Numerical Study on Coupled Combustion of PMMA Counter-Directional Flame Spread at Variable Slope
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FDS Numerical Simulation
2.1.1. Pyrolysis Model
2.1.2. Turbulent Combustion Model
2.1.3. Radiation Model
2.1.4. Material Parameter Setting
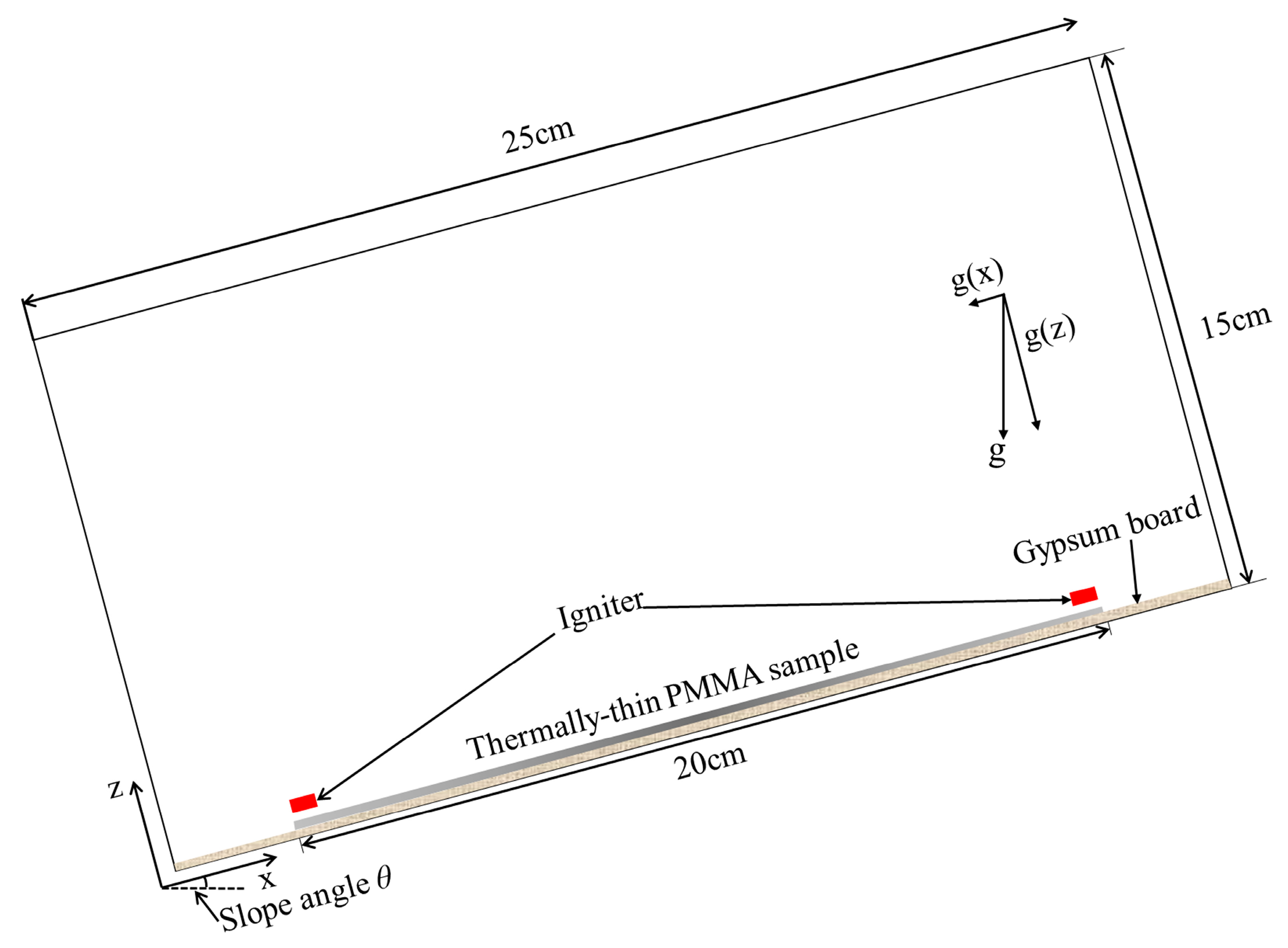
2.2. Simulation Configuration
2.3. Meshing and Grid Independence Validation
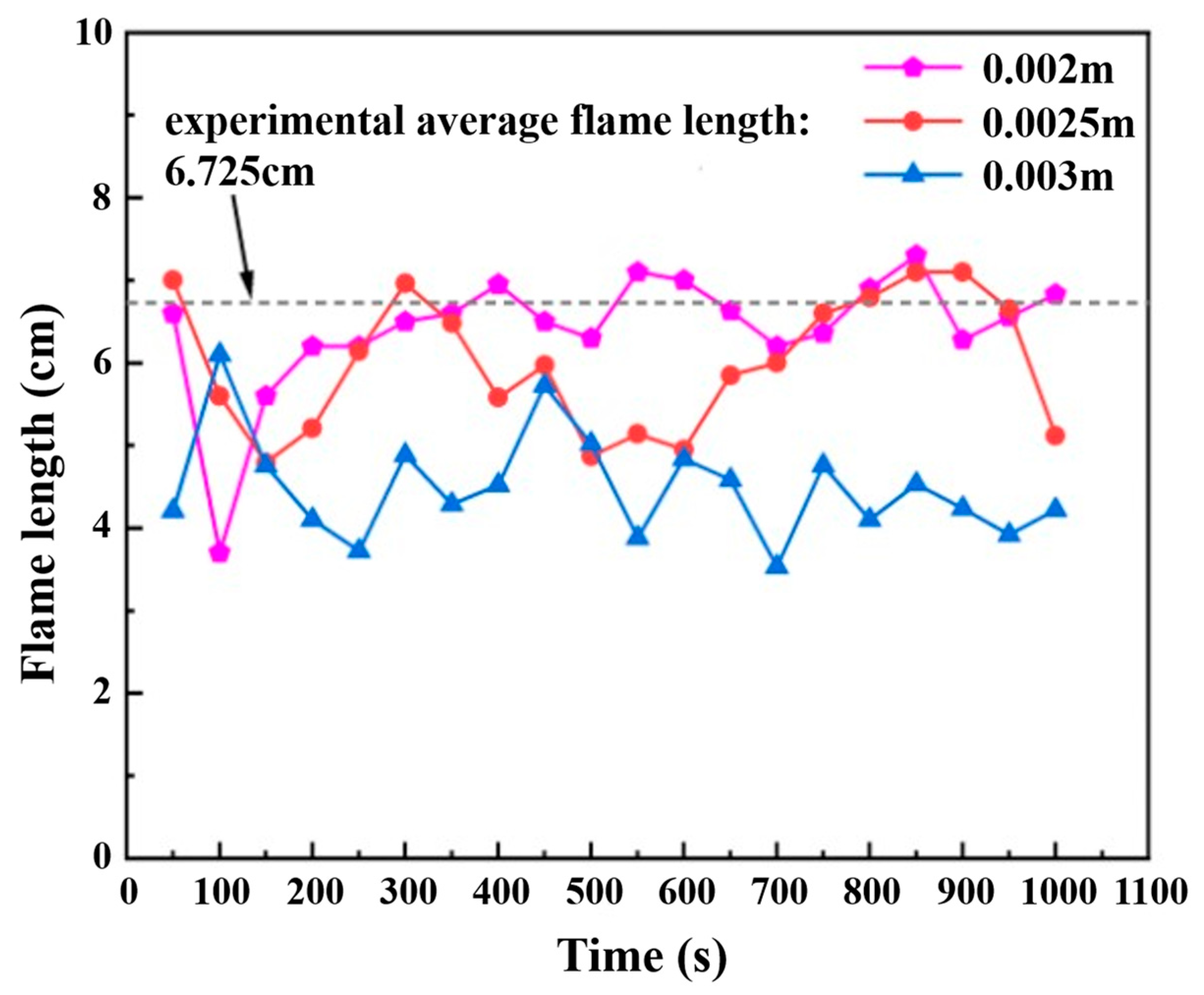
2.4. Model Validation
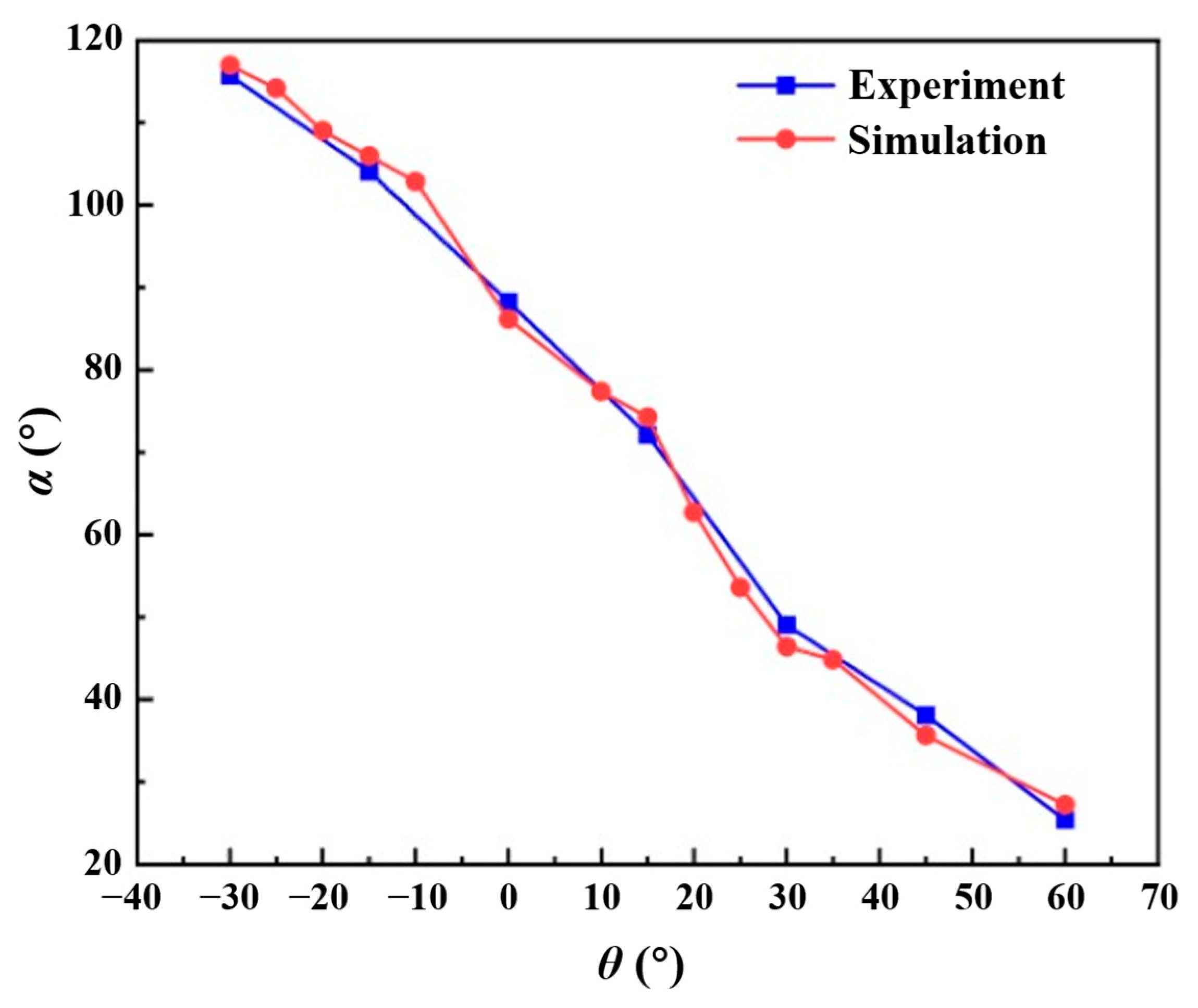
2.4.1. Validation Based on Flame Morphology
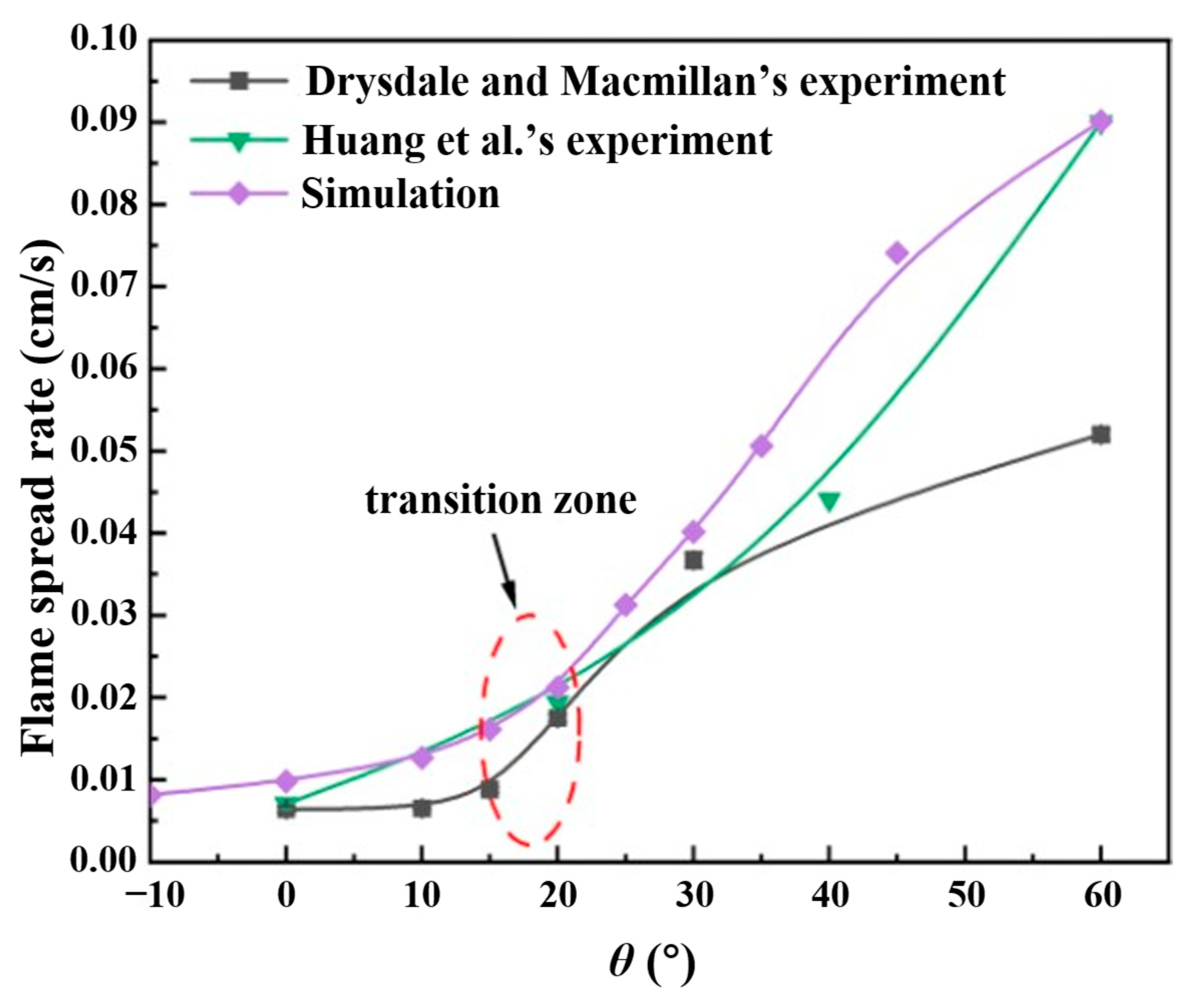
