A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Postmaneuver Rehabilitation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. General Guidelines Applied in the Present Study
2.2. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Cochrane Risk of Bias Tool
2.7. Statistical Analysis
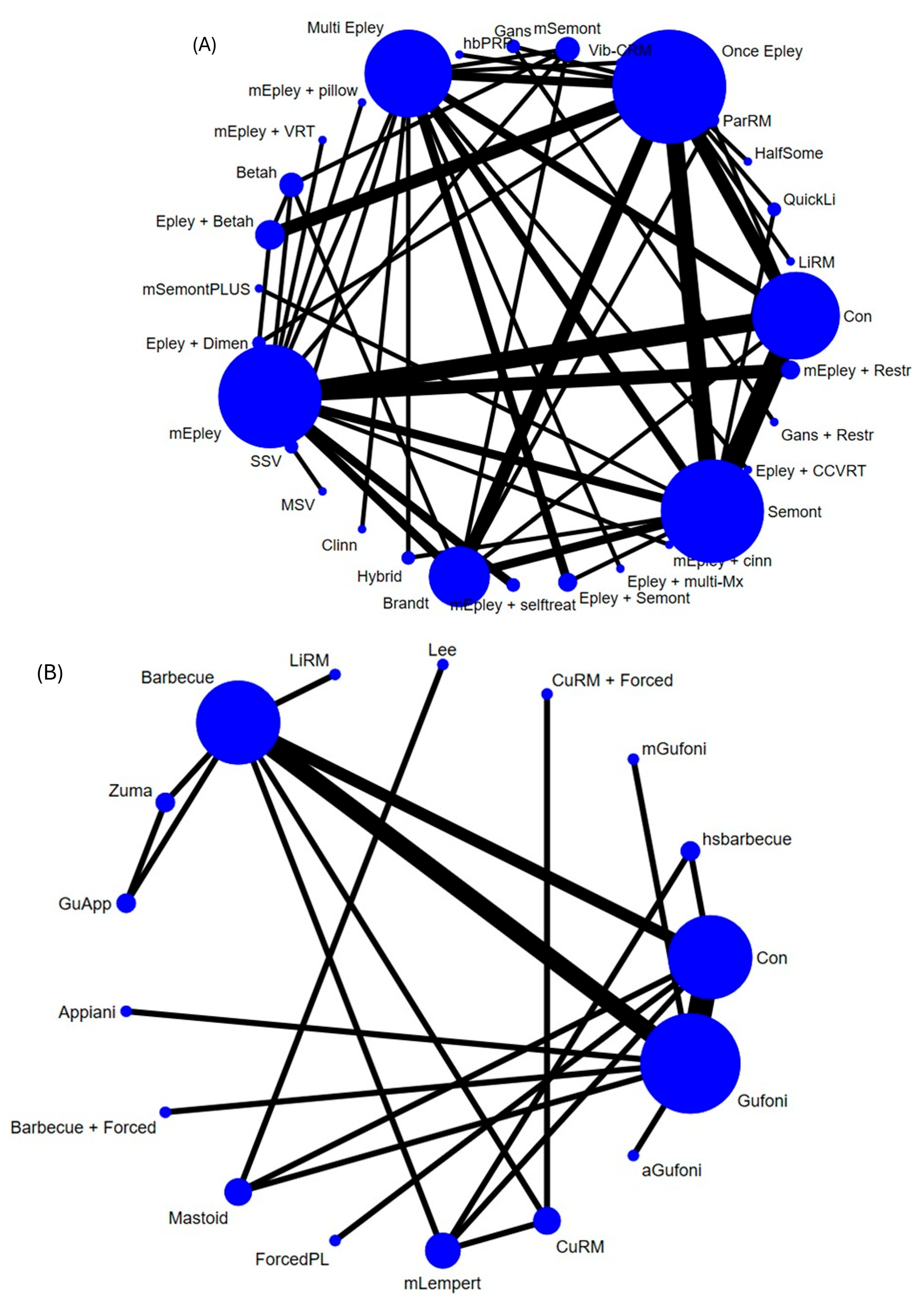
3. Results
3.1. Subgroup Part of the Posterior Canal BPPV
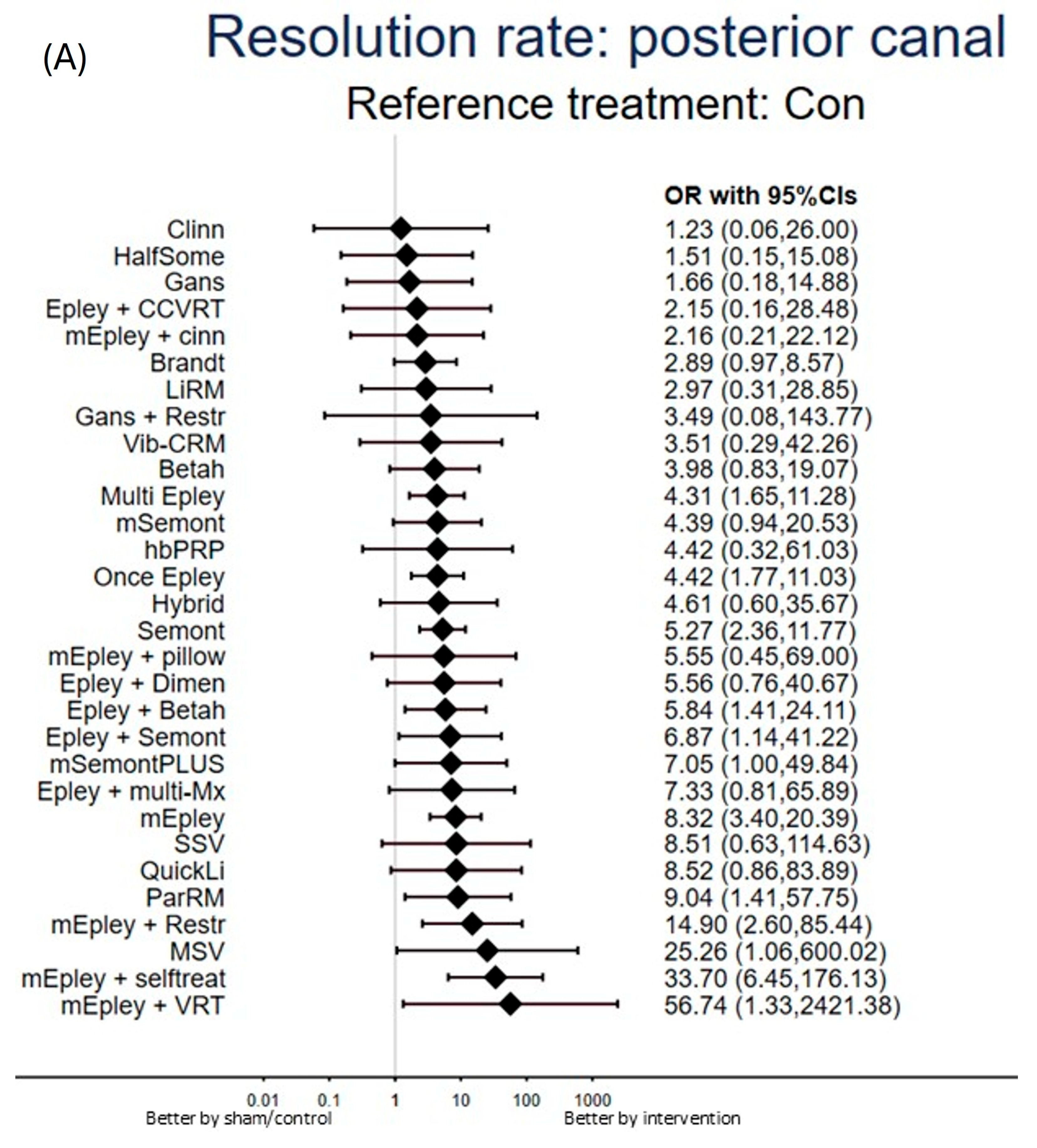
3.1.1. Primary Outcome: Resolution Rate
3.1.2. Secondary Outcome: Changes in Dizziness Severity
3.1.3. Safety Profile: Recurrence Rate
3.1.4. Safety Profile: Transition/Conversion Rate
3.1.5. Acceptability with Respect to the Dropout Rate
3.2. Subgroup Part of Horizontal Canal BPPV
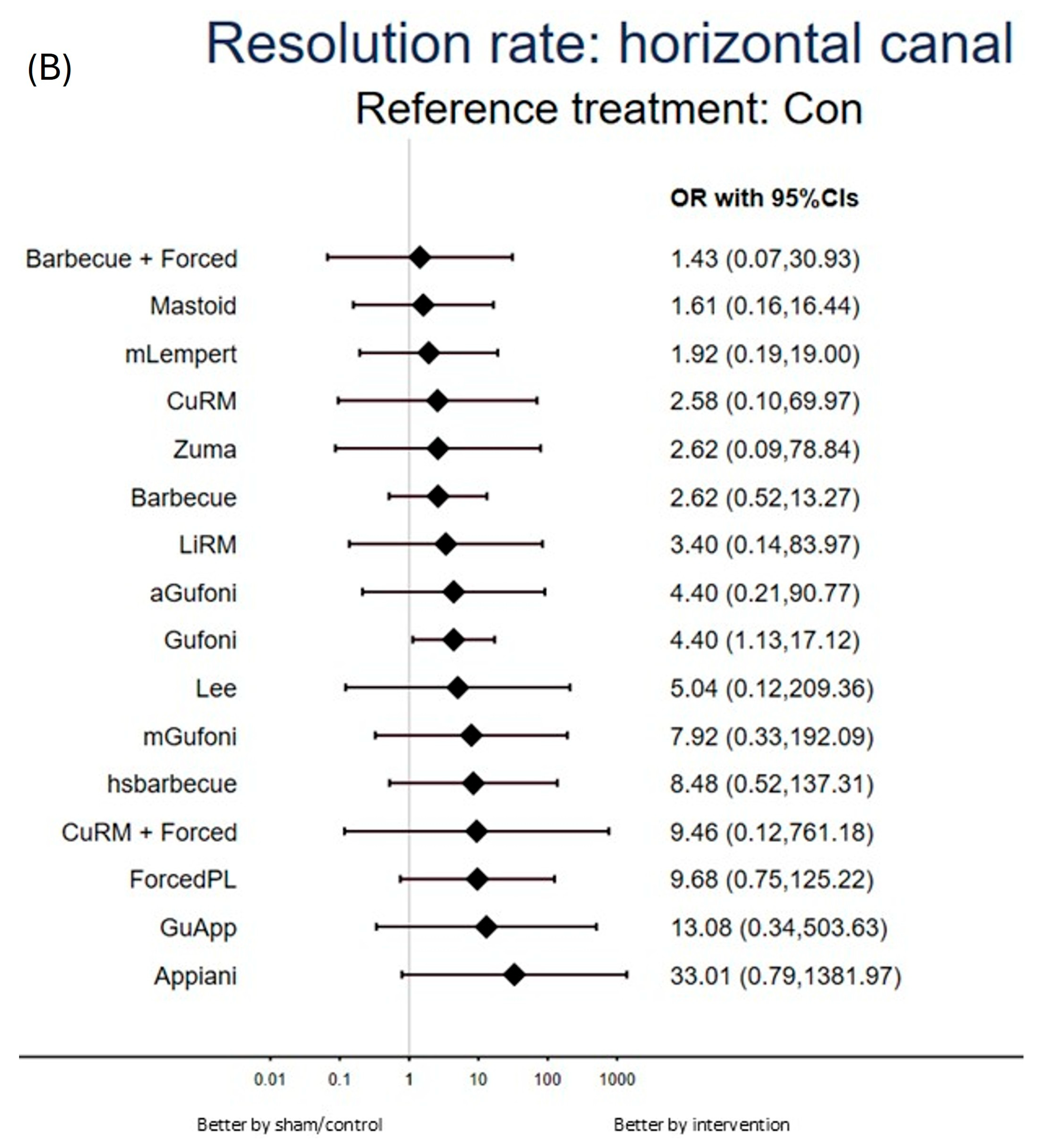
3.2.1. Primary Outcome: Resolution Rate
3.2.2. Secondary Outcome: Changes in Dizziness Severity
3.2.3. Safety Profile: Recurrence Rate
3.2.4. Safety Profile: Transition/Conversion Rate
3.2.5. Acceptability with Respect to the Dropout Rate
3.3. Risk of Bias, Inconsistency, Heterogeneity, and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
References
- You, P.; Instrum, R.; Parnes, L. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.H.; Song, M.H.; Shim, D.B. Recurrence Rate and Risk Factors of Recurrence in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Single-Center Long-Term Prospective Study With a Large Cohort. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Clin. Neurol. 2010, 6, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, D.U.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, K.D.; Moon, I.S.; Kim, B.K.; Oh, H.J.; et al. Randomized clinical trial for apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2012, 78, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, A.B.; Bai, X.; Zhang, S. Epley and Semont maneuvers for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A network meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cheng, D.; Yang, W.; Chen, T.; Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y. Current Therapies in Patients With Posterior Semicircular Canal BPPV, a Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, N.; Liu, M.; Chang, W. Effect of different maneuvers of repositioning on benign paroxysmal vertigo: A network meta-analysis. BMC Neurol. 2025, 25, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Welton, N.J. Network meta-analysis: A norm for comparative effectiveness? Lancet 2015, 386, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strupp, M.; Goldschagg, N.; Vinck, A.S.; Bayer, O.; Vandenbroeck, S.; Salerni, L.; Hennig, A.; Obrist, D.; Mandala, M. BPPV: Comparison of the SemontPLUS With the Semont Maneuver: A Prospective Randomized Trial. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 652573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Yu, D.; Yin, S.; Feng, Y.; Tan, J.; Song, Q.; Chen, B. Complementary self-treatment for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2014, 28, 693–696. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, K.M.; Ferreira, L.M.; Freitas, R.V.; Silva, C.N.; Deshpande, N.; Guerra, R.O. "Positive to Negative" Dix-Hallpike test and Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo recurrence in elderly undergoing Canalith Repositioning Maneuver and Vestibular Rehabilitation. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 20, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Zeng, B.S.; Liang, C.S.; Zeng, B.Y.; Hung, C.M.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, Y.W.; Lei, W.T.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, P.H.; et al. The Preventive Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and SGLT2 Inhibitors on Cancer Metastasis: A Network Meta-Analysis of 67 Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.M.; Zeng, B.Y.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, P.H.; Sun, C.K.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Lei, W.T.; et al. The different colorectal tumor risk related to GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors use: A network meta-analysis of 68 randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Surg. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Hung, C.M.; Liang, C.S.; Su, K.P.; Carvalho, A.F.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Lei, W.T.; et al. Risk of Hearing Loss in Patients Treated with Exendin-4 Derivatives: A Network Meta-Analysis of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, S.; Khoujah, D.; Greer, A.; Naples, J.G.; Upadhye, S.; Edlow, J.A. Vestibular suppressants for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2023, 30, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; He, J.; Wei, X.; Xie, M. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo recurrence: A meta-analysis. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211024569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qian, X.; Lu, L.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Lin, C.; Gao, X. Effects of Semont maneuver on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A meta-analysis. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, M.P.; Pinder, D.K. The Epley (canalith repositioning) manoeuvre for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD003162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, W.T.; Zimmermann, E.F.; Hilton, M.P. Modifications of the Epley (canalith repositioning) manoeuvre for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD008675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulovski, S.; Klokker, M. Repositioning Chairs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo—A Systematic Review. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerber, K.A. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Opportunities squandered. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1343, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehmer, D. Self-treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with DizzyFix, a new dynamic visual device. