Radiological and Pathological Features of Cyst Formation in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease
Abstract
Highlights
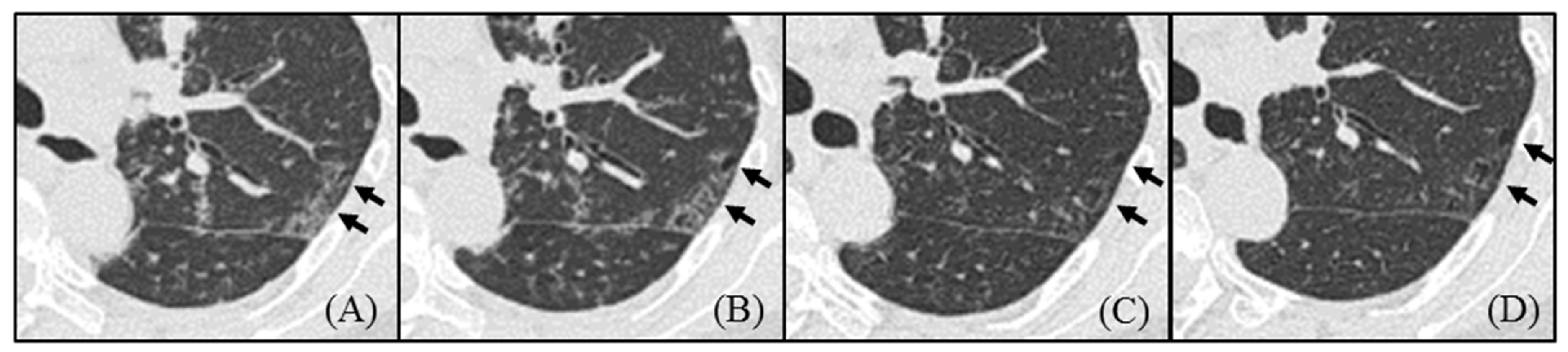
- Pulmonary cysts in idiopathic Castleman disease (MCD) emerged from the area of ground-glass attenuation (GGA) on HRCT, and the cysts did not regress by treatment.
- The pathological evaluation showed a high degree of plasma cell infiltration and loss of elastic fibers around the cyst wall.
- The loss of elastic fibers may be an important factor in cyst formation in idiopathic MCD.
- Introducing anti-inflammatory therapy, such as tocilizumab, before pathologic loss of elastic fibers occurs might prevent irreversible cyst formation in MCD.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Radiological Findings
2.3. Pathological Findings
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
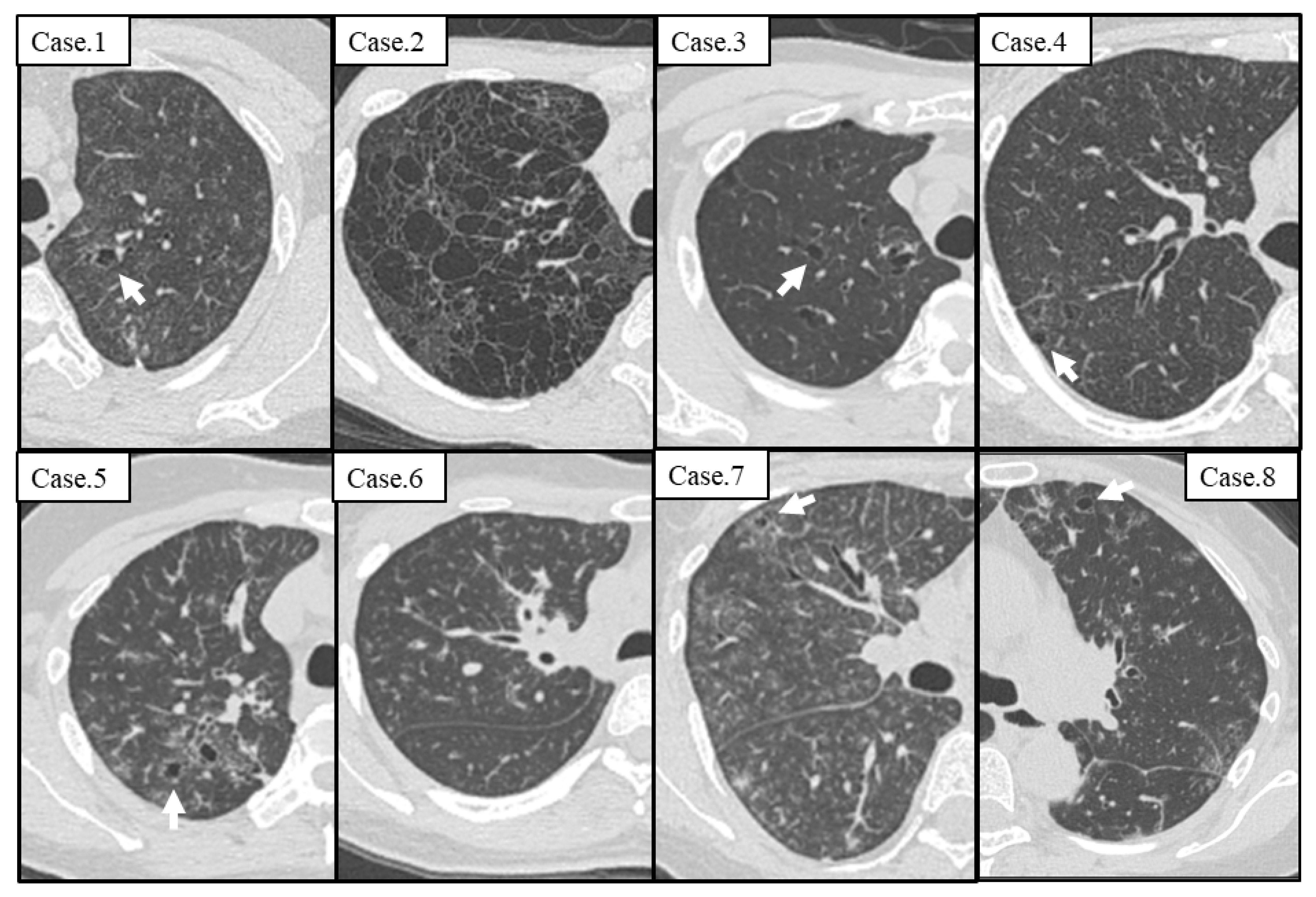
3.2. Radiological Findings on the Initial Visit
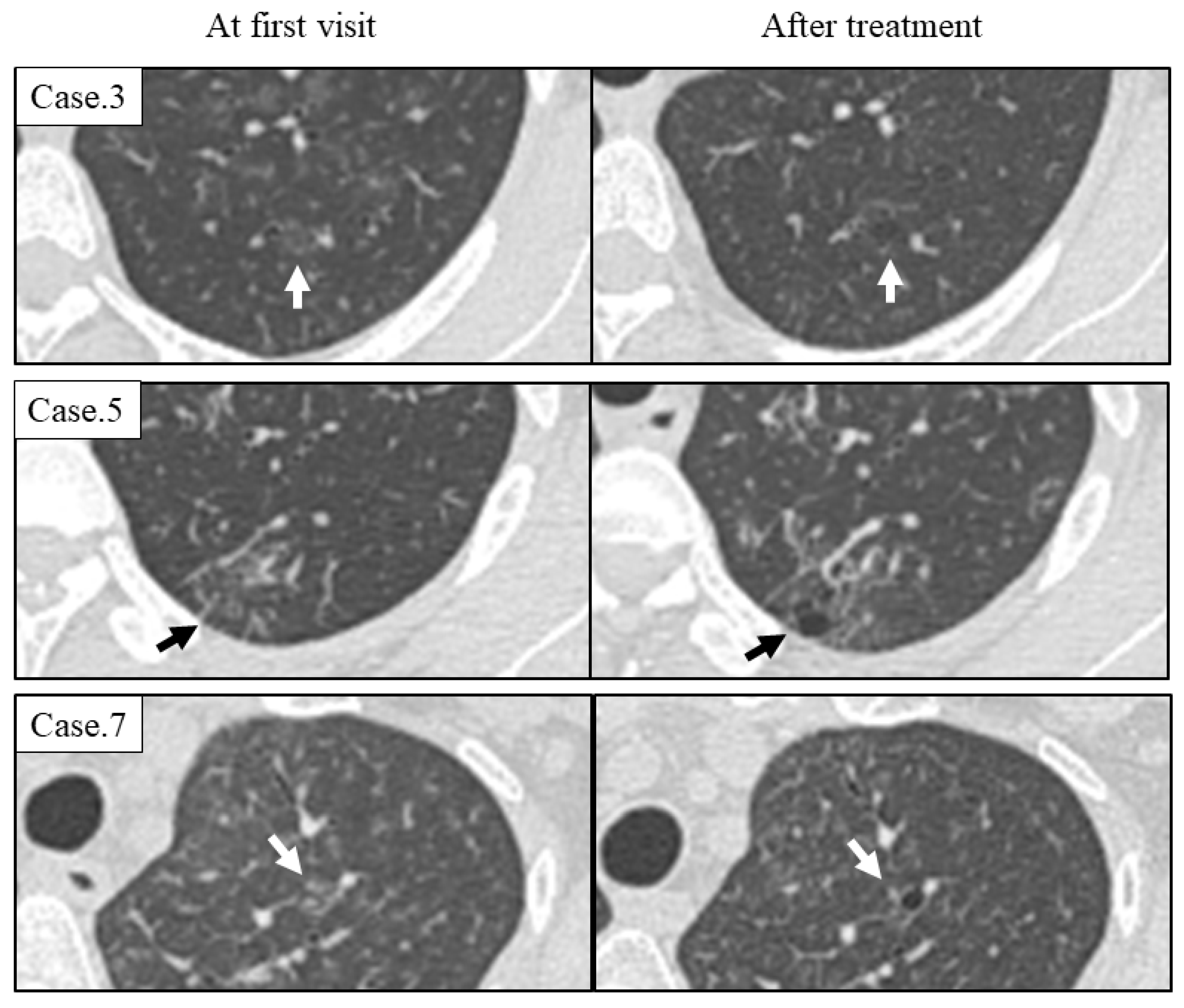
3.3. Radiological Course of Cysts
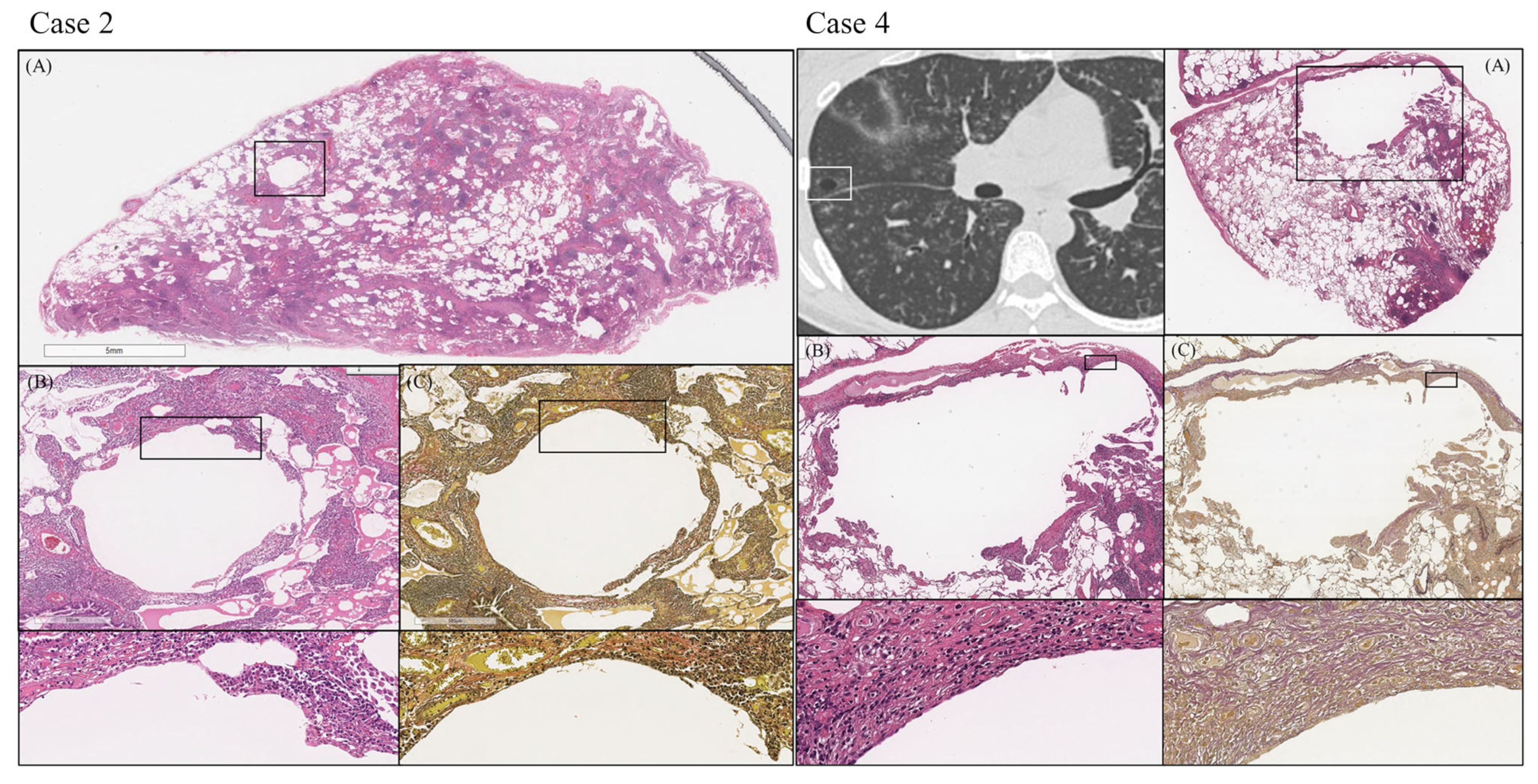
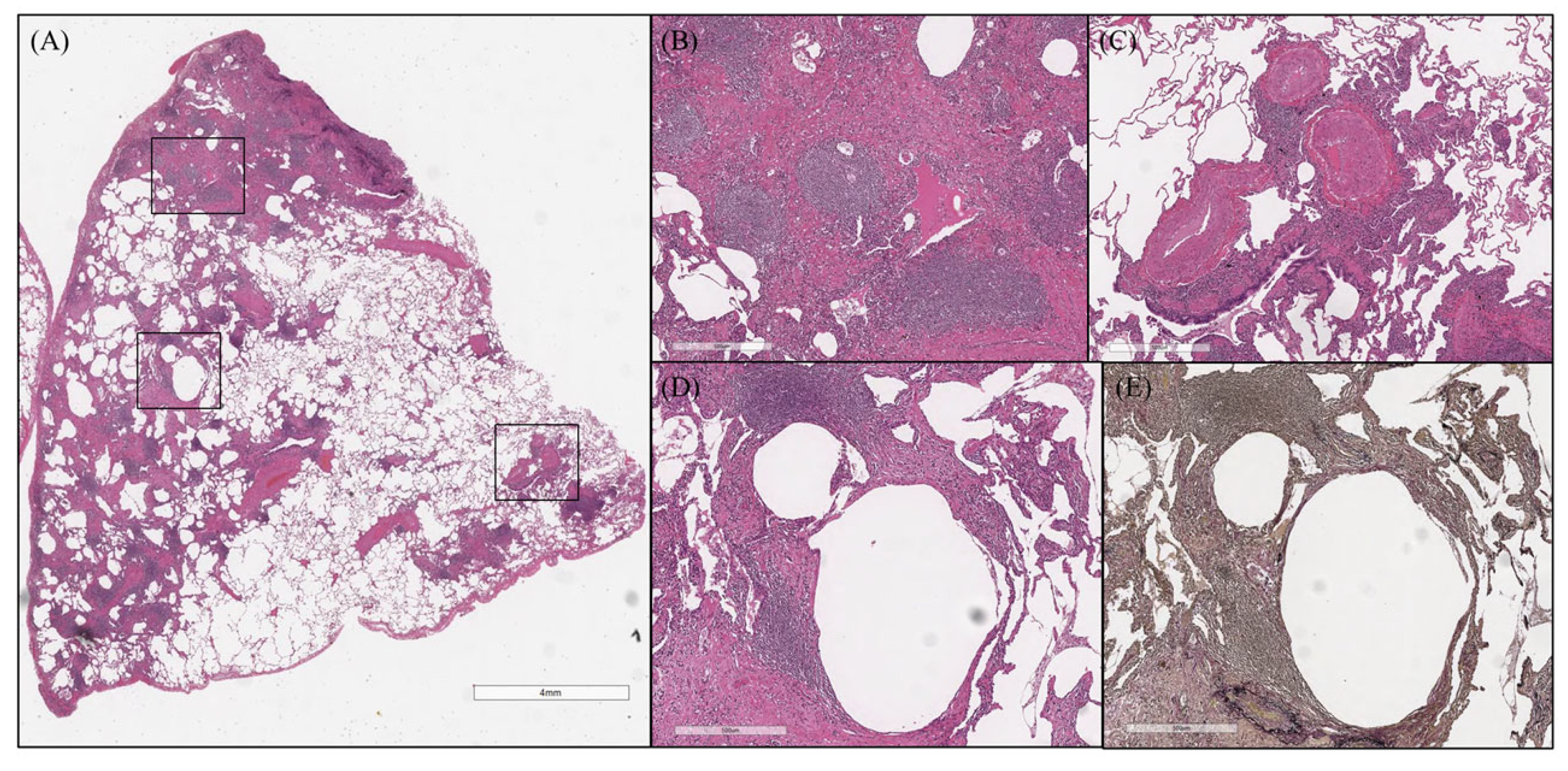
3.4. Pathological Findings
Case Presentation (Case 8)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castleman, B.; Iverson, L.; Menendez, V.P. Localized mediastinal lymphnode hyperplasia resembling thymoma. Cancer 1956, 9, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castleman, B. CASE records of the Massachusetts General Hospital Weekly Clinicopathological Exercises: Case 40011. N. Engl. J. Med. 1954, 250, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fajgenbaum, D.C.; Uldrick, T.S.; Bagg, A.; Frank, D.; Wu, D.; Srkalovic, G.; Simpson, D.; Liu, A.Y.; Menke, D.; Chandrakasan, S.; et al. International, evidence-based consensus diagnostic