2.4.2. Validation Based on Flame Spread Rate
3. Results and Discussion
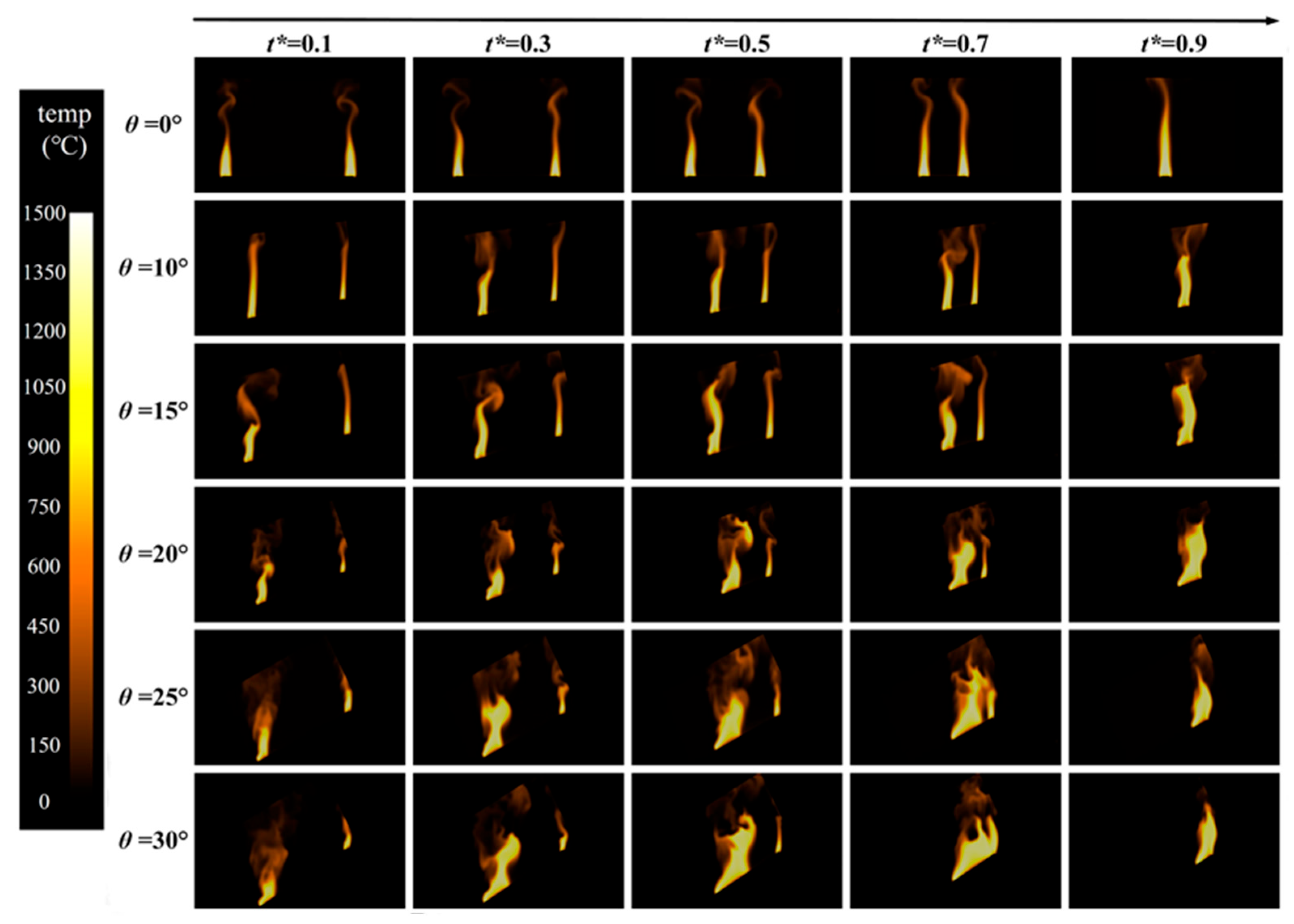
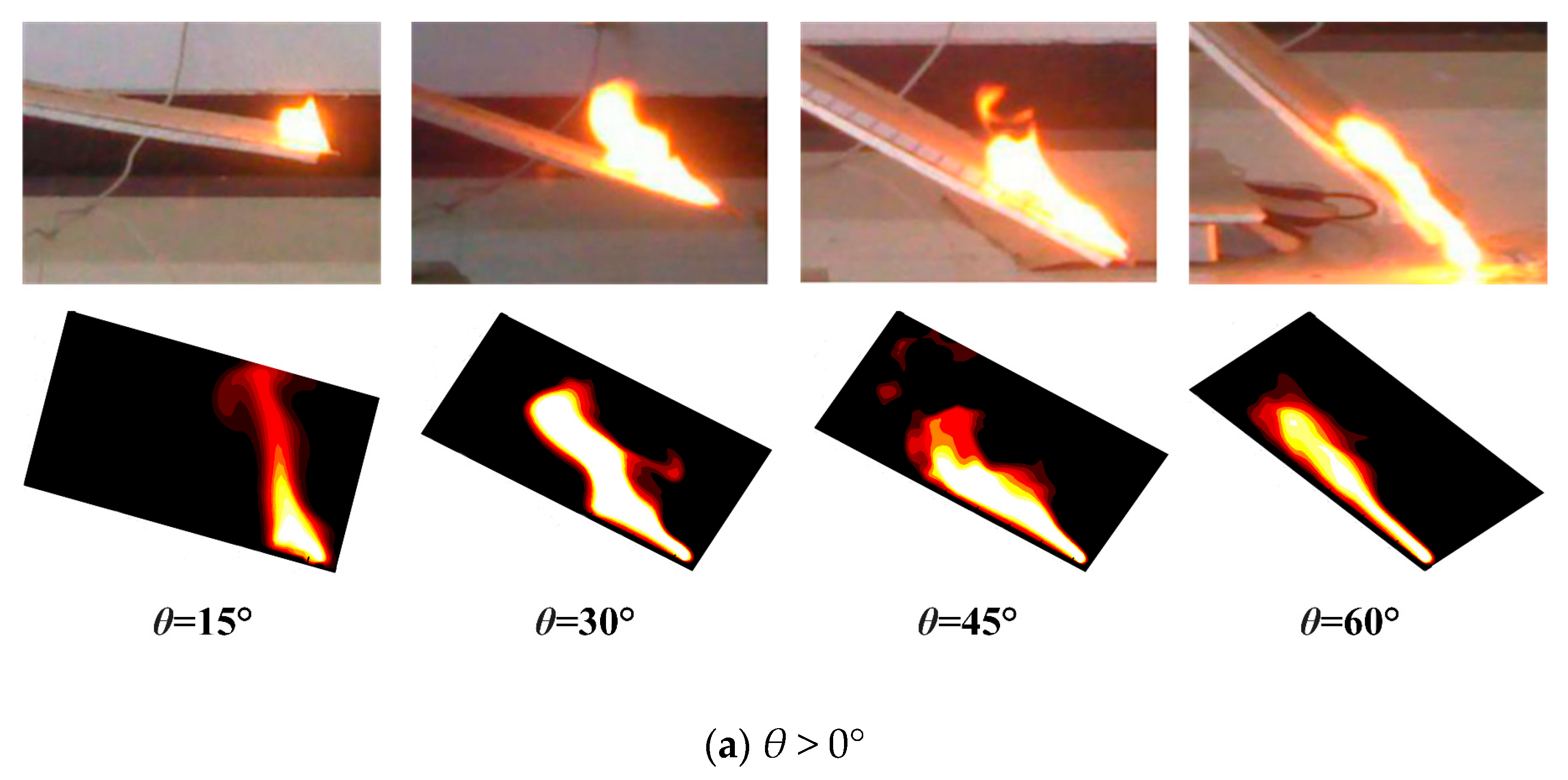
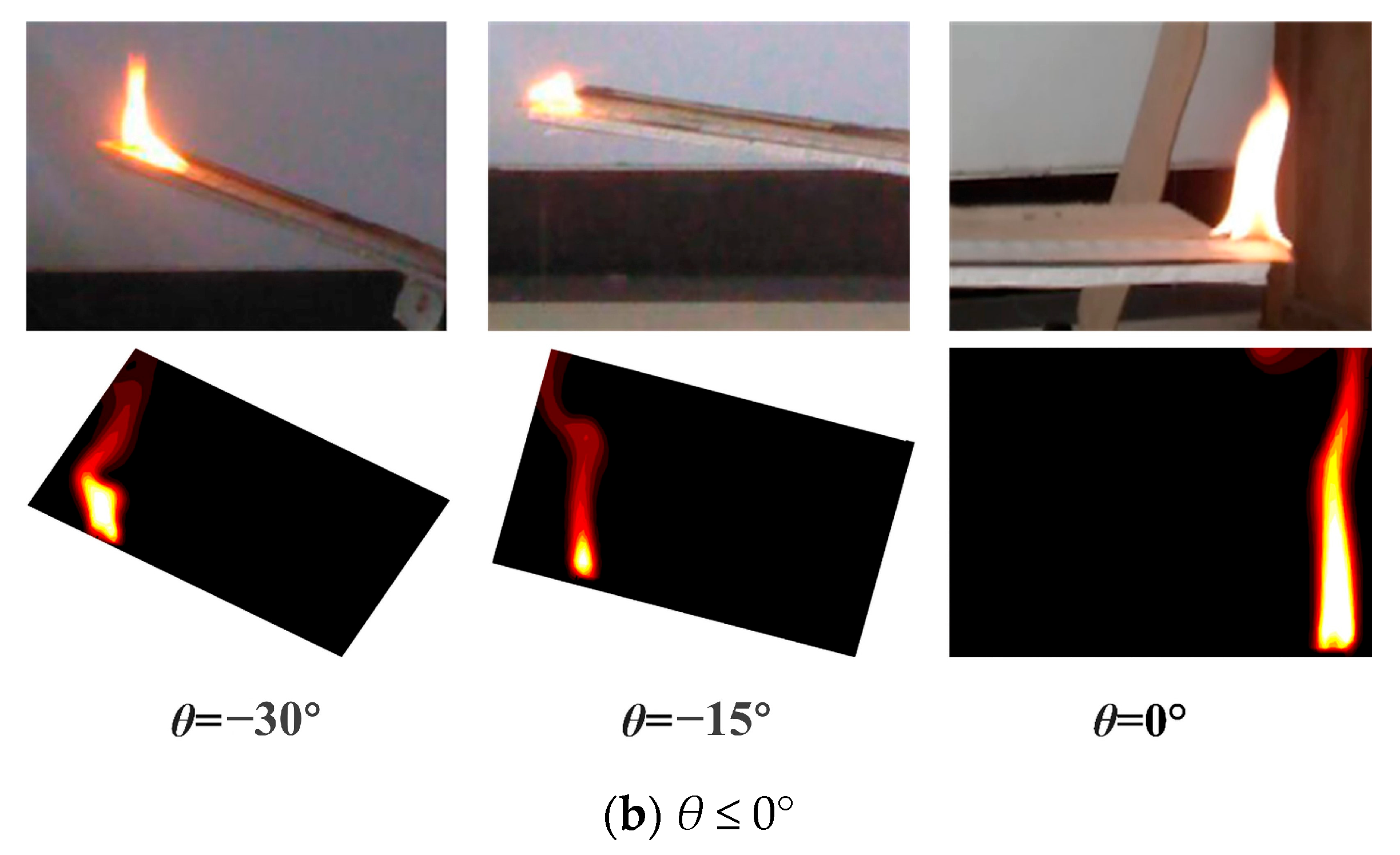
3.1. Flame Morphology
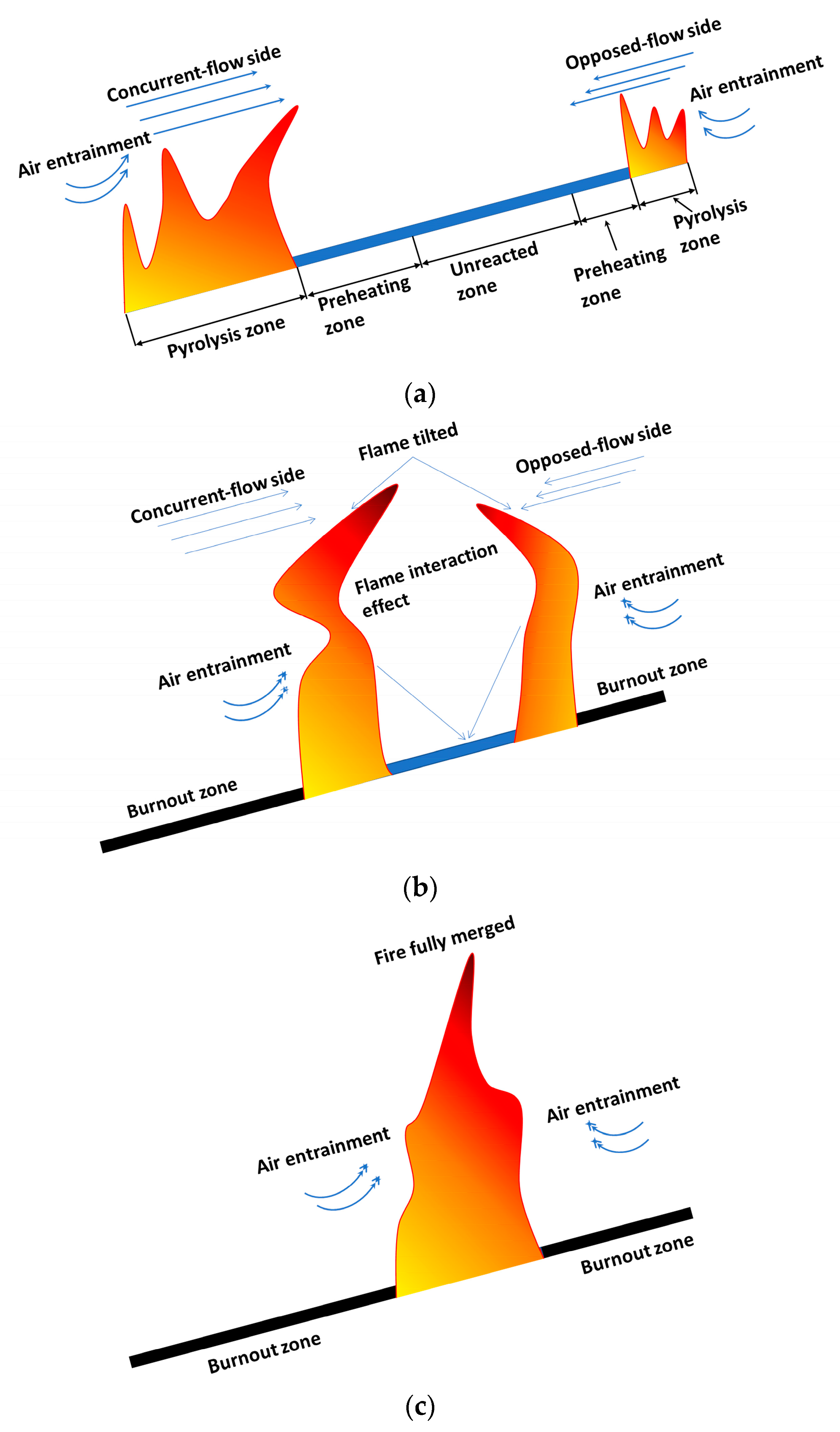
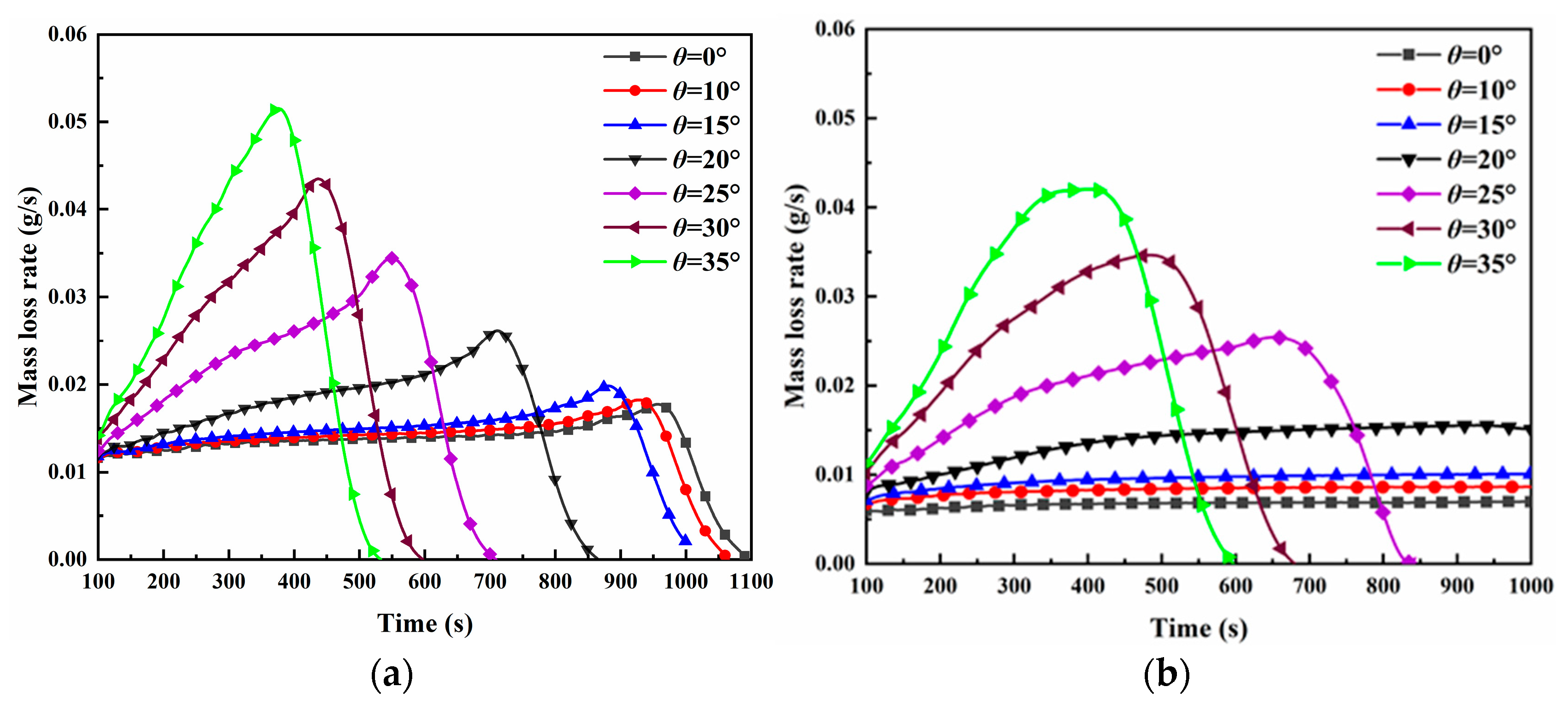
