Origin of Temperature Coefficient of Resonance Frequency in Rutile Ti1−xZrxO2 Microwave Ceramics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussions
4. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balunarayanan, R.; Aiswarya, S.; Sreekala, C.; Menon, S.K. Nano Cylindrical Dielectric Resonator Antenna Using Titanium dioxide for Wi-Fi Applications. Proceddings of the 2021 Fourth International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Technologies (ICECCT), Coimbatore, India, 15–17 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, S.B. Microwave bandpass filters containing high-Q dielectric resonators. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 1968, 16, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehara, K.; Hoshina, T.; Takeda, H.; Tsurumi, T. Terahertz permittivity of rutile TiO2 single crystal measured by anisotropic far-infrared ellipsometry. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 123, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mett, R.R.; Sidabras, J.W.; Anderson, J.R.; Klug, C.S.; Hyde, J.S. Rutile dielectric loop-gap resonator for X-band EPR spectroscopy of small aqueous samples. J. Magn. Reson. 2019, 307, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanaor, D.A.; Sorrell, C.C. Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 855–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongyong, N.; Chanlek, N.; Srepusharawoot, P.; Thongbai, P. Origins of giant dielectric properties with low loss tangent in rutile (Mg1/3Ta2/3)0.01Ti0.99O2 ceramic. Molecules 2021, 26, 6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanamoon, N.; Chanlek, N.; Moontragoon, P.; Srepusharawoot, P.; Thongbai, P. Microstructure, low loss tangent, and excellent temperature stability of Tb + Sb-doped TiO2 with high dielectric permittivity. Results Phys. 2022, 37, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, P.; Chen, C.; Cui, B.; Li, J.; Xu, D.; Tang, B. Influence of the electric field on flash-sintered (Zr + Ta) co-doped TiO2 colossal permittivity ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 6016–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanamoon, N.; Chanlek, N.; Srepusharawoot, P.; Swatsitang, E.; Thongbai, P. Microstructural Evolution and High-Performance Giant Dielectric Properties of Lu3+/Nb5+ Co-Doped TiO2 Ceramics. Molecules 2021, 26, 7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wei, X.; Hao, J. Disappearance and recovery of colossal permittivity in (Nb + Mn) co-doped TiO2. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 12395–12400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-H.; Huang, C.-L. Microwave dielectric properties of ultra-low-temperature-sintered TiO2 as a τ f compensator. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yue, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Temperature-dependent dielectric properties, thermally-stimulated relaxations and defect-property correlations of TiO2 ceramics for wireless passive temperature sensing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 1923–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabstanowicz, L.R.; Gao, S.; Li, T.; Rickard, R.M.; Rajh, T.; Liu, D.-J.; Xu, T. Facile oxidative conversion of TiH2 to high-concentration Ti3+-self-doped rutile TiO2 with visible-light photoactivity. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 3884–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeton, A.; Wang, X.; Penn, S.J.; Webb, S.J.; Cohen, L.F.; Alford, N.M. Microwave dielectric loss of titanium oxide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2000, 83, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, J.H.; Jung, H.S.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, J.-R.; Hong, K.S. Microwave dielectric properties of nanocrystalline TiO2 prepared using spark plasma sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 2937–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Z.; Wu, C.; Xiong, Z.; Feng, Y.; AminiRastabi, H.; Song, C.; Xue, H. Low temperature sintering and microwave dielectric properties of TiO2 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 37, 4667–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullar, R.C.; Penn, S.J.; Wang, X.; Reaney, I.M.; Alford, N.M. Dielectric loss caused by oxygen vacancies in titania ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 29, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Liu, L.; Yang, Z.J.; Li, L.; Chen, X.M. Structure and microwave dielectric characteristics of Hf1–xTixO2 ceramics. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2022, 105, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Yang, J.; Gong, M.; Ao, L.; Fang, Z.; Kashif, K.; Qu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Xiong, Z.; et al. The improved microwave dielectric characteristics of TiO2 ceramics produced by Mn2+ and W6+ co-substitution. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 27041–27052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kang, D.H. Relationships between crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of (Zn1/3B2/35+)xTi1−xO2 (B5+ = Nb, Ta) ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2008, 34, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, K.; Awai, R.K. Microwave characteristics of TiO2-Bi2O3 dielectric resonator. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 32, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jing, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, H. Novel Tri-rutile Ni0.5Ti0.5TaO4 Microwave Dielectric Ceramics: Crystal Structure Chemistry, Raman Vibration Mode, and Chemical Bond Characteristic In-Depth Studies. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 14680–14692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.V.C.; Castro, P.J.; Nono, M.d.C.d.A.; Mineiro, S.L. Microstructure, crystalline phase, and dielectric property analyses of TiO2 composition with ZrO2 addition. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2010, 660, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, A.C.; Von Dreele, R.B. General Structure Analysis System; Report LAUR 86-748; Los Alamos National Laboratory: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 2004.