criteria for HHV-8-negative/idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease. Blood 2017, 129, 1646–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, E.; Massarelli, G.; Soggia, G.; Tanda, F. Multicentric giant lymph node hyperplasia. A hyperimmune syndrome with a rapidly progressive course. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 73, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frizzera, G.; Banks, P.M.; Massarelli, G.; Rosai, J. A systemic lymphoproliferative disorder with morphologic features of Castleman’s disease. Pathological findings in 15 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1983, 7, 211–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulier, J.; Grollet, L.; Oksenhendler, E.; Cacoub, P.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Babinet, P.; d’Agay, M.F.; Clauvel, J.P.; Raphael, M.; Degos, L.; et al. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood 1995, 86, 1276–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, H.; Kadowaki, N.; Nishikori, M.; Kitawaki, T.; Kondo, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Yoshifuji, H.; Yamakawa, N.; Imura, Y.; Mimori, T.; et al. Clinical features and treatment of multicentric castleman’s disease: A retrospective study of 21 Japanese patients at a single institute. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2013, 53, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, M.; Nakamura, N.; Tsukamoto, N.; Otuski, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Itoh, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Murase, T.; Masawa, N.; et al. Clinical implications of idiopathic multicentric castleman disease among Japanese: A report of 28 cases. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2008, 16, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.M.