Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Associated with E200K Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pure Coincidence or Neurodegenerative Acceleration?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
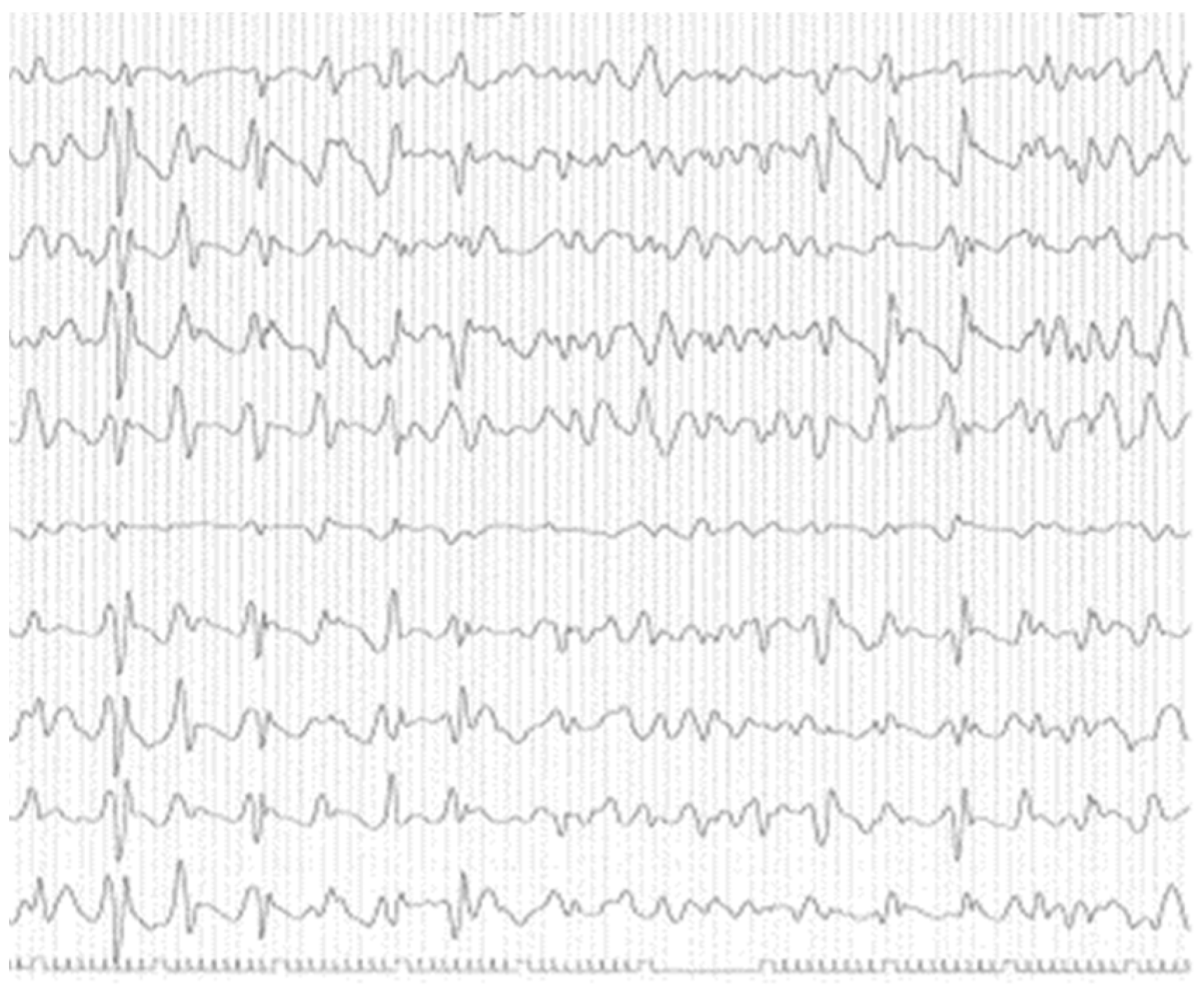
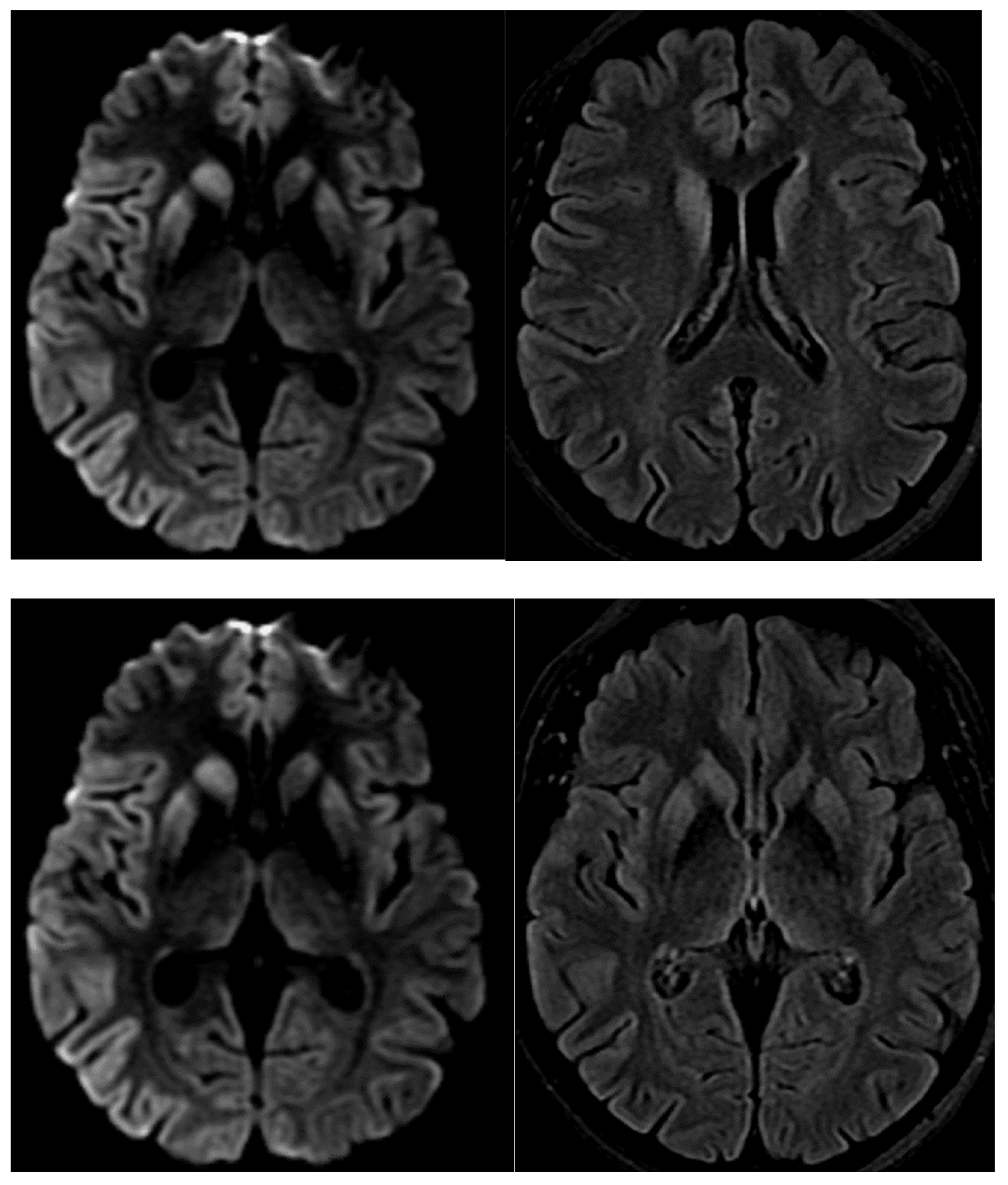
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bezzini, D.; Schiavetti, I.; Manacorda, T.; Franzone, G.; Battaglia, M.A. First Wave of COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy: Data and Evidence. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1353, 91–113. [Google Scholar]
- Farheen, S.; Agrawal, S.; Zubair, S.; Agrawal, A.; Jamal, F.; Altaf, I.; Anwar, A.K.; Umair, S.M.; Owais, M. Patho-physiology of aging and immune-senescence: Possible correlates with comorbidity and mortality in middle-aged and old COVID-19 patients. Front. Aging 2021, 2, 748591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.W.; Xu, H.S.; Liu, S.J. COVID-19 and neurodegenerative diseases. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Jaber, V.R.; Lukiw, W.J. SARS-CoV-2, long COVID, prion disease and neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1002770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, L.I.; Poleggi, A.; Poggiolini, I.; Suardi, S.; Grznarova, K.; Shi, S.; de Vil, B.; Sarros, S.; Satoh, K.; Cheng, K.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid real-time quaking-induced conversion is a robust and reliable test for sporadic creutzfeldt-jakob disease: An international study. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerr, I.; Schmitz, M. Genetic Prion Disease. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirza, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2003; Updated 7 January 2021; pp. 1993–2024. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, A.; Pai, H.; Clack, A. Rapid progression of probable Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with concomitant COVID-19 infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2023, 16, e254402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciolac, D.; Racila, R.; Duarte, C.; Vasilieva, M.; Manea, D.; Gorincioi, N.; Condrea, A.; Crivorucica, I.; Zota, E.; Efremova, D.; et al. Clinical and radiological deterioration in a case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Hints to accelerated age-dependent neurodegeneration. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, H.C.; Xiao, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Chen, G. Long COVID and its Management. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 4768–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minikel, E.V.; Vallabh, S.M.; Lek, M.; Estrada, K.; Samocha, K.E.; Sathirapongsasuti, J.F.; McLean, C.Y.; Tung, J.Y.; Yu, L.P.C.; Gambetti, P.; et al. Quantifying prion disease penetrance using large population control cohorts. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 322ra9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladogana, A.; Kovacs, G.G. Chapter 13—Genetic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Pocchiari, M., Manson, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 153, pp. 219–242. [Google Scholar]
