Abstract
Hearing loss is not uncommon among patients with Down syndrome (DS). It has been reported in 38–78% of the Down syndrome population. However, profound hearing loss in DS patients is rarely noticed due to its low incidence. In this article, we reported two Down syndrome patients with bilateral profound hearing loss in two cases. The first case involved an eight-year-old DS child experiencing extremely severe defects in terms of language and severe defects in terms of gross motor function, adaptability, and sociability. The second case revolved around another DS child with bilateral cochlear nerve absence. We review literature on the DS patients with hearing loss and conclude that profound sensorineural hearing loss in those patients has not received enough attention so far. We also recommend that cochlear implantation (CI) suitability assessment and timely intervention via cochlear implantation are necessary in DS patients. Besides, benefits from CI would be limited and hearing rehabilitation process could be much slower when compared with children without additional inabilities.
1. Case Introduction
1.1. Case 1
An eight-year-old boy, who failed in hearing screening test and was diagnosed with Down syndrome post-natally, attended our clinic over his inability to respond to sound and to talk.
Auditory brainstem response (ABR) and multiple-frequency auditory steady-state evoked responses (ASSR) were performed when he was 29-month-old at the second affiliated hospital of China medical university. The ABR results showed the bilateral hearing thresholds were greater than 90 dB. The ASSR results showed the bilateral hearing thresholds were greater than 110 dB. In addition, tympanometry was also performed and type C tympanogram could be observed in both ears during the test. Meanwhile, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) results suggested that there were no anatomical anomalies and deformities in the middle and inner ear.
The developmental quotients (DQ), based on Gesell Developmental schedules (GDS), was examined in the Chinese people’s liberation army navy general hospital when he was 44 months old. In terms of gross motor function, he could stand independently for only dozens of seconds and he could walk only when others held one of his hands; he was unable to identify objects in terms of cognitive level; he could only pronounce the “ah” sound in terms of language expression. The detailed DQ scores were shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
DQ score based on Gesell Developmental Schedules (GDS).
His ear drum was normal according to oto-endoscopic examination in our clinic this time. Although they visited many hospitals and consulted a lot of doctors, there was no intervention for the DS boy according to the complaints of his parents. It seems the only effective intervention for his hearing restoration is cochlear implantation (CI). However, considering his verbal skill and age, even if the surgery succeeds, most probably the child is unable to understand what others try to convey and to communicate with others. Thus, his parents had no choice but to give up any further intervention.
1.2. Case 2
Another four-year-old DS patient, who also failed to pass the distortion product otoacoustic emission (DPOAE) test, was found that the bilateral hearing thresholds were greater than 95 dB in ABR test when she was one-year-old. ASSR results suggested the bilateral hearing thresholds were greater than 110 dB. Besides, bilateral cochlear foramen stenoses and narrow internal auditory canal on the right side were indicted by horizontal and coronal CT (Figure 1) of middle and inner ear. Moreover, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan (Figure 2) demonstrated the patient’s cochlear nerves on both sides were absent. Considering the absence of cochlear nerve is a contraindication to cochlear implantation, no further intervention was conducted.
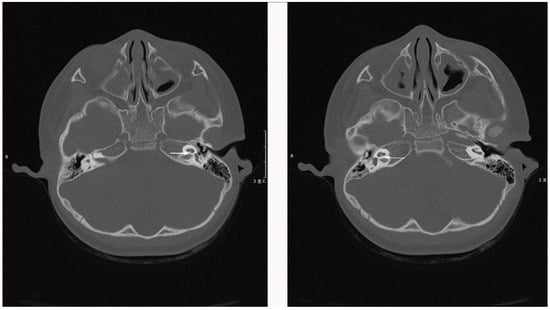
Figure 1.
High-resolution computed tomography of the temporal bones demonstrating bilateral cochlear foramen stenoses in Case 2.
