Effects of Different Lipopolysaccharide Doses on Short- and Long-Term Spatial Memory and Hippocampus Morphology in an Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Treatment Preparation
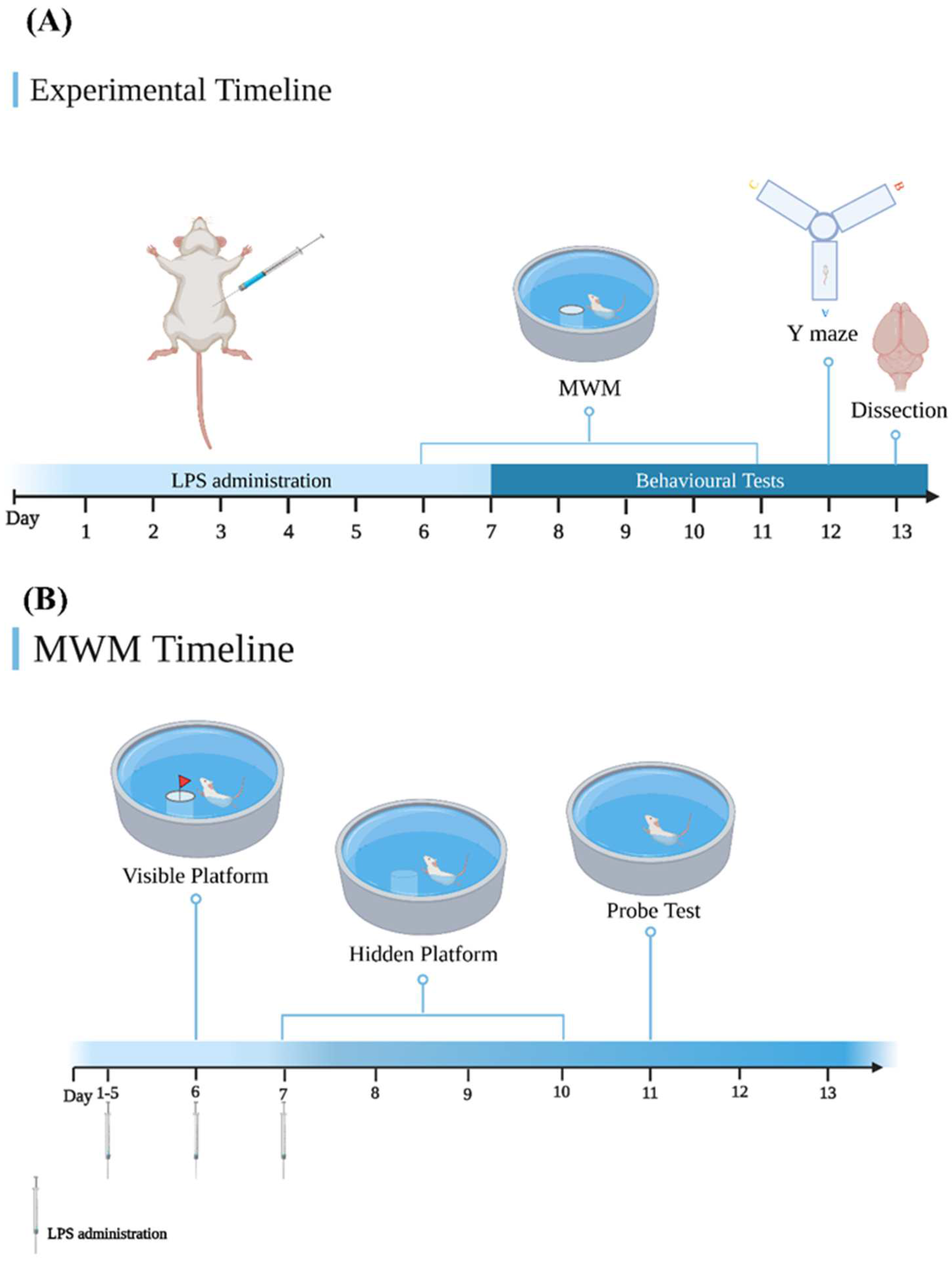
2.3. Experimental Design
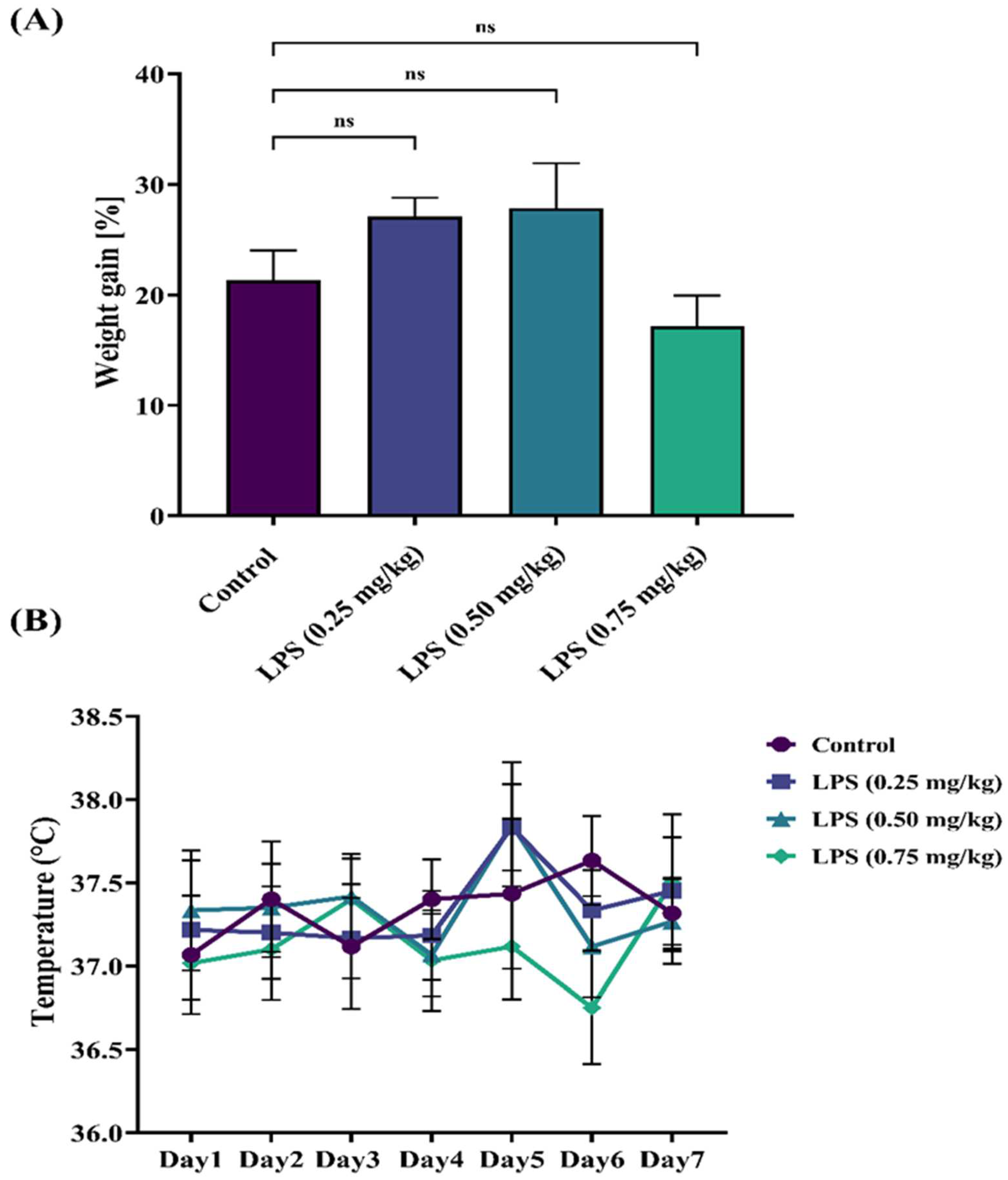
2.4. Weight and Temperature
2.5. Behavioral Tests
2.5.1. Morris Water Maze (MWM) Test
2.5.2. Y Maze
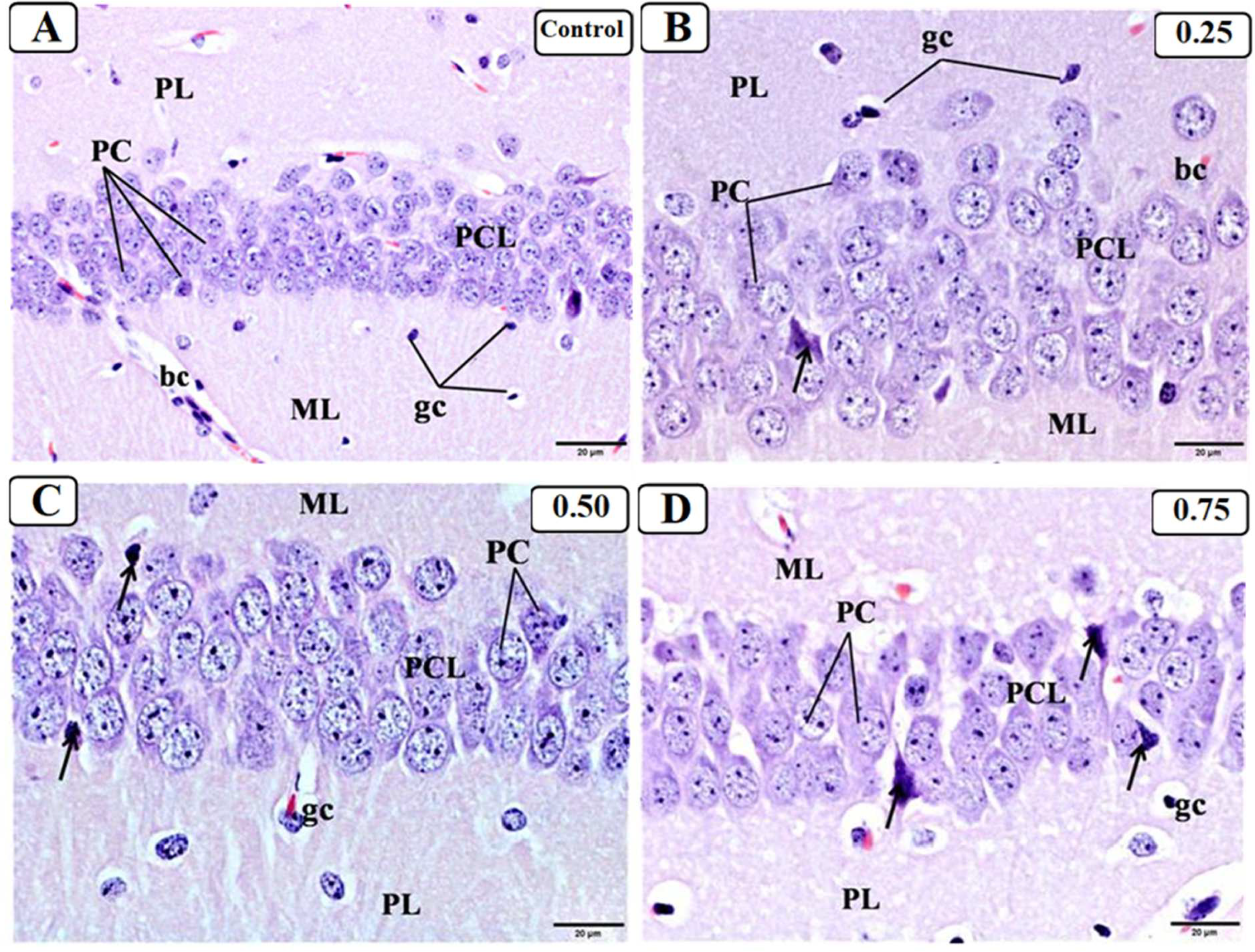
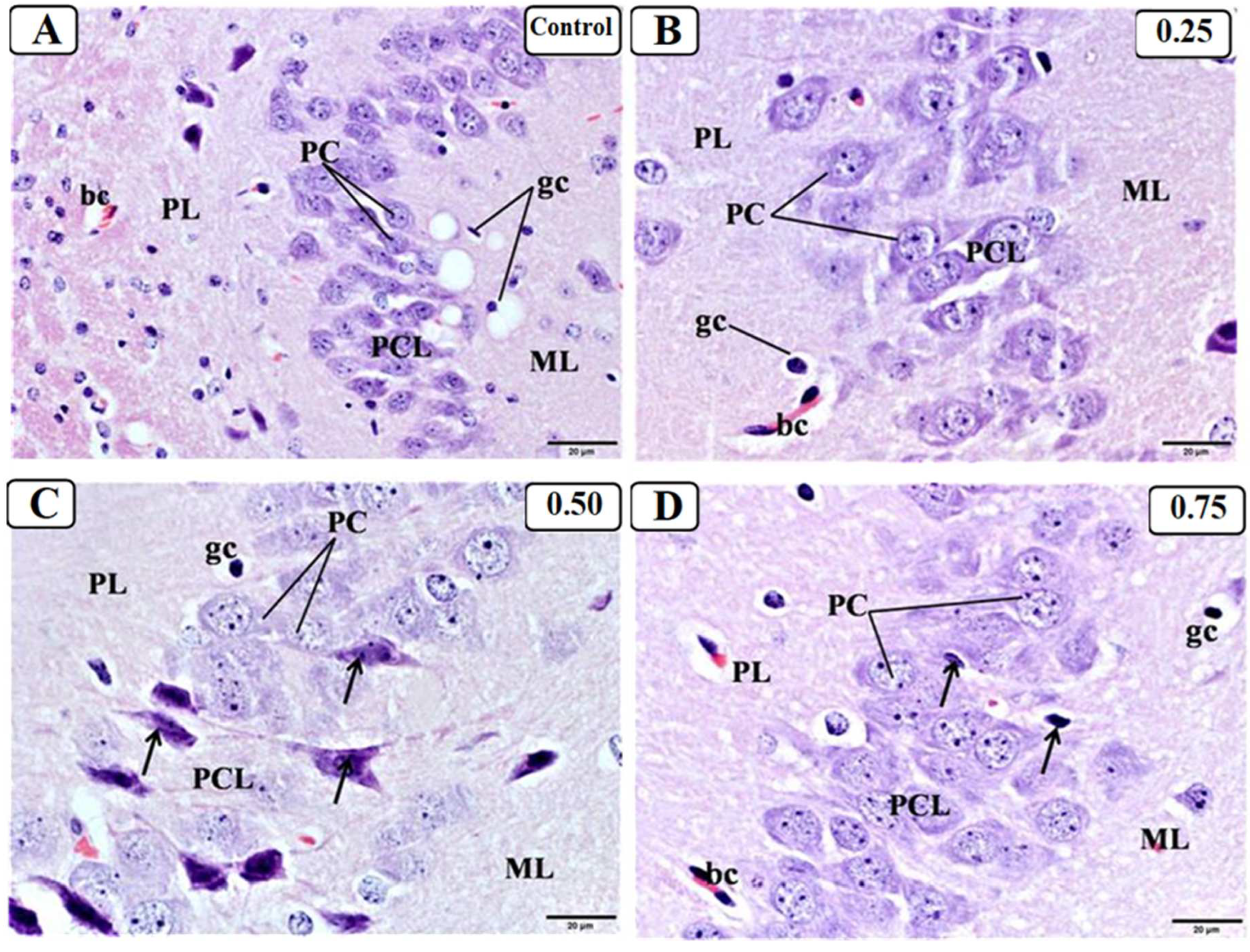
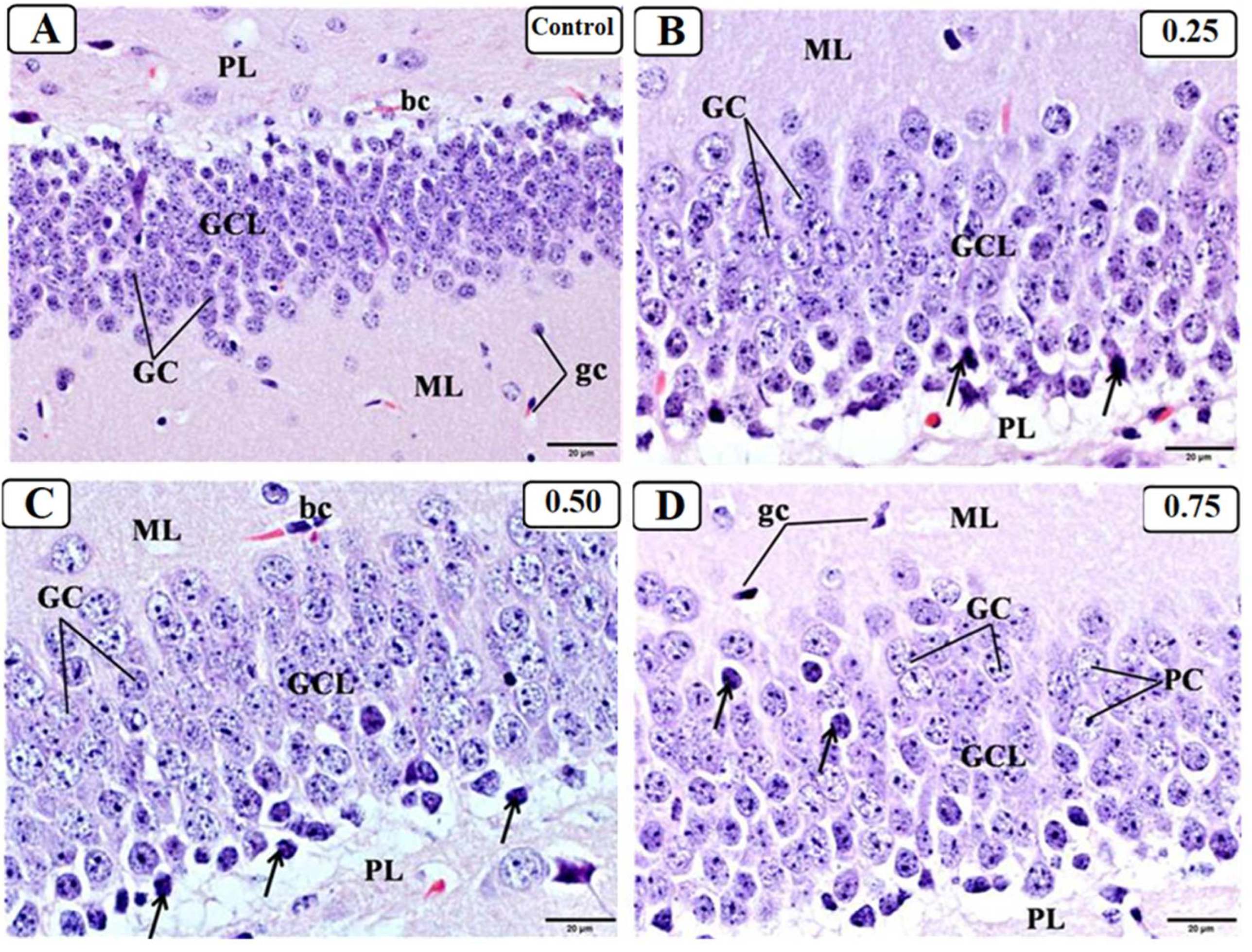
2.5.3. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of LPS on Weight and Temperature
3.2. Behavioral Tests
3.2.1. Effect of LPS on Long-Term Spatial Memory
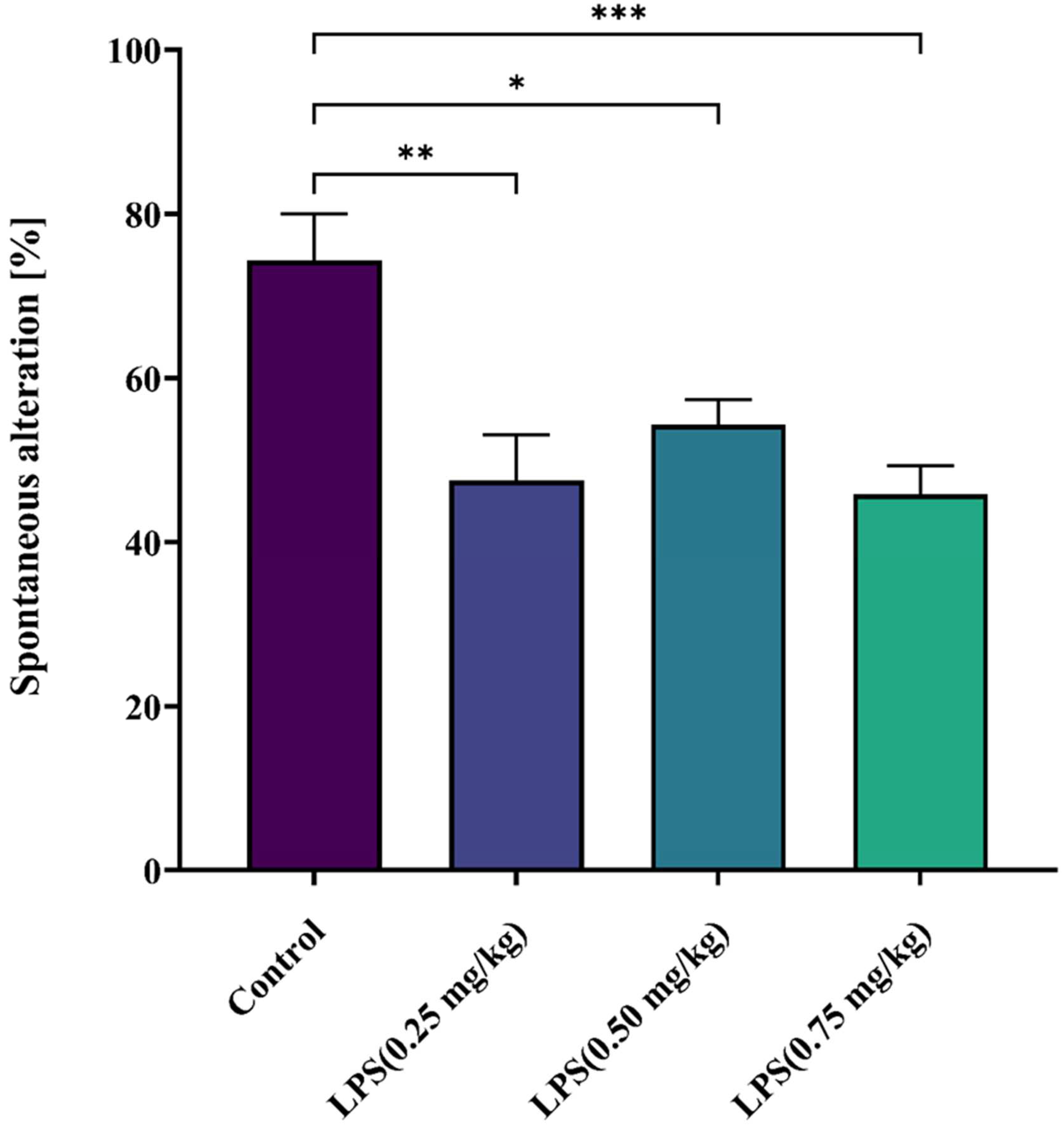
3.2.2. Effect of LPS on Short-Term Spatial Memory
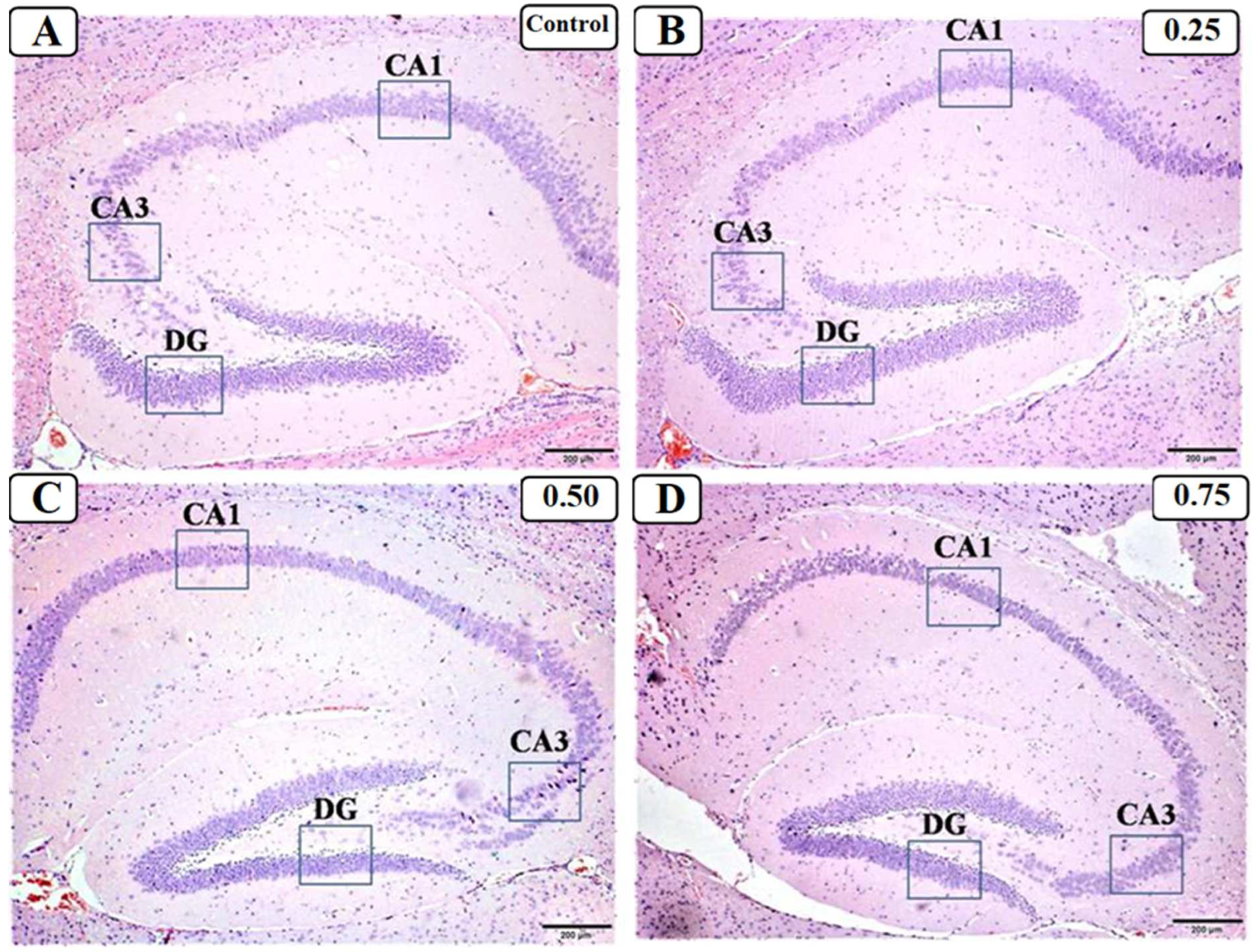
3.3. Effect of LPS on the Hippocampus
4. Discussion
4.1. This Work
4.2. Contributions and Limitations
4.3. Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wang, X.; Geng, M. Alzheimer’s disease hypothesis and related therapies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2018, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, R.; Wan Yaacob, W.; Othman, Z.; Long, I.; Ahmad, A.; Al-Rahbi, B. Lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in rats: A model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, M.; Rinaldi, C.; Santoro, G.; Crisafulli, C. The biological pathways of Alzheimer disease: A review. AIMS Neurosci. 2021, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, J.W.; Bemiller, S.M.; Murtishaw, A.S.; Leisgang, A.M.; Salazar, A.M.; Lamb, B.T. Inflammation as a central mechanism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2018, 4, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiannopoulou, K.G.; Papageorgiou, S.G. Current and future treatments in Alzheimer disease: An update. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2020, 12, 1179573520907397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Xue, J.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, O. Isoliquiritigenin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. BMC Neurosci. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glachet, O.; El Haj, M. Effects of olfactory stimulation on past and future thinking in Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Senses 2020, 45, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olton, D.S. Spatial memory. Sci. Am. 1977, 236, 82–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikbladh, O.M.; Meager, M.R.; King, J.; Blackmon, K.; Devinsky, O.; Shohamy, D.; Burgess, N.; Daw, N.D. Hippocampal contributions to model-based planning and spatial memory. Neuron 2019, 102, 683–693.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Watrous, A.J.; Tsitsiklis, M.; Lee, S.A.; Sheth, S.A.; Schevon, C.A.; Smith, E.H.; Sperling, M.R.; Sharan, A.; Asadi-Pooya, A.A. Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, R.F.; Zheng, J.; Mnatsakanyan, L.; Vadera, S.; Knight, R.T.; Lin, J.J.; Yassa, M.A. Hippocampal CA1 gamma power predicts the precision of spatial memory judgments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10148–10153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Rakoczy, S.; Brown-Borg, H. Assessment of spatial memory in mice. Life Sci. 2010, 87, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, N. What are the differences between long-term, short-term, and working memory? Prog. Brain Res. 2008, 169, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freedman, M.L.; Martin, R.C. Dissociable components of short-term memory and their relation to long-term learning. Cogn. Neuropsychol. 2001, 18, 193–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowan, N. The many faces of working memory and short-term storage. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 2017, 24, 1158–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, A.R.; Yshii, L.M.; Viel, T.A.; Buck, H.S.; Mattson, M.P.; Scavone, C.; Kawamoto, E.M. Intermittent fasting attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lively, S.; Schlichter, L.C. Microglia responses to pro-inflammatory stimuli (LPS, IFNγ+ TNFα) and reprogramming by resolving cytokines (IL-4, IL-10). Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yin, S.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Dong, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, S. LPS-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression in human airway epithelial cells and macrophages via NF-κB, STAT3 or AP-1 activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5484–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; Jiang, K.; Wu, H.; Qiu, C.; Guo, M.; Deng, G. Oridonin attenuates the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264. 7 cells and acute lung injury. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavaillon, J.-M. Exotoxins and endotoxins: Inducers of inflammatory cytokines. Toxicon 2018, 149, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmand, M.J.; Rajaei, Z. Effects of crocin on spatial or aversive learning and memory impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Avicenna J. Phytomed. 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Batista, C.R.A.; Gomes, G.F.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Fiebich, B.L.; De Oliveira, A.C.P. Lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation as a bridge to understand neurodegeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andy, S.N.; Pandy, V.; Alias, Z.; Kadir, H.A. Deoxyelephantopin ameliorates lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced memory impairments in rats: Evidence for its anti-neuroinflammatory properties. Life Sci. 2018, 206, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastinu, A.; Bonini, S.A.; Rungratanawanich, W.; Aria, F.; Marziano, M.; Maccarinelli, G.; Abate, G.; Premoli, M.; Memo, M.; Uberti, D. Gamma-oryzanol prevents LPS-induced brain inflammation and cognitive impairment in adult mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thingore, C.; Kshirsagar, V.; Juvekar, A. Amelioration of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment using Rosmarinic acid in mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2021, 36, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, K.; Quesada-Yamasaki, D.; Fornaguera-Trías, J. A Protocol to Perform Systemic Lipopolysacharide (LPS) Challenge in Rats. Odovtos-Int. J. Dent. Sci. 2019, 21, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley-Brits, K.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease model mice. JoVE 2011, 20, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, T.; Ikram, M.; Ullah, R.; Rehman, S.U.; Kim, M.O. Hesperetin, a citrus flavonoid, attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation, apoptosis and memory impairments by modulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazem, A.; Sankowski, R.; Bacher, M.; Al-Abed, Y. Rodent models of neuroinflammation for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Tan, X.; Yuan, T.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Supplementation of lycopene attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced amyloidogenesis and cognitive impairments via mediating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 56, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, M.A.; Hartvigson, P.E.; Morofuji, Y.; Owen, J.B.; Butterfield, D.A.; Banks, W.A. Lipopolysaccharide impairs amyloid beta efflux from brain: Altered vascular sequestration, cerebrospinal fluid reabsorption, peripheral clearance and transporter function at the blood–brain barrier. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, X.; Li, G.; Liu, D. The effects of curcumin on depressive-like behavior in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 274, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.C.; Lawson, M.A.; Andre, C.; Moreau, M.; Lestage, J.; Castanon, N.; Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Lipopolysaccharide-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activation in mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Bi, W.; Xiao, S.; Lan, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, H. Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, Z.; Gholamnezhad, Z.; Hosseini, M. The effects of exercise on hippocampal inflammatory cytokine levels, brain oxidative stress markers and memory impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorhees, C.V.; Williams, M.T. Assessing spatial learning and memory in rodents. ILAR J. 2014, 55, 310–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, C.-M.; Magda, G.; Abel, S. Spatial memory: Theoretical basis and comparative review on experimental methods in rodents. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 203, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdi, S.P.; Raval, A.; Nakhate, K.T. Phloridzin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment via antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and neuromodulatory activities. Cytokine 2021, 139, 155408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ali, T.; Rehman, S.U.; Khan, M.S.; Alam, S.I.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Saeed, K.; Badshah, H.; Kim, M.O. Neuroprotective effect of quercetin against the detrimental effects of LPS in the adult mouse brain. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Y-maze for assessment of spatial working and reference memory in mice. In Pre-Clinical Models; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, A.A.; Gawali, N.B.; Shinde, P.; Munshi, R.; Juvekar, A.R. Imperatorin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide induced memory deficit by mitigating proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and modulating brain-derived neurotropic factor. Cytokine 2018, 110, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emokpae, O.; Ben-Azu, B.; Ajayi, A.M.; Umukoro, S. D-Ribose-L-cysteine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory deficits through inhibition of oxidative stress, release of proinflammatory cytokines, and nuclear factor-kappa B expression in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Yu, X.; Huang, K.; Zheng, T.; Cheng, X.; Zeng, S.; Liu, X. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of intact tissues via delipidation and ultrasound. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.F.; Nolan, Y.M. Inflammation and the developing brain: Consequences for hippocampal neurogenesis and behavior. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2014, 40, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrientos, R.; Kitt, M.; Watkins, L.; Maier, S. Neuroinflammation in the normal aging hippocampus. Neuroscience 2015, 309, 84–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shen, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X. Chicoric acid supplementation prevents systemic inflammation-induced memory impairment and amyloidogenesis via inhibition of NF-κB. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1494–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eduviere, A.T.; Umukoro, S.; Adeoluwa, O.A.; Omogbiya, I.A.; Aluko, O.M. Possible mechanisms involved in attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced memory deficits by methyl jasmonate in mice. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 3239–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Yan, S.; Zheng, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C. Eriodictyol attenuates LPS-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis, and cognitive impairments via the inhibition of NF-κB in male C57BL/6J mice and BV2 microglial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10205–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Wu, X.; Block, M.L.; Liu, Y.; Breese, G.R.; Hong, J.S.; Knapp, D.J.; Crews, F.T. Systemic LPS causes chronic neuroinflammation and progressive neurodegeneration. Glia 2007, 55, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, E.; Agrawal, R.; Nath, C.; Shukla, R. Influence of LPS-induced neuroinflammation on acetylcholinesterase activity in rat brain. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 205, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, T.; Chen, H.; Kevala, K.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, H.