Impact of Combined Zr, Ti, and V Additions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Al-Cu Cast Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
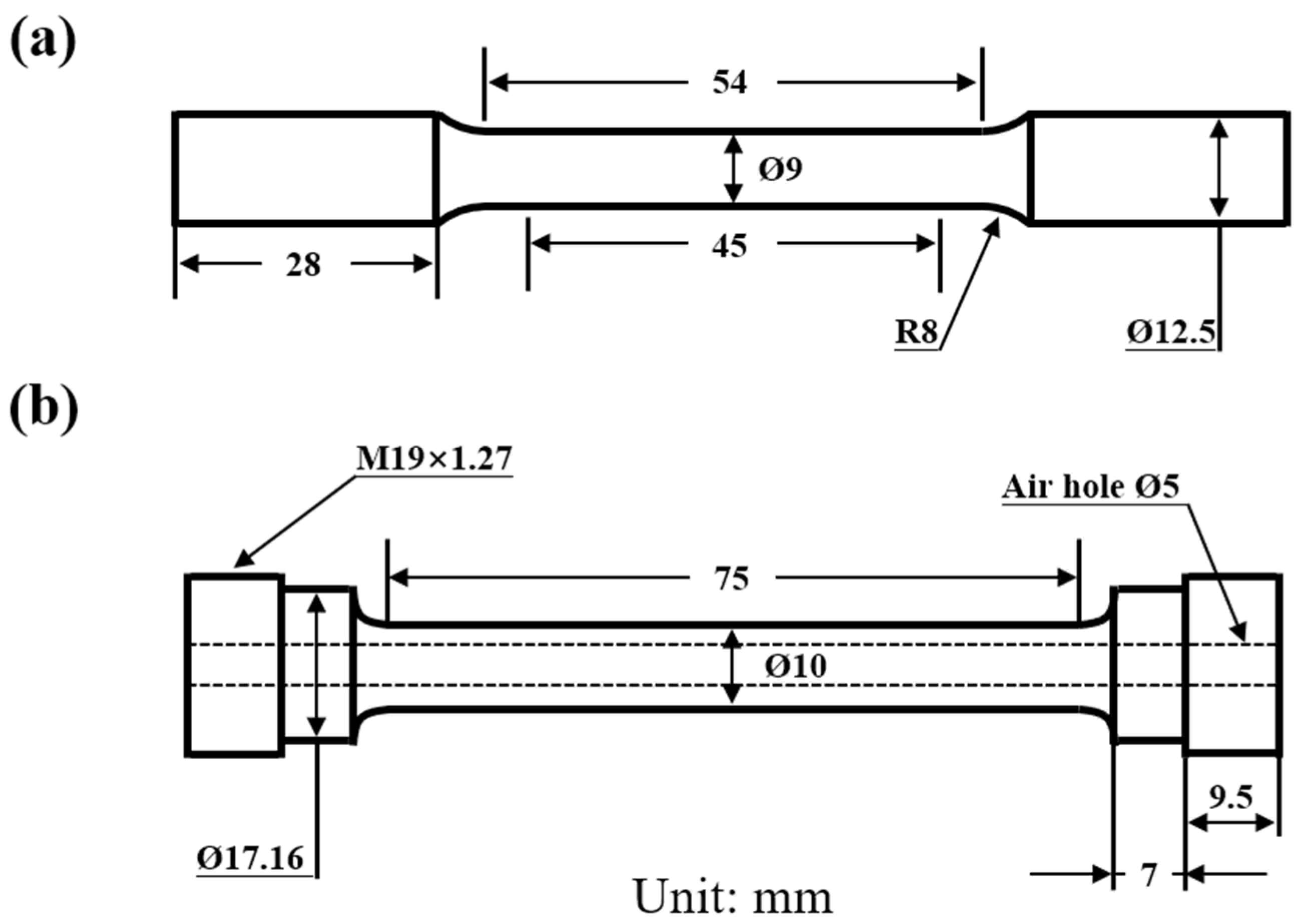
