Abstract
The thalamus, and its projections to the cerebral cortex, are crucial for regulating sleep rhythms, such as sleep spindles, and for maintaining arousal and sleep homeostasis. Moreover, they play a significant role in memory, executive functioning, and attention. Altered thalamocortical circuitry caused by vascular lesions affects sleep–wake architecture and may contribute to cognitive deficits observed in thalamic stroke patients. This review summarizes the biology of the thalamus and current knowledge regarding the impact of thalamic circuitry on sleep regulation and cognition, drawing from clinical and pre-clinical studies. Furthermore, deep brain stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation are discussed as possible therapeutic approaches targeting thalamic circuits. Understanding the role of the thalamus in sleep and cognition opens new avenues for developing novel therapeutic strategies to improve sleep and cognitive functions in affected individuals.
Keywords:
thalamus; cognitive functioning; sleep; memory; sleep spindles; slow waves; attention; arousal; stroke; thalamic stroke 1. Introduction
Cognition refers to the ability of the brain to perceive, identify, memorize, and remember complex stimuli as a fundamental aspect of brain function. Conversely, cognitive dysfunction is an umbrella term covering deficiencies in any cognitive domain (e.g., memory), usually defined as a decline in neuropsychological performance [1].
Cognitive functioning is linked to demographic, developmental, genetic, cardiovascular, and metabolic profiles, with cognitive dysfunction being most common in neurological and psychiatric illnesses including brain injury, progressive neurological diseases, and depression [2,3]. Cognitive dysfunction also manifests in diagnostically healthy individuals, for example after sleep deprivation [4].
Sleep is another factor that is related to cognition and cognitive dysfunction: sufficient sleep is necessary for normal cognitive performance, whereas sleep–wake disorders (SWD) are associated with cognitive dysfunction [4]. While the specific functions of sleep are still a matter of ongoing research, they may include memory consolidation, brain clearance, anabolism, and plasticity [5,6]. Indeed, clinical studies have demonstrated the negative impact of SWD (i.e., insomnia, sleep-disordered breathing (SDB), daytime dysfunction, rapid eye movement (REM), sleep behavior disorder) and alterations in sleep duration on cognitive abilities [7,8,9].
Several brain circuits have been identified as being particularly significant for sleep–wake and cognition. They include the reticular activating system (arousal, attention, sleep–wake transitions, and circadian rhythms [10]), the cortical–hippocampal–cortical circuit (sleep-dependent memory consolidation [11,12]), the basal forebrain circuit (REM sleep, cortical activation, attention [13,14,15]), and the prefrontal–amygdala circuit (sleep-related emotional reactivity, attention [16,17,18]).
Emerging research provides compelling evidence for the crucial role of sleep in plasticity and memory consolidation [19,20,21,22,23,24]. Through a dynamic interaction between hippocampal (HC) and neocortical networks, new memories, acquired during wakefulness, transform into stable long-term representations during sleep. During NREM sleep, information flows via complex loops characterized by the co-occurrence of slow waves (transient oscillatory events between 1 and 4 Hz), spindles (oscillations between 10 and 16 Hz), and hippocampal ripples. This process optimizes plasticity [25] and leads to long-term synaptic modifications, often in a region-specific manner. Slow waves and spindles are known to be generated and modulated by thalamocortical loops, which rely on a delicate balance of excitation and inhibition in thalamic and cortical circuits. Furthermore, the coupling of hippocampal and neocortical networks requires interregional cross-frequency coordination, incorporating sleep oscillations such as slow waves and spindles in thalamocortical circuits, along with hippocampal ripples driven by hippocampal–entorhinal cortex synaptic activity [26,27]. Despite accumulating evidence, gaps still exist in our understanding of the mechanisms supporting memory consolidation. These mechanisms might include the propagation of slow oscillations propagating from the anterior to the posterior cortex and the consistent occurrence of spindles in centroparietal regions.
In summary, sleep, as an essential physiological process, has a paramount impact on brain functioning. Impaired sleep may lead to cognitive dysfunction and impede restorative processes, potentially contributing to chronic conditions. Recognizing the importance of sleep and addressing SWD is crucial for sustaining optimal cognitive function and overall well-being.
This review focuses on the thalamus and its associated neuronal circuits, with the aim of providing a current synopsis of their role in sleep and cognition. Studying thalamic lesions enables researchers to follow an experiment of nature that offers a unique view for investigating sleep and cognition. Therefore, case–control studies involving patients with isolated thalamic stroke were analyzed to determine the impact of thalamic vascular lesions on sleep and cognition in humans. Additionally, the article explores the function of thalamic circuits based on experimental studies. Finally, prospective therapeutic approaches targeting the thalamus are discussed.
2. Thalamus and Anatomical Vascular Territories
The thalamus of mammals encompasses several groups of nuclei with predominant specialized roles, including the anterior nuclei (cognition, sleep), medial nuclei (cognition, sleep), ventral and lateral nuclei (motor and sensory processing), geniculate nuclei (vision and hearing), pulvinar (attention and visuo-spatial orientation), and intralaminar nuclei (pain and spatial orientation) [28,29,30,31]. The evolutionary development of the forebrain, including the thalamus, occurred independently in various groups of vertebrates [32]. Nonetheless, mammals share a considerable proportion of structures (Figure 1A). The thalamus is densely interconnected with the cerebral cortex in primates, forming reciprocal relationships critical for consciousness, perception, and cognition [33].
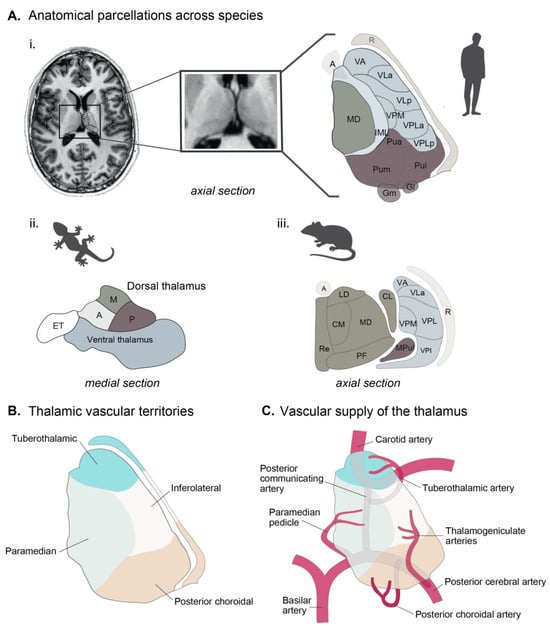
Figure 1.
The thalamus in humans. (A) A 7T T1-weighted MRI of the human thalamus and main thalamic nuclei. Main thalamic nuclei across species: (i) anatomical parcellation from the human thalamus (adapted from [31]. (ii) Salamander (adapted from Wicht, 1988 [34]), and (iii) mouse (adapted from Jankowski, 2013 [35]) and human (adapted from Mai & Majtanik, 2017 [36]). (B) Vascular supply of the thalamus. (C) Thalamic vascular territories. Abbreviations: A—anterior, CL—centrolateral, CM—centromedial, ET—eminentia thalami, Gl—lateral geniculate, Gm—medial geniculate, IL—intralaminar, LD—laterodorsal, M—medial, MD—mediodorsal, PF—parafascicular, Pua—pulvinar anterior, Pul—pulvinar lateral, Pum—pulvinar medial, R—reticularis, VA—ventral anterior, VLa—ventrolateral anterior, VLp—ventrolateral posterior, VPLa—ventroposterolateral anterior, VPLa—ventroposterolateral posterior, VPM—ventroposteromedial.
Although specificities in connectivity or activity exist between species, these differences in complexity are thought to fulfill needs in the physiological regulation of each species. The pulvinar, for example, is the largest thalamic nucleus in primates, and it has evolved to be particularly large and complex in humans compared to other mammals [28]. The causes for this development are most likely related to the primates’ unique behavioral and cognitive abilities (e.g., visual information processing, coordination of responses to visual stimuli, and integration of visual data with other sensory modalities [37,38]). However, the precise roles of the pulvinar are still being researched. Similarly, the human prefrontal cortex is markedly larger than that of other primates and rodents and may be shaped by human-specific executive functions, emotions, and social interactions [39]. Additionally, neuronal firing patterns may vary between rodents and humans, reflecting subtle differences in sleep–wake cycles. For example, the quicker sleep–wake cycle in rodents might correspond to faster shifts in neuronal activity in the hypothalamus [40,41,42] in response to metabolic need, which differs between species.
In terms of vasculature, the thalamus is predominantly supplied by small vessels originating from the posterior communicating artery and the P1 and P2 segments of the posterior cerebral artery [43] (Figure 1C). Despite the wide variation, thalamic vascular supply is categorized into anterior, paramedian, inferolateral, and posterior territories [44]. The vascular supply of the thalamus in rodents follows similar principles. In mice, for example, the thalamus is mostly supplied by the branches of the posterior cerebral artery; however, the exact distributions of small branches may vary [44]. Furthermore, it should be noted that the anterior choroidal artery is responsible for supplying the dorsal part of the thalamus in mice, whereas this vascular supply is not observed in humans [44].
Despite the challenges arising from the lack of standardized nomenclature, particularly with respect to the lateral nuclei, discrepancies in anatomical variation, the impact of age-related microstructural degradation [36], and interspecies variations, investigations involving human and animal subjects provide valuable insights into understanding the role of the thalamus in sleep and cognition. Table 1 summarizes case–control studies in thalamic stroke patients, whereas Box 1 and Figure 2 illustrate the principles applied to the models of thalamic stroke in rodents.

