Quantification of Wettability and Surface Tension of Liquid Aluminum 7075 Alloy on Various Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Method
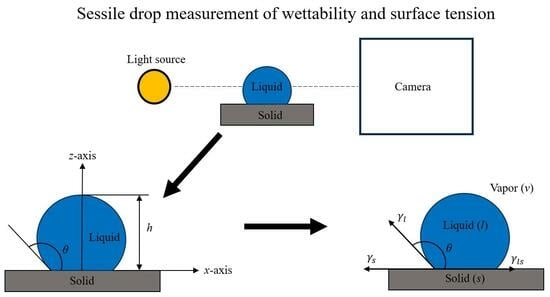
2.3.1. Sessile Drop Experiments
2.3.2. Surface Tension Measurement of Liquid Al 7075-T6 Alloy on Different Substrates
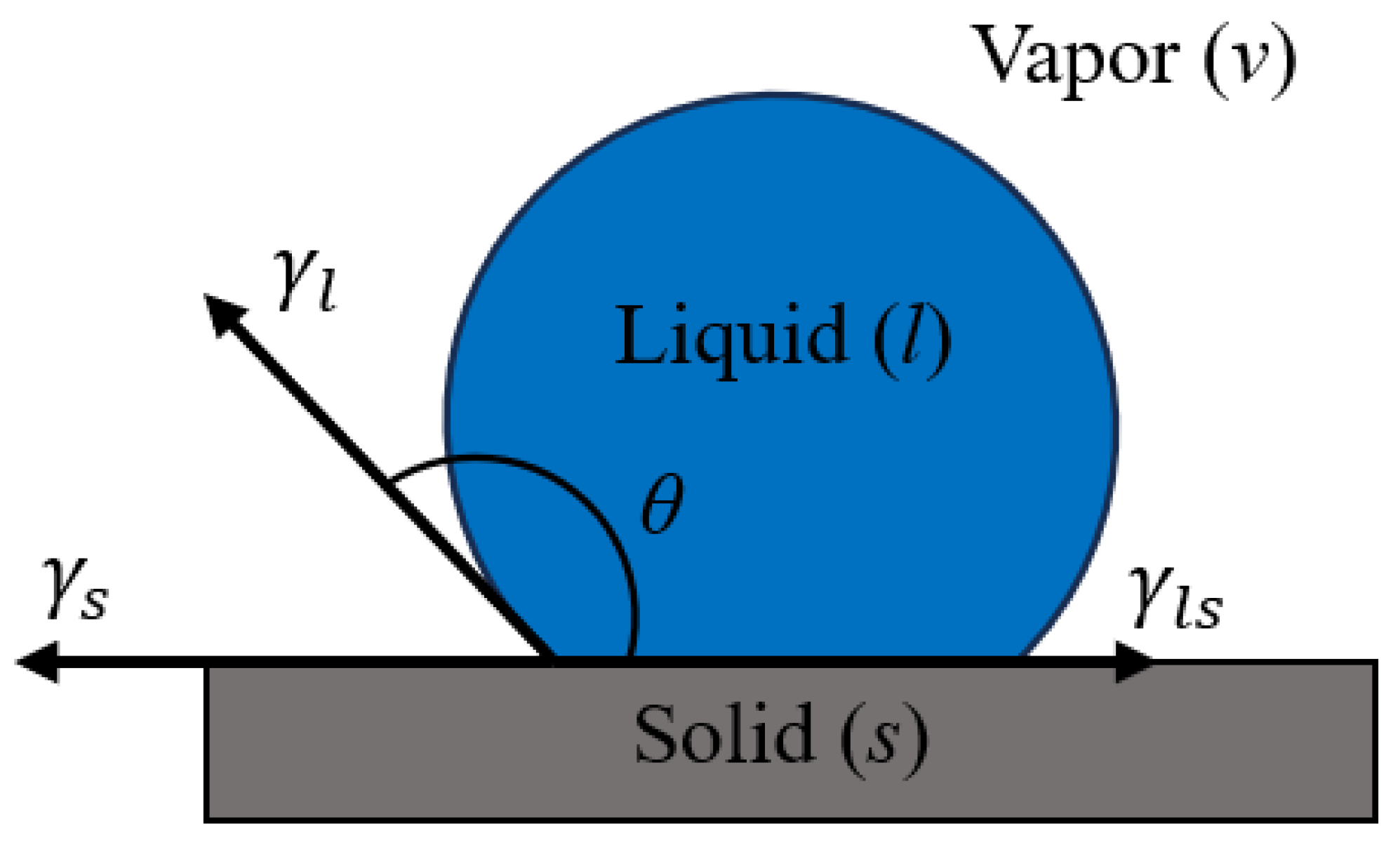
2.3.3. Solid–Gas FE Measurement of the Different Substrates
2.3.4. Liquid–Solid IFT
2.3.5. Work of Adhesion
