Study of the Agreement of the Apnea–Hypopnea Index Measured Simultaneously by Pressure Transducer via Respiratory Polygraphy and by Thermistor via Polysomnography in Real Time with the Same Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. PSG Device
2.3. PG Device
2.4. Procedure
2.4.1. Alice PDx
2.4.2. Alice NightOne
2.5. PSG Data Score
2.6. PG Data Score
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Study Subjects
3.2. Comparison of Respiratory Events between PSG and PG
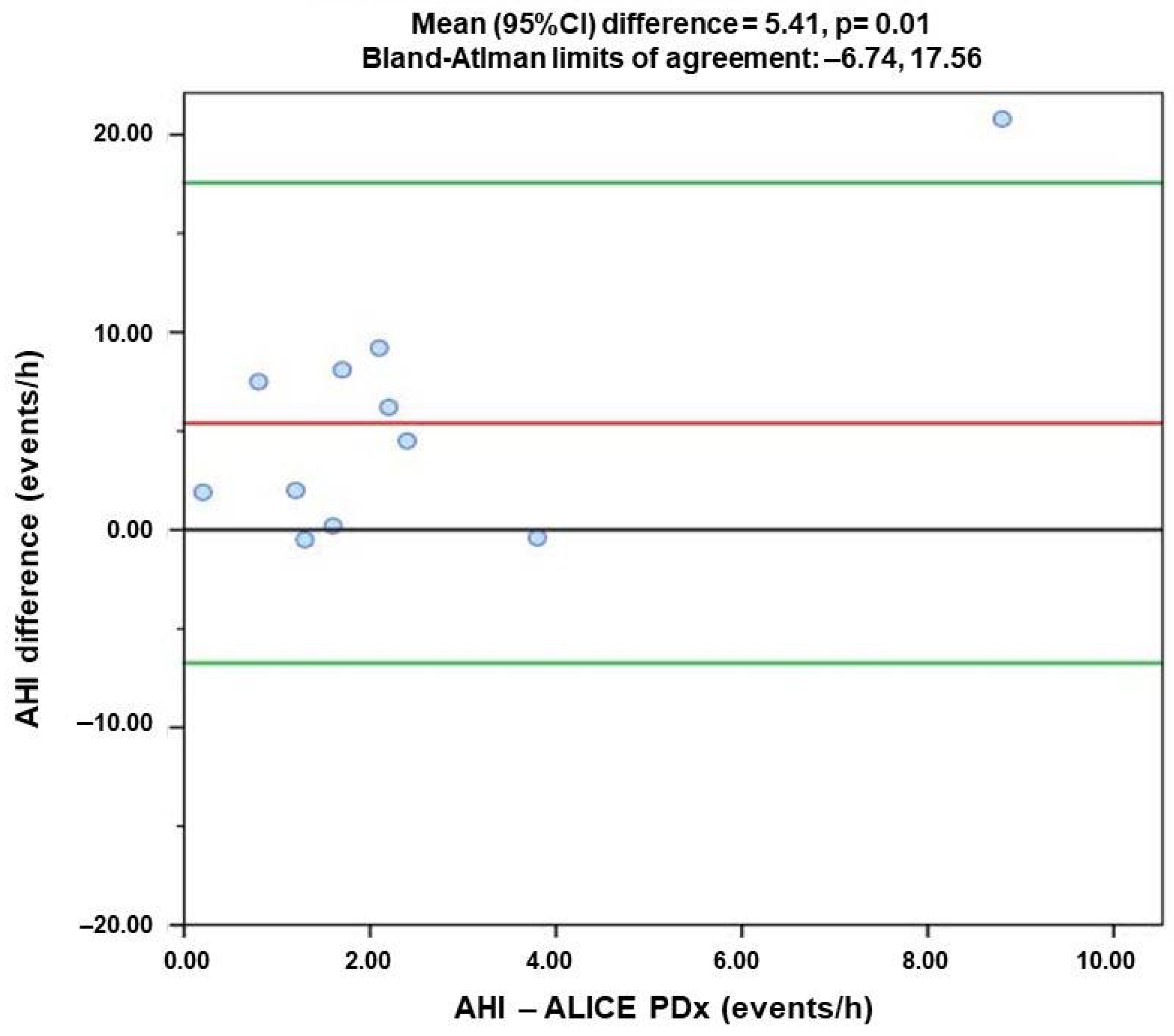
- Apnea–Hypopnea Index (AHI)
- b.
