4 August 2018, during the Carr Fire and a visual satellite image of the Carr Fire on 4 August 2016, from NASA WorldView (MODIS Aqua). The Carr Fire is circled in red. The smaller orange dots represent thermal anomalies captured by MODIS Terra and Aqua, showing the location of the fire. This is an example of a day with numerous smoke plumes that mix in the atmosphere.
Table 1.
Fire information for the three large fire case studies from each FEI, showing the start date, the fire length, the number of non-consecutive (or missing) days within the fire, the total fire PM2.5 emissions in kg, and the total fire burned area in km2. Burned area values differ slightly between inventories due to differences in how burned area is detected and defined. These variations reflect the methods used within each fire emission inventory.
Table 1.
Fire information for the three large fire case studies from each FEI, showing the start date, the fire length, the number of non-consecutive (or missing) days within the fire, the total fire PM2.5 emissions in kg, and the total fire burned area in km2. Burned area values differ slightly between inventories due to differences in how burned area is detected and defined. These variations reflect the methods used within each fire emission inventory.
| Fire Name | Start Date | Length | Missing Days | PM2.5 Emissions (kg) | Burned Area (km2) |
|---|
| FEI_BASE |
| Rim Fire | 13 August 2013 | 42 | 5 | | 892.0 |
| Soberanes Fire | 21 July 2016 | 70 | 2 | | 536.0 |
| Carr Fire | 16 July 2018 | 101 | 2 | | 722.0 |
| FEI_COMBO |
| Rim Fire | 13 August 2013 | 42 | 5 | | 892.0 |
| Soberanes Fire | 21 July 2016 | 70 | 2 | | 536.0 |
| Carr Fire | 16 July 2018 | 102 | 2 | | 722.0 |
| FEI_COMBO+CC |
| Rim Fire | 13 August 2013 | 42 | 0 | | 894.0 |
| Soberanes Fire | 21 July 2016 | 71 | 0 | | 536.0 |
| Carr Fire | 16 July 2018 | 102 | 0 | | 720.0 |
Table 2.
HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient concentrations in vertically allocated at four atmospheric levels for each year and fire emission inventory.
Table 2.
HYSPLIT PM2.5 ambient concentrations in vertically allocated at four atmospheric levels for each year and fire emission inventory.
| Year | FEI | 10 m PM2.5 () | 100 m PM2.5 () | 1000 m PM2.5 () | 5000 m PM2.5 () | Total Column PM2.5 () |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | | | | | |
| 2013 | COMBO | | | | | |
| 2013 | COMBO+CC | | | | | |
| 2016 | BASE | | | | | |
| 2016 | COMBO | | | | | |
| 2016 | COMBO+CC | | | | | |
| 2018 | BASE | | | | | |
| 2018 | COMBO | | | | | |
| 2018 | COMBO+CC | | | | | |
Table 3.
The domain-wide normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
Table 3.
The domain-wide normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations. Note: EPA measurements are not wildfire smoke specific and includes PM2.5 from all sources.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 11.13 | 24.52 | 0.30 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 10.99 | 26.05 | 0.28 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 10.73 | 27.26 | 0.28 |
| 2016 | BASE | 9.62 | 11.59 | 0.05 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 9.29 | 14.99 | 0.06 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 9.19 | 14.90 | 0.07 |
| 2018 | BASE | 11.38 | 16.91 | 0.16 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 11.16 | 18.58 | 0.09 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 10.96 | 19.24 | 0.09 |
Table 4.
Bakersfield, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 4.
Bakersfield, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 16.46 | 20.48 | 0.08 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 16.55 | 20.46 | 0.17 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 16.63 | 20.53 | 0.25 |
| 2016 | BASE | 12.81 | 14.90 | 0.00 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 12.69 | 15.25 | −0.01 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 12.71 | 15.25 | 0.00 |
| 2018 | BASE | 14.67 | 18.17 | 0.14 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 14.59 | 18.24 | 0.11 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 14.63 | 18.15 | 0.13 |
Table 5.
Carson City, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 5.
Carson City, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 8.19 | 42.37 | 0.45 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 8.76 | 42.50 | 0.44 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 8.01 | 38.34 | 0.46 |
| 2016 | BASE | 4.89 | 6.19 | 0.07 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 4.56 | 9.17 | 0.05 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 4.80 | 6.23 | 0.05 |
| 2018 | BASE | 10.31 | 17.69 | 0.16 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 10.40 | 17.47 | 0.15 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 10.24 | 17.48 | 0.19 |
Table 6.
Fresno, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 6.
