Effect of Rubber Heat Treatment on Rubberized-Concrete Mechanical Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
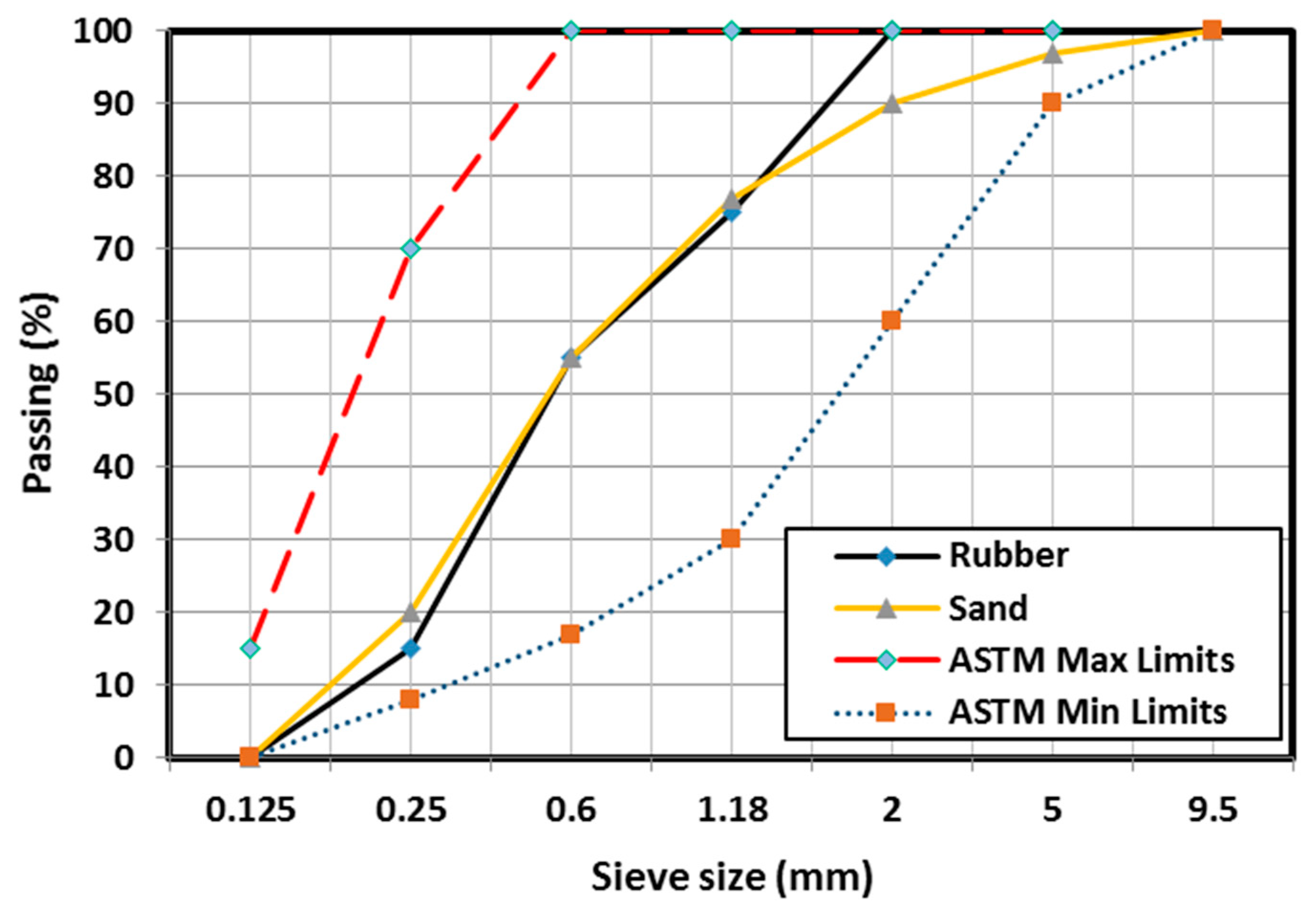
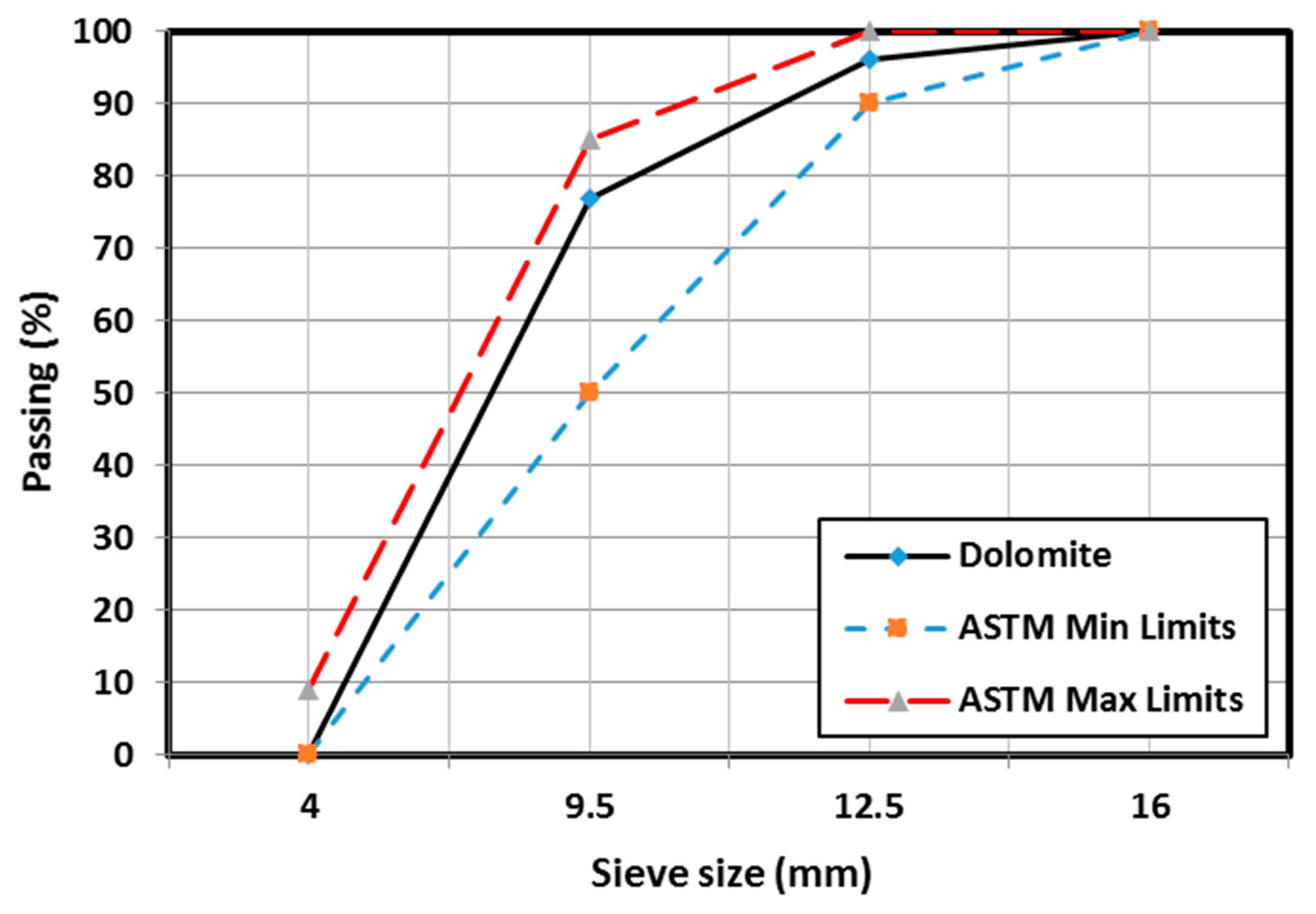
2. Experimental Program
3. Results and Discussion
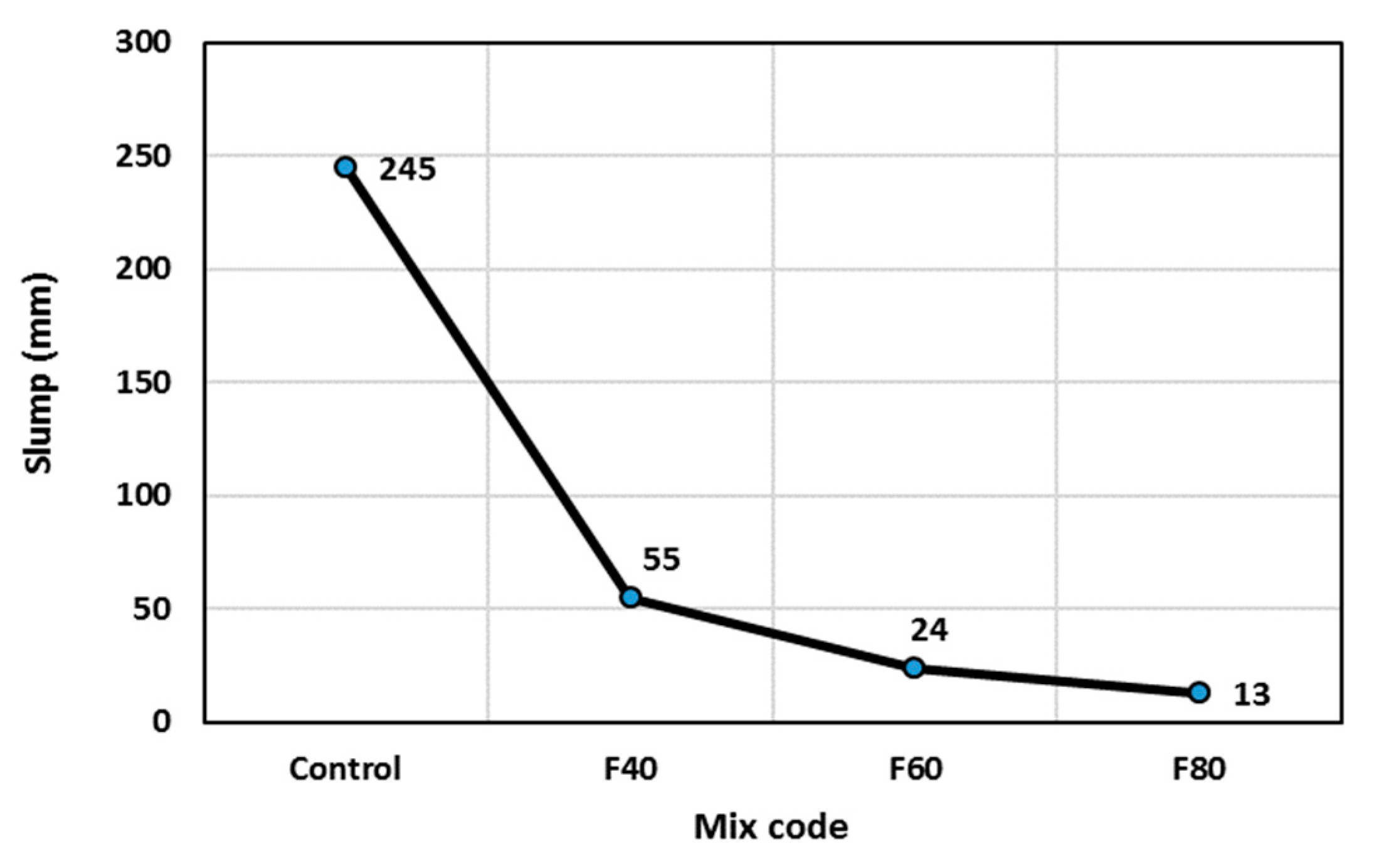
3.1. Workability
3.2. Fresh and Hardened Density
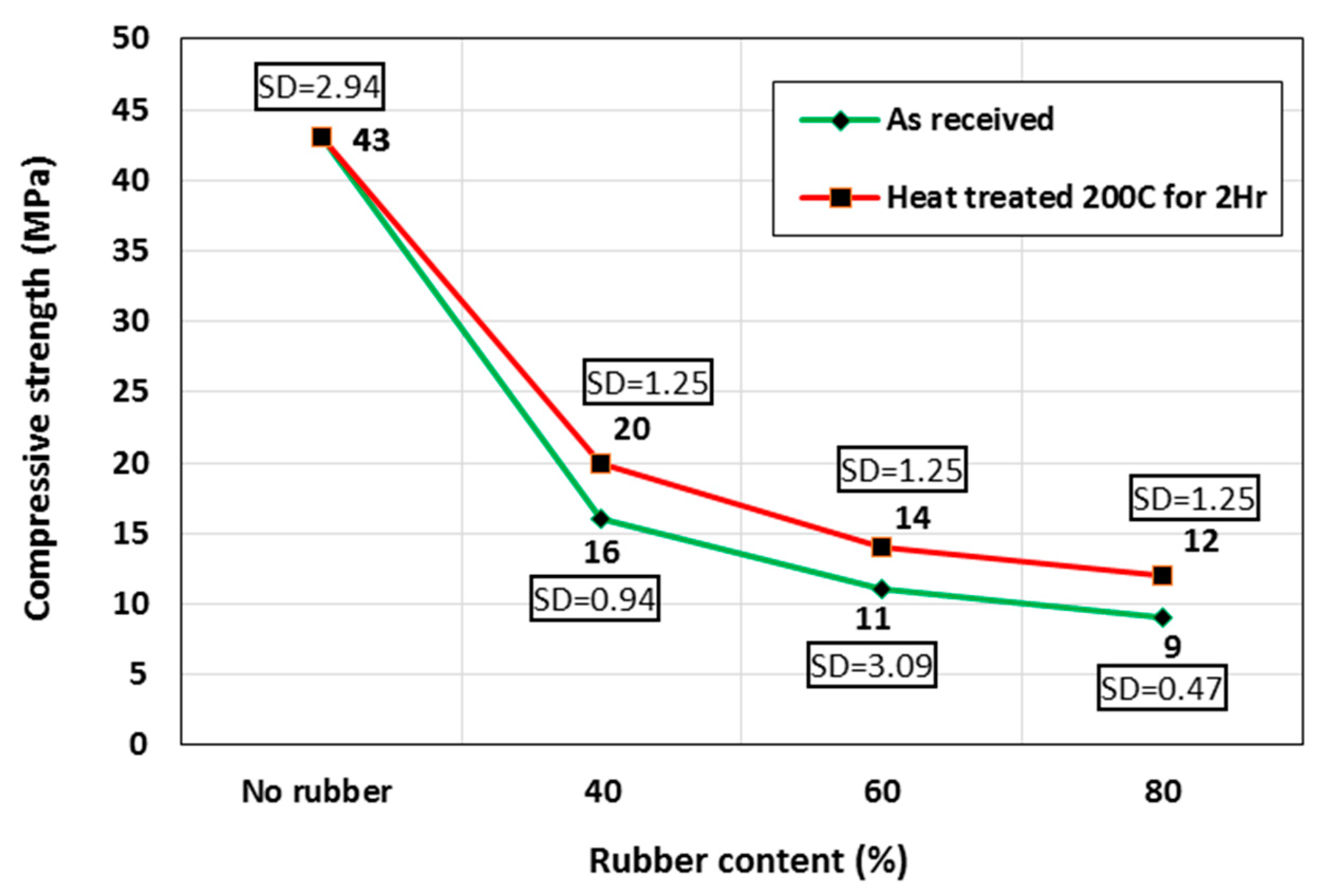
3.3. Compressive Strength
3.4. Impact Resistance
4. Conclusions
- Incorporation of as-received crumb rubber in concrete with contents of 40%, 60%, and 80% decreases its slump by 77%, 90%, and 95%, respectively. However, using saturated-surface dry (SSD) rubber showed an insignificant effect on concrete slump regardless of the rubber volume used, or the heat treatment conducted.
- Increasing the untreated rubber content to 40%, 60% and 80% decreased the compressive strength by 63%, 74% and 79%, respectively. Using heat-treated rubber (at 200 °C for 2 h) of 40%, 60%, and 80% displayed compressive strength recoveries of 14.9%, 10.4% and 9.7%, respectively.
- Using 40% as-received rubber content increased the impact resistance by 14% for ultimate failure. Increasing the rubber content to 60% and 80% decreased the impact energy by 11% and 22%, respectively, compared with that of Control mix. Heat treatment of 40%, 60%, and 80% rubber contents at 200 °C for 2 h increased the impact resistance by 57%, 28%, and 7%, respectively, for ultimate failure, compared with those of Control mix. The thermal treatment enhanced the impact resistance at ultimate failure by 37%, 28%, and 15%, respectively, for mixes containing 40%, 60%, and 80% rubber contents compared with those of the as-received rubber.