- Central Apnea Index (CAI)
- c.
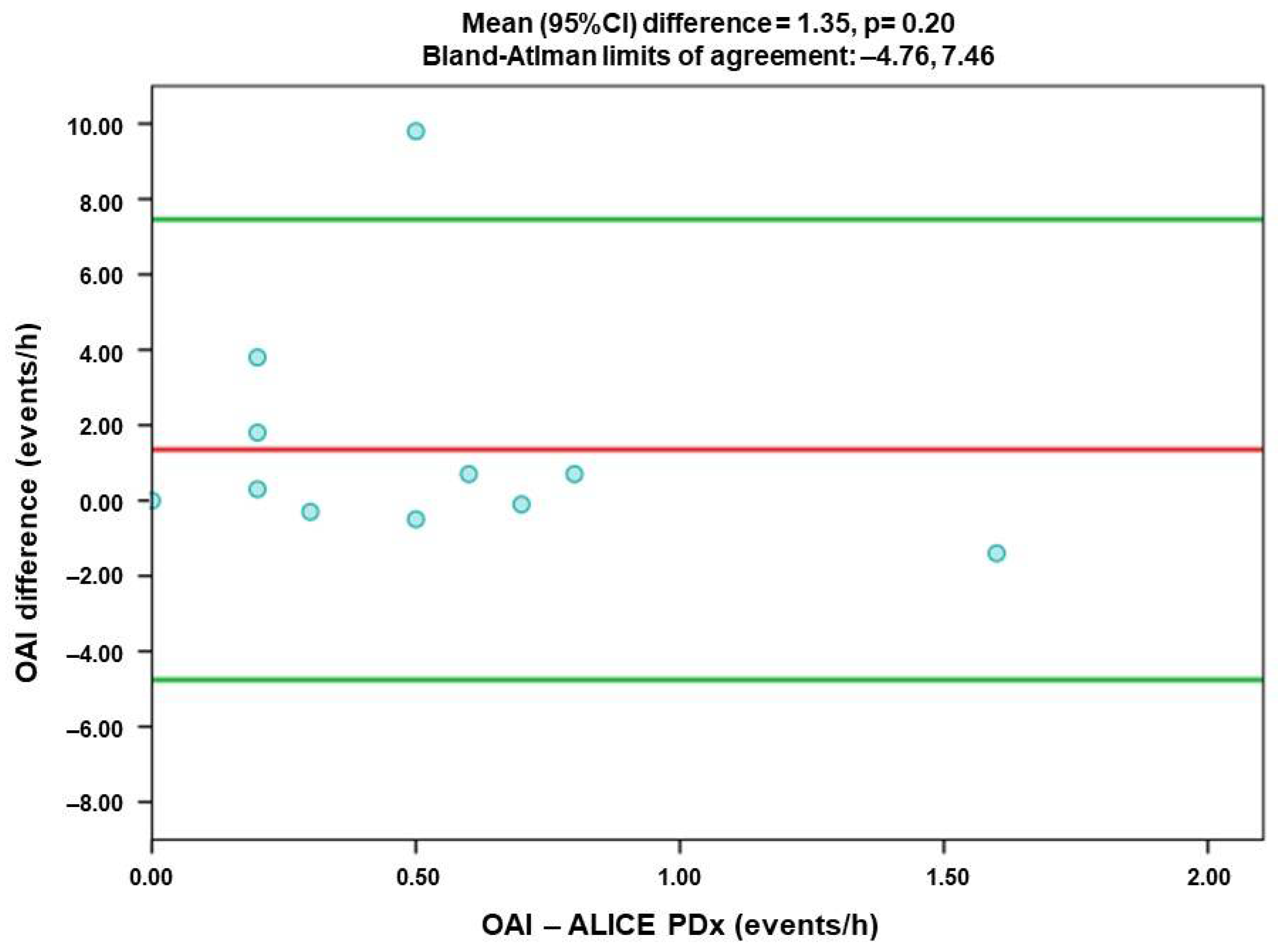
- Obstructive Apnea Index (OAI)
- d.