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2010, 7, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.T.; Yang, C.P.; Su, K.P.; Chen, T.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Lin, P.Y.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Matsuoka, Y.J.; et al. The association between melatonin and episodic migraine: A pilot network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to compare the prophylactic effects with exogenous melatonin supplementation and pharmacotherapy. J. Pineal Res. 2020, 69, e12663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Zeng, B.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Hung, C.M.; Sun, C.K.; Cheng, Y.S.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Brunoni, A.R.; et al. The beneficial effect on cognition of noninvasive brain stimulation intervention in patients with dementia: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.T.; Zeng, B.S.; Hung, C.M.; Liang, C.S.; Stubbs, B.; Carvalho, A.F.; Brunoni, A.R.; Su, K.P.; Tu, Y.K.; Wu, Y.C.; et al. Assessment of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Interventions for Negative Symptoms of Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tseng, P.T.; Hu, X.; Zeng, B.Y.; Chang, J.P.; Liu, Y.; Chu, W.J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhou, Z.L.; Chu, C.S.; et al. Comparative efficacy of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on major cardiovascular events: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Prog. Lipid Res. 2022, 88, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.T.; Zeng, B.S.; Suen, M.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Correll, C.U.; Zeng, B.Y.; Kuo, J.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Tu, Y.K.; et al. Efficacy and acceptability of anti-inflammatory eicosapentaenoic acid for cognitive function in Alzheimer’s dementia: A network meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials with omega-3 fatty acids and FDA-approved pharmacotherapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 111, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Zeng, B.S.; Su, K.P.; Wu, Y.C.; Tu, Y.K.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Hsu, C.W.; et al. Network Meta-analysis of Different Treatments for Vestibular Migraine. CNS Drugs 2023, 37, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.; Green, S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 5.0.2; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus, A.C.; Bender, R.; Skipka, G. The Peto odds ratio viewed as a new effect measure. Stat. Med. 2014, 33, 4861–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, I.R. Network meta-analysis. Stata, J. 2015, 15, 951–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puhan, M.A.; Schunemann, H.J.; Murad, M.H.; Li, T.; Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Singh, J.A.; Kessels, A.G.; Guyatt, G.H.; Group, G.W. A GRADE Working Group approach for rating the quality of treatment effect estimates from network meta-analysis. BMJ 2014, 349, g5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, B.; Karasen, R.M.; Buran, Y. Efficacy of medical therapy in the prevention of residual dizziness after successful repositioning maneuvers for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). B-ENT 2015, 11, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, K.; Bronstein, A.M.; Faldon, M.E.; Mandala, M.; Murray, K.; Silove, Y. Visual dependence and BPPV. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amor-Dorado, J.C.; Barreira-Fernandez, M.P.; Aran-Gonzalez, I.; Casariego-Vales, E.; Llorca, J.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A. Particle repositioning maneuver versus Brandt-Daroff exercise for treatment of unilateral idiopathic BPPV of the posterior semicircular canal: A randomized prospective clinical trial with short- and long-term outcome. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastasopoulos, D.; Lempert, T.; Gianna, C.; Gresty, M.A.; Bronstein, A.M. Horizontal otolith-ocular responses to lateral translation in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 1997, 117, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andera, L.; Azeredo, W.J.; Greene, J.S.; Sun, H.; Walter, J. Optimizing Testing for BPPV - The Loaded Dix-Hallpike. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2020, 16, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, S.I.; Hawley, R.; Gomez, O. Systematic approach to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in the elderly. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2003, 128, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asawavichianginda, S.; Isipradit, P.; Snidvongs, K.; Supiyaphun, P. Canalith repositioning for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomized, controlled trial. Ear Nose Throat J. 2000, 79, 732–734, 736–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, W.M.; Gad El-Mawla, E.K.; Chedid, A.E.; Mustafa, A.H. Effect of a hybrid maneuver in treating posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2015, 26, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balatsouras, D.G.; Korres, S.G. Subjective benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balikci, H.H.; Ozbay, I. Effects of postural restriction after modified Epley maneuver on recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Auris Nasus Larynx 2014, 41, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballve, J.L.; Carrillo-Munoz, R.; Rando-Matos, Y.; Villar, I.; Cunillera, O.; Almeda, J.; Rodero, E.; Monteverde, X.; Rubio, C.; Moreno, N.; et al. Effectiveness of the Epley manoeuvre in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomised clinical trial in primary care. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 69, e52–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bech, M.W.; Staffe, A.T.; Hougaard, D.D. A mechanical rotation chair provides superior diagnostics of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1040701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigelow, R.T.; Carey, J.P. Randomized controlled trial in support of vitamin D and calcium supplementation for BPPV. Neurology 2020, 95, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Izcovich, A.; Rochwerg, B.; Florez, I.D.; Hazlewood, G.; Alhazanni, W.; Yepes-Nunez, J.; Santesso, N.; Guyatt, G.H.; Schunemann, H.J.; et al. GRADE approach to drawing conclusions from a network meta-analysis using a partially contextualised framework. BMJ 2020, 371, m3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromwich, M.A.; Parnes, L.S. The DizzyFix: Initial results of a new dynamic visual device for the home treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2008, 37, 380–387. [Google Scholar]