-Y. N-Docosahexaenoylethanolamine ameliorates LPS-induced neuroinflammation via cAMP/PKA-dependent signaling. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabab, T.; Khanabdali, R.; Moghadamtousi, S.Z.; Kadir, H.A.; Mohan, G. Neuroinflammation pathways: A general review. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.; Muhammad, T.; Ikram, M.; Kim, M.O. Dietary supplementation of the antioxidant curcumin halts systemic LPS-induced neuroinflammation-associated neurodegeneration and memory/synaptic impairment via the JNK/NF-κB/Akt signaling pathway in adult rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, I.J.; Yun, J.; Son, D.J.; Han, S.-B.; Hong, J.T. Antifungal drug miconazole ameliorated memory deficits in a mouse model of LPS-induced memory loss through targeting iNOS. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Elamipretide (SS-31) improves mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic and memory impairment induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fu, J. Curcumin inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation by promoting microglial M2 polarization via TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB pathways in BV2 cells. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 116, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Liu, Q.; Li, D.; Zheng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Li, J. Acute nicotine treatment attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive dysfunction by increasing BDNF expression and inhibiting neuroinflammation in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 604, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saral, S.; Topçu, A.; Alkanat, M.; Mercantepe, T.; Akyıldız, K.; Yıldız, L.; Tümkaya, L.; Yazıcı, Z.A.; Yılmaz, A. Apelin-13 activates the hippocampal BDNF/TrkB signaling pathway and suppresses neuroinflammation in male rats with cisplatin-induced cognitive dysfunction. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 408, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajic, D.; Selakovic, D.; Jovicic, N.; Joksimovic, J.