- Toby, B.H. EXPGUI, a graphical user interface for GSAS. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2001, 34, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupka, J. Frequency domain complex permittivity measurements at microwave frequencies. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, R55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Wang, E.; Cao, Y. Doping behavior of Zr4+ ions in Zr4+-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 27120–27126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-M.; Doong, R.-A. Characterization of Zr-doped TiO2 nanocrystals prepared by a nonhydrolytic sol−gel method at high temperatures. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 20808–20814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, R.D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Cryst. Phys. Diffr. Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatyuk, Y.; Smirnova, N.; Korduban, O.; Eremenko, A. Effect of zirconium incorporation on the stabilization of TiO2 mesoporous structure. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 42, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Lin, J.; Kwok, R.W. Ti1–xZrxO2 Solid Solutions for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Acetone in Air. J. Phys. Chem. B. 1998, 102, 5094–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, V.; Muddle, B.C.; Dai, Q. Size-dependent modifications of the Raman spectrum of rutile TiO2. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 163118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Harris, C.X.; Wallenmeyer, P.; Murowchick, J.; Chen, X. Asymmetric lattice vibrational characteristics of rutile TiO2 as revealed by laser power dependent Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 24015–24022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Gao, L.; Omran, M.; Chen, G. Microwave drying method investigation for the process and kinetics of drying characteristics of high-grade rutile TiO2. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 15618–15628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Nian, W.; Fan, J. Enhanced relative permittivity in niobium and europium co-doped TiO2 ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. Dielectric Materials for High Power Energy Storage; Queen Mary University of London: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Di Valentin, C.; Pacchioni, G.; Selloni, A. Reduced and n-type doped TiO2: Nature of Ti3+ species. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20543–20552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chester, P. Cross-Doping Agents for Rutile Masers. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 866–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiwi, J.; Suss, J.; Szapiro, S. EPR spectra of niobium-doped TiO2 and imiplications for water photocleavage processes. Chem. Phy. Lett. 1984, 106, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, M.; Paganini, M.C.; Livraghi, S.; Giamello, E. Charge trapping in TiO2 polymorphs as seen by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9435–9447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno, F.; Hernández-Alonso, M.D.; Tudela, D.; Coronado, J.M.; Soria, J. Photocatalytic degradation of toluene over doped and coupled (Ti, M) O2 (M = Sn or Zr) nanocrystalline oxides: Influence of the heteroatom distribution on deactivation. Appl. Catal. B 2008, 84, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.P.; Gopal, N.O.; Wang, T.C.; Wong, M.-S.; Ke, S.C. EPR investigation of TiO2 nanoparticles with temperature-dependent properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 5223–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livraghi, S.; Maurelli, S.; Paganini, M.C.; Chiesa, M.; Giamello, E. Probing the local environment of Ti3+ ions in TiO2 (rutile) by 17O HYSCORE. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8038–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Li, J.; Shao, J.; Cao, Y.; Li, K.; Zhao, W. An investigation into the enhanced permittivity properties of Zr co-doped (Ga0.5Nb0.5)0.03Ti0.97O2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 