Monolayers of Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Stearate at the Water/Vapor Interface: A Physico-Chemical Study of Components of the Meibum Layer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Lipid Monolayers
2.3. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Equilibrium Behavior of Langmuir Monolayers of Pure Componentes at 24 °C: Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Estearate
3.2. Equilibrium Behavior of Langmuir Monolayers of Cholesterol-Cholesteryl Estearate Mixtures at 24 °C
3.3. Equilibrium Behavior of Langmuir Monolayers of Cholesterol-Cholesteryl Estearate Mixtures at 35 °C
3.4. Response of Langmuir Monolayers of Cholesterol-Cholesteryl Estearate Mixtures upon Dilational Stresses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lam, S.M.; Tong, L.; Duan, X.; Petznick, A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G. Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchman, D. Lipid conformational order and the etiology of cataract and dry eye. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butovich, I.A. Meibomian glands, meibum, and meibogenesis. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 163, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, N.; Bron, A.J.; Georgiev, G.A. The Precorneal Tear Film as a Fluid Shell: The Effect of Blinking and Saccades on Tear Film Distribution and Dynamics. Ocul. Surf. 2014, 12, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, R.E.; Corrsin, S. A surface tension gradient mechanism for driving the pre-corneal tear film after a blink. J. Biomech. 1974, 7, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Eftimov, P.; Yokoi, N. Structure-function relationship of tear film lipid layer: A contemporary perspective. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 163, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murube, J. The Origin of Tears. III. The Lipid Component in the XIX and XX Centuries. Ocul. Surf. 2012, 10, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, J.P.; Tomlinson, A. Importance of the lipid layer in human tear film stability and evaporation. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1997, 74, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Tiffany, J.M.; Gouveia, S.M.; Yokoi, N.; Voon, L.W. Functional aspects of the tear film lipid layer. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butovich, I.A. Tear film lipids. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulley, J.P.; Shine, W. A compositional based model for the tear film lipid layer. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1997, 95, 79–88, discussion 88–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borchman, D.; Foulks, G.N.; Yappert, M.C.; Bell, J.; Wells, E.; Neravetla, S.; Greenstone, V. Human Meibum Lipid Conformation and Thermodynamic Changes with Meibomian-Gland Dysfunction. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3805–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faheem, S.; Kim, S.-H.; Nguyen, J.; Neravetla, S.; Ball, M.; Foulks, G.N.; Yappert, M.C.; Borchman, D. Wax-tear and meibum protein, wax–β-carotene interactions in vitro using infrared spectroscopy. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 100, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bland, H.C.; Moilanen, J.A.; Ekholm, F.S.; Paananen, R.O. Investigating the Role of Specific Tear Film Lipids Connected to Dry Eye Syndrome: A Study on O-Acyl-ω-hydroxy Fatty Acids and Diesters. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2019, 35, 3545–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, S.L.; Hallock, K.J.; Funari, S.S.; Vaz, W.L.C.; Hamilton, J.A.; Melo, E. Study of the miscibility of cholesteryl oleate in a matrix of ceramide, cholesterol and fatty acid. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2011, 164, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Borchman, D.; Eftimov, P.; Yokoi, N. Lipid Saturation and the Rheology of Human Tear Lipids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, J.A. Dry Eye. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2212–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayton, J.L. Etiology, prevalence, and treatment of dry eye disease. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2009, 3, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachaj-Brekiesz, A.; Wnętrzak, A.; Lipiec, E.; Kobierski, J.; Dynarowicz-Latka, P. Perfluorohexyloctane (F6H8) as a delivery agent for cyclosporine A in dry eye syndrome therapy–Langmuir monolayer study complemented with infrared nanospectroscopy. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 184, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchman, D.; Ramasubramanian, A.; Foulks, G.N. Human Meibum Cholesteryl and Wax Ester Variability With Age, Sex, and Meibomian Gland Dysfunction. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, R.K.; Borchman, D.; Foulks, G.N.; Yappert, M.C.; Milliner, S.E. Analysis of the Composition of Lipid in Human Meibum from Normal Infants, Children, Adolescents, Adults, and Adults with Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Using 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 7350–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Smith, P.E.; Hinel, E.A.; Nichols, J.J. Application of a novel interferometric method to investigate the relation between lipid layer thickness and tear film thinning. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2418–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Matar, O.K.; Craster, R.V. Analysis of tear film rupture: Effect of non-Newtonian rheology. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 262, 130–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemp, M.A.; Crews, L.A.; Bron, A.J.; Foulks, G.N.; Sullivan, B.D. Distribution of aqueous-deficient and evaporative dry eye in a clinic-based patient cohort: A retrospective study. Cornea 2012, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiklik, L. Tear film lipid layer: A molecular level view. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembranes 2016, 1858, 2421–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.M.; Tong, L.; Yong, S.S.; Li, B.; Chaurasia, S.S.; Shui, G.; Wenk, M.R. Meibum lipid composition in Asians with dry eye disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birdi, K.S. Lipid and Biopolymer Monolayers at Liquid Interfaces; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Doughty, M.J. Further Assessment of Gender- and Blink Pattern-Related Differences in the Spontaneous Eyeblink Activity in Primary Gaze in Young Adult Humans. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2002, 79, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purslow, C.; Wolffsohn, J.S. Ocular surface temperature: A review. Eye Contact Lens 2005, 31, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hifeda, Y.F.; Rayfield, G.W. Evidence for first-order phase transitions in lipid and fatty acid monolayers. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 1992, 8, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, F.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Dilatational rheology of insoluble polymer monolayers: Poly(vinylacetate). Phys. Rev. E 1998, 58, 7629–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.; Liggieri, L.; Santini, E.; Ferrari, M.; Ravera, F. Influence of silica nanoparticles on dilational rheology of DPPC–palmitic acid Langmuir monolayers. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 3938–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggieri, L.; Santini, E.; Guzmán, E.; Maestro, A.; Ravera, F. Wide-frequency dilational rheology investigation of mixed silica nanoparticle–CTAB interfacial layers. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7699–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.J.; Guzmán, E.; Martínez-Pedrero, F.; Ritacco, H.; Rubio, R.G.; Ortega, F.; Starov, V.M.; Miller, R. Particle laden fluid interfaces: Dynamics and interfacial rheology. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 206, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy, F.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G.; Velarde, M.G. Surface rheology, equilibrium and dynamic features at interfaces, with emphasis on efficient tools for probing polymer dynamics at interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 134–135, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llamas, S.; Guzman, E.; Akanno, A.; Fernandez-Pena, L.; Ortega, F.; Campbell, R.A.; Miller, R.; Rubio, R.G. Study of the Liquid/Vapor Interfacial Properties of Concentrated Polyelectrolyte-Surfactant Mixtures Using Surface Tensiometry and Neutron Reflectometry: Equilibrium, Adsorption Kinetics, and Dilational Rheology. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 4419–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaby, J.M.; Brockman, H.L. Novel surface phase containing cholesteryl esters. 2. Nonequivalence of cholesteryl arachidonate and those with 18-carbon, cis-unsaturated acyl groups. Biochemistry 1981, 20, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, C.N.; Heikkila, R.E.; Cornwell, D.G. Properties of cholesteryl esters in pure and mixed monolayers. J. Lipid Res. 1971, 12, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthman, L.A.D.; Nag, K.; Davis, P.J.; Keough, K.M.W. Cholesterol in condensed and fluid phosphatidylcholine monolayers studied by epifluorescence microscopy. Biophys. J. 1997, 72, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.; Liggieri, L.; Santini, E.; Ferrari, M.; Ravera, F. Mixed DPPC–cholesterol Langmuir monolayers in presence of hydrophilic silica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 105, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.; Ferrari, M.; Santini, E.; Liggieri, L.; Ravera, F. Effect of silica nanoparticles on the interfacial properties of a canonical lipid mixture. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 136, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przykaza, K.; Woźniak, K.; Jurak, M.; Wiącek, A.E.; Mroczka, R. Properties of the Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett monolayers of cholesterol-cyclosporine A on water and polymer support. Adsorption 2019, 25, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Hofmann, A.M.; Busse, K.; Frey, H.; Kressler, J. Langmuir and Langmuir−Blodgett Films of Multifunctional, Amphiphilic Polyethers with Cholesterol Moieties. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1978–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, A.; Rodríguez Niño, M.R.; Gunning, A.P.; Morris, V.J.; Wilde, P.J.; Rodríguez Patino, J.M. Effect of Hydrocarbon Chain and pH on Structural and Topographical Characteristics of Phospholipid Monolayers. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 7651–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, E.; Liggieri, L.; Santini, E.; Ferrari, M.; Ravera, F. DPPC–DOPC Langmuir monolayers modified by hydrophilic silica nanoparticles: Phase behaviour, structure and rheology. Colloids Surf. A 2012, 413, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.T.; Rideal, E.K. Interfacial Phenomena; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- López-Montero, I.; Arriaga, L.R.; Rivas, G.; Vélez, M.; Monroy, F. Lipid domains and mechanical plasticity of Escherichia coli lipid monolayers. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2010, 163, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Santini, E.; Zabiegaj, D.; Ferrari, M.; Liggieri, L.; Ravera, F. Interaction of Carbon Black Particles and Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at the Water/Air Interface: Thermodynamics and Rheology. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 26937–26947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King-Smith, P.E.; Bailey, M.D.; Braun, R.J. Four characteristics and a model of an effective tear film lipid layer (TFLL). Ocul. Surf. 2013, 11, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetman, Z.A.; Borchman, D. Concentration dependent cholesteryl-ester and wax-ester structural relationships and meibomian gland dysfunction. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2020, 21, 100732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wydro, P. Sphingomyelin/phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol monolayers–analysis of the interactions in model membranes and Brewster Angle Microscopy experiments. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 93, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, R.A.; Bruckdorfer, K.R.; van Deenen, L.L.M. Structural requirements of sterols for the interaction with lecithin at the air-water interface. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembranes 1972, 255, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demel, R.A.; Geurts van Kessel, W.S.M.; van Deenen, L.L.M. The properties of polyunsaturated lecithins in monolayers and liposomes and the interactions of these lecithins with cholesterol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembranes 1972, 266, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videv, P.; Mladenov, N.; Andreeva, T.; Mladenova, K.; Moskova-Doumanova, V.; Nikolaev, G.; Petrova, S.D.; Doumanov, J.A. Condensing Effect of Cholesterol on hBest1/POPC and hBest1/SM Langmuir Monolayers. Membranes 2021, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiarotti, A.; Galassi, V.V.; Puentes, E.N.; Oliveira, R.G.; del Pópolo, M.G.; Wilke, N. Hopanoids Like Sterols Form Compact but Fluid Films. Langmuir 2019, 35, 9848–9857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurak, M. Thermodynamic Aspects of Cholesterol Effect on Properties of Phospholipid Monolayers: Langmuir and Langmuir–Blodgett Monolayer Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3496–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheyne, R.B.; Moffitt, M.G. Novel Two-Dimensional “Ring and Chain” Morphologies in Langmuir−Blodgett Monolayers of PS-b-PEO Block Copolymers: Effect of Spreading Solution Concentration on Self-Assembly at the Air−Water Interface. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5453–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.-C.; Lee, M.-T.; Chen, F.-Y.; Huang, H.W. The Condensing Effect of Cholesterol in Lipid Bilayers. Biophys. J. 2007, 92, 3960–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Feng, S.S.; Go, M.L.; Soew, P.H. Effects of pH on the stability and compressibility of DPPC/cholesterol monolayers at the air-water interface. Colloids Surf. A 2002, 207, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, T.; Kato, S. Detailed Analysis of the Surface Area and Elasticity in the Saturated 1,2-Diacylphosphatidylcholine/Cholesterol Binary Monolayer System. Langmuir: The ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2015, 31, 