Four New Cases of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) and a Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Patients Reports
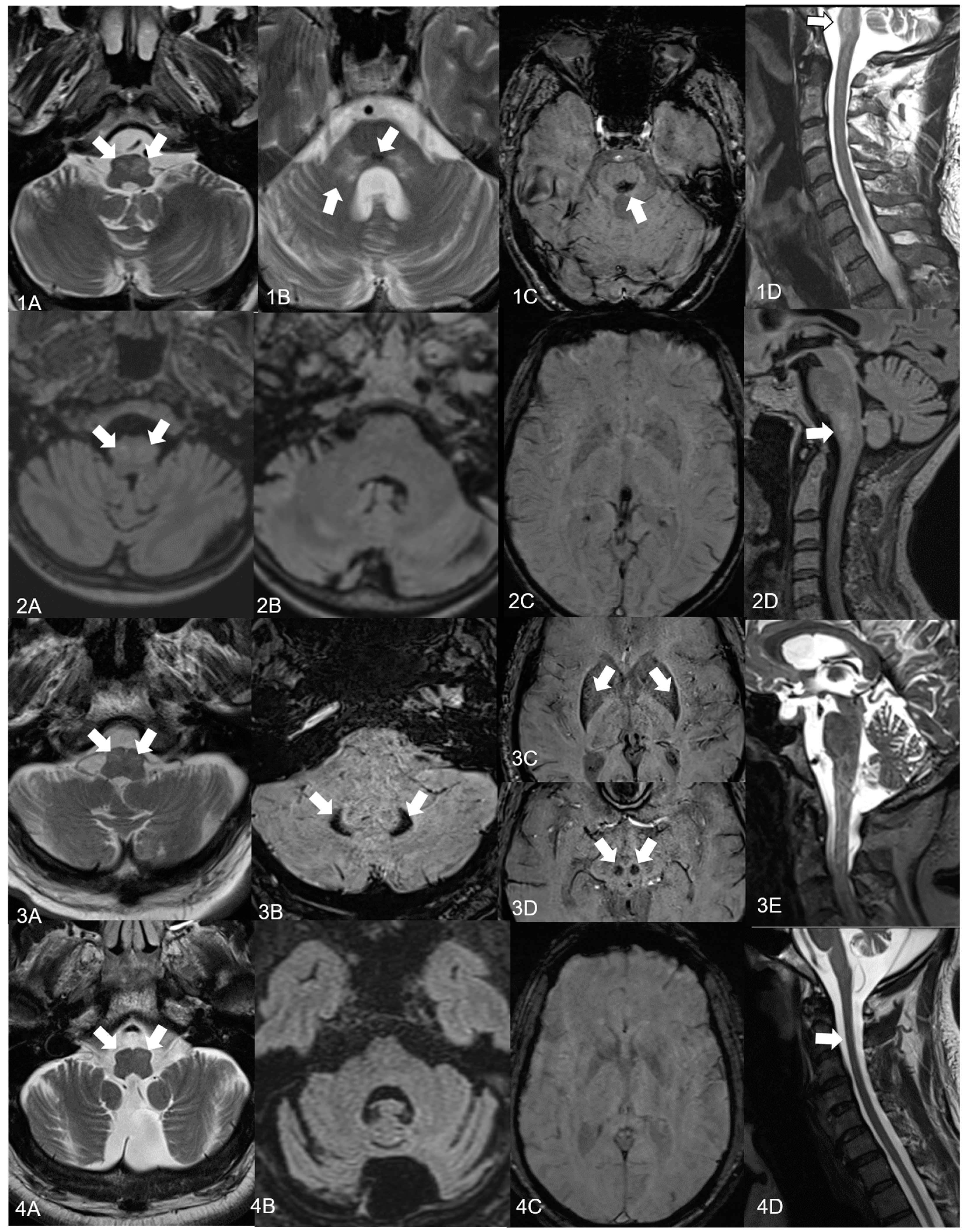
3.1. Patient 1
3.2. Patient 2
3.3. Patient 3
3.4. Patient 4
4. Discussion
4.1. Patient 1
4.2. Patient 2
4.3. Patient 3
4.4. Patient 4
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| HSP7 [22,74] | Adult-Onset Alexander’s Disease [21,22,42,43,72,75] | Spinocerebellar Ataxia 20 [19,44] | POLG [55,76] | Neuroferritinopathy/Aceruloplasminemia [57,59] | Late-Onset GM2-Gangliosidosis [45,77,78,79] | CTX [80] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at onset | 11–72 | 13–62 | 19–64 | adolescent/adult | early to mid-adulthood | 10–54 | 23–44 |
| Oculomotor symptoms | ptosis nystagmus ophthalmoplegia | ptosis nystagmus diplopia | dysmetric saccades | ptosis external ophthalmoplegia | blepharospasm in aceruloplaminemia | dysmetric saccades | − |
| Bulbar symptoms | + | ++ | dysarthria, dysphonia | + | +/− | + | +/− |
| PT | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Hearing loss | + | − | − | + | − | − | − |
| Gait abn. | +++ | ++ | + | + | +/− | ++ | + |
| Axial ataxia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Limb ataxia | + | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Spasticity | +++ | ++ | +/− | − | − | +/− | + |
| Paresis | ++ | + | − | limb weakness | − | ++ | + |
| Babinski sign | ++ | + | − | − | − | ++ | + |
| Amyotrophy | + | + | − | − | − | ++ | +/− (myopathy) |
| PNP | + | +/− | − | + | − | + | + |
| Other typ. symptoms | optic atrophy | − | tremor | myoclonus epilepsy movement disorders, multiorgan involvement possible | movement disorders (chorea, dystonia, facial dyskinesia) multiorgan involvement | movement disorders (dystonia) | cataract, tendon xanthomas epilepsy, parkinsonism, multiorgan involvement |
| Cognitive abn. | +/− | − | − | + | ++ | + | + |
| Psychiatric disease | − | − | − | + | + | + | + |
| Sleep disturbance | + | + | − | + | − | + | − |
| Scoliosis | + | +/− | − | − | − | − | − |
| Sphincter abn. | + | + | − | − | − | +/− | +/− |
| Dysautonomy | − | + | − | − | − | +/− | +/− |
| MRI findings | cerebellar atrophy, white matter abnormalities | atrophy of medulla oblongata and cervical spine (“tadpole pattern of atrophy” [42,72]) HOD, supratentorial white matter abnormalities | HOD, isolated dentate calcification | mild cerebellar atrophy, HOD | iron deposits in iron-rich brain regions: basal ganglia, thalamus, dentate nucleus, substancia nigra, cerebral atrophy | cerebellar atrophy, hypodensity of thalamus | cerebellar atrophy, white matter signal alterations, symmetric hyperintensities in the dentate nuclei |
References
- Deuschl, G.; Bain, P.; Brin, M. Consensus statement of the Movement Disorder Society on Tremor. Ad Hoc Scientific Committee. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13 (Suppl. S3), 2–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadikoff, C.; Lang, A.E.; Klein, C. The ‘essentials’ of essential palatal tremor: A reappraisal of the nosology. Brain 2006, 129, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilikete, C.; Desestret, V. Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration and Palatal or Oculopalatal Tremor. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, M. Symptomatic myoclonus. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2006, 36, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S. Palatal Tremor-Pathophysiology, Clinical Features, Investigations, Management and Future Challenges. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2020, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Torun, N.; Tuite, P.J.; Sharpe, J.A.; Lang, A.E. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor (PAPT): Clinical and MRI assessment with review of palatal tremors. Brain 2004, 127, 1252–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, M.R.; Herrmann, C., Jr. Syndrome of palatal myoclonus and progressive ataxia: Two cases with magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology 1985, 35, 1212–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, M. Palatal Myoclonus: Further Clinical and Pathophysiological Observations. AMA Arch. Neurol. Psychiatry 1956, 75, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.F.; Faust-Socher, A.; Al-Murshed, M.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Lang, A.E.; Munoz, D.G. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor: Two autopsy cases of a novel tauopathy. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mari, Z.; Halls, A.J.M.; Vortmeyer, A.; Zhukareva, V.; Uryu, K.; Lee, V.M.; Hallett, M. Clinico-Pathological Correlation in Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor: A Novel Tauopathy. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2014, 1, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezuka, T.; Takahata, K.; Tagai, K.; Ueda, R.; Ito, D.; Takeda, H.; Takahashi, S.; Nakahara, J.; Higuchi, M.; Seki, M. Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor Showing Characteristic Tau Depositions in [F]PM-PBB3 PET. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Eggers, S.D.; Milone, M.; Keegan, B.M. Acquired progressive ataxia and palatal tremor: Importance of MRI evidence of hemosiderin deposition and vascular malformations. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peikert, K.; Gerber, J.; Winzer, S.; Schäfer, J.; Reichmann, H.; Hermann, A. Palatal Tremor with Progressive Ataxia Secondary to A Dural Arteriovenous Fistula. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2019, 6, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamelou, M.; Adams, M.; Davagnanam, I.; Batla, A.; Sheerin, U.; Talbot, K.; Bhatia, K.P. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor associated with dense pontine calcification: A unique case. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 1155–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kheder, A.; Currie, S.; Romanowski, C.; Hadjivassiliou, M. Progressive ataxia with palatal tremor due to gluten sensitivity. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 62–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggenberger, E.; Cornblath, W.; Stewart, D.H. Oculopalatal tremor with tardive ataxia. J. Neuroophthalmol. 2001, 21, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicastro, N.; Ranza, E.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Horvath, J. Pure Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) Associated with a New Polymerase Gamma (POLG) Mutation. Cerebellum 2016, 15, 829–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongin, M.; Delorme, C.; Lenglet, T.; Jardel, C.; Vignal, C.; Roze, E. Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor: Think about POLG Mutations. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2016, 6, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, E.; Gardner, R.J. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 20. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2012, 103, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, J.M.; Cheema, A.; Jackson, J.; Blackburn, P.R.; Van Gerpen, J.; Atwal, P.S. Novel GFAP Variant in Adult-onset Alexander Disease With Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor. Neurologist 2017, 22, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, K.L.; Hall, D.A.; Moon, M.; Agarwal, P.; Newman, E.; Brenner, M. Adult-onset Alexander disease with progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gass, J.; Blackburn, P.R.; Jackson, J.; Macklin, S.; van Gerpen, J.; Atwal, P.S. Expanded phenotype in a patient with spastic paraplegia 7. Clin. Case Rep. 2017, 5, 1620–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidiropoulos, C.; Sripathi, N.; Nasrallah, K.; Mitsias, P. Oculopalatal tremor, facial myokymia and truncal ataxia in a patient with neurosarcoidosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 2255–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.; Taylor, R.; Simonds, A.; Chawda, S. Respiratory difficulty with palatal, laryngeal and respiratory muscle tremor in adult-onset Alexander’s disease. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeep, S.; Grewal, P.; Jahan, S.; Raslau, F.D.; Slevin, J.T. Pearls & Oy-sters: Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor: Imaging and disease course. Neurology 2020, 94, e1445–e1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, I.I.; John, J.K.; Al-Hashel, J.Y. A Syndrome of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) in a Patient with Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2020, 23, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainline, C.; Neophytides, A.; Borja, M.J.; Galetta, S.L. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, e37–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasi, C.; Rizzo, V.; Di Lella, G.; Modoni, A.; Calcagni, M.L.; Picciotti, P.M.; Silvestri, G. Serial neuroimaging findings in a novel case of sporadic progressive ataxia and palatal tremor (PAPT). J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 379, 16–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuzuárregui, J.R.; Frank, S.A. Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.L.; Pinto, W.B.; Souza, P.V.; Rivero, R.L.; Barsottini, O.G. Neuroimaging features of progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2015, 73, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, J.; Joutsa, J.; Rinne, J.O.; Bergman, J.; Kaasinen, V. Hypermetabolism of Olivary Nuclei in a Patient with Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2015, 5, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yared, J.H.; Lopes, B.S.; Rogério, R.M.; Amaral, L.L.; Ferreira, N.F. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor: T1-weighted with magnetization transfer pulse hyperintensity in the inferior olivary nucleus. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2013, 71, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papachatzaki, M.M.; Ali, N.; Arshad, Q.; Cader, S.; Peppas, I.; Everett, C.; Bronstein, A.M.; Schmierer, K. Progressive ataxia with oculo-palatal tremor and optic atrophy. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2903–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, F.J.; Boon, A.J. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor--two cases with an unusual clinical presentation and course. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 904–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassani, R.; Mariotti, C.; Nanetti, L.; Grisoli, M.; Savoiardo, M.; Pareyson, D.; Salsano, E. Pendular nystagmus in progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. J. Neurol. 2011, 258, 1877–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinar, V.V.; Barun, B.; Zadro, I.; Ozretic, D.; Habek, M. Progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1248–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Moon, S.Y.; Choi, K.D.; Kim, J.H.; Sharpe, J.A. Patterns of ocular oscillation in oculopalatal tremor: Imaging correlations. Neurology 2007, 68, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, R.; Righini, A.; Marotta, G.; Benti, R.; Marconi, R.; Isaias, I.U.; Pezzoli, G.; Antonini, A. Clinical and imaging characterization of a patient with idiopathic progressive ataxia and palatal tremor. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 944–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, L.F.; Carvalho, V.M.D.; Pedroso, J.L.; Duarte, M.L.; Massaud, R.M. Simultaneous mixed phenotype and neuroimaging of progressive supranuclear palsy, progressive ataxia and palatal tremor: Two different faces of tauopathies. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2022, 80, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaron, G.; Willis, M.A.; Ontaneda, D.; Fernandez, H.; Kim, S.; Jones, S.E.; Pioro, E.P.; Cohen, J.A. Palatal myoclonus, abnormal eye movements, and olivary hypertrophy in GAD65-related disorder. Neurology 2020, 94, 273–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kothari, D.S.; Tanenbaum, Z.G.; Abdel-Wahed, L.; Cho, T.A.; Hoffman, H.T. Palato-Pharyngo-Laryngeal Rhythmic Myoclonus in Neuro-Behcet Syndrome: A Case Report. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2022, 132, 34894221120124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Fancellu, R.; Mariotti, C.; Romano, S.; Salmaggi, A.; Carella, F.; Girotti, F.; Gattellaro, G.; Carriero, M.R.; Farina, L.; et al. Adult-onset Alexander disease: A series of eleven unrelated cases with review of the literature. Brain 2008, 131, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spritzer, S.D.; Zarkou, S.; Ireland, S.P.; Carter, J.L.; Goodman, B.P. Autonomic dysfunction in adult-onset alexander disease: A case report and review of the literature. Clin. Auton. Res. 2013, 23, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, M.A.; Gardner, R.J.; Bahlo, M.; Matsuura, T.; Dixon, J.A.; Forrest, S.M.; Storey, E. Dominantly inherited ataxia and dysphonia with dentate calcification: Spinocerebellar ataxia type 20. Brain 2004, 127, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretegiani, E.; Rosini, F.; Federighi, P.; Cerase, A.; Dotti, M.T.; Rufa, A. Pendular nystagmus, palatal tremor and progressive ataxia in GM2-gangliosidosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, e67–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; Cesarini, M.; Gatto, E.M.; Cammarota, A.; Merello, M. A Treatable Rare Cause of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor. Tremor Other Hyperkinetic Mov. 2018, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danila, E.; Norkūniene, J.; Jurgauskiene, L.; Malickaite, R. Diagnostic role of BAL fluid CD4/CD8 ratio in different radiographic and clinical forms of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Clin. Respir. J. 2009, 3, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drent, M.; Wagenaar, S.S.; Mulder, P.H.; van Velzen-Blad, H.; Diamant, M.; van den Bosch, J.M. Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid profiles in sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, and non-Hodgkin’s and Hodgkin’s disease. An evaluation of differences. Chest 1994, 105, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinas, F.C.; Rengachary, S. Diagnosis and management of neurosarcoidosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2001, 8, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsappidi, S.; Hui, F.; Turan, T.N.; Hunter, S. Intracerebral hemorrhage: An unusual presentation of neurosarcoidosis. Neurologist 2011, 17, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Versnick, E.; Tuite, P.; Cyr, J.S.; Kucharczyk, W.; Montanera, W.; Willinsky, R.; Mikulis, D. Hypertrophic olivary degeneration: Metaanalysis of the temporal evolution of MR findings. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2000, 21, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chow, J.; Rahman, J.; Achermann, J.C.; Dattani, M.T.; Rahman, S. Mitochondrial disease and endocrine dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinghorn, K.J.; Kaliakatsos, M.; Blakely, E.L.; Taylor, R.W.; Rich, P.; Clarke, A.; Omer, S. Hypertrophic olivary degeneration on magnetic resonance imaging in mitochondrial syndromes associated with POLG and SURF1 mutations. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.K.; Bindoff, L.A.; Rydland, J.; Aasly, J.O. Palatal tremor and facial dyskinesia in a patient with POLG1 mutation. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1624–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchikviladzé, M.; Gilleron, M.; Maisonobe, T.; Galanaud, D.; Laforêt, P.; Durr, A.; Eymard, B.; Mochel, F.; Ogier, H.; Béhin, A.; et al. A diagnostic flow chart for POLG-related diseases based on signs sensitivity and specificity. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, B.W.; Westeneng, H.J.; van Hal, M.A.; van Engelen, B.G.; Overeem, S. Sleep disturbances in chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayflick, S.J.; Kurian, M.A.; Hogarth, P. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 147, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wills, A.J.; Sawle, G.V.; Guilbert, P.R.; Curtis, A.R. Palatal tremor and cognitive decline in neuroferritinopathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 73, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruer, M.C.; Boddaert, N. Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation: A diagnostic algorithm. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2012, 19, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehéricy, S.; Roze, E.; Goizet, C.; Mochel, F. MRI of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2020, 33, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.S. Brain Iron Accumulation in Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes: In vivo MRI Evidences for Distinctive Patterns. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Butros, S.R.; Shuai, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, M.; Haacke, E.M.; Hu, J.; Xu, H. Different iron-deposition patterns of multiple system atrophy with predominant parkinsonism and idiopathetic Parkinson diseases demonstrated by phase-corrected susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2012, 33, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, M.; Sanjo, N.; Hattori, T.; Oyama, J.; Hamada, M.; Ozaki, K.; Yokota, T. Olivary hypertrophy improved by steroid treatment: Two case reports with unique presentations. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 334, 577003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tison, F.; Arne, P.; Henry, P. Myoclonus and adult coeliac disease. J. Neurol. 1989, 236, 307–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finelli, P.F.; McEntee, W.J.; Ambler, M.; Kestenbaum, D. Adult celiac disease presenting as cerebellar syndrome. Neurology 1980, 30, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjivassiliou, M.; Sanders, D.S.; Woodroofe, N.; Williamson, C.; Grünewald, R.A. Gluten ataxia. Cerebellum 2008, 7, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelpi, E.; Höftberger, R.; Graus, F.; Ling, H.; Holton, J.L.; Dawson, T.; Popovic, M.; Pretnar-Oblak, J.; Högl, B.; Schmutzhard, E.; et al. Neuropathological criteria of anti-IgLON5-related tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 531–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, J.-A.; Norcliffe-Kaufmann, L.; Kaufmann, H. Diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. Auton. Neurosci. 2018, 211, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Du, J. Hypertrophic olivary degeneration: A comprehensive review focusing on etiology. Brain Res. 2019, 1718, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlot, R.; Kojović, M. Palatal tremor in progressive supranuclear palsy: A case report. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliverstov, Y.; Suslin, A.; Kremneva, E.; Krotenkova, M. Segmental Myorhythmia with Palatal Tremor Due to Bilateral Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration in Wilson Disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 845–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namekawa, M.; Takiyama, Y.; Honda, J.; Shimazaki, H.; Sakoe, K.; Nakano, I. Adult-onset Alexander disease with typical “tadpole” brainstem atrophy and unusual bilateral basal ganglia involvement: A case report and review of the literature. BMC Neurol. 2010, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Lenka, A.; Stezin, A.; Kamble, N.; Pal, P.K. Overview of sleep disturbances and their management in Parkinson plus disorders. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 415, 116891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casari, G.; Marconi, R. Spastic Paraplegia 7; Adam, M.P., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; GeneReviews®: Seattle, WA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, O.; Rowe, D.B. Adult-onset Alexander’s disease mimicking degenerative disease. Pract. Neurol. 