Fresno, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 14.03 | 18.16 | −0.03 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 13.99 | 18.13 | −0.03 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 13.60 | 19.47 | 0.00 |
| 2016 | BASE | 11.78 | 13.53 | 0.08 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 11.29 | 15.01 | 0.16 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 10.88 | 15.46 | 0.16 |
| 2018 | BASE | 13.05 | 17.92 | 0.14 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 12.69 | 18.34 | 0.08 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 12.17 | 22.86 | 0.05 |
Table 7.
Las Vegas, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 7.
Las Vegas, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 7.87 | 24.91 | 0.09 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 7.85 | 25.64 | 0.09 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 8.12 | 22.48 | 0.09 |
| 2016 | BASE | 10.29 | 12.20 | 0.05 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 10.35 | 12.04 | 0.05 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 10.14 | 12.23 | 0.01 |
| 2018 | BASE | 8.04 | 11.11 | 0.10 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 8.13 | 9.97 | 0.12 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 8.24 | 9.72 | 0.08 |
Table 8.
Modesto, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 8.
Modesto, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 12.24 | 16.25 | 0.00 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 11.89 | 16.43 | 0.00 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 11.96 | 16.58 | 0.01 |
| 2016 | BASE | 10.85 | 12.35 | −0.01 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 10.73 | 12.23 | 0.08 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 10.66 | 12.34 | 0.03 |
| 2018 | BASE | 11.88 | 20.57 | 0.22 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 11.21 | 27.91 | 0.09 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 11.29 | 23.82 | 0.14 |
Table 9.
Reno, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 9.
Reno, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 9.34 | 17.70 | 0.34 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 8.06 | 26.89 | 0.24 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 9.07 | 20.68 | 0.30 |
| 2016 | BASE | 7.37 | 8.59 | 0.18 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 7.30 | 8.70 | 0.02 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 7.30 | 8.69 | 0.03 |
| 2018 | BASE | 11.00 | 15.73 | 0.10 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 10.83 | 15.75 | 0.13 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 10.84 | 16.01 | 0.05 |
Table 10.
Sparks, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 10.
Sparks, NV, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 9.65 | 23.68 | 0.23 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 9.90 | 25.47 | 0.18 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 7.85 | 42.35 | 0.25 |
| 2016 | BASE | 7.12 | 8.28 | 0.01 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 6.81 | 8.71 | −0.02 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 6.77 | 8.71 | −0.03 |
| 2018 | BASE | 9.91 | 14.72 | 0.20 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 9.85 | 15.23 | 0.10 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 9.43 | 16.61 | 0.08 |
Table 11.
Visalia, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
Table 11.
Visalia, CA, site-specific normalized mean bias (%), domain-wide RMSE in for each year and FEI, and domain-wide correlation based on HYSPLIT PM2.5 concentrations and EPA measured PM2.5 concentrations.
| Year | FEI | NMB (%) | RMSE (g) | Correlation |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 13.67 | 18.08 | 0.05 |
| 2013 | COMBO | 13.03 | 18.13 | 0.09 |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 13.01 | 17.63 | 0.14 |
| 2016 | BASE | 13.11 | 14.79 | 0.21 |
| 2016 | COMBO | 10.21 | 41.73 | 0.12 |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 9.91 | 41.71 | 0.12 |
| 2018 | BASE | 15.35 | 18.97 | 0.23 |
| 2018 | COMBO | 14.02 | 24.78 | 0.09 |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 12.29 | 33.36 | 0.07 |
Table 12.
The number of fire days, total annual PM2.5 concentrations in kg from HYSPLIT over the entire domain, and the percent increase in the number of locations with downwind PM2.5 concentration estimated by HYSPLIT between FEIs. Note that there may be more than one fire per day.
Table 12.
The number of fire days, total annual PM2.5 concentrations in kg from HYSPLIT over the entire domain, and the percent increase in the number of locations with downwind PM2.5 concentration estimated by HYSPLIT between FEIs. Note that there may be more than one fire per day.
| Year | FEI | Fire Days | Annual 10 m PM2.5 Concentrations (kg) | % Increase in Concentrations | % Increase in Downwind Locations |
|---|
| 2013 | BASE | 284 | | – | – |
| 2013 | COMBO | 286 | | 7% | 8% |
| 2013 | COMBO + CC | 319 | | 12% | 12% |
| 2016 | BASE | 268 | | – | – |
| 2016 | COMBO | 245 | | 204% | 0.4% |
| 2016 | COMBO + CC | 285 | | 21% | 22% |
| 2018 | BASE | 301 | | – | – |
| 2018 | COMBO | 301 | | 35% | 29% |
| 2018 | COMBO + CC | 337 | | 23% | 11% |