Table 1.
The overview of case–control studies in thalamic stroke (TS) patients compared to the control group investigating sleep and cognitive functioning.
Table 1.
The overview of case–control studies in thalamic stroke (TS) patients compared to the control group investigating sleep and cognitive functioning.
| Reference | TS | Control | Time Post-Stroke | Sleep Symptoms | Sleep Assessment | Sleep Alterations | Cognitive Assessment | Cognitive Domains Affected | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Santamaria et al., 2000 [45] | Unilateral TS | N = 13 | Age- and sex- matched volunteers | N = 18 | 7–21 dps | Hypersomnolence, daytime sleepiness, altered level of consciousness | PSG | ↓ TST, ↓ NREM2, ↓ SS density | - | - |
| Hermann et al., 2008 [46] | Paramedian TS | N = 31 | Age-matched patients with PNS | N = 12 | 5–30 dps | Hypersomnolence, psychomotor slowing | PSG | ↑ NREM1, ↓ NREM2, ↓ SS density, ↓ SS power | Attention, executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, object naming | Attention, executive functioning, verbal and visual memory |
| Danet et al., 2015 [47] | Unilateral left TS | N = 12 | Age- and education-matched volunteers | N = 25 | <90 dps | - | - | - | Executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, object naming | Verbal memory, executive functioning, object naming |
| Kraft et al., 2015 [48] | Isolated unilateral TS | N = 16 | Age- and sex- matched volunteers | N = 52 | 1–132 mps | - | - | - | Computer-based attention tests | Spatial bias, processing speed |
| Wu et al., 2016 [49] | Minor TS | N = 27 | Age and sex-matched volunteers, ↑RDI in TS | N = 12 | 14 and 90 dps | Hypersomnolence, daytime sleepiness | PSG | ↑ SL, ↓ SE, ↑ NREM1, ↓ NREM2, ↓ NREM3 | Global cognitive functioning, verbal memory | Global cognitive functioning, verbal memory |
| Mensen et al., 2018 [50] | Uni- and bilateral TS | N = 9 | Young healthy adults | N = 9 | 5–8 dps | - | hd -EEG | ↓ SS power | - | - |
| Jaramillo et al., 2021 [51] | Unilateral TS | N = 12 | Age-, sex- and AHI-matched extrathalamic stroke patients | N = 11 | 3 dps | Daytime sleepiness | hd -EEG | ↓ SWA | Visual memory, visuospatial functioning | No significant differences |
| Temel et al., 2021 [52] | Thalamic hemorrhage | N = 28 | Age-, sex- and AHI-matched volunteers | N = 28 | 3–6 mps | - | - | - | Global cognitive functioning, verbal memory, executive functioning, verbal fluency | Global cognitive functioning, verbal memory, executive functioning, verbal fluency |
| Scharf et al., 2022 [53] | Unilateral TS | N = 37 | Age- and sex-matched volunteers | N = 37 | 1, 6, 12, 24 mps | Hypersomnolence, reduced vigilance | - | - | Attention, executive functioning, verbal memory, visual memory, verbal fluency | Verbal memory, executive functioning, verbal fluency |
AHI—apnea-hypopnea index, dps—days post-stroke, ESS—Epworth Sleepiness Scale, hd-EEG—high-density EEG, mps—months post-stroke, PSG—polysomnography, SE – sleep efficiency, SL—sleep latency, SS—sleep spindle, SWA—slow wave activity, TS—thalamic stroke, TST—total sleep time.
Box 1. Stroke animal models.
The validation of animal models used to study brain disorders relies on (1) the ability of those models to re-capitulate human disorders and physiological response to treatments; (2) the level of similarity between their symptomatology and that found in humans; and (3) the analogy between the etiology of the disorder in mice and in humans. During the history of stroke research, several models of this pathology have been developed, all pre-senting advantages and disadvantages. Stroke animal models offer the opportunity for invasive measurements and interventions that are not feasible in human studies. Techniques such as electrophysiology, optogenetics, pharmacological manipulations, and recently stroke lesions in the thalamus (Figure 2) can provide detailed in-sights into thalamic activity and its impact on sleep and cognition. Lastly, animal models facilitate longitudinal and developmental studies, enabling the investigation of dynamic changes in thalamic structure and function over time from the onset of the stroke. Moreover, animal models permit the study of the thalamic vasculature, providing insights into the relationship between thalamic blood flow, neuronal activity, circuit plasticity, and cognitive processes. By leveraging these advantages, animal models play a crucial role in advancing our under-standing of the thalamus and its contributions to sleep, cognition, and vascular dynamics.
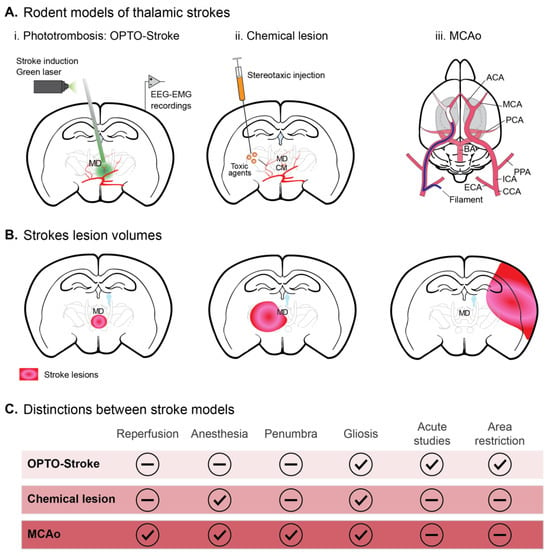
Figure 2.
Models of thalamic stroke in rodents. (A) Experimental manipulations. (i) Photothrombosis. Opto-STROKE: This method involves injecting a photosensitive dye into the bloodstream and then activating it with focused light to induce clot formation in a specific thalamic vessel. The new approach to light-induced stroke allowing increased spatial resolution is opto-STROKE [54]. (ii) Chemical lesion: Direct stereotactic injection. Agents like excitotoxins (e.g., NMDA or quinolinic acid) or thrombotic agents (e.g., endothelin) can be injected directly into the thalamus to create localized lesions that mimic the effects of a stroke [55,56]. (iii) MCAo model: Middle Cerebral Artery (MCA) Occlusion (MCAo) via a filament inserted through the external carotid artery to MCA origin. Although the MCA primarily supplies the cerebral cortex, this method can affect deeper structures like the thalamus, depending on the extent and duration of the occlusion [57]. (B) Schematic representation of the stroke lesion across animal models shown in (A). (C) Key distinctions per stroke model. Abbreviations: ACA—anterior cerebral artery, BA—basilar artery, CCA—common carotid artery, ECA—external carotid artery, EEG—electroencephalography, EEG—electromyography, ICA—internal carotid artery, MCA—middle cerebral artery, MCAo—middle cerebral artery occlusion, MD—mediodorsal thalamus, PCA—posterior cerebral artery, PPA—pterygopalatine artery.
3. The Thalamus and Sleep
The thalamus plays a multifaceted role in sleep regulation and involves several complex aspects (Figure 3A). Firstly, the thalamocortical circuitry is of paramount importance for the generation and coordination of electroencephalographic (EEG) rhythms during sleep. Sleep spindles, which are the cortical manifestations of thalamic neuronal oscillations, are affected in patients with thalamic stroke [58]. Section 5 provides details about the effect of thalamic lesions on sleep spindles. According to studies conducted on humans, the anterior, mediodorsal, and posterior thalamic nuclei are involved in spindle generation [47,48,49,50]. However, little is known about the thalamic contribution to functionally distinct sleep spindle subtypes, predominantly frontal slow (8–12 Hz) and predominantly parietal fast (12–16 Hz) spindles [59,60]. Fast spindles have been linked to sleep-dependent memory consolidation [60], whereas knowledge about slow spindles’ function is sparse. The neuroimaging study by Schabus et al., which showed that thalamic peak voxels for slow spindles were compatible with the mediodorsal nucleus, while peak voxels for fast spindles were compatible with the ventral posterior lateral and pulvinar nuclei, lends support to the heterogeneity in thalamic sleep spindle regulation [61].
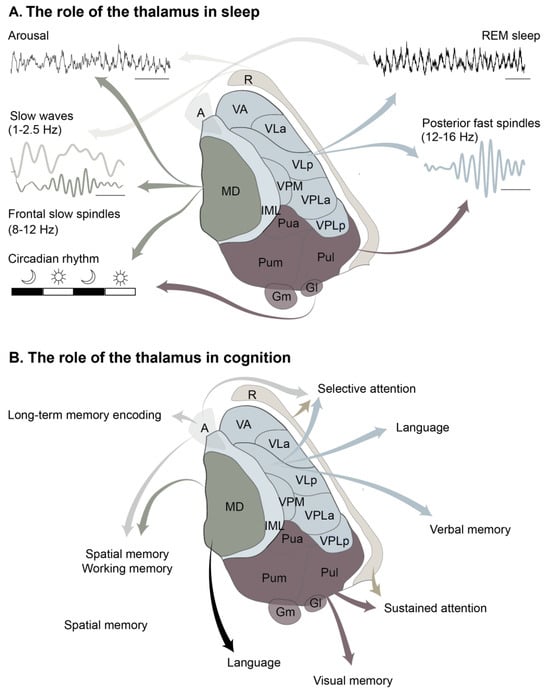
Figure 3.
