Experiments Using Different Types of Waste to Manufacture Ceramic Materials: Examples on a Laboratory Scale
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Traditional Ceramic Covering Tiles Obtained by Recycling Marble Waste and MSW Fly Ash
2.2. Characterisation and Glass-Ceramic Capabilities of Glassy Slag Rich in Manganese Oxide
2.3. Vitrification of a Soil Contaminated by Cr (VI) from a Nearby Urban and Industrial Area
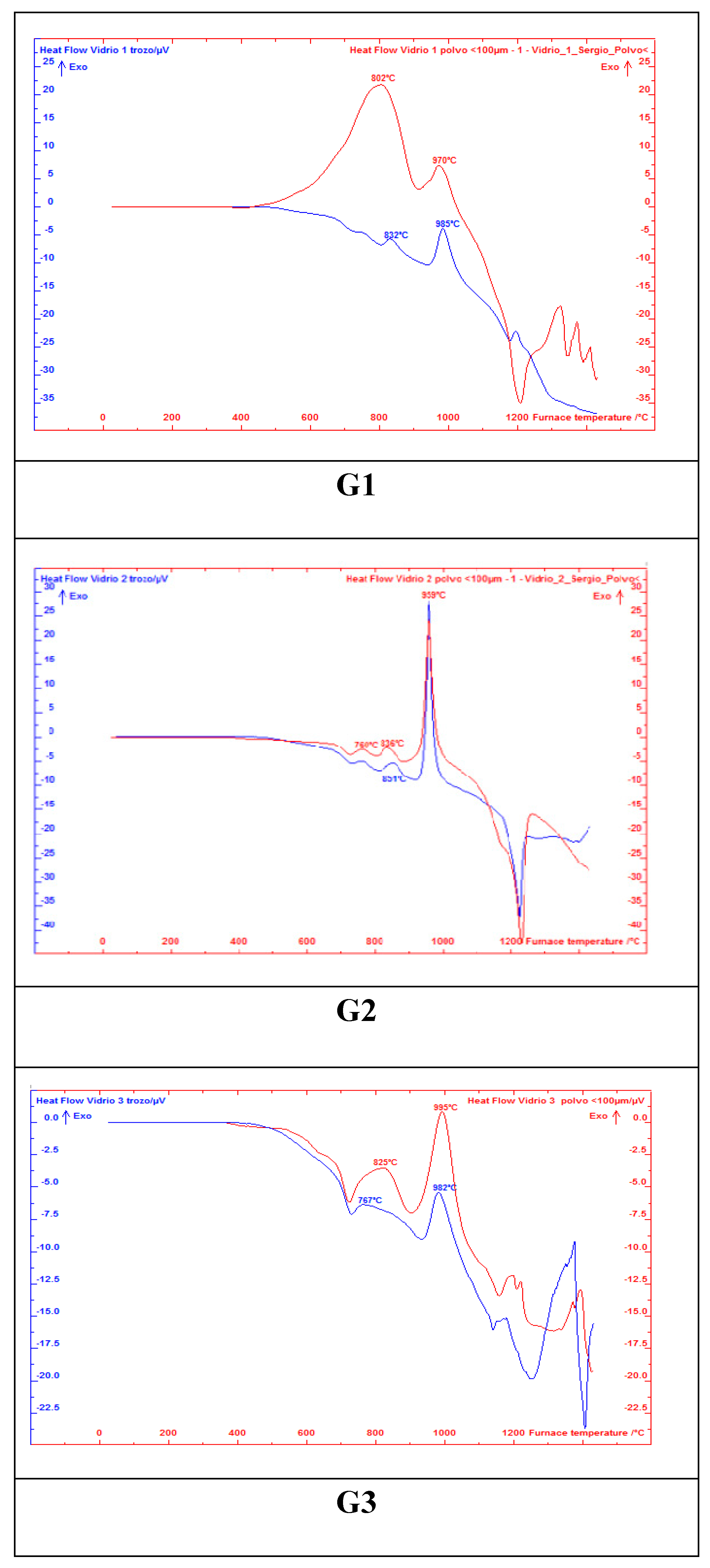
3. Results
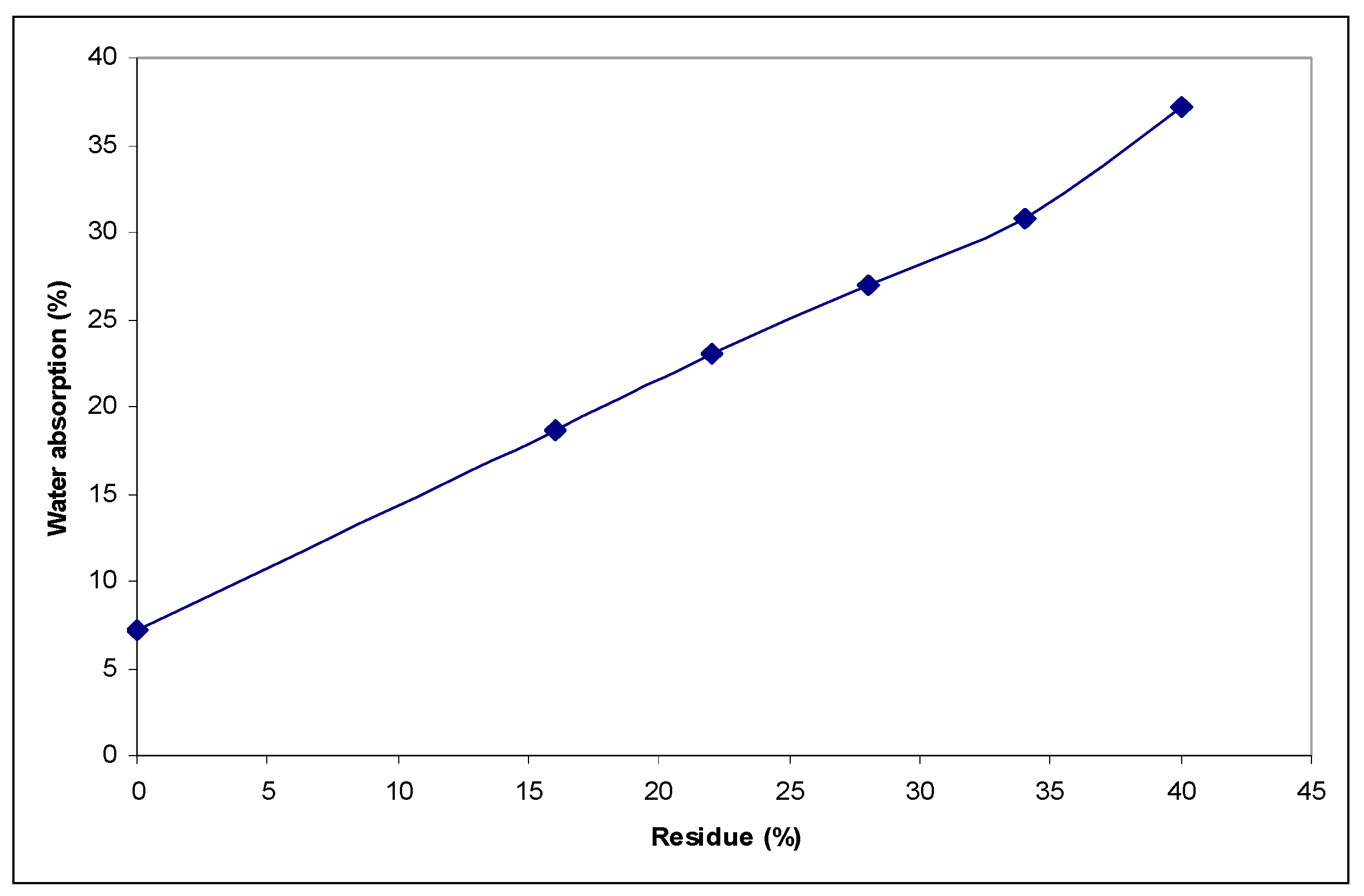
3.1. Traditional Ceramic Covering Tiles Obtained by Recycling Marble Waste and MSW Fly Ash
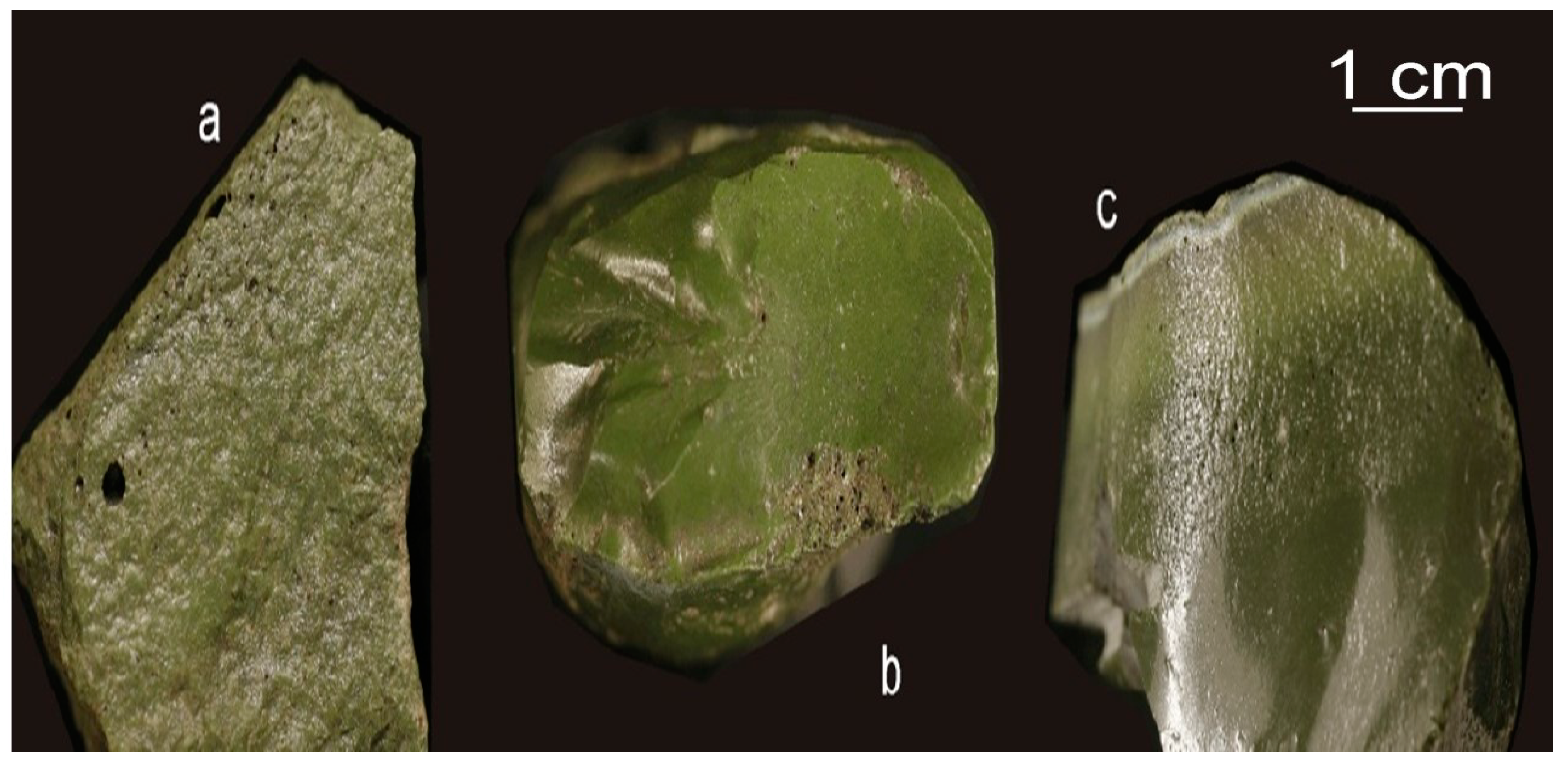
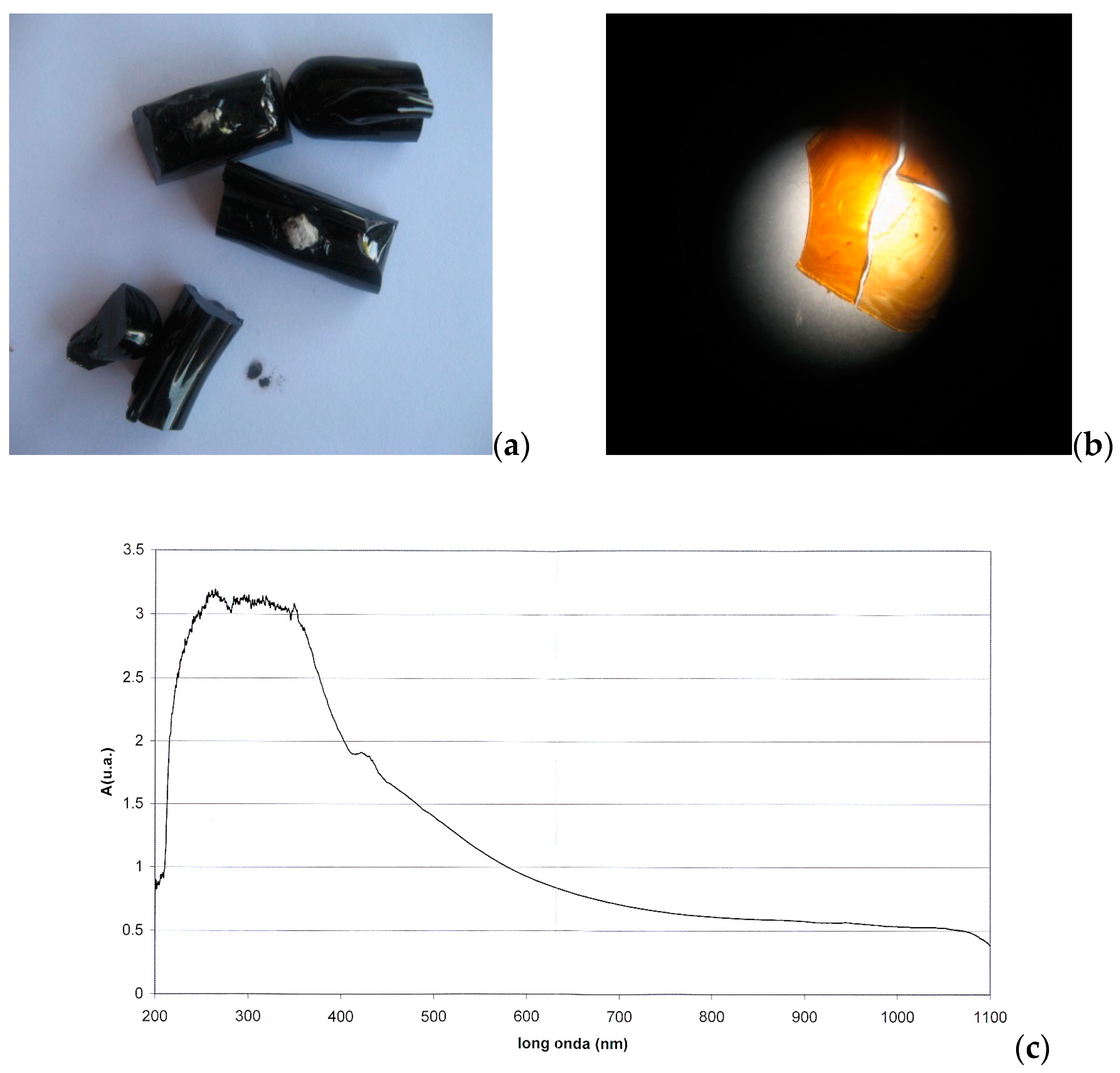
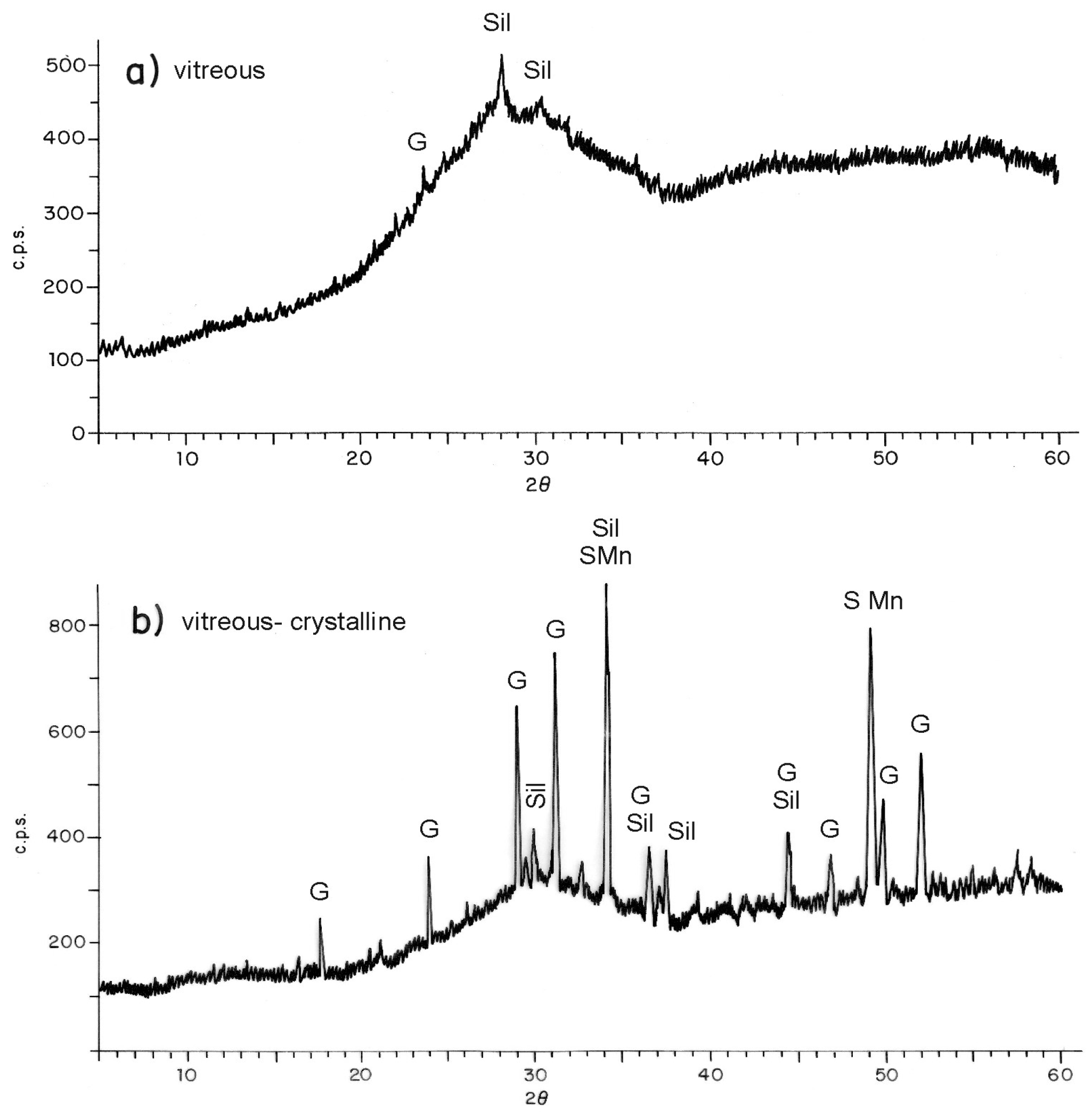
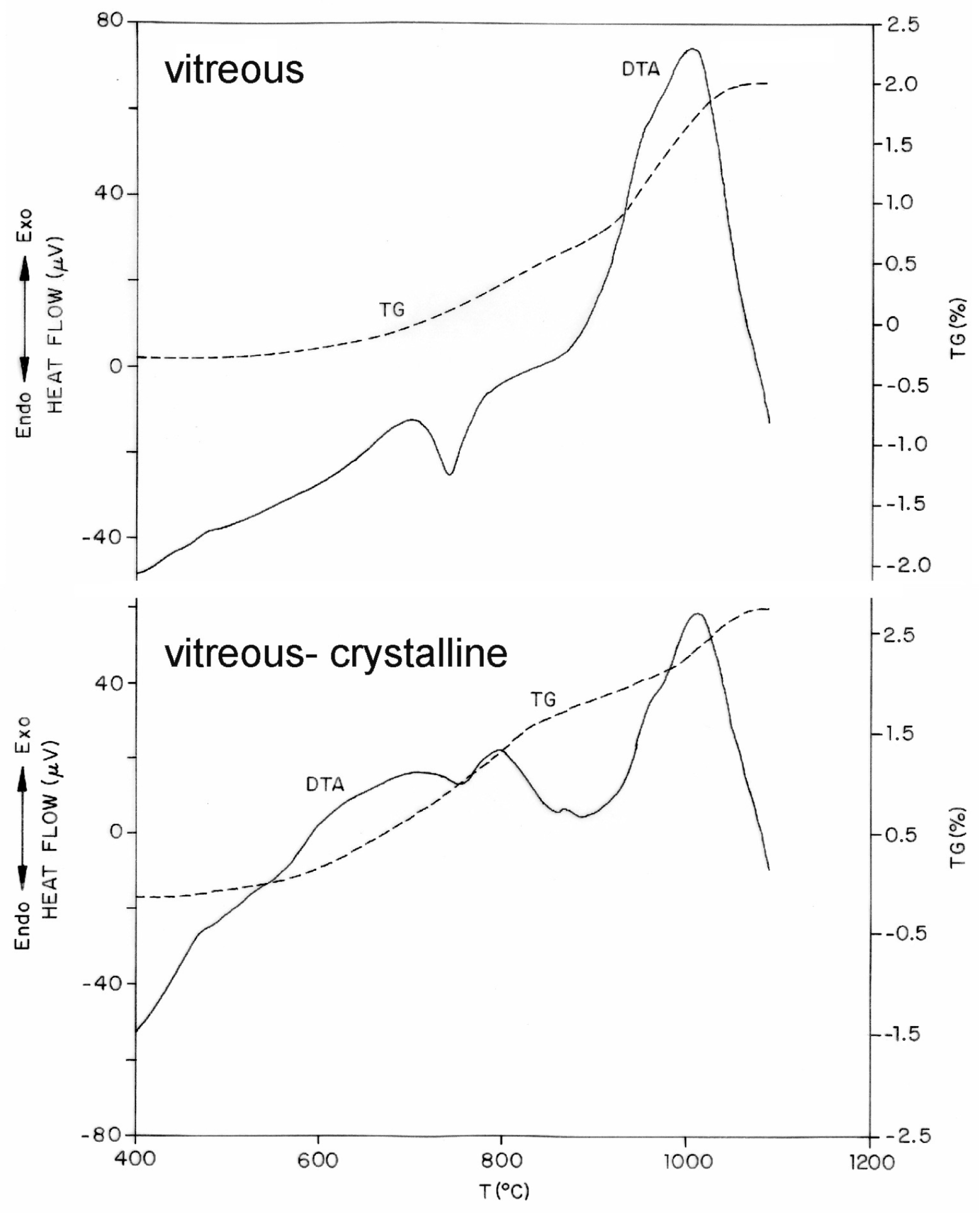
3.2. Characterisation and Glass-Ceramic Capabilities of Glassy Slag Rich in Manganese Oxide
3.3. Vitrification of an Urban Soil Contaminated by Cr (VI) from a Nearby Urban and Industrial Area
4. Conclusions
5. Suggestion for Future Lines of Research
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jordán, M.M.; Montero, M.A.; Rincón-Mora, B.; Rincón, J.M.A.; Sanfeliu, T. Rustic ceramic covering tiles obtained by recicling of marbre resisues and MSW fly ashes. Fresenious Environ. Bull. 2015, 2, 533–538. [Google Scholar]
- Tayibi, H.; Peña, C.; López, F.A.; López-Delgado, A. Management of MSW in Spain and recovery of packaging steel scrap. Waste Manag. 2006, 27, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costi, P.; Minciardi, R.; Robba, M.; Rovatti, M.; Sacile, R. An environmentally sustainable decision model for urban solid waste management. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 277–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Crespo, M.S.; Rincón, J. New porcelainized stoneware materials obtained by recycling of MSW incinerator fly ashes and granite sawing residues. Ceram. Int. 2001, 27, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, M.A.; Jordan, M.M.; Almendro-Candel, M.B.; Sanfeliu, T.; Hernández-Crespo, M.S. Use of a calcium carbonate residue from the stone industry in manufacturing of ceramic tiles bodies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 43, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, A. Abfallstoffe und ihre Möglichkeiten, Rohmaterialien in Kalksandsteinen zu ersetzen. Waste materials and the possible ways they can replace primary raw materials in sand-lime bricks. ZKG Int. 2000, 53, 534–543. [Google Scholar]
- Dondi, M.; Marsigli, M.; Fabbri, B. Recycling of industrial and Urban Wastes in Brick Production—A Review. Tile Brick Int. 1997, 13, 218–315. [Google Scholar]
- Dondi, M.; Ercolani, G.; Guarini, G.; Raimondo, M. Orimulsion fly ash in clay bricks—Part 1: Composition thermal behaviour of ash. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2002, 22, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweben, C. Ceramic matrix composites mechanical properties and test methods. Ceram. Eng. Sci. Proc. 1991, 12, 409–503. [Google Scholar]
- Jordán, M.M.; Boix, A.; Sanfeliu, T.; de la Fuente, C. Firing transformations of cretaceous clays used in the manufacturing of ceramic tiles. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T.J.; Jenny, J.P. Mineralogical Study of the Firing Characteristics of Brick Clays; Beiträge zur Geologie der Schweiz, Geotechnische Serie; Georessourcen Schweiz: Zürich, Switzerland, 1973; Volume 50, p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Pollifrone, G.G.; Ravaglioly, A. Le argile: Compendio genético, mineralógico e chimico fisico. Ceram. Inform. 1973, 7, 565–581. [Google Scholar]
- González-García, F.; Romero-Acosta, V.; García Ramos, G.; González Rodríguez, M. Firing transformations of mixtures of clays containing illite, kaolinite and calcium carbonate used by ornamental tile industries. Appl. Clay Sci. 1990, 5, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.M.; Boix, A.; Sanfeliu, T.; de la Fuente, C. The mineralogy of Cretaceous clays in Castellon and their application in the ceramic industry. Int. Ceram. J. 1995, 10, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Bramha, S.N.; Mohanty, A.K.; Satpathy, K.K.; Kanagasabapathy, K.V.; Panigrahi, S.; Samantara, M.K.; Prasad, M.V.R. Heavy metal content in the beach sediment with respect to contamination levels and sediment quality guidelines: A study at Kalpakkam coast, southeast coast of India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4463–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-Mora, B.; Muñoz-García, M.B.; Rincón, J.M.; Jordán, M.M. Characterization of a locally deposited material on Arnela Beach (Galicia Coast, Spain). J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 174, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, M.; Callejas, P.; Rincón, J.M. Microstructure characterization of basalt glass–ceramics. In Ceramic Microstructures ‘86. The Role of Interfaces 1; Pask, J., Evans, A., Eds.; Plenum Publishing Corp.