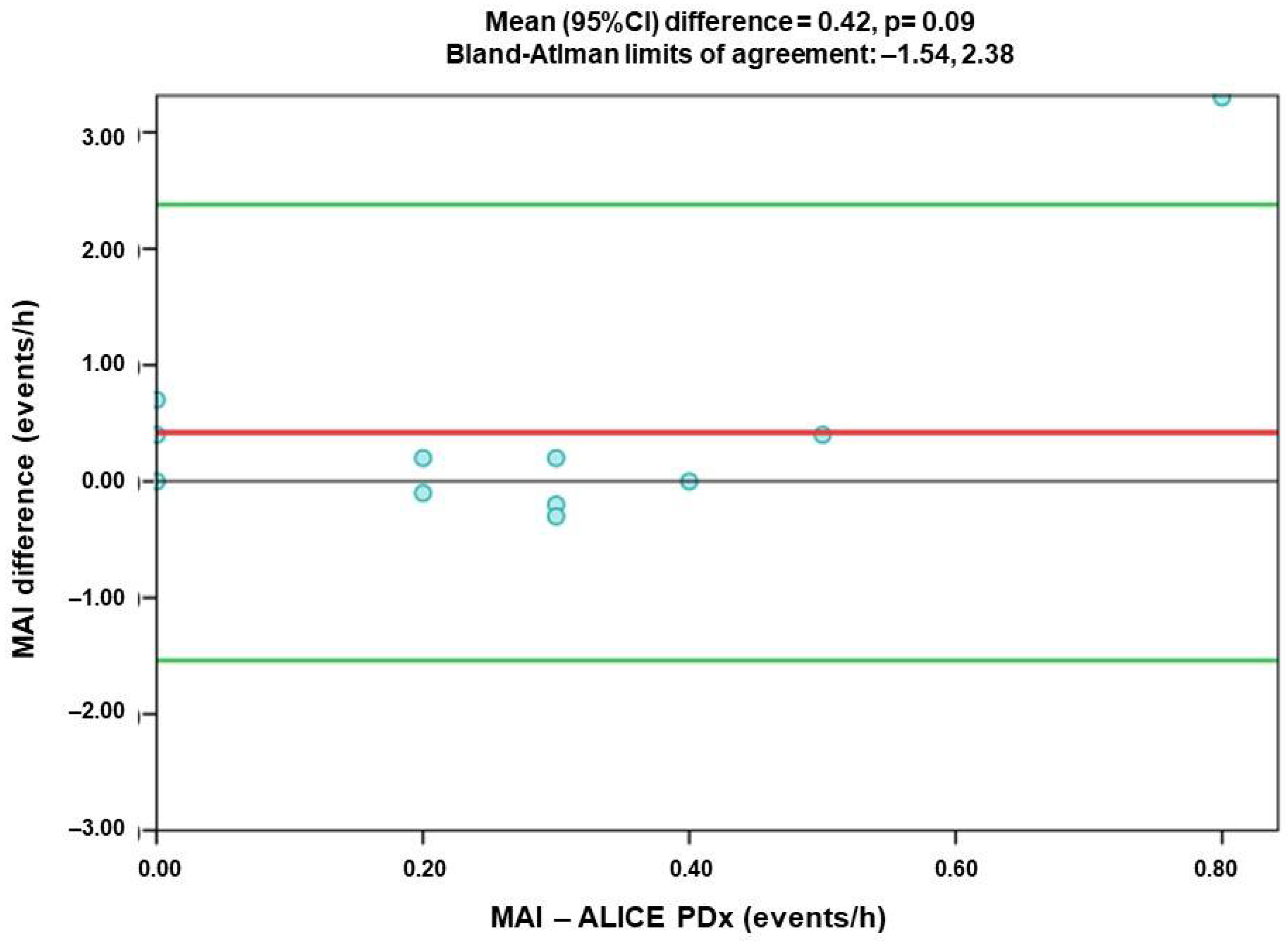
- Mixed Apnea Index (MAI)
- e.
