Comparative Analysis of Strategies for De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Prokaryotes: Streptomyces clavuligerus as a Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
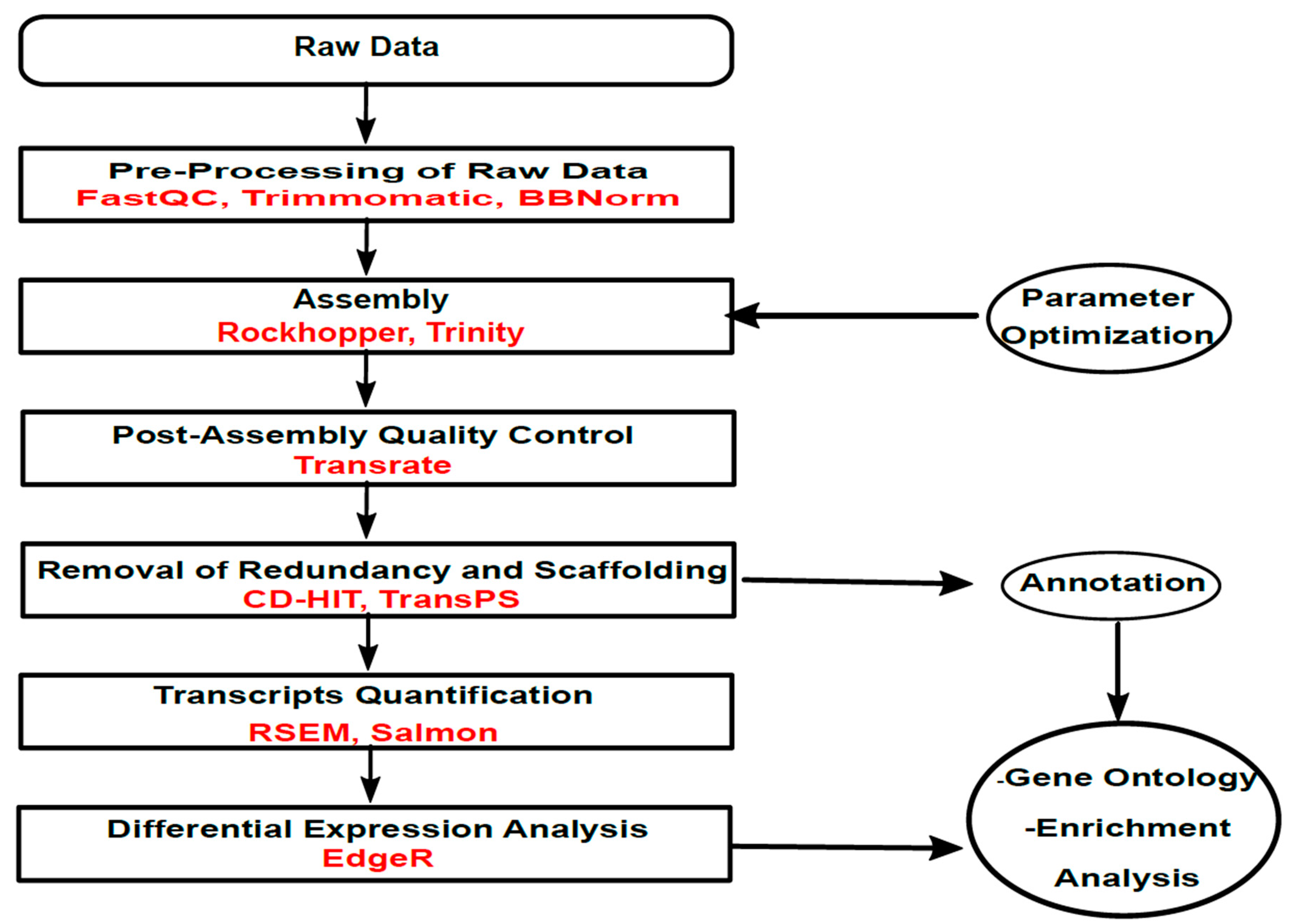
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA Extraction, Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.2. Pre-Processing of Raw Data
2.3. Transcriptome Assembly
2.4. Transcriptome Assembly Quality Evaluation
2.5. Transcript Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis
2.6. Annotation
2.7. Referenced-Based Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control of Raw Data
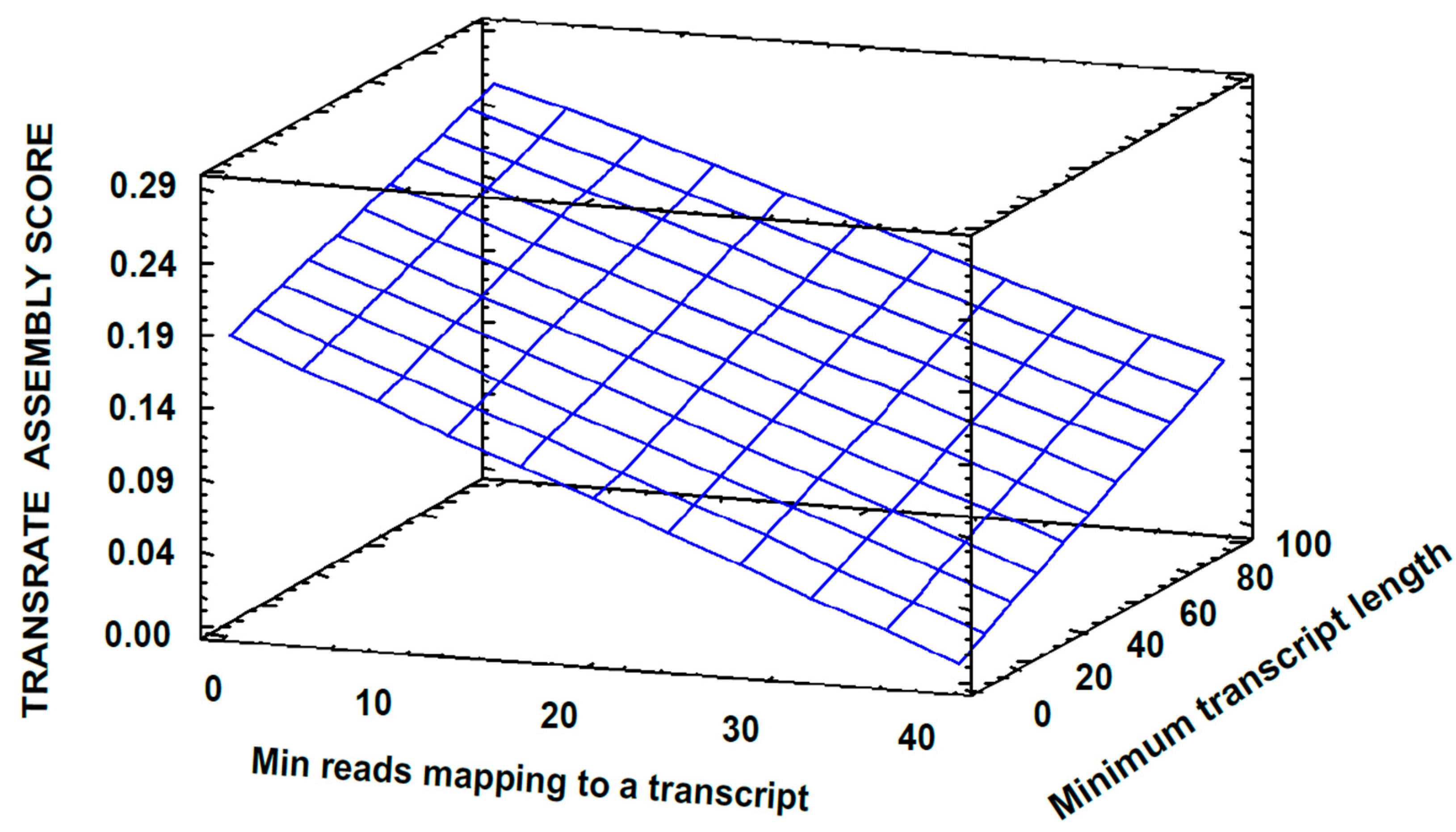
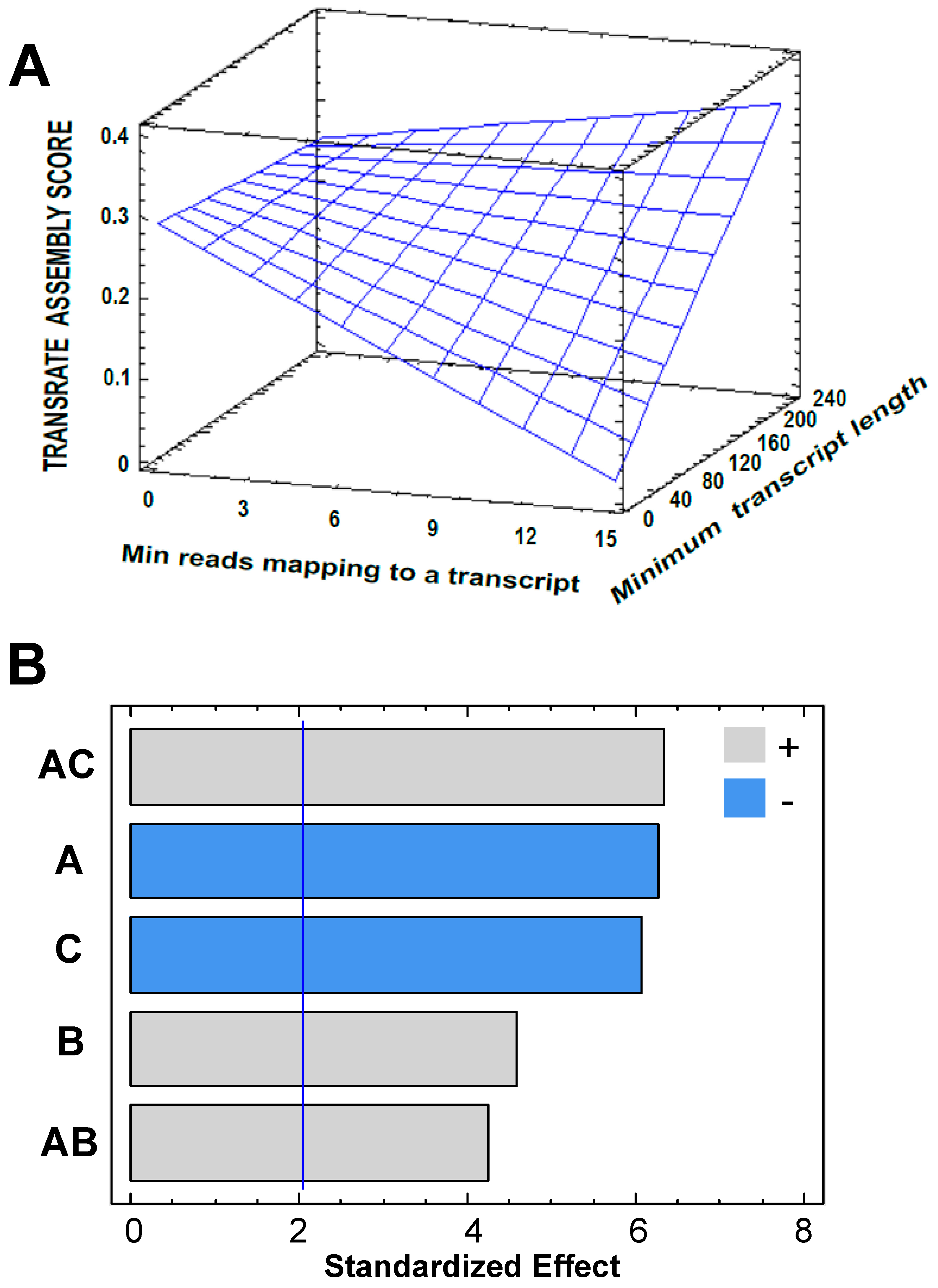
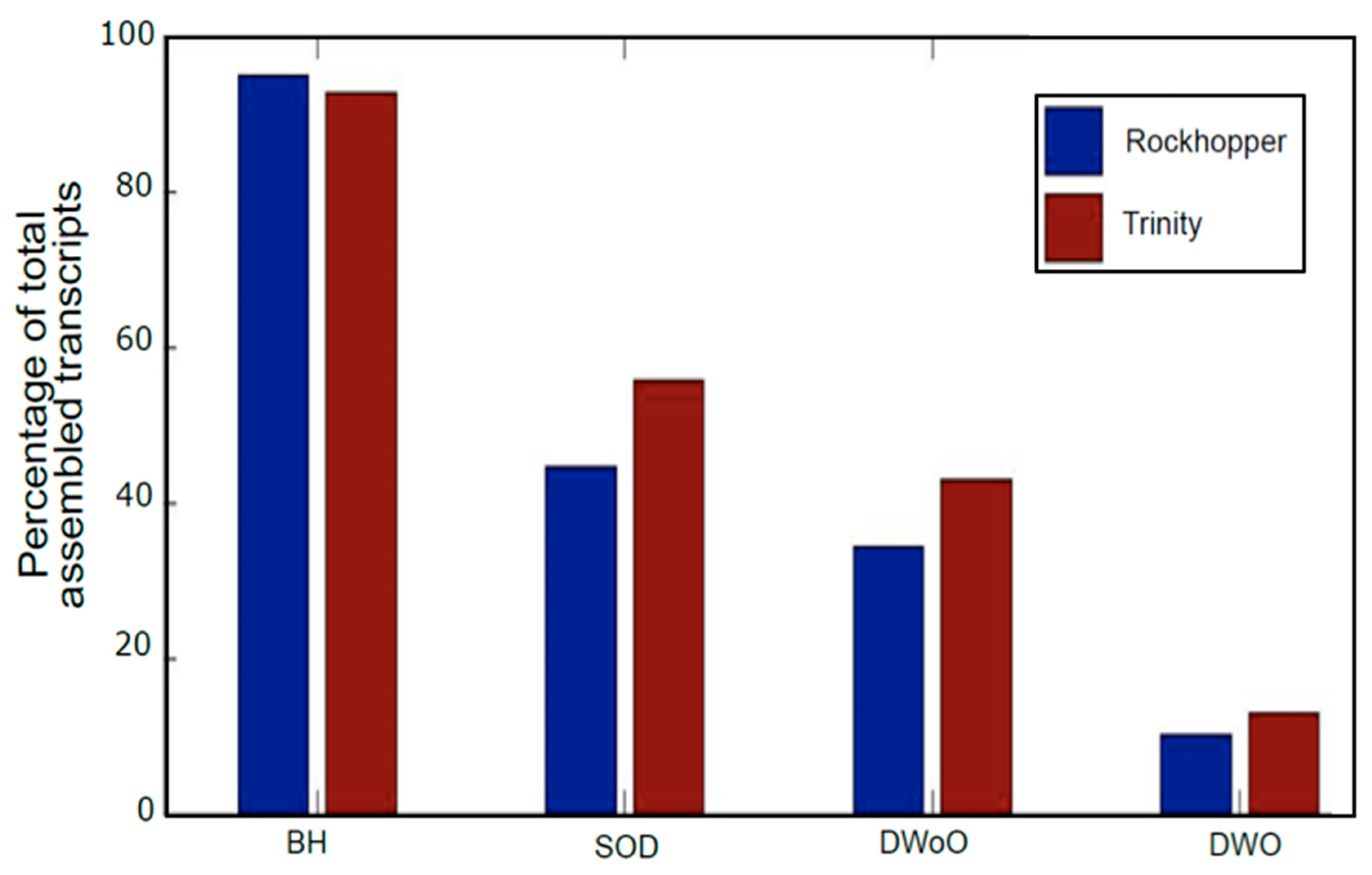
3.2. Transcriptome Assembly
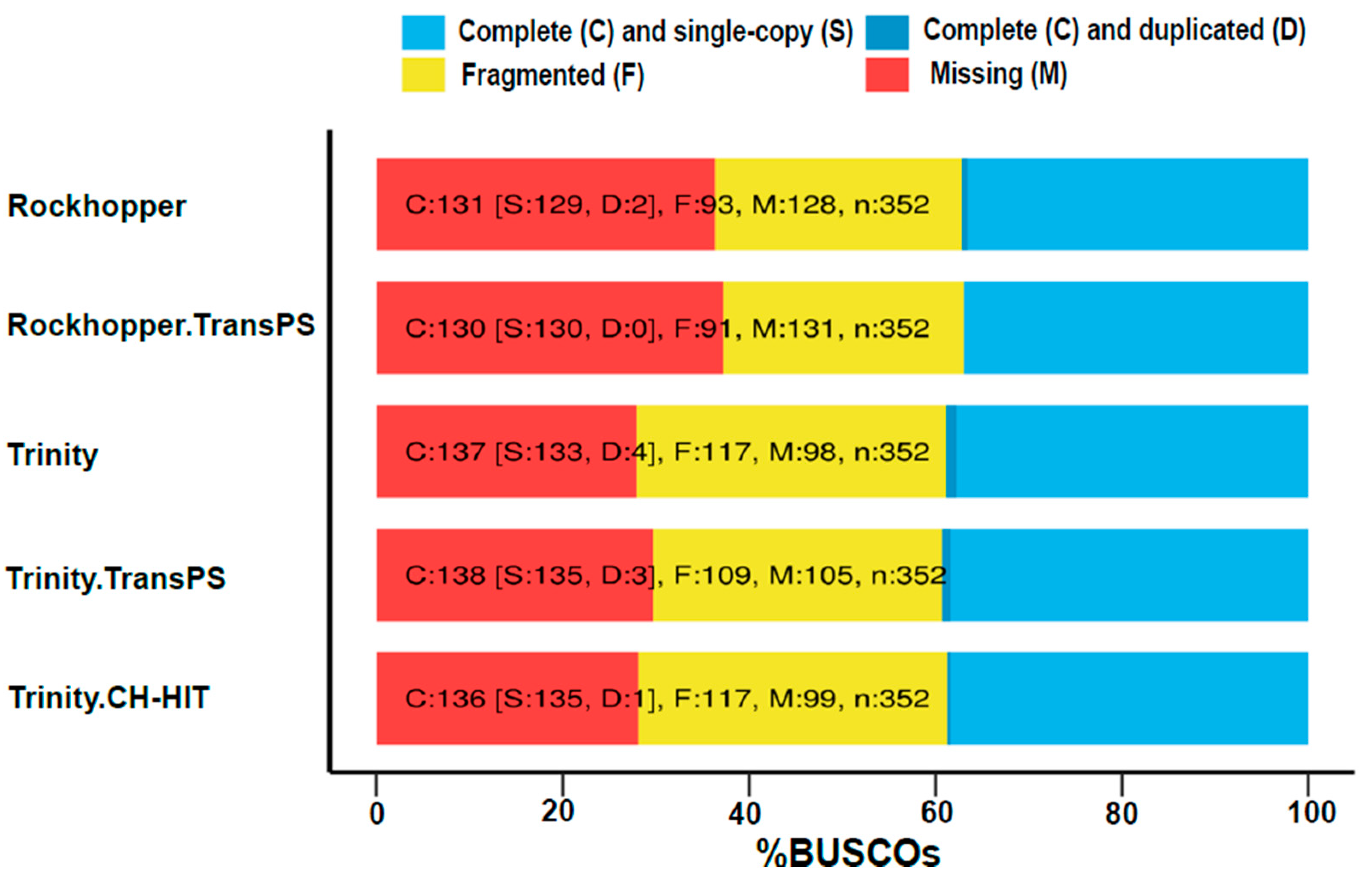
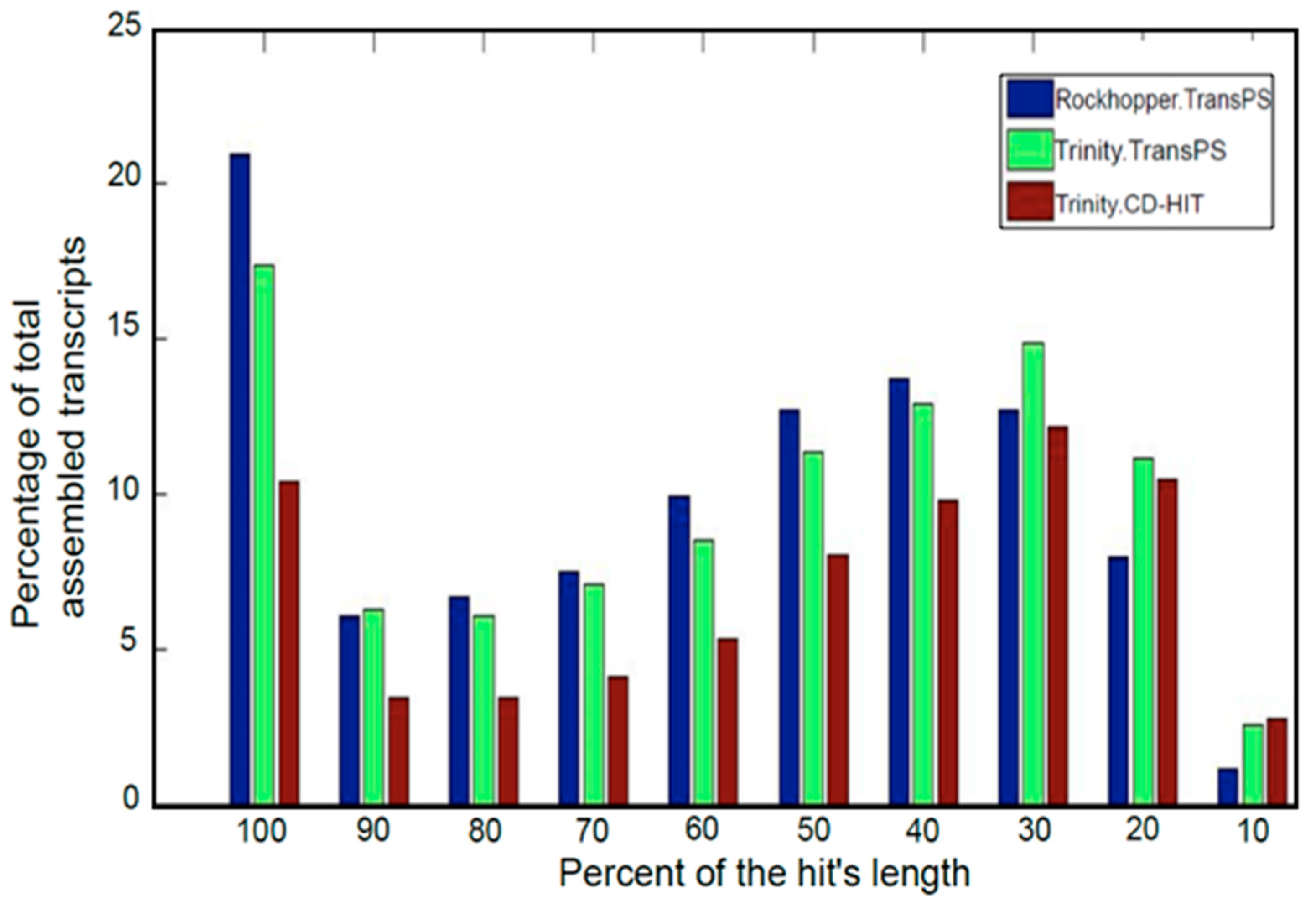
3.3. Post-Assembly Quality Control
3.4. Transcript Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis
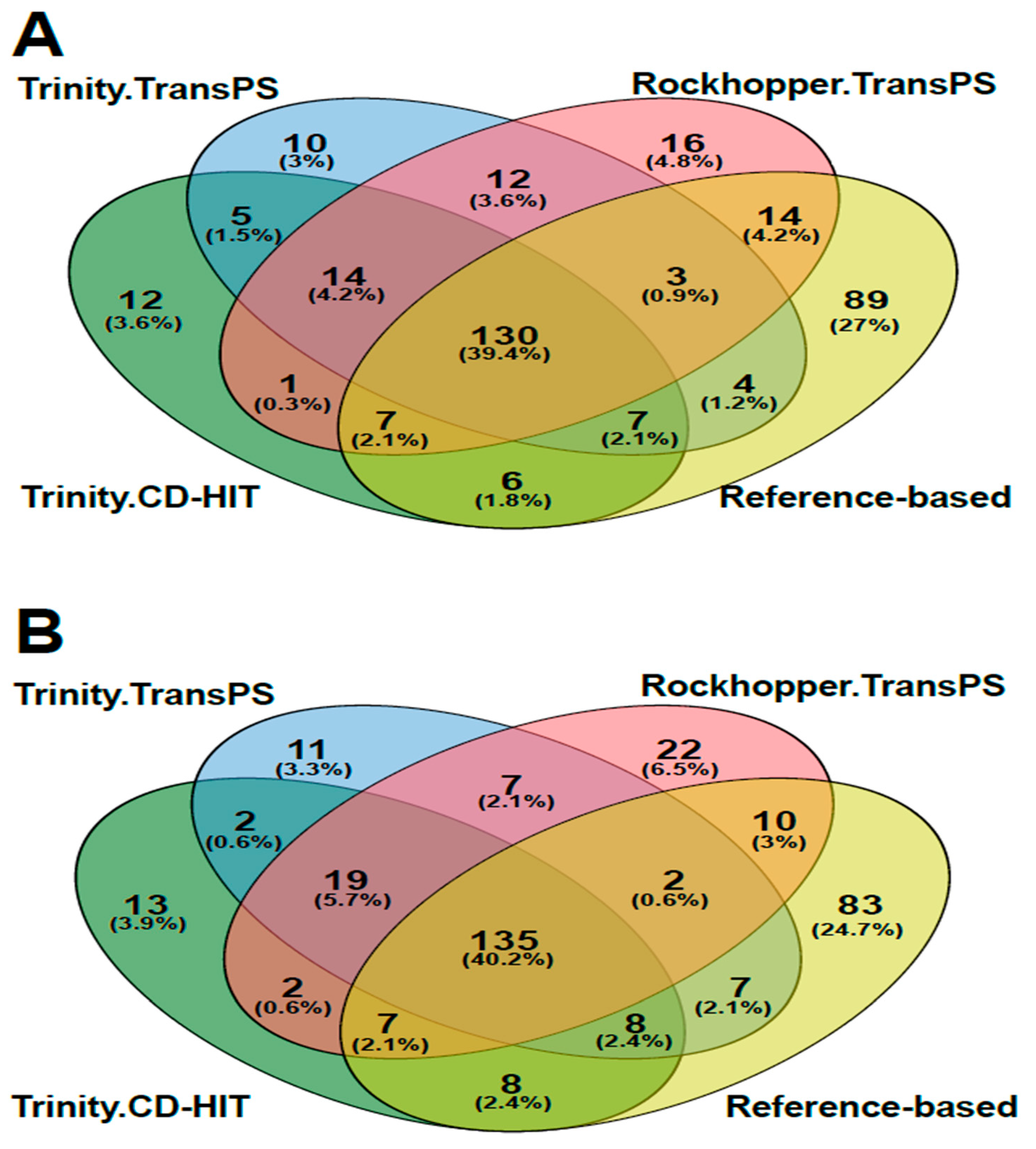
3.5. Annotation and Gene Ontology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.A.; Wang, Z. Next-generation transcriptome assembly. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-Seq: Reference generation and analysis with Trinity. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Verk, M.C.; Hickman, R.; Pieterse, C.M.J.; van Wees, S.C.M. RNA-Seq: Revelation of the messengers. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjaden, B. De novo assembly of bacterial transcriptomes from RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.H.; Zerbino, D.R.; Vingron, M.; Birney, E. Oases: Robust de novo RNA-seq assembly across the dynamic range of expression levels. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, I.; Jackman, S.D.; Nielsen, C.B.; Qian, J.Q.; Varhol, R.; Stazyk, G.; Morin, R.D.; Zhao, Y.; Hirst, M.; Schein, J.E.; et al. De novo transcriptome assembly with ABySS. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ashby, C.; Liu, D.; Cramer, C.L.; Huang, X. Bridger: A new framework for de novo transcriptome assembly using RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wu, G.; Tang, J.; Luo, R.; Patterson, J.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; He, G.; Gu, S.; Li, S.; et al. SOAPdenovo-Trans: De novo transcriptome assembly with short RNA-Seq reads. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Leung, H.C.M.; Yiu, S.M.; Lv, M.J.; Zhu, X.G.; Chin, F.Y.L. IDBA-tran: A more robust de novo de Bruijn graph assembler for transcriptomes with uneven expression levels. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safikhani, Z.; Sadeghi, M.; Pezeshk, H.; Eslahchi, C. SSP: An interval integer linear programming for de novo transcriptome assembly and isoform discovery of RNA-seq reads. Genomics 2013, 102, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S.; Hui, J.; Mazooji, K. Shannon: An Information-Optimal de Novo RNA-Seq Assembler. bioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, G.; Chang, Z.; Yu, T.; Liu, B.; McMullen, R.; Chen, P.; Huang, X. BinPacker: Packing-Based De Novo Transcriptome Assembly from RNA-seq Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szcześniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X.; et al. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fillmore, N.; Bai, Y.; Collins, M.; Thomson, J.A.; Stewart, R.; Dewey, C.N. Evaluation of de novo transcriptome assemblies from RNA-Seq data. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Unna, R.; Boursnell, C.; Patro, R.; Hibberd, J.M.; Kelly, S. TransRate reference-free quality assessment of de novo transcriptome assemblies. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surget-Groba, Y.; Montoya-Burgos, J. Optimization of de novo transcriptome assembly from next-generation sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y.-M.; Luo, D.; Li, X.; Hao, P. Optimizing de novo transcriptome assembly from short-read RNA-Seq data: A comparative study. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Smith, S.A. Optimizing de novo assembly of short-read RNA-seq data for phylogenomics. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, X.-G.; Armbruster, P.A. Comparative performance of transcriptome assembly methods for non-model organisms. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honaas, L.A.; Wafula, E.K.; Wickett, N.J.; Der, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Edger, P.P.; Altman, N.S.; Pires, J.C.; Leebens-Mack, J.H.; DePamphilis, C.W. Selecting superior de novo transcriptome assemblies: Lessons learned by leveraging the best plant genome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misner, I.; Bicep, C.; Lopez, P.; Halary, S.; Bapteste, E.; Lane, C.E. Sequence comparative analysis using networks: Software for evaluating de novo transcript assembly from next-generation sequencing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushmanova, E.; Antipov, D.; Lapidus, A.; Suvorov, V.; Prjibelski, A.D. RnaQUAST: A quality assessment tool for de novo transcriptome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2210–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.; Sinaimeri, B.; Sacomoto, G.; Lopez-Maestre, H.; Marchet, C.; Miele, V.; Sagot, M.F.; Lacroix, V. Playing hide and seek with repeats in local and global de novo transcriptome assembly of short RNA-seq reads. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2017, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreton, J.; Izquierdo, A.; Emes, R.D. Assembly, assessment, and availability of De novo generated eukaryotic transcriptomes. Front. Genet. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresko Lab. RNA-Seqlopedia. Available online: http://rnaseq.uoregon.edu/ (accessed on 22 August 2016).
- Cabau, C.; Escudié, F.; Djari, A.; Guiguen, Y.; Bobe, J.; Klopp, C. Compacting and correcting Trinity and Oases RNA-Seq de novo assemblies. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, R.; Balasubramanian, D.; Sun, Y.; Bobrovskyy, M.; Sumby, P.; Genco, C.A.; Vanderpool, C.K.; Tjaden, B. Computational analysis of bacterial RNA-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.; Cockell, S.J.; Zenkin, N. Deep sequencing approaches for the analysis of prokaryotic transcriptional boundaries and dynamics. Methods 2017, 120, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.K.; Scholz, M.B.; Teal, T.K.; Abramovitch, R.B. SPARTA: Simple Program for Automated reference-based bacterial RNA-seq Transcriptome Analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinilla, L.; Toro, L.F.; Avignone-Rossa, C.; Peñuela, M.; Rios-Estepa, R. Streptomyces clavuligerus strain selection for clavulanic acid biosynthesis: A study based on culture composition effects and statistical analysis. DYNA 2018, 85, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.; Liras, P.; Martin, J.F. Dissociation of cephamycin and clavulanic acid biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1984, 20, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomczynski, P.; Mackey, K. Modification of the TRI reagent procedure for isolation of RNA from polysaccharide- and proteoglycan-rich sources. Biotechniques 1995, 19, 942–945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pinilla, L.; Toro, L.F.; Laing, E.; Alzate, J.F.; Ríos-Estepa, R. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Streptomyces Clavuligerus in Response to Favorable and Restrictive Nutritional Conditions. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S. FastQC. Available online: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 1 November 2015).
- Kopylova, E.; Noé, L.; Touzet, H. SortMeRNA: Fast and accurate filtering of ribosomal RNAs in metatranscriptomic data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3211–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, B.; Lohse, A.M.; Usadel, M. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bushnell, B. BBMap: A Fast, Accurate, Splice-Aware Aligner; Lawrence Berkeley National Lab.(LBNL): Berkeley, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Trinity: Reconstructing a full-length transcriptome without a genome from RNA-Seq data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- VecScreen: Screen a Sequence for Vector Contamination. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/vecscreen/ (accessed on 17 May 2017).
