Abstract
This study examines the dry milling process of a rare-earth-based magnesium alloy, emphasizing the optimization of the milling parameters and their impact on the surface quality, cutting forces, and the rate of material removal. The objective is to improve our comprehension of the milling behavior of the Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloy. The Taguchi technique is adopted to formulate the experimental design. This study methodically investigates the influence of heat treatment (T4 and T6) on milling performance, and the effects of speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. The output variables considered for this investigation are the surface roughness (Ra, Rz, Sa, and Sz), material removal rate (MRR), and cutting force. To optimize the milling parameters and achieve superior outcomes, the multi-objective optimization technique TOPSIS is used. At a feed rate of 150 mm/min, a spindle speed of 1500 rpm, and a depth of cut of 1 mm, the T4-treated sample exhibits a minimum surface roughness value of 0.0305 µm. The highest resultant force values of 96.4416 N and 176.1070 N for 200 °C and 225 °C T6-treated alloys are obtained by combining process parameters such as a spindle speed of 1500 rpm, a feed rate of 50 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 1.5 mm. Furthermore, the maximum closeness coefficient value is achieved by combining a spindle speed of 1000 to 1500 rpm, a feed rate of 150 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 0.5 mm to 1 mm. The closeness coefficient value is significantly influenced by the most significant process parameters, as indicated by the ANOVA results.
1. Introduction
A variety of industries use magnesium (Mg) alloys because of their distinctive combination of features, which include high specific strength, low density, and good machinability. Automotive components that use magnesium alloys are lighter and more fuel-efficient [1,2]. Mg alloys are being utilized more frequently in biomedical applications, including orthopedic implants, screws, pins, and plates, because of their biocompatibility and biodegradability. Additionally, magnesium will progressively degrade inside the human body, eliminating the necessity for a subsequent surgical procedure [3]. In industrial manufacturing, dry milling is a highly effective cutting technology that is frequently employed. Machinability is primarily influenced by the cutting parameters, coolant, and tool geometry. Two typical criteria utilized to assess the quality of the machining process in relation to the condition of the workpiece are the cutting force and surface irregularity [4]. In order to optimize the surface quality of the specimen, it is imperative to select the appropriate parameters. Therefore, many researchers have conducted a substantial quantity of research on the optimization of process parameters through the use of various methods. Their research has been centered on identifying the machining conditions’ effect or influence on the specimens’ surface quality. The cutting forces, cutting temperature, and chip morphology of the Mg AZ31B alloy were examined in relation to the process parameters by Gobivel et al. [5]. Additionally, Mostafapour A et al. investigated the impact of milling parameters on the surface character of the AZ91C Mg alloy [6]. Similarly, Ahuja et al. studied the effect of wire electric discharge machining parameters on the surface roughness and corrosion resistance in the ZM21 Mg alloy [7]. According to Chirita et al., the Mg AZ61A alloy can be enhanced by combining a higher cutting speed, a lower feed, and a deeper cut to provide a better surface [8]. N. Wojtowicz et al. [9] reported that the feed rate, nose radius, and nose feed contact influence the surface roughness of the Elektron21 Mg alloy being turned. A. Suresh et al. investigated the effect of solution treatment on the cutting force and the surface irregularity of the AZ91 Mg alloy. The solution-treated sample required more cutting force during the turning operation than the AZ91 alloy [10]. According to Xu et al., the feed per tooth is an important factor in the surface quality of the GW63K Mg alloy. The best circumstances for producing an excellent surface finish (0.06 µm), with reduced cutting force and temperature, are a greater cutting speed and a lower feed per tooth, combined with MQL conditions [11]. Li et al. investigated the machinability of the sand-casted GW63K Mg alloy using various coated tools in dry machining conditions and with MQL lubrication [12]. S. Dinesh et al. observed that cryogenic cooling can lower the cutting temperature by 60% and the surface roughness by 25 to 40% during the milling of the Mg ZK60 alloy [13]. Furthermore, Jouini et al. demonstrated that cryogenic cutting can extend tool life by eight times over dry milling [14]. Shi et al. used the gray relational approach (GRA) to optimize process parameters and increase surface quality [15]. The multi-response optimization methods such as the Passing Vehicle Search (PSV) algorithm [16], the Technique for Order of Preference by Similarity to Ideal Solution (TOPSIS), and the GRA have been used to improve the process parameters of various machining operations on Mg alloys. The gray relational analysis (GRA) shows that the feed and the spindle speed have the greatest influence on the surface roughness and corrosion rate of the ZE41A Mg alloy [17]. R. Kumar et al. used the gray relational analysis (GRA) to optimize the wire electric discharge machining (WEDM) process parameters while milling the ZE41A Mg alloy [18]. Sunesh and Sivapragash found that the GRA and the TOPSIS yielded the same optimum parameter settings during the micro-milling of the Mg-3Zn-0.7Zr-1Cu alloy [19]. Although the GRA has certain advantages, the TOPSIS offers a more comprehensive, adaptive, and user-friendly technique for multi-criteria decision-making and optimization, making it the better choice for complicated decision-making procedures. Several experiments have been undertaken on machining commercial mg alloys like the AZ and ZE series. In contrast to other mg alloys, those containing rare earth elements have been subjected to limited machining investigations.