14983–14990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, S.; Petrovsky, V.; Dogan, F. Effects of sintering temperature on the microstructure and dielectric properties of titanium dioxide ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 6685–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, W. Multi-layer and open three-dimensionally ordered macroporous TiO2–ZrO2 composite: Diversified design and the comparison of multiple mode photocatalytic performance. Mater. Des. 2015, 86, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.U.; Khan, I.; Ali, B.; Muhammad, R.; Samad, A.; Shah, A.; Song, K.; Wang, D. Structural, dielectric, optical, and electrochemical performance of Li4Mo5O17 for ULTCC applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 160, 112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Woodford, W.H.; Randall, C.A. Band gap energy of perovskite structured ABO3 compounds. In Proceedings of the 2008 17th IEEE International Symposium on the Applications of Ferroelectrics, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 24–27 February 2008; Volume 1, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, P.; Sinha, E. Structural, photophysical and microwave dielectric properties of α-ZnMoO4 phosphor. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 795, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Yu, S. Preparation and Characterization of Zr–N-Codoped TiO2 Nano-Photocatalyst and Its Activity Enhanced-Mechanism. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 6965–6969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, C.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Shen, S. Impact of Zr-doped TiO2 photocatalyst on formaldehyde degradation by Na addition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 14044–14051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, E.H.; Sabur, D.A.; Chiad, S.S.; Fadhil, N. Physical properties of nanostructured li-doped ZrO2 thin films. J. Green Eng. 2020, 10, 8390–8400. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, L.J.; Chakrabarty, B. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of TiO2-ZrO2 nanocomposite by hydrothermal method. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2013, 4, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juma, A.; Acik, I.O.; Oluwabi, A.; Mere, A.; Mikli, V.; Danilson, M.; Krunks, M. Zirconium doped TiO2 thin films deposited by chemical spray pyrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmamalini, N.; Ambujam, K. Structural and dielectric properties of ZrO2–TiO2–V2O5 nanocomposite prepared by CO-precipitation calcination method. Mater. Sci. Semicond. 2016, 41, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Hao, J.; Xue, X.; Si, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, H. Rutile TiO2 microwave dielectric ceramics prepared via cold sintering assisted two step sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3459–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, R.D. Dielectric polarizabilities of ions in oxides and fluorides. J. Appl. Phys. 1993, 73, 348–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.; Bharambe, V.; Mummareddy, B.; Martin, J.; McKnight, J.; Abraham, M.A.; Walker, J.M.; Rogers, K.; Conner, B.; Cortes, P.; et al. Microwave dielectric properties of zirconia fabricated using NanoParticle Jetting™. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 586–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, R.; Wang, A.X.; Wager, J.F. Solid state dielectric screening versus band gap trends and implications. Opt. Mater. 2016, 60, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervé, P.; Vandamme, L. General relation between refractive index and energy gap in semiconductors. Infrared Phy. Techn. 1994, 35, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.-X.; Tang, B.; Li, E.; Zhang, S.-R. High-Q microwave dielectric properties in the Na0.5Sm0.5TiO3+Cr2O3 ceramics by one synthetic process. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 705, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Yang, H.; Yang, H.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, P.; Tang, B. Ilmenite-type MgTiO3 ceramics by complex (Mn1/2W1/2)4+ cation co-substitution producing improved microwave characteristics. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 21388–21397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Tang, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. The effect of Mn addition on phase development, microstructure and microwave dielectric properties of ZrTi2O6–ZnNb2O6 ceramics. Mater. Lett. 2012, 80, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, D.; Yao, X. Sintering behavior, structures, and microwave dielectric properties of (LixNb3x)Ti1−4xO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 91, 2947–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Chun, B.S.; Freer, R.; Cernik, R.J. Effects of packing fraction and bond valence on microwave dielectric properties of A2+ B6+ O4 (A2+: Ca, Pb, Ba; B6+: Mo, W) ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaney, I.M.; Iddles, D. Microwave dielectric ceramics for resonators and filters in mobile phone networks. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 2063–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hong, K.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, I.-T. Dielectric Properties of MNb2O6 Compounds (Where M = Ca, Mn, Co, Ni, or Zn). Mater. Res. Bull. 1997, 32, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosman, A.J.; Havinga, E.E. Temperature dependence of dielectric constants of cubic ionic compounds. Phys. Rev. 1963, 129, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, E. Effects of ZrO2 substitution on crystal structure and microwave dielectric properties of Zn0.15Nb0.3(Ti1–xZrx)0.55O2 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 22710–22717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.t.; Shannon, R. Empirical bond-strength–bond-length curves for oxides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A Cryst. Phys. Diffr. Theor. Gen. Crystallogr. 1973, 29, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, I.t.; Wu, K.K. Empirical parameters for calculating cation–oxygen bond valences. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B Struct. Crystallogr. Cryst. Chem. 1976, 32, 1957–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Guo, R.Z.; Li, L.; Chen, X.M. Improvement of τf in HfTiO4 microwave dielectric ceramics with Zr-and Sn-substitution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 2337–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Van Dover, R. Correlation between temperature coefficient of resonant frequency and tetragonality ratio. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 89, 1144–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Kang, D.H.; Kim, S.J. Effect of crystal structure on microwave dielectric properties of (Ni1/3B2/3)1–xTixO2 (B = Nb and Ta). Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 46, 7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
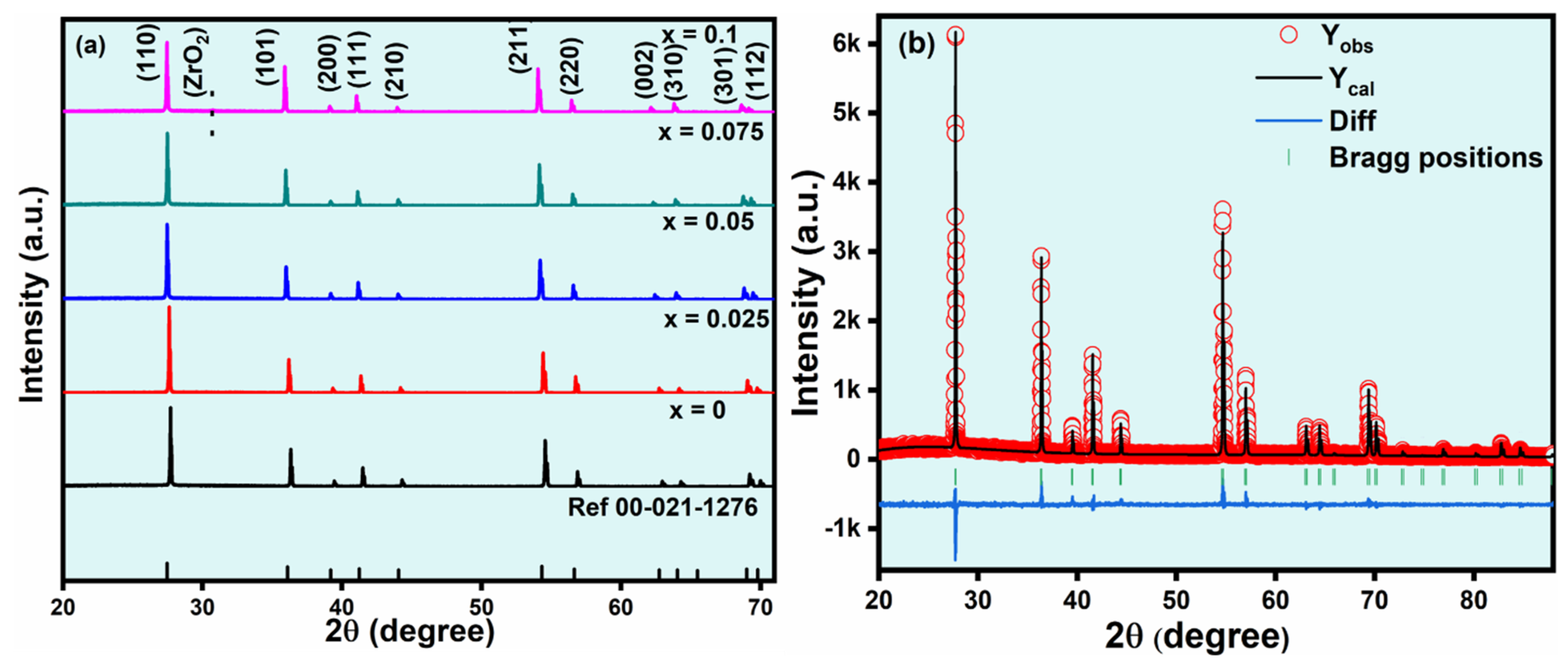
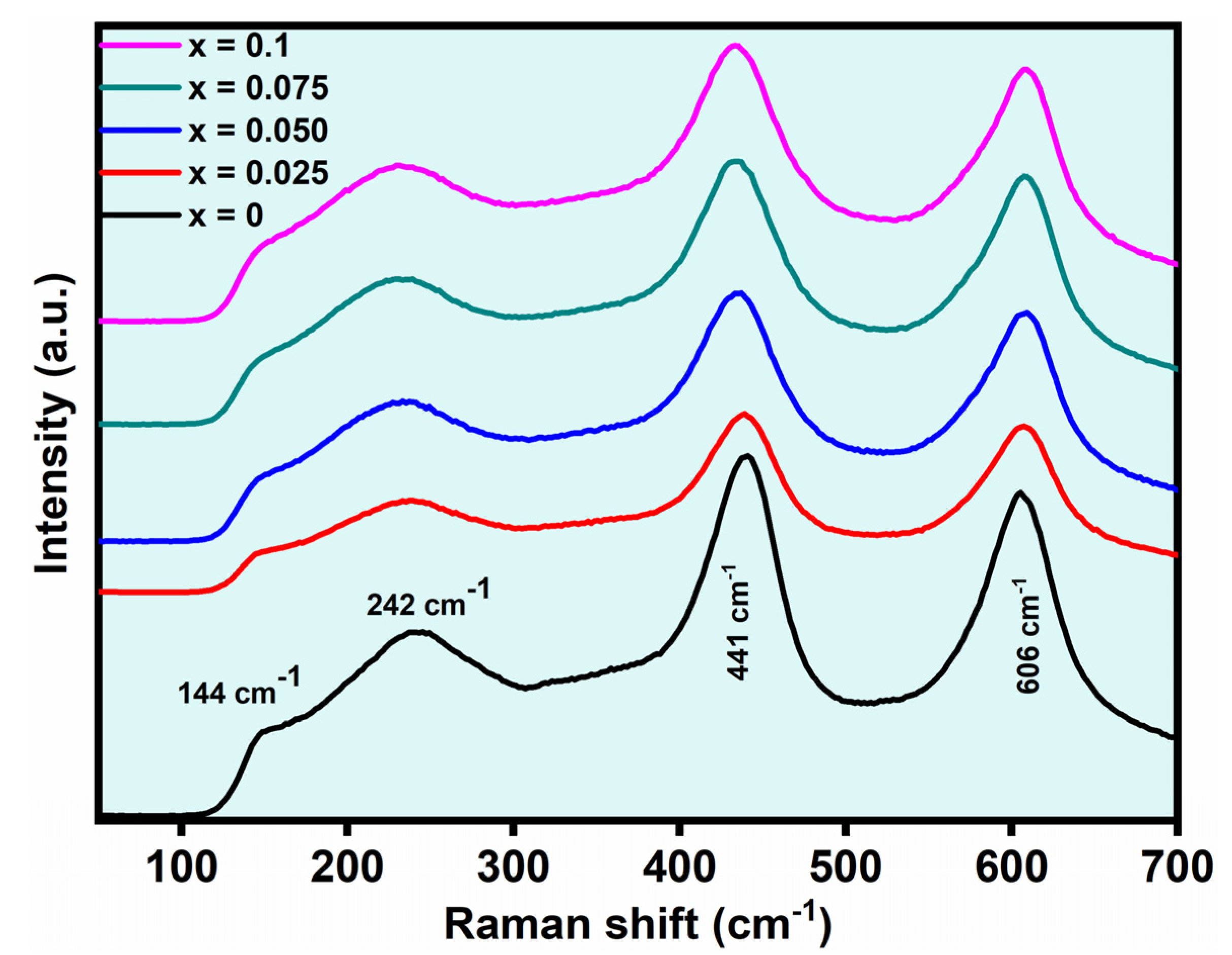
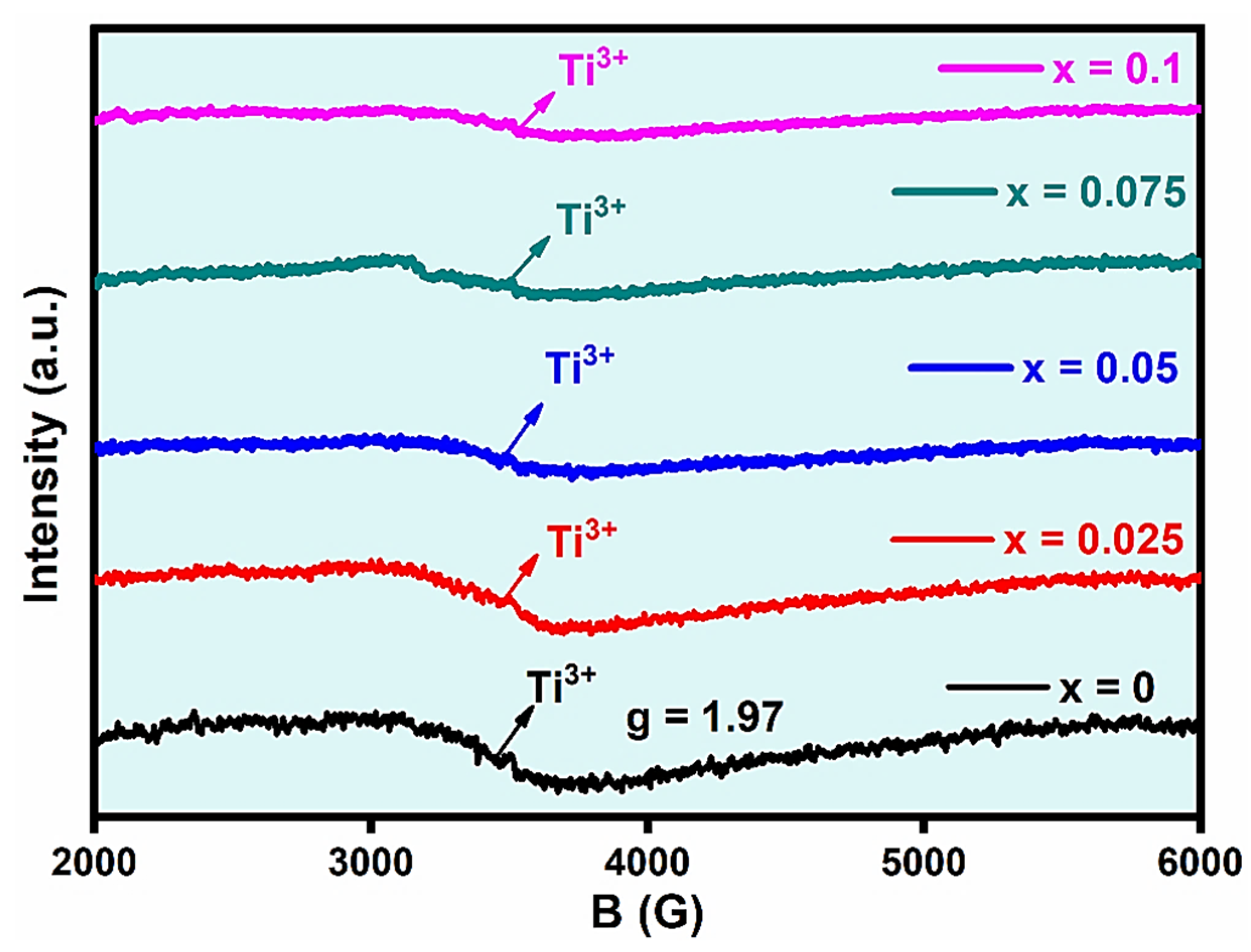
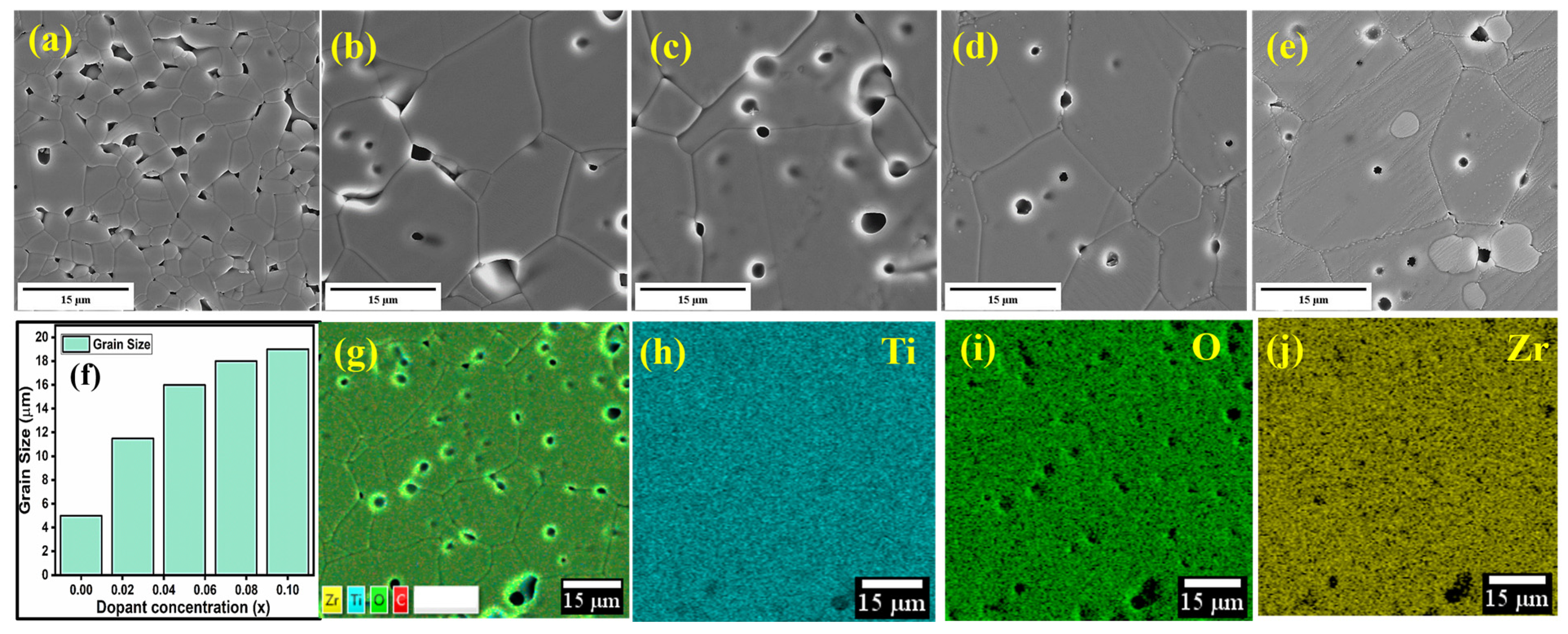
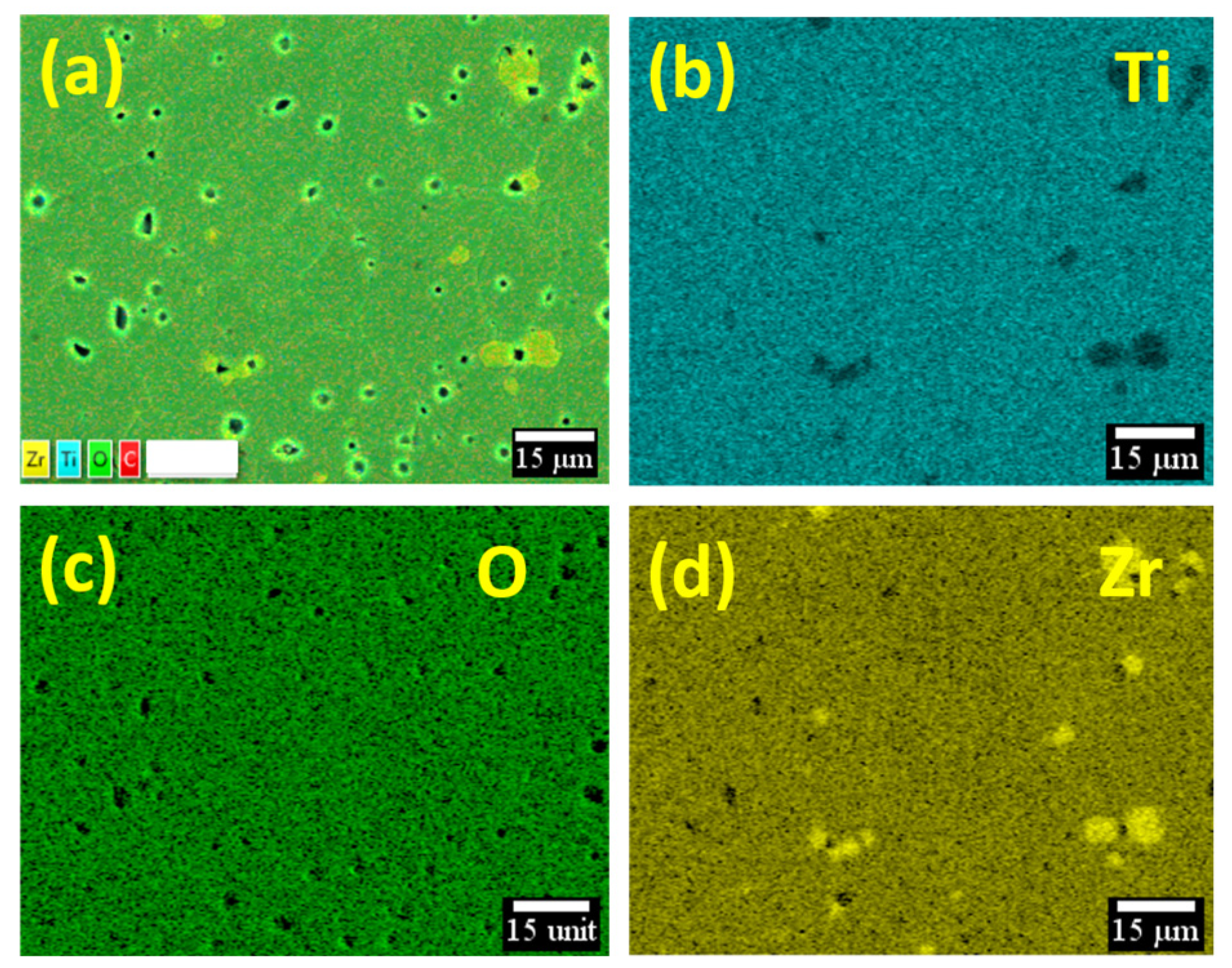
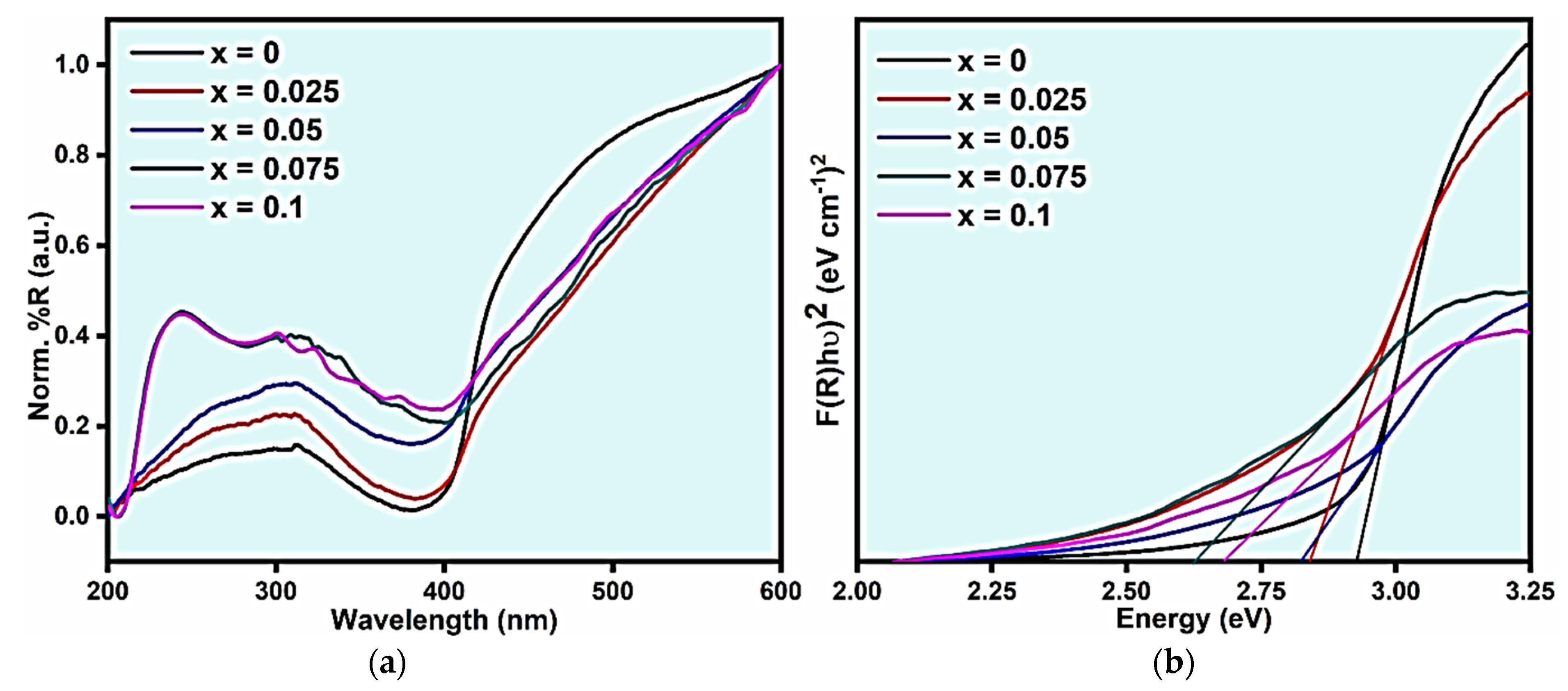
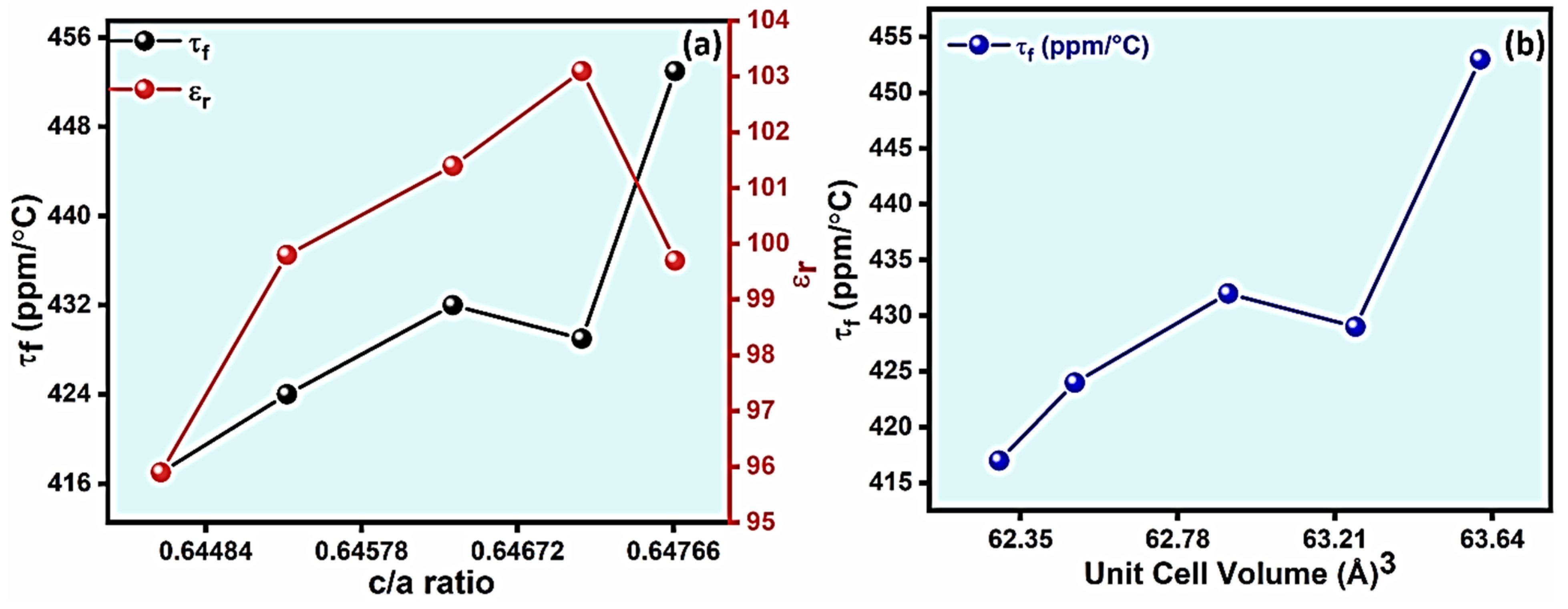
| x Values | 0 | 0.025 | 0.05 | 0.075 | 0.1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a = b (Å) | 4.5890 (7) | 4.5923 (2) | 4.6001 (5) | 4.6061 (5) | 4.6137 (9) | |
| c (Å) | 2.9579 (8) | 2.9635 (7) | 2.9732 (6) | 2.9811 (1) | 2.9882 (8) | |
| α = β = γ (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | 90 | |
| c/a | 0.6445 | 0.6453 | 0.6463 | 0.6471 | 0.6476 | |
| Vcell (Å)3 | 62.29 | 62.45 | 62.92 | 63.26 | 63.61 | |
| Rwp (%) | 11.36 | 14.12 | 12.06 | 11.98 | 12.97 | |
| Rp (%) | 8.82 | 10.91 | 9.17 | 9.21 | 10.09 | |
| χ2 | 1.49 | 2.14 | 1.66 | 1.71 | 1.96 | |
| Atomic positions (x, y, z) | Ti | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) |
| O | (0.3025, 0.3025, 0) | (0.3053, 0.3053, 0) | (0.3026, 0.3026, 0) | (0.3050, 0.3050, 0) | (0.2956, 0.2956, 0) | |
| Zr | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) | (0, 0, 0) |
| x | ST (°C) | Relative Density (%) | εr | αtheo (Å3) | Q × fo (GHz) | τf (ppm/°C) | Packing Fraction (%) | Bandgap Energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1300 | 93 | 96 | 6.95 | 9500 | 417 | 70.6 | 2.92 |