2.3.6. Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
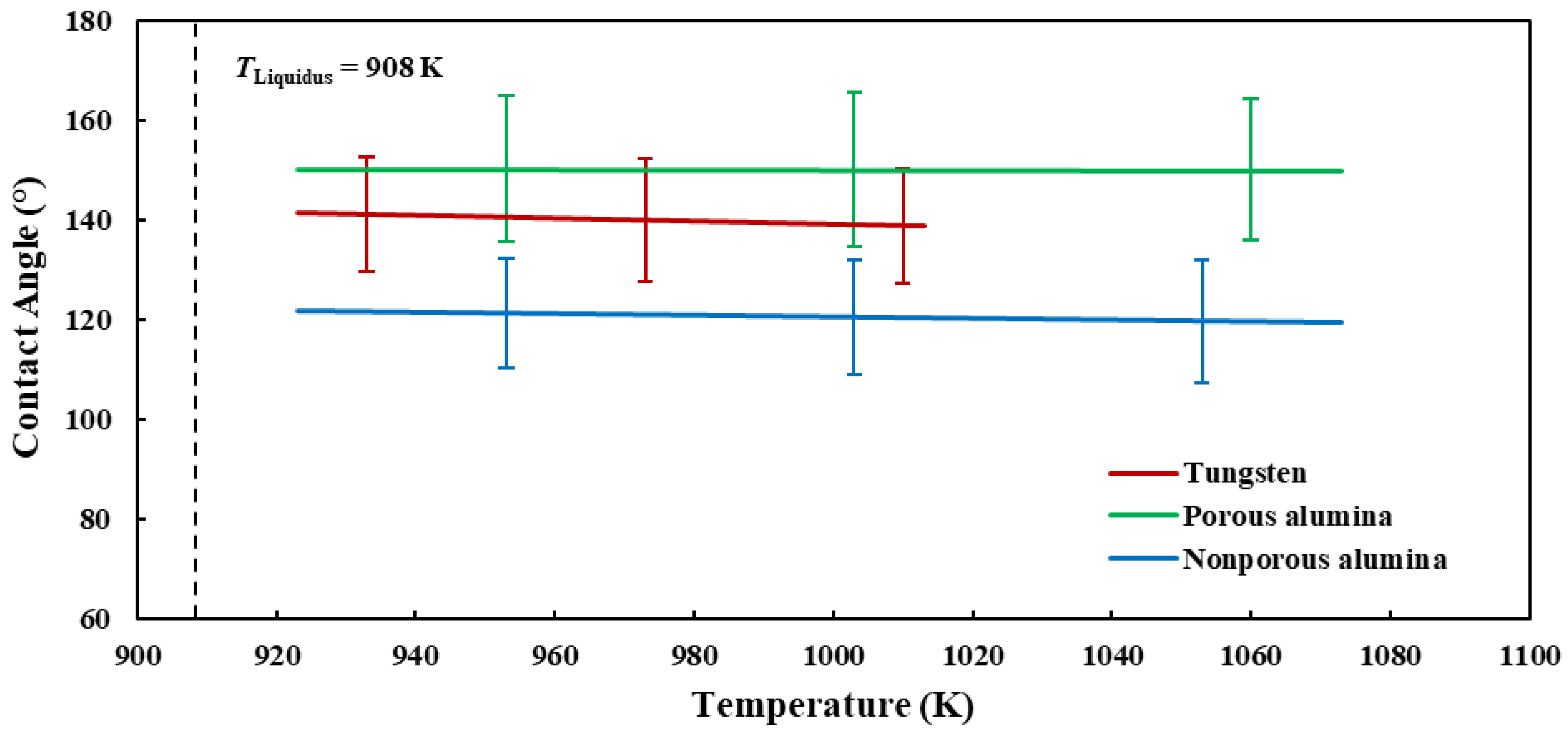
3.1. Wetting Behavior of Liquid Al 7075-T6 Alloy on the Different Substrates
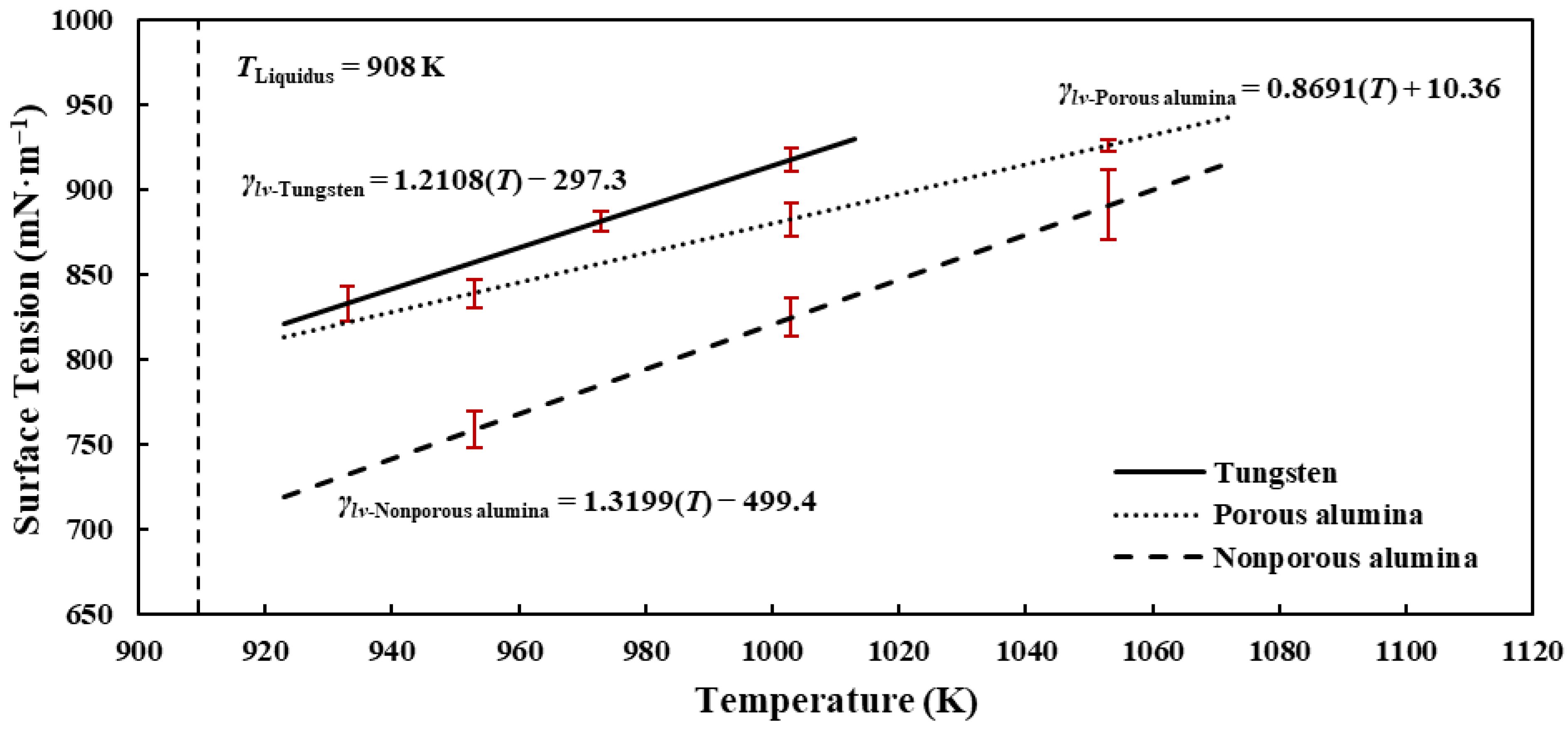
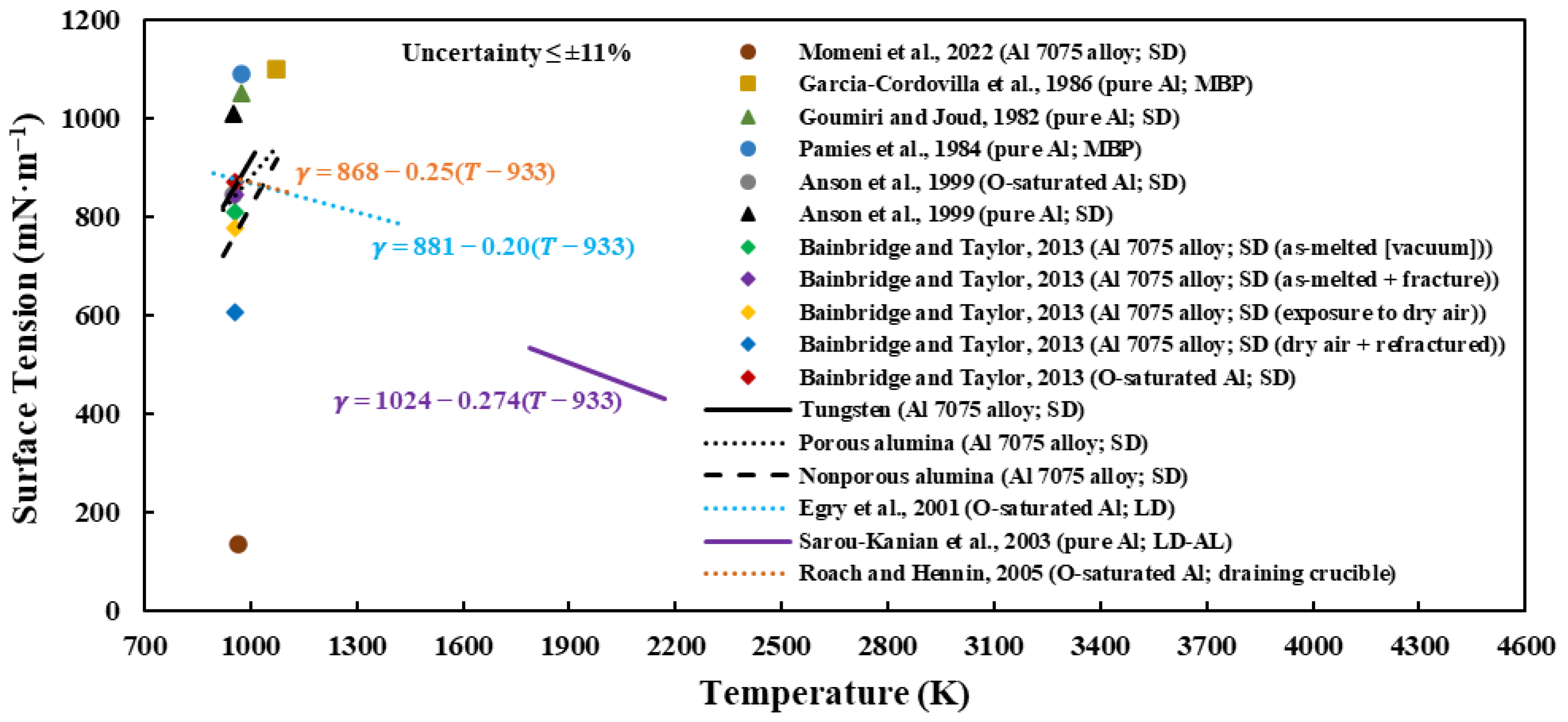
3.2. Surface Tension of Liquid Al 7075-T6 Alloy on Different Substrates
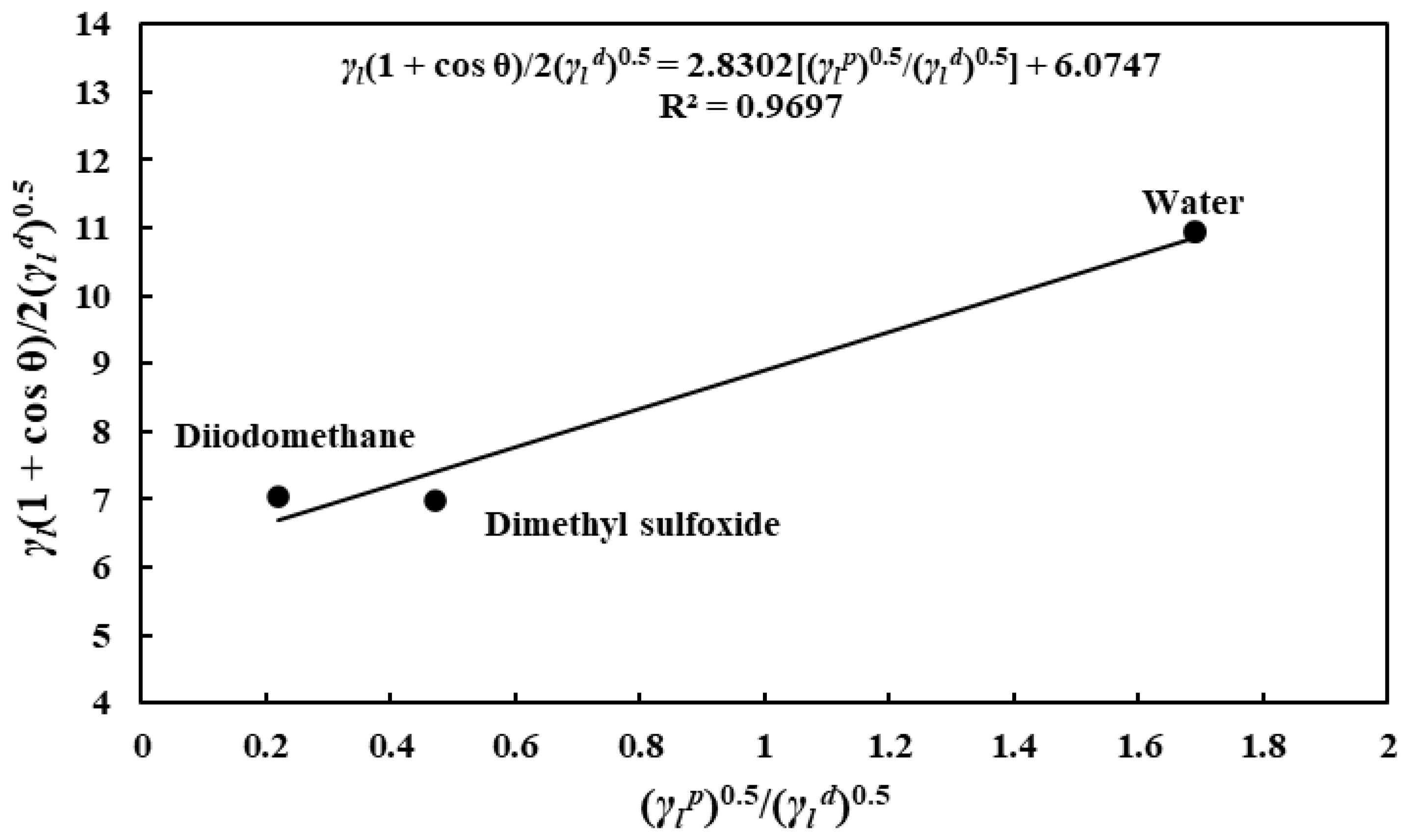
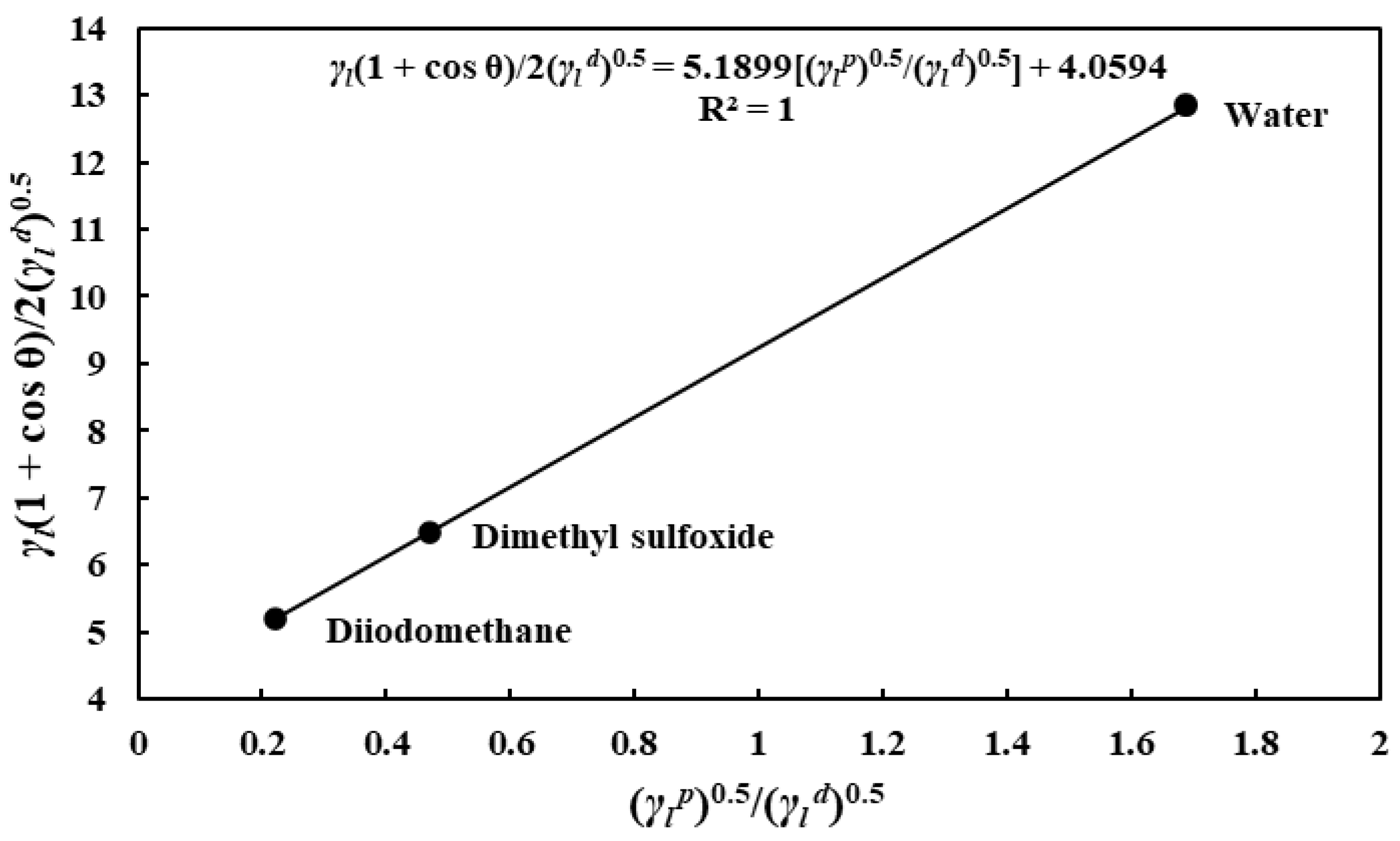
3.3. Solid–Gas FE of the Different Substrates