Rare-earth-based magnesium alloys are produced by incorporating rare earth materials, including La, Ce, Re, Gd, and Y, into the Mg matrix. Due to their exceptional properties at both room and elevated temperatures, magnesium rare-earth (Mg-RE) alloys, including the Mg-Gd, Mg-Y, and Mg-Gd-Y systems, have attracted attention [20,21,22]. The solid solubility limit of elements such as Gd and Y in the magnesium matrix is 23.49 wt% and 15.28 wt%, respectively, at their eutectic temperature. Consequently, Mg alloys that contain Gd and Y will exhibit a favorable solid-solution strengthening effect [23,24,25]. Similarly, precipitate hardening is a thermal treatment that will effectively enhance the mechanical properties of the Mg-RE system [26]. The alloy Mg-7.8Gd-2.7Y-2Ag-0.4Zr has an ultimate tensile strength (UTS) of 410 MPa following a 32 h age-hardening procedure at 200 °C [27]. In addition, the hydrostatic extruded Mg–12Gd–3Y–0.6Zr alloy exhibits an elongation of 4% and a UTS of 510 MPa following the T5 treatment (225 °C for 9 h) [28]. The thermal stability of Mg-Gd-Y alloys is improved by the presence of thermally stable inter-metallic phases, such as Mg5Gd and Mg24Y5, which prevent the coarsening of precipitates and the growth of grains at high temperatures [14]. The fatigue strength of the hot-rolled Mg–12Gd–3Y alloy is 150 MPa after 107 cycles, which is 50% greater than that of the AZ80 Mg alloy [29]. At 107 cycles following 10 h at 225 °C, the fatigue strength of the extruded Mg-10Gd-3Y alloy is 165 MPa, and its UTS is 445 MPa [30]. In comparison to other commercial alloys, the Mg-Gd alloy system demonstrates superior mechanical properties. While most research has been on commercial cast mg alloy machining, this study uses the Taguchi L9 orthogonal array to shed light on the milling behavior of stir-casted and heat-treated Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloys. This study aims to improve the dry milling efficiency of the Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloy by examining the effect of milling parameters on the cutting force, material removal rate (MRR), surface roughness (Ra, Rz, Sa, and Sz), and overall milling efficiency. The multi-objective optimization technique known as TOPSIS was implemented (i) to improve the MRR, (ii) to reduce the cutting force to limit the energy source, and (iii) to improve the surface finish to produce high-quality products.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Material Preparation Methods
The stir casting technique was utilized to fabricate the Mg-RE (Mg-Gd-Y-Er) alloy in an induction-based crucible furnace. Amounts of pure magnesium ingots and alloying elements were heated to 800 °C and agitated at 600 RPM for 5 min. The molten metal was subsequently poured into the preheated mild steel mold at 150 °C while at a temperature of 750 °C. The casted specimens were subjected to the solutionizing and age-hardening process. The samples were quenched in boiling water at a temperature ranging from 60 °C to 80 °C after the solutionizing process was conducted for one hour at 500 °C. The solutionizing temperature was selected to avoid eutectic melting at the grain boundaries during the solution treatment. For the age-hardening process, the temperature was maintained at 200 °C for 16 h and 225 °C for 8 h which leads to the better age-hardening effect of the Mg-Gd alloy system [31,32]. With the use of wire electric discharge machining, the 50 × 30 × 5 mm workpiece was prepared. To clean the surface of the as-cast and heat-treated samples, we used an ultrasonic sonication technique for 10 minutes to remove any debris and then polished them with silicon carbide sheets up to a grit size of 2000. A computer numerical control vertical milling machine was used to carry out the dry milling procedure. A high-speed steel (HSS) end mill cutter with a diameter of 6 mm, an overall length of 57 mm, a cutter length of 19 mm, and a helix angle of 45° with 4 flutes was utilized for the dry milling process.
2.2. Process Parameters and Design of Experiments (DOE)
Table 1 contains three process parameters, including the spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut, which were selected based on the literature survey, and the designs of the experiments are given in Table 2. The process parameters significantly affect the response variables and the cutting tool. The cutting tool’s temperature distribution is enhanced at spindle speeds between 1000 and 5000 RPM, according to research on Mg AZ31 [33]. The depth-of-cut value affects the surface area and temperature at the tool–workpiece interface [34]. After reviewing the mentioned literature findings and considering the CNC machine’s input parameter range, the process parameter values were finalized. With the addition of each input factor, the total number of degrees of freedom increases to six. The L9 orthogonal array can support up to four factors with three layers and features eight degrees of freedom. Therefore, the trials were conducted using L9 experiments. As-cast, solutionizing, and age-hardening samples were subjected to experimental trials using the Taguchi L9 orthogonal array.