| 0.025 | 1375 | 91 | 99 | 6.81 | 32,360 | 424 | 70.4 | 2.84 |
| 0.05 | 1375 | 89 | 101 | 6.96 | 29,710 | 432 | 70.0 | 2.81 |
| 0.075 | 1400 | 89 | 103 | 6.97 | 21,050 | 429 | 69.6 | 2.62 |
| 0.1 | 1400 | -- | 99 | 6.98 | 18,800 | 453 | 69.3 | 2.68 |
| x | Bond Type | R (Å) | R1 | N | s | fc | Covalency (%) | Degree of Covalency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Ti−O | 1.9601 | 1.806 | 5.2 | 0.6532 | 0.2511 | 38.441 | 38.441 |
| 0.025 | Ti−O | 1.9633 | 1.806 | 5.2 | 0.6477 | 0.2477 | 38.255 | 38.496 |
| Zr−O | 1.950 | 6 | 0.9600 | 0.4596 | 47.874 | |||
| 0.05 | Ti−O | 1.9664 | 1.806 | 5.2 | 0.6424 | 0.2446 | 38.077 | 38.554 |
| Zr−O | 1.950 | 6 | 0.9509 | 0.4528 | 47.616 | |||
| 0.075 | Ti−O | 1.9699 | 1.806 | 5.2 | 0.6365 | 0.2411 | 37.876 | 38.585 |
| Zr−O | 1.950 | 6 | 0.9408 | 0.4453 | 47.327 | |||
| 0.1 | Ti−O | 1.9710 | 1.806 | 5.2 | 0.6346 | 0.2400 | 37.814 | 38.756 |
| Zr−O | 1.950 | 6 | 0.9377 | 0.4429 | 47.237 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, I.; Khan, A.; Muhammad, R.; Mao, M.; Han, D.; Song, K.; Lei, W.; Wang, D. Origin of Temperature Coefficient of Resonance Frequency in Rutile Ti1−xZrxO2 Microwave Ceramics. Ceramics 2024, 7, 698-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020046
Khan I, Khan A, Muhammad R, Mao M, Han D, Song K, Lei W, Wang D. Origin of Temperature Coefficient of Resonance Frequency in Rutile Ti1−xZrxO2 Microwave Ceramics. Ceramics. 2024; 7(2):698-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Izaz, Aneela Khan, Raz Muhammad, Minmin Mao, Dandan Han, Kaixin Song, Wen Lei, and Dawei Wang. 2024. "Origin of Temperature Coefficient of Resonance Frequency in Rutile Ti1−xZrxO2 Microwave Ceramics" Ceramics 7, no. 2: 698-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020046
APA StyleKhan, I., Khan, A., Muhammad, R., Mao, M., Han, D., Song, K., Lei, W., & Wang, D. (2024). Origin of Temperature Coefficient of Resonance Frequency in Rutile Ti1−xZrxO2 Microwave Ceramics. Ceramics, 7(2), 698-711. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020046










