A Novel CAE Method for Compression Molding Simulation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Sheet Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Challenges and Approaches
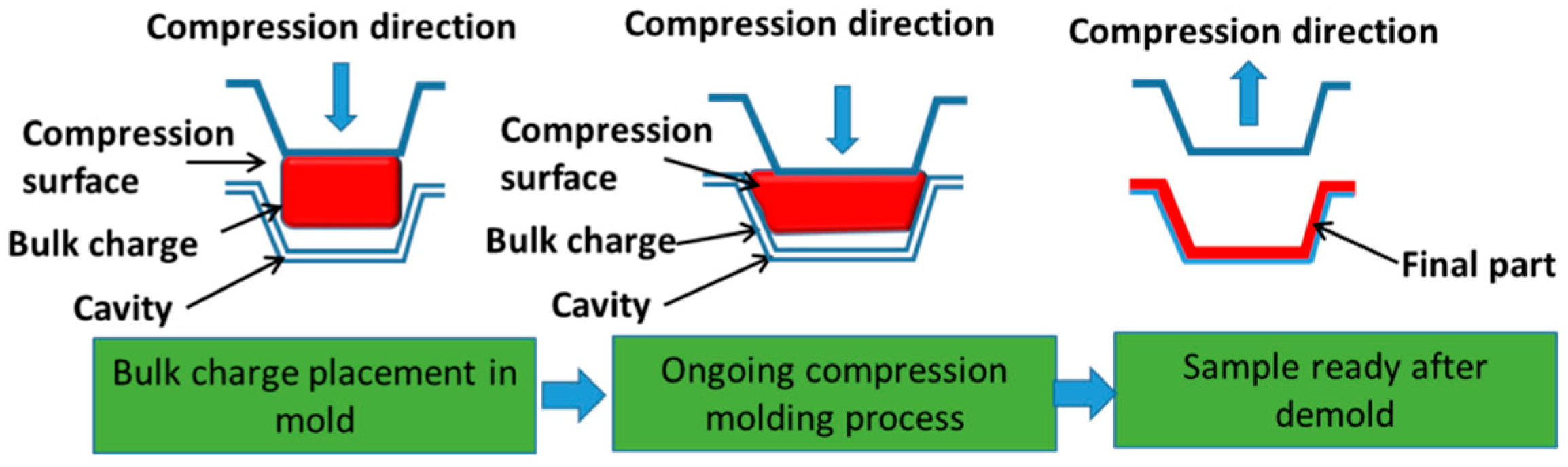
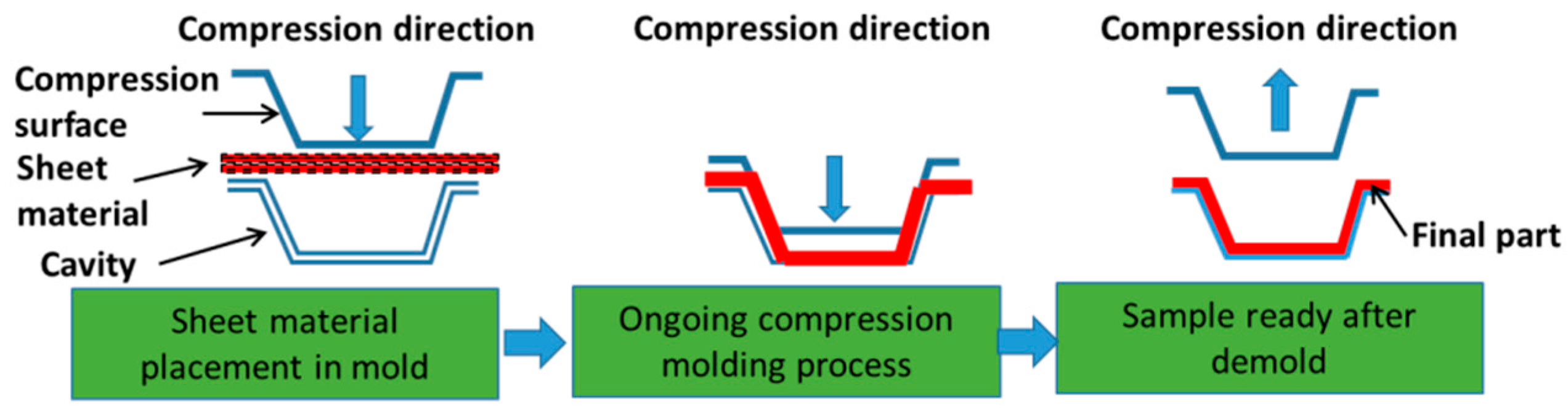
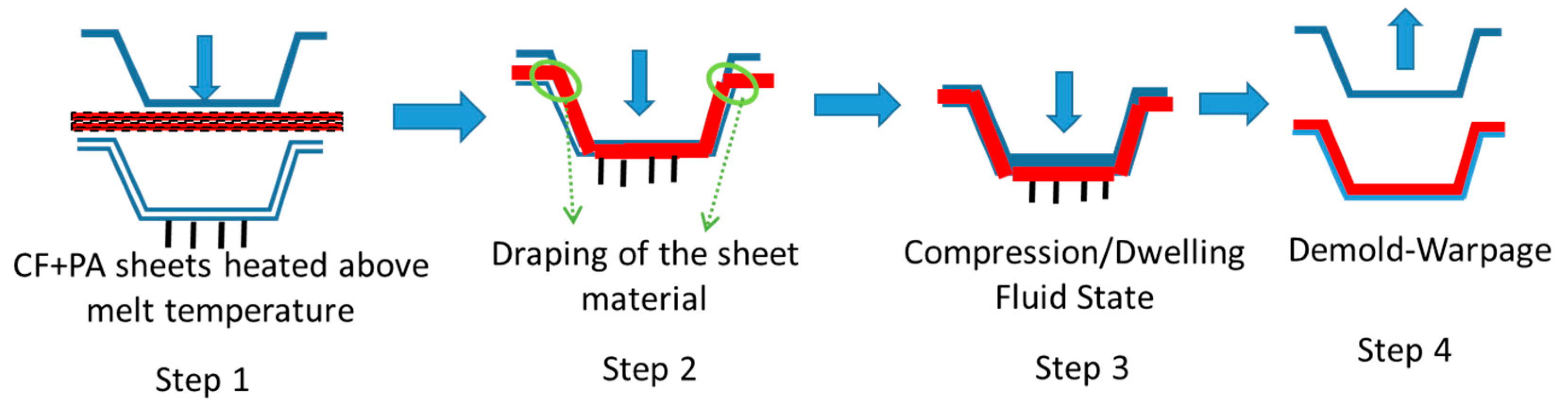
2.1. Sheet Material Compression Molding Issues
2.2. Measurement of Material Properties of the Sheet Material
2.2.1. Sheet Material Properties Measured for Draping Analysis
2.2.2. Sheet Material Properties Measured for Compression Molding Analysis
3. CAE Simulation
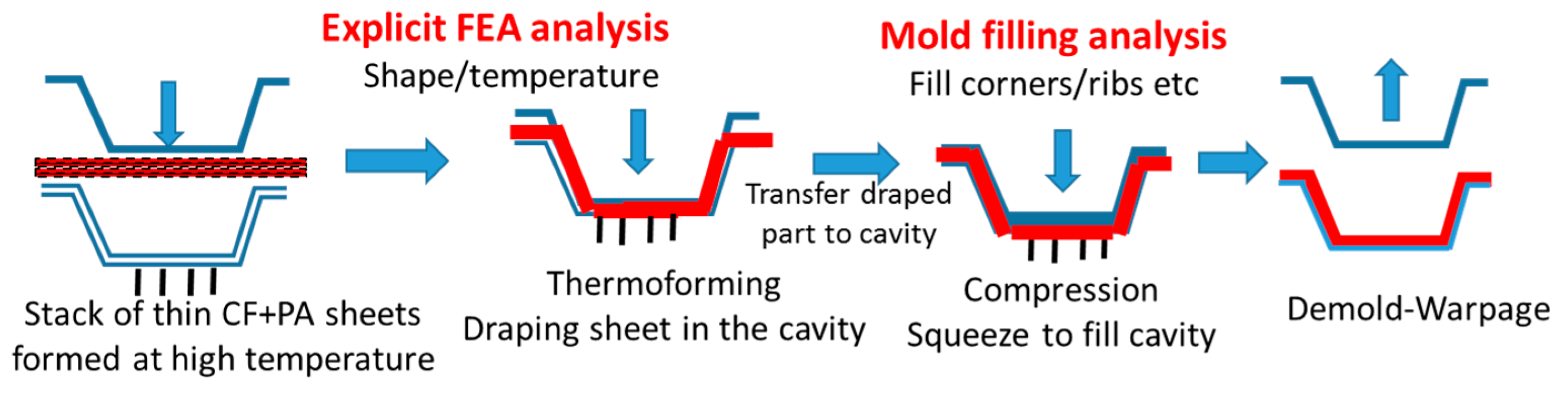
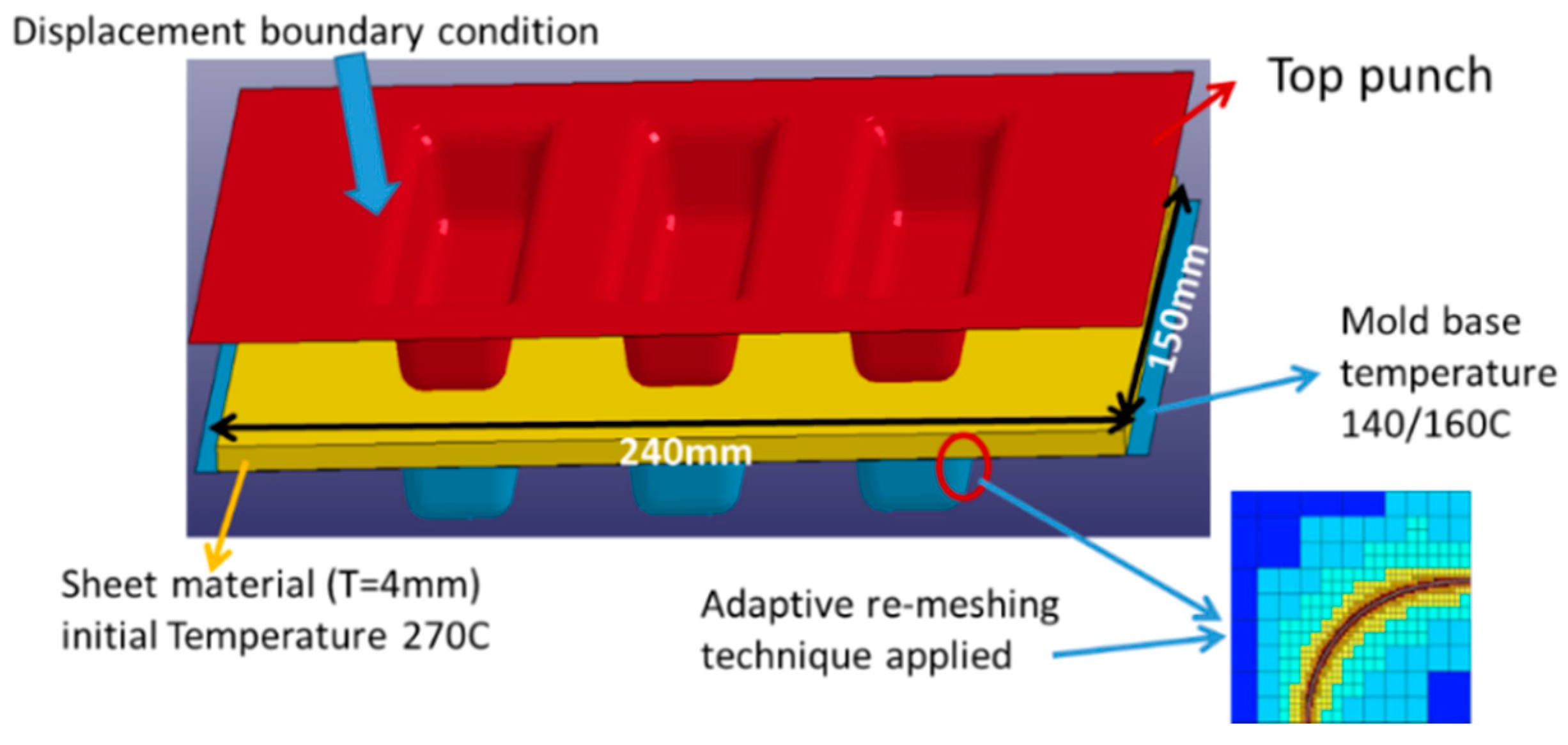
3.1. Overall CAE Simulation Concept and Steps
3.2. Draping Analysis with LS-DYNA
3.3. Compression Molding Analysis with Moldex3D
4. Experimental Procedure
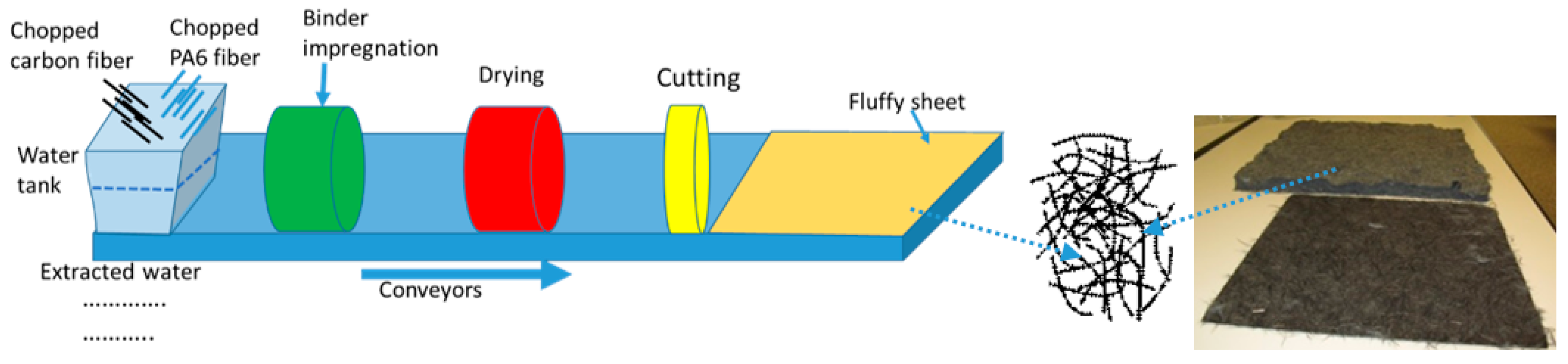
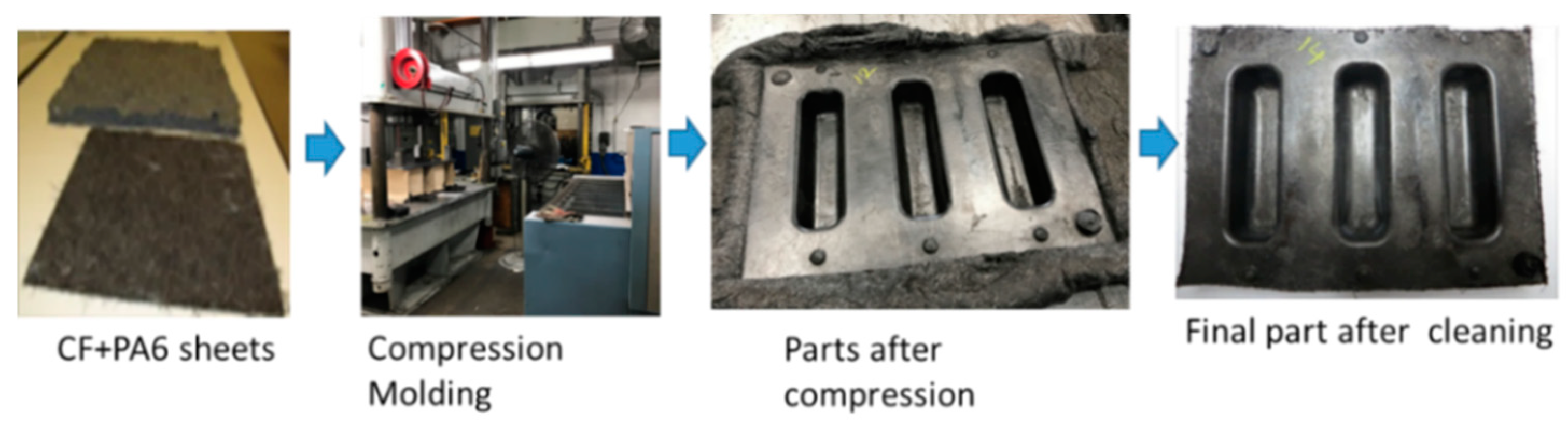
4.1. Carbon Fiber Sheet Material Manufacturing
4.2. Actual Part Manufacturing
5. Results
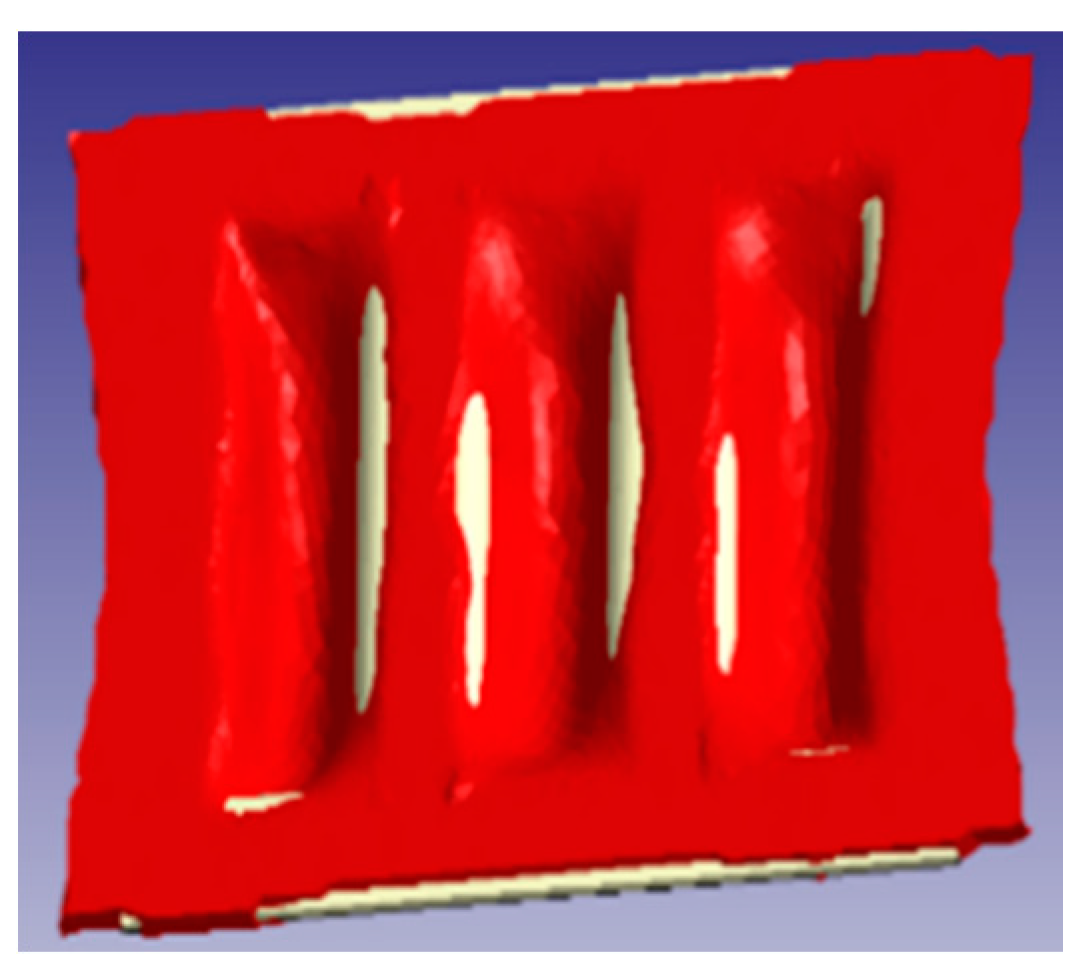
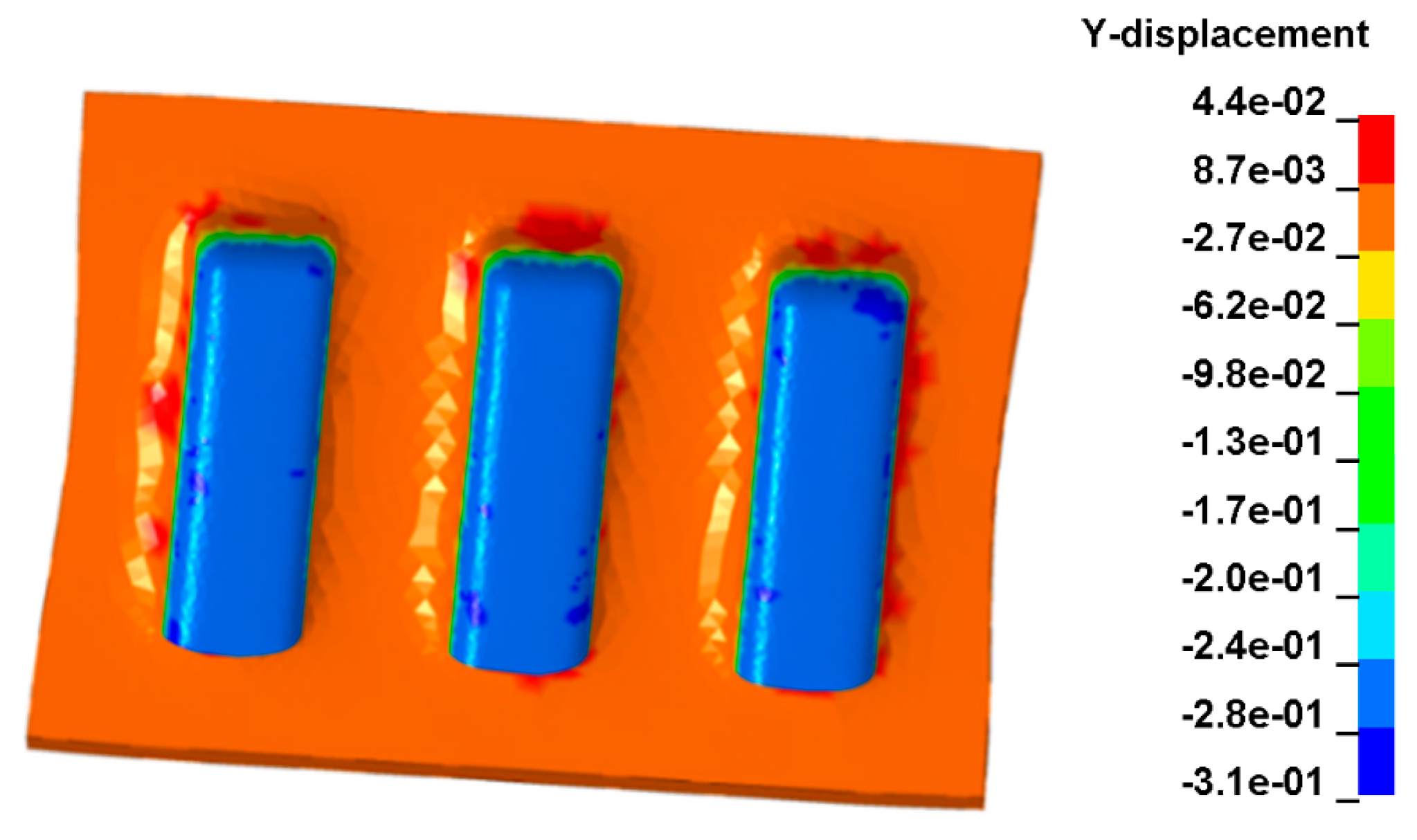
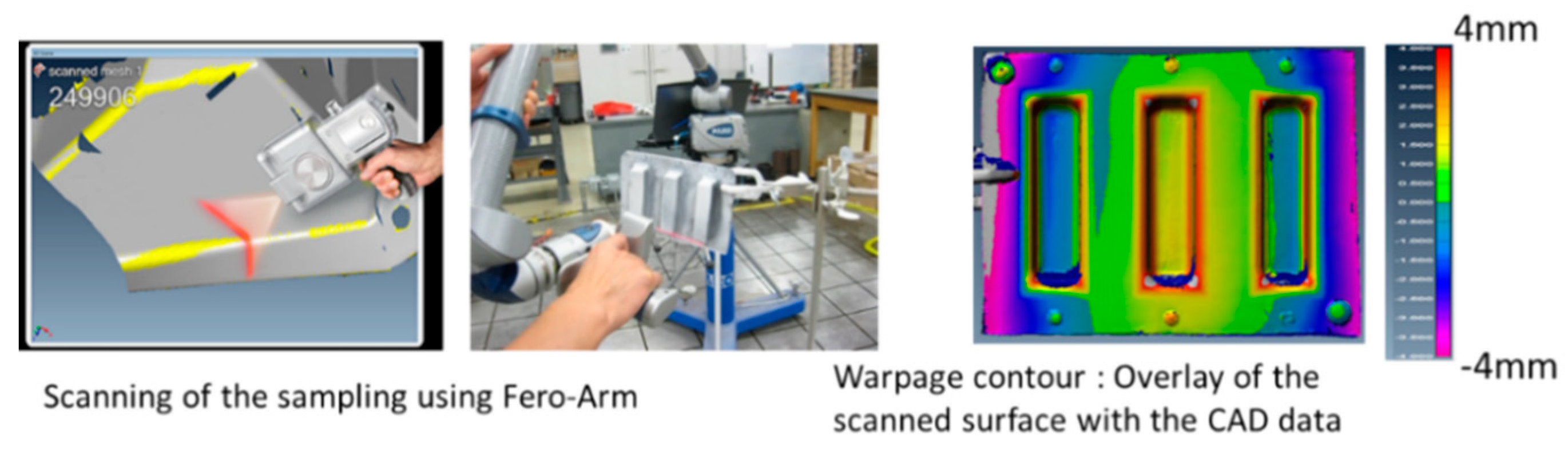
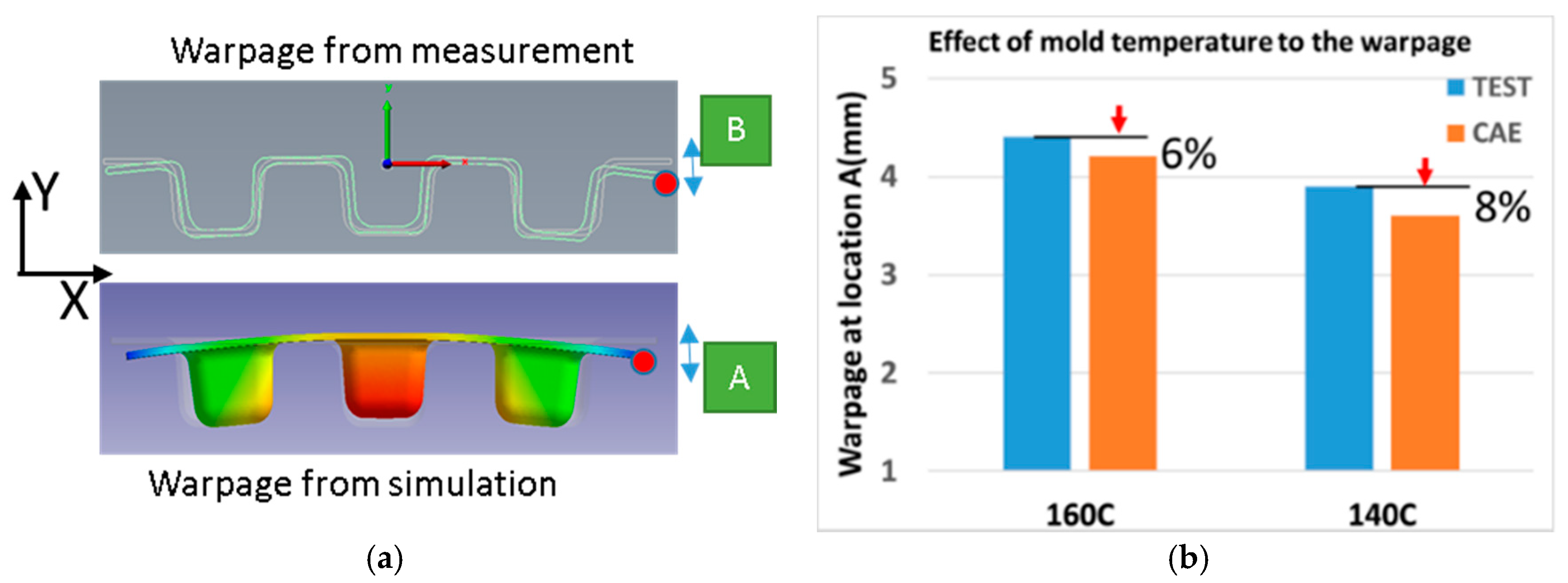
5.1. Warpage Comparison
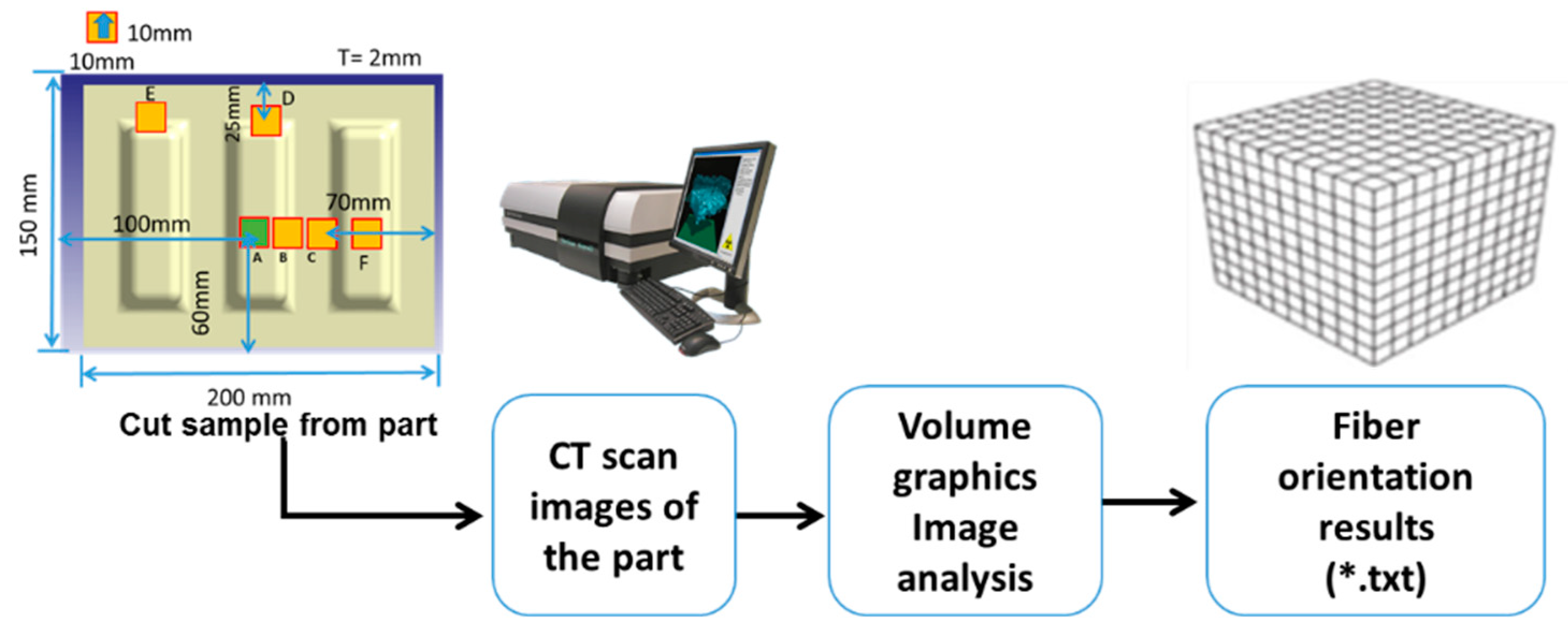
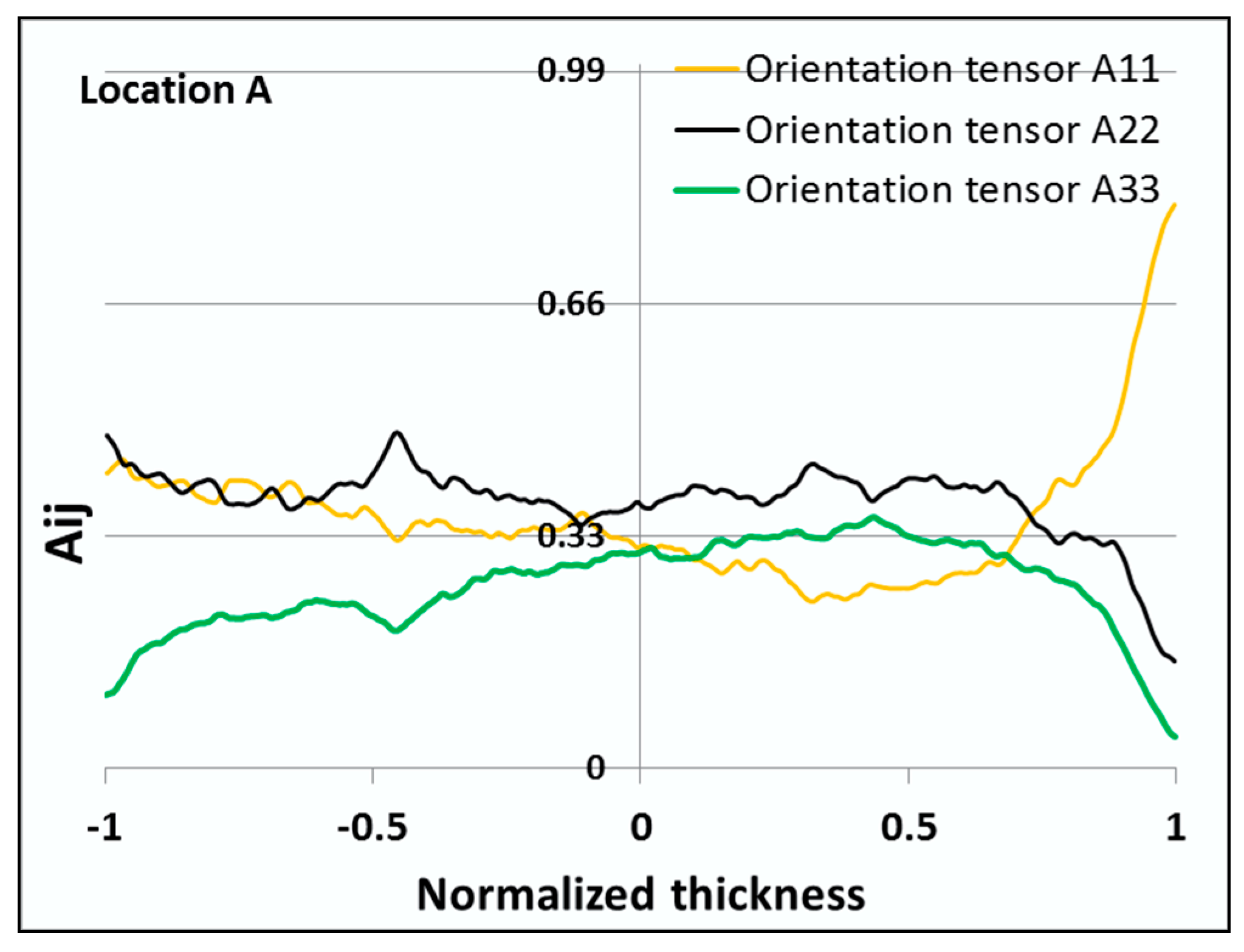
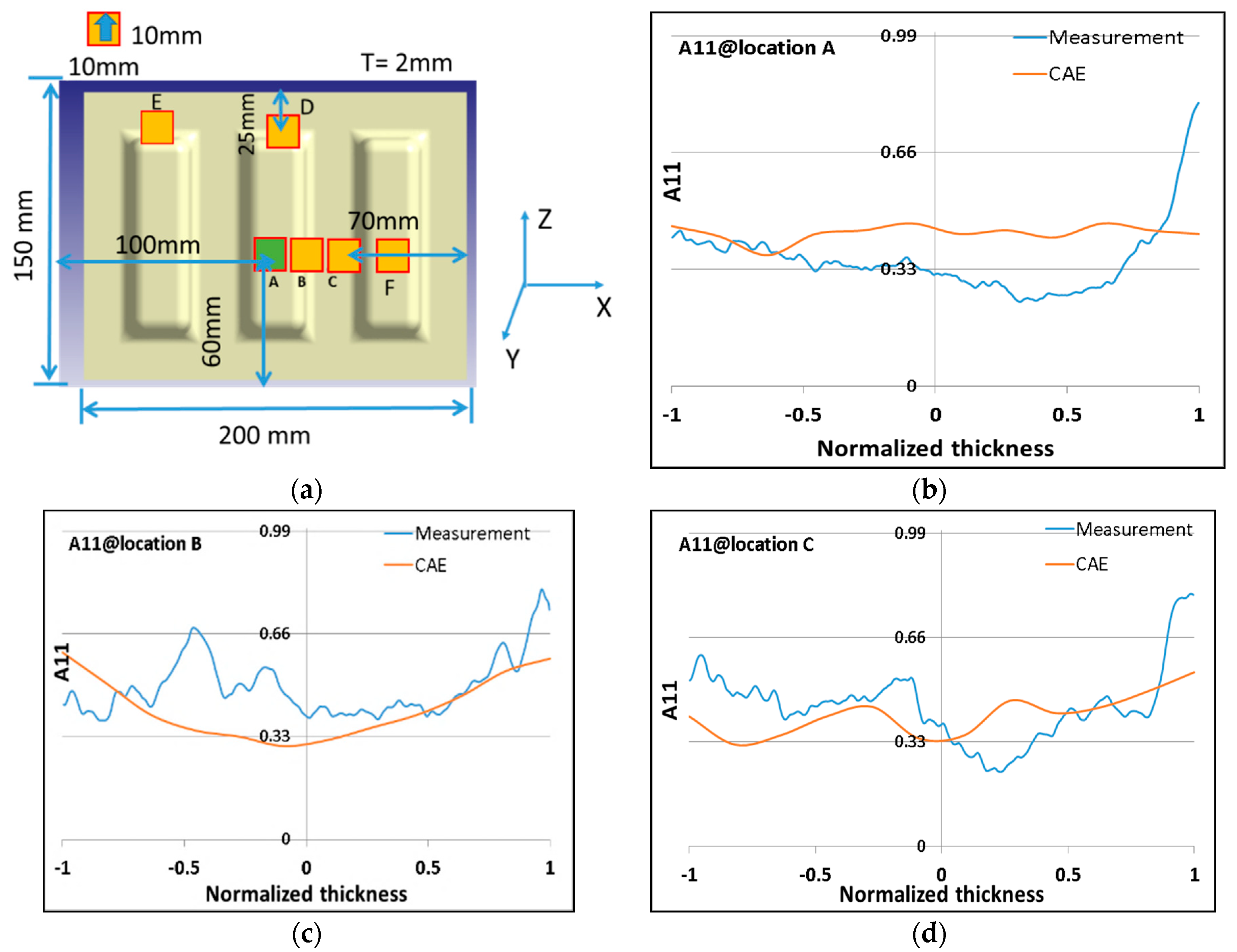
5.2. Fiber Orientation Comparison