Table 1.
Process parameters and their levels.

Table 2.
Design of experiments.
2.3. Measurements of Responses and Optimization
The chips formed during milling were collected and removed from the milled samples. Then, the samples were subjected to ultrasonic cleaning to remove the fine chips on the surface before weight measurement and profilometer recordings. The workpiece was affixed to the Kistler dynamometer (9257B), which is employed to quantify the cutting force (CF) generated during the milling process. The surface roughness (SR) of the milled surface was measured using the Taylor Hobson optical profilometer (Talysurf CCI) with an objective lens of 20x and a measurement area of 0.8 mm2. The weight of the samples was measured using a weighing balance (Mettler Toledo, ME204) before and after machining three times, and the duration of each trial run was recorded. The material removal rate (MRR) was determined by dividing the weight loss of the specimen during the milling process by the duration of the machining process.
Equations (1) through (5) outline the several stages that make up the TOPSIS [19]. The experimental results of this study are divided into two main areas: first, achieving a higher material removal rate, and second, achieving a decrease in the surface roughness and cutting force. Consequently, it is challenging to compare the response variables because each one has distinct units. To make a comparison between the response variables, the normalized response variable needs to be calculated using Equation (1). In this study, all response variables are given identical weights, which amounts to 16.7%. Equation (2) was used to determine the weighted response variable (Vij) by multiplying the normalized response value by each response variable’s weightage (Wj). The best and worst response variables for each alternative were calculated. The positive () and negative () ideal solutions of the weighted normalized values were calculated as per the best values of the response variables using Equations (3) and (4). Equation (5) was used to calculate the closeness coefficient value (Ci), which is the overall performance measure. An optimal experimental run is one with a closeness coefficient as high as possible.
3. Results and Discussions
The 2D and 3D plots of the milled surface are presented in Figure 1, where S represents speed, F stands for feed rate, and D represents the depth of cut. The experimental results of the SR, CF, and MRR are given in Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6. Micrometers, gm/min, and N are the units of measurement for the SR value, the MRR, and the CF, respectively. The speed was set to 500 rpm, the feed was 150 mm/min, and the depth of cut was 1.5 mm to obtain the lowest surface roughness value (Ra value of 0.08 µm) for the as-cast condition. In contrast, the highest surface roughness value (0.21 µm) was achieved in the fifth experimental trial with a cutting force of 17.35 N. The lowest levels of all three parameters were observed in run number 1, which was characterized by the maximum material removal rate of 1.53 gm/min. The T4-treated sample achieved the lowest surface roughness value and the highest resultant force of 49.57 N in run number 3, with a spindle speed of 1500 rpm, a feed rate of 150 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 1 mm. Additionally, the material removal rate was higher, at 1.55 gm/min. The surface roughness value of the T4-treated sample was between 0.04 µm (run number 9) and 0.21 µm (run number 2). In cycle number 7, the T6-treated alloys (225 °C