Transport of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Porous Media: Characterization and Quantification of Retention Informed by Atomic Force Microscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiment Approach
2.3. Atomic Force Microscope Measurements
2.4. Transport Experiments
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
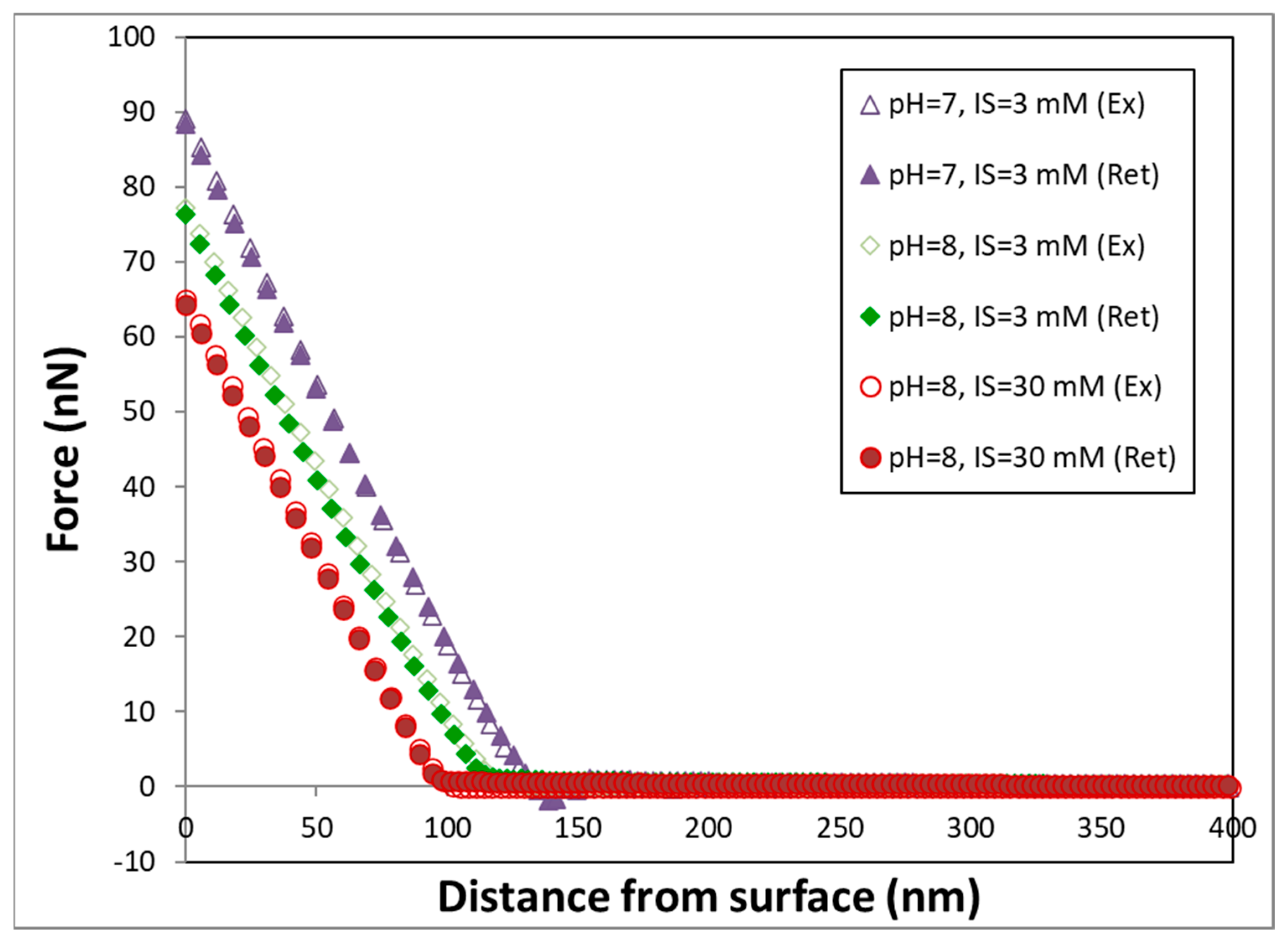
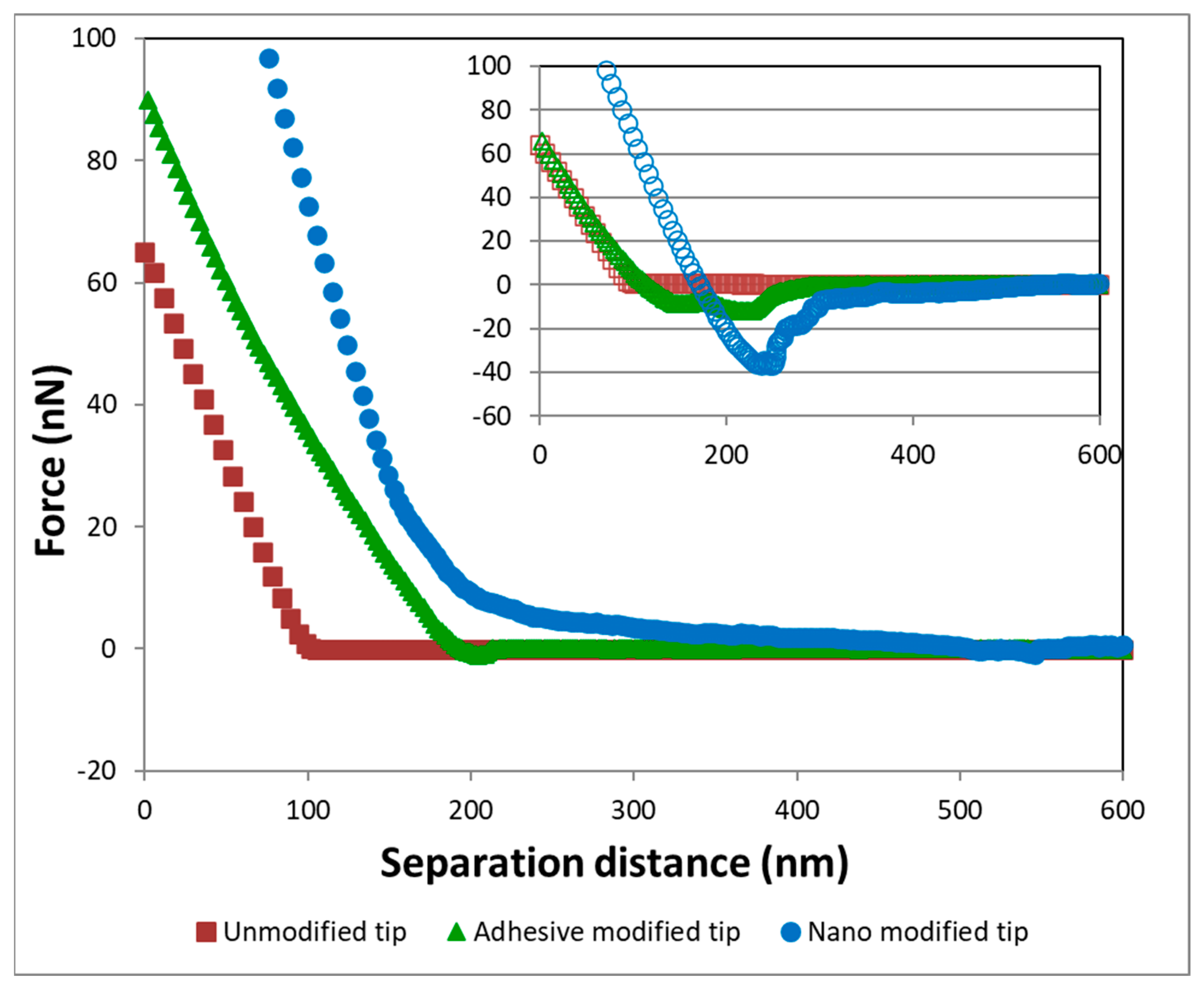
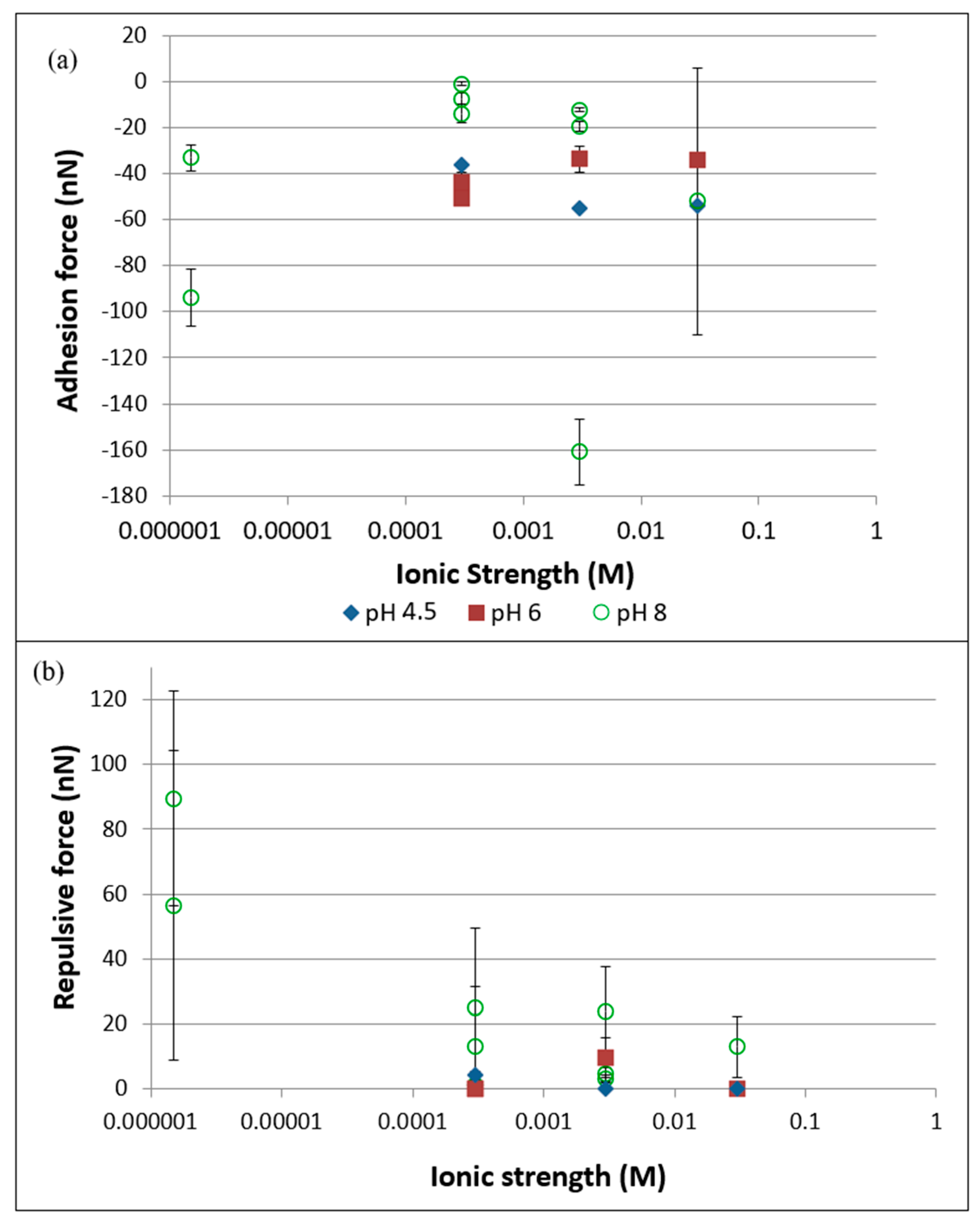
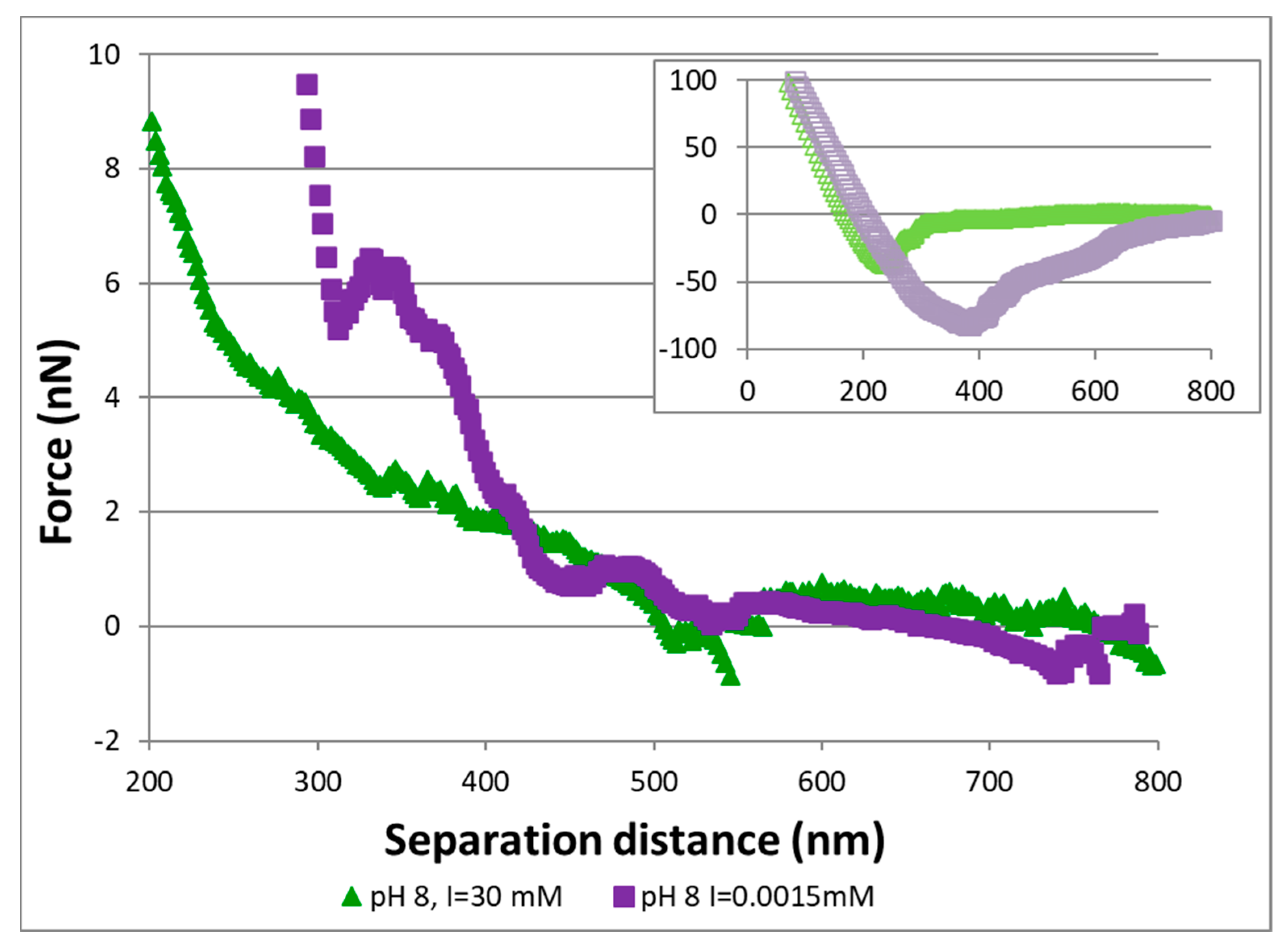
3.2. AFM Experiments
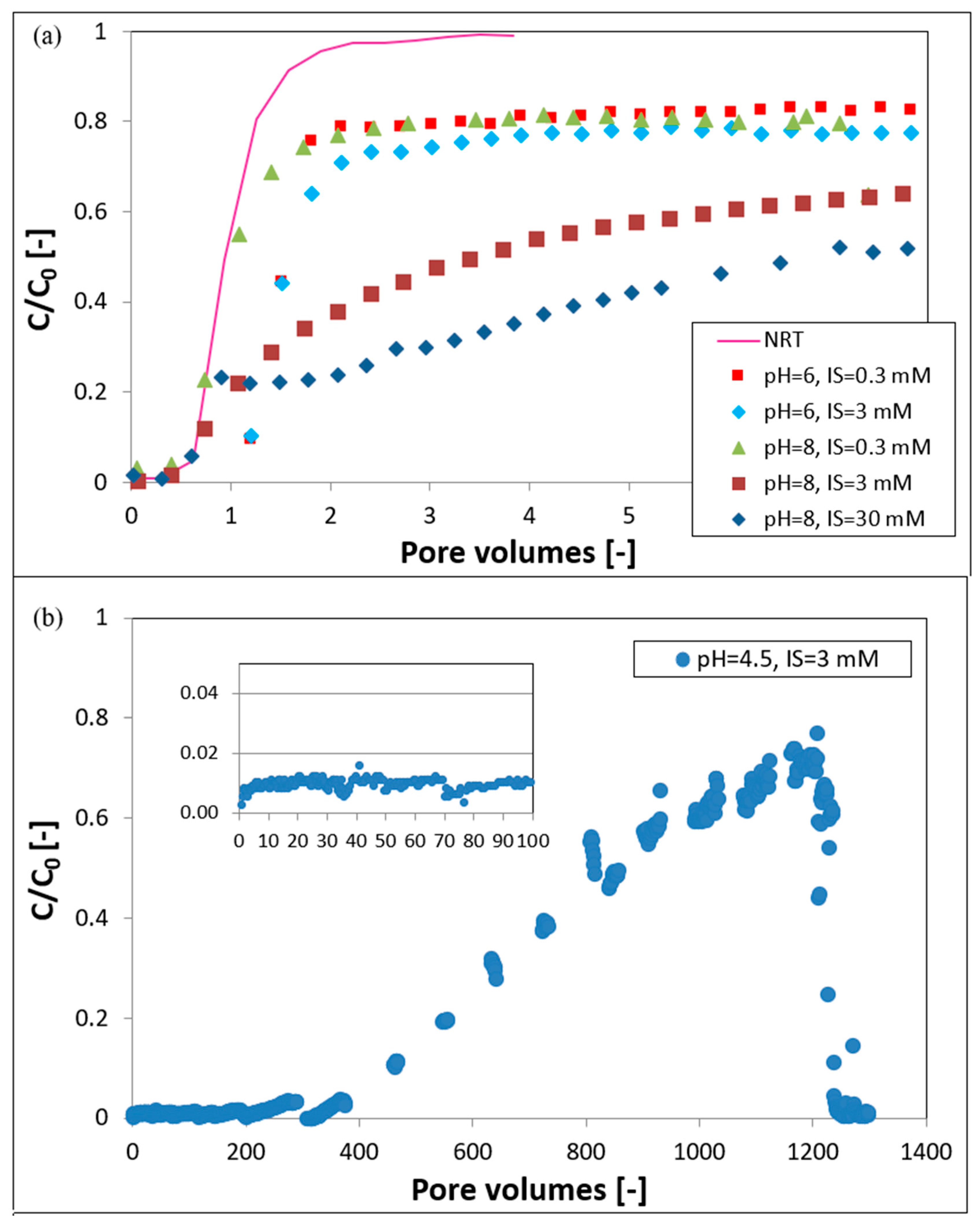
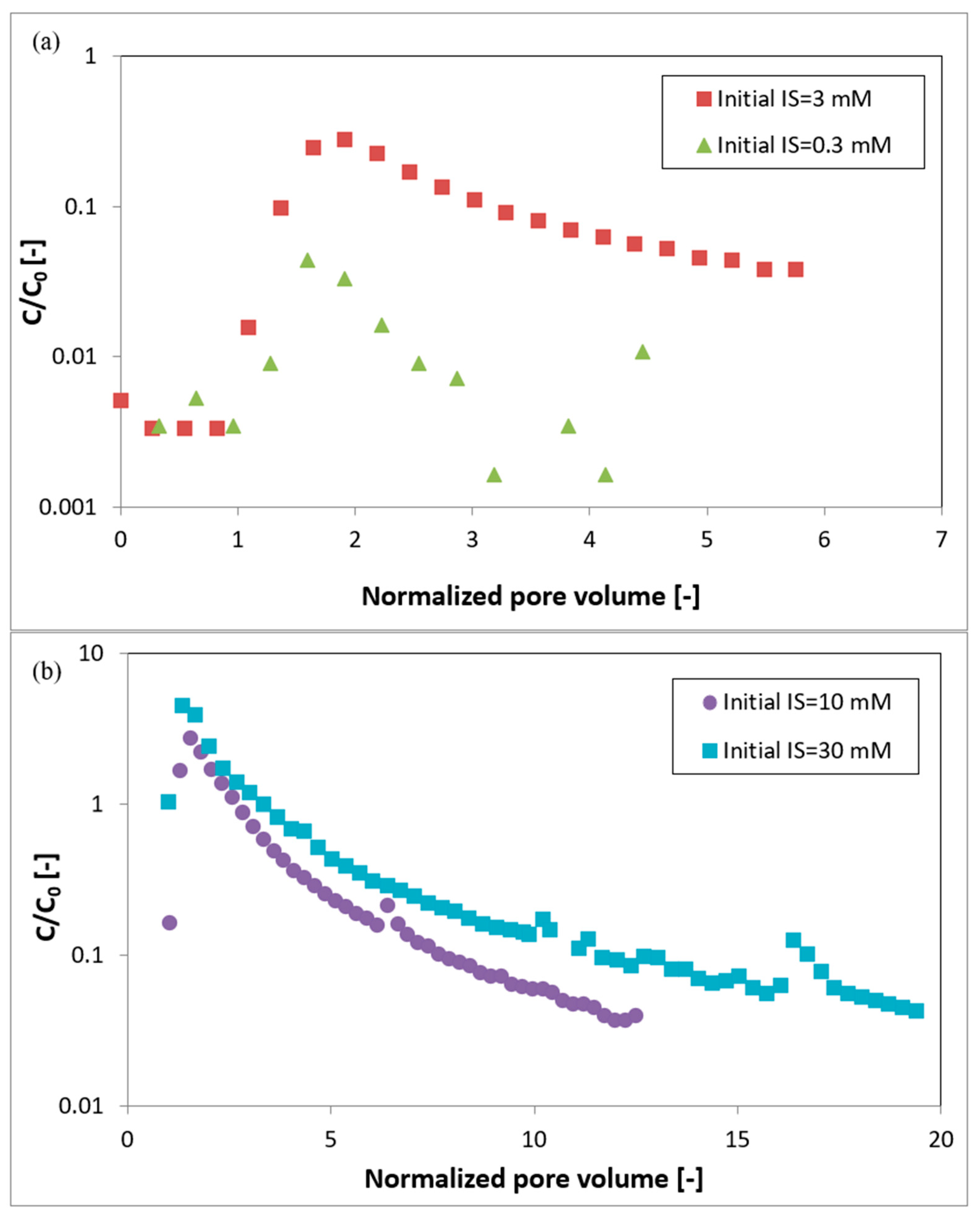
3.3. Transport Experiments
4. Discussion
4.1. DLVO Predictions vs. Measured Data
4.2. Implications of AFM Measurements for Transport Behavior
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, T.-K.; Nguyen, M.-K.; Lin, C.; Hoang, T.-D.; Nguyen, T.-C.; Lone, A.M.; Khedulkar, A.P.; Gaballah, M.S.; Singh, J.; Chung, W.J.; et al. Review on fate, transport, toxicity and health risk of nanoparticles in natural ecosystems: Emerging challenges in the modern age and solutions toward a sustainable environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 912, 169331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gao, B.; Tang, D. Review of key factors controlling engineered nanoparticle transport in porous media. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Yang, D. Critical Review of Stabilized Nanoparticle Transport in Porous Media. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 2019, 141, 070801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangani, M.F.; Owens, G.; Fotovat, A. Transport of engineered nanoparticles in soils and aquifers. Environ. Rev. 2019, 27, 43–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, E.O.; Amber, I.; Officer, S.; Oluyemi, G.F. Transport of nanoparticles in porous media and associated environmental impact: A review. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 12, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinno, F.; Gottschalk, F.; Seeger, S.; Nowack, B. Industrial production quantities and uses of ten engi-neered nanomaterials in Europe and the world. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, C.O.; Uyar, A.E.; Darby, M.R.; Zucker, L.G.; Wiesner, M.R. Estimates of upper bounds and trends in nano-TiO2 production as a basis for exposure assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4227–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiers, J.E.; Hornberger, G.M.; Liang, L. First- and second-order kinetics approaches for modeling the transport of colloidal particles in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy Guzman, K.A.; Finnegan, M.P.; Banfield, J.F. Influence of Surface Potential on Aggregation and Transport of Titania Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7688–7693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.C.; Wazne, M.; Meng, X. Application of an empirical transport model to simulate retention of nanocrystalline titanium dioxide in sand columns. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Shan, X.-Q.; Wen, B.; Lin, J.-M.; Owens, G. Stability of titania nanoparticles in soil suspensions and transport in saturated homogeneous soil columns. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Su, C. Transport and Retention of TiO2 Rutile Nanoparticles in Saturated Porous Media under Low-Ionic-Strength Conditions: Measurements and Mechanisms. Langmuir 2011, 27, 5393–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, I.; Hong, Y.; Honda, R.J.; Walker, S.L. Mechanisms of TiO2 nanoparticle transport in porous media: Role of solution chemistry, nanoparticle concentration, and flowrate. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 360, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinez, I.G.; Darnault, C.J. Aggregation and transport of nano-TiO2 in saturated porous media: Effects of pH, surfactants and flow velocity. Water Res. 2011, 45, 839–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Tong, M.; Wang, X.; Kim, H. Influence of Clay Particles on the Transport and Retention of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Quartz Sand. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7323–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Peng, S.; Wu, D.; Tong, M. Effect of different-sized colloids on the transport and deposition of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in quartz sand. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 208, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher-Power, L.M.; Cheng, T. Nanoscale Titanium Dioxide (nTiO2) Transport in Natural Sediments: Importance of Soil Organic Matter and Fe/Al Oxyhydroxides. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikopoulos, C.V.; Fountouli, T.V. Cotransport of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and formaldehyde in saturated and unsaturated columns packed with quartz sand. Vadose Zone J. 2022, 22, e20175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tu, C.