The functions of the thalamus. (A) The role of the thalamus in sleep. (B) The role of the thalamus in cognition. Abbreviations: A—anterior, CL—centrolateral, CM—centromedial, ET—eminentia thalami, Gl—lateral geniculate, Gm—medial geniculate, IL—intralaminar, LD—laterodorsal, M—medial, MD—mediodorsal, PF—parafascicular, Pua—pulvinar anterior, Pul—pulvinar lateral, Pum—pulvinar medial, R—reticularis, VA—ventral anterior, VLa—ventrolateral anterior, VLp—ventrolateral posterior, VPLa—ventroposterolateral anterior, VPLa—ventroposterolateral posterior, VPM—ventroposteromedial. Parcellation adapted from Carrera [31].
Spindles originate mainly in the thalamus during sleep, and are modulated through corticothalamic and intrathalamic mechanisms [62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70], while thalamic slow waves, large-scale neuronal activity, are principally driven by global cortical activity [71]. Throughout the slow oscillations, neocortical and thalamic neurons fluctuate between periods of intense synaptic activity (up states) and almost complete silence (down states) [72]. An experimental study in naturally sleeping–waking rats showed that blocking thalamic output to the neocortex markedly (up to 50%) reduced the frequency of slow waves; however, the selective stimulation of thalamocortical neurons enhanced slow waves in a low delta frequency band (0.75–1.5 Hz) [73]. Clinical studies in thalamic stroke lesions have further contributed to the evidence for the role of the thalamus in sleep, which is emphasized in Section 5 of this review. Moreover, the evidence from intracranial recordings from human epilepsy patients demonstrated that slow oscillations in the anterior thalamus precede neocortical slow oscillations, whereas concurrently recorded slow oscillations in the mediodorsal thalamus are led by neocortical slow oscillations [74].
Thalamocortical networks, which include the reticular nucleus and the neocortex, have been shown to enhance cortical slow oscillations and decrease arousal [75]. Alternative evidence suggests that the thalamus plays a regulatory role in the states of wakefulness and alertness, operating within the context of the ascending reticular arousal system, which serves as the primary network responsible for arousal in the brain [76]. During wakefulness, this system originates in the brainstem and activates the thalamus and the cortex via a well-defined ‘bottom-up’ pathway [76]. Local interactions may also be considered, in which thalamic-layer-specific inputs into the cortex may reflect arousal degrees [77,78]. Recent studies suggest the existence of a less investigated ‘top-down’ pathway that also contributes to arousal maintenance. This ‘top-down’ pathway includes the projections from the neocortex (salience network), amygdala (to the medial geniculate nucleus), or hypothalamus to the thalamus [76,78,79,80,81,82,83]. The mediodorsal thalamus, which is part of the paramedian vascular territory, projects to the prefrontal cortex and has been identified as a key effector in the arousal circuitry [84]. Additionally, glutamatergic neurons of the paraventricular thalamus (PVT), a component of the mediodorsal thalamus, are highly active during wakefulness [81]. PVT suppression reduces wakefulness, while PVT activation induces a transition from sleep to wakefulness [81]. The projections from the nucleus accumbens and from hypocretin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus to PVT glutamatergic neurons act as effector pathways for wakefulness [81]. It has been demonstrated that stimulating the ventromedial thalamus causes awakening from NREM sleep and cortical activation [85]. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that a brainstem-to-mediodorsal thalamic glutamatergic pathway mediates sound-induced arousal from slow-wave sleep, enabling the transition to wakefulness [86]. Overall, the mediodorsal thalamus constitutes a key diencephalic node that controls forebrain arousal.
Lastly, the thalamus might regulate circadian rhythms. Experimental studies have shown that PVT is interconnected with the master circadian pacemaker, the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus, and is densely innervated by orexinergic neurons, which play a key role in arousal and state transitions [87]. Furthermore, PVT [87] and intergeniculate and ventrolateral geniculate nuclei [88] all receive direct and indirect photic input that might contribute to the transition to vigilance in response to light. Similar results were acquired by Chrobok et al., who identified the lateral geniculate nucleus as a light-entrainable oscillator, whose phase may be advanced by retinal input at the beginning of the projected night [89]. Finally, in mice, the centromedial thalamus was found to modulate transitions between sleep stages, transitions between sleep and wake, and brain-wide cortical activity during sleep [90].
Albeit less investigated, the recent evidence points to the involvement of the thalamus in the regulation of REM sleep, as it receives cholinergic activation from the brainstem during this sleep stage [91]. In mice, the optogenetic activation of neurons in the anterior dorsal thalamus increased the sleep spindle rate and the likelihood of transition to REM sleep [92]. Moreover, imaging studies of sleep have shown high activity in the thalamus during REM sleep [93,94,95], especially during phasic REM sleep [95,96]. Notably, projections from the central medial thalamus to the prefrontal cortex have been found to modulate parvalbumin cells in cortical layers 2/3, which are necessary for the consolidation of emotional memories during REM-sleep [97]. Although experimental findings suggest that the thalamus is involved in the regulation of REM sleep, no significant differences in REM sleep quantity have been observed in thalamic stroke patients [45,46,50,51]. The microarchitecture of REM sleep (e.g., saw-tooth waves) in thalamic stroke patients is still not well characterized, and this topic may open new avenues for future research.
4. The Thalamus and Cognition
Clinical studies have greatly advanced our understanding of the role of the thalamus in cognition and consciousness [42,57,60,65,93]. Section 5 provides insights into the impact of thalamic vascular lesions on sleep and cognition.
Based on corroborating works in the clinical literature, experimental studies conducted on rodents have demonstrated that lesions in the anterior thalamic nucleus result in substantial deficits in reference, spatial, and working memory. Supporting the clinical literature, experimental studies in rodents have demonstrated that the lesions of the anterior thalamic nucleus led to substantial deficits in reference, spatial, and working memory [98,99]. Consequently, the lesions of the anterior thalamic nucleus disrupted the processing of environmental cues and the monitoring of the position of the animal within the environment [100]. These spatial impairments align with the electrophysiological properties of the anterior thalamic nucleus, which contains cells encoding information about spatial location [101,102,103]. A study in mice has confirmed that the anteroventral subdivision of the anterior thalamic nucleus is required during the maintenance phase of a spatial working memory task. This function engages the anteroventral–parasubiculum–entorhinal cortex circuit [101,102,103]. Moreover, the lesions of the anterior thalamic nucleus impair performance when animals are expected to combine item memory with additional features, like temporal order and location [104,105]. The anteromedial thalamus preferentially encodes salient memories and gradually increases correlations with the cortex to facilitate the tuning and synchronization of cortical ensembles, as well as the gating of long-term memory consolidation in the cortex [106].
Similarly, lesions of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus in rodents cause impairments in spatial and temporal discrimination [107], but temporal order memory impairments following the lesions of the anterior thalamic nucleus emerge only in the presence of multiple items [108,109]. While the lesions of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus disrupt performance in spatial and working memory tasks, this is due to strategic components of the task rather than deficiencies in spatial memory [110]. Remarkably, memory deficits were correlated with spindle and slow wave decline following opto-stroke [54]. This supports the prevailing assumption that the mediodorsal thalamus plays a crucial role in working memory due to its projections to the prefrontal cortex [111,112].
The thalamus regulates attentional selection, and all major components appear to be involved. A functional magnetic resonance imaging study in healthy volunteers showed the role of the ventrolateral and, notably, anterior thalamus in biasing attention [113]. Responses in the ventrolateral and anterior thalamic nuclei tracked the learning of the predictiveness of abstract associations and their application in directing attention [113]. Moreover, a study in epileptic patients demonstrated that the high frequency electric stimulation of the anterior thalamus improved attentional capture by emotional stimuli [114]. According to an experimental study in ferrets, theta oscillations in the posterior thalamus play a central role in orchestrating thalamic signaling during sustained attention [114]. Using multi-electrode recordings in mice, Chen et al. demonstrated that the neurons of the thalamic reticular nucleus, which are associated with sleep spindles, were also linked to alpha oscillations during attention [115].
Figure 3 provides a simplified summary of the role of the thalamus in cognition based on reports in human and animal models.
5. Thalamic Stroke: A Model for Sleep-Dependent Plasticity and Cognition
Table 1 outlines how thalamic stroke can cause a wide range of SWD and cognitive deficits. Given the profound impact that sleep and cognitive functioning have on the recovery process and overall quality of life after stroke, medical practitioners could derive significant advantages from understanding these symptoms.
Hypersomnolence is a distinguishing feature of sleep symptoms associated with thalamic stroke. This phenomenon, which has been well-documented in multiple case–control studies and case reports, is particularly prevalent in patients with anterior (80%) and paramedian (50%) thalamic stroke [53]. In some cases, hypersomnolence may manifest as up to 20 h of daily sleep behavior [116]. Moreover, patients with thalamic stroke may exhibit the symptoms of excessive daytime sleepiness [117]. Specifically, an Epworth Sleepiness Scale score in thalamic stroke patients was reported as a mean of 8–9 points, compared to 5–6 in the control group (extrathalamic and no-stroke) [49,51]. The stroke restricted to paramedian thalamus was described as being associated with severe arousal disturbances. In the case of a patient with bilateral thalamic stroke, the arousal index, both in NREM and REM sleep, was lower in acute stroke compared to 6 weeks post-stroke [118].