and 200 °C) exhibited lower surface roughness and a higher material removal rate. Furthermore, the highest resultant force values of 96.44 and 176.11 N for the 200 °C and 225 °C T6-treated alloy were also measured in run number 7 (spindle speed: 1500 rpm, input rate: 50 mm/min, and depth of cut: 1.5 mm). The hardness of the mg alloy was enhanced when it was age-hardened at 200 °C and 225 °C due to the development of β′ precipitates [27]. This is because the microstructural changes and the change in hardness cause the age-hardened sample to display a cutting force that is substantially higher than that of the casted sample. The heat treatment of the AZ91 alloy changes its microstructure and phase fractions, which influences its machine behavior by increasing its cutting forces [10]. The milling of the Mg GW63K alloy resulted in a maximal resultant cutting force of 140 N, as reported by Xu et al. [11]. The surface roughness values are minimal as a consequence of the higher speed level and the lower depth of cut. The findings of Reddy and Rao [35] and Danesh and Ramli [36] are consistent with the trend of these results. Also, Salahshoor and Guo mentioned that the higher spindle speed would result in a better surface finish [37]. As the depth of cut increases, the cutting force and contact area both rise, making the tool and the workpiece unstable. Furthermore, the machining process distorts the sample surface due to the increased torque produced by the lower spindle velocities [34]. In addition, creating a more consistent and polished surface requires higher spindle speeds, reducing chip fractures [38]. The closeness coefficient (Ci) is the primary focus of the TOPSIS optimization results, whereas the Taguchi method is usually used for single-response optimization. When the Taguchi analysis is combined with multi-response optimization methods such as the TOPSIS, it assists in evaluating the impact of milling parameters on the closeness coefficient (Ci), a metric that encompasses all six responses. Optimized parameters are identified by the maximum closeness coefficient value, which leads to improved responses. The values of the closeness coefficients for the as-cast, T4-treated, and two T6-treated samples (200 °C for 16 h and 225 °C for 8 h) were 0.66, 0.76, 0.67, and 0.60, respectively. The optimal parameters for a Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloy that has been stir-casted and age-hardened at 225 °C for 8 h are a feed rate of 150 mm/min, a spindle speed of 1000 rpm, and a depth of cut of 0.5 mm, as per the closeness coefficient value. In contrast, the optimum parameters for the T4-treated and age-hardened at 200 °C for 16 h alloys are a spindle speed of 1500 rpm, a feed rate of 150 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 1 mm (run number 9). In addition, it can be noticed that run number 9 is ranked second in the as-cast and age-hardened (225 °C for 8 h) sample. The stir-casted, T4-treated, and T6-treated alloys have a feed rate of 150 mm/min as the optimum parameter. When comparing the optimum experimental runs of different processed samples, it is observed that the T4-treated alloy has the highest material removal rate (1.29 gm/min) and the lowest surface roughness value (0.04 µm).
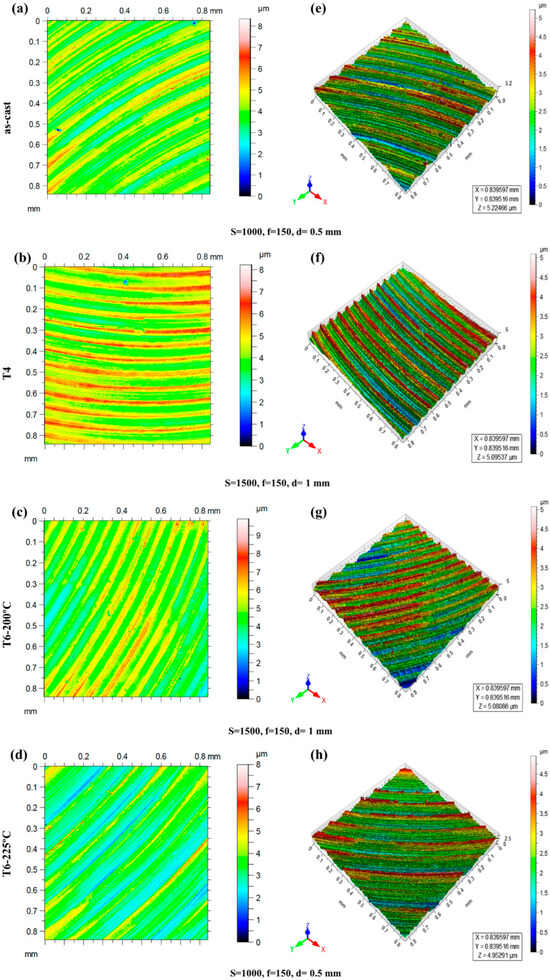
Figure 1.
Two-dimensional and three-dimensional surface profiles. (a–d) Two-dimensional surface profile, (e–h) three-dimensional surface profile, (a,e) as-cast sample, (b,f) T4-treated sample, (c,g) age-hardened sample (20 °C for 16 h), and (d,h) age-hardened sample (225 °C for 8 h).