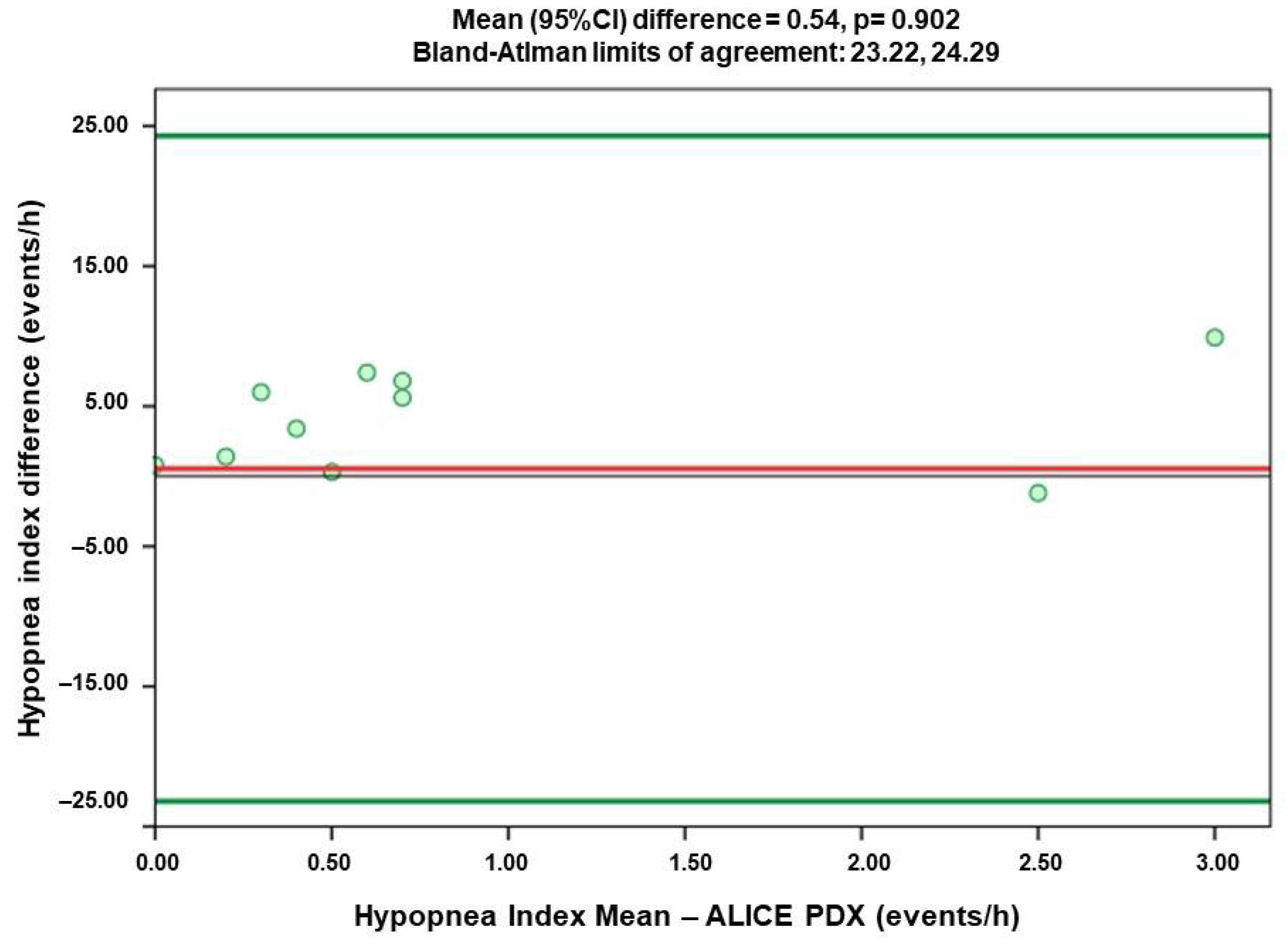
- Hypopnea Index (HI)
- f.
- Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
3.3. Comparison of Agreement of Respiratory Index Measured by Alice PDX (PSG) and Alice NightOne (PG)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spicuzza, L.; Caruso, D.; Di Maria, G. Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and its management. Ther. Adv. Chronic. Dis. 2015, 6, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lyons, M.M.; Bhatt, N.Y.; Pack, A.I.; Magalang, U.J. Global burden of sleep-disordered breathing and its implications. Respirology 2020, 25, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong-Quy, S.; Van N, T.; Hua-Huy, T.; Chalumeau, F.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T.; Soyez, F.; Martin, F. Study about the prevalence of the obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome in Vietnam. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2018, 35, 14–24. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, N.; Edara, P.; Sun, C. Sleep disorders and risk of traffic crashes: A naturalistic driving study analysis. Saf. Sci. 2021, 140, 105295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajzadeh, M.; Hosseini, M.; Mohtashami, J.; Chaibakhsh, S.; Tafreshi, M.Z.; Gheshlagh, R.G. The Association Between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Depression in Older Adults. Nurs. Midwifery Stud. 2016, 5, e32585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorajja, D. Independent Association between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0012369215496813 (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Reutrakul, S.; Mokhlesi, B. Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Diabetes. Chest 2017, 152, 1070–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darien, I.L. Economic Burden of Undiagnosed Sleep Apnea in the U.S. is nearly $150B per Year, American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Available online: https://aasm.org/economic-burden-of-undiagnosed-sleep-apnea-in-u-s-is-nearly-150b-per-year/ (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- Tan, H.L.; Gozal, D.; Ramirez, H.M.; Bandla, H.P.; Kheirandish-Gozal, L. Overnight polysomnography versus respiratory polygraphy in the diagnosis of pediatric obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2014, 37, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J. Rules for scoring respiratory events in sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Deliberations of the Sleep Apnea Definitions Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eckert, D.J.; Jordan, A.S.; Merchia, P.; Malhotra, A. Central sleep apnea: Pathophysiology and treatment. Chest 2007, 131, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J., Jr.