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
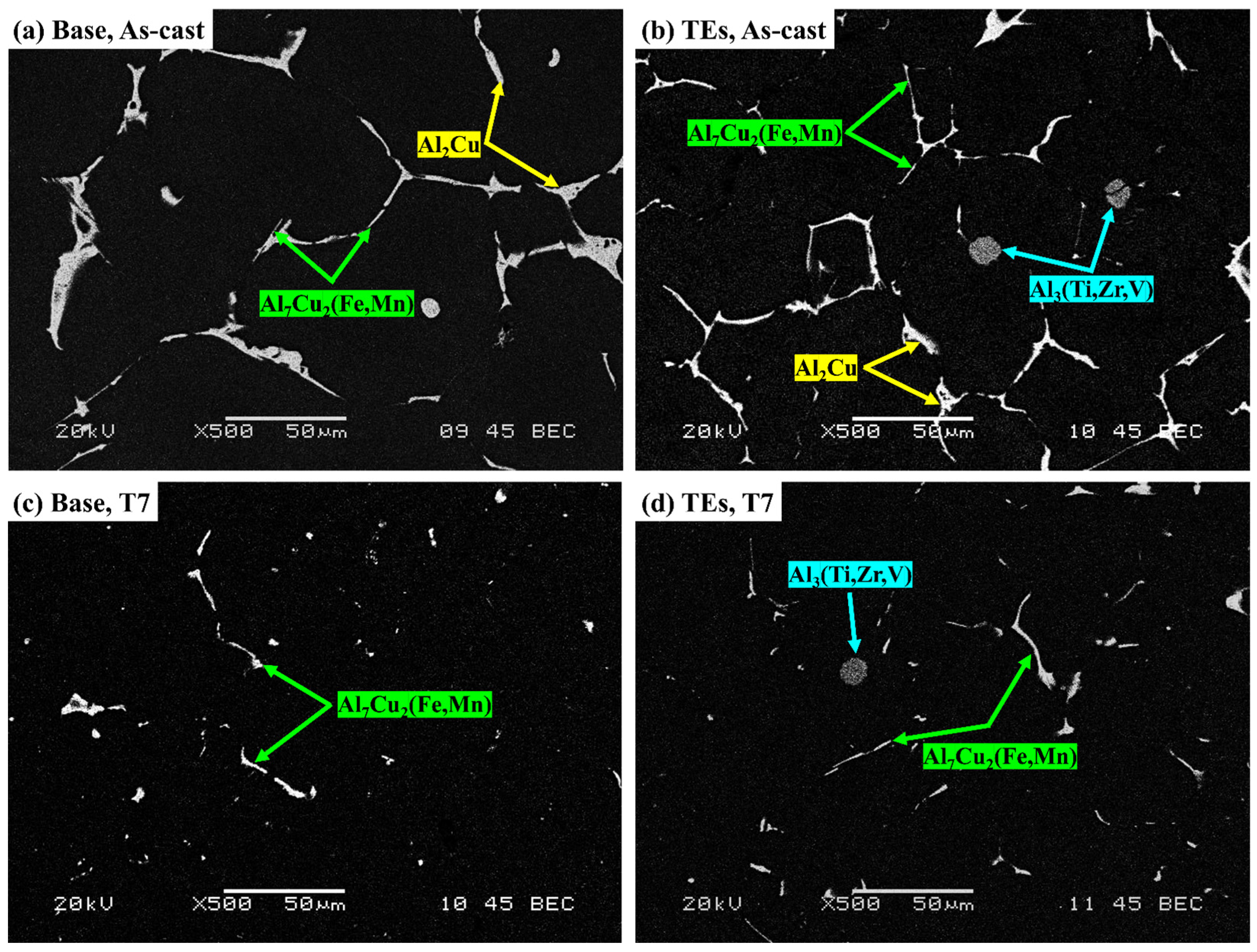
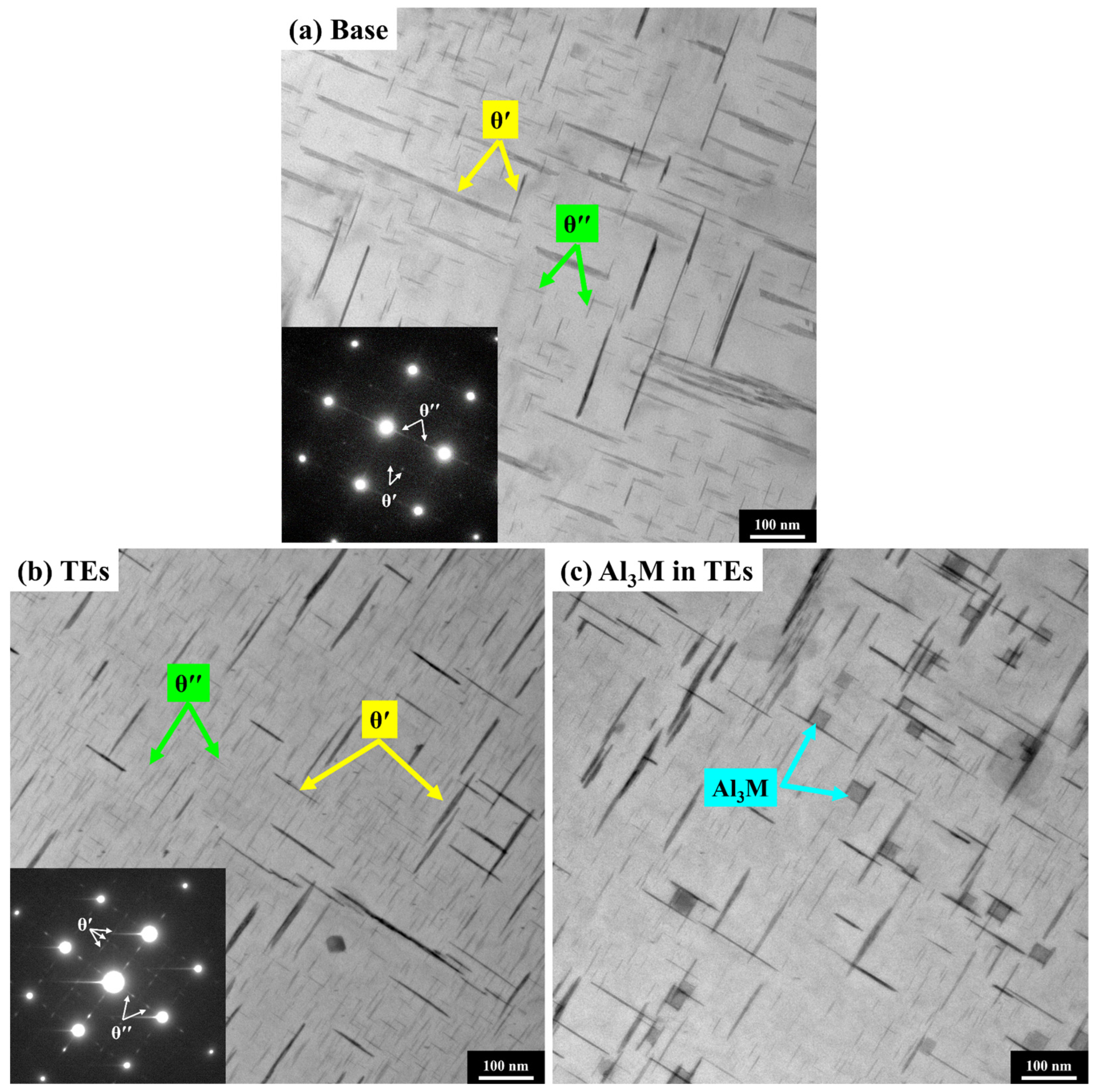
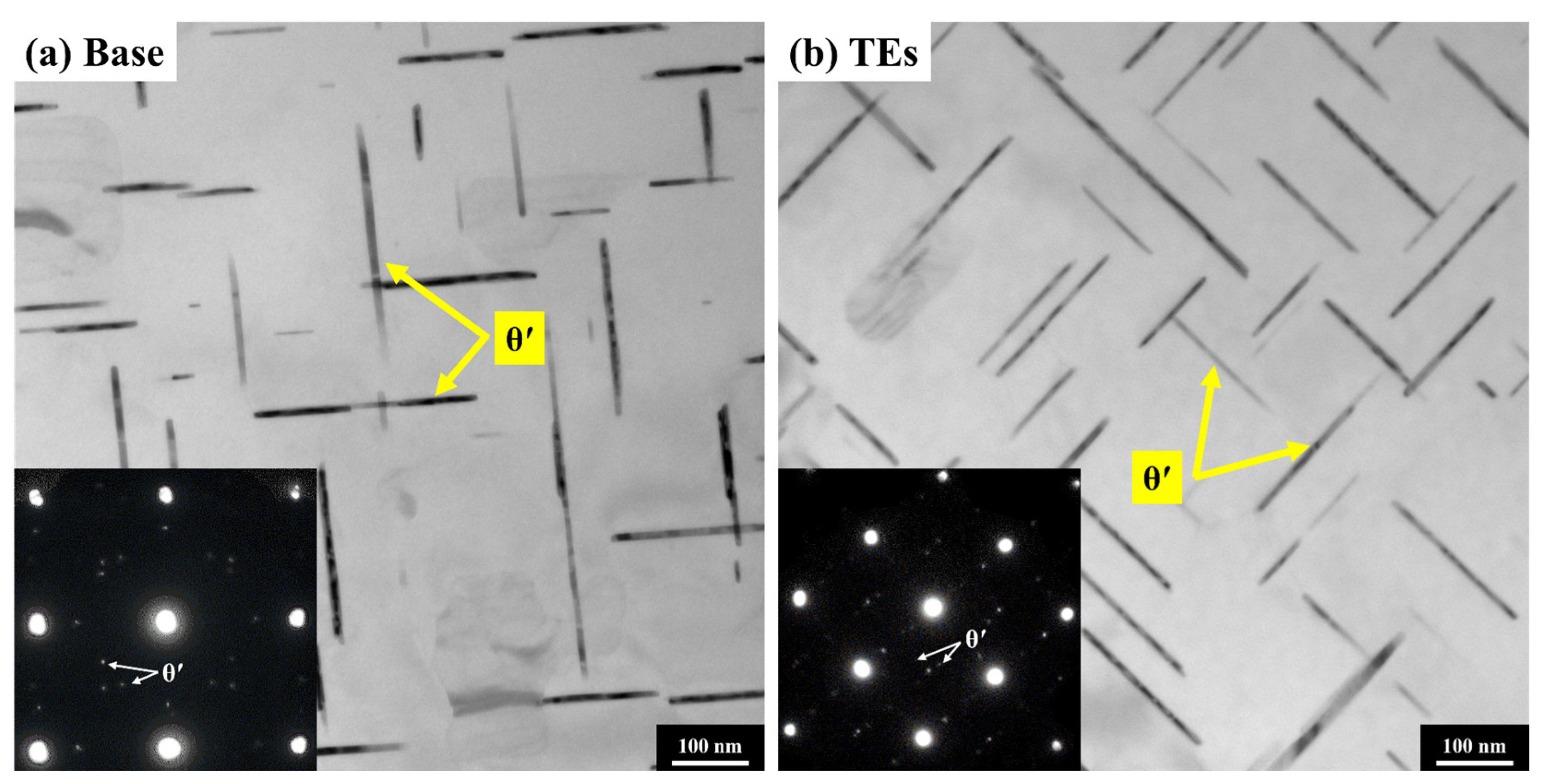
3.1. Microstructures in As-Cast and T7 States