These sleep alterations were mostly linked with the features of non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep in thalamic stroke patients. Individuals with paramedian thalamic stroke and severe hypersomnia, for example, experienced a reduced quantity of slow-wave NREM3 sleep [116]. The reduction in NREM2 and NREM3 in thalamic stroke patients was also described in comparison to an age- and sex-matched no-stroke control group [45,49]. Overall, vigilance disturbances are more common in patients with bilateral paramedian compared to unilateral paramedian thalamic stroke (92% versus 21%) [119].
There is consistent evidence that thalamic stroke alters NREM-sleep microarchitecture. Several studies reported the decrease in slow spindle density and power in thalamic stroke patients [45,46,50]. Sleep spindles were the most affected in frontal and central regions [46]. Mensen et al. showed that left-sided and bilateral lesions of the paramedian thalamus affect sleep spindles to the larger extent compared to right-sided lesions using high-density electroencephalography (hd-EEG) [50]. However, since the study is small (N = 9) and the authors do not report the lesion volume, the effect of the lesion volume rather than its laterality on sleep spindles cannot be ruled out. An additional hd-EEG study showed the reduced overnight slow wave (SW) slope changes in thalamic versus extrathalamic stroke [51]. Interestingly, the subjective sleepiness in these patients tended to be high in patients with a pronounced reduction in overnight slope changes [51].
Considering the well-known role of sleep spindles and slow waves in neuroplasticity [60,120], changes in NREM-sleep microarchitecture following thalamic stroke might underlie the cognitive deficits described in these patients. However, the primary impact of the thalamic lesion on these cognitive deficits remains unclear.
Among the most noteworthy cognitive manifestations in thalamic stroke are thalamic amnesia and thalamic dementia. Thalamic amnesia, a memory impairment unique to thalamic stroke, often results in deficits in verbal and working memory, but not in visual memory [46,47,49,53]. Danet et al. showed that lesions of the mammillothalamic tract and of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus cause memory impairment, more severely in the case of the mammillothalamic tract and less so in the case of the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus, thus highlighting the role played by these two structures in memory circuits [47]. In addition, verbal memory deficits have been attributed to lesions in anterior and inferolateral vascular territories, whereas visual memory impairments have been reported in lesions affecting posterior territory [43,46,48,53].
In contrast, thalamic dementia—typically caused by anterior or paramedian thalamic stroke [46,53,121,122] —is characterized by temporal and spatial disorientation, behavioral changes (e.g., agitation or apathy), the impairment of executive functions (e.g., abstract thinking, working memory, cognitive flexibility), attentional deficits, and the relative preservation of motor or sensory functions [46,121,122,123,124,125]. Such complex impairments accentuate the role of the thalamus in diverse cognitive functions.
Moreover, other deficits of high brain functions have been described in thalamic stroke and have been attributed to specific lesion topography. Cohort studies have reported instances of mood lability, including depression and anxiety in thalamic stroke patients [46,121,122,123,124,125]. However, the evidence concerning the association of mood disturbances with thalamic stroke topography is limited. Liebermann et al. showed that patients with lesions of the posterior thalamus had significantly more emotional disturbances and elevated anxiety levels (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Anxiety Score) than patients with anterior lesions [126], whereas the recent study by Scharf et al. showed the association of depression and anxiety (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Anxiety and Depression Score) with anterior but not paramedian or inferolateral thalamic stroke [127]. These affective disturbances, while multifactorial, emphasize the role of the thalamus in emotional regulation.
Lastly, disinhibition syndromes, including delirium or inappropriate behaviors, have been reported in thalamic stroke, specifically paramedian stroke [31,128,129]. These data indicated that the involvement of the dorsomedian nucleus, intralaminar nuclei, and medial part of the ventral lateral nucleus in the modulation of social behaviors and impulse regulation.
Mounting evidence points to the role of REM sleep in cognition and emotional regulation. Although cognitive disturbances in thalamic stroke have been linked to the changes in NREM-sleep, emotional disturbance might indicate the involvement of REM sleep. While the studies in thalamic stroke patients did not demonstrate statistically significant differences in the quantity of REM sleep, knowledge of the microarchitecture of REM sleep in thalamic stroke patients is limited (as shown in Table 1). Future studies should focus on the inclusion of REM sleep as a possible contributor to cognitive and emotional disorders, especially in patients with medial and anterior thalamic stroke.
Despite the consistent evidence of the influence of the thalamic lesion per se on sleep and cognition, recent advances in stroke animal models (see Box 1 and Figure 2) allow precise experimental control and enable researchers to observe the effects of the manipulation of specific thalamic circuits on sleep and cognition [54,92,130,131,132].
Lenzi et al. adopted the following approach, using an “opto-Stroke” model (shown in Figure 2) to selectively induce a lesion in the medial thalamus [54]. Their study in mice effectively replicated the reduction in NREM sleep and increased sleep instability, common in patients with medial thalamic stroke [54]. Furthermore, a lesion in the medial thalamus reduced alpha EEG power during transitions from wakefulness to NREM sleep as well as a significant reduction in frontal sleep spindle power, which was positively correlated with deficiencies in working memory [54]. Interestingly, there was no alteration in motor performance and anxiety, highlighting the specificity of the effects related to medial thalamic lesions [54].
These investigations underline the value of animal models in understanding the role of the thalamus in sleep and cognition and offer the opportunity for invasive measurements and interventions that are not feasible in human studies.
6. The Thalamus and the Interaction between Sleep and Cognition
The thalamus might modulate the association between healthy sleep and cognition.
Firstly, as previously mentioned, the thalamus participates in the regulation of local sleep oscillations during NREM sleep, such as sleep spindles and slow waves. These local sleep oscillations are associated with memory consolidation during sleep [133,134], learning [135,136,137], and executive functions [138,139], possibly providing the environment for neuroplasticity and cellular homeostasis [70,140]. In a general sample of stroke patients, Siccolli et al. described a correlation between the amount of slow-wave sleep and REM sleep with attention at acute stroke and with verbal and visual memory at subacute stroke [141]. Despite not achieving statistical significance, a study in patients with isolated thalamic stroke found deficits in the short-term visual memory of patients with diminished nighttime slope changes, suggesting a central role of the thalamus in synaptic renormalization [51].
Overall, thalamic stroke patients often exhibit incomplete neurological and functional recovery [46,53]. Based on the findings from Jaramillo et al. [51], this could be pathophysiologically attributed to the reduced neuroplasticity related to changes in sleep. Hermann et al. showed that patients with incomplete recovery from chronic stroke had a high need for sleep both immediately after their stroke and after one year, even though there was no association between stroke outcome and the severity of neurological symptoms, sleep efficiency, and sleep architecture [46]. Anterior and paramedian thalamic stroke is associated with the most significant changes in sleep (see above). However, Scharf et al. reported a satisfactory cognitive recovery in patients with anterior and paramedian thalamic stroke, whereas the recovery in patients with inferolateral thalamic stroke was incomplete [53]. This discrepancy could be attributed to different compensatory mechanisms (e.g., multiple centers in the brain with homologous functions), or recovery potentials (e.g., good synaptic plasticity due to the vascular collaterals). Moreover, the inferolateral region has been implicated in the control of fast sleep spindle activity [61]. In turn, fast sleep spindle activity has been shown to be essential for sleep-dependent neuroplasticity [142] compared to slow spindle activity emerging from the mediodorsal thalamic nucleus [61].
Secondly, while REM microarchitecture was not reported in thalamic stroke patients, evidence from translational studies points to the involvement of the thalamus in the regulation of REM sleep [93,94]. REM sleep, in turn, provides an environment for the synaptic remodeling essential to cognitive functioning by activating salient features such as ponto-geniculo-occipital waves, theta synchrony, and the increased transcription of plasticity-related genes [143].
Certain chronic sleep–wake disorders, such as insomnia [144], sleep-disordered breathing [145], and narcolepsy [146], have been associated with long-term changes in the thalamocortical circuitry that might lead to cognitive dysfunction, with sleep patterns and cognitive changes resembling those seen in thalamic stroke patients. Excessive daytime sleepiness, for example, is a common symptom of sleep–wake disorders. It is often accompanied by attention deficits [147] and may foreshadow cognitive decline [148]. Plante et al. described the association between excessive daytime sleepiness and the reduced resting-state connectivity between the bilateral thalamus and left rostral striatum (caudate/putamen) [149]. Moreover, excessive daytime sleepiness was shown to be related to the disrupted dopaminergic and serotonergic modulation of the thalamus [146,150].
Overall, this evidence emphasizes the crucial role of the thalamus in the modulation of the association between healthy sleep and cognition through the regulation of local sleep oscillations and through the contribution to synaptic remodeling and neuroplasticity. Furthermore, the evidence from patients suffering from thalamic stroke and other sleep–wake disorders further suggests that disruptions in thalamocortical circuitry may result in cognitive dysfunction.
7. Thalamic Dynamics as the Window of Opportunity
Understanding the complex relationship between the thalamus, sleep, and cognition provides us with valuable insights into potential therapeutic interventions for cognitive impairment linked to sleep. Consequently, targeting the thalamus appears to be a promising approach to enhance both sleep and cognition in neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Although existing drugs that influence major neurotransmitter systems in the thalamus, such as GABA or glutamate, play vital roles in regulating cognition, sleep, and wakefulness [151], there is still room to explore alternative clinical approaches that may offer new options. Some examples are provided below.
Neuromodulation by Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) involves the surgical implantation of an electrode to transmit electrical impulses to specific parts of the brain. DBS has been utilized to treat various neurological conditions (e.g., Parkinson’s disease and epilepsy) [152]. It may help to restore normal thalamocortical activity if applied to the thalamus, potentially improving sleep and cognition. Buenzli et al. showed that DBS applied to the anterior nucleus of the thalamus increased slow wave activity in NREM sleep [153].