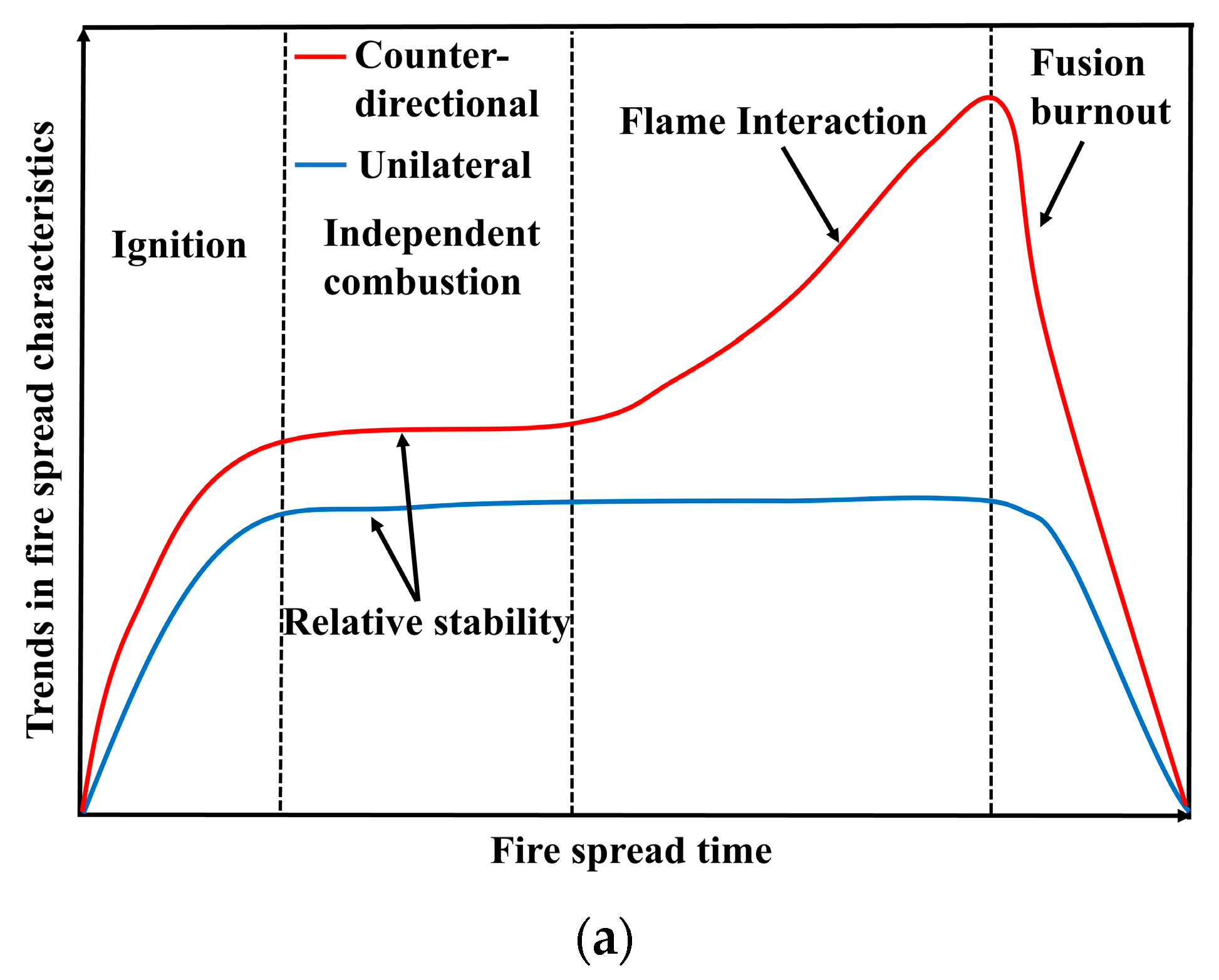
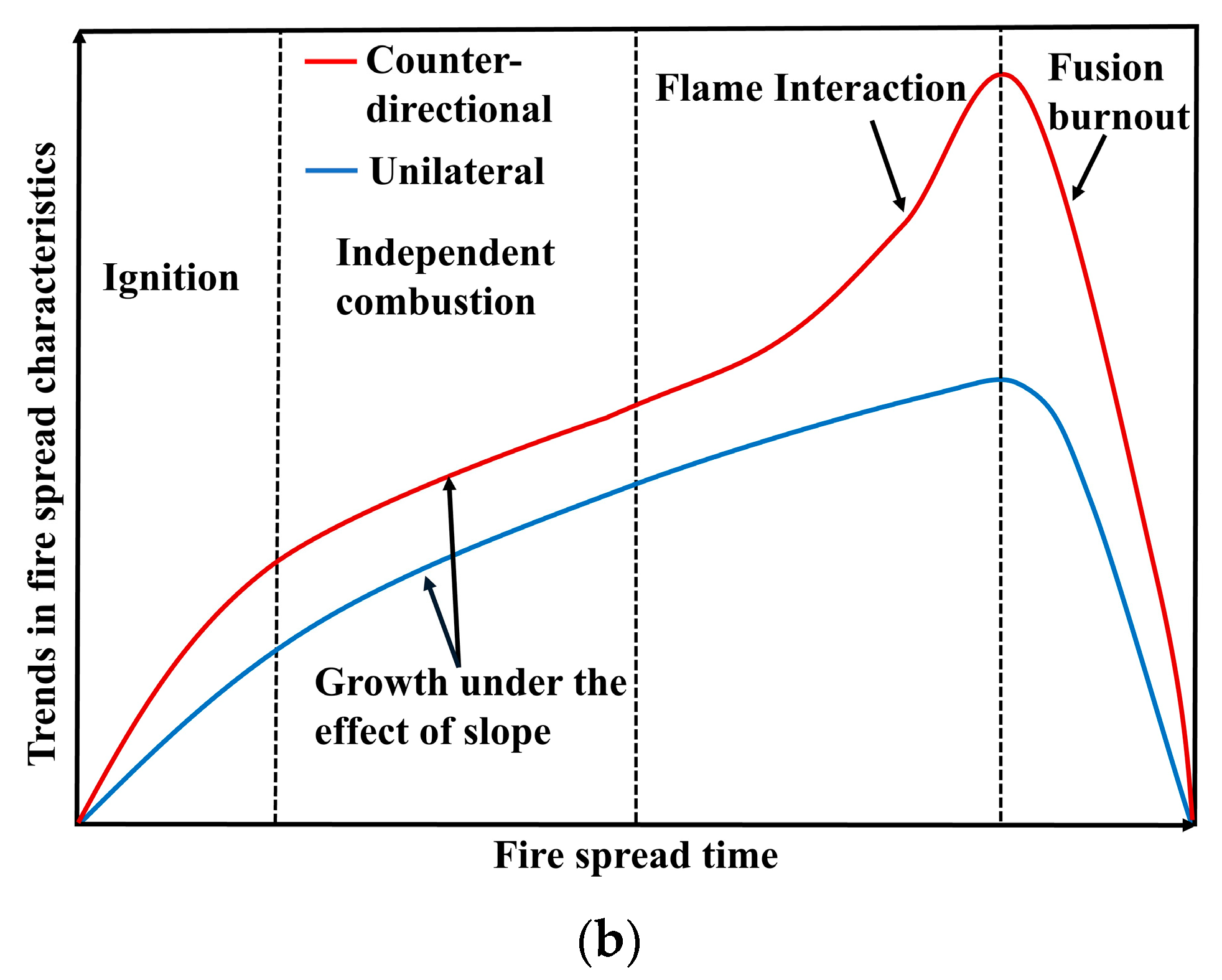
3.1.1. Flame Evolution Hypothesis
3.1.2. Flame Morphology Analysis
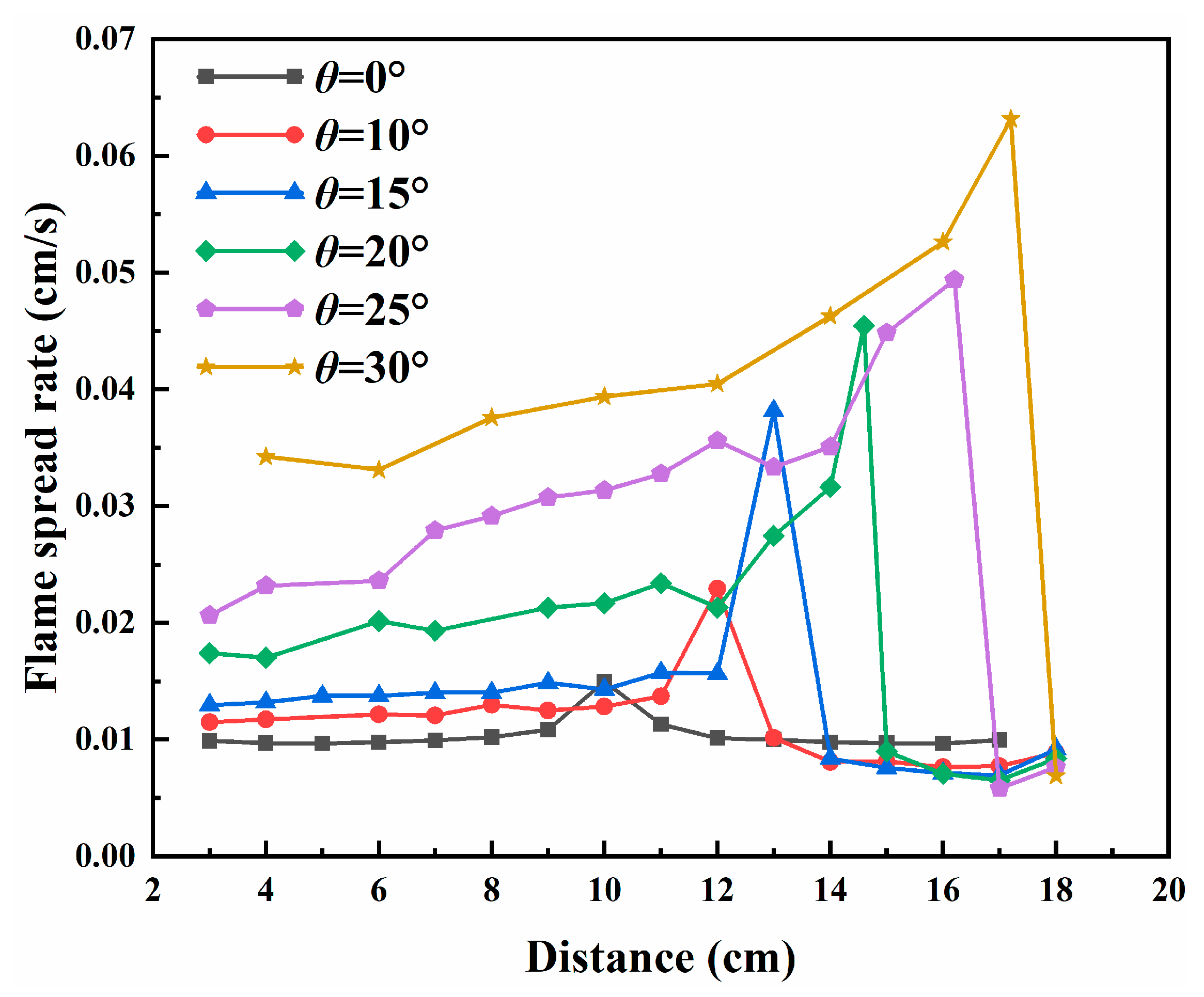
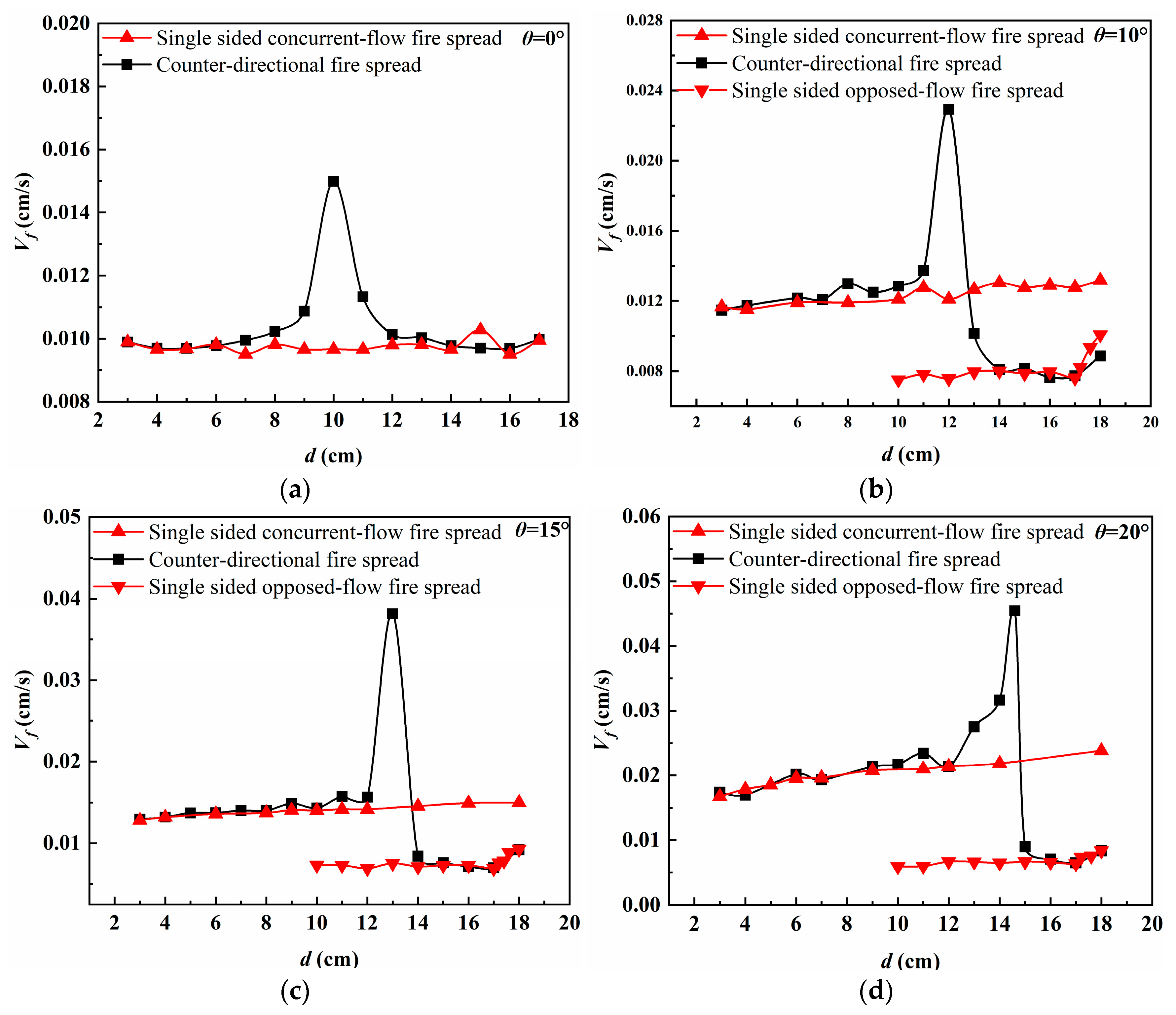
3.2. Flame Spread Rate
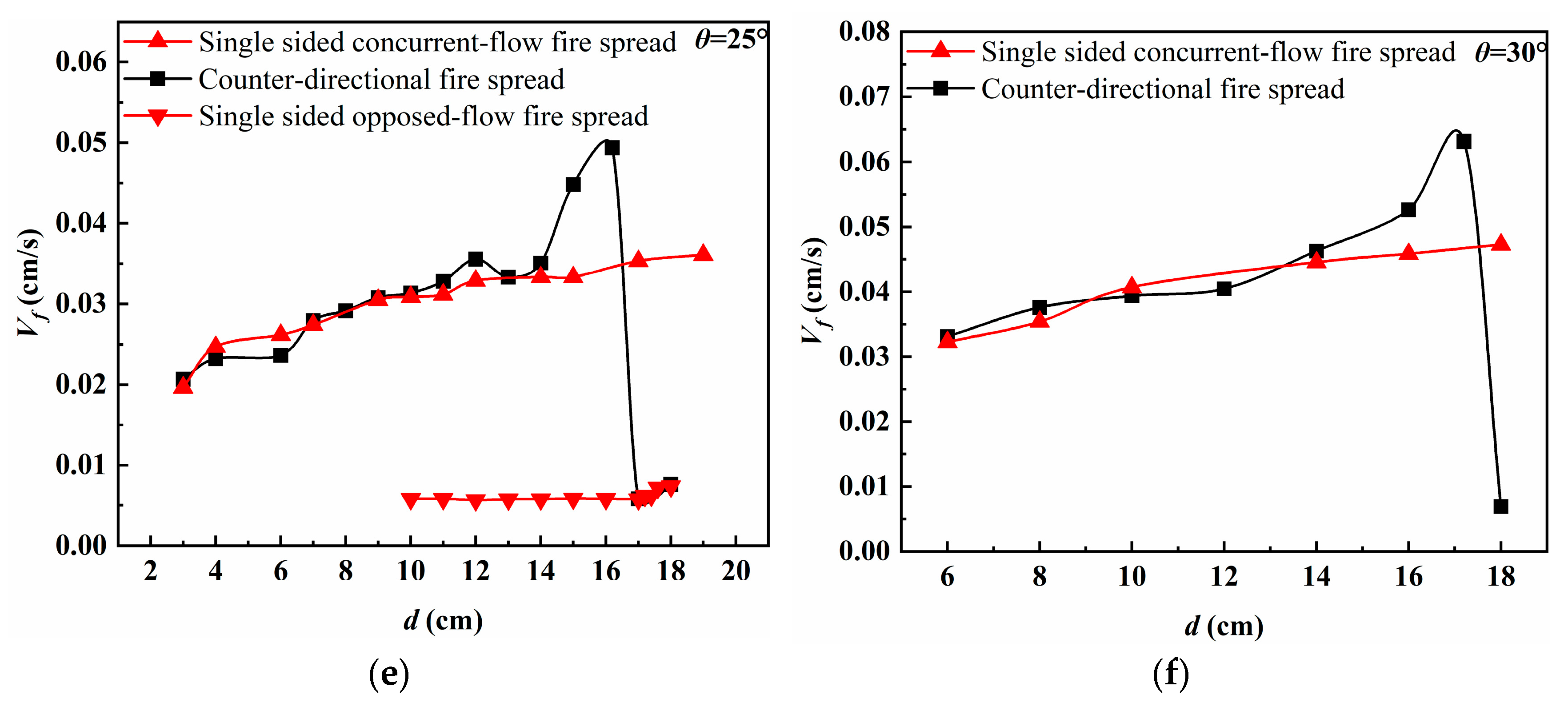
