Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ball Milling Activation
2.2. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Formation α- and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles
3.2. Infrared Spectroscopy
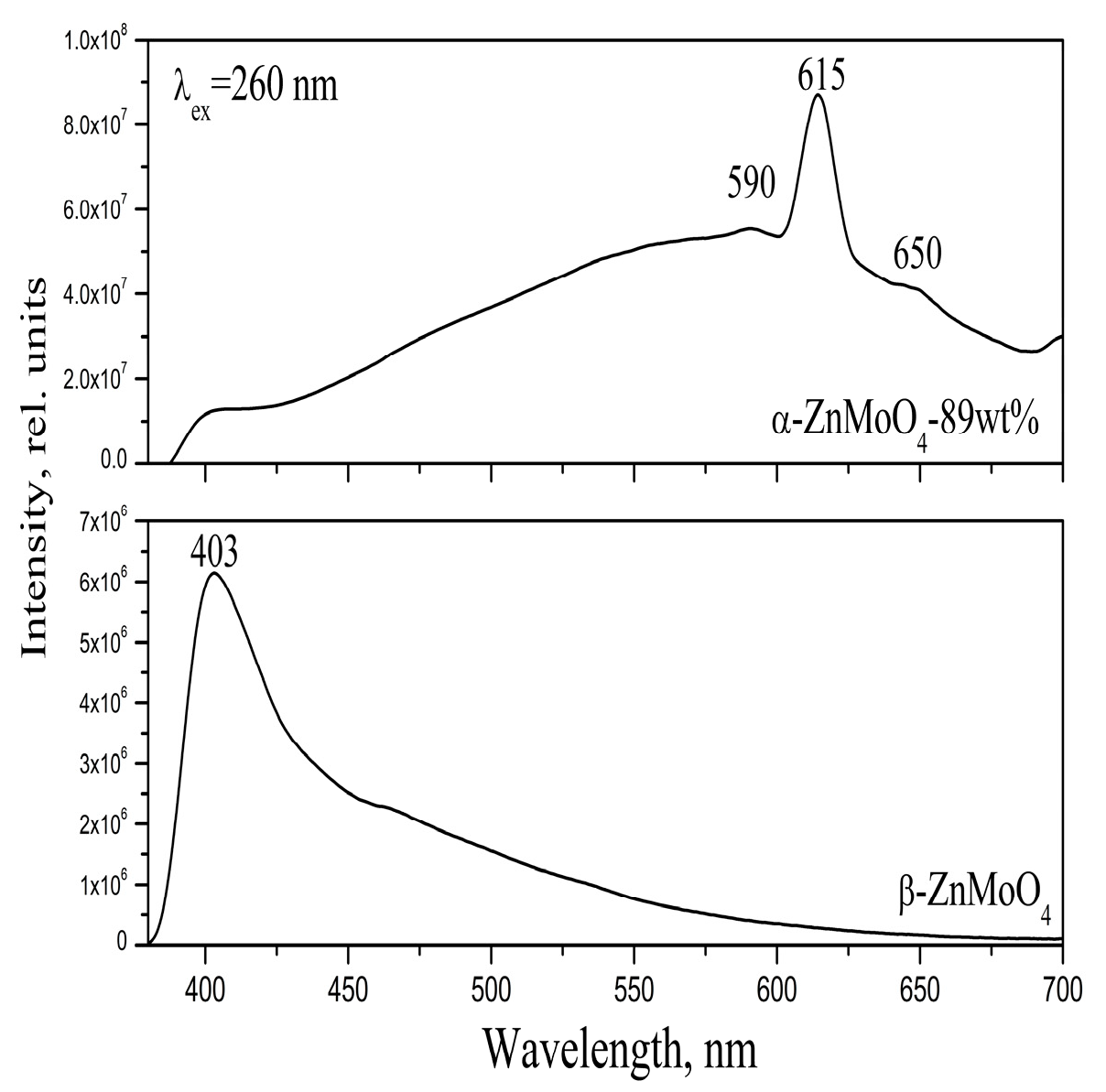
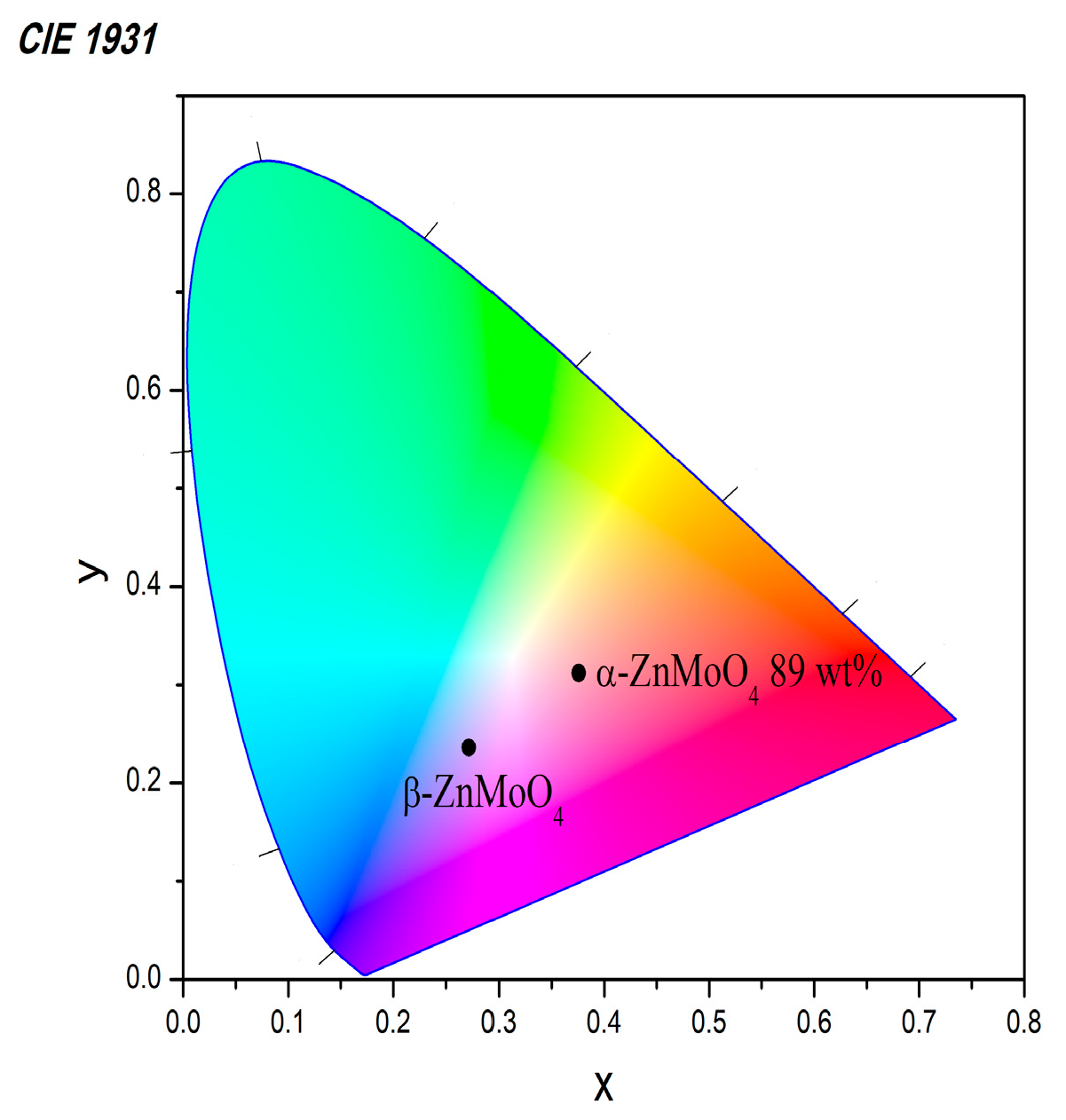
3.3. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhai, B.; Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.M. Growth of ZnMoO4 nanowires via vapor deposition in air. Mater. Lett. 2017, 188, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keereeta, Y.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Characterization of ZnMoO4 nanofibers synthesized by electrospinning–calcination combinations. Mater. Lett. 2012, 68, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, L.S.; Moraes, E.; Almeida, M.A.P.; Dalmaschio, C.J.; Batista, N.C.; Varela, J.A.; Longo, E.; Li, M.S.; Andrés, J.; Beltrán, A. A combined theoretical and experimental study of electronic structure and optical properties of β-ZnMoO4 microcrystals. Polyhedron 2013, 54, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Keereeta, Y.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Effect of medium solvent ratios on morphologies and optical properties of a-ZnMoO4, b-ZnMoO4 and ZnMoO4.0.8H2O crystals synthesized by microwave-hydrothermalsolvothermal method. Superlattices Microstruct. 2014, 69, 253–264. [Google Scholar]
- Hizhnyi, Y.; Zatovsky, I.; Nedilko, S.; Boiko, R.; Li, J.; Han, W.; Klyui, N.I. Origin of luminescence in ZnMoO4 crystals: Insights from spectroscopic studies and electronic structure calculations. J. Lumin. 2019, 211, 127–137. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasree, A.S.; Rahulan, K.M.; Sujatha, R.A.; Vinitha, G.; Flower, N.A.L. Influence of Ni doping on the structural and third order nonlinear optical properties of ZnMoO4 nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 29267–29273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Wei, J.S.; Gong, F.Z.; Huang, J.L.; Yi, L.H. A potential red phosphor ZnMoO4:Eu3+ for light-emitting diode application. J. Solid State Chem. 2008, 181, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovisa, L.X.; Oliveira, M.C.; Andrés, J.; Gracia, L.; Li, M.S.; Longo, E.; Tranquilin, R.L.; Bomio, M.R.D.; Motta, F.V. Structure, morphology and photoluminescence emissions of ZnMoO4: RE3+ = Tb3+ − Tm3+ − Eu3+ (x = 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3 mol%) particles obtained by the sonochemistry method. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 750, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.; Ma, Q.; Yang, L.; Huan, Y.M. Effects of sintering temperature on the morphology and photoluminescence of Eu3+ doped zinc molybdenum oxide hydrate. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 7418508. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, N.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, R.K.; Singh, J.; Singh, R.A. Enhanced photoluminescence behaviour of Eu3+ activated ZnMoO4 nanophosphors via Tb3+ co-doping for light emitting diode. J. Lumin. 2017, 168, 504–513. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, P.; Sinha, E. Structural, photophysical and microwave dielectric properties of α-ZnMoO4 phosphor. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 795, 446–453. [Google Scholar]