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1988; pp. 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Rincon, J.M. Principles of nucleation and controlled crystallization of glasses. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 1992, 31, 309–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, K.K.; Mohanty, A.K.; Prasad, M.V.R.; Natesan, U.; Sarkar, S.K. Studies on the variations of heavy metals in the marine sediments of Kalpakkam, east coast of India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turdokan, E.T. Crystal growth in undercooled liquids and glasses. In Physico-Chemical Properties of Molten Slags and Glasses; The Metals Society: London, UK, 1983; Volume 1, 373p. [Google Scholar]
- Uhlmann, D.R. Nucleation crystallization glass formation. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1980, 38–39, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Mingarro, I.; Callejas, P.; Rincón, J.M. Microestructura y microanálisis de piroxenos cristalizados en vidrios obtenidos a partir de rocas basálticas canarias. Bol. Soc. Española Mineral. 1991, 14, 95–105. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Mingarro, I.; Callejas, P.; Carda, J.; Sales, M.; Rincón, J.M. TEM/STEM/EDX. Investigation of glass–ceramics obtained from canarian álcali-basalts. In Electron Microscopy 92. EUREM 92 2; Lopez-Galindo, A., Rodríguez-García, M.I., Eds.; Universidad de Granada: Granada, Spain, 1992; pp. 405–406. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Mingarro, I.; Rincón, J.M.; Bowles, P.; Rawlings, R.D.; Rogers, P.S. Viscosity measurements on glasses obtained from Canary Islands alkali volcanic rocks. Glass Technol. 