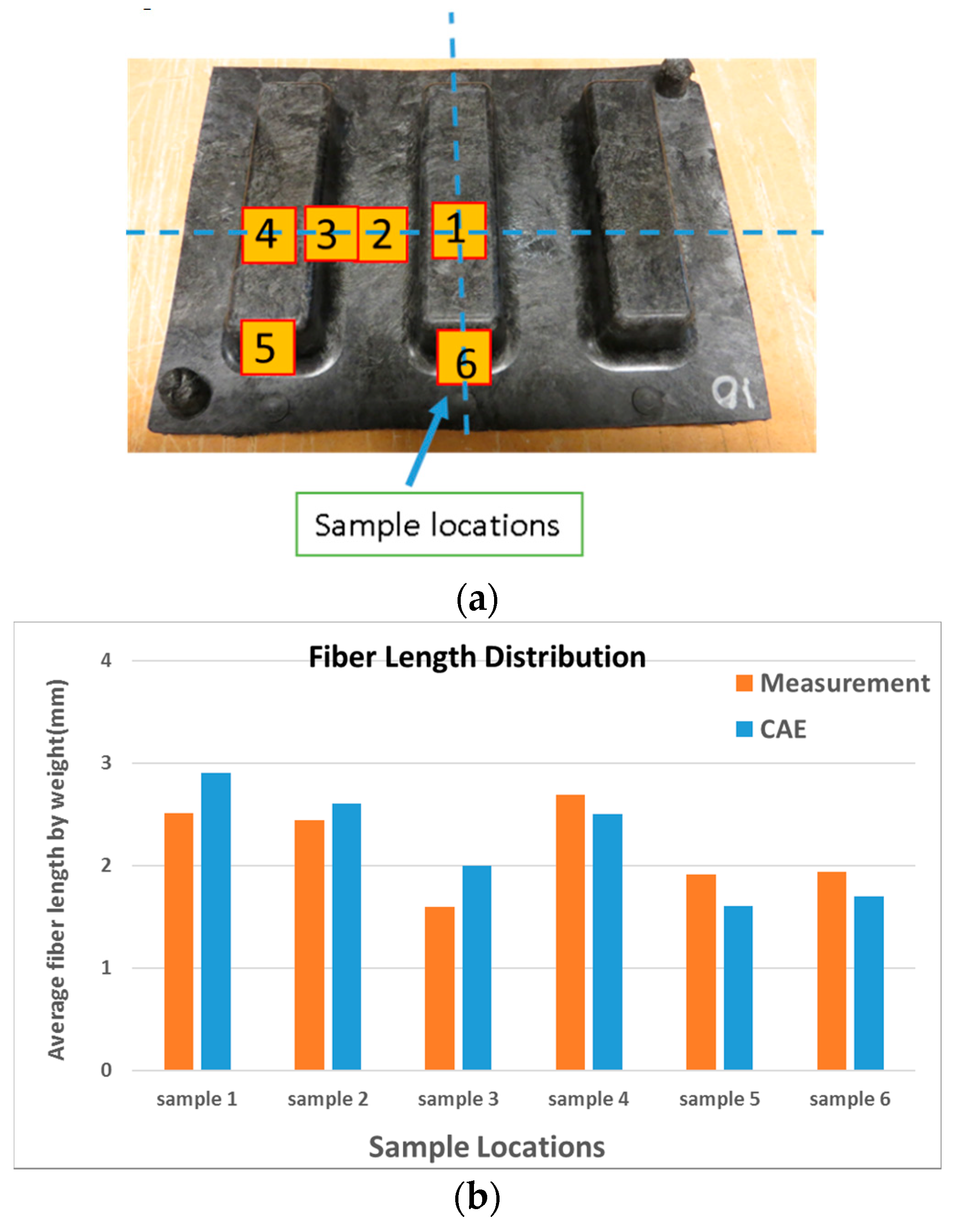
5.3. Fiber Length Comparison
5.4. Stroke Distance Effect
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Isayev, A. Injection and Compression Molding Fundamentals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Beardmore, P.; Harwood, J.J.; Kinsman, K.R.; Robertson, R.E. Fiber-reinforced composites engineered structural materials. Science 1980, 208, 832–840. [Google Scholar]
- Biron, M. Thermoplastics and Thermoplastic Composites; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Long, A.C. (Ed.) Composites Forming Technologies; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Baird, D.G.; Collias, D.I. Polymer Processing: Principles and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dumont, P.; Orgéas, L.; Favier, D.; Pizette, P.; Venet, C. Compression moulding of SMC: In situ experiments, modelling and simulation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Hayashi, K.; Yoshimoto, K.; Katahira, N. Development of Thermoplastic CFRP for Stack Frame. In SAE Technical Paper; SAE International: Detroit, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, A.D.; Oswald, T.A. Compression Molding; Hanser Publications: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Osswald, T.A.; Tucker, C.L. A boundary element simulation of compression mold filling. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1988, 28, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, T.A. Numerical Models for Compression Mold Filling Simulation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois, Champaign, IL, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Advani, S.G.; Tucker, C.L. A numerical simulation of short fiber orientation in compression molding. Polym. Compos. 1990, 11, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozer, E.M.; Advani, S.G. Process Modeling in Composites Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, A.; Davis, B.; Gramann, P. Computer Aided Engineering in Compression Molding. In Proceedings of the Composites Fabricators Association, Tampa, FL, USA, 3–6 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, M.R.; Caulk, D.A. A model for the flow of a chopped fiber reinforced polymer compound in compression molding. J. Appl. Mech. 1986, 53, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hamila, N.; Boisse, P. Thermoforming simulation of multilayer composites with continuous fibres and thermoplastic matrix. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 52, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.W.; Kikuchi, N. Numerical analysis and optimal design of composite thermoforming process. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1999, 177, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okine, R.K. Analysis of forming parts from advanced thermoplastic composite sheet materials. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 1989, 2, 50–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gandhi, U.; Pérez, C.; Osswald, T.; Vallury, S.; Yang, A. Method to account for the fiber orientation of the initial charge on the fiber orientation of finished part in compression molding simulation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 100, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of Moldex3D Software; CoreTech. Inc.: Taipei, Taiwan, 2014.
- Manual of Moldflow Software; Autodesk. Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014.
- ASTM D638-02a, Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. 2002. Available online: https://www.astm.org/DATABASE.CART/HISTORICAL/D638-02A.htm (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Eberle, A.P.; Baird, D.G.; Wapperom, P. Rheology of non-Newtonian fluids containing glass fibers: A review of experimental literature. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 3470–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 17 744:2004, Plastics—Determination of Specific Volume as a Function of Temperature and Pressure; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D4440-15, Standard Test Method for Plastics: Dynamic Mechanical Properties Melt Rheology, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. 2015. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/D4440.htm (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- ASTM D5930-16, Standard Test Method for Thermal Conductivity of Plastics by Means of a Transient Line-Source Technique, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. 2016. Available online: https://www.astm.org/DATABASE.CART/HISTORICAL/D5930-16.htm (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- ASTM E1269-11, Standard Test Method for Determining Specific Heat Capacity Differential Scanning Calorimetry, West Conshohocken, PA, USA. 2011. Available online: https://www.astm.org/Standards/E1269.htm (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Plewa, T.; Linde, T.; Weirs, V.G. Adaptive mesh refinement-theory and applications. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Eng. 2005, 41, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, R.J.T.; Bhattacharyya, D. Finite element simulation on thermoforming acrylic sheets using dynamic explicit method. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2006, 14, 307–328. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Lai, D.L.; Huang, C.T.; Wang, C.C. Numerical Simulation for the Viscoelastic Effects on the Birefringence Variation for an Injected Optical Lens. SPE ANTEC Indianap. 2016, 2016, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Baird, D.G.; McGrath, J.E. Development of fuel cell bipolar plates from graphite filled wet-lay thermoplastic composite materials. J. Power Sources 2005, 150, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, A.C. Processing of Composites; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2000; p. 320. [Google Scholar]
- Loos, A.C. Low-cost fabrication of advanced polymeric composites by resin infusion processes. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2001, 10, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faro Arm Measuring System. Available online: http://www.faro.com/en-us/products/metrology/measuring-arm-faroarm/overview (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Verma, K.; Columbus, D.; Han, B. Development of real time/variable sensitivity warpage measurement technique and its application to plastic ball grid array package. IEEE Trans. Electron. Packag. Manuf. 1999, 22, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manual of Volume Graphics Software; Volume Graphics GmbH: Heidelberg, Germany, 2014.