- Mafa, P.J.; Ntsendwana, B.; Mamba, B.B.; Kuvarega, A.T. Visible light driven ZnMoO4/BiFeWO6/rGO Z scheme photocatalyst for the degradation of anthraquinonic dye. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 20605–20616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Huang, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Jia, H.; Sun, J.; Guan, M. Phase- and Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of Zinc Molybdate for Excellent Photocatalytic Property. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 42, 4939–4946. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.R.; Lee, W.W.; Chen, K.T.; Wang, M.C.; Chang, K.H.; Chen, C.C. Hydrothermal synthesis of b-ZnMoO4 crystals and their photocatalytic degradation of Victoria Blue R and phenol. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Firmansyah, R.; Bakri, R.; Yualizar, Y. Enhancement of photocatalytic activity of ZnO by ZnMoO4 compositing under light via hydrothermal green synthesis. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 110893–110902. [Google Scholar]
- Raj, A.M.E.S.; Mallika, C.; Swaminathan, K.; Sreedharan, O.M.; Nagaraja, K.S. Zinc(II) oxidezinc(II) molybdate composite humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 81, 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Tamta, A.; Chandra, B.; Kandpal, N.D.; Jadaun, S.S.; Panwar, A.K.; Babu, K.V.; Justin, P.; Rao, H.S.; Sekhar, K.S.K.R.C. Structural, Optical, Electrical, and Electrochemical properties of ZnMoO4 microspheres synthesized by the twin crystal method. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 38047–38057. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Ge, R.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H. A facile and energy-saving preparation of α-ZnMoO4 nanorods for enhanced Li-ion intercalation application. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126737–126743. [Google Scholar]