- Won, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. Elevated E200K Somatic Mutation of the Prion Protein Gene (PRNP) in the Brain Tissues of Patients with Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulbright, R.K.; Kingsley, P.B.; Guo, X.; Hoffmann, C.; Kahana, E.; Chapman, J.C.; Prohovnik, I. The imaging appearance of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease caused by the E200K mutation. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2006, 24, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsan, Z.; Cohen, O.S.; Chapman, J.; Kahana, E.; Korczyn, A.D.; Appel, S.; Osherov, M.; Rosenmann, H.; Milo, R. Familial Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease homozygous to the E200K mutation: Clinical characteristics and disease course. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2455–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, B.F. NeuroCOVID-19: A critical review. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatria 2022, 80, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.; Yura, T.; Kak, V. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease with COVID-19 Infection: A Case Report. Cureus 2023, 15, e45757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, J.A.; Thorpe, L.E.; Simon, N.M.; de Havenon, A.; Yaghi, S.; Sabadia, S.B.; Yang, D.; Lewis, A.; Melmed, K.; Balcer, L.J.; et al. Post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 symptom phenotypes and therapeutic strategies: A prospective, observational study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.J.; O’Hare, M.; Matiello, M.; Schmahmann, J.D. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a man with COVID-19: SARS-CoV-2-accelerated neurodegeneration? Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.-S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogue, A.I.; Lukiw, W.J. microRNA-146a-5p, neurotropic viral infection and prion disease (PrD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.J.; Jaber, V.R.; Pogue, A.I.; Zhao, Y. SARS-CoV-2 Invasion and Pathological Links to Prion Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivo, S.; Furlanis, G.; Stella, A.B.; Fabris, M.; Milanic, R.; Zanusso, G.; Manganotti, P. Rapidly evolving Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease in COVID-19: From early status epilepticus to fatal outcome. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2022, 123, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Ray, B.; Tuladhar, S.; Bhat, A.; Paneyala, S.; Patteswari, D.; Sakharkar, M.K.; Hamdan, H.; Ojcius, D.M.; Bolla, S.R.; et al. Does COVID-19 contribute to development of neurological disease? Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.J.; Feigen, C.M.; Vazquez, J.P.; Kobets, A.J.; Altschul, D.J. Neurological Sequelae of COVID-19. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 21, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetz, G.; Tetz, V. Prion-like domains in spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 differ across its variants and enable changes in affinity to ACE2. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Groveman, B.R.; Winkler, C.; Williams, K.; Walters, R.; Yuan, J.; Zou, W.; Peterson, K.; Foliaki, S.T.; Haigh, C.L. Stress and viral insults do not trigger E200K PrP conversion in human cerebral organoids. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.S.; Vallabh, S.M. Genetic counseling for prion disease: Updates and best practices. Anesthesia Analg. 2022, 24, 1993–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, N.; Brandel, J.P.; Green, A.; Hermann, P.; Ladogana, A.; Lindsay, T.; Mackenzie, J.; Pocchiari, M.; Smith, C.; Zerr, I.; et al. The importance of ongoing international surveillance for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 362–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colaizzo, E.; Prosperini, L.; Petrucci, A.; Perna, A. Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Associated with E200K Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pure Coincidence or Neurodegenerative Acceleration? Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2024, 8, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn8020016
Colaizzo E, Prosperini L, Petrucci A, Perna A. Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Associated with E200K Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pure Coincidence or Neurodegenerative Acceleration? Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2024; 8(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn8020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleColaizzo, Elisa, Luca Prosperini, Antonio Petrucci, and Alessia Perna. 2024. "Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Associated with E200K Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pure Coincidence or Neurodegenerative Acceleration?" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 8, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn8020016
APA StyleColaizzo, E., Prosperini, L., Petrucci, A., & Perna, A. (2024). Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease Associated with E200K Mutation and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Pure Coincidence or Neurodegenerative Acceleration? Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 8(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn8020016