3.3. Mass Loss Rate
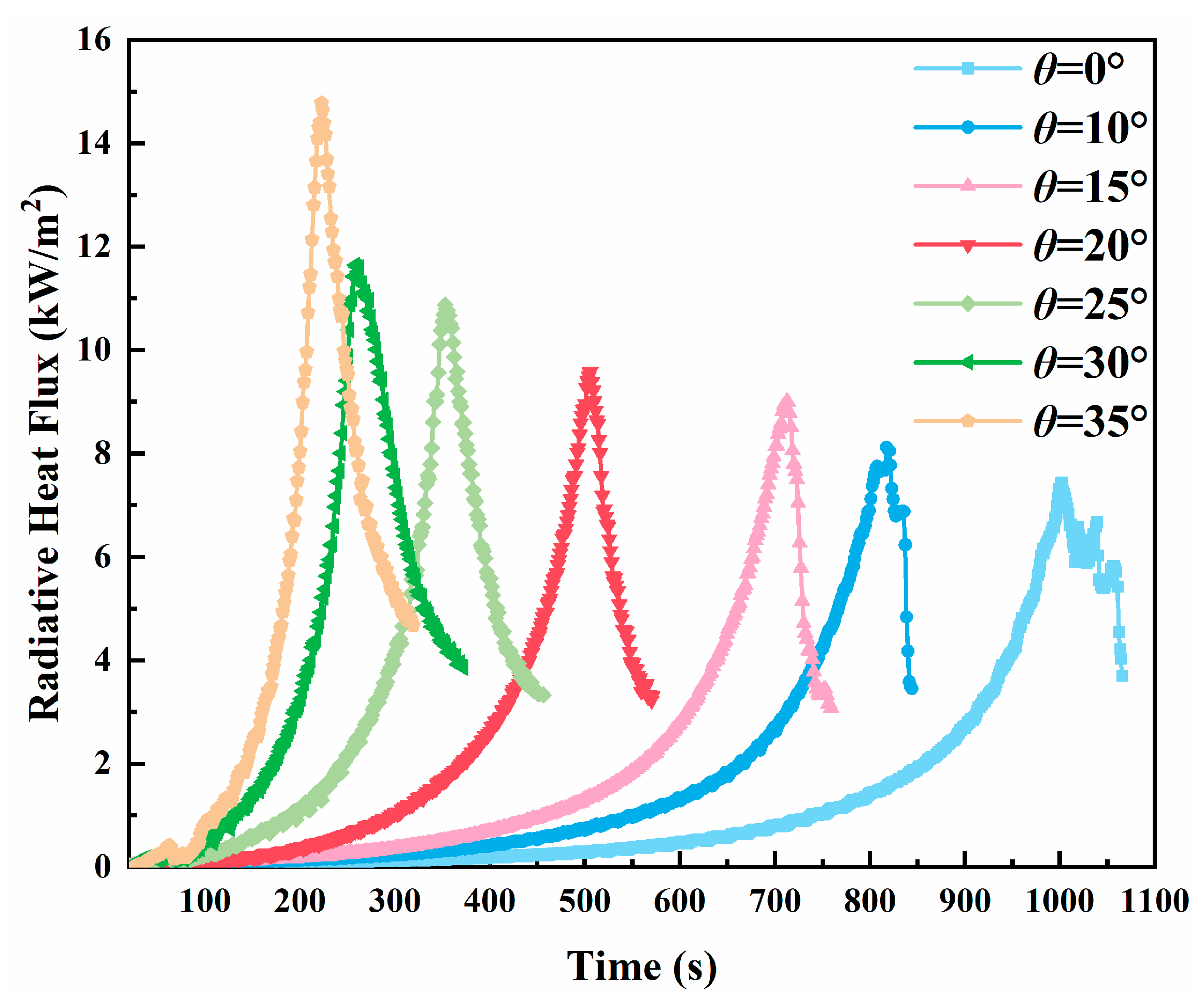
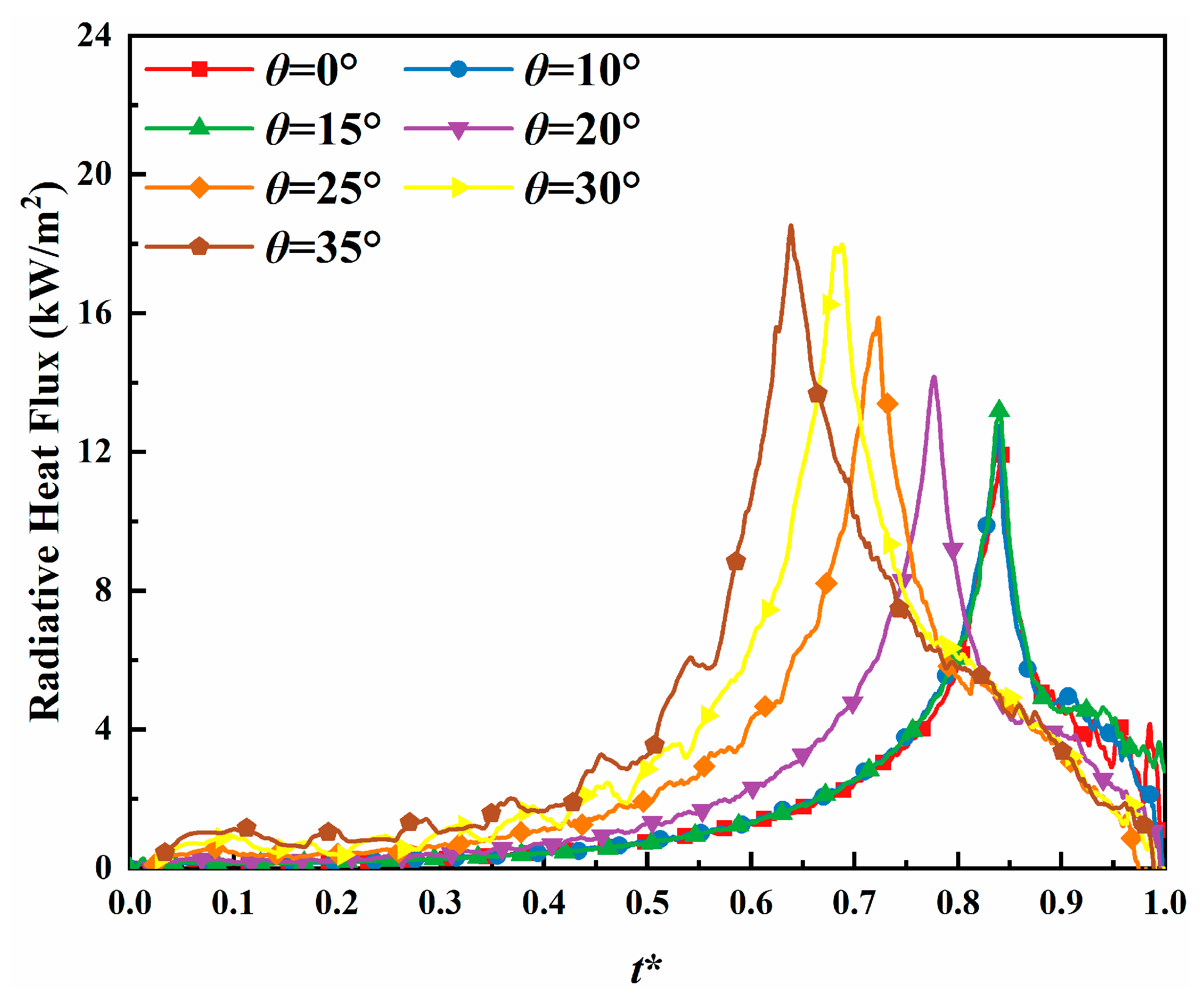
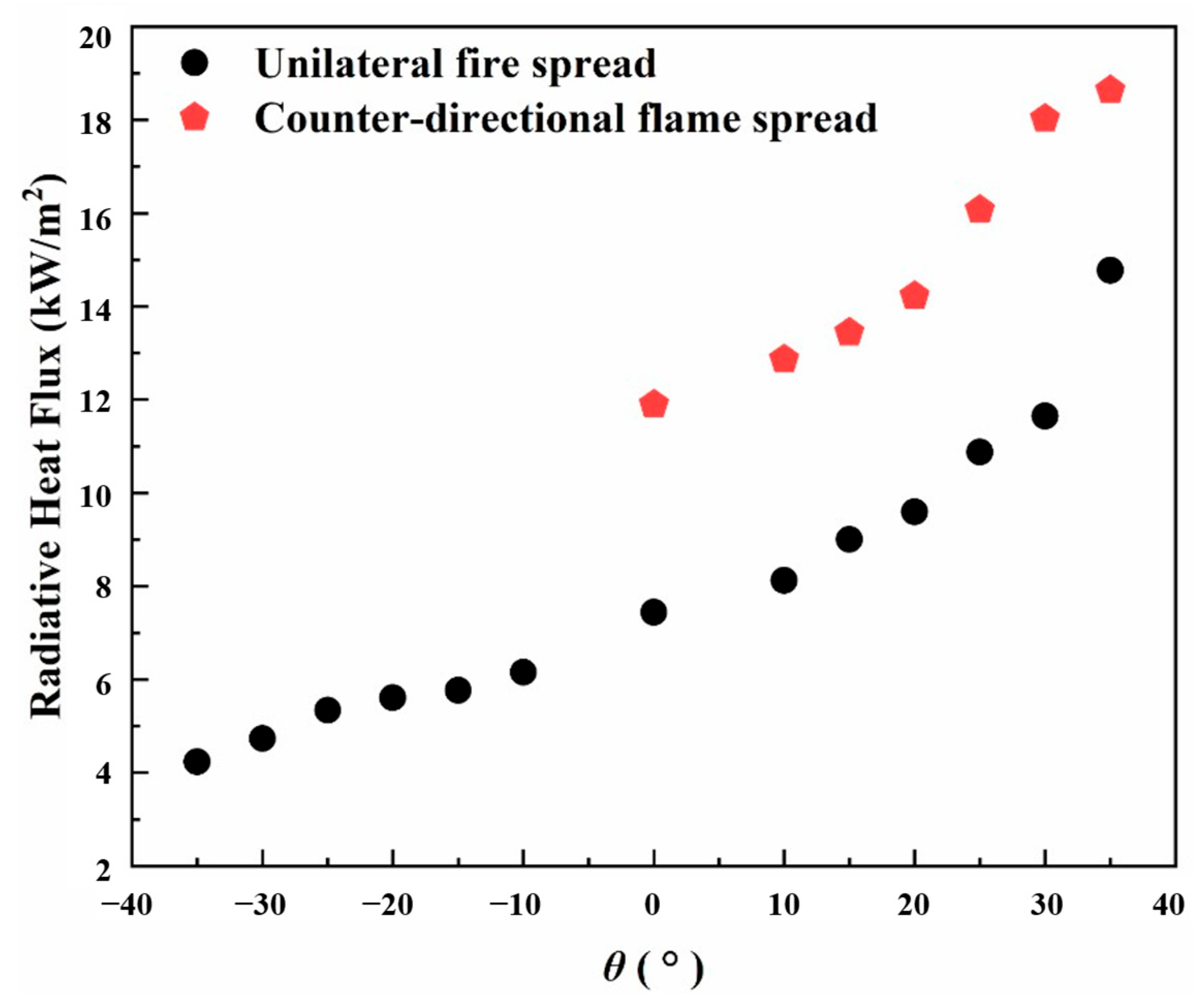
3.4. Radiative Heat Flux
3.5. Analysis of the Effects of Flame Interactions
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The morphological analysis of counter-directional flame propagation revealed distinct slope-dependent characteristics. While horizontal propagation (0° slope) exhibited symmetric flame structures on both sides, inclined conditions induced asymmetric flame development. This asymmetry manifested as two distinct flame regimes: a concurrent-flow side with enhanced flame attachment and tilt toward the fuel surface, and an opposed-flow side demonstrating reduced flame inclination and weaker fuel preheating. These morphological differences confirmed the fundamental counter-directional combustion phenomenon hypothesized in this study.