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Cao, J.; Xu, K.; Bi, Y.L.; E Feng, R.; Huang, C.; Qin, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.J.; et al. Clinical spectrum of intrathoracic Castleman disease: A retrospective analysis of 48 cases in a single Chinese hospital. BMC Pulm. Med. 2015, 15, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, N.; Kanakura, Y.; Aozasa, K.; Johkoh, T.; Nakamura, M.; Nakano, S.; Nakano, N.; Ikeda, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Nishioka, K.; et al. Humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody treatment of multicentric Castleman disease. Blood 2005, 106, 2627–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johkoh, T.; Muller, N.L.; Ichikado, K.; Nishimoto, N.; Yoshizaki, K.; Honda, O.; Tomiyama, N.; Naitoh, H.; Nakamura, H.; Yamamoto, S. Intrathoracic multicentric Castleman disease: CT findings in 12 patients. Radiology 1998, 209, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Feng, R.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Xu, K.; Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Bi, Y.; Xu, Z. Castleman disease-associated diffuse parenchymal lung disease: A STROBE-compliant retrospective observational analysis of 22 cases in a tertiary Chinese hospital. Medicine 2017, 96, e8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nei, T.; Oiwa, T.; Saitoh, Y.; Abe, S.; Motegi, T.; Usuki, J.; Azuma, A.; Kudoh, S.; Hirai, K.; Koizumi, K.; et al. A case of multicentric Castleman disease showing diffuse cystic change in the lung. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi J. Jpn. Respir. Soc. 2006, 44, 468–473. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.; Shi, J.; Feng, R. Multicentric Castleman Disease as a Rare Cause of Diffuse Lung Cysts. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1292–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombat, M.; Caudroy, S.; Lagonotte, E.; Mal, H.; Danel, C.; Stern, M.; Fournier, M.; Birembaut, P. Pathomechanisms of cyst formation in pulmonary light chain deposition disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhe, X.; Yang, Y.; Jakkaraju, S.; Schuger, L. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-3 downregulation in lymphangioleiomyomatosis: Potential consequence of abnormal serum response factor expression. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 28, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Fleming, M.V.; Fishback, N.; Koss, M.N.; A Liotta, L.; Ferrans, V.J.; Travis, W.D. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol. 1996, 149, 1241–1256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Case | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 33 | 40 | 48 | 36 | 44 | 45 | 48 | 57 | 44.5 |
| Sex | Male | Male | Male | Female | Female | Female | Female | Female | |
| Smoking history | Never | Never | Current | Never | Never | Former | Former | Never | |
| Pack years | 0 | 0 | 28 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 22 | 0 | |
| Symptom | Cough | Dyspnea | Chest pain | Fatigue | Nothing | Cough | Fatigue | Dyspnea | |
| Duration from onset to first visit (months) | 45 | 274 | 2 | 9 | 15 | 8 | 62 | 60 | 30 |
| Laboratory data | |||||||||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 15.4 | 8.0 | 11.8 | 10.4 | 10.6 | 10.8 | 11.8 | 8.9 | 10.7 |