The experimental study in mice showed a proof-of-principle restoration of electrophysiologic and behavioral measures of consciousness with a stimulation of intralaminar thalamic nuclei after seizures [154]. Moreover, the stimulation of the auditory thalamus could generate auditory percepts [155,156], and this finding is being investigated for potential treatments for conditions such as tinnitus [157].
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain [158] and can be applied to target the thalamus. However, applying TMS to deeper structures like the thalamus remains challenging, and hence continued research is needed to develop effective protocols. A recent trial demonstrated an antalgic effect of TMS for 10 consecutive days in patients with thalamic pain [159]. Moreover, potential alternative targeting areas for TMS have surfaced. Targeting the cerebellum, which projects to the thalamus, for example, showed promising results in the treatment of various neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions, including ataxia, essential tremor, dystonia, depression, schizophrenia, and autism spectrum disorders [160]. However, further research is needed to uncover the therapeutic potential of TMS, including the optimal stimulation protocols and long-term consequences.
Neurofeedback is a type of biofeedback that uses real-time displays of brain activity—most commonly, EEG—to teach the self-regulation of brain function [161]. Individuals who learn to consciously control their thalamocortical activity may potentially improve sleep and cognition. Bearden at al. reported that biofeedback training improved EEG characteristics in a patient with thalamic and cortical stroke [154,162]. The trial of the real-time functional MRI neurofeedback showed an increase in the activity of mediodorsal thalamic nuclei and posterior alpha EEG power [163].
8. Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the thalamus is a true powerhouse for the regulation of sleep and cognition, with involvements spanning across multiple aspects.
Clinical and experimental models have supported the role of the thalamus in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. Mounting evidence indicates its involvement in the generation and synchronization of sleep rhythms, with the anterior and medial parts recently being highlighted. Key studies have addressed the complex task of the circuit dissection in order to distinguish the contribution of different thalamic nuclei to specific cognitive domains, including sleep-dependent memory consolidation and emotional regulation. Concurrently, functional imaging and clinical studies have further supported the topographic role of different thalamic nuclei to these important physiological processes.
It is essential to recognize the large impact of thalamic dynamics on the regulation of NREM sleep and sleep-dependent physiological processes. Nevertheless, recent research has revealed a gap in our understanding of the involvement of the thalamus in regulating REM sleep and REM-dependent cognitive functions, such as emotional regulation. This knowledge gap presents an excellent opportunity for further exploration and investigation.
Furthermore, the thalamus participates in arousal regulation through the ascending reticular arousal system. The thalamus also influences circadian rhythms and facilitates transitions between different sleep stages. It remains unclear whether sleep–wake alterations in thalamic stroke are caused by a homeostatic sleep drive, sleep fragmentation, or imbalances in neurotransmitter systems, like serotonin and GABA, that have a strong impact on state transition. The field of stroke research, both clinically and experimentally, offers a promising pathway for addressing these numerous unanswered inquiries.
The thalamus is essential for cognitive function. The anterior and mediodorsal thalamic nuclei are vital for memory and executive functioning, whereas other thalamic areas are crucial for attention. Given the overlap in the functions of different thalamic regions, further investigation into the specific involvement of thalamic nuclei in cognition is required, especially with the rodent models allowing specific nuclei targeting.
The interaction between sleep and cognition is complex, and disruptions in thalamocortical circuitry associated with chronic sleep–wake disorders can contribute to cognitive impairments and impede recovery from thalamic stroke. Since therapeutic approaches targeting the thalamus hold promise in improving sleep and cognition in individuals with neurological and psychiatric disorders, the detailed shifts in EEG dynamics following thalamic stroke and their cascading effects on sleep and cognitive functions warrant further exploration.
We are currently on the cusp of technological advancements that, when combined with novel improvements in computational modeling, will enable us to predict recovery based on EEG patterns and implement non-invasive therapeutic approaches. Sleep provides an opportunity to improve plasticity and to restore proper brain dynamics observed in neurological disorders.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, I.F. and C.G.H.; review and editing, I.F. and C.G.H.; visualization, I.F. and C.G.H.; supervision, C.L.A.B. and C.G.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the University of Bern Interfaculty Research Collaboration Grant “Decoding Sleep” and by the European Stroke Research Foundation (year 2021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank A. Adamantidis for the insightful discussion and his comments on previous versions of this review.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jak, A.J.; Bondi, M.W.; Delano-Wood, L.; Wierenga, C.; Corey-Bloom, J.; Salmon, D.P.; Delis, D.C. Quantification of five neuropsychological approaches to defining mild cognitive impairment. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2009, 17, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nys, G.M.S.; Van Zandvoort, M.J.E.; De Kort, P.L.M.; Jansen, B.P.W.; De Haan, E.H.F.; Kappelle, L.J. Cognitive disorders in acute stroke: Prevalence and clinical determinants. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2007, 23, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.W.; Kennedy, S.H.; McIntyre, R.S.; Khullar, A. Cognitive dysfunction in major depressive disorder: Effects on psychosocial functioning and implications for treatment. Can. J. Psychiatry 2014, 59, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Ren, Q. Sleep disorders affect cognitive function in adults: An overview of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Sleep Biol. Rhythms. 2023, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinzing, J.G.; Niethard, N.; Born, J. Mechanisms of systems memory consolidation during sleep. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.I.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.C.; Groeger, J.A.; Cheng, G.H.; Dijk, D.J.; Chee, M.W.L. Self-reported sleep duration and cognitive performance in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2016, 17, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.; Bucks, R.S. Memory and obstructive sleep apnea: A meta-analysis. Sleep 2013, 36, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Huang, X.; Yu, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, Y.; Tang, B.; Guo, J. Association between REM Sleep Behavior Disorder and Cognitive Dysfunctions in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 577874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguinchona, J.H.; Tadi, P. Neuroanatomy, Reticular Activating System; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild, G.; Eban, E.; Frank, L.M. A cortical-hippocampal-cortical loop of information processing during memory consolidation. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Moroni, F.; De Gennaro, L.; Nobili, L. Hippocampal sleep features: Relations to human memory function. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, W.; Ma, Y.; Tossell, K.; Harris, J.J.; Harding, E.C.; Ba, W.; Miracca, G.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; et al. GABA and glutamate neurons in the VTA regulate sleep and wakefulness. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmond, C.H.; Chatfield, D.A.; Menon, D.K.; Pickard, J.D.; Sahakian, B.J. Cognitive sequelae of head injury: Involvement of basal forebrain and associated structures. Brain 2005, 128, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaclet, C.; Pedersen, N.P.; Ferrari, L.L.; Venner, A.; Bass, C.E.; Arrigoni, E.; Fuller, P.M. Basal forebrain control of wakefulness and cortical rhythms. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, E.B.; Oren, N.; Sharon, H.; Kirschner, A.; Goldway, N.; Okon-Singer, H.; Tauman, R.; Deweese, M.M.; Keil, A.; Hendler, T. Losing neutrality: The neural basis of impaired emotional control without sleep. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 13194–13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, C.J.; Daniel Salzman, C. The Amygdala and basal forebrain as a pathway for motivationally guided attention. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 13757–13767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motomura, Y.; Kitamura, S.; Nakazaki, K.; Oba, K.; Katsunuma, R.; Terasawa, Y.; Hida, A.; Moriguchi, Y.; Mishima, K. Recovery from unrecognized sleep loss accumulated in daily life improved mood regulation via prefrontal suppression of amygdala activity. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudai, Y.; Karni, A.; Born, J. The Consolidation and Transformation of Memory. Neuron 2015, 88, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tononi, G.; Cirelli, C. Sleep and the Price of Plasticity: From Synaptic and Cellular Homeostasis to Memory Consolidation and Integration. Neuron 2014, 81, 12–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekelmann, S.; Born, J. The memory function of sleep. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; MacLean, R.R. Neurobiological mechanisms for the regulation of mammalian sleep–wake behavior: Reinterpretation of historical evidence and inclusion of contemporary cellular and molecular evidence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 775–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, M.P.; Stickgold, R. Sleep-Dependent Learning and Memory Consolidation. Neuron 2004, 44, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maquet, P. The Role of Sleep in Learning and Memory. Science 2001, 294, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibt, J.; Richard, C.J.; Sigl-Glöckner, J.; Takahashi, N.; Kaplan, D.I.; Doron, G.; de Limoges, D.; Bocklisch, C.; Larkum, M.E. Cortical dendritic activity correlates with spindle-rich oscillations during sleep in rodents. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirota, A.; Buzsáki, G. Interaction between neocortical and hippocampal networks via slow oscillations. Thalamus Relat. Syst. 2005, 3, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, H.-V.; Fell, J.; Staresina, B. Sleep spindles mediate hippocampal-neocortical coupling during long-duration ripples. Elife 2020, 9, e57011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieve, K.L.; Acuña, C.; Cudeiro, J. The primate pulvinar nuclei: Vision and action. Trends Neurosci. 2000, 23, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percheron, G.; Franqois, C.; Talbi, B.; Yelnik, J.; Ffnelon, G. The primate motor thalamus. Brain Res. Rev. 1996, 22, 93–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griin, A.L.; Piriz, J.; Ferbinteanu, J.; Vertes, R.P. Structural and functional organization of the midline and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 6, 964644. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera, E.; Bogousslavsky, J. The thalamus and behavior: Effects of anatomically distinct strokes. Neurology 2006, 66, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.B. Evolution of the thalamus: A morphological and functional review. Thalamus Relat. Syst. 2008, 4, 35–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.M.; Kambi, N.A.; Redinbaugh, M.J.; Mohanta, S.; Saalmann, Y.B. Disentangling the influences of multiple thalamic nuclei on prefrontal cortex and cognitive control. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 128, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicht, H.; Himstedt, W. Topologic and Connectional Analysis of the Dorsal Thalamus of Rturus alpestris (Amphibia, Urodela, Salamandridae). J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 267, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, M.M.; Ronnqvist, K.C.; Tsanov, M.; Vann, S.D.; Wright, N.F.; Erichsen, J.T.; Aggleton, J.P.; O’Mara, S.M. The anterior thalamus provides a subcortical circuit supporting memory and spatial navigation. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, J.K.; Majtanik, M. Toward a common terminology for the Thalamus. Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, J.H.; Baldwin, M.K.L. The evolution of the pulvinar complex in primates and its role in the dorsal and ventral streams of cortical processing. Vision 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, M.K.L.; Balaram, P.; Kaas, J.H. The evolution and functions of nuclei of the visual pulvinar in primates. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 3207–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teffer, K.; Semendeferi, K. Human prefrontal cortex: Evolution, development, and pathology. Prog. Brain Res. 2012, 195, 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saper, C.B.; Scammell, T.E.; Lu, J. Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms. Nature 2005, 437, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Ramanathan, L.; Siegel, J.M. Rapid changes in glutamate levels in the posterior hypothalamus across sleep-wake states in freely behaving rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R2041–R2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Kahn, M.C.; Prius-Mengual, J.; Meijer, E.; Šabanović, M.; Guillaumin, M.C.C.; van der Vinne, V.; Huang, Y.G.; McKillop, L.E.; Jagannath, A.; et al. The hypothalamic link between arousal and sleep homeostasis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101580118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmahmann, J.D. Vascular syndromes of the thalamus. Stroke 2003, 34, 2264–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Li, A.; Lou, Y.; Chen, S.; Long, B.; Peng, J.; Yang, Z.; Xu, T.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; et al. Precise Cerebral Vascular Atlas in Stereotaxic Coordinates of Whole Mouse Brain. Front. Neuroanat. 2017, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria, J.; Pujol, M.; Orteu, N.; Solanas, A.; Cardenal, C.; Santacruz, P.; Chimeno, E.; Moon, P. Unilateral thalamic stroke does not decrease ipsilateral sleep spindles. Sleep 2000, 23, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, D.M.; Siccoli, M.; Brugger, P.; Wachter, K.; Mathis, J.; Achermann, P.; Bassetti, C.L. Evolution of neurological, neuropsychological and sleep-wake disturbances after paramedian thalamic stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danet, L.; Barbeau, E.J.; Eustache, P.; Planton, M.; Raposo, N.; Sibon, I.; Albucher, J.F.; Bonneville, F.; Peran, P.; Pariente, J. Thalamic amnesia after infarct. Neurology 2015, 85, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, A.; Irlbacher, K.; Finke, K.; Kaufmann, C.; Kehrer, S.; Liebermann, D.; Bundesen, C.; Brandt, S.A. Dissociable spatial and non-spatial attentional deficits after circumscribed thalamic stroke. Cortex 2015, 64, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Cui, L.; Fu, Y.; Tian, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Du, N.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Song, Y.; et al. Sleep and Cognitive Abnormalities in Acute Minor Thalamic Infarction. Neurosci. Bull. 2016, 32, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensen, A.; Poryazova, R.; Huber, R.; Bassetti, C.L. Individual spindle detection and analysis in high-density recordings across the night and in thalamic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, V.; Jendoubi, J.; Maric, A.; Mensen, A.; Heyse, N.C.; Eberhard-Moscicka, A.K.; Wiest, R.; Bassetti, C.L.; Huber, R. Thalamic Influence on Slow Wave Slope Renormalization during Sleep. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 90, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temel, M.; Polat, B.S.A.; Kayali, N.; Karadas, O. Cognitive profile of patients with thalamic hemorrhage according to lesion localization. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Dis. Extra 2021, 11, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, A.C.; Gronewold, J.; Todica, O.; Moenninghoff, C.; Doeppner, T.R.; de Haan, B.; Bassetti, C.L.; Hermann, D.M. Evolution of Neuropsychological Deficits in First-Ever Isolated Ischemic Thalamic Stroke and Their Association with Stroke Topography: A Case-Control Study. Stroke 2022, 53, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzi, I.; Borsa, M.; Czekus, C.; Rusterholz, T.; Bassetti, C.L.; Gutierrez Herrera, C. Optical mini-stroke of thalamic networks impairs sleep stability, topography and cognition. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.G.; Xavier, G.F. Anterior thalamic NMDA-induced damage impairs extrapolation relying on serial stimulus patterns, in rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2021, 185, 107536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, F.; Hérisson, F.; Wang, S.; Mao, J.; Ayata, C. Late-Onset Thermal Hypersensitivity after Focal Ischemic Thalamic Infarcts as a Model for Central Post-Stroke Pain in Rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.H.; Liu, K.-F.; Ho, K.-L. Neuronal Necrosis after Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Wistar Rats Progresses at Different Time Intervals in the Caudoputamen and the Cortex. Stroke 1995, 26, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steriade, M. Sleep oscillations in corticothalamic neuronal networks and their development into self-sustained paroxysmal activity. Rom. J. Neurol. Psychiatry 1993, 31, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warby, S.C.; Wendt, S.L.; Welinder, P.; Munk, E.G.S.; Carrillo, O.; Sorensen, H.B.D.; Jennum, P.; Peppard, P.E.; Perona, P.; Mignot, E. Sleep-spindle detection: Crowdsourcing and evaluating performance of experts, non-experts and automated methods. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, R.; Schapiro, A.C.; Manoach, D.S.; Stickgold, R. Individual Differences in Frequency and Topography of Slow and Fast Sleep Spindles. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schabus, M.; Dang-Vu, T.T.; Albouy, G.; Balteau, E.; Boly, M.; Carrier, J.; Darsaud, A.; Degueldre, C.; Desseilles, M.; Gais, S.; et al. Hemodynamic cerebral correlates of sleep spindles during human non-rapid eye movement sleep. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13164–13169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak-Mccully, R.A.; Rolland, M.; Sargsyan, A.; Gonzalez, C.; Magnin, M.; Chauvel, P.; Rey, M.; Bastuji, H.; Halgren, E. Coordination of cortical and thalamic activity during non-REM sleep in humans. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthi, A. Sleep Spindles. Neuroscientist 2014, 20, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osorio-Forero, A.; Cardis, R.; Vantomme, G.; Guillaume-Gentil, A.; Katsioudi, G.; Devenoges, C.; Fernandez, L.M.J.; Lüthi, A. Noradrenergic circuit control of non-REM sleep substates. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 5009–5023.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantomme, G.; Osorio-Forero, A.; Lüthi, A.; Fernandez, L.M.J. Regulation of Local Sleep by the Thalamic Reticular Nucleus. Front Neurosci. 2019, 13, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-García, M.; Wallman, M.-J.; Timofeev, I. Somatotopic organization of ferret thalamus. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeev, I.; Chauvette, S. The Spindles: Are They Still Thalamic? Sleep 2013, 36, 825–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halassa, M.M.; Chen, Z.; Wimmer, R.D.; Brunetti, P.M.; Zhao, S.; Zikopoulos, B.; Wang, F.; Brown, E.N.; Wilson, M.A. State-Dependent Architecture of Thalamic Reticular Subnetworks. Cell 2014, 158, 808–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonjean, M.; Baker, T.; Lemieux, M.; Timofeev, I.; Sejnowski, T.; Bazhenov, M. Corticothalamic Feedback Controls Sleep Spindle Duration In Vivo. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9124–9134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, L.M.J.; Lüthi, A. Sleep spindles: Mechanisms and functions. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 100, 805–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujma, P.P.; Szalárdy, O.; Fabó, D.; Erőss, L.; Bódizs, R. Thalamic activity during scalp slow waves in humans. Neuroimage 2022, 257, 119325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neske, G.T. The slow oscillation in cortical and thalamic networks: Mechanisms and functions. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, F.; Schmiedt, J.T.; Taylor, H.L.; Orban, G.; Di Giovanni, G.; Uebele, V.N.; Renger, J.J.; Lambert, R.C.; Leresche, N.; Crunelli, V. Essential thalamic contribution to slow waves of natural sleep. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 19599–19610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiner, T.; Kaufmann, E.; Noachtar, S.; Mehrkens, J.H.; Staudigl, T. The human thalamus orchestrates neocortical oscillations during NREM sleep. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, L.D.; Voigts, J.; Flores, F.J.; Ian Schmitt, L.; Wilson, M.A.; Halassa, M.M.; Brown, E.N. Thalamic reticular nucleus induces fast and local modulation of arousal state. Elife 2015, 4, e08760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krone, L.; Frase, L.; Piosczyk, H.; Selhausen, P.; Zittel, S.; Jahn, F.; Kuhn, M.; Feige, B.; Mainberger, F.; Klöppel, S.; et al. Top-down control of arousal and sleep: Fundamentals and clinical implications. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 31, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redinbaugh, M.J.; Phillips, J.M.; Kambi, N.A.; Mohanta, S.; Andryk, S.; Dooley, G.L.; Afrasiabi, M.; Raz, A.; Saalmann, Y.B. Thalamus Modulates Consciousness via Layer-Specific Control of Cortex. Neuron 2020, 106, 66–75.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halassa, M.M.; Kastner, S. Thalamic functions in distributed cognitive control. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppla, C.A.; Keyes, L.R.; Glober, G.; Matthews, G.A.; Batra, K.; Jay, M.; Feng, Y.; Chen, H.S.; Mills, F.; Delahanty, J.; et al. Thalamus sends information about arousal but not valence to the amygdala. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.K.; Dunlop, K.; Downar, J. Cortico-striatal-thalamic loop circuits of the salience network: A central pathway in psychiatric disease and treatment. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, Y.; Yue, F.; Cheng, X.; Dang, R.; Qiao, Q.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, Q.; Yao, J.; et al. The paraventricular thalamus is a critical thalamic area for wakefulness. Science 2018, 362, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergola, G.; Danet, L.; Pitel, A.-L.; Carlesimo, G.A.; Segobin, S.; Pariente, J.; Suchan, B.; Mitchell, A.S.; Barbeau, E.J. The Regulatory Role of the Human Mediodorsal Thalamus. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2018, 22, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saper, C.B.; Fuller, P.M. Wake–sleep circuitry: An overview. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 44, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnaudeau, S.; Bolkan, S.S.; Kellendonk, C. The Mediodorsal Thalamus: An Essential Partner of the Prefrontal Cortex for Cognition. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz, J.T.; Christian, C.A.; Parada, I.; Prince, D.A.; Huguenard, J.R. Focal Cortical Infarcts Alter Intrinsic Excitability and Synaptic Excitation in the Reticular Thalamic Nucleus. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 5465–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, A.; Park, S.; Shin, W.; Woo, J.; Jeong, M.; Kim, J.; Kim, D. A brainstem-to-mediodorsal thalamic pathway mediates sound-induced arousal from slow-wave sleep. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 875–885.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colavito, V.; Tesoriero, C.; Wirtu, A.T.; Grassi-Zucconi, G.; Bentivoglio, M. Limbic thalamus and state-dependent behavior: The paraventricular nucleus of the thalamic midline as a node in circadian timing and sleep/wake-regulatory networks. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 54, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, O.; Gelegen, C.; Sully, P.; Salgarella, I.; Jager, P.; Menage, L.; Mehta, I.; Jęczmień-Łazur, J.; Djama, D.; Strotheret, L.; et al. A Role for Thalamic Projection GABAergic Neurons in Circadian Responses to Light. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 9158–9179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrobok, L.; Pradel, K.; Janik, M.E.; Sanetra, A.M.; Bubka, M.; Myung, J.; Rahim, A.R.; Klich, J.D.; Jeczmien-Lazur, J.; Palus-Chramiec, K.; et al. Intrinsic circadian timekeeping properties of the thalamic lateral geniculate nucleus. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 3306–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, T.C.; Bandarabadi, M.; Herrera, C.G.; Adamantidis, A.R. Thalamic dual control of sleep and wakefulness. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, M.; Sakai, K.; Jouvet, M. Bulbo-thalamic neurons related to thalamocortical activation processes during paradoxical sleep. Exp. Brain Res. 1984, 54, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarabadi, M.; Herrera, C.G.; Gent, T.C.; Bassetti, C.; Schindler, K.; Adamantidis, A.R. A role for spindles in the onset of rapid eye movement sleep. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maquet, P.; Peters, J.M.; Aerts, J.; Delfiore, G.; Degueldre, C.; Luxen, A.; Franck, G. Functional neuroanatomy of human rapid-eye-movement sleep and dreaming. Nature 1996, 383, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchsbaum, M.S.; Hazlett, E.A.; Wu, J.; Bunney, W.E. Positron emission tomography with deoxyglucose-F18 imaging of sleep. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, S50–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, A. Regional cerebral blood flow throughout the sleep-wake cycle. An H2(15)O PET study. Brain 1997, 120, 1173–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehrle, R.; Kaufmann, C.; Wetter, T.C.; Holsboer, F.; Auer, D.P.; Pollmächer, T.; Czisch, M. Functional microstates within human REM sleep: First evidence from fMRI of a thalamocortical network specific for phasic REM periods. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, M.; Calcini, N.; Borsa, M.; Campelo, T.; Rusterholz, T.; Sattin, A.; Fellin, T.; Adamantidis, A. Paradoxical somatodendritic decoupling supports cortical plasticity during REM sleep. Science 2022, 376, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, E.C.; Aggleton, J.P. Differential deficits in the Morris water maze following cytotoxic lesions of the anterior thalamus and fornix transection. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 98, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frohardt, R.J.; Bassett, J.P.; Taube, J.S. Path integration and lesions within the head direction cell circuit: Comparison between the roles of the anterodorsal thalamus and dorsal tegmental nucleus. Behav. Neurosci. 2006, 120, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Groen, T.; Kadish, I.; Michael Wyss, J. Role of the anterodorsal and anteroventral nuclei of the thalamus in spatial memory in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 132, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurens, J.; Kim, B.; Dickman, J.D.; Angelaki, D.E. Gravity orientation tuning in macaque anterior thalamus. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1566–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsanov, M.; Chah, E.; Vann, S.D.; Reilly, R.B.; Erichsen, J.T.; Aggleton, J.P.; O’Mara, S.M. Theta-modulated head direction cells in the rat anterior thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9489–9502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, M.M.; Passecker, J.; Islam, N.; Vann, S.; Erichsen, J.T.; Aggleton, J.P.; O’Mara, S.M. Evidence for spatially-responsive neurons in the rostral thalamus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doumont, J.R.; Aggleton, J.P. Dissociation of recognition and recency memory judgments after anterior thalamic nuclei lesions in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2013, 127, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.J.D.; Vann, S.D. Mammilliothalamic tract lesions disrupt tests of visuo-spatial memory. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 128, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toader, A.C.; Regalado, J.M.; Li, Y.R.; Terceros, A.; Yadav, N.; Kumar, S.; Satow, S.; Hollunder, F.; Bonito-Oliva, A.; Rajasethupathy, P. Anteromedial thalamus gates the selection and stabilization of long-term memories. Cell 2023, 186, 1369–1381.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, L.; Brown, M.W.; Aggleton, J.P.; Warburton, E.C. The medial dorsal thalamic nucleus and the medial prefrontal cortex of the rat function together to support associative recognition and recency but not item recognition. Learn. Mem. 2013, 20, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.J.D.; Vann, S.D. The importance of mammillary body efferents for recency memory: Towards a better understanding of diencephalic amnesia. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.S.; Dalrymple-Alford, J.C. Dissociable memory effects after medial thalamus lesions in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, P.R.; Aggleton, J.P. An examination of the spatial working memory deficit following neurotoxic medial dorsal thalamic lesions in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1998, 97, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Cruz, H.; Sousa, M.; Vieira, J.B.; Lima, D.; Galhardo, V. Prefrontal cortex and mediodorsal thalamus reduced connectivity is associated with spatial working memory impairment in rats with inflammatory pain. Pain 2013, 154, 2397–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolkan, S.S.; Stujenske, J.M.; Parnaudeau, S.; Spellman, T.J.; Rauffenbart, C.; Abbas, A.I.; Harris, A.Z.; Gordon, J.A.; Kellendonk, C. Thalamic projections sustain prefrontal activity during working memory maintenance. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bourbon-Teles, J.; Bentley, P.; Koshino, S.; Shah, K.; Dutta, A.; Malhotra, P.; Egner, T.; Husain, M.; Soto, D. Thalamic control of human attention driven by memory and learning. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Peräkylä, J.; Polvivaara, M.; Öhman, J.; Peltola, J.; Lehtimäki, K.; Huhtala, H.; Hartikainen, K.M. Human anterior thalamic nuclei are involved in emotion-attention interaction. Neuropsychologia 2015, 78, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wimmer, R.D.; Wilson, M.A.; Halassa, M.M. Thalamic circuit mechanisms link sensory processing in sleep and attention. Front. Neural Circuits 2016, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, C.; Mathis, J.; Gugger, M.; Lovblad, K.O.; Hess, C.W. Hypersomnia following paramedian thalamic stroke: A report of 12 patients. Ann. Neurol. 1996, 39, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetti, C.L.; Valko, P. Poststroke Hypersomnia. Sleep Med. Clin. 2006, 1, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Broccolini, A.; Vollono, C.; Dittoni, S.; Frisullo, G.; Pilato, F.; Profice, P.; Losurdo, A.; Morosetti, R.; et al. Bilateral thalamic stroke transiently reduces arousals and NREM sleep instability. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 300, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, M.; Villringer, K.; Ganeshan, R.; Rangus, I.; Nolte, C.H. Frequency, clinical presentation and outcome of vigilance impairment in patients with uni- and bilateral ischemic infarction of the paramedian thalamus. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 4340–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchin, L.; Schöne, C.; Mensen, A.; Bandarabadi, M.; Pilotto, F.; Saxena, S.; Libourel, P.A.; Bassetti, C.L.A.; Adamantidis, A.R. Slow waves promote sleep-dependent plasticity and functional recovery after stroke. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 8637–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Mohan, A.; Yeh, B.-Y.; Ghebrendrias, Y.; Brentlinger, G.; Han, J. Thalamic Dementia in Acute Inpatient Rehabilitation—Role for Amantadine? Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2021, 100, e9–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanna, M.E.D.O.; Madeira, D.M.; Alves, G.; Alves, C.E.; Valente, L.E.; Laks, J.; Engelhardt, E. Vascular dementia by thalamic strategic infarct. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2008, 66, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Catsman-Berrevoets, C.E.; Harskamp, F.v. Compulsive pre-sleep behavior and apathy due to bilateral thalamic stroke: Response to bromocriptine. Neurology 1988, 38, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longarzo, M.; Cavaliere, C.; Orsini, M.; Tramontano, L.; Aiello, M.; Salvatore, M.; Grossi, D. A Multimodal Imaging Study in a Case of Bilateral Thalamic Damage with Multidomain Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 14, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbruzzese, G.; Arata, L.; Bino, G.; Dall’Agata, D.; Leonardi, A. Thalamic dementia: Report of a case with unusual lesion location. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1986, 7, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebermann, D.; Ostendorf, F.; Kopp, U.A.; Kraft, A.; Bohner, G.; Nabavi, D.G.; Kathmann, N.; Ploner, C.J. Subjective cognitive-affective status following thalamic stroke. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharf, A.-C.; Gronewold, J.; Eilers, A.; Todica, O.; Moenninghoff, C.; Doeppner, T.R.; de Haan, B.; Bassetti, C.L.; Hermann, D.M. Depression and anxiety in acute ischemic stroke involving the anterior but not paramedian or inferolateral thalamus. Front. Psychol. 2023, 14, 1218526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, J.T.; Quijije, N.; Sheyner, I.; Stover, K.T. Delirium without focal signs related to a thalamic stroke. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2433–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogousslavsky, J.; Ferrazzini, M.; Regli, F.; Assal, G.; Tanabe, H.; Delaloye-Bischof, A. Manic delirium and frontal-like syndrome with paramedian infarction of the right thalamus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, C.G.; Cadavieco, M.C.; Jego, S.; Ponomarenko, A.; Korotkova, T.; Adamantidis, A. Hypothalamic feedforward inhibition of thalamocortical network controls arousal and consciousness. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekus, C.; Steullet, P.; Orero López, A.; Bozic, I.; Rusterholz, T.; Bandarabadi, M.; Do, K.Q.; Herrera, C.G. Alterations in TRN-anterodorsal thalamocortical circuits affect sleep architecture and homeostatic processes in oxidative stress vulnerable Gclm−/− mice. Mol. Psychiatry. 2022, 27, 4394–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamantidis, A.R.; Gutierrez Herrera, C.; Gent, T.C. Oscillating circuitries in the sleeping brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 20, 746–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geva-Sagiv, M.; Nir, Y. Local sleep oscillations: Implications for memory consolidation. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, S.M.; Smith, C.T. The function of the sleep spindle: A physiological index of intelligence and a mechanism for sleep-dependent memory consolidation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, A.; Doyon, J.; Dostie, V.; Barakat, M.; Tahar, A.H.; Korman, M.; Benali, H.; Karni, A.; Ungerleider, L.G.; Carrier, J. Motor sequence learning increases sleep spindles and fast frequencies in post-training sleep. Sleep 2008, 31, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schmidt, C.; Peigneux, P.; Muto, V.; Schenkel, M.; Knoblauch, V.; Münch, M.; de Quervain, D.J.F.; Wirz-Justice, A.; Cajochen, C. Encoding difficulty promotes postlearning changes in sleep spindle activity during napping. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 8976–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, S.M.; Nader, R.; Cote, K.A.; Smith, C.T. Sleep spindles and learning potential. Behav. Neurosci. 2007, 121, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.C.M.; Van der Heijden, K.B.; Swaab, H.; Van Someren, E.J.W. Sleep spindle characteristics and sleep architecture are associated with learning of executive functions in school-age children. J. Sleep Res. 2019, 28, e12779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadagni, V.; Byles, H.; Tyndall, A.V.; Parboosingh, J.; Longman, R.S.; Hogan, D.B.; Hanly, P.J.; Younes, M.; Poulin, M.J. Association of sleep spindle characteristics with executive functioning in healthy sedentary middle-aged and older adults. J. Sleep Res. 2020, 30, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Andrés, I.; Garzón, M.; Reinoso-Suárez, F. Functional anatomy of non-REM sleep. Front. Neurol. 2011, 2, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siccoli, M.M.; Rölli-Baumeler, N.; Achermann, P.; Bassetti, C.L. Correlation between sleep and cognitive functions after hemispheric ischaemic stroke. Eur. J. Neurol. 2008, 15, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Matsuoka, T.; Nittono, H.; Hori, T. Fast Sleep Spindle (13–15 Hz) Activity Correlates with Sleep-Dependent Improvement in Visuomotor Performance. Sleep 2008, 31, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poe, G.R.; Walsh, C.M.; Bjorness, T.E. Cognitive Neuroscience of Sleep. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 185, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, J.; Qin, L.; Shao, Y.; Yao, P.; Sun, H.; Zou, Q.; et al. Altered thalamic connectivity in insomnia disorder during wakefulness and sleep. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2021, 42, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarnecchi, E.; Sprugnoli, G.; Sicilia, I.; Dukart, J.; Neri, F.; Romanella, S.M.; Cerase, A.; Vatti, G.; Rocchi, R.; Rossi, A. Thalamic altered spontaneous activity and connectivity in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. J. Neuroimaging 2022, 32, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.W.; Oh, Y.S.; Ryu, D.W.; Lee, K.S.; Lyoo, C.H.; Kim, J.S. Low thalamic monoamine transporter availability is related to excessive daytime sleepiness in early Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramm, M.; Boentert, M.; Lojewsky, N.; Jafarpour, A.; Young, P.; Heidbreder, A. Disease-specific attention impairment in disorders of chronic excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep Med. 2019, 53, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapanou, A.; Gu, Y.; O’Shea, D.; Eich, T.; Tang, M.X.; Schupf, N.; Manly, J.; Zimmerman, M.; Scarmeas, N.; Stern, Y. Daytime somnolence as an early sign of cognitive decline in a community-based study of older people. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2016, 31, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plante, D.T.; Birn, R.M.; Walsh, E.C.; Hoks, R.M.; Cornejo, M.D.; Abercrombie, H.C. Reduced resting-state thalamostriatal functional connectivity is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness in persons with and without depressive disorders. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, T.; Pagano, G.; Niccolini, F.; Politis, M. Increased dopaminergic function in the thalamus is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness. Sleep Med. 2018, 43, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, G.M.; Mayeli, A.; Yushmanov, V.E.; Hetherington, H.P.; Ferrarelli, F. Reduced GABA/glutamate in the thalamus of individuals at clinical high risk for psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 2021, 46, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Tian, Y.; Ko, W.K.D.; Wang, Z.; Jia, F.; Horn, A.; De Ridder, D.; Choi, K.S.; Bari, A.A.; Wang, S.; et al. Deep Brain Stimulation Initiative: Toward Innovative Technology, New Disease Indications, and Approaches to Current and Future Clinical Challenges in Neuromodulation Therapy. Front. Neurol. 2021, 11, 597451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenzli, J.C.; Werth, E.; Baumann, C.R.; Belvedere, A.; Renzel, R.; Stieglitz, L.H.; Imbach, L.L. Deep brain stimulation of the anterior nucleus of the thalamus increases slow wave activity in NREM sleep. Epilepsia 2023, 64, 2044–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gummadavelli, A.; Motelow, J.E.; Smith, N.; Zhan, Q.; Schiff, N.D.; Blumenfeld, H. Thalamic stimulation to improve level of consciousness after seizures: Evaluation of electrophysiology and behavior. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolattaro, M.M.; Halverson, H.E.; Freeman, J.H. Medial auditory thalamic stimulation as a conditioned stimulus for eyeblink conditioning in rats. Learn. Mem. 2007, 14, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ponnath, A.; Farris, H.E. Sound-by-sound thalamic stimulation modulates midbrain auditory excitability and relative binaural sensitivity in frogs. Front. Neural Circuits 2014, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Caspary, D.M.; Llano, D.A. Auditory thalamic circuits and GABAA receptor function: Putative mechanisms in tinnitus pathology. Hear. Res. 2017, 349, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaucheur, J.P.; Aleman, A.; Baeken, C.; Benninger, D.H.; Brunelin, J.; Di Lazzaro, V.; Filipović, S.R.; Grefkes, C.; Hasan, A.; Hummel, F.C.; et al. Evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS): An update (2014–2018). Clin. Neurophysiol. 2020, 131, 474–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, W.; Ni, J.; Wang, Y. Clinical study of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the motor cortex for thalamic pain. Medicine 2018, 97, e11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minks, E.; Kopickova, M.; Marecek, R.; Streitova, H.; Bares, M. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of the cerebellum. Biomed. Papers. 2010, 154, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaram, R.; Ros, T.; Stoeckel, L.; Haller, S.; Scharnowski, F.; Lewis-Peacock, J.; Weiskopf, N.; Blefari, M.L.; Rana, M.; Oblak, E.; et al. Closed-loop brain training: The science of neurofeedback. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, T.S.; Cassisi, J.E.; Pineda, M. Neurofeedback Training for a Patient with Thalamic and Cortical Infarctions. Appl. Psychophysiol. Biofeedback. 2003, 28, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zotev, V.; Misaki, M.; Phillips, R.; Wong, C.K.; Bodurka, J. Real-time fMRI neurofeedback of the mediodorsal and anterior thalamus enhances correlation between thalamic BOLD activity and alpha EEG rhythm. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2018, 39, 1024–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).