3.4. Liquid–Solid IFT Between Liquid Al 7075-T6 Alloy and the Different Substrates
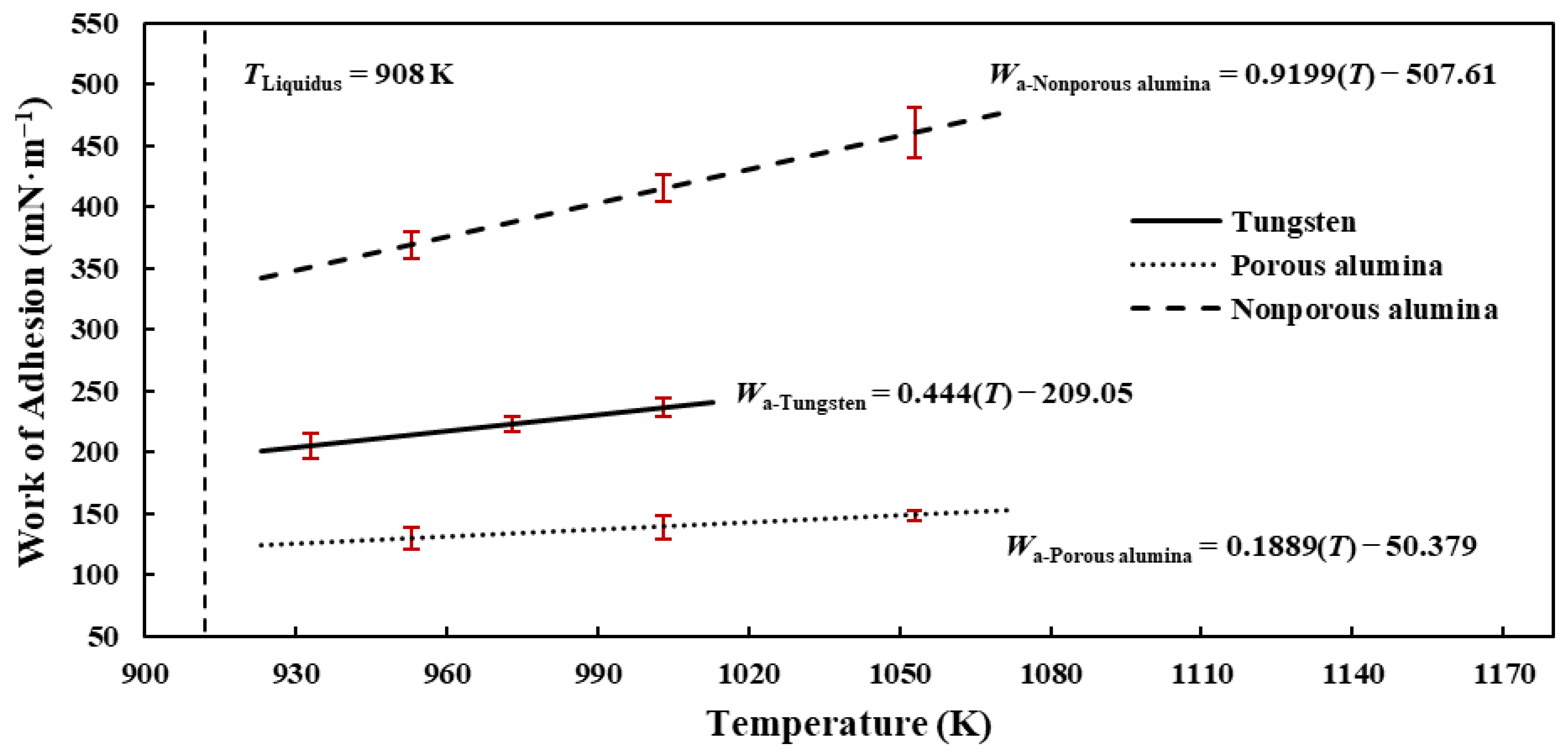
3.5. Work of Adhesion
3.6. Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
- The contact angle results over the investigated temperature ranges reveal the poor wettability characteristics of liquid Al 7075-T6 alloy on the three substrates in decreasing order of porous alumina, tungsten, and nonporous alumina.
- The surface tension values ranged from 718.87 to 942.90 mN·m−1 in decreasing