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y. Enhancing effects of dissolved and media surface-bound organic matter on titanium dioxide nanoparticles transport in iron oxide-coated porous media under acidic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M. Effect of Particle Size on the Kinetics of Particle Deposition under Attractive Double Layer Interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 164, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Scheibe, T.D.; Johnson, W.P. Apparent Decreases in Colloid Deposition Rate Coefficients with Distance of Transport under Unfavorable Deposition Conditions: A General Phenomenon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5616–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufenkji, N.; Elimelech, M. Deviation from the classical colloid filtration theory in the pres-ence of repulsive DLVO interactions. Langmuir 2004, 20, 10818–10828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, B.D.; Epstein, N. Fine particle deposition in smooth parallel-plate channels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 72, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, G.M.; Olson, T.M. Particle size effects on colloid deposition kinetics: Evidence of secondary minimum deposition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1996, 107, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grolimund, D.; Elimelech, M.; Borkovec, M. Aggregation and deposition kinetics of mobile colloidal particles in natural porous media. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2001, 191, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Torkzaban, S.; Walker, S.L. Coupling of physical and chemical mechanisms of colloid straining in saturated porous media. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3012–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelley, A.J.; Tufenkji, N. Effect of particle size and natural organic matter on the migration of nano- and microscale latex particles in saturated porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 321, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Q.K.; Sokolov, I. Attachment of nanoparticles to the AFM tips for direct measurements of interaction between a single nanoparticle and surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 310, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attinti, R.; Wei, J.; Kniel, K.; Sims, J.T.; Jin, Y. Virus’ (MS2, ϕX174, and Aichi) Attachment on Sand Measured by Atomic Force Microscopy and Their Transport through Sand Columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2426–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thio, B.J.R.; Lee, J.-H.; Meredith, J.C.; Keller, A.A. Measuring the Influence of Solution Chemistry on the Adhesion of Au Nanoparticles to Mica Using Colloid Probe Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13995–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmulski, M. The significance of the difference in the point of zero charge between rutile and anatase. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 99, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusseau, M.; Oleen, J.; Santamaria, J.; Cheng, L.; Orosz-Coghlan, P.; Chetochine, A.; Blanford, W.; Rykwalder, P.; Gerba, C. Transport of microsporidium Encephalitozoon intestinales spores in sandy porous media. Water Res. 2005, 39, 3636–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaría, J.; Brusseau, M.L.; Araujo, J.; Blanford, W.J.; Gerba, C.P.; Orosz-Coghlan, P. Transport and Retention of Cryptosporidium Parvum Oocysts in Sandy Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L.D. Theory of the Stability of Strongly Charged Lyophobic Sols and of the Adhesion of Strongly Charged Particles in Solutions of Electrolytes. Acta Phys. Chim. URSS 1941, 14, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids: The Inter-Action of Sol Particles Having an Electric Double Layer; Elsevier Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, S.A.; Yates, S.R.; Bettahar, M.; Simunek, J. Physical factors affecting the transport and fate of colloids in saturated porous media. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 63-1–63-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.P.; Pazmino, E.; Ma, H. Direct observations of colloid retention in granular media in the presence of energy barriers, and implications for inferred mechanisms from indirect observations. Water Res. 2010, 44, 1158–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoanet, H.F.; Weisner, M.R. Velocity effects on fullerene and oxide nanoparticle deposition in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4377–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoanet, H.F.; Bottero, J.Y.; Wiesner, M.R. Laboratory assessment of the mobility of nano-materials in porous media. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 5164–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogami, I.; Ise, N. On the electrostatic interaction in macroionic solutions. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 81, 6320–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, M.B.; Baveye, P. Diffuse Double-Layer Models, Long-Range Forces, and Ordering in Clay Colloids. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell-Boyer, L.M. Chemical mobilization of micron-sized particles in saturated porous media under steady flow conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1992, 26, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.W.; O’Melia, C.R. Deposition and Reentrainment of Brownian Particles in Porous Media under Unfavorable Chemical Conditions: Some Concepts and Applications. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 38, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Jin, Y. Kinetics of Coupled Primary and Secondary-Minimum Deposition of Colloids under Unfavorable Chemical Conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6976–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Measured | Predicted | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH [−] | IS [mM] | 2 Minima [nN] | Repulsive Barrier [nN] | 2 Minima [nN] | Repulsive Barrier [nN] |
| 8 | 30 | −0.9 | 12.9 | −0.014 | 1.2 |
| 3 | −1.25 | 10.5 | −0.0008 | 1.6 | |
| 0.3 | −0.12 | 19 | 0 | 1.0 | |
| 0.0015 | −0.82 | 73 | n/a | n/a | |
| 6 | 30 | 0 | 0 | −0.015 | 0.17 |
| 3 | 0 | 9.7 | −0.0008 | 0.64 | |
| 0.3 | −0.18 | 0.54 | 0 | 0.65 | |
| 4.5 | 30 | 0 | 4.1 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| pH [−] | I [mM] | Zeta Potential [mV] |
|---|---|---|
| 4.5 | 0.3 | 13* |
| 3 | 13 | |
| 30 | 13* | |
| 6 | 0.3 | −40 |
| 3 | −48 | |
| 30 | −52* | |
| 8 | 15 | −42 |
| 15 | −49 | |
| 30 | −54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cox, H.; Brusseau, M.L. Transport of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Porous Media: Characterization and Quantification of Retention Informed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Colloids Interfaces 2025, 9, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050072
Cox H, Brusseau ML. Transport of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Porous Media: Characterization and Quantification of Retention Informed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Colloids and Interfaces. 2025; 9(5):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050072
Chicago/Turabian StyleCox, Hazel, and Mark L. Brusseau. 2025. "Transport of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Porous Media: Characterization and Quantification of Retention Informed by Atomic Force Microscopy" Colloids and Interfaces 9, no. 5: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050072
APA StyleCox, H., & Brusseau, M. L. (2025). Transport of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Porous Media: Characterization and Quantification of Retention Informed by Atomic Force Microscopy. Colloids and Interfaces, 9(5), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids9050072