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecks, J.; Nekrutenko, A.; Taylor, J. Galaxy: A comprehensive approach for supporting accessible, reproducible, and transparent computational research in the life sciences. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hillman-Jackson, J.; Clements, D.; Blankenberg, D.; Taylor, J.; Nekrutenko, A.; The Galaxy Team. Using galaxy to perform large-scale interactive data analyses. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2012, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Adelman, Z.N.; Myles, K.M.; Zhang, L. A Transcriptome Post-Scaffolding Method for Assembling High Quality Contigs. Comput. Biol. J. 2014, 2014, 961823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides accurate, fast, and bias-aware transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2009, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: Accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supek, F.; Bošnjak, M.; Škunca, N.; Šmuc, T. Revigo summarizes and visualizes long lists of gene ontology terms. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryant, D.M.; Johnson, K.; DiTommaso, T.; Tickle, T.; Couger, M.B.; Payzin-Dogru, D.; Lee, T.J.; Leigh, N.D.; Kuo, T.H.; Davis, F.G.; et al. A Tissue-Mapped Axolotl De Novo Transcriptome Enables Identification of Limb Regeneration Factors. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K. BLAST plus: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kersey, P.J.; Allen, J.E.; Allot, A.; Barba, M.; Boddu, S.; Bolt, B.J.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Christensen, M.; Davis, P.; Grabmueller, C.; et al. Ensembl Genomes 2018: An integrated omics infrastructure for non-vertebrate species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D802–D808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2013, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq-A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Bateman, A.; Marshall, M.; Khanna, A.; Eddy, S.R. Rfam: An RNA family database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ono, H.; Ishii, K.; Kozaki, T.; Ogiwara, I.; Kanekatsu, M.; Yamada, T. Removal of redundant contigs from de novo RNA-Seq assemblies via homology search improves accurate detection of differentially expressed genes. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, H.; Yu, Z.-L.; Sun, L.-N.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.-Y. De novo transcriptome sequencing and analysis of Rapana venosa from six different developmental stages using Hi-seq 2500. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D. Genom. Proteom. 2016, 17, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzerand, M.; Marz, M. De novo transcriptome assembly: A comprehensive cross-species comparison of short-read RNA-Seq assemblers. GigaScience 2019, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Mbandi, S.K.; Hesse, U.; van Heusden, P.; Christoffels, A. Inferring bona fide transfrags in RNA-Seq derived-transcriptome assemblies of non-model organisms. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, B.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Q.; Wei, C.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y. Optimal assembly strategies of transcriptome related to ploidies of eukaryotic organisms. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, B.X.; Zeng, Z.B.; Shi, T.L. Comparative study of de novo assembly and genome-guided assembly strategies for transcriptome reconstruction based on RNA-Seq. Sci. China Life Sci. 2013, 56, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amin, S.; Prentis, P.J.; Gilding, E.K.; Pavasovic, A. Assembly and annotation of a non-model gastropod (Nerita melanotragus) transcriptome: A comparison of De novo assemblers. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijay, N.; Poelstra, J.W.; Künstner, A.; Wolf, J.B.W. Challenges and strategies in transcriptome assembly and differential gene expression quantification. A comprehensive in silico assessment of RNA-seq experiments. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Gribskov, M. Comprehensive evaluation of de novo transcriptome assembly programs and their effects on differential gene expression analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 27–323. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, W.R.; Christianson, L.M.; Kiko, R.; Powers, M.L.; Shaner, N.C.; Haddock, S.H.D. A comparison across non-model animals suggests an optimal sequencing depth for de novo transcriptome assembly. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kornobis, E.; Cabellos, L.; Aguilar, F.; Frías-López, C.; Rozas, J.; Marco, J.; Zardoya, R. TRUFA: A User-Friendly Web Server for de novo RNA-seq Analysis Using Cluster Computing. Evol. Bioinform. 2015, 11, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.; Irizarry, R.; Kingsford, C. Salmon’s Documentation. 2017. Available online: http://salmon.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ (accessed on 25 October 2017).
- Langmead, B. Alignment short sequencing reads with Bowtie. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 32, 11.7.1–11.7.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Quality Metric | Rockhopper2 Default Parameters | Rockhopper2 Optimized Parameters | Trinity Default Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Sequences | 1129 | 3459 | 6488 |
| Mean Length | 243.13 | 604.088 | 483.83 |
| Number with ORF | 165 | 1528 | 1919 |
| Fragments | 638,046 | 638,046 | 638,046 |
| Mapped | 478,534 (75%) | 571,882(89%) | 602,400(94%) |
| TAS | 0.19001 | 0.55092 | 0.58337 |
| Quality Metric | Trinity CD-HIT | Trinity TransPS | Rockhopper TransPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Sequences | 6373 | 3825 | 2481 |
| Mean Length | 479.36 | 743.95 | 687.89 |
| Number with ORF | 1861 | 1758 | 1323 |
| Fragments | 638,046 | 638,046 | 638,046 |
| Mapped | 602,657 (94%) | 555,748 (87%) | 530,315(83%) |
| TAS | 0.6122 | 0.5303 | 0.5405 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caicedo-Montoya, C.; Pinilla, L.; Toro, L.F.; Yepes-García, J.; Ríos-Estepa, R. Comparative Analysis of Strategies for De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Prokaryotes: Streptomyces clavuligerus as a Case Study. High-Throughput 2019, 8, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8040020
Caicedo-Montoya C, Pinilla L, Toro LF, Yepes-García J, Ríos-Estepa R. Comparative Analysis of Strategies for De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Prokaryotes: Streptomyces clavuligerus as a Case Study. High-Throughput. 2019; 8(4):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaicedo-Montoya, Carlos, Laura Pinilla, León F. Toro, Jeferyd Yepes-García, and Rigoberto Ríos-Estepa. 2019. "Comparative Analysis of Strategies for De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Prokaryotes: Streptomyces clavuligerus as a Case Study" High-Throughput 8, no. 4: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8040020
APA StyleCaicedo-Montoya, C., Pinilla, L., Toro, L. F., Yepes-García, J., & Ríos-Estepa, R. (2019). Comparative Analysis of Strategies for De Novo Transcriptome Assembly in Prokaryotes: Streptomyces clavuligerus as a Case Study. High-Throughput, 8(4), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ht8040020