1992, 33, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Rincón-Mora, B.; Jordán, M.M.; Rincón, J.M. Chromium oxide additions in lithium disilicate glass crystallization. Mater. Lett. 2016, 179, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Rincón, J.M.; Rincón-Mora, B.; Jordán, M.M. Vitrification of urban soil contamination by hexavalent chromium. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 174, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Rincón, J.M. Vitrification of a Mexican chromium sludge with the production of a basalt like petrurgical glass ceramic. In Proceedings of the International Congress on Valorization and Recycling of Wastes, VARIREI 2005, L’Aquila, Italy, 28 June–1 July 2005. 6p. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, S.; Rincón, J.M. Microstructure and Microanalysis of Porous Glass Obtained by Sintering of Vitreous Powders from Cr-Ni Sludge. Microsc. Microanal. 2011, 17, 1904–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, S.; Parga, J.R.; Romero, M.; Rincón, J.M. Vitrification of a Mexican sludge with the production of a basalt like petrurgical glass ceramic. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium of Hybridized Materials with Super 3D Functions, Japan-Mexico Joint Meeting 1, Monterrey, Mexico, 3–6 December 2006; Torres, L., Ed.; University of Nuevo Leon: Monterrey, Mexico, 2006. 217p. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, S.; Parga, J.R.; Delgado, A.; Cano, J.; Rincón, J.M. Electron Microscopy Study of Vitrified Materials from Chemicals Containing Chromium Contaminated Soil Confined Mud Waste with Chrome III and VI Joint Meeting of the Spanish and Portuguese Microscopies Societies 1; IE University: Segovia, Spain, 2009; pp. 289–290. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, S.; Parga, J.; Rincón, J.M. Vitrificación para Inmovilizar Residues Peligrosos, Ciencia y Desarrollo; Conacyt Ed.: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010; Volume 243, pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Crespo, M.S.; Romero, M.; Rincón, J.M. Nucleation crystal growth of glasses produced by a generic plasma arc-process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2006, 26, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, L.F.; Zorzi, J.E.; Cruz, R.C.D. Basaltic glass-ceramic: A short review. Bol. Soc. Esp. Ceram. Vidr. 2022, 61, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.D.; Shripad, P.K. Recent advances in silica-based materials for the removal of hexavalent chromium: A review. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 2521–2540. [Google Scholar]
- Ladrón de Guevara, J.; Moya, V. Toxicología Médica (Clínica e Industrial); McGraw-Hill Interamericana: Madrid, Spain, 1995; 700p. [Google Scholar]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Kamolpornwijit, W.K.; Charleston, G. Construction use of vitrified chromium contaminated soils. In Practical Periodical of Hazardous, Toxic and Radioactive Waste Management; ASCE Library, American Society of Civil Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, C.D.; Wittbrodt, P.R. Processes affecting the remediation of chromium-contaminated sites. Environ. Health Perspect. 1991, 92, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almendro-Candel, M.B.; Jordán Vidal, M.M. Glasses, Frits and Glass-Ceramics: Processes and Uses in the Context of Circular Economy and Waste Vitrification. Coatings 2024, 14, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holand, W.; Beall, G.H. Glass-Ceramic Technology, 3rd ed.; The American Ceramic Society: Westerville, OH, USA; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Baino, F.; Tomalino, M.; Tulyaganov, D. (Eds.) Ceramics, Glass and Glass-Ceramics from Early Manufacturing Steps towards Modern Frontiers; PoliTO Springer Series; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]

| Waste | Material | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Concrete from demolitions | Fired clay ceramics | Construction |
| Glass containers: bottles, flat glass, TV screens and PCs | Gresites | Coatings (facades, tunnels, balconies, shops, gymnasiums, etc.) |
| Sludge: Hydrometallurgical, from wastewater treatment plants, estuaries, lakes, natural stone, etc. | Porcelain stoneware tiles, bricks, roof tiles | Flooring and coating |
| All types of slag: from smelting, plasma arc, etc. | Glassceramics, tiles, porous materials, etc. | Building and public works |
| Fly ash from municipal solid waste incinerators or thermal power stations | Bricks, traditional slabs, frits, glass-ceramics | Facades, producing enamels |
| Composite materials (fibreglass composites) | Sintered tiles from fibres | Flooring and coating |
| Initial Sample Contaminated with Cr6+ | Formulating the Glasses | Glass Samples (Quenched) | Glass-Ceramic Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 (soil) | S1 + added feldspar gravel (70-25-5% of coke ash) | G1 | GC1 |