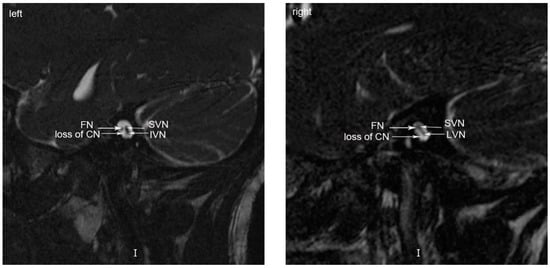
Figure 2.
Magnetic resonance scan (MRI) demonstrating bilateral cochlear nerve loss in Case 2. FN: facial nerve; SVN: superior vestibular nerve; LVN: inferior vestibular nerve; CN: cochlear nerve.
2. Discussion
Down syndrome (DS), caused by the presence of a third copy of chromosome 21, is the most common genetic disorders, which affects 1 out of 1000 live births [1]. Thanks to evidences stockpiled in past 30 years, it is now crystal clear that the incidence of hearing loss in DS patients is much higher than general population, estimated at 38–78% in comparison with 2.5% [2]. Besides, conductive hearing loss, which most commonly comes in the wake of uncontrolled otitis media with effusion in this population, usually accounts for more than 50% of all hearing-impaired DS patients. Other reasons for conductive hearing loss in this population include cerumen impaction, congenital malformation of ossicular chain, and other abnormal structures in middle and/or external ear [3]. As for sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL), which is thought to be associated with inner ear structural abnormalities in this population, holds a comparatively smaller proportion in DS patients suffering from hearing impairment, and the incidence of SNHL in this population differs between studies [4]. For instance, Saliba et al. [5] reported the rate of SNHL in this population is around 41% while Lau et al. [6] reported the percentage is about 28%. However, Austeng et al. [7] and Park et al. [8] unveiled much lower incidences of SNHL in DS patients—18% and 6% respectively.
Moreover, the majority of DS patients with SNHL are suffering from mild to moderate degree of hearing loss; and severe or profound degree of sensorineural hearing loss in this population—including its causes and managements—is scarcely recorded in literature. Some studies utilized CT and/or MRI to identify inner ear anomalies in DS patients and uncovered a much higher incidence of inner ear anomalies in this population, which may partly explain profound SNHL in DS patients. The management of profound SNHL in DS patients has not drawn enough attention so far, and there is little reported evidence in respect to the outcomes of management of severe or profound SNHL. According to Blaser et al. [1], unlike mild-to-moderate SNHL, very limited benefit could be obtained from conventional amplification hearing aids in DS patients with profound SNHL; and recent evidence suggests cochlear implantation (CI) could be a choice for DS patients with profound SNHL. Hans [9] reported four DS children suitable for CI achieved obviously objective improvement in communication after the CI surgery, although the outcomes were relatively compromised in comparison to other children without additional disabilities. For example, a child with the longest history of implant use had the best outcomes in all four children reported by Hans. Before that child’s use of cochlear implant, he had no oral communication. However, after 50 months of implant use, he could understand common phrases without lip reading. Phelan [10] also proposed that cognitive impairment and intellectual disability in DS patients should not be considered as contraindications to CI, though the outcomes of CI are most likely poorer in those patients than children without additional disabilities.
Now, we come back to our first case, in which the eight-year-old patient shows exceedingly low language developmental quotients scores and can only pronouncing ‘ah’ sound. Besides, the child’s motor ability, adaptability, and sociability are far from satisfactory and cannot even be compared with his peers—other Down syndrome patients without such a degree of SNHL. To the best of our knowledge, for example, developmental milestone of children with down syndrome was delayed with the ability to crawl typically occurring around eight months and the ability to walk independently typically occurring around 21 months; besides, they typically do relatively well with social skills. Consequently, the first child in our report can hardly match with general DS patients in those aspects. It is well known that even a mild degree of hearing loss can have negative consequences for speech, language understanding, and academics, not to mention profound hearing loss. Without timely intervention on patients with prelingual profound hearing loss, those patients’ language skills can hardly be developed. Thus, those patients’ sociability would be tremendously impaired. Furthermore, to develop better motor skills in DS patients, sometimes physical therapy, speech, and language therapy are needed. Without interventions on DS patients with profound hearing loss, speech and language therapy can hardly be achieved. So, we firmly believe that with relaxation of candidacy criteria, if CI could be implemented in a timely manner, these kinds of children can benefit from the surgery—especially in terms of communication skills, sociability, and life quality—though their hearing rehabilitation process may be much slower than children without additional inabilities.