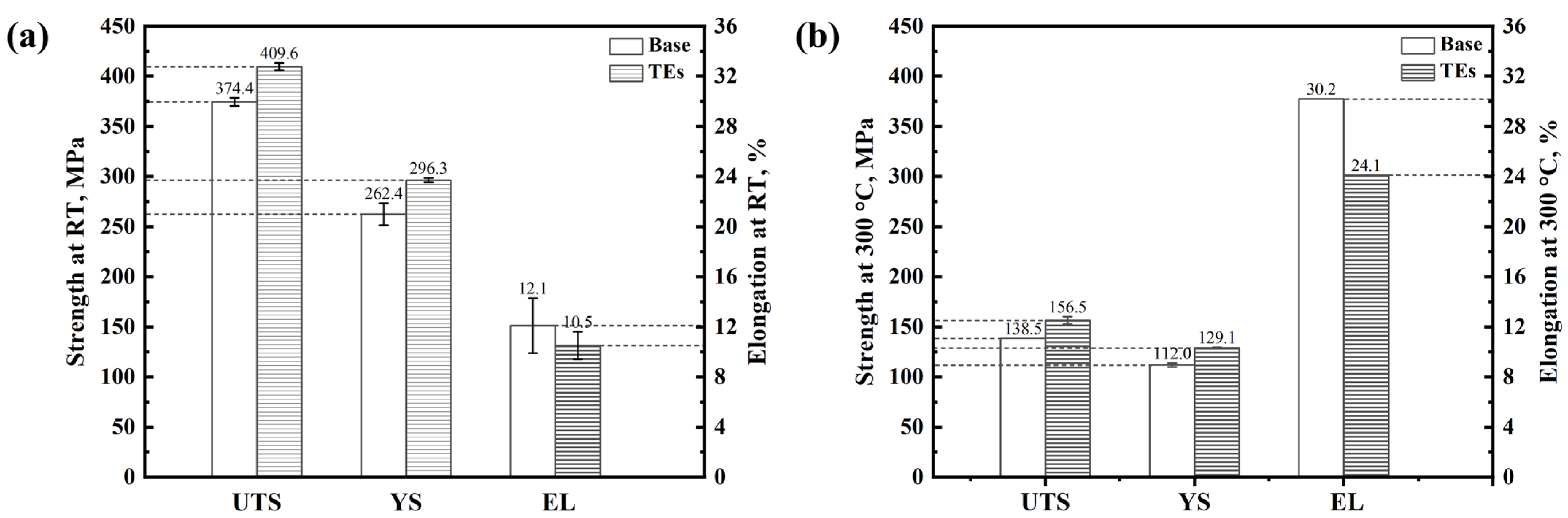
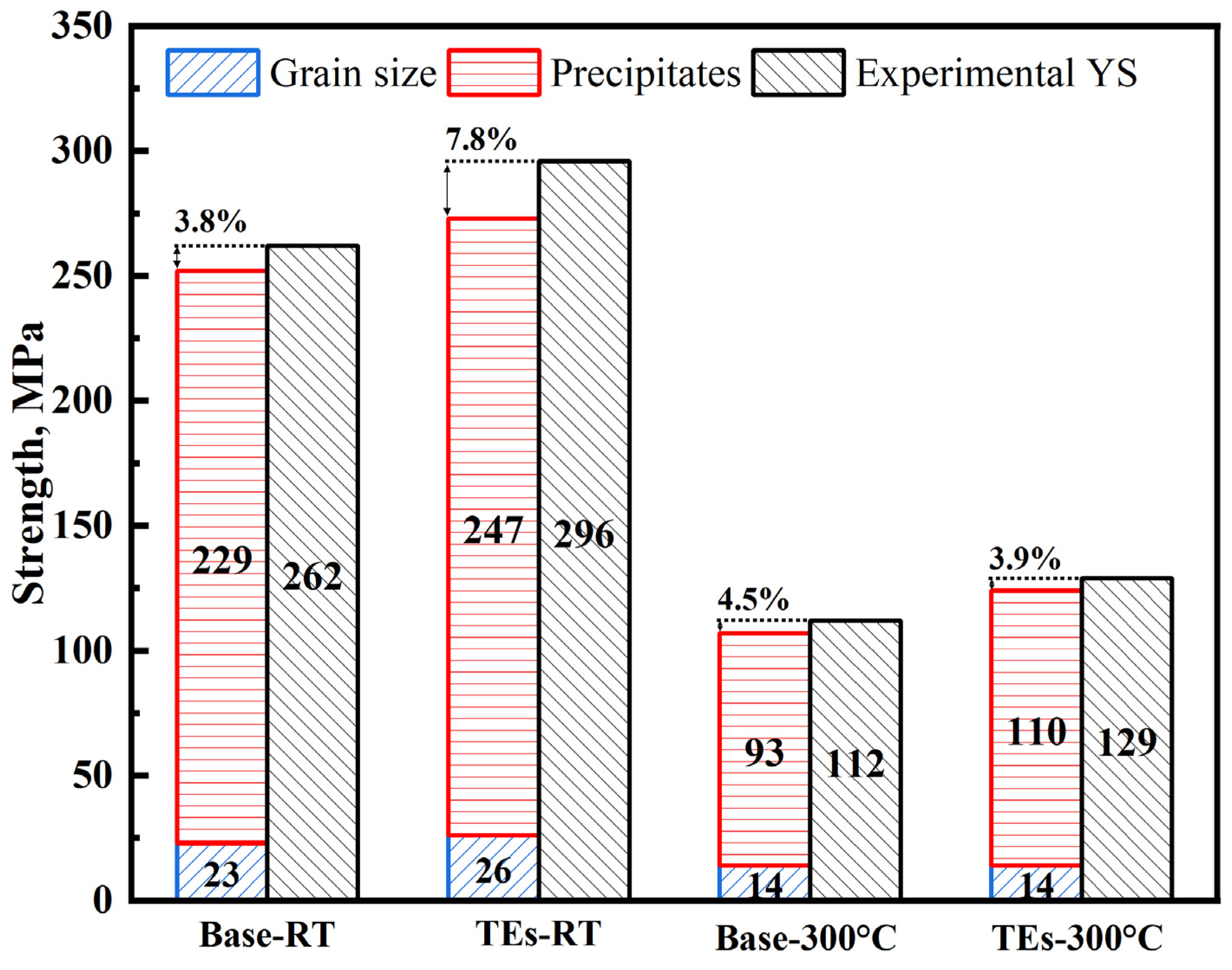
3.2. Mechanical Properties Under Both RT and 300 °C
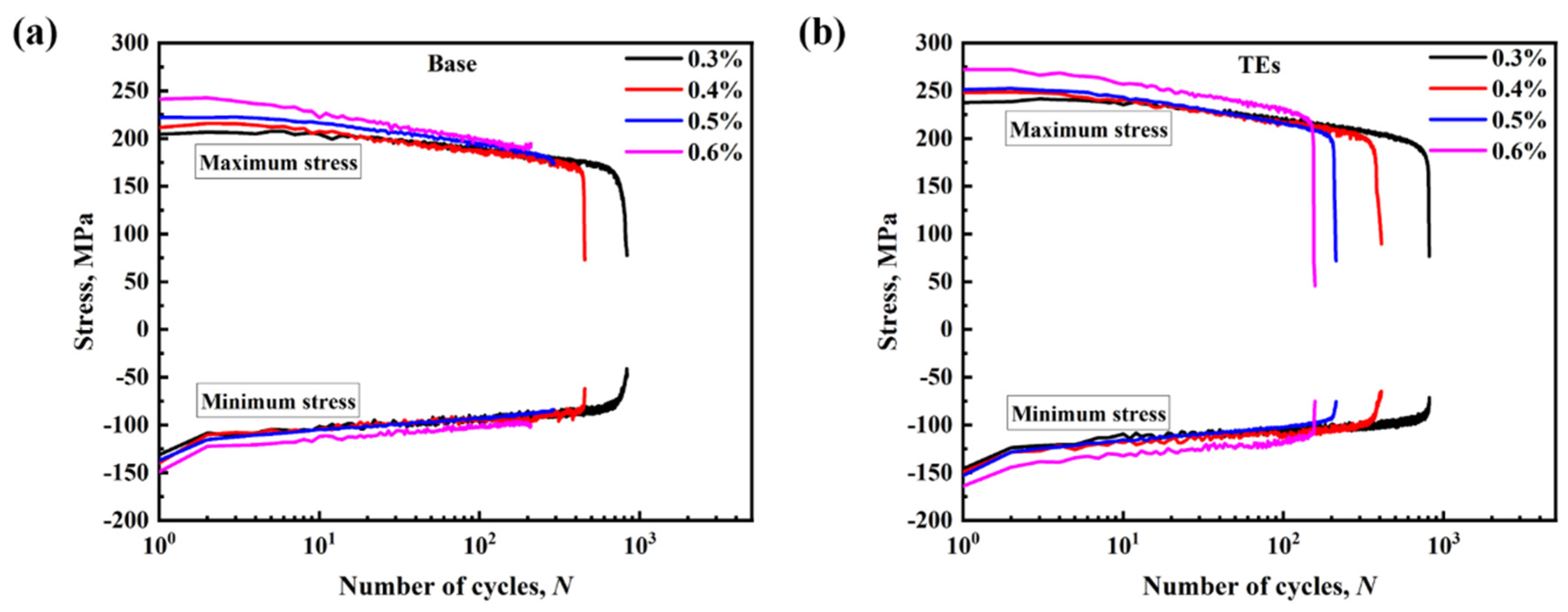
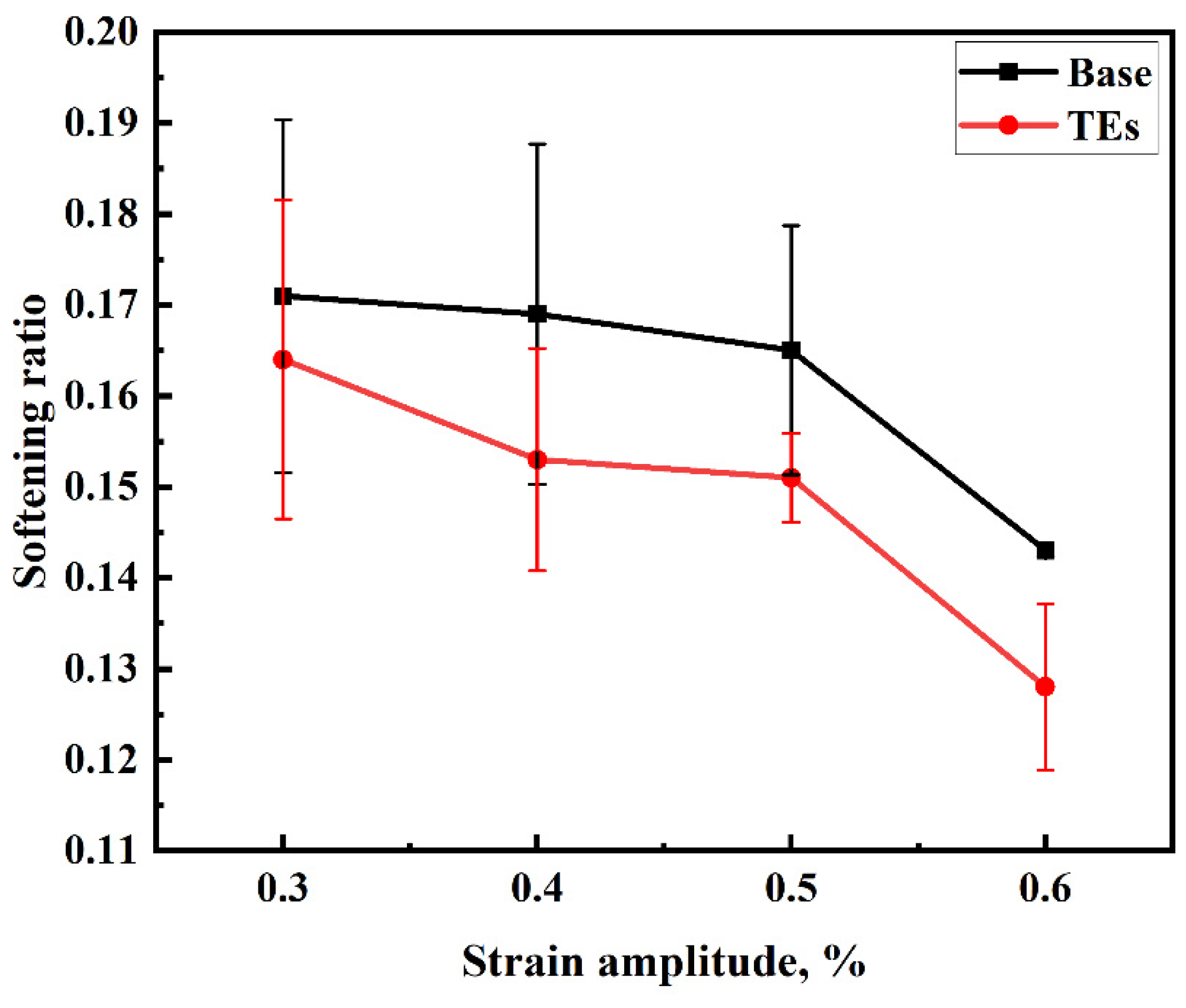