- (2)
- The propagation dynamics of counter-directional flames, including spread velocity and mass loss rate, exhibited significant dependence on inter-flame spacing during interaction phases. Both parameters showed progressive enhancement with slope, mirroring the behavior observed in peak radiative heat flux density for both unilateral and counter-directional propagation modes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| FDS | Fire dynamics simulator |
| fvDOM | Finite volume Discrete Ordinates Model |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| PMMA | Polymethylmethacrylate |
| RTE | Radiative Transfer Equation |
References
- Zhou, Y.; Xiao, H.H.; Sun, J.H.; Zhang, X.N.; Yan, W.G.; Huang, X.J. Experimental study of horizontal flame spread over rigid polyurethane foam on a plateau: Effects of sample width and ambient pressure. Fire Mater. 2015, 39, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, H.; An, W.; Xia, Y. Experimental study of moisture content effects on horizontal flame spread over thin cotton fabric. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liao, Y.T.T. Numerical investigation of flame splitting phenomenon in upward flame spread over solids with a two-stage pyrolysis model. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2018, 190, 2082–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xie, Q.; Qiu, R. Melting and dripping flow behaviors on the downward flame spread of a wide XPS foam. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 2055–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, L.K.; Ronney, P.D. Mechanisms of concurrent-flow flame spread over solid fuel beds. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2000, 28, 2793–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drysdale, D.D.; Macmillan, A.J.R. Flame spread on inclined surfaces. Fire Saf. J. 1992, 18, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintiere, J.G. The effects of angular orientation on flame spread over thin materials. Fire Saf. J. 2001, 36, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, K.; Lin, Y. Surface inclination effects on heat transfer during flame spread acceleration based on FireFOAM. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 32, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, N.; Chen, Y.; Jonathan, W.; Margaret, M.; Patrick, H. Experimental study of flame spread over thermally-thin inclined fuel surface and controlling heat transfer mechanism under concurrent wind. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 165, 106936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Kohyu, S.; Zhu, J. Burn-out time data analysis on interaction effects among multiple fires in fire arrays. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2007, 31, 2589–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.X.; Raposo, J.R.; Davim, D.A.; Rossa, C.G. Study of the jump fire produced by the interaction of two oblique fire fronts. Part 1. Analytical model and validation with no-slope laboratory experiments. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2012, 21, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Wang, S. Non-Dimensional correlations on flame height and axial temperature profile of a buoyant turbulent line-source jet fire plume. J. Fire Sci. 2014, 32, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. A new mathematical method for quantifying trajectory of buoyant line-source gaseous fuel jet diffusion flames in cross air flows. Fuel 2016, 177, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, W.; Miller, C.; Sun, J.-H.; Gollner, M.J. Flame spread and burning rates through vertical arrays of wooden dowels. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2019, 37, 3767–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Raghavan, V.; Trubachev, S.A.; Shmakov, A.G.; Korobeinichev, O.P.; Kumar, B.P. Numerical and experimental study of downward flame spread along multiple parallel fuel sheets. Fire Saf. J. 2021, 125, 103414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Zhou, X.D.; Zhao, K.; Wu, Z.B.; Yang, L.Z. Experimental and numerical study on effect of sample orientation on auto-ignition and piloted ignition of poly (methyl methacrylate). Materials 2015, 8, 4004–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, H.R.; Korobeinichev, O.P.; Harish, A.; Raghavan, V.; Kumar, A.; Gerasimov, I.E.; Gonchikzhapov, M.B.; Tereshchenko, A.G.; Trubachev, S.A.; Shmakov, A.G. Investigation of the structure and spread rate of flames over PMMA slabs. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 130, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, P.; Wang, Y.; Meredith, K.V.; Dorofeev, S.B. Application of a subgrid soot-radiation model in the numerical simulation of a heptane pool fire. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2015, 35, 2573–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinali, D.; Gupta, A.; Maragkos, G.; Agarwal, G.; Beji, T.; Chaos, M.; Wang, Y.; Degroote, J.; Merci, B. Study of the importance of non-uniform mass density in numerical simulations of fire spread over MDF panels in a corner configuration. Combust. Flame 2019, 200, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, A.; Kashiwagi, T. Characterization of flame spread over PMMA using holographic interferometry sample orientation effects. Combust. Flame 1988, 71, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, F.H.; Xiao, H.H.; Jiang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, M.M. Upward flame spread over an array of discrete thermally-thin PMMA plates. Fire Technol. 2021, 57, 1381–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoliarov, S.I.; Crowley, S.; Lyon, R.E.; Linteris, G.T. Prediction of the burning rates of non-charring polymers. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 1068–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; King, M.D.; Paolini, C. Structure of downward spreading flames: A comparison of numerical simulation, experimental results and a simplified parabolic theory. Combust. Theory Model. 2003, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; Tang, G.; Zhang, H. Flame Spread Characteristics over Building Decoration Material of PMMA with Different Placed Angles. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2018, 18, 454–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J. Prediction of the critical condition for flame acceleration over wood surface with different sample orientations. Combust. Flame 2012, 159, 2999–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Bian, N.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Shi, L. Experimental study on coupled combustion of PMMA counter-directional flame spread in the horizontal direction. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2023, 143, 110850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; DesJardin, P.E. An embedded upward flame spread model using 2D direct numerical simulations. Combust. Flame 2009, 156, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Du, B.; Yan, Q.; Shi, L.; Li, M.; Li, Z. Study on coupled combustion behavior of two parallel line fires. Fire 2022, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Q.; Lozano, J.S.; Shu, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Deng, Z.; Satoh, K. Global burning rate of square fire arrays: Experimental correlation and interpretation. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2009, 32, 2519–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Units | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Density | kg/m3 | 1190 |
| Specific heat | kJ/kg/K | 2.2 |
| Conductivity | W/m/K | 0.2 |
| Emissivity | – | 0.85 |
| Absorption coefficient | m−1 | 2700 |
| Pre-exponential factor | s−1 | 8.5 × 1012 |
| Activation energy | kJ/kmol | 1.88 × 105 |
| Heat of reaction | kJ/kg | 870 |
| θ (°) | g(x) (m/s2) | g(z) (m/s2) | θ (°) | g(x) (m/s2) | g(z) (m/s2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0 | −9.81 | 25° | 4.146 | −8.891 |
| 10° | 1.704 | −9.661 | 30° | 4.905 | −8.496 |
| 15° | 2.539 | −9.476 | 35° | 5.627 | −8.036 |
| 20° | 3.355 | −9.218 |
| Forms of Fire Spread | Calculation Area (x, y, z) | Number of Grids |
|---|---|---|
| Unilateral fire spread | 25 cm × 5 cm × 10 cm | 156,250 |
| Counter-directional flame spread | 25 cm × 5 cm × 15 cm | 234,375 |
| Slope | Contact Time of the Flame Front | Fire Spread Distance on the Concurrent-Flow Side | Fire Spread Distance on the Opposed-Flow Side |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0° | 917.8 | 10 | 10 |
| 10° | 884.3 | 12 | 8 |
| 15° | 832.3 | 13 | 7 |
| 20° | 661.7 | 14.6 | 5.4 |
| 25° | 502.4 | 16.2 | 3.8 |
| 30° | 392.5 | 17.2 | 2.8 |
| 35° | 329.6 | 17.8 | 2.2 |
| Slope | I(a)-Concurrent-Flow Side | I(a)-Opposed-Flow Side |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.08348 | 0.08348 |
| 10° | 0.07751 | 0.08458 |
| 15° | 0.06681 | 0.08599 |
| 20° | 0.06526 | 0.1267 |
| 25° | 0.05617 | 0.14061 |
| 30° | 0.05239 | 0.18821 |
| 35° | 0.05206 | 0.20636 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Q.; Li, K.; Yuan, C.; Bian, N.; Li, Z.; Xu, W.; Chen, J. Numerical Study on Coupled Combustion of PMMA Counter-Directional Flame Spread at Variable Slope. Fire 2025, 8, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060219
Liu Q, Li K, Yuan C, Bian N, Li Z, Xu W, Chen J. Numerical Study on Coupled Combustion of PMMA Counter-Directional Flame Spread at Variable Slope. Fire. 2025; 8(6):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060219
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Qiong, Kehong Li, Chao Yuan, Ning Bian, Zhi Li, Weilin Xu, and Jinrong Chen. 2025. "Numerical Study on Coupled Combustion of PMMA Counter-Directional Flame Spread at Variable Slope" Fire 8, no. 6: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060219
APA StyleLiu, Q., Li, K., Yuan, C., Bian, N., Li, Z., Xu, W., & Chen, J. (2025). Numerical Study on Coupled Combustion of PMMA Counter-Directional Flame Spread at Variable Slope. Fire, 8(6), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8060219