- Ebewele, R.O. Polymer Science and Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, B.N.; Fifield, L.S.; Gandhi, U.N.; Mori, S.; Wollan, E.J. Predictive Engineering Tools for Injection-Molded Long-Carbon-Thermoplastic Composites: Weight and Cost Analysis (No. PNNL-25646); Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Papathanasiou, T.D.; Guell, D.C. Flow-Induced Alignment in Composite Materials; Woodhead: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- FASEP Fiber Length Measurement System. Available online: http://www.fasep.biz/ (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Huang, C.T.; Tseng, H.C.; Vlcek, J.; Chang, R.Y. Fiber breakage phenomena in long fiber reinforced plastic preparation. Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 87, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
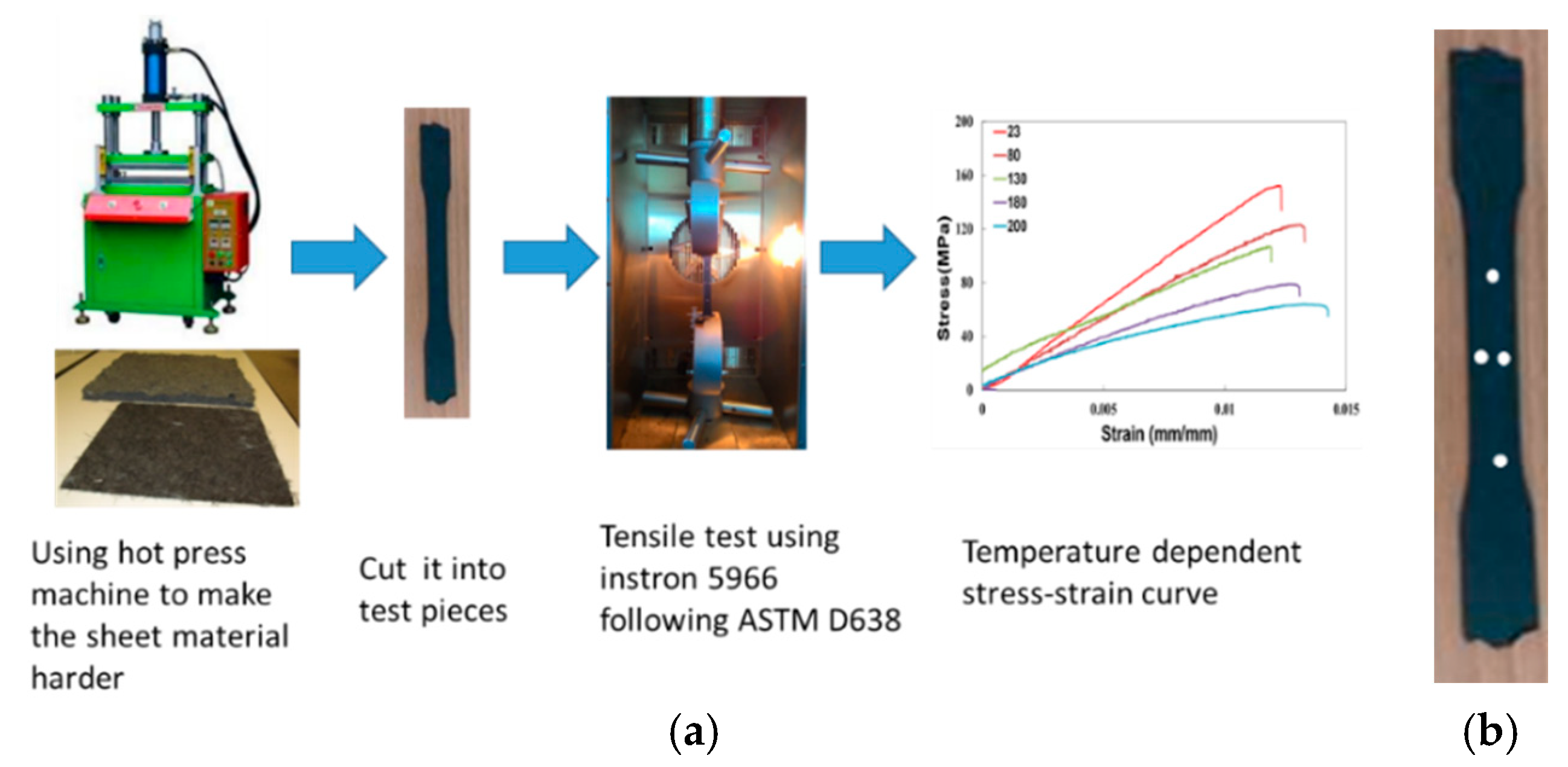
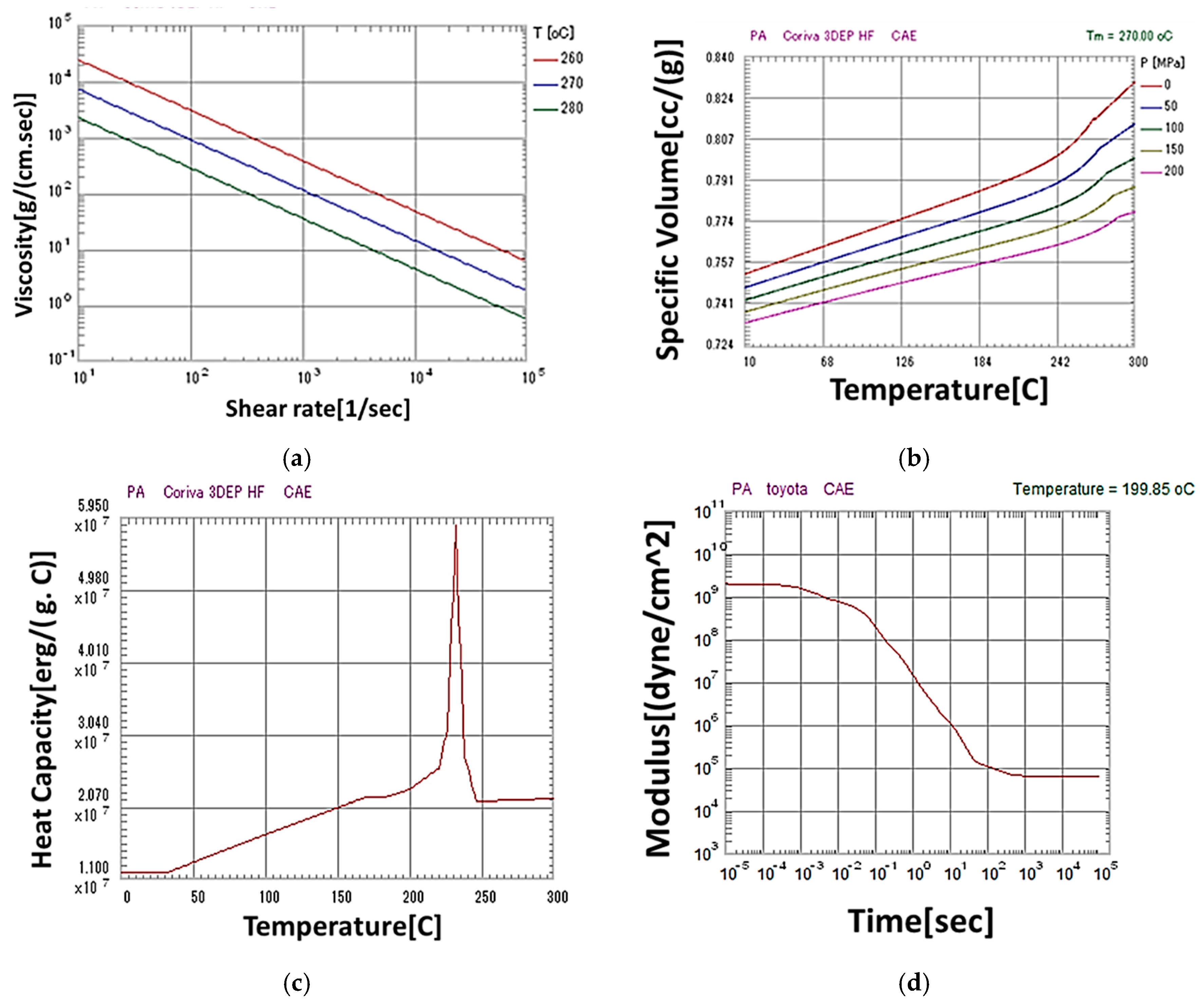
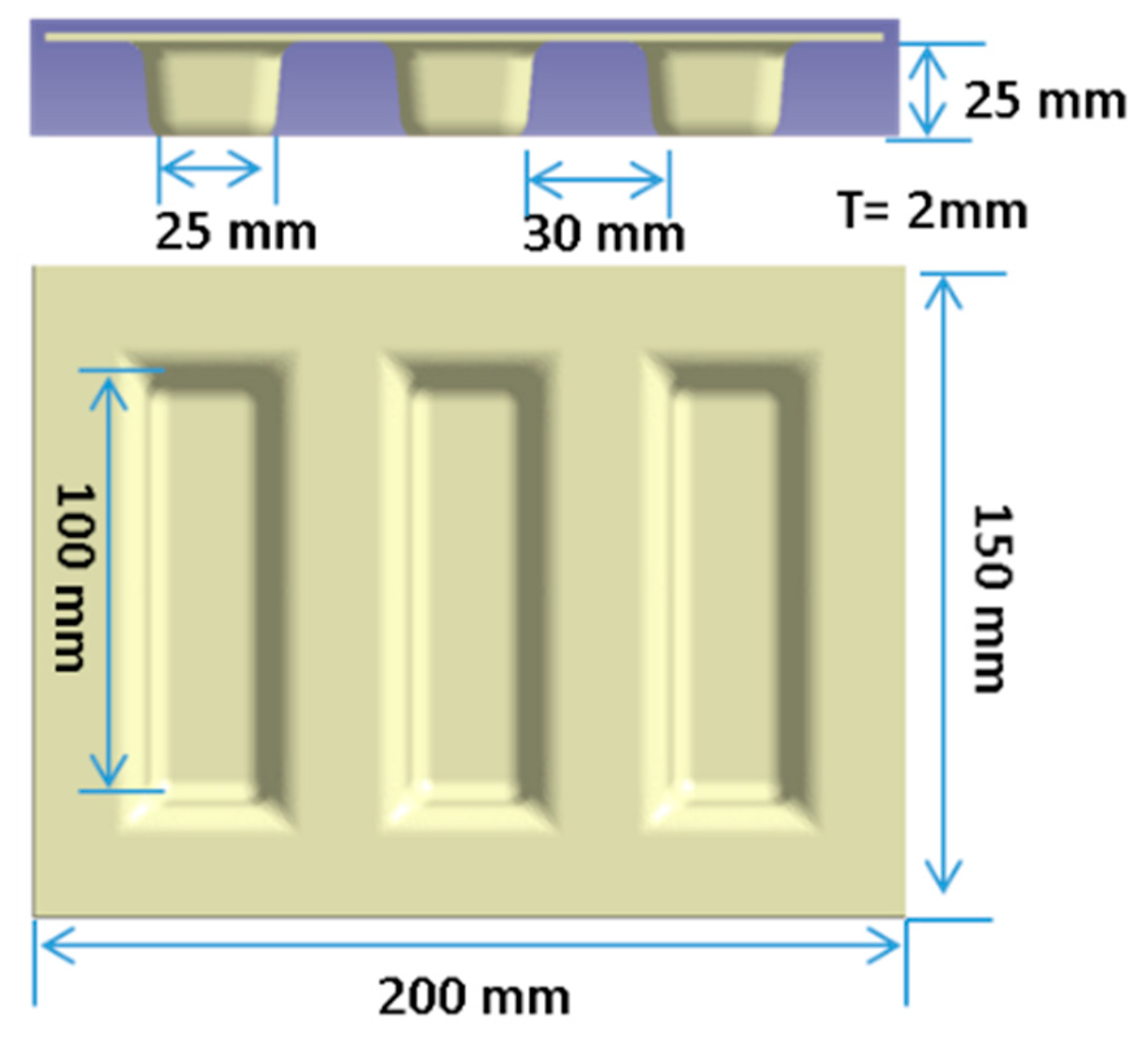
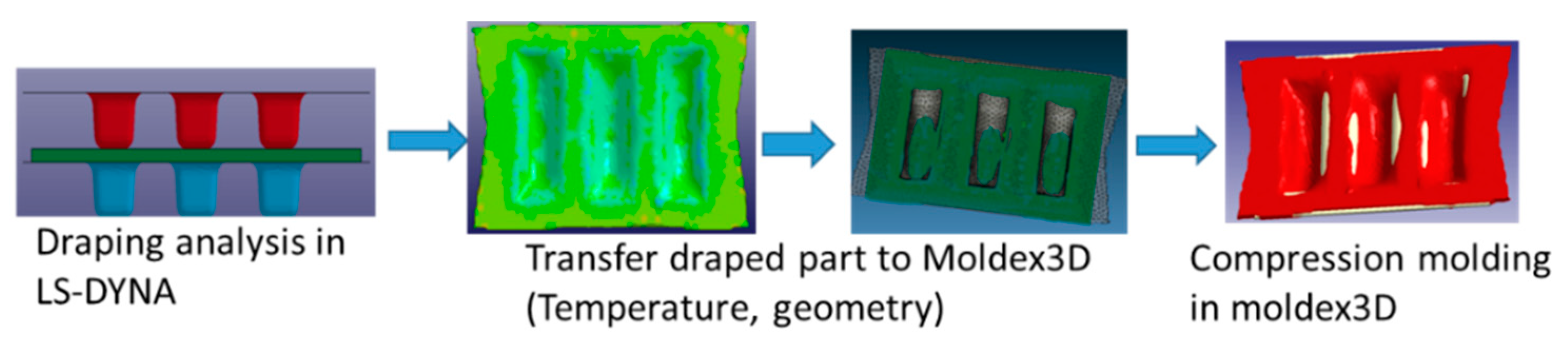


| Temperature (C) | Modulus (Mpa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 23 | 14,091 | 0.339 |
| 80 | 10,444 | 0.239 |
| 130 | 10,118 | 0.237 |
| 180 | 8728 | 0.179 |
| 200 | 7380 | 0.403 |
| Items | Carbon Fiber | PA6 |
|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cc) | 1.78 | 1.13 |
| Fiber Weight Percentage | 35% | N/A |
| Young’s Modulus E1 (Mpa) | 230,000 | 2400 |
| Young’s Modulus E2 (Mpa) | 23,000 | 2400 |
| Poisson’s Ratio | 0.26 | 0.42 |
| Fiber Aspect Ratio | 400 | N/A |
| Fiber CLTE at fiber direction (1/K) | 1 × 10−6 | N/A |
| Fiber CLTE at transverse direction (1/K) | 1 × 10−5 | N/A |
| Polymer CLTE (1/K) | N/A | 8.3 × 10−5 |