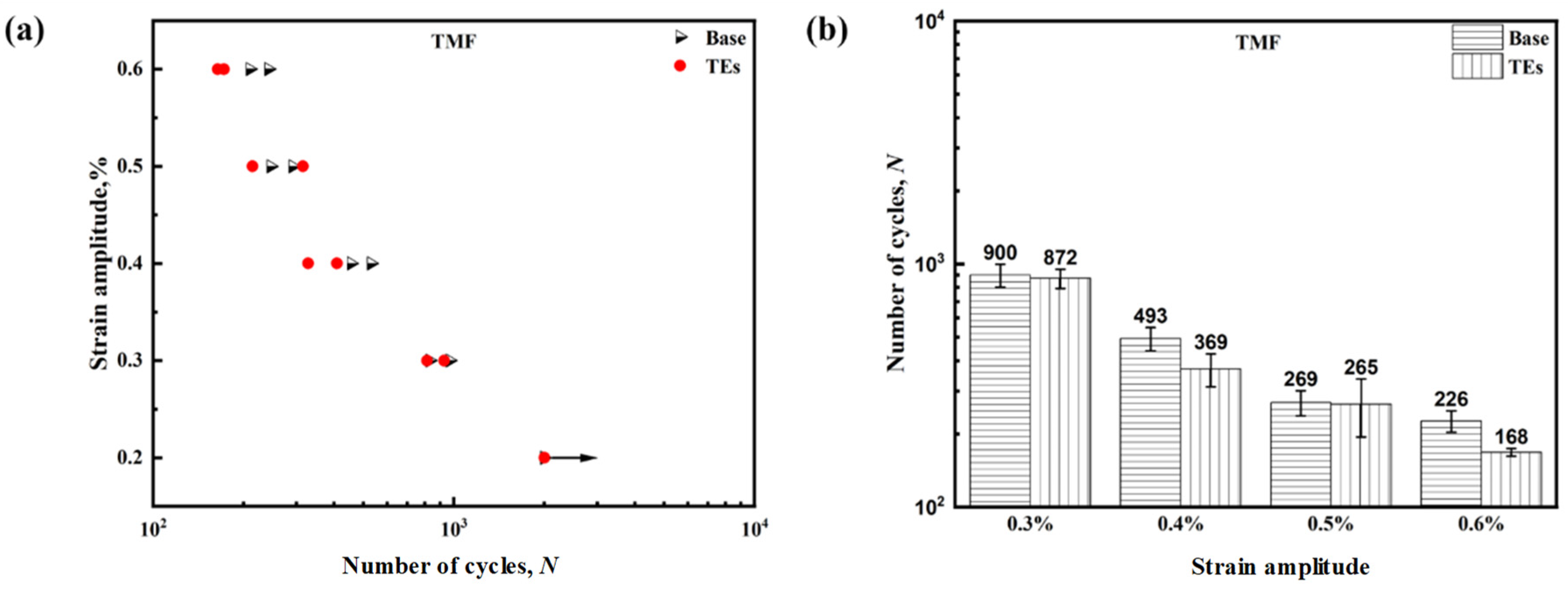
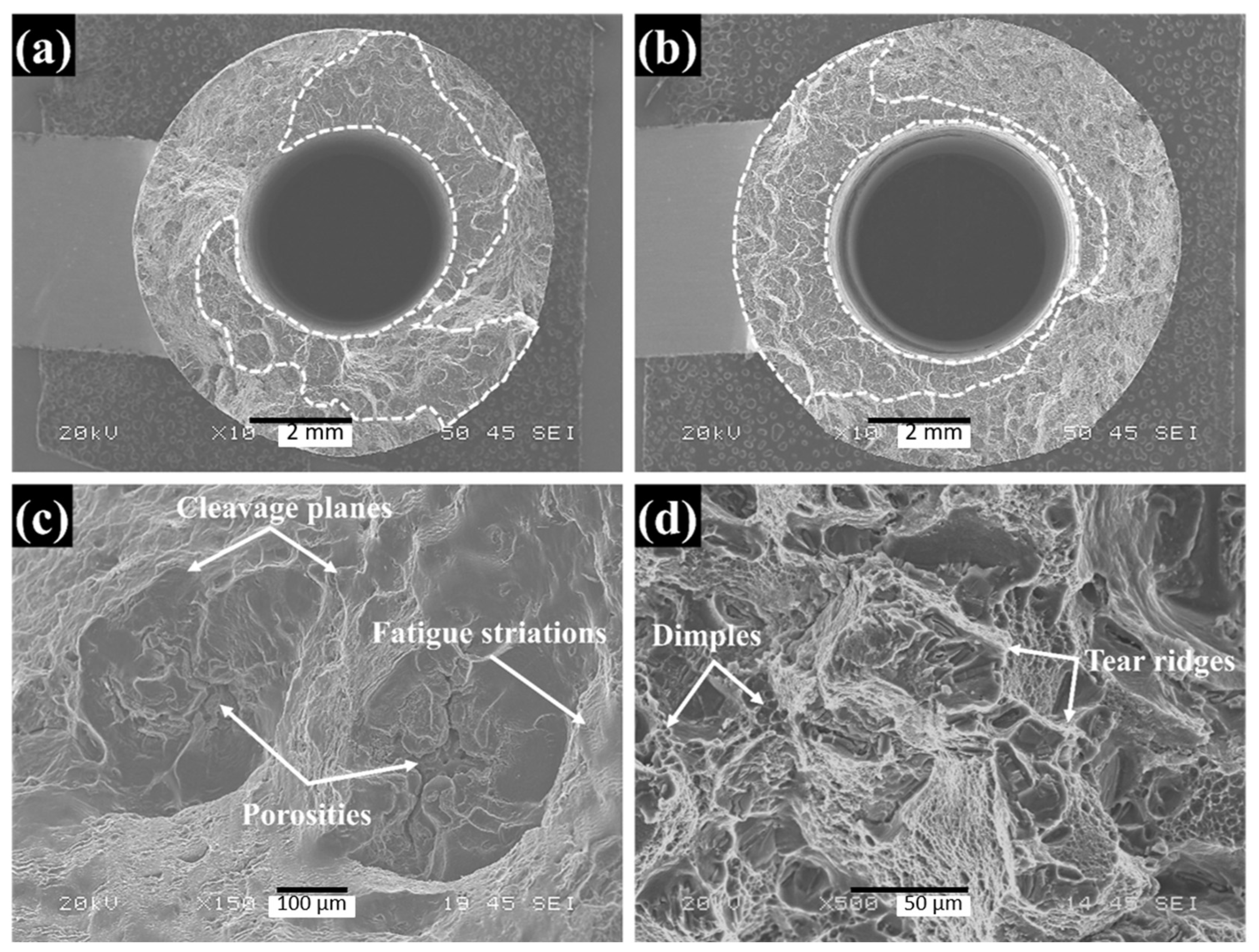
3.3. OP-TMF Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The introduction of TEs into the Al-Cu 224 alloy resulted in a refinement of the grain structure and yielded finer and denser coexisting θ″ and θ′ precipitates.
- The UTS and YS at both RT and 300 °C were enhanced by the addition of the TEs. The theoretical analyses of the YS contribution indicated that precipitation strengthening of θ″ and θ′ was the primary strengthening mechanism for the tested alloys, and the calculated YS values were in good agreement with experimentally measured data.