| Platelet (×104/uL) | 24.3 | 42.6 | 53.6 | 42.8 | 28.0 | 49.6 | 39.5 | 47.8 | 42.7 |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 4.6 | 7.9 | 6.3 | 7.4 | 6.2 | 1.5 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 6.3 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.89 | 1.38 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.67 |
| Total protein | 10.1 | 11.9 | 10.3 | 10.5 | 9.3 | 9.1 | 12.0 | 8.9 | 10.2 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.0 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.8 |
| IgG (mg/dL) | 4341 | 8184 | 4779 | 5169 | 4730 | 3988 | 5974 | 3846 | 4755 |
| IgG4 (mg/dL) | 57 | 1812 | 416 | 242 | N.E. | 94 | 72 | 142 | 142 |
| KL-6 (U/mL) | 1453 | 973 | 285 | 574 | 256 | 448 | 507 | 1172 | 540.5 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 16 | 20 | 28 | 17 | 16 | 10 | 14 | 35 | 16.5 |
| Anti-nuclear antibodies | 0 | 160 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 40 | 40 | 80 | |
| Rheumatoid factor (IU/mL) | 23 | 17 | 13 | 7 | 11 | 9 | 14 | 23 | |
| Specific autoantibody | – | RNP | – | RNP, SS-A | – | – | – | – | |
| Diagnosis of autoimmune disease | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Diagnosis of malignant disease | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Infectious disease | |||||||||
| HIV antigen | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| HHV-8 qPCR | – | – | – | – | N.E. | – | – | ||
| CT Findings | n = 8 |
|---|---|
| Mediastinal lymphadenopathy | 8 (100%) |
| Interlobular septal thickening | 8 (100%) |
| Centrilobular nodules | 8 (100%) |
| Ground-grass attenuation | 8 (100%) |
| Cyst formation | 7 (87.5%) |
| Thickening of the bronchovascular bundles | 6 (75%) |
| Air trapping (n = 6) | 5 (83.3%) |
| Consolidation | 1 (12.5%) |
| Bronchiectasis | 1 (12.5%) |
| Pleural effusion | 0 (0%) |