2015, 15, 393–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumpf, J.D.; Saneto, R.P.; Copeland, W.C. Clinical and molecular features of POLG-related mitochondrial disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a011395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masingue, M.; Dufour, L.; Lenglet, T.; Saleille, L.; Goizet, C.; Ayrignac, X.; Ory-Magne, F.; Barth, M.; Lamari, F.; Mandia, D.; et al. Natural History of Adult Patients with GM2 Gangliosidosis. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 87, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, C.D.; Balkwill, D.; James, P.; Haxton, E.; Sassower, K.; Schmahmann, J.D.; Eichler, F.; Lewis, R. Quantitative oculomotor and nonmotor assessments in late-onset GM2 gangliosidosis. Neurology 2020, 94, e705–e717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cachon-Gonzalez, M.B.; Zaccariotto, E.; Cox, T.M. Genetics and Therapies for GM2 Gangliosidosis. Curr. Gene Ther. 2018, 18, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.; Chen, G.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y. Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: A comprehensive review of pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| sex/AAO/DD | m/40/16 | f/42/26 | m/65/9 | m/50/4 |
| family history | − | − | − | − |
| first symptom | gait ataxia | gait disturbances | gait ataxia | gait disturbances, dysarthria, dysphagia |
| PAPT | + | + | + | + |
| PT with ear clicks | − | − | + | − |
| oculomotor symptoms | directional/pendular nystagmus horizontal gaze palsy | fixation deficit macro-square-wave-jerks dysmetric saccades | saccadic eye movement | hypometric saccades rotatory nystagmus |
| dysarthria/dysphagia | +/− | +/+ | +/+ | +/+ |
| spasticity | lower extremities | − | elevated reflex levels | spastic paresis of legs |
| polyneuropathy | − | + | − | + |
| hearing loss | − | + | − | − |
| autonomic dysregulation | − | − | − | + |
| cognitive symptoms | no impairment | 24 points (MoCA) | 23 points (MoCA) | 18 points (MoCA) |
| further neurologic symptoms | myocloni of the lateral neck fine motor disturbances | − | arm swing reduced | facial myoclonus hallucinations |
| medical history | possible sarcoidosis with neurological manifestations, mediastinal lymphoma | DM type 2, hypothyroidism, depression fatigue, daytime sleepiness | abdominal aortic aneurysm, extensive nicotine consumption | latent pulmonary tuberculosis |
| MRI cerebellar atrophy brainstem atrophy supratentorial atrophy HOD left/right further findings | + − − +/+ (sequential) SWI lesion in dorsomedial pons T2 signal alterations of the cerebellar peduncles | + − − +/+ | + − + +/+ susceptibility artefacts in the posterior and lateral putamen, red nucleus, dentate nucleus on SWI | + + + +/+ (sequential) |
| Serum abnormalities | − | − | elevated ferritin level | gliadin Ig A |
| CSF abnormalities | slightly elevated liquor–serum–albumin index | − | − | slightly elevated cell count (5–8 cells/µL) and protein |
| genetic testing | − | − | − | negative |
| PSG | AHI 5.7/h, ESS 1/24p. slight PLM no RBD no stridor | AHI 60.3/h, ESS 12/24p, FSS 63/63p. severe obstructive sleep apnoea fragmentation of sleep without REM sleep | AHI 21.1/h (Apnoe-Link) PSG was refused by patient ESS 6/24p. | AHI 71.6/h, ESS 10/24p. reduced sleep latency severe obstructive sleep apnoea, hypercapnia (mean CO2 54 mmHg) PLM, no RBD |
| presumed aetiology | paramedian pons bleeding possibly due to neurosarcoidosis/pons cavernoma | genetic, neurodegenerative? | neurodegenerative | neurodegenerative |
| therapy | prednisolone, azathioprine for years, 2 cycles rituximab without neurologic improvement | levodopa treatment over 3 months without significant improvement 4-Aminopyridin for 4 months: no significant improvement in gait | prednisolone, intravenous immunoglobulins, gluten-free diet without neurologic improvement levetiracetam did not improve PT |