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L.; Rosic, G. The role of galectin-3 in modulation of anxiety state level in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 78, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima Giacobbo, B.; Doorduin, J.; Klein, H.C.; Dierckx, R.A.; Bromberg, E.; de Vries, E.F. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain disorders: Focus on neuroinflammation. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 3295–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bahaidrah, K.A.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Aldhahri, R.S.; Mansouri, R.A.; Alghamdi, B.S. Effects of Different Lipopolysaccharide Doses on Short- and Long-Term Spatial Memory and Hippocampus Morphology in an Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 2022, 6, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn6030020
Bahaidrah KA, Alzahrani NA, Aldhahri RS, Mansouri RA, Alghamdi BS. Effects of Different Lipopolysaccharide Doses on Short- and Long-Term Spatial Memory and Hippocampus Morphology in an Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience. 2022; 6(3):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn6030020
Chicago/Turabian StyleBahaidrah, Khulud Abdullah, Noor Ahmed Alzahrani, Rahaf Saeed Aldhahri, Rasha Abdulrashed Mansouri, and Badrah Saeed Alghamdi. 2022. "Effects of Different Lipopolysaccharide Doses on Short- and Long-Term Spatial Memory and Hippocampus Morphology in an Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model" Clinical and Translational Neuroscience 6, no. 3: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn6030020
APA StyleBahaidrah, K. A., Alzahrani, N. A., Aldhahri, R. S., Mansouri, R. A., & Alghamdi, B. S. (2022). Effects of Different Lipopolysaccharide Doses on Short- and Long-Term Spatial Memory and Hippocampus Morphology in an Experimental Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Clinical and Translational Neuroscience, 6(3), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/ctn6030020