5. Future Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, C.; Lu, X.; Li, H.; Tian, T. Experimental study on seismic behavior of circular RC columns strengthened with pre-stressed FRP strips. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2013, 12, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-X.; Zhao, G.-H. Typical Bridge Damage Analysis in “5.12” Wenchuan Earthquake. J. Archit. Civ. Eng. 2009, 2, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, J. Earthquake-induced damage analysis of highway bridges in Wenchuan earthquake and countermeasures. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 7, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Youssf, O.; Mills, J.E.; Ellis, M.; Benn, T.; Zhuge, Y.; Ma, X.; Gravina, R.J. Practical Application of Crumb Rubber Concrete in Residential Slabs. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; ElGawady, M.A.; Mills, J.E. Experimental investigation of crumb rubber concrete columns under seismic loading. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Youssf, O.; Hassanli, R.; Mills, J.E.; Ma, X.; Zhuge, Y. Cyclic Performance of Steel–Concrete–Steel Sandwich Beams with Rubcrete and LECA Concrete Core. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanli, R.; Youssf, O.; Mills, J.E. Seismic Performance of Precast Posttensioned Segmental FRP-Confined and Unconfined Crumb Rubber Concrete Columns. J. Compos. Constr. 2017, 21, 04017006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanli, R.; Youssf, O.; Mills, J.; Fakharifar, M. Analytical Study of Force–Displacement Behavior and Ductility of Self-centering Segmental Concrete Columns. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2017, 11, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; ElGawady, M.A.; Mills, J.E. Static cyclic behaviour of FRP-confined crumb rubber concrete columns. Eng. Struct. 2016, 113, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanli, R.; Youssf, O.; Manalo, A.; Najafgholipour, M.A.; Elchalakani, M.; Castillo, E.D.R.; Lutze, D. An Experimental Study of the Behavior of GFRP-Reinforced Precast Concrete Culverts. J. Compos. Constr. 2022, 26, 04022043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattuhi, N.; Clark, L. Cement-based materials containing shredded scrap truck tyre rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 1996, 10, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Huo, X.S.; Yuan, Y. Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, and Brittleness Index of Rubberized Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2008, 20, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Elchalakani, M.; Hassanli, R.; Roychand, R.; Zhuge, Y.; Gravina, R.J.; Mills, J.E. Mechanical performance and durability of geopolymer lightweight rubber concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 45, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, R.J.; Xie, T.; Roychand, R.; Zhuge, Y.; Ma, X.; Mills, J.E.; Youssf, O. Bond behaviour between crumb rubberized concrete and deformed steel bars. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Hassanli, R.; Mills, J.E.; Zhuge, Y. Axial Compression Behaviour of Hybrid Double-Skin Tubular Columns Filled with Rubcrete. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Hassanli, R.; Mills, J.E.; Skinner, W.; Ma, X.; Zhuge, Y.; Roychand, R.; Gravina, R. Influence of Mixing Procedures, Rubber Treatment, and Fibre Additives on Rubcrete Performance. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayeb, E.; Ma, X.; Zhuge, Y.; Youssf, O.; Mills, J. Influence of rubber particles on the properties of foam concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2020, 30, 101217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltayeb, E.; Ma, X.; Zhuge, Y.; Xiao, J.; Youssf, O. Composite walls Composed of profiled steel skin and foam rubberised concrete subjected to eccentric compressions. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 46, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelisser, F.; Zavarise, N.; Longo, T.A.; Bernardin, A.M. Concrete made with recycled tire rubber: Effect of alkaline activation and silica fume addition. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjian, E.; Khorami, M.; Maghsoudi, A.A. Scrap-tyre-rubber replacement for aggregate and filler in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pang, S.-S.; Ibekwe, S.I. FRP tube encased rubberized concrete cylinders. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najim, K.; Hall, M. A review of the fresh/hardened properties and applications for plain- (PRC) and self-compacting rubberised concrete (SCRC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 2043–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, K.S.; Hajirasouliha, I.; Pilakoutas, K. Strength and deformability of waste tyre rubber-filled reinforced concrete columns. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.-C. Effects of compaction method and rubber content on the properties of concrete paving blocks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; ElGawady, M.; Mills, J.; Ma, X. An experimental investigation of crumb rubber concrete confined by fibre reinforced polymer tubes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 53, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Mills, J.E.; Hassanli, R. Assessment of the mechanical performance of crumb rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Hassanli, R.; Mills, J.E. Retrofitting square columns using FRP-confined crumb rubber concrete to improve confinement efficiency. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153 (Suppl. C), 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; ElGawady, M.A.; Mills, J.E.; Ma, X. Analytical Modeling of the Main characteristics of Crumb Rubber Concrete. ACI Spec. Publ. 2017, 314, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.