- Fei, J.; Sun, Q.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Huang, J.; Hui, W.; Hu, H. Synthesis and electrochemical performance of α-ZnMoO4 nanoparticles as anode material for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Lett. 2017, 198, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Shao, Z. Synthesis and electrochemical properties of cubic-like ZnMoO4 anode materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 13905–13915. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahams, S.C. Crystal Structure of the Transition-Metal Molybdates and Tungstates. III. Diamagnetic α-ZnMoO4. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 46, 2052–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Mtioui-Sghaier, O.; Mendoza-Merono, R.; Ktari, L.; Dammak, M.; Garcıa-Granda, S. Redetermination of the β-zinc molybdate from single—Crystal X-ray diffraction date. Acta Cryst. 2015, E71, i6–i7. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, Y.; Holzwarth, N.A.W.R.; Williams, T. Electronic structure and optical properties of CdMoO4 and CdWO4. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, P.; Li, H.B.; Yang, G.W. ZnMoO4 Micro- and nanostructures synthesized by electrochemistry-assisted laser ablation in liquids and their optical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar]
- Cavalcante, L.S.; Sczancoski, J.C.; Li, M.S.; Longo, E.; Varela, J.A. β-ZnMoO4 microcrystals synthesized by the surfactant-assisted hydrothermal method: Growth process and photoluminescence properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 396, 346–351. [Google Scholar]
- Sachuk, O.V. Nanodispersed Zn—MoO3 catalysts of selective ethanol oxidation synthesized by nontraditional methods. Rep. Natl. Acad. Sci. Ukr. 2019, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Singh, A.; Yadav, P.; Sonu, B.K.; Verma, R.; Rou, S.K.; Sinha, E. Structural and dielectric properties of Cu doped α ZnMoO4 ceramic system for enhanced green light emission and potential microwave application. J. Mater. Sci. Electron. 