Concentration and Dilution of Ultrafine Bubbles in Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generation of Ultrafine Bubbles in Ultrapure Water
2.2. Ultrapure Water and Glassware
2.3. Dilution with Air-Saturated and Degassed Water
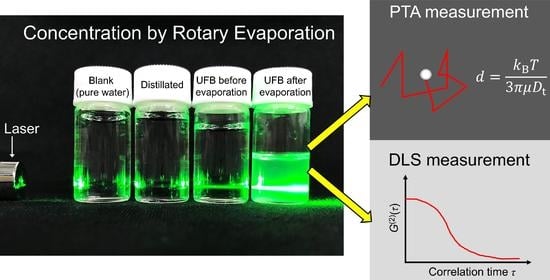
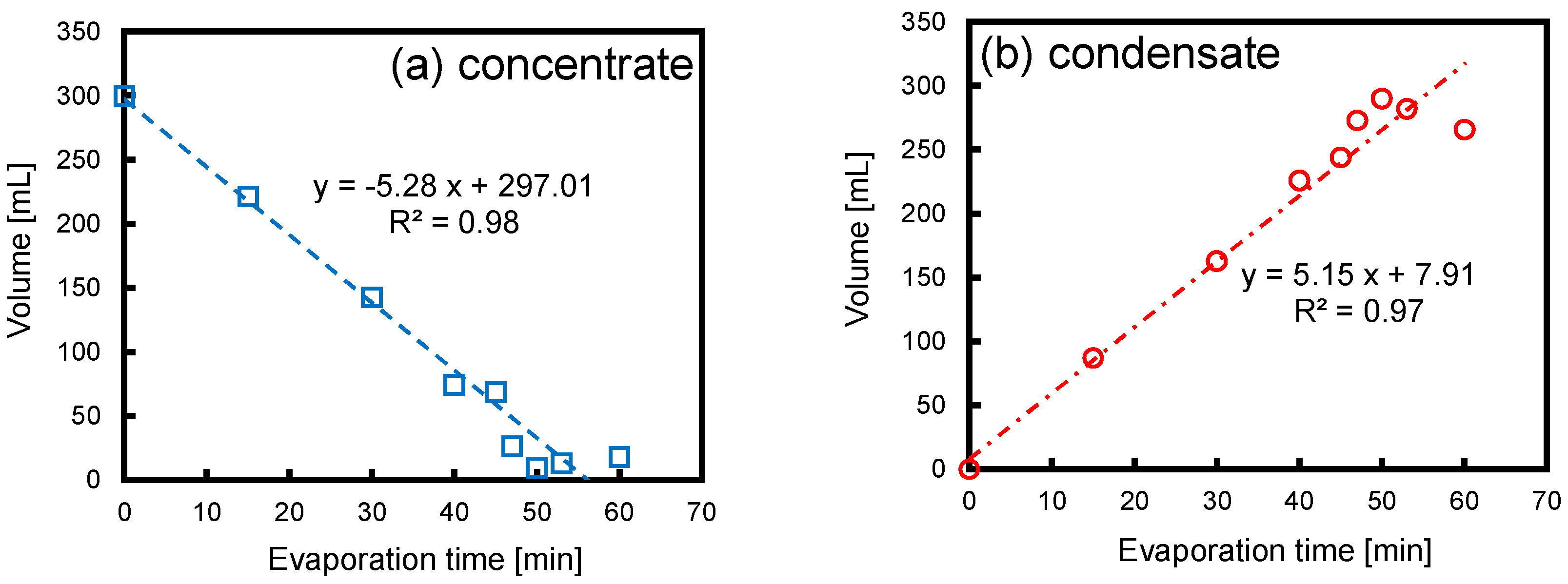
2.4. Rotary Evaporation
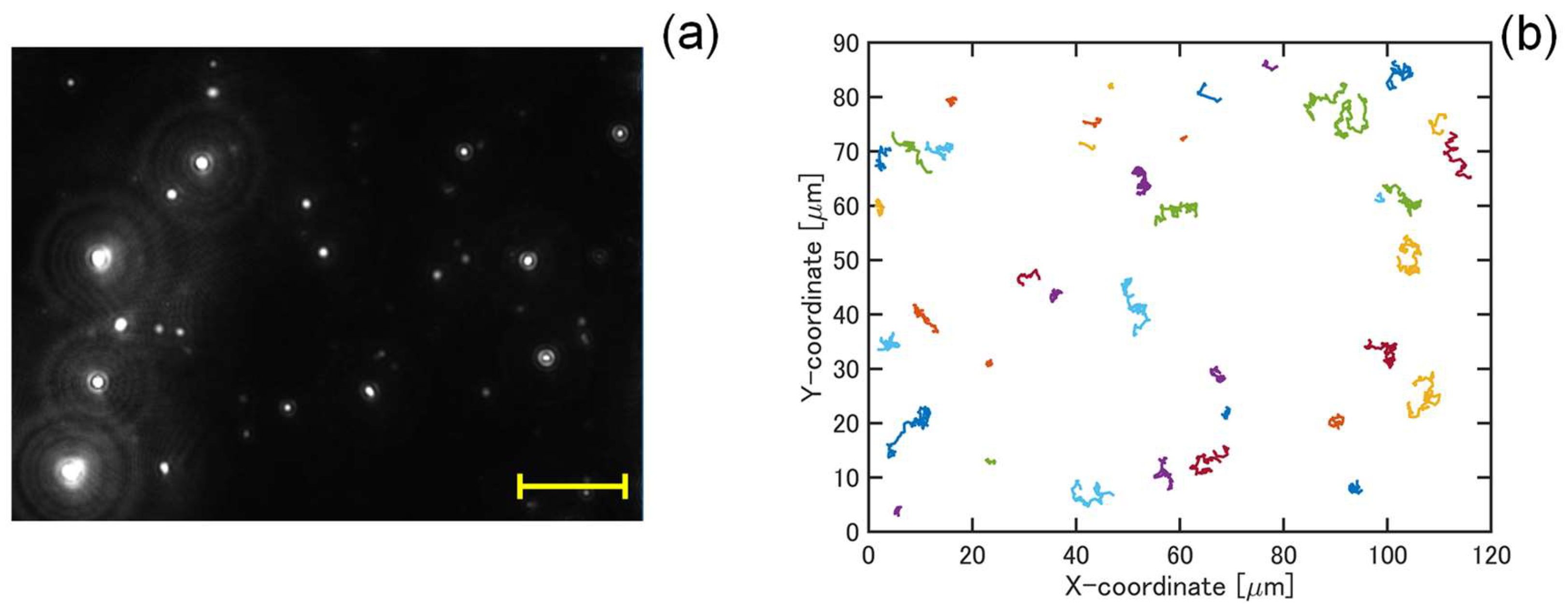
2.5. Particle Tracking Analysis
2.6. Dynamic Light Scattering
3. Results and Discussion
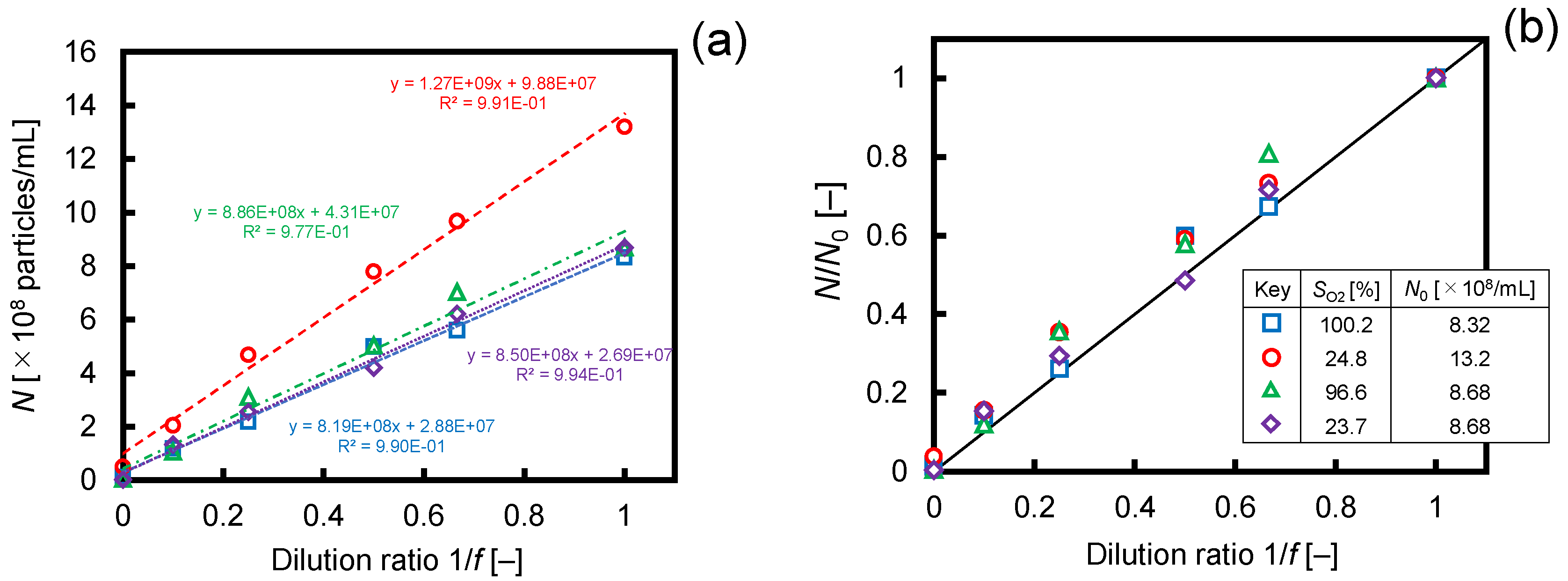
3.1. Dilution of Ultrafine Bubble Dispersions
3.2. Evaporation of Ultrafine Bubble Dispersions
3.3. Size Measurement with Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- ISO 20480-1:2017. Fine Bubble Technology—General Principles for Usage and Measurement of Fine Bubbles—Part 1: Terminology; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Genève, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/68187.html?browse=tc (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Alheshibri, M.; Qian, J.; Jehannin, M.; Craig, V.S.J. A History of Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11086–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.; Oliveira, H.; Rubio, J. Bulk