-H.; Guo, Y.-C.; Liu, L.-S.; Xie, Z.-H. Compressive and flexural behaviours of a new steel-fibre-reinforced recycled aggregate concrete with crumb rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 79, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segre, N.; Joekes, I. Use of tire rubber particles as addition to cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1421–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; ElGawady, M.A. An overview of sustainable concrete made with scrap rubber. In Proceedings of the 22nd Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials (ACMSM 22), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 December 2012; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 1039–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Savas, B.Z.; Ahmad, S.; Fedroff, D. Freeze-thaw durability of concrete with ground waste tire rubber. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 1997, 1574, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssf, O.; Mills, J.E.; Benn, T.; Zhuge, Y.; Ma, X.; Roychand, R.; Gravina, R. Development of Crumb Rubber Concrete for Practical Application in the Residential Construction Sector–Design and Processing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-C.; Zhang, J.-H.; Chen, G.-M.; Xie, Z.-H. Compressive behaviour of concrete structures incorporating recycled concrete aggregates, rubber crumb and reinforced with steel fibre, subjected to elevated temperatures. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 72, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Garrick, G.; Eggers, J.; Abadie, C.; Stubblefield, M.A.; Pang, S.-S. Waste tire fiber modified concrete. Compos. Part B Eng. 2004, 35, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaha, M.; Badawy, A.; Hashish, M. Effect of using ground waste tire rubber as fine aggregate on the behaviour of concrete mixes. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2007, 14, 427. [Google Scholar]
- Eldin, N.N.; Senouci, A.B. Rubber-Tire Particles as Concrete Aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1993, 5, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneyisi, E.; Gesoğlu, M.; Özturan, T. Properties of rubberized concretes containing silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, I.; Khabbaz, H.; Vessalas, K. Enhancing mechanical performance of rubberised concrete pavements with sodium hydroxide treatment. Mater. Struct. 2015, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yang, J.; Ghataora, G.S.; Dirar, S. Surface modified used rubber tyre aggregates: Effect on recycled concrete performance. Mag. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, D.M.; Ghedan, R.H. Effect of Rubber Treatment on Compressive Strength and Thermal Conductivity of Modified Rubberized Concrete. J. Eng. Dev. 2011, 15, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Raffoul, S.; Garcia, R.; Pilakoutas, K.; Guadagnini, M.; Medina, N.F. Optimisation of rubberised concrete with high rubber content: An experimental investigation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, N.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Pawar, T.; Gunde, V. Experimental investigation on strength characteristics of concrete using tyre rubber as aggregates in concrete. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. Dev. 2014, 4, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y. Research on Modifier and Modified Process for Rubber-Particle Used in Rubberized Concrete for Road. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 243–249, 4125–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Stubblefield, M.A.; Garrick, G.; Eggers, J.; Abadie, C.; Huang, B. Development of waste tire modified concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turatsinze, A.; Bonnet, S.; Granju, J.-L. Potential of rubber aggregates to modify properties of cement based-mortars: Improvement in cracking shrinkage resistance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, C.; Camacho, N.; Reyes, J.; Feliu, J.; Hernández, M. Influence of scrap rubber addition to Portland I concrete composites: Destructive and non-destructive testing. Compos. Struct. 2005, 71, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Shu, X.; Cao, J. A two-staged surface treatment to improve properties of rubber modified cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Huang, B.; Shu, X. Rubber modified concrete improved by chemically active coating and silane coupling agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, A.I.; Ahmed, S.H. Effect of Rubber Treated by Acidic Solution on Some Mechanical Properties of Rubberize Cement Mortar. Eng. Technol. J. 2011, 29, 2793. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, G.; Luo, B.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Chen, L. Influence of silane coupling agent on quality of interfacial transition zone between concrete substrate and repair materials. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Mu, Y. Surface modification of crumb rubber and its influence on the mechanical properties of rubber-cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinyele, J.O.; Salim, R.W.; Kupolati, W.K. The impact of rubber crumb on the mechanical and chemical properties of concrete. Eng. Struct. Technol. 2015, 7, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elaal, E.-S.; Araby, S.; Mills, J.; Youssf, O.; Roychand, R.; Ma, X.; Zhuge, Y.; Gravina, R.J. Novel approach to improve crumb rubber concrete strength using thermal treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ES 4756-1:2013; Cement Part: (1) Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. EOS: Cairo, Egypt, 2009.
- C 494/C 494M; Standard Specification for Chemical Admixtures for Concrete. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001.