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Ramar, K.; Rogers, R.; Schwab, R.J.; Weaver, E.M.; et al. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Sohn, M.K.; Jeon, M.; Jee, S. Clinical Characteristics of Sleep-Disordered Breathing in Subacute Phase of Stroke. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 41, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindemann, J.; Augenstein, B. Diagnostic accuracy of outpatient polygraphy devices: A comparison with inpatient polysomnography in clinical routine. HNO 2017, 65, 134–140. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabil, A.; Glos, M.; Günther, A.; Schöbel, C.; Veauthier, C.; Fietze, I.; Penzel, T. Comparison of Apnea Detection Using Oronasal Thermal Airflow Sensor, Nasal Pressure Transducer, Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography, and Tracheal Sound Sensor. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Parameters | N | % | Mean | SD | Min–Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 11 | 100 | 22.7 | 0.6 | 22–24 |
| Sex | |||||
| Male | 7 | 63.6 | - | - | - |
| Female | 4 | 36.4 | - | - | - |
| Height (cm) | 11 | 100 | 164.7 | 7.1 | 154–174 |
| Weight (kg) | 11 | 100 | 59.5 | 8.9 | 45–74 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 11 | 100 | 21.8 | 2.2 | 17.4–24.4 |
| Sleep disorders | |||||
| Snoring at night | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| Insomnia | 0 | 0 | - | - | - |
| AHI (apnea–hypopnea index) | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 2.4 | 2.2 | 0.2–8.8 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 0.8–29.6 |
| CAI (central apnea index) | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.0–3.9 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.0–2.4 |
| OAI (obstructive apnea index) | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.0–1.6 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 0.0–10.3 |
| MAI (mixed apnea index) | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.0–0.8 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.0–4.1 |
| HI (hypopnea index) | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 4.9 | 10.4 | 0.0–37.0 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 4.7 | 3.7 | 0.8–12.9 |
| SpO2 | |||||
| PDx | 11 | 100 | 94.2 | 1.0 | 92–96 |
| NightOne | 11 | 100 | 94.0 | 1.0 | 92–95 |