Furthermore, owing to the high incidence of inner ear anomalies, CI suitability assessment by CT and MRI must be carried out before the surgery. As mentioned in our second case, the four-year-old girl had bilateral congenital cochlear nerve absence (more common in DS patients than general population), which is a contraindication to CI. Last but not the least, after the surgery, professionals and parents ought to bear in mind that the outcomes would not be as good as other children without additional inabilities.
3. Conclusions
With inclusion criteria expanding, DS children having profound sensorineural hearing loss—previously thought to be unsuitable for CI due to their communication difficulties and intellectual disability—should be considered as candidates for CI. Also owing to the high incidence of inner ear anomalies, which may become contraindications to CI, comprehensive suitability assessments, primarily via CT and MRI, have to be conducted. Besides, the negative impacts of intellectual disability and cognitive impairment upon the outcome of CI are not supposed to be neglected. Benefit from CI would be limited and hearing rehabilitation process could be much slower when compared with children without additional inabilities. However, it is safe to say that DS children suitable for CI are able to benefit a lot from this surgery in term of communication skills, socialization, and quality of life.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.-L.C.; Resources, M.Z. and X.-Q.Q.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, Y.Z.; Writing—Review & Editing, Y.Z. and J.-M.Y.; Supervision, J.-M.Y. and F.-L.C.; Funding Acquisition, F.-L.C.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) grant number 81420108010.
Acknowledgments
We are obliged to extend our sincere thanks to Fang Zhang and Yang Li from the imaging department of the Eye Ear Nose and Throat Hospital, Fudan University for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent and Ethic Relative
The study was approved by Ethical Board of Eye Ear Nose and Throat Hospital of Fudan University (NO. 2014004) and guardians of two patients had provided written informed consent.
References
- Blaser, S.; Propst, E.J.; Martin, D.; Feigenbaum, A.; James, A.L.; Shannon, P.; Papsin, B.C. Inner ear dysplasia is common in children with Down syndrome (trisomy 21). Laryngoscope 2006, 116, 2113–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roizen, N.J.; Wolters, C.; Nicol, T.; Blondis, T.A. Hearing loss in children with Down syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1993, 123, S9–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shott, S.R. Down syndrome: Common otolaryngologic manifestations. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2006, 142, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intrapiromkul, J.; Aygun, N.; Tunkel, D.E.; Carone, M.; Yousem, D.M. Inner ear anomalies seen on CT images in people with Down syndrome. Pediatr. Radiol. 2012, 42, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliba, I.; Sbeity, S.; El-Zir, E.; Yammine, F.G.; Noun, C.T.; Haddad, A. Down syndrome: An electrophysiological and radiological profile. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, E141–E147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, W.L.; Ko, C.H.; Cheng, W.W. Prevalence and parental awareness of hearing loss in children with Down syndrome. Chin. Med. J. 2015, 128, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Austeng, M.E.; Akre, H.; Falkenberg, E.; Øverland, B.; Abdelnoor, M.; Kværner, K.J. Hearing level in children with Down syndrome at the age of eight. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, A.H.; Wilson, M.A.; Stevens, P.T.; Harward, R.; Hohler, N. Identification of Hearing Loss in Pediatric Patients with Down Syndrome. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 146, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hans, P.S.; England, R.; Prowse, S.; Young, E.; Sheehan, P.Z. UK and Ireland experience of cochlear implants in children with Down Syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 74, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, E.; Pal, R.; Henderson, L.; Green, K.M.J.; Bruce, I.A. The management of children with Down syndrome and profound hearing loss. Cochlear Implant. Int. 2015, 17, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).