Nanobubbles in the Mineral and Environmental Areas: Updating Research and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 271, 101992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alheshibri, M.; Craig, V.S.J. Differentiating between Nanoparticles and Nanobubbles by Evaluation of the Compressibility and Density of Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21998–22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheshibri, M.; Jehannin, M.; Coleman, V.A.; Craig, V.S.J. Does Gas Supersaturation by a Chemical Reaction Produce Bulk Nanobubbles? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alheshibri, M.; Craig, V.S.J. Generation of Nanoparticles upon Mixing Ethanol and Water; Nanobubbles or Not? J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 542, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.J.; Barigou, M. Bulk Nanobubbles or Not Nanobubbles: That is the Question. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1699–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantra, R.; Schulze, P.; Quincey, P. Effect of Nanoparticle Concentration on Zeta-potential Measurement Results and Reproducibility. Particuology 2010, 8, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuziuti, T.; Yasui, K.; Kanematsu, W. Influence of Addition of Degassed Water on Bulk Nanobubbles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 43, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasaka, K.; Himuro, S.; Ando, K.; Hata, T. Introduction to Fine Bubble Science and Technology; Nikkan Kogyo Shimbun, Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2016; ISBN 9784526076251. [Google Scholar]
- IDEC Global. Ultrafine Bubble Generation Technology. Available online: https://www.idec.com/home/finebubble/index.html (accessed on 1 September 2020).
- Filipe, V.; Hawe, A.; Jiskoot, W. Critical Evaluation of Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) by NanoSight for the Measurement of Nanoparticles and Protein Aggregates. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 796–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 19430:2016. Particle Size Analysis—Particle Tracking Analysis (PTA) Method; International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Genève, Switzerland, 2016; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/64890.html (accessed on 23 October 2020).