- Bruintjes, T.D.; Companjen, J.; van der Zaag-Loonen, H.J.; van Benthem, P.P. A randomised sham-controlled trial to assess the long-term effect of the Epley manoeuvre for treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2014, 39, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, B.O.; Ercan, I.; Cakir, Z.A.; Turgut, S. Efficacy of postural restriction in treating benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, L.; Capparuccia, P.G.; Di Maria, D.; Melillo, M.G.; Villari, D. Treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal by "Quick Liberatory Rotation Manoeuvre". Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2003, 23, 161–167. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo Munoz, R.; Ballve Moreno, J.L.; Villar Balboa, I.; Rando Matos, Y.; Cunillera Puertolas, O.; Almeda Ortega, J.; Vertigo Study Group in Florida Primary, C. A single Epley manoeuvre can improve self-perceptions of disability (quality of life) in patients with pc-BPPV: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. Aten. Primaria 2021, 53, 102077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casani, A.P.; Nacci, A.; Dallan, I.; Panicucci, E.; Gufoni, M.; Sellari-Franceschini, S. Horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Effectiveness of two different methods of treatment. Audiol. Neurootol. 2011, 16, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casani, A.P.; Navari, E.; Albera, R.; Agus, G.; Asprella Libonati, G.; Chiarella, G.; Lombardo, N.; Marcelli, V.; Ralli, G.; Scotto di Santillo, L.; et al. Approach to residual dizziness after successfully treated benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Effect of a polyphenol compound supplementation. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 11, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celis-Aguilar, E.; Mayoral-Flores, H.O.; Torrontegui-Zazueta, L.A.; Medina-Cabrera, C.A.; Leon-Leyva, I.C.; Dehesa-Lopez, E. Effectiveness of Brandt Daroff, Semont and Epley maneuvers in the treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Indian. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, Y.S.; Cagac, A.; Duzenli, U.; Bozan, N.; Elasan, S. Residual Dizziness in Elderly Patients after Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2022, 84, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, Y.S.; Ozmen, O.A.; Demir, U.L.; Kasapoglu, F.; Basut, O.; Coskun, H. Comparison of the effectiveness of Brandt-Daroff Vestibular training and Epley Canalith repositioning maneuver in benign Paroxysmal positional vertigo long term result: A randomized prospective clinical trial. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.C.; Yang, Y.R.; Hsu, L.C.; Chern, C.M.; Wang, R.Y. Balance improvement in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Clin. Rehabil. 2008, 22, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H. Short-term efficacy of Semont maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A double-blind randomized trial. Otol. Neurotol. 2012, 33, 1127–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.Y.; Cho, J.W.; Choi, J.H.; Oh, E.H.; Choi, K.D. Effect of the Epley Maneuver and Brandt-Daroff Exercise on Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Involving the Posterior Semicircular Canal Cupulolithiasis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 603541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.S.; Jerabek, J. Efficacy of treatments for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 1999, 109, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.S.; Kimball, K.T. Treatment variations on the Epley maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2004, 25, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.S.; Kimball, K.T. Effectiveness of treatments for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of the posterior canal. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.S.; Sangi-Haghpeykar, H. Canalith repositioning variations for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2010, 143, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, F.; Castelhano, L.; Cavilhas, P.; Escada, P. Lateral semicircular canal-BPPV: Prospective randomized study on the efficacy of four repositioning maneuvers. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 73, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Stefano, A.; Dispenza, F.; Citraro, L.; Petrucci, A.G.; Di Giovanni, P.; Kulamarva, G.; Mathur, N.; Croce, A. Are postural restrictions necessary for management of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2011, 120, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Yang, C.; Xiong, M.; Fu, X.; Lai, H.; Huang, W. Danhong enhances recovery from residual dizziness after successful repositioning treatment in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2014, 35, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dispenza, F.; Kulamarva, G.; De Stefano, A. Comparison of repositioning maneuvers for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal: Advantages of hybrid maneuver. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2012, 33, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlugaiczyk, J.; Thiemer, M.; Neubert, C.; Schorn, B.A.; Schick, B. The aVOR App Increases Medical Students’ Competence in Treating Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e401–e406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco-Gutierrez, V.; Perez-Guillen, V.; Gil-Aguilar, M.T.; Franco-Gutierrez, R.; Alvarez-Zapico, M.J.; Garcia-Zamora, E.; Perez-Vazquez, P. Comparative Analysis of the Efficiency of Two Treatment Protocols for Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 73, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehling, D.A.; Bowen, J.M.; Mohr, D.N.; Brey, R.H.; Beatty, C.W.; Wollan, P.C.; Silverstein, M.D. The canalith repositioning procedure for the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2000, 75, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yang, H.; He, F.; Wei, D.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, W.; Han, J. Self-Treatment of Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Preliminary Study. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 654637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, D.; Musazzi, M.; Perez Akly, M.; Cherchi, M.; Yacovino, D.A. A comparative study of two methods for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in the emergency department. J. Otol. 2021, 16, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guneri, E.A.; Kustutan, O. The effects of betahistine in addition to epley maneuver in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 146, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Lee, J.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Treatment Efficacy of Forced Prolonged Position After Cupulolith Repositioning Maneuver in Apogeotropic HSCC BPPV. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 103, NP234–NP240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helminski, J.O.; Janssen, I.; Kotaspouikis, D.; Kovacs, K.; Sheldon, P.; McQueen, K.; Hain, T.C. Strategies to prevent recurrence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 131, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdman, S.J.; Tusa, R.J.; Zee, D.S.; Proctor, L.R.; Mattox, D.E. Single treatment approaches to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1993, 119, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Ahadi, M.; Jalaei, B.; Maarefvand, M.; Talebi, H. The Additional Effect of Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy on Residual Dizziness After Successful Modified Epley Procedure for Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Am. J. Audiol. 2021, 30, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horinaka, A.; Kitahara, T.; Shiozaki, T.; Ito, T.; Wada, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Nario, K. Head-Up Sleep May Cure Patients With Intractable Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A six-Month Randomized Trial. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2019, 4, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.; Kim, S.H.; Kang, K.W.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, S.H. Canalith repositioning in apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Do we need faster maneuvering? J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 358, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Okumura, T.; Sato, T.; Takeda, N.; Ohta, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Inohara, H. Effects of Interval Time of the Epley Maneuver on Immediate Reduction of Positional Nystagmus: A Randomized, Controlled, Non-blinded Clinical Trial. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaradisaikul, S.K.; Chowsilpa, S.; Hanprasertpong, C.; Rithirangsriroj, T. Single Cycle Versus Multiple Cycles of Canalith Repositioning Procedure for Treatment of Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Otol. Neurotol. 2021, 42, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, M.; Ghous, M.; Ayaz, M.; Khan, A.A.; Akbar, A.; Haleem, F. Effects of Half-Somersault and Brandt-Daroff exercise on dizziness, fear of fall and quality of life in patients with posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomised control trial. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2023, 73, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.M.; Gerami, H.; Saberi, A.; Razaghi, S. The Impact of Betahistine versus Dimenhydrinate in the Resolution of Residual Dizziness in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2020, 129, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, J.P.; Metzger, M.; Sforza, E. Impact of volume targeting on efficacy of bi-level non-invasive ventilation and sleep in obesity-hypoventilation. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.J.; Lee, D.H.; Park, J.M.; Oh, J.H.; Seo, J.H. The efficacy of a modified Dix-Hallpike test with a pillow under shoulders. J. Vestib. Res. 2019, 29, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Koo, J.W.; Choi, K.D.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Oh, S.Y.; et al. Prevention of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo with vitamin D supplementation: A randomized trial. Neurology 2020, 95, e1117–e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.J.; Koo, J.W.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, J.S.; Song, J.J. Anxiolytics reduce residual dizziness after successful canalith repositioning maneuvers in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012, 132, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, A.; Alptekin, H.K.; Capan, N.; Diracoglu, D.; Saral, I.; Aydin, S.; Aksoy, C. The efficacy of vestibular electrical stimulation on patients with unilateral vestibular pathologies. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2017, 63, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanjai, S.; Saha, A.K. Evaluation of vestibular exercises in the management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2010, 62, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Shamanna, K. Management of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Comparative Study between Epleys Manouvre and Betahistine. Int. Tinnitus J. 2017, 21, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerber, K.A.; Damschroder, L.; McLaughlin, T.; Brown, D.L.; Burke, J.F.; Telian, S.A.; Tsodikov, A.; Fagerlin, A.; An, L.C.; Morgenstern, L.B.; et al. Implementation of Evidence-Based Practice for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in the Emergency Department: A Stepped-Wedge Randomized Trial. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2020, 75, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaftari, M.D.; Ahadi, M.; Maarefvand, M.; Jalaei, B. The Efficacy of the Half Somersault Maneuver in Comparison to the Epley Maneuver in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.A.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.; Kang, B.G.; Lee, J.; Han, B.I.; Seok, J.I.; Chung, E.J.; Kim, J.; Lee, H. Efficacy of mastoid oscillation and the Gufoni maneuver for treating apogeotropic horizontal benign positional vertigo: A randomized controlled study. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, K.D.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Jung, I.; Park, J.H. Effect of Self-treatment of Recurrent Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, D.U.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, K.D.; Moon, I.S.; Kim, B.K.; Kim, H.J. Randomized clinical trial for geotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Neurology 2012, 79, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.B.; Lee, H.S.; Ban, J.H. Vestibular suppressants after canalith repositioning in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 2400–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitahara, T.; Horinaka, A.; Shiozaki, T.; Ito, T.; Wada, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Nario, K. Combination of head-up sleep and vertical recognition training may cure intractable motion-evoked dizziness with unknown origin. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, T.H.; Song, M.H.; Kang, J.W.; Shim, D.B. Double-blind randomized controlled trial on efficacy of cupulolith repositioning maneuver for treatment of apogeotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2020, 140, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcu, D.G.; Yanik, B.; Boynukalin, S.; Kurtais, Y. Efficacy of a home-based exercise program on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo compared with betahistine. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 37, 373–379. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, T.H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. New Therapeutic Maneuver for Horizontal Semicircular Canal Cupulolithiasis: A Prospective Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Jeon, E.J.; Lee, D.H.; Seo, J.H. Therapeutic Efficacy of the Modified Epley Maneuver With a Pillow Under the Shoulders. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 13, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.H.; Noh, H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Immediate and short-term effects of Gufoni and Appiani liberatory maneuver for treatment of ageotropic horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A prospective randomized trial. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2021, 6, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Shim, D.B.; Park, H.J.; Song, C.I.; Kim, M.B.; Kim, C.H.; Byun, J.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Kim, T.S.; Park, K.H.; et al. A multicenter randomized double-blind study: Comparison of the Epley, Semont, and sham maneuvers for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Audiol. Neurootol. 2014, 19, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, S.; Zou, S. Efficacy of the Li maneuver in treating posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2017, 137, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zou, S.; Tian, S. A prospective randomized controlled study of Li quick repositioning maneuver for geotropic horizontal canal BPPV. Acta Otolaryngol. 2018, 138, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, J.D.; Ellensohn, A.; Massingale, S.; Gerkin, R. Vibration with the canalith repositioning maneuver: A prospective randomized study to determine efficacy. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancera Sanchez, J.; Hernaiz Leonardo, J.C.; Ishiwara Niembro, J.K.; Lesser, J.C. Therapeutic Effect of the Correction of Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. A Randomized Clinical Trial. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 26, e666–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, M.; Califano, L.; Casani, A.P.; Faralli, M.; Marcelli, V.; Neri, G.; Pecci, R.; Scasso, F.; Scotto di Santillo, L.; Vannucchi, P.; et al. Double-Blind Randomized Trial on the Efficacy of the Forced Prolonged Position for Treatment of Lateral Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1296–E1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, M.; Pepponi, E.; Santoro, G.P.; Cambi, J.; Casani, A.; Faralli, M.; Giannoni, B.; Gufoni, M.; Marcelli, V.; Trabalzini, F.; et al. Double-blind randomized trial on the efficacy of the Gufoni maneuver for treatment of lateral canal BPPV. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 1782–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandala, M.; Santoro, G.P.; Asprella Libonati, G.; Casani, A.P.; Faralli, M.; Giannoni, B.; Gufoni, M.; Marcelli, V.; Marchetti, P.; Pepponi, E.; et al. Double-blind randomized trial on short-term efficacy of the Semont maneuver for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 882–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, C.; Goplen, F.K.; Aasen, T.; Gjestad, R.; Nordfalk, K.F.; Nordahl, S.H.G. Treatment of horizontal canal BPPV-a randomized sham-controlled trial comparing two therapeutic maneuvers of different speeds. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslovara, S.; Soldo, S.B.; Puksec, M.; Balaban, B.; Penavic, I.P. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): Influence of pharmacotherapy and rehabilitation therapy on patients’ recovery rate and life quality. NeuroRehabilitation 2012, 31, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, W.J.; Johnson, P.; Brown, D.; Tsodikov, A.; Rowell, B.; Fagerlin, A.; Telian, S.A.; Damschroder, L.; An, L.C.; Morgenstern, L.B.; et al. An Educational Intervention for Acute Dizziness Care: A Randomized, Vignette-based Study. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e830–e838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Olavarria, C.; Sarria-Echegaray, P.; Til-Perez, G.; Carnevale, C. Role of Intratympanic Dexamethasone for Intractable Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Int. Tinnitus J. 2021, 25, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, J.E.; Miklea, J.T.; Howard, M.; Springate, R.; Kaczorowski, J. Canalith repositioning maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Randomized controlled trial in family practice. Can. Fam. Physician Med. De Fam. Can. 2007, 53, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, K.D.; Park, J.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.S.; Yang, T.H.; Kim, H.J. Switch to Semont maneuver is no better than repetition of Epley maneuver in treating refractory BPPV. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1892–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, B.; Liu, H.; Bromwich, M. An iPhone-assisted particle repositioning maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): A prospective randomized study. J. Am. Board. Fam. Med. 2015, 28, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, J.E.P.; Moreno, J.L.B.; Matos, Y.R.; Ortega, J.A.; Puertolas, O.C.; Munoz, R.C.; Balboa, I.V.; Compta, X.G.; Agudelo, O.L.A.; Munoz, S.C.; et al. Effectiveness of a training intervention to improve the management of vertigo in primary care: A multicentre cluster-randomised trial, VERTAP. Trials 2022, 23, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Guillen, V.; Franco-Gutierrez, V.; Aguilar, M.T.G.; Zamora, E.G.; Perez-Vazquez, P. Can Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Be Treated in a One Session? Otol. Neurotol. 2020, 41, e727–e734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piromchai, P.; Eamudomkarn, N.; Srirompotong, S.; Ratanaanekchai, T.; Yimtae, K. The Efficacy of a Home Treatment Program Combined With Office-Based Canalith Repositioning Procedure for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo-A Randomized Controlled Trial. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, L.; Gilad, R.; Michael, T. Unilateral mimicking bilateral BPPV- a forgotten entity? Characteristics of a large cohort of patients, comparison with posterior canal BPPV and clinical implications. J. Otol. 2021, 16, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, L.; Michael, T. Bilateral Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Tends to Reoccur. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wang, B.; Yu, W.; Zheng, Z.; Yang, J. Clinical efficacy and quality of life evaluation of BPPV by different reduction methods. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2016, 30, 392–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ranju, R.L.; Lepcha, A.; Mammen, M.D.; Vasanthan, L.T.; Augustine, A.M.; Philip, A. An Effective Home-Based Particle Repositioning Procedure for Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV). Indian. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 74, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, K.M.; Freitas, R.V.; Ferreira, L.M.; Deshpande, N.; Guerra, R.O. Effects of balance Vestibular Rehabilitation Therapy in elderly with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A randomized controlled trial. Disabil. Rehabil. 2017, 39, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.A.; Gans, R.E.; DeBoodt, J.L.; Lister, J.J. Treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Necessity of postmaneuver patient restrictions. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2005, 16, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.L.; Ledesma, A.L.L.; Pires de Oliveira, C.A.; Bahmad, F., Jr. Effect of Vestibular Exercises Associated With Repositioning Maneuvers in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Otol. Neurotol. 2019, 40, e824–e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, A.; Nemati, S.; Sabnan, S.; Mollahoseini, F.; Kazemnejad, E. A safe-repositioning maneuver for the management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Gans vs. Epley maneuver; a randomized comparative clinical trial. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 2973–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.R.; Burmeister, D.B.; Rupp, V.A.; Greenberg, M.R. Management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomized controlled trial. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 46, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Khosravi, M.H.; Bayatpoor, M.E. Comparing the Effects of Epley Maneuver and Cinnarizine on Benign Positional Paroxysmal Vertigo; A Randomized Clinical Trial. Galen. Med. J. 2019, 8, e866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvinelli, F.; Casale, M.; Trivelli, M.; D’Ascanio, L.; Firrisi, L.; Lamanna, F.; Greco, F.; Costantino, S. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A comparative prospective study on the efficacy of Semont’s maneuver and no treatment strategy. La Clin. Ter. 2003, 154, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Salvinelli, F.; Trivelli, M.; Casale, M.; Firrisi, L.; Di Peco, V.; D’Ascanio, L.; Greco, F.; Miele, A.; Petitti, T.; Bernabei, R. Treatment of benign positional vertigo in the elderly: A randomized trial. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammartino, G.; Mariniello, M.; Scaravilli, M.S. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo following closed sinus floor elevation procedure: Mallet osteotomes vs. screwable osteotomes. A triple blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Oral. Implants Res. 2011, 22, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayin, I.; Koc, R.H.; Temirbekov, D.; Gunes, S.; Cirak, M.; Yazici, Z.M. Betahistine add-on therapy for treatment of subjects with posterior benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomized controlled trial. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 88, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuricht, A.; Hougaard, D.D. Is a Mechanical Rotational Chair Superior to Manual Treatment Maneuvers on an Examination Bed in the Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo? Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e235–e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Se To, P.L.; Singh, D.K.A.; Whitney, S.L. Effects of customized vestibular rehabilitation plus canalith repositioning maneuver on gait and balance in adults with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Vestib. Res. 2022, 32, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Peng, X.; Wang, E. Efficacy of computer-controlled repositioning procedure for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, D.; Massoud, E.A. Treatment outcomes of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. J. Otolaryngol. 2001, 30, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoceli, L.; Bittar, R.S.; Greters, M.E. Posture restrictions do not interfere in the results of canalith repositioning maneuver. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2005, 71, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsamutpadung, C.; Kulthaveesup, A. Comparison of outcomes of the Epley and Semont maneuvers in posterior canal BPPV: A randomized controlled trial. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2021, 6, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.M.; Marroney, N.; Beattie, J.; Newdick, A.; Tahtis, V.; Burgess, C.; Marsden, J.; Seemungal, B.M. A mixed methods randomised feasibility trial investigating the management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in acute traumatic brain injury. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2020, 6, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.H.; Kong, T.H.; Shim, D.B. Optimal reassessment time for treatment response in posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Panda, N.; Raghunathan, M. Efficacy of particle repositioning maneuver in BPPV: A prospective study. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2003, 24, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenerson, R.L.; Cronin, G.W. Comparison of the canalith repositioning procedure and vestibular habituation training in forty patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 114, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita-Kitajima, A.; Sato, S.; Mikami, K.; Mukaide, M.; Koizuka, I. Does vertigo disappear only by rolling over? Rehabilitation for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010, 130, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.B.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Wang, B.Q.; Yu, W.Y.; Yang, J.; Guo, W.J.; Ren, H.J. Curative effect analysis of the vestibular rehabilitation training on residual dizziness after successful canalith repositioning maneuvers in patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2017, 31, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan, I.; Rangachari, V.; Sumathi, V.; Kumar, K. Epley’s manoeuvre versus Epley’s manoeuvre plus labyrinthine sedative as management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Prospective, randomised study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2011, 125, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabanfar, R.; Chan, H.H.L.; Lin, V.; Le, T.; Irish, J.C. Development and face validation of a Virtual Reality Epley Maneuver System (VREMS) for home Epley treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A randomized, controlled trial. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacalan, E.; Inal, H.S.; Senturk, M.N.; Mengi, E.; Alemdaroglu-Gurbuz, I. Effectiveness of the Epley maneuver versus Cawthorne-Cooksey vestibular exercises in the treatment of posterior semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV): A randomized controlled trial. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2021, 28, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Yu, D.; Feng, Y.; Song, Q.; You, J.; Shi, H.; Yin, S. Comparative study of the efficacy of the canalith repositioning procedure versus the vertigo treatment and rehabilitation chair. Acta Otolaryngol. 2014, 134, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimoto, H.; Doi, K.; Katata, K.; Nibu, K.I. Self-treatment for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of the posterior semicircular canal. Neurology 2005, 65, 1299–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, D.; Castaldo, G.; De Santis, C.; Trusio, A.; Motta, G. Treatment of horizontal canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A new rehabilitation technique. ScientificWorldJournal 2012, 2012, 160475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Sheng, H.B.; Wang, J.; Luo, X.; Yu, J.; Jia, X.H.; Cheng, X.; Han, Z.; Chi, F.L. Comparative Study on the Roles of the Number of Accelerations and Rotation Angle in the Treatment Maneuvers for Posterior Semicircular Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2016, 78, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toupet, M.; Ferrary, E.; Bozorg Grayeli, A. Effect of repositioning maneuver type and postmaneuver restrictions on vertigo and dizziness in benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. ScientificWorldJournal 2012, 2012, 162123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uz, U.; Uz, D.; Akdal, G.; Celik, O. Efficacy of Epley Maneuver on Quality of Life of Elderly Patients with Subjective BPPV. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2019, 15, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, D.P.; Gazzola, J.M.; Lanca, S.M.; Dorigueto, R.S.; Kasse, C.A. Clinical and functional aspects of body balance in elderly subjects with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 79, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Seelig, T.; Radtke, A.; Tiel-Wilck, K.; Neuhauser, H.; Lempert, T. Short-term efficacy of Epley’s manoeuvre: A double-blind randomised trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; An, F.; Xie, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y. The treatment of benign positional paroxysmal vertigo of posterior semicircular canal by Epley maneuver combined with Semont maneuver. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2014, 28, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, M.; Hertanu, T.; Novikov, I.; Kronenberg, J. Epley’s manoeuvre for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A prospective study. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1999, 24, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xing, Y.Z.; Bi, W.; Liu, J.X. The value of lean nystagmus and sitting to supine positioning nystagmus in the diagnosis of horizontal semicircular canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2019, 33, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.X.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, H.W. Intervention strategies for residual dizziness after successful repositioning maneuvers in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A single center randomized controlled trial. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 56, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, N. Efficacy of different treatment on residual symptoms aftercanalith repositioning procedure in patients withbenign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2016, 30, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimtae, K.; Srirompotong, S.; Srirompotong, S.; Sae-Seaw, P. A randomized trial of the canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope 2003, 113, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, F. The effect of combination of Brandt-Daroff training and otolith reposition instrument pair in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 35, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Geng, M.; Yan, B.; Lu, X. Epley’s manoeuvre versus Epley’s manoeuvre plus labyrinthine sedative in the management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Prospective, randomised study. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2012, 26, 750–752. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Wu, C.L.; Xiao, G.R.; Zhong, F.F. Comparison of three types of self-treatments for posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: Modified Epley maneuver, modified Semont maneuver and Brandt-Daroff maneuver. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2012, 47, 799–803. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, S.Z.; Li, J.R.; Tian, S.Y.; Ju, J.; Jia, M.Y. A randomized controlled trial on short-term efficacy of the modified Semont maneuver for the treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2017, 31, 1468–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Chang, C.H.; Hu, L.Y.; Tu, M.S.; Lu, T.; Chen, P.M.; Shen, C.C. Increased risk of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in patients with anxiety disorders: A nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Quan, X.; Ren, Y.; Rong, K.; Pan, S.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Tian, C.; et al. Global research trends in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A bibliometric analysis. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1204038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Stubbs, B.; Chen, T.Y.; Liang, C.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Hyper-IgE Syndrome: A Systematic Review of Characteristics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Liang, C.S.; Chen, Y.W.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Patients with Hashimoto’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiological Features in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.Y.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction Related to Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Hsu, C.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Chen, T.Y.; Zeng, B.S.; Tseng, P.T. Audiovestibular Dysfunction in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Lui, C.C.; Chen, T.Y.; Tseng, P.T.; Hung, C.M. The Tyndall Effect in High-Resolution Computed Tomography of Semicircular Canalolithiasis with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.-J.; Zeng, B.-Y.; Zeng, B.-S.; Chu, C.-S.; Liang, C.-S.; Wu, Y.-C.; Stubbs, B.; Su, K.-P.; Tu, Y.-K.; Chen, T.-Y.; et al. A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Postmaneuver Rehabilitation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Treatment. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2025, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020023
Chen J-J, Zeng B-Y, Zeng B-S, Chu C-S, Liang C-S, Wu Y-C, Stubbs B, Su K-P, Tu Y-K, Chen T-Y, et al. A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Postmaneuver Rehabilitation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Treatment. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine. 2025; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jiann-Jy, Bing-Yan Zeng, Bing-Syuan Zeng, Che-Sheng Chu, Chih-Sung Liang, Yi-Cheng Wu, Brendon Stubbs, Kuan-Pin Su, Yu-Kang Tu, Tien-Yu Chen, and et al. 2025. "A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Postmaneuver Rehabilitation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Treatment" Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine 6, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020023
APA StyleChen, J.-J., Zeng, B.-Y., Zeng, B.-S., Chu, C.-S., Liang, C.-S., Wu, Y.-C., Stubbs, B., Su, K.-P., Tu, Y.-K., Chen, T.-Y., Chen, Y.-W., Hsu, C.-W., Shiue, Y.-L., & Tseng, P.-T. (2025). A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Efficacy of Postmaneuver Rehabilitation in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Treatment. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine, 6(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm6020023