| S2 (slag) | S2 + S1 (soil)+ added feldspar gravel | G2 | GC2 |
| S3 (concrete from construction and demolition waste) | Milled as received | G3 | GC3 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|
| % (Weight) of Waste Added | Raw Paste | Sintered Paste |
| 0 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 13.5 ± 3 |
| 16 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 12.3 ± 2 |
| 22 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 10.0 ± 1 |
| 28 | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 9.5 ± 2 |
| 34 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 8.7 ± 1 |
| 40 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 6.9 ± 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jordán Vidal, M.M. Experiments Using Different Types of Waste to Manufacture Ceramic Materials: Examples on a Laboratory Scale. Ceramics 2024, 7, 504-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020033
Jordán Vidal MM. Experiments Using Different Types of Waste to Manufacture Ceramic Materials: Examples on a Laboratory Scale. Ceramics. 2024; 7(2):504-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleJordán Vidal, Manuel M. 2024. "Experiments Using Different Types of Waste to Manufacture Ceramic Materials: Examples on a Laboratory Scale" Ceramics 7, no. 2: 504-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020033
APA StyleJordán Vidal, M. M. (2024). Experiments Using Different Types of Waste to Manufacture Ceramic Materials: Examples on a Laboratory Scale. Ceramics, 7(2), 504-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/ceramics7020033