- Gross, J.; Sayle, S.; Karow, A.R.; Bakowsky, U.; Garidel, P. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis of Particle Size and Concentration Detection in Suspensions of Polymer and Protein Samples: Influence of Experimental and Data Evaluation Parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 104, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 22412:2017. Particle Size Analysis—Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS); International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Genève, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/65410.html (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Provencher, S.W. Contin: A General Purpose Constrained Regularization Program for Inverting Noisy Linear Algebraic and Integral Equations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1982, 27, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.L.; Hanson, R.J. Solving Least Squares Problems; Prentice-Hall series in automatic computation; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1974; ISBN 9780138225858. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, D.W. An Algorithm for Least-Squares Estimation of Nonlinear Parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalkar, N.; Pacek, A.W.; Barigou, M. Interpreting the Interfacial and Colloidal Stability of Bulk Nanobubbles. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 9643–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häbich, A.; Ducker, W.; Dunstan, D.E.; Zhang, X. Do Stable Nanobubbles Exist in Mixtures of Organic Solvents and Water? J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 6962–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Yamazaki, K.; Gohara, K. Generation of Micro- and Nano-bubbles in Water by Dissociation of Gas Hydrates. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, T.; Liu, S.; Enari, M.; Oshita, S.; Yamazaki, K.; Gohara, K. Effect of NaCl on the Lifetime of Micro- and Nanobubbles. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.H.; Kim, J. Generation and Stability of Bulk Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 3818–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weijs, J.H.; Seddon, J.R.T.; Lohse, D. Diffusive Shielding Stabilizes Bulk Nanobubble Clusters. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Tuziuti, T.; Kanematsu, W.; Kato, K. Dynamic Equilibrium Model for a Bulk Nanobubble and a Microbubble Partly Covered with Hydrophobic Material. Langmuir 2016, 32, 11101–11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, K.; Kestens, V.; Braun, A.; Roebben, G.; Linsinger, T.P.J. Non-Equivalence of Different Evaluation Algorithms to Derive Mean Particle Size from Dynamic Light Scattering Data. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, P. A Practical Minicourse in Dynamic Light Scattering. Available online: http://www.eng.uc.edu/~beaucag/Classes/Characterization/DLS/PaulRussoLSU2012DLS_Minicourse.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Stetefeld, J.; McKenna, S.A.; Patel, T.R. Dynamic Light Scattering: A Practical Guide and Applications in Biomedical Sciences. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Measurand | Value |
|---|---|
| Number concentration of foreign particles [particles/mL] | <1 × 107 |
| Total organic carbon concentration [μg/L] | <50 |
| Electrical conductivity [mS/m] | <0.01 |
| Temperature [°C] | 24 ± 2.0 |
| Dissolved oxygen concentration C [mg/L] | 8.3–8.7 |
| Oxygen saturation SO2 [%] | 97–103 |
| Method | Algorithm | Intensity Weighted Size [nm] 1 | Number Weighted Size [nm] 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DLS | Cumulant | 179 ± 0.5 | n/a |
| NNLS | 196 ± 9 2 | 1.6 ± 0.1 2 | |
| CONTIN | 209 ± 2 2 | 1.5 ± 0.1 2 | |
| Marquardt | 203 ± 2 | 135 ± 7 | |
| PTA | — | n/a | 135 ± 5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, S.; Naruse, Y.; Terasaka, K.; Fujioka, S. Concentration and Dilution of Ultrafine Bubbles in Water. Colloids Interfaces 2020, 4, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4040050
Tanaka S, Naruse Y, Terasaka K, Fujioka S. Concentration and Dilution of Ultrafine Bubbles in Water. Colloids and Interfaces. 2020; 4(4):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4040050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Shunya, Yuri Naruse, Koichi Terasaka, and Satoko Fujioka. 2020. "Concentration and Dilution of Ultrafine Bubbles in Water" Colloids and Interfaces 4, no. 4: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4040050
APA StyleTanaka, S., Naruse, Y., Terasaka, K., & Fujioka, S. (2020). Concentration and Dilution of Ultrafine Bubbles in Water. Colloids and Interfaces, 4(4), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/colloids4040050