- ECP 203-2020; Egyptian Code of Practice for Design and Construction of Reinforced Concrete Structures. ECP: Singapore, 2020.
- ES 8411-2:2020; Testing Fresh Concrete–Part 2: Slump Test. EOS: Cairo, Egypt, 2020.
- ES 8411-6:2020; Testing Fresh Concrete–Part 6: Density. EOS: Cairo, Egypt, 2020.
- ES 1658-6:2020; Testing Hardened Concrete, Part 6 Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. EOS: Cairo, Egypt, 2018.
- Batayneh, M.K.; Marie, I.; Asi, I. Promoting the use of crumb rubber concrete in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topçu, I.B. The properties of rubberized concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.scraptirenews.com/crumb.php (accessed on 4 January 2022).
- Ossola, G.; Wojcik, A. UV modification of tire rubber for use in cementitious composites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 52, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dai, Q.; Si, R.; Sun, X.; Lu, C. Evaluation of properties and performance of rubber-modified concrete for recycling of waste scrap tire. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148 (Suppl. C), 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tayeb, M.M.; Bakar, B.A.; Ismail, H.; Akil, H.M. Impact Resistance of Concrete with Partial Replacements of Sand and Cement by Waste Rubber. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2012, 51, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Mix Code | Dolomite (kg) | Fine Aggregate (kg) | Cement (kg) | SP (kg) | Water (kg) | Heat Treatment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | Rubber | ||||||
| Control | 1070 | 890 | 0 | 360 | 3 | 144 | -- |
| F40 | 1070 | 534 | 131.8 | 360 | 3 | 144 | No |
| F60 | 1070 | 356 | 197.7 | 360 | 3 | 144 | No |
| F80 | 1070 | 178 | 263.6 | 360 | 3 | 144 | No |
| F40T | 1070 | 534 | 131.8 | 360 | 3 | 144 | Yes |
| F60T | 1070 | 356 | 197.7 | 360 | 3 | 144 | Yes |
| F80T | 1070 | 178 | 263.6 | 360 | 3 | 144 | Yes |
| Mix Code | Slump (mm) | Fresh Density (kg/m3) | Hardened Density (kg/m3) | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Impact Resistance (Blow) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As Received | Heat Treated | Value | SD | Value | SD | Value | SD | First Crack | SD | Ult Crack | SD | |
| Control | 245 | 245 | 2470 | 16.3 | 2350 | 24.5 | 43 | 2.94 | 9 | 2.59 | 14 | 3.90 |
| F40 | 55 | 220 | 2250 | 20.4 | 2170 | 16.3 | 16 | 0.94 | 10 | 2.98 | 16 | 5.65 |
| F60 | 24 | 215 | 2130 | 4.1 | 2070 | 8.2 | 11 | 3.09 | 8 | 2.21 | 14 | 5.80 |
| F80 | 13 | 215 | 2020 | 13.9 | 1930 | 9.8 | 9 | 0.47 | 7 | 2.26 | 13 | 2.40 |
| F40T | -- | 225 | 2255 | 12.2 | 2175 | 4.1 | 20 | 1.25 | 15 | 3.91 | 22 | 6.21 |
| F60T | -- | 225 | 2133 | 2.4 | 2073 | 6.5 | 14 | 1.25 | 13 | 2.83 | 18 | 4.75 |
| F80T | -- | 215 | 2025 | 20.4 | 1930 | 16.3 | 12 | 1.25 | 10 | 3.45 | 15 | 3.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Swilam, A.; Tahwia, A.M.; Youssf, O. Effect of Rubber Heat Treatment on Rubberized-Concrete Mechanical Performance. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100290
Swilam A, Tahwia AM, Youssf O. Effect of Rubber Heat Treatment on Rubberized-Concrete Mechanical Performance. Journal of Composites Science. 2022; 6(10):290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100290
Chicago/Turabian StyleSwilam, Abdelrahman, Ahmed M. Tahwia, and Osama Youssf. 2022. "Effect of Rubber Heat Treatment on Rubberized-Concrete Mechanical Performance" Journal of Composites Science 6, no. 10: 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100290
APA StyleSwilam, A., Tahwia, A. M., & Youssf, O. (2022). Effect of Rubber Heat Treatment on Rubberized-Concrete Mechanical Performance. Journal of Composites Science, 6(10), 290. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs6100290