| Case | Detail Characteristics of Cyst at First Visit | Clinical Course | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cyst | Number | Size | Wall | GGA around Cysts | Distribution | Treatment | The Number of Cysts | ||
| Upper /Lower | Subpleural Area /Interstitial Area /Random | ||||||||
| 1 | + | 2 | 8 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | TCZ | No change |
| 2 | + | >100 | 3–30 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Random | TCZ | No change |
| 3 | + | 25 | 2–10 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | TCZ | Increase |
| 4 | + | 12 | 2–8 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | PSL + TCZ | Increase |
| 5 | + | 14 | 3–8 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | Observation | Increase |
| 6 | − | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | NE | TCZ | Increase |
| 7 | + | 3 | 2–3 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | TCZ | Increase |
| 8 | + | 32 | 3–9 mm | <2 mm | + | Upper | Interstitial area | TCZ | Increase |
| Summary | 7/8 (87.5%) | 1–9; 2 10–99; 4 >100; 1 | <10 mm; 6 >10 mm; 1 | <2 mm; 7 >2 mm; 0 | 7/7 (100%) | Upper; 7 Lower; 0 | Subpleural; 0 Interstitial; 6 Random; 1 | TCZ; 6 PSL + TCZ; 1 Observation; 1 | Increase; 6 No change; 2 Decrease; 0 |
| Pathological Findings | n = 8 |
|---|---|
| Type (Hypervascular/ Mixed/ Plasmacytic) | 0/0/8 |
| Distribution | |
| Bronchovascular bundle (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 0/0/7/1 |
| Interlobular septa (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 0/3/3/2 |
| Alveolar wall (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 0/5/0/3 |
| Fibrosis (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 1/5/2/0 |
| Cell infiltration | |
| Plasma cell (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 0/0/0/8 |
| Lymphoid follicles with germinal center (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 0/4/2/2 |