2021, 32, 12881–12889. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Tong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, X. Metastable monoclinic ZnMoO4: Hydrothermal synthesis, optical properties and photocatalytic performance. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 9506–9514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Koo, S.M.; Yoon, J.W.; Lim, C.S.; Shim, K.B. Synthesis of nanocrystalline MMoO4 (M = Ni, Zn) phosphors via a citrate complex route assisted by microwave irradiation and their photoluminescence. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 1702–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassky, D.A.; Mikhailin, V.V.; Savon, A.E.; Galashov, E.N.; Shlegel, V.N.; Vasiliev, Y.V. Low temperature luminescence of ZnMoO4 single crystals grown by low temperature gradient Czochralski technique. Opt. Mater. 2012, 34, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.F.L.; Nobre, F.X.; Batista, F.M.C.; Cabot, A.; Vendrell, X.; Mestres, L.; Mendes, O.C.; Ferreira, R.D.; Ruiz, Y.L.; Quaresma, J.N.N. BaNb2O6 at room temperature by ball milling method: Structural, optical, morphology, and electrochemistry properties. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 16323–16328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, H.R. Mechanochemistry as a reconstruction tool of decomposed metal–organic frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 11825–11829. [Google Scholar]
- Mancheva, M.N.; Iordanova, R.S.; Klissurski, D.G.; Tyuliev, G.T.; Kunev, B.N. Direct Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline NiWO4. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Dimitriev, Y. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnWO4 at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancheva, M.; Naydenov, A.; Iordanova, R.; Nihtianova, D.; Stefanov, P. Mechanochemically assisted solid state synthesis, characterization, and catalytic properties of MgWO4. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancheva, M.; Rojac, T.; Iordanova, R.; Piroeva, I.; Ivanov, P. Structural and optical properties of MgMoO4 prepared by mechanochemical technique. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 7149–17156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Koseva, I.; Avdeev, G.; Burdina, G.; Ivanov, P. Synthesis and luminescent properties of barium molybdate nanoparticles. Materials 2023, 16, 7025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmac, T.; Courtney, T.H. Milling and mechanical alloying of inorganic nonmetallics. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhu, M. Nanostructured WC/Co composite powder prepared by high energy ball milling. Scr. Mater. 2003, 49, 1123–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J. Absorption edge and internal electric fields in amorphous semiconductors. Mater. Res. Bull. 1970, 5, 721–729. [Google Scholar]
- Klissurski, D.; Mancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Tyuliev, G.; Kunev, B. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline nickel molybdates. J. Alloys Compd. 2006, 422, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Axs Bruker. V.4 Topas, 2: General Profile and Structure Analysis Software for Powder Diffraction Data—User’s Manual; Bruker AXS: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aitahsaine, H.; Zbair, M.; Ezahri, M.; Benlhachemi, A.; Bakiz, B.; Guinnetonb, F.; Gavarri, J.-R. Structural and Temperature-dependent vibrational analyses of the non-centrosymmetric ZnMoO4 molybdate. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 3076–3083. [Google Scholar]