- The addition of TEs caused a slight reduction in the OP-TMF lifetime under the same strain amplitudes as the base alloy. However, during the fatigue process, the TE-added alloy exhibited a lower coarsening ratio, indicating the higher thermal stability of the precipitates, which compensated for the negative impact on the fatigue performance to some extent.
- Despite the minor reduction in the OP-TMF performance, the incorporation of small amounts of Zr, Ti, and V is recommended to achieve a refined grain structure, enhanced mechanical properties, and improved thermal stability in Al-Cu 224 cast alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, Y.H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cao, L.F.; Liu, G.; Sun, J.; Ma, E. Stabilizing Nanoprecipitates in Al-Cu Alloys for Creep Resistance at 300 °C. Mater. Res. Lett. 2018, 7, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenevisi, M.S.; Yu, Y.; Lin, F. A Review on Additive Manufacturing of Al–Cu (2xxx) Aluminium Alloys: Processes and Defects. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 37, 805–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Aluminium Automotive Manual, Version 2015; European Aluminium Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2015.
- Guinier, A. Heterogeneities in Solid Solutions. In Solid State Physics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1959; Volume 9, pp. 293–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, V.A. High Resolution Electron Microscope Observations on Precipitation in Al-3.0% Cu Alloy. Acta Metall. 1975, 23, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, S.; Xiong, L.; Allard, L.F.; Michi, R.A.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Chuang, A.C.; Singh, D.; Watkins, T.R.; Shin, D.; Haynes, J.A.; et al. Aging Behavior and Strengthening Mechanisms of Coarsening Resistant Metastable θ’ Precipitates in an Al–Cu Alloy. Mater. Des. 2021, 198, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Shyam, A.; Lee, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; Haynes, J.A. Solute Segregation at the Al/θ′-Al2Cu Interface in Al-Cu Alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 141, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam, A.; Roy, S.; Shin, D.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Allard, L.F.; Yamamoto, Y.; Morris, J.R.; Mazumder, B.; Idrobo, J.C.; Rodriguez, A.; et al. Elevated Temperature Microstructural Stability in Cast AlCuMnZr Alloys Through Solute Segregation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 765, 138279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplawsky, J.D.; Milligan, B.K.; Allard, L.F.; Shin, D.; Shower, P.; Chisholm, M.F.; Shyam, A. The Synergistic Role of Mn and Zr/Ti in Producing θ′/L12 Co-Precipitates in Al-Cu Alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 194, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmonov, J.U.; Bahl, S.; Shyam, A.; Dunand, D.C. Cavitation-Resistant Intergranular Precipitates Enhance Creep Performance of θ′-Strengthened Al-Cu Based Alloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 228, 117788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; Geng, J.W.; Bian, Z.Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.L.; Chen, D.; Ma, N.H.; Wang, H.W. Enhanced Thermal Stability and Mechanical Properties of High-Temperature Resistant Al–Cu Alloy with Zr and Mn Micro-Alloying. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Effect of Mg Microalloying on Elevated-Temperature Creep Resistance of Al–Cu 224 Cast Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 851, 143649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Effects of Individual and Combined Additions of Transition Elements (Zr, Ti, and V) on the Microstructure Stability and Elevated-Temperature Properties of Al–Cu 224 Cast Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 867, 144718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipling, K.E.; Dunand, D.C.; Seidman, D.N. Criteria for Developing Castable, Creep-Resistant Aluminum-Based Alloys—A Review. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouxel, B.; Ramajayam, M.; Langan, T.J.; Lamb, J.; Sanders, P.G.; Dorin, T. Effect of Dislocations, Al3(Sc, Zr) Distribution and Ageing Temperature on θ′ Precipitation in Al-Cu-(Sc)-(Zr) Alloys. Mater. 2020, 9, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondol, S.; Kashyap, S.; Kumar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Improvement of High Temperature Strength of 2219 Alloy by Sc and Zr Addition Through a Novel Three-Stage Heat Treatment Route. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 732, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.G. Enhanced Elevated-Temperature Mechanical Properties of Hot-Rolled Al–Cu Alloys: Effect of Zirconium Addition and Homogenization. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 11424–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidani, M.; Larouche, D. Application of Cast Al-Si Alloys in Internal Combustion Engine Components. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 132–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedler, M.; Leitner, H.; Prillhofer, B.; Winter, G.; Eichlseder, W. Lifetime Simulation of Thermo-Mechanically Loaded Components. Meccanica 2007, 42, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minichmayr, R.; Riedler, M.; Winter, G.; Leitner, H.; Eichlseder, W. Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Life Assessment of Aluminium Components Using the Damage Rate Model of Sehitoglu. Int. J. Fatigue 2008, 30, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G.; Apelian, D.; Lados, D.A. Fatigue Behavior of A356-T6 Aluminum Cast Alloys. Part I. Effect of Casting Defects. J. Light Met. 2001, 1, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, M.J.; Neeson, A.E.; Griffiths, J.R. Casting Defects and the Fatigue Behaviour of an Aluminium Casting Alloy. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1990, 13, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbertjean, A.; Beck, T. Effect of the Casting Process on Microstructure and Lifetime of the Al-Piston-Alloy AlSi12Cu4Ni3 Under Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue with Superimposed High-Cycle Fatigue Loading. Int. J. Fatigue 2013, 53, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G.; Apelian, D.; Lados, D.A. Fatigue Behavior of A356/357 Aluminum Cast Alloys. Part II–Effect of Microstructural Constituents. J. Light Met. 2001, 1, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huter, P.; Oberfrank, S.; Grün, F.; Stauder, B. Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Influence of Copper and Silicon on Hypo-Eutectic Al–Si–Cu and Al–Si–Mg Cast Alloys Used in Cylinder Heads. Int. J. Fatigue 2016, 88, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, T.Y.; Han, S.W.; Lee, H.M. Effects of Mn on the Crystal Structure of α-Al (Mn, Fe) Si Particles in A356 Alloys. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 291, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Effect of Mg on Elevated-Temperature Low Cycle Fatigue and Thermo-Mechanical Fatigue Behaviors of Al-Cu Cast Alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 885, 145588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Liu, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.G. Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior and Its Life Prediction of AlSi9Cu3.5 Cast Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 8022–8039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karayaka, M.; Sehitoglu, H. Thermomechanical fatigue of particulate-reinforced aluminum 2xxx-T4. Metall. Trans. A 1991, 22, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM B557-15; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum- and Magnesium-Alloy Products. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- ASTM E21; Standard Test Methods for Elevated Temperature Tension Tests of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Qin, J.; Racine, D.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.G. Strain-controlled thermo-mechanical fatigue testing of aluminum alloys using the Gleeble 3800 system. In Proceedings of the 16th International Aluminum Alloys Conference (ICAA 16), Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM E606; Standard Test Method for Strain-Controlled Fatigue Testing. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM E2368; Standard Practice for Strain Controlled Thermomechanical Fatigue Testing. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Roy, S.; Allard, L.F.; Rodriguez, A.; Porter, W.D.; Shyam, A. Comparative Evaluation of Cast Aluminum Alloys for Automotive Cylinder Heads: Part II: Mechanical and Thermal Properties. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2543–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F.; Muddle, B.C. Strengthening of an Al–Cu–Sn Alloy by Deformation-Resistant Precipitate Plates. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 3490–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hage, F.S.; Ramasse, Q.M.; Schumacher, P. The Nucleation Sequence of α-Al on TiB₂ Particles in Al-Cu Alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 206, 116652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Fan, Z. Effects of Solute Content on Grain Refinement in an Isothermal Melt. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Ding, Q.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z. Atomic-Scale Mechanism of the θ″ → θ′ Phase Transformation in Al-Cu Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolverton, C. Solute–Vacancy Binding in Aluminum. Acta Mater. 2007, 55, 5867–5872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makineni, S.K.; Sugathan, S.; Meher, S.; Banerjee, R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Kumar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Enhancing Elevated Temperature Strength of Copper Containing Aluminium Alloys by Forming L12 Al3Zr Precipitates and Nucleating θ″ Precipitates on Them. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondol, S.; Makineni, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K. Enhancement of High Temperature Strength of 2219 Alloys Through Small Additions of Nb and Zr and a Novel Heat Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 3047–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, G.E.; Bacon, D. Mechanical Metallurgy; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 3, pp. 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, M.; Farrahi, G.H.; Winter, G.; Eichlseder, W. Fatigue Lifetime of AZ91 Magnesium Alloy Subjected to Cyclic Thermal and Mechanical Loadings. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadi, M.; Farrahi, G.H.; Winter, G.; Eichlseder, W. Thermo-Mechanical Behaviours of Light Alloys in Comparison to High Temperature Isothermal Behaviours. Mater. High Temp. 2014, 31, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.G.; Lee, S.B.; Byun, T.S. Temperature Effect on the Low-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Type 316L Stainless Steel: Cyclic Non-Stabilization and an Invariable Fatigue Parameter. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 457, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| ID | Cu | Mn | Mg | Zr | Ti | V | Si | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 4.70 | 0.35 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.12 | Bal. |
| TEs | 4.69 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.11 | Bal. |
| Alloy | Precipitates | Length (dt), nm | Thickness (tt), nm | Number Density (Nv), nm−3 | Volume Fraction (f), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | θ′ | 159.5 ± 50.4 | 5.6 ± 2.0 | 2.5 × 10−7 | 2.8 |
| θ″ | 32.4 ± 10.7 | 3.2 ± 0.8 | 3.1 × 10−6 | 0.8 | |
| TEs | θ′ | 102.7 ± 43.3 | 5.3 ± 1.8 | 2.9 × 10−7 | 1.3 |
| θ″ | 32.2 ± 13.0 | 2.9 ± 0.8 | 7.6 × 10−6 | 2.3 |
| Alloy | Length (dt), nm | Thickness (tt), nm | Number Density (Nv), nm−3 | Volume Fraction (f), % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| base | 173.9 ± 87.5 | 12.4 ± 4.7 | 1.2 × 10−7 | 3.2 |
| TEs | 170.3 ± 84.0 | 11.1 ± 3.8 | 1.6 × 10−7 | 3.9 |
| Symbol | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| σppt | YS provided by precipitates | -- |
| σgb | YS due to the grain boundaries | -- |
| M | Taylor factor | 3.06 [36] |
| G | Shear modulus of α–Al matrix | 28 GPa at RT [42]; 21.2 GPa at 300 °C [17] |
| ε | Lattice strain | 0.006 [42] |
| b | Magnitude of Burgers vector for Al | 0.286 nm [36] |
| ν | Poison’s ratio | 1/3 [36] |
| dt | Effective length precipitates | Refer to Table 2 and Table 3 |
| tt | Effective thickness of precipitates | Refer to Table 2 and Table 3 |
| Nv | Number density of precipitates | Refer to Table 2 and Table 3 |
| f | Volume fraction of precipitates | Refer to Table 2 and Table 3 |
| σi | YS for pure Al with infinite grain size | 16 MPa at RT [36] |
| ki | Hall-Petch constant | 0.065 MPa·m1/2 [36] |
| D | Average grain size | 99 µm (Base); 40 µm (TEs) |
| M | Exponent for grain boundary strengthening | 0.5 [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, P.; Liu, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X.-G. Impact of Combined Zr, Ti, and V Additions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Al-Cu Cast Alloys. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060250
Hu P, Liu K, Pan L, Chen X-G. Impact of Combined Zr, Ti, and V Additions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Al-Cu Cast Alloys. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2024; 8(6):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060250
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Peng, Kun Liu, Lei Pan, and X.-Grant Chen. 2024. "Impact of Combined Zr, Ti, and V Additions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Al-Cu Cast Alloys" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 8, no. 6: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060250
APA StyleHu, P., Liu, K., Pan, L., & Chen, X.-G. (2024). Impact of Combined Zr, Ti, and V Additions on the Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Thermomechanical Fatigue Behavior of Al-Cu Cast Alloys. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 8(6), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8060250