9086–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Kister, A.T. Algebraic Representation of Thermodynamic Properties and the Classification of Solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1948, 40, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonales, L.J.; Martínez-Pedrero, F.; Rubio, M.A.; Rubio, R.G.; Ortega, F. Phase Behavior of Dense Colloidal Binary Monolayers. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16555–16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, E.; Orsi, D.; Cristofolini, L.; Liggieri, L.; Ravera, F. Two-Dimensional DPPC Based Emulsion-like Structures Stabilized by Silica Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11504–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, J.P.; McConnell, H.M. Liquid-liquid immiscibility in lipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1997, 1329, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowlinson, J.S.; Widom, B. The Molecular Theory of Capillarity; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, D.J.; McConnell, H.M.; Moy, V.T. Theory of superstructures in lipid monolayer phase transitions. J. Phys. Chem. 1986, 90, 2311–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gzyl-Malcher, B.; Handzlik, J.; Klekowska, E. Temperature dependence of the interaction of prazosin with lipid Langmuir monolayers. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 112, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benesch, M.G.K.; McElhaney, R.N. A comparative calorimetric study of the effects of cholesterol and the plant sterols campesterol and brassicasterol on the thermotropic phase behavior of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembranes 2014, 1838, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, F.; Smit, B. Effect of cholesterol on the structure of a phospholipid bilayer. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 2009, 106, 3654–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baoukina, S.; Mendez-Villuendas, E.; Tieleman, D.P. Molecular View of Phase Coexistence in Lipid Monolayers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 17543–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, E.; Pérez-Gil, J. Structure-function relationships in pulmonary surfactant membranes: From biophysics to therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2014, 1838, 1568–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardino de la Serna, J.; Perez-Gil, J.; Simonsen, A.C.; Bagatolli, L.A. Cholesterol rules: Direct observation of the coexistence of two fluid phases in native pulmonary surfactant membranes at physiological temperatures. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 40715–40722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