- Tana, W.; Luan, J. Investigation into the synthesis conditions of CuMoO4 by an in situ method and its photocatalytic properties under visible light irradiation. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 9745–9759. [Google Scholar]
- Fomichev, V.V.; Kondratov, O.I. Vibration spectra of compounds with the wolframite structure. Spectrochim. Acta 1994, A50, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, M.; Louis, C.; Che, M.; Chaquin, P.; Masure, D. Polyoxometallates as models for oxide catalysts: Part I. An UV-visible reflectance study of polyoxomolybdates: Influence of polyhedra arrangement on the electronic transitions and comparison with supported molybdenum catalysts. J. Catal. 1989, 119, 400–414. [Google Scholar]
- Jeziorowski, H.; Knoezinger, H. Raman and ultraviolet spectroscopic characterization of molybdena on alumina catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. 1979, 83, 1166–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, T.; Li, Z.; Ding, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Fu, X. Characterizations and properties of Eu3+-doped ZnWO4 prepared via a facile self-propagating combustion method. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Jayaprakash, J.; Krishnakumar, V. Synthesis and optical characterization of cerium doped MgWO4 phosphor. Mater. Today Proceed. 2020, 26, 3514–3517. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ding, Y. Preparation, structural and optical properties of ZnWO4 and CdWO4 nanofilms. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4887–4891. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Z.; Hao, J.; Cocivera, M. Luminescence of ZnWO4 and CdWO4 thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. J. Lumin. 2002, 99, 349–354. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Khare, A.; Tiwari, S.; Kshatri, D.S. Diminution in photoluminescent intensity of SrS: Ce3+ phosphor due to increased milling time. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar]
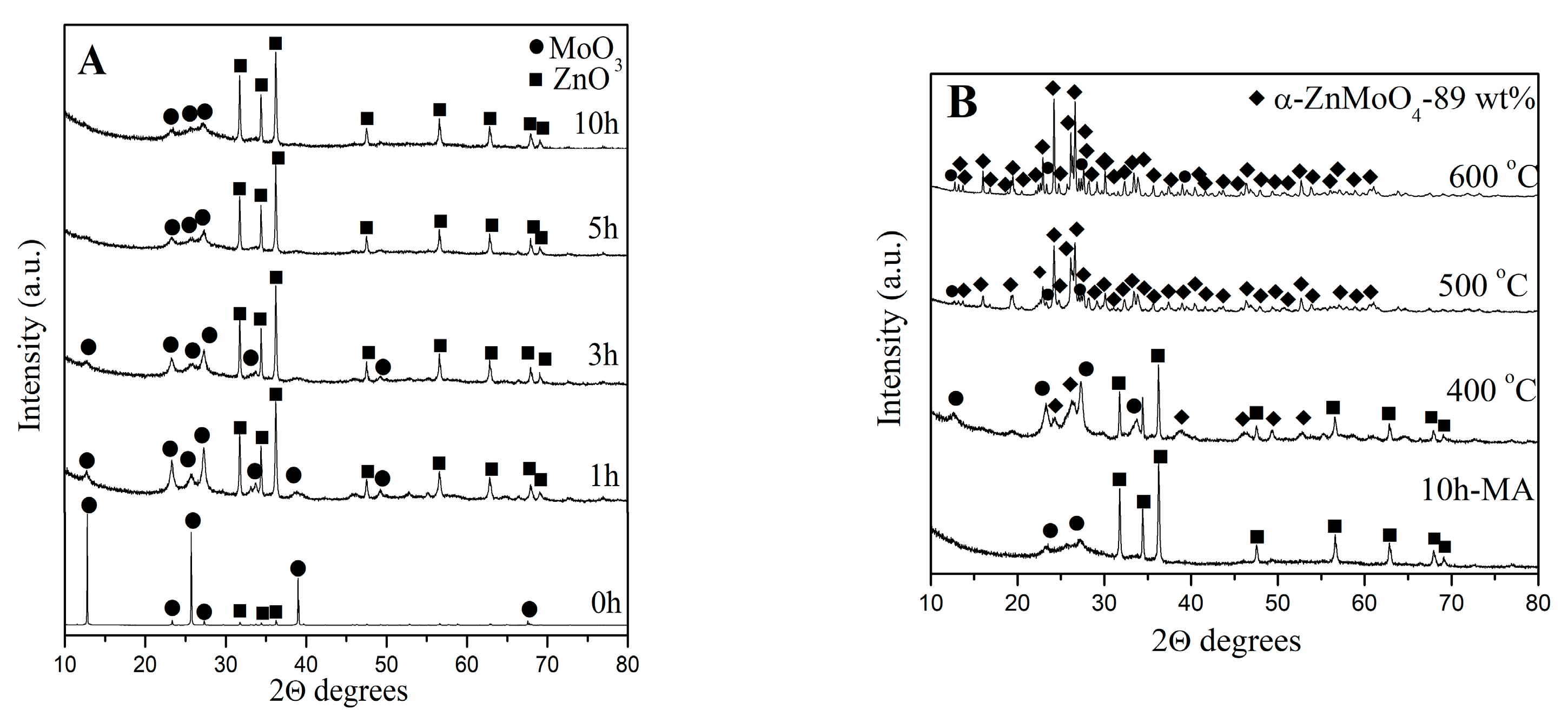

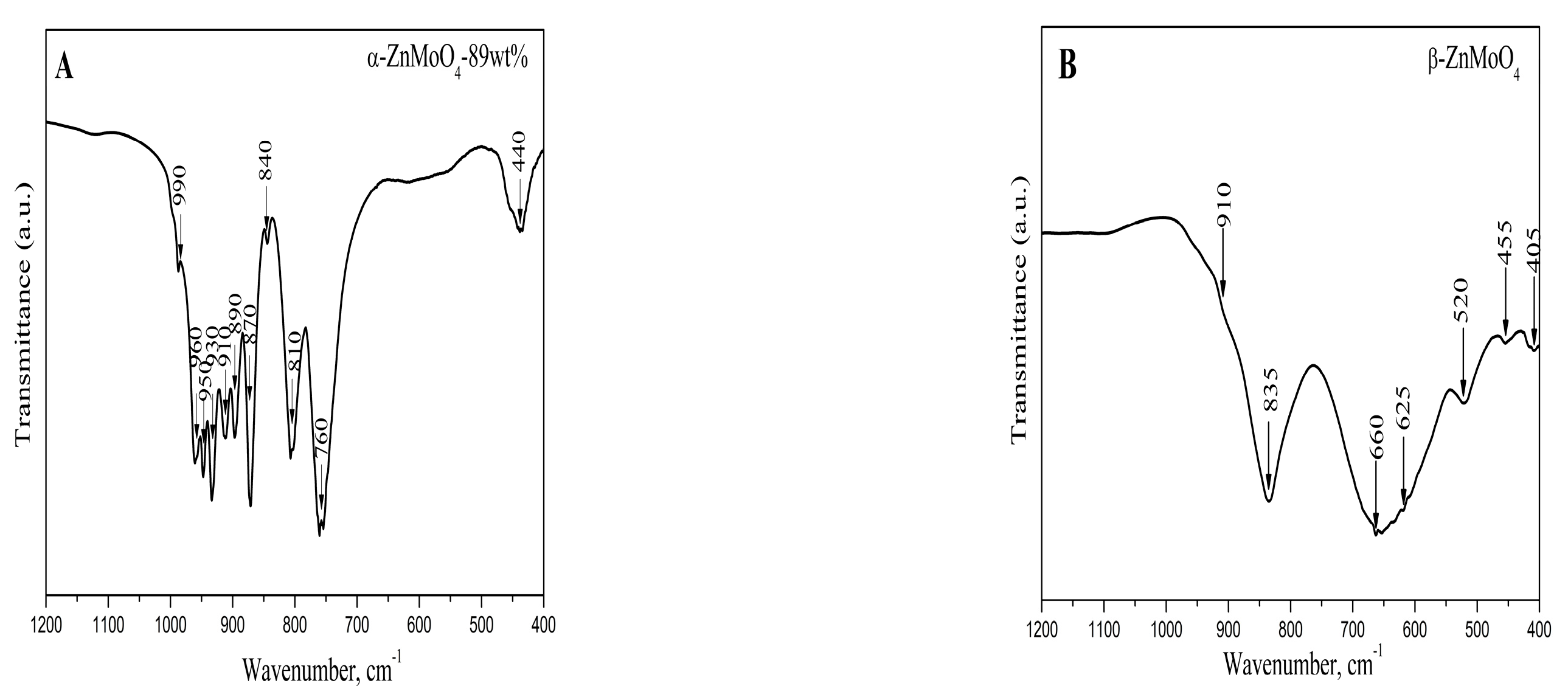
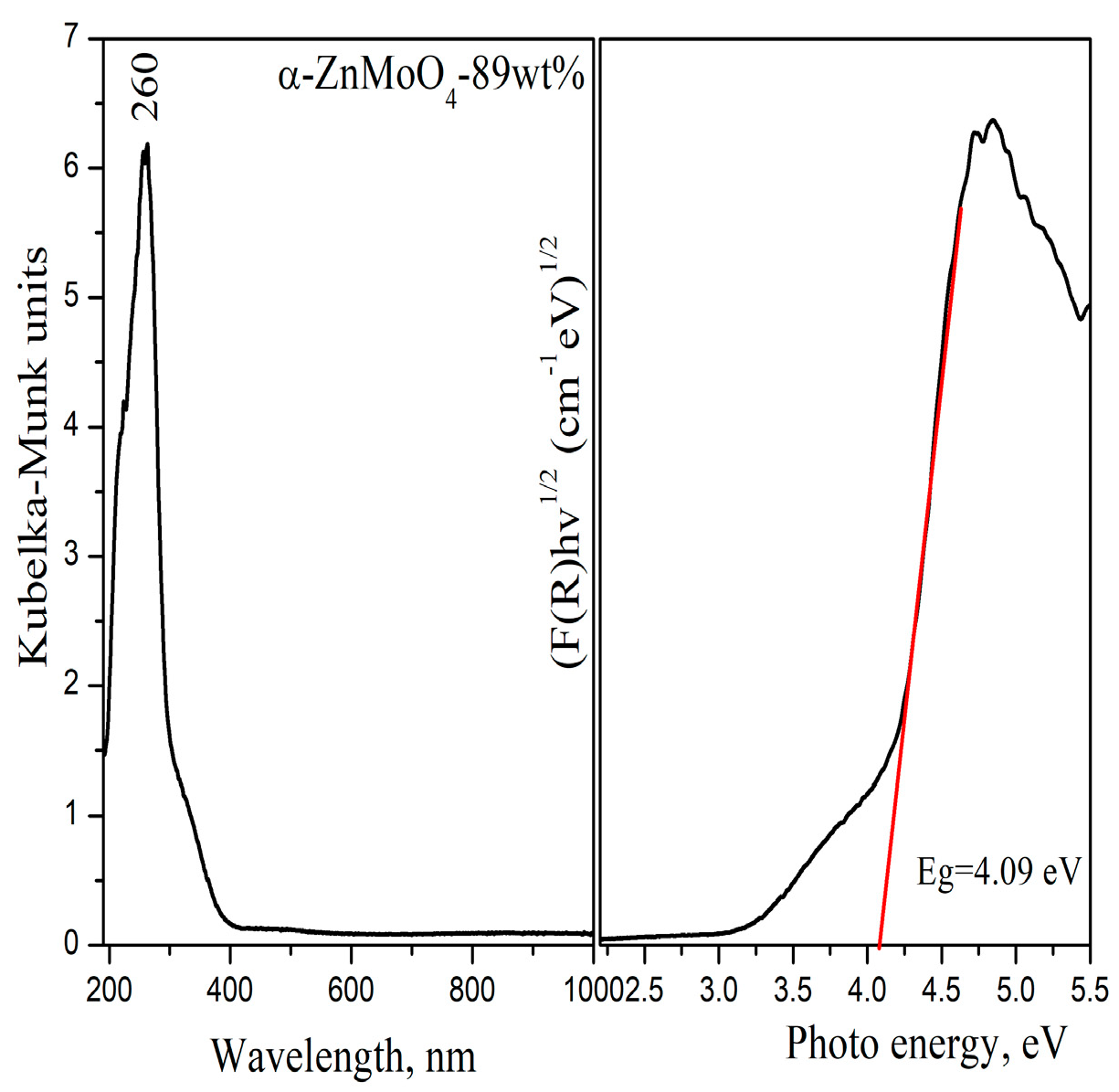
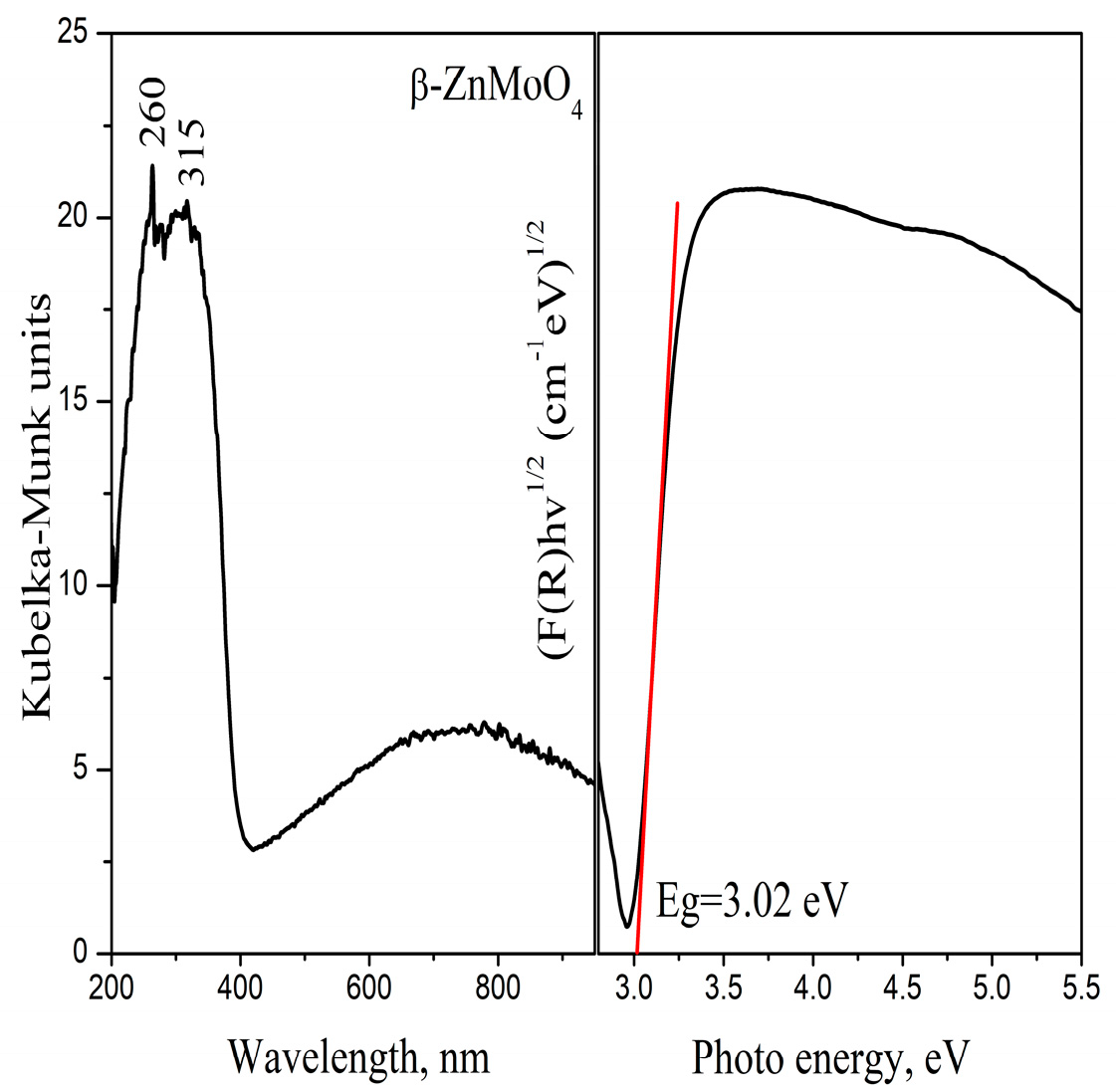
| Samples | Phase Composition, wt% | Crystallite Size, nm |
|---|---|---|
| 10 h milling time, at 500 rpm | 49 wt% ZnO 51 wt% MoO3 | |
| 10 h milling time, heated at 400 °C | 15 wt% α-ZnMoO4 40 wt% ZnO 45 wt% MoO3 | α-ZnMoO4-20 nm (±3) |
| 10 h milling time, heated at 500 °C | 80 wt% α-ZnMoO4 20 wt% o-MoO3 | α-ZnMoO4-75 nm (±4) |
| 10 h milling time, heated at 600 °C | 89 wt% α-ZnMoO4 11 wt% o-MoO3 | α-ZnMoO4-85 nm (±5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Ivanov, P.; Yordanova, A. Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040118
Gancheva M, Iordanova R, Ivanov P, Yordanova A. Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2025; 9(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040118
Chicago/Turabian StyleGancheva, Maria, Reni Iordanova, Petar Ivanov, and Aneliya Yordanova. 2025. "Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 9, no. 4: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040118
APA StyleGancheva, M., Iordanova, R., Ivanov, P., & Yordanova, A. (2025). Effect of Ball Milling Speeds on the Phase Formation and Optical Properties of α-ZnMoO4 and ß-ZnMoO4 Nanoparticles. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 9(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp9040118