Table 3.
The experimental results and closeness coefficient values of the as-cast sample.

Table 4.
The experimental results and closeness coefficient values of T4-treated sample.

Table 5.
The experimental results and closeness coefficient values of T6-treated sample (200 °C for 16 h).

Table 6.
The experimental results and closeness coefficient values of T6-treated sample (225 °C for 8 h).
Figure 2 exhibits the contour diagram, which illustrates the correlation between the closeness coefficient (Ci) and the selected milling parameters. The maximal value of the closeness coefficient (Ci) is indicated by the dark green region on the plot. The optimum closeness coefficient value is achieved at a spindle speed of 1000 rpm, a feed rate of 150 mm/min, and a depth of cut of 0.5 mm based on the contour plots of the as-cast and the age-hardened alloy samples (225 °C for 8 h). The as-cast sample exhibits the lowest closeness coefficient value due to the combination of a higher level of depth of cut, a moderate speed, and the feed rate. When considering the T4-treated sample, the maximum value of the closeness coefficient is attained by combining a medium level of depth of cut, higher feed rates, and a higher speed level. In the same vein, the age-hardened sample (200 °C for 16 h) exhibits the highest Ci value when a combination of a reduced depth of cut, higher feed rates, and a higher speed level is employed. The maximum closeness coefficient value is achieved by combining a higher feed rate (150 mm/min) with a moderate depth of cut (0.5 mm to 1 mm) and a higher level of spindle speed (1000 to 1500 rpm), regardless of the sample condition. In general, it is observed that the closeness coefficient value is improved with the combination of a lower depth of cut value and a higher spindle speed and feed rate.
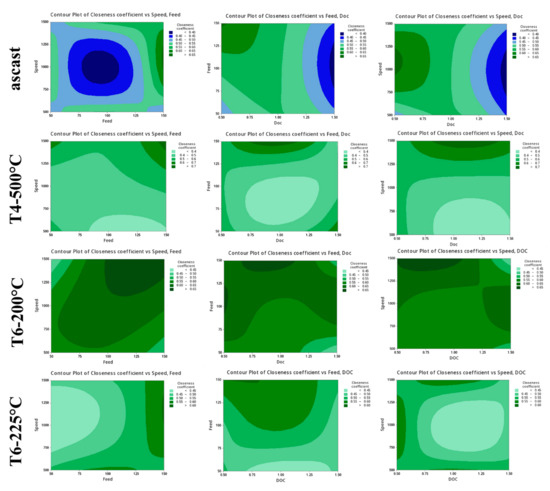
Figure 2.
Contour plots of closeness coefficient value of Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloy.
ANOVA is a statistical technique used to identify the most influencing factors over the response variables [8]. Table 7, Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 provide the ANOVA results for the closeness coefficient value of various processed samples. For the as-cast sample, the depth of cut was the most significant parameter in determining the closeness coefficient value, contributing 60.21%. The feed rate followed, contributing 12.51%. In contrast, the spindle speed (56.09%) was the most influencing factor on the closeness coefficient value in the T4-treated Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloy. Moreover, the spindle speed and depth of cut were the least significant factors in the closeness coefficient value of the as-cast and the T4-treated Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloys, respectively. The feed rate is the most influencing parameter on the closeness coefficient value in both T6-treated samples, with a respective contribution of 37.49% and 54.35% as per the ANOVA results. In the same vein, it is observed that the depth of cut is the second most significant parameter in the closeness coefficient value, with a contribution of 30.21% and 13.14%, respectively. According to Shi et al., the feed rate (mm/rev) is the most significant factor in the gray relational grade during the dry milling of Mg AZ91D [15]. The machining performance can be influenced by other factors that were not accounted for in this study, as evidenced by the fact that the residual error in all conditions exceeds 20%.

Table 7.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) of closeness coefficient values of as-cast sample.

Table 8.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) of closeness coefficient values of T4-treated sample.

Table 9.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) of closeness coefficient values of T6-treated sample (200 °C for 16 h).

Table 10.
Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) of closeness coefficient values of T6-treated sample (225 °C for 8 h).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, the optimal combination of process parameters for the multiple objectives (