order of tungsten, porous alumina, and nonporous alumina and are close to the few literature-reported results.
- The SFE measurement results revealed that the substrates’ SFE values differ slightly in decreasing order of porous alumina, nonporous alumina, and tungsten. Surprisingly, unlike other substrates, the polar SFE component of the nonporous alumina substrate exceeds the dispersive component.
- The calculated liquid–solid IFT values as a function of the three substrates range from 539.24 to 835.51 mN·m−1 in decreasing order of porous alumina, tungsten, and nonporous alumina. Unlike other substrates, the relatively low liquid–solid IFT values between the liquid Al 7075-T6 alloy droplet and the nonporous alumina substrate indicate the weak attraction between them, which permits more wetting and adhesion.
- The calculated work of adhesion values of the liquid Al 7075-T6 alloy droplet on the substrates range from 123.97 to 479.44 mN·m−1 in decreasing order of nonporous alumina, tungsten, and porous alumina. Unlike other substrates, the droplet is relatively more wettable and adheres to the nonporous alumina substrate due to weak attractive forces, thereby exhibiting higher work of adhesion and lower contact angle characteristics.
- Furthermore, for all experiments conducted, positive surface tension–temperature, liquid–solid interfacial energy–temperature, and work of adhesion–temperature gradients were obtained.