| Eosinophils (Grade 0/1/2/3) | 3/4/1/0 |
| Characteristics of cyst wall | n = 4 |
| Prominent infiltration of plasma cells | 4 (100%) |
| Prominent infiltration of macrophages | 0 (0%) |
| Granuloma | 0 (0%) |
| Opening of bronchi | 4 (100%) |
| Loss of elastic fibers | 4 (100%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otoshi, R.; Sekine, A.; Muraoka, T.; Iwasawa, T.; Takemura, T.; Matsushita, S.; Okudela, K.; Kitamura, H.; Baba, T.; Ogura, T. Radiological and Pathological Features of Cyst Formation in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease. Adv. Respir. Med. 2023, 91, 164-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020014
Otoshi R, Sekine A, Muraoka T, Iwasawa T, Takemura T, Matsushita S, Okudela K, Kitamura H, Baba T, Ogura T. Radiological and Pathological Features of Cyst Formation in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease. Advances in Respiratory Medicine. 2023; 91(2):164-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtoshi, Ryota, Akimasa Sekine, Tatsuya Muraoka, Tae Iwasawa, Tamiko Takemura, Shoichiro Matsushita, Koji Okudela, Hideya Kitamura, Tomohisa Baba, and Takashi Ogura. 2023. "Radiological and Pathological Features of Cyst Formation in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease" Advances in Respiratory Medicine 91, no. 2: 164-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020014
APA StyleOtoshi, R., Sekine, A., Muraoka, T., Iwasawa, T., Takemura, T., Matsushita, S., Okudela, K., Kitamura, H., Baba, T., & Ogura, T. (2023). Radiological and Pathological Features of Cyst Formation in Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease. Advances in Respiratory Medicine, 91(2), 164-173. https://doi.org/10.3390/arm91020014