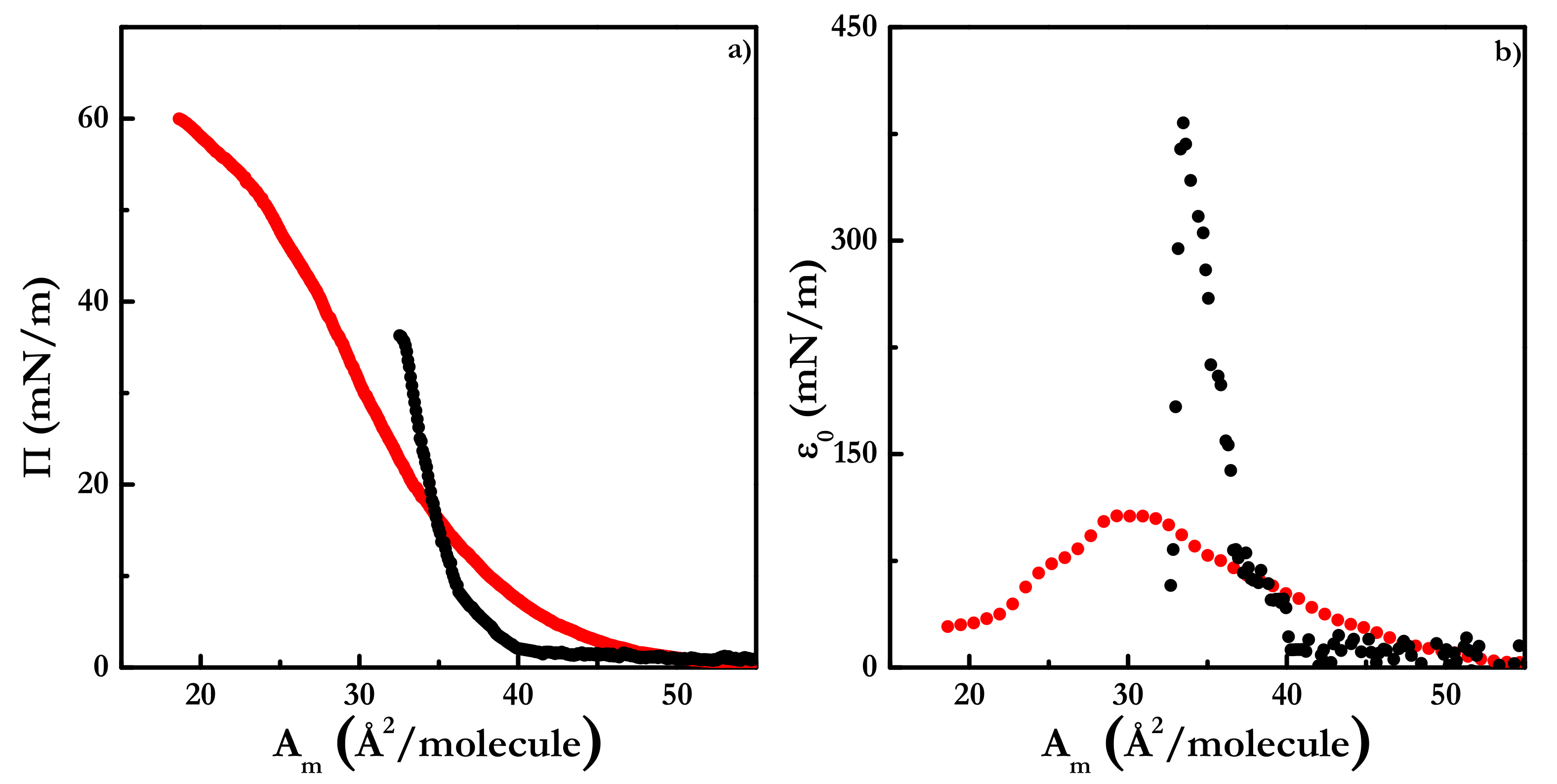


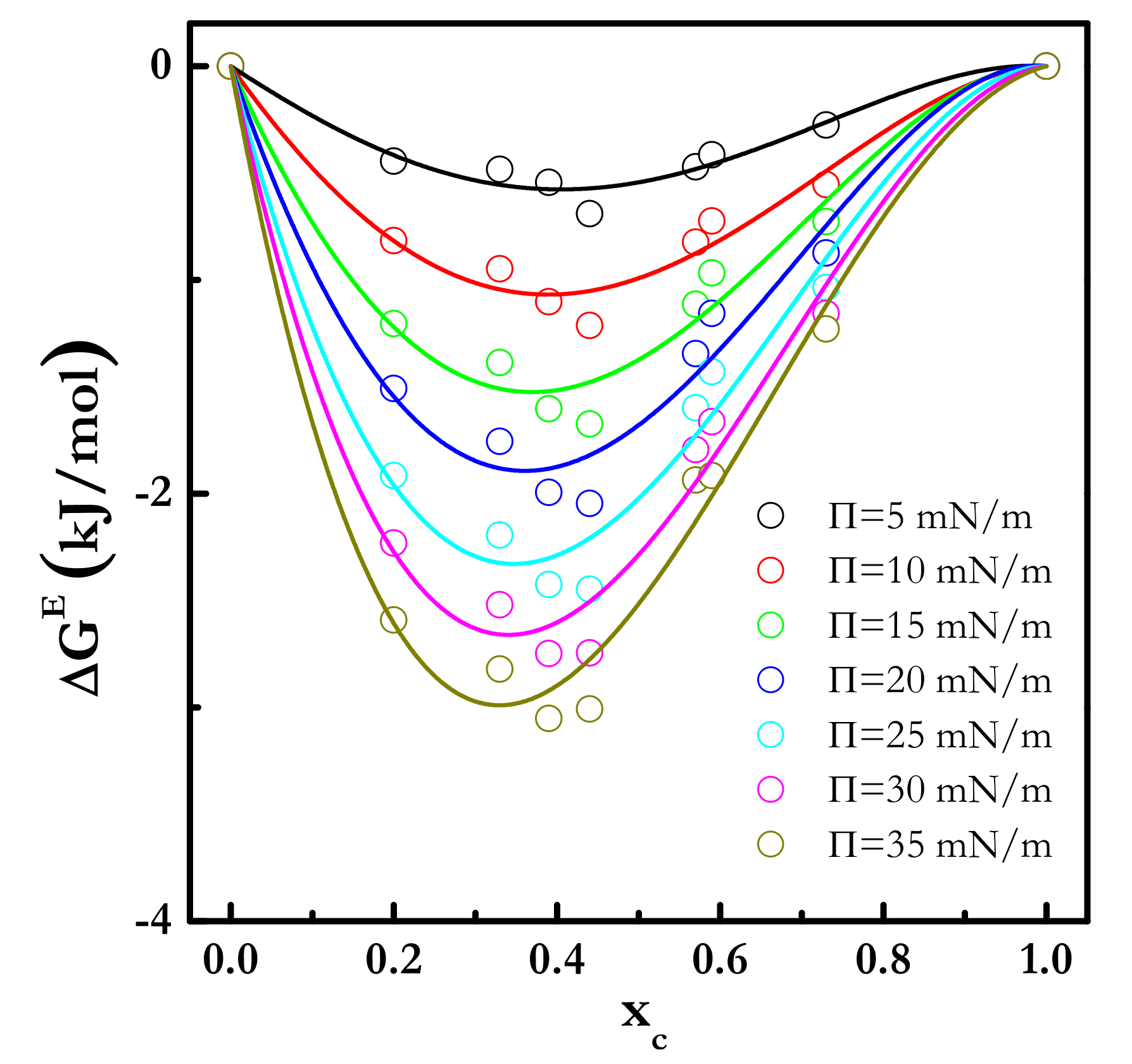
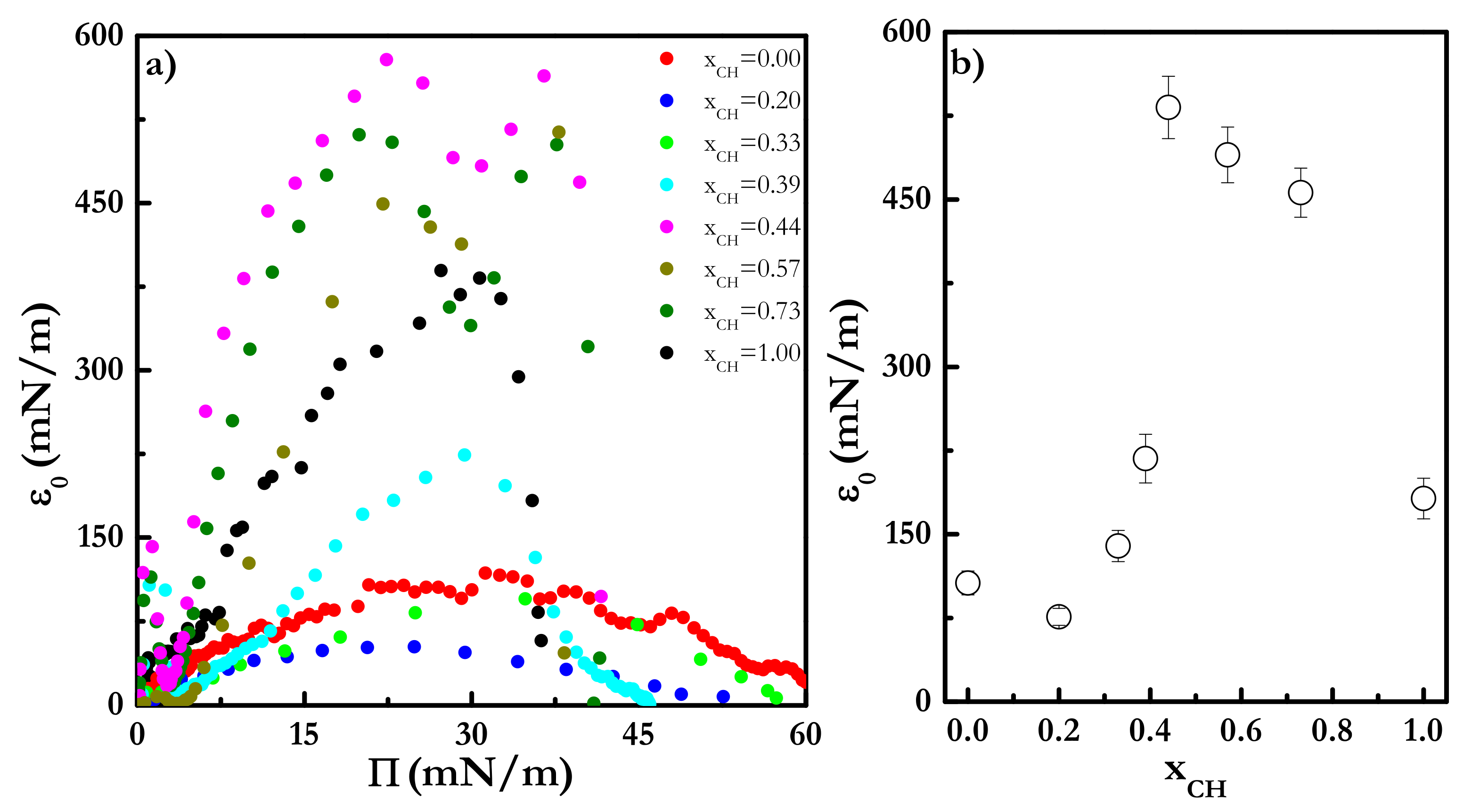

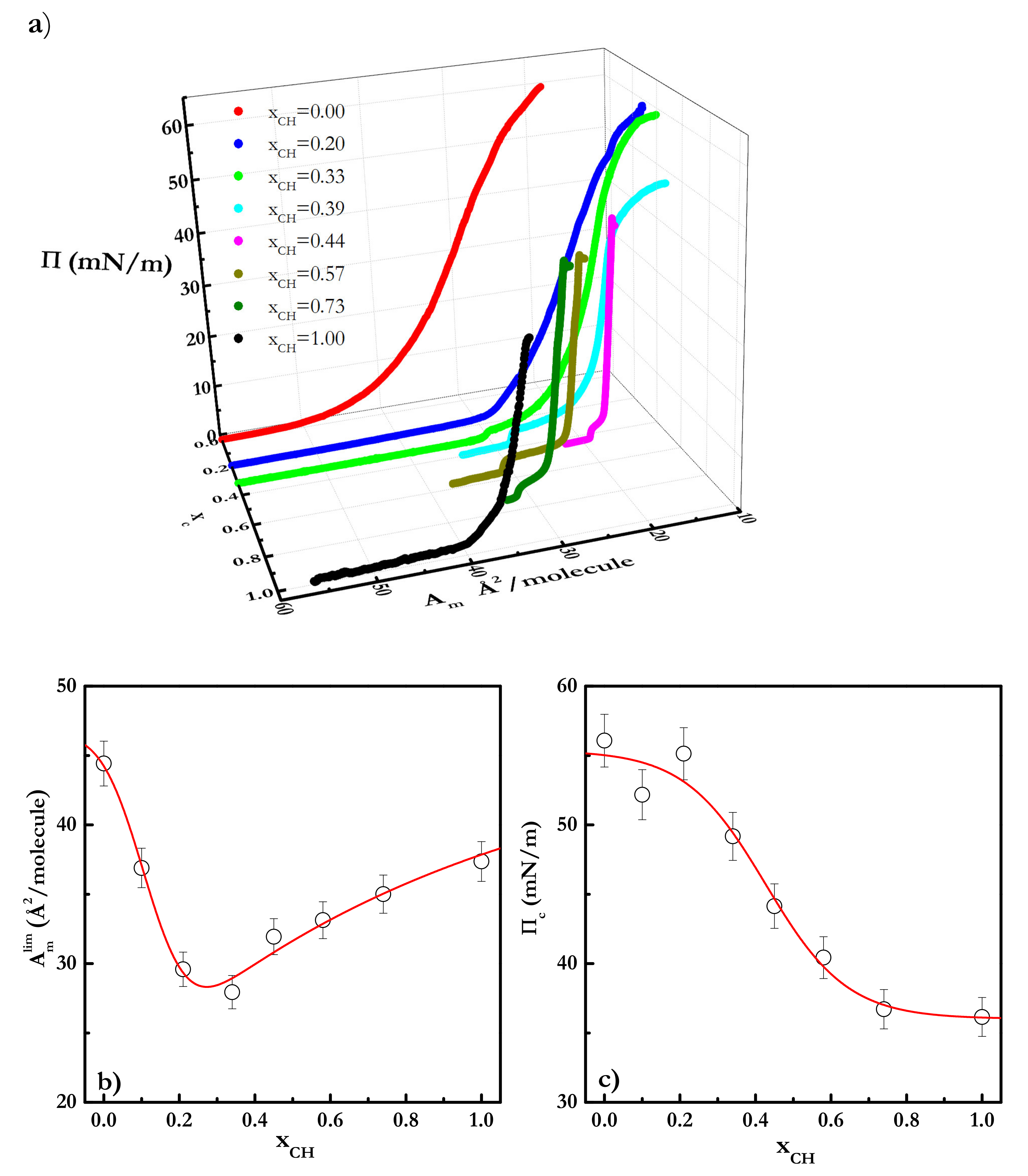
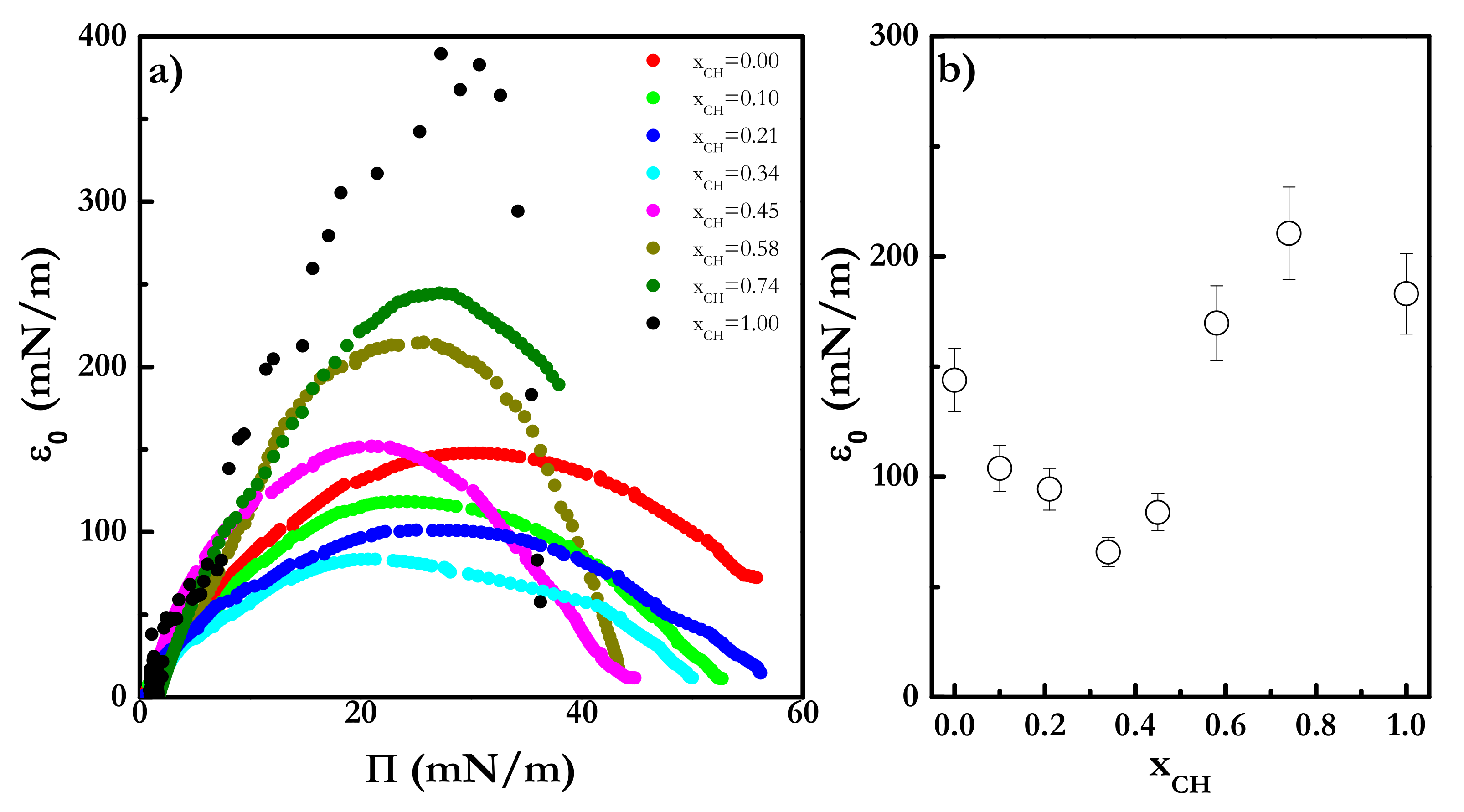
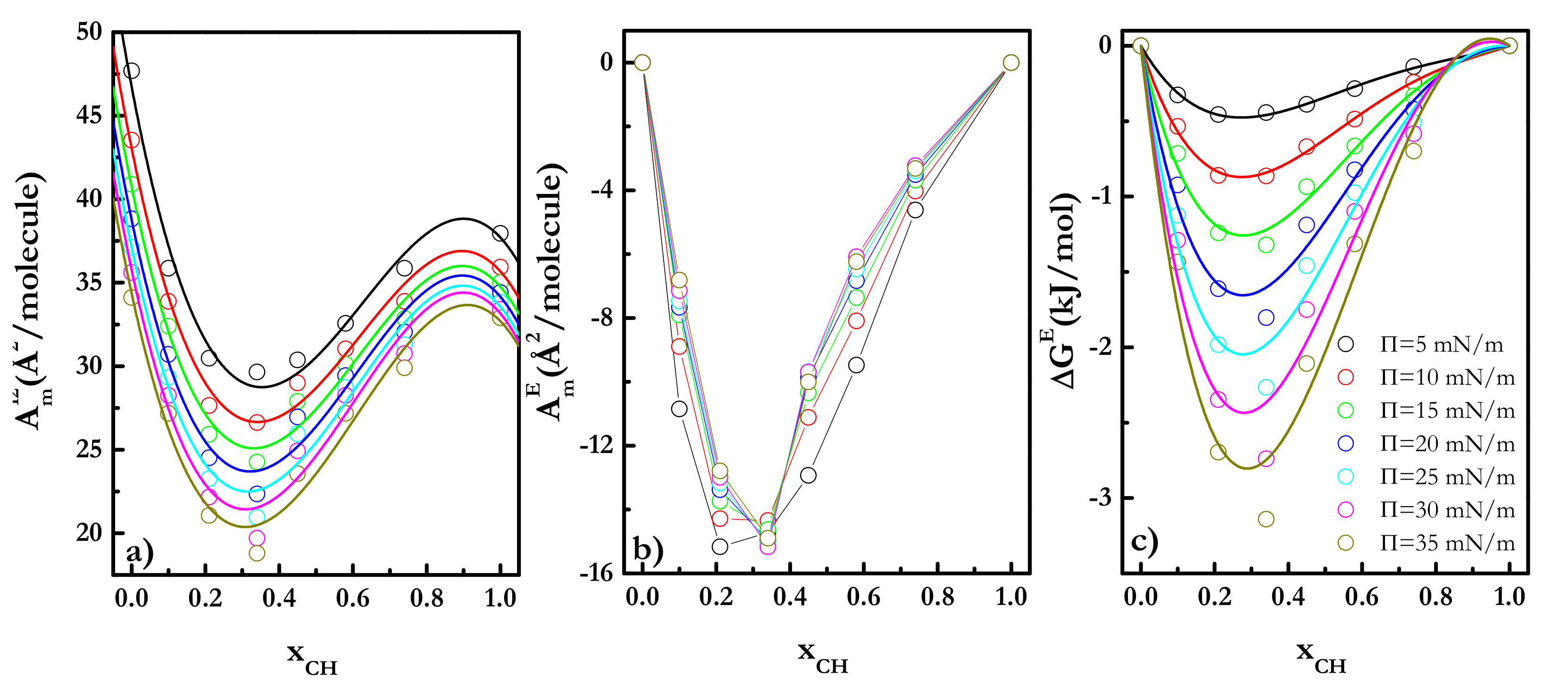

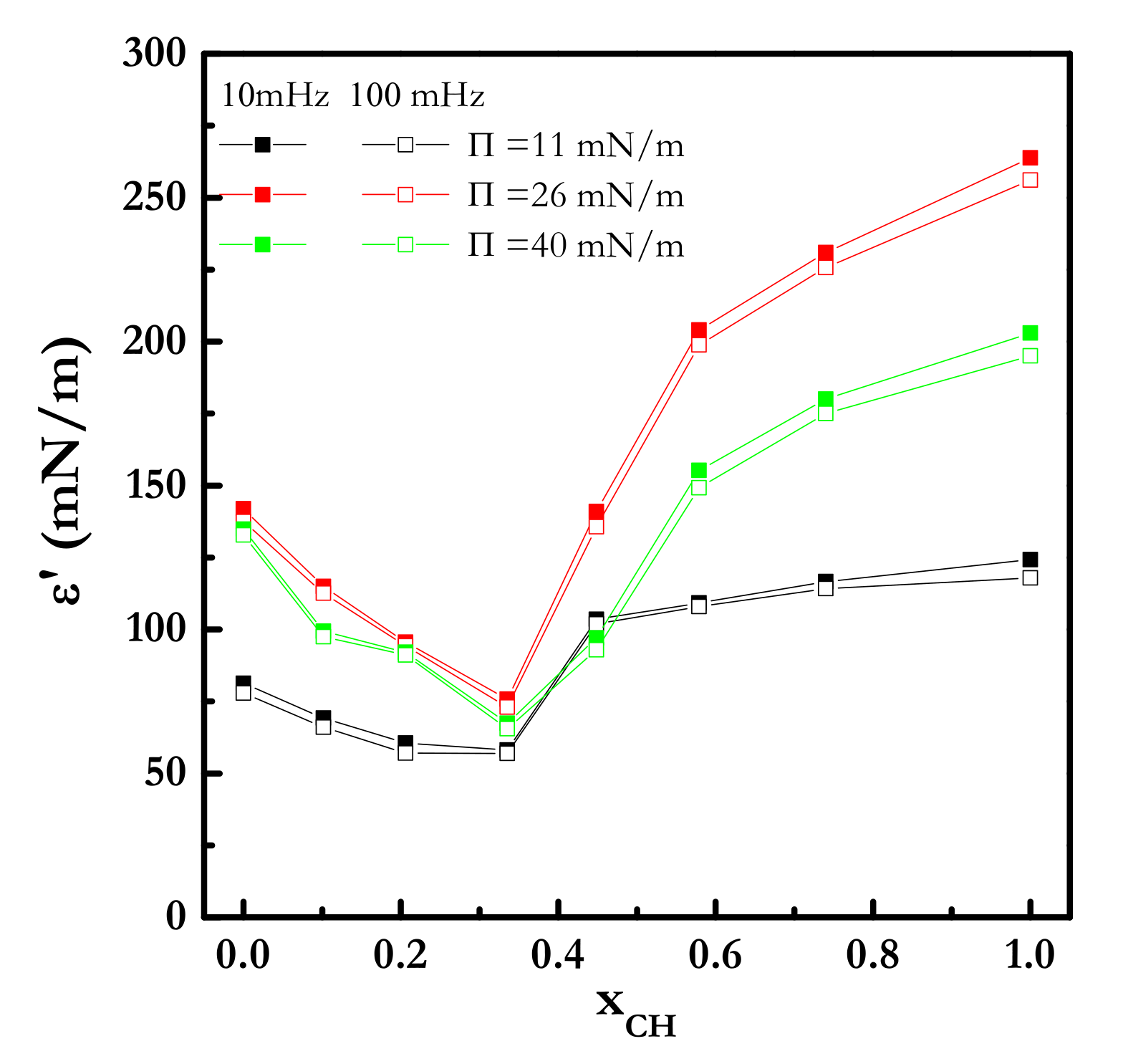
| Π (mN/m) | A1 (kJ/mol) | A2 (kJ/mol) | A3 (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | −2.17 | 1.35 | 1.06 |
| 10 | −3.97 | 2.65 | 1.24 |
| 15 | −5.49 | 4.38 | 1.35 |
| 20 | −6.72 | 5.75 | 1.39 |
| 25 | −8.09 | 7.37 | 0.70 |
| 30 | −9.14 | 8.53 | 0.16 |
| 35 | −10.06 | 9.91 | −0.81 |
| Π (mN/m) | A1 (kJ/mol) | A2 (kJ/mol) | A3 (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | −1.37 | 1.77 | −1.09 |
| 10 | −2.48 | 3.42 | −1.74 |
| 15 | −3.59 | 5.15 | −1.99 |
| 20 | −4.66 | 6.98 | −2.50 |
| 25 | −5.72 | 8.78 | −2.91 |
| 30 | −6.83 | 10.71 | −2.78 |
| 35 | −8.12 | 12.15 | −2.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rubio, R.G.; Guzmán, E.; Ortega, F.; Liggieri, L. Monolayers of Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Stearate at the Water/Vapor Interface: A Physico-Chemical Study of Components of the Meibum Layer. Colloids Interfaces 2021, 5, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020030
Rubio RG, Guzmán E, Ortega F, Liggieri L. Monolayers of Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Stearate at the Water/Vapor Interface: A Physico-Chemical Study of Components of the Meibum Layer. Colloids and Interfaces. 2021; 5(2):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020030
Chicago/Turabian StyleRubio, Ramón G., Eduardo Guzmán, Francisco Ortega, and Libero Liggieri. 2021. "Monolayers of Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Stearate at the Water/Vapor Interface: A Physico-Chemical Study of Components of the Meibum Layer" Colloids and Interfaces 5, no. 2: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020030
APA StyleRubio, R. G., Guzmán, E., Ortega, F., & Liggieri, L. (2021). Monolayers of Cholesterol and Cholesteryl Stearate at the Water/Vapor Interface: A Physico-Chemical Study of Components of the Meibum Layer. Colloids and Interfaces, 5(2), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids5020030