| PAPT Syndrome | Number of Cases | Age at Onset in Years (Mean ± Standard Deviation) | Gender (Female) | Cerebellar Atrophy (%, n) | Hypertrophic Olivary Degeneration (%, n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| idiopathic/neurodegenerative [6,9,10,11,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39] | 51 | 54.7 ± 13.8 | 24% (12/49) | 79% (31/39) | 86% (32/37) |
| structural (vascular, infectious, autoimmune) [12,13,14,15,16,23,40,41] | 15 | 50.9 ± 14.4 | 53% (8/15) | 50% (8/15) | 93% (14/15) |
| genetic/familial (confirmed or suspected) [6,17,18,19,20,21,22,24,42,43,44,45,46] | 34 | 41.7 ± 12.2 | 54% (13/24) | 88% (29/33) | 56% (10/18) |
| p < 0.001 | p = 0.02 | p = 0.03 | p = 0.009 |
| PAPT Syndrome | Additional Assessments in PT/Ataxia | |
|---|---|---|
| serum | Anti-gliadin antibodies (gluten sensitivity) [15] ACE (Sarcoidosis) [23] Copper/coeruloplasmin (Wilson’s disease) [71] Ferritin (NBIA) [58] Cholesterine, cholestanol, bile alcohol (CTX) [46] Autoimmune encephalitis antibodies (anti-NMDA-receptor, IgLON5, Anti-GAD65 [40] if appropriate consider panel diagnostic) [63,67] If appropriate: hexosaminidase enzymatic activity in leukocytes and serum [45] | Infectious disease (HIV, Syphilis, Lyme disease, Vitamins E and B12, folic acid Anti-TG/-TPO antibodies (Hashimoto thyroiditis) ANA, anti-SSA(Ro) (connective tissue disease) Paraneoplastic antibodies (if appropriate consider panel diagnostic: Anti-Hu, Yo, Ri, Tr, ZIC4, GAD, CRMP-5, Ma1, Ma2, Amphiphysin) If appropriate: long-chain fatty acids |
| urine | Copper in 24 h urine (Wilson’s disease) [71] | |
| CSF | Cell count, protein (infectious/autoimmune), ACE (Sarcoidosis) [23] | Oligoclonal bands (demyelinating disease) Malignant cells PCR for Whipple’s disease If appropriate: Mycobacterial culture |
| MRI | MRI of brain and spine: Atrophy of cerebellum, medulla, cervical spine (tadpole pattern of atrophy [72]) HOD (unilateral, bilateral) [69] Haemorrhage, cavernoma, vascular malformation, tumour especially in pons, midbrain, cerebellum [13] Superficial hemosiderosis, iron deposits? [12,60] Calcifications (SCA20, pons calcification [14]) | |
| electrophysiological study | Polyneuropathy screening Muscle atrophies, myopathy Surface EMG (frequency of PT) If appropriate: audiometry | EEG (seizure) |
| genetic study | Consider panel analysis, including mutations in: GFAP (Alexander’s disease) [20,21], HSP7 [22], SCA20 [19], Mitochondrial diseases (POLG, SURF1) [17,18,53], HEXA/HEXB (GM2-gangliosidosis) [45], CYP27A1 (CTX) [46], Ferritin light chain [58] | Consider genetic panel analysis |
| other | Video-polysomnography (NREM/REM sleep, hypoventilation, sleep apnoea) Screening for M. Behçet [41] If appropriate: video-oculography if appropriate: CT/PET-CT of chest, abdomen: tumour, sarcoidosis, other organ involvement | If appropriate: Dopamine-Transporter Scan (degenerative parkinsonism) Extended tumour search |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silimon, N.; Wiest, R.; Bassetti, C.L.A. Four New Cases of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) and a Literature Review. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2023, 7, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7040032
Silimon N, Wiest R, Bassetti CLA. Four New Cases of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) and a Literature Review. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2023; 7(4):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7040032
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilimon, Norbert, Roland Wiest, and Claudio L. A. Bassetti. 2023. "Four New Cases of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) and a Literature Review" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 7, no. 4: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7040032
APA StyleSilimon, N., Wiest, R., & Bassetti, C. L. A. (2023). Four New Cases of Progressive Ataxia and Palatal Tremor (PAPT) and a Literature Review. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 7(4), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn7040032