| Process Conditions | Actual Values |
|---|---|
| Melt Temperature | 270 °C |
| Mold Temperature | 70 °C |
| Compression time | 60 s |
| Compression pressure | 2000 KN |
| Charge weight | 150 gm |
| Location/Modulus | E11 (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Using Predicted Fiber Orientation | Using Measured Fiber Orientation | Agreement | |
| A | 23,855 | 21,972 | 8.6% |
| B | 23,252 | 25,524 | 8.9% |
| C | 22,791 | 24,353 | 6.4% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Gandhi, U.; Sekito, T.; Vaidya, U.K.; Hsu, J.; Yang, A.; Osswald, T. A Novel CAE Method for Compression Molding Simulation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Sheet Materials. J. Compos. Sci. 2018, 2, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020033
Song Y, Gandhi U, Sekito T, Vaidya UK, Hsu J, Yang A, Osswald T. A Novel CAE Method for Compression Molding Simulation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Sheet Materials. Journal of Composites Science. 2018; 2(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yuyang, Umesh Gandhi, Takeshi Sekito, Uday K. Vaidya, Jim Hsu, Anthony Yang, and Tim Osswald. 2018. "A Novel CAE Method for Compression Molding Simulation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Sheet Materials" Journal of Composites Science 2, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020033
APA StyleSong, Y., Gandhi, U., Sekito, T., Vaidya, U. K., Hsu, J., Yang, A., & Osswald, T. (2018). A Novel CAE Method for Compression Molding Simulation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composite Sheet Materials. Journal of Composites Science, 2(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs2020033