| Parameters | Spearman’s Rho | Mean Difference | Lower LOA | Upper LOA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHI | 0.545 | 5.41 * | −6.74 | 17.56 |
| CAI | 0.674 * | −0.12 | −1.18 | 0.95 |
| OAI | 0.06 | 1.35 | −4.76 | 7.46 |
| MAI | 0.431 | 0.42 | −1.54 | 2.38 |
| HI | 0.309 | 0.54 | −23.22 | 24.29 |
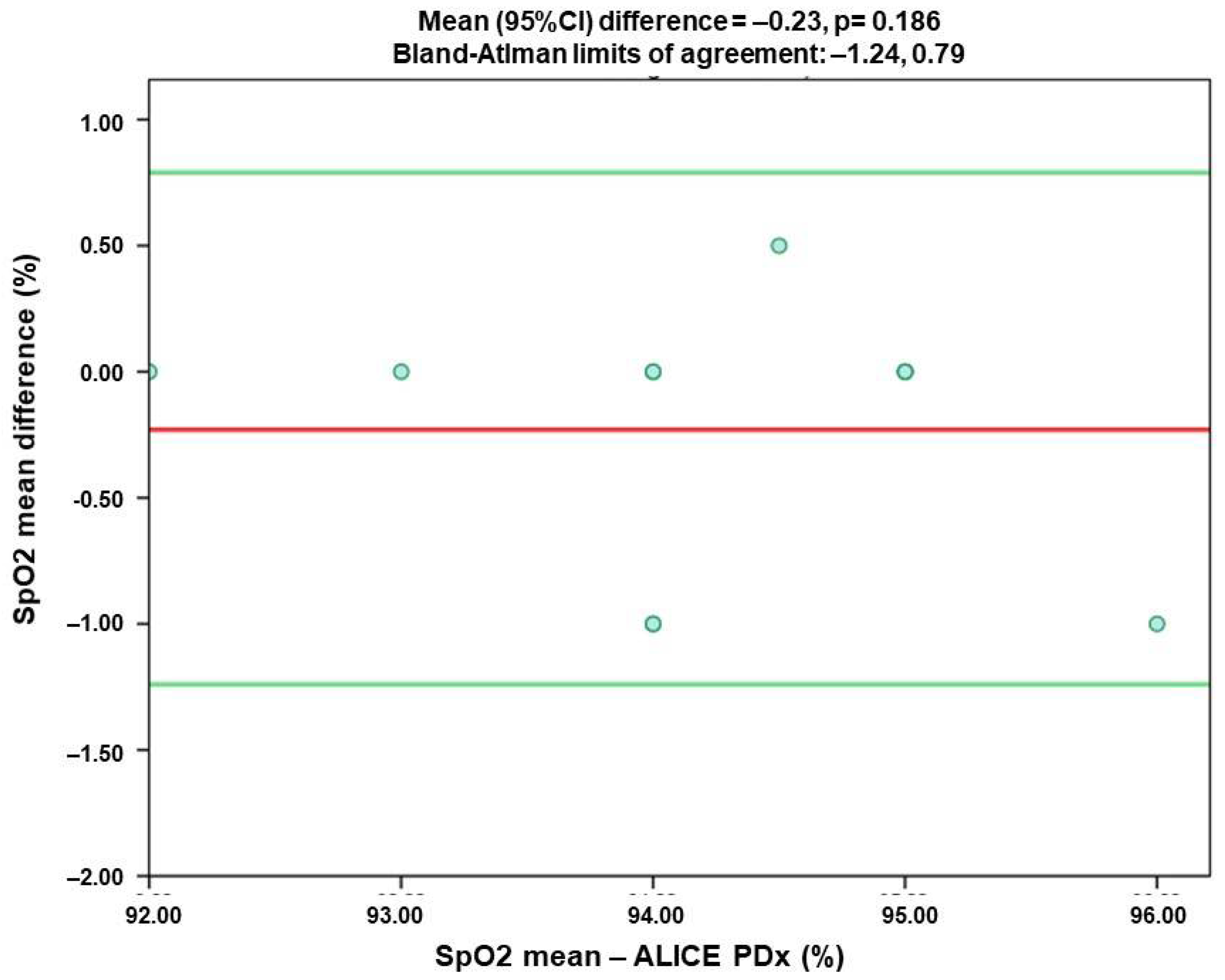
| SpO2 | 0.923 * | −0.23 | −1.24 | 0.79 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran-Thi, B.-T.; Quach-Thieu, M.; Le-Tran, B.-N.; Nguyen-Duc, D.; Tran-Hiep, N.; Nguyen-Thi, T.; Nguyen-Ngoc, Y.-L.; Nguyen-Tuan, A.; Tang-Thi-Thao, T.; Nguyen-Van, T.; et al. Study of the Agreement of the Apnea–Hypopnea Index Measured Simultaneously by Pressure Transducer via Respiratory Polygraphy and by Thermistor via Polysomnography in Real Time with the Same Individuals. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Hear. Balance Med. 2022, 3, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3020004
Tran-Thi B-T, Quach-Thieu M, Le-Tran B-N, Nguyen-Duc D, Tran-Hiep N, Nguyen-Thi T, Nguyen-Ngoc Y-L, Nguyen-Tuan A, Tang-Thi-Thao T, Nguyen-Van T, et al. Study of the Agreement of the Apnea–Hypopnea Index Measured Simultaneously by Pressure Transducer via Respiratory Polygraphy and by Thermistor via Polysomnography in Real Time with the Same Individuals. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine. 2022; 3(2):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3020004
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran-Thi, Bich-Ty, Minh Quach-Thieu, Bao-Ngoc Le-Tran, Duy Nguyen-Duc, Nguyen Tran-Hiep, Thao Nguyen-Thi, Yen-Linh Nguyen-Ngoc, Anh Nguyen-Tuan, Tram Tang-Thi-Thao, Toi Nguyen-Van, and et al. 2022. "Study of the Agreement of the Apnea–Hypopnea Index Measured Simultaneously by Pressure Transducer via Respiratory Polygraphy and by Thermistor via Polysomnography in Real Time with the Same Individuals" Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine 3, no. 2: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3020004
APA StyleTran-Thi, B.-T., Quach-Thieu, M., Le-Tran, B.-N., Nguyen-Duc, D., Tran-Hiep, N., Nguyen-Thi, T., Nguyen-Ngoc, Y.-L., Nguyen-Tuan, A., Tang-Thi-Thao, T., Nguyen-Van, T., & Duong-Quy, S. (2022). Study of the Agreement of the Apnea–Hypopnea Index Measured Simultaneously by Pressure Transducer via Respiratory Polygraphy and by Thermistor via Polysomnography in Real Time with the Same Individuals. Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, Hearing and Balance Medicine, 3(2), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/ohbm3020004