- Although the experiments herein were conducted under an argon atmosphere, the EDS results confirm the presence of oxygen and corroborate its effect on the surface tension values reported herein. The surface compositions of oxygen exceeded the bulk compositions for all tested samples due to the formation of aluminum oxide.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AL | Aerodynamic levitation |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| EL | Electromagnetic levitation |
| FE | Free energy |
| IFT | Interfacial tension |
| LD | Levitated drop |
| MBP | Maximum bubble pressure |
| OWRK | Owens–Wendt–Rabel–Kaelble |
| PD | Pendant drop |
| SCA | Static contact angle |
| SE | Surface energy |
| SFE | Surface free energy |
| SD | Sessile drop |
References
- Molina, J.M.; Voytovych, R.; Louis, E.; Eustathopoulos, N. The surface tension of liquid aluminium in high vacuum: The role of surface condition. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2007, 27, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, K.; Neshani, S.; Uba, C.; Ding, H.; Raush, J.; Guo, S. Engineering the Surface Melt for In-Space Manufacturing of Aluminum Parts. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 6092–6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egry, I.; Ricci, E.; Novakovic, R.; Ozawa, S. Surface Tension of Liquid Metals and Alloys—Recent Developments; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, B.J. Review of data for the surface tension of pure metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 1993, 38, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laty, P.; Joud, J.C.; Desré, P.; Lang, G. Tension superficielle d’alliages liquides aluminium-cuivre. Surf. Sci. 1977, 69, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cordovilla, C.; Louis, E.; Pamies, A. The surface tension of liquid pure aluminium and aluminium-magnesium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 1986, 21, 2787–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.S.; Ayushina, G.D.; Geld, P.V. Density and surface-energy polytherms of liquid (molten) aluminum. High Temp. 1968, 6, 416–418. [Google Scholar]
- Naidich, Y.V.; Eremenko, V.N. Large drop method for determining the surface tension and density of molten metals at high temperatures. Fiz. Met. Metalloved. 1961, 11, 883–888. [Google Scholar]
- Goumiri, L.; Joud, J.C.; Desre, P.; Hicter, J.M. Tensions superficielles d’alliages liquides binaires présentant un caractère dimmiscibilité: Al-Pb, Al-Bi, Al-Sn et Zn-Bi. Surf. Sci. 1979, 83, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egry, I.; Schneider, S.; Seyhan, I.; Volkmann, T. Surface Tension Measurements of High Temperature Metallic Melts; Transactions of Joining and Welding Research Institute, Osaka University: Osaka, Japan, 2001; Volume 30, pp. 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Goumiri, L.; Joud, J.C. Auger electron spectroscopy study of aluminium-tin liquid system. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 1397–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamies, A.; Cordovilla, C.G.; Louis, E. The measurement of surface tension of liquid aluminium by means of the maximum bubble pressure method: The effect of surface oxidation. Scr. Metall. 1984, 18, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarou-Kanian, V.; Millot, F.; Rifflet, J.C. Surface Tension and Density of Oxygen-Free Liquid Aluminum at High Temperature. Int. J. Thermophys. 2003, 24, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Su, Y.C. Review of surface tension data for metallic elements and alloys: Part 1—Pure metals. Int. Mater. Rev. 2006, 51, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anson, J.P.; Drew, R.A.L.; Gruzleski, J.E. The Surface Tension of Molten Aluminum and Al-Si-Mg Alloy under Vacuum and Hydrogen Atmospheres. Met. Mater. Trans. B 1999, 30, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, I.F.; Taylor, J.A. The surface tension of pure aluminum and aluminum alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2013, 44, 3901–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huang, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yao, C. Effect of tungsten mesh interlayer on microstructure and mechanical performance of A6061/Ti6Al4V dissimilar joints. Mater. Charact. 2021, 182, 111569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez, A.; Al Yasari, M.; Yasari, A.; Mahdi, A.A. Phase Transformation in the Aluminum/Tungsten System. Browse all Theses and Dissertations. 2434. 2021. Available online: https://corescholar.libraries.wright.edu/etd_all/2434 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Determination of the Surface Energy of a Solid—DataPhysics Instruments. Available online: https://www.dataphysics-instruments.com/us/knowledge/understanding-interfaces/solid-surface-energy/#! (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Narender, K.; Rao, A.S.M.; Rao, K.G.K.; Krishna, N.G. Temperature Dependence of Density and Thermal Expansion of Wrought Aluminum Alloys 7041, 7075 and 7095 by Gamma Ray Attenuation Method. J. Mod. Phys. 2013, 4, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCGM. Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement. 2008. Available online: www.bipm.org (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Sun, C.C.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, W.C.; Hwang, J.S.; Tang, I.T.; Fu, Y.S. Surface free energy of alloy nitride coatings deposited using closed field unbalanced magnetron sputter ion plating. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloubek, J. Development of methods for surface free energy determination using contact angles of liquids on solids. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 1992, 38, 99–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.K.; Rao, K.H. Analysis of different approaches for evaluation of surface energy of microbial cells by contact angle goniometry. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 341–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibowski, E.; Perea-Carpio, R. Problems of contact angle and solid surface free energy determination. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.J. Contact angle, wetting, and adhesion: A critical review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 6, 1269–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozbial, A.; Li, Z.; Conaway, C.; McGinley, R.; Dhingra, S.; Vahdat, V.; Zhou, F.; D’urso, B.; Liu, H.; Li, L. Study on the surface energy of graphene by contact angle measurements. Langmuir 2014, 30, 8598–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, M.; Gopinadhan, K.; Han, S.A.; Saha, S.; Park, H.J.; Cho, E.B.; Kumar, B.; Patra, A.; Kim, S.-W.; Venkatesan, T. Surface energy and wettability of van der Waals structures. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 5764–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptay, G. On the solid/liquid interfacial energies of metals and alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3767–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, H.; Kenza, K. Adhesion Phenomenon of Liquid Metals. In Liquid Metals; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaro, S. Investigation of Solid-Liquid Interactions in High Temperature Metal-Ceramic Systems. Università Degli Studi Di Genova. 2018. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/162442639.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Brennan, J.J.; Pask, J.A. Effect of Nature of Surfaces on Wetting of Sapphire by Liquid Aluminum. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1968, 51, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, V.; Chatain, D.; Chatillon, C.; Eustathopoulos, N. Wettability of monocrystalline alumina by aluminium between its melting point and 1273 K. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 1797–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholas, M.G.; Mortimer, D.A.; Jones, L.M.; Crispin, R.M. Some observations on the wetting and bonding of nitride ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. 1990, 25, 2679–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prin, G.R.; Baffie, T.; Jeymond, M.; Eustathopoulos, N. Contact angles and spreading kinetics of Al and Al-Cu alloys on sintered AlN. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 298, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Suzuki, S.; Hibiya, T.; Fukuyama, H. Influence of oxygen partial pressure on surface tension and its temperature coefficient of molten iron. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 014902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapczynski, V.; Le Maux, D.; Courtois, M.; Bertrand, E.; Paillard, P. Surface Tension Measurements of Liquid Pure Iron and 304L Stainless Steel Under Different Gas Mixtures; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Fukuyama, H.; Watanabe, M. Temperature Dependence of Surface Tension of Molten Iron Under Reducing Gas Atmosphere. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 327, 012020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubberstein, T.; Heller, H.P.; Klostermann, J.; Schwarze, R.; Brillo, J. Surface tension and density data for Fe–Cr–Mo, Fe–Cr–Ni, and Fe–Cr–Mn–Ni steels. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 7227–7237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Element | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Zn | Ti | V | Zr | Other | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Min | 0 | 0 | 1.20 | 0 | 2.10 | 0.18 | 5.10 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0.05 | Remainder |
| Max | 0.40 | 0.50 | 2.00 | 0.30 | 2.90 | 0.28 | 6.10 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.15 |
| Liquids | Surface Tension Data (mN·m−1) | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 72.30 | 18.70 | 53.60 | Rabel |
| Dimethyl sulfoxide | 44.00 | 36.00 | 8.00 | Erbil |
| Diiodomethane | 50.80 | 48.50 | 2.30 | Fowkes |
| Substrates | Contact Angle (°) for Water | Contact Angle (°) for Dimethyl Sulfoxide | Contact Angle (°) for Diiodomethane |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous alumina | 72.07 ± 0.45 | 25.25 ± 0.10 | 21.30 ± 0.28 |
| Nonporous alumina | 57.67 ± 0.28 | 39.40 ± 0.17 | 64.83 ± 0.11 |
| Tungsten | 61.76 ± 0.12 | 30.13 ± 0.10 | 58.83 ± 0.10 |
| Substrates | (mN·m−1) | (mN·m−1) | (mN·m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porous alumina | 44.92 ± 0.26 | 36.94 ± 0.10 | 7.98 ± 0.24 |
| Nonporous alumina | 43.32 ± 0.42 | 16.53 ± 0.09 | 26.79 ± 0.21 |
| Tungsten | 42.03 ± 0.18 | 21.23 ± 0.02 | 20.80 ± 0.07 |
| Elements | Porous Alumina Substrate | Tungsten Substrate | Nonporous Alumina Substrate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Composition (wt.%) | Bulk Composition (wt.%) | Surface Composition (wt.%) | Bulk Composition (wt.%) | Surface Composition (wt.%) | Bulk Composition (wt.%) | |
| C | 12.49 | 13.98 | 17.99 | 15.70 | 24.02 | 21.79 |
| O | 18.88 | 0.56 | 13.28 | 1.03 | 14.89 | 1.35 |
| Al | 63.69 | 82.73 | 65.45 | 80.01 | 59.22 | 74.70 |
| Fe | 1.03 | 0.22 | 0.88 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 0.12 |
| Cu | 2.96 | 1.85 | 2.17 | 2.37 | 1.52 | 1.72 |
| Cr | 0.05 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.33 | 0.10 | 0.08 |
| Mn | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.05 | - | 0.03 |
| Mg | 0.80 | - | 0.10 | 0.03 | - | - |
| Si | 0.05 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 0.11 | - | 0.16 |
| Ti | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | 0.06 |
| V | - | - | - | - | 0.05 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uba, C.U.; Raush, J.R. Quantification of Wettability and Surface Tension of Liquid Aluminum 7075 Alloy on Various Substrates. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050165
Uba CU, Raush JR. Quantification of Wettability and Surface Tension of Liquid Aluminum 7075 Alloy on Various Substrates. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(5):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050165
Chicago/Turabian StyleUba, Chukwudalu Uchenna, and Jonathan Richard Raush. 2025. "Quantification of Wettability and Surface Tension of Liquid Aluminum 7075 Alloy on Various Substrates" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 5: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050165
APA StyleUba, C. U., & Raush, J. R. (2025). Quantification of Wettability and Surface Tension of Liquid Aluminum 7075 Alloy on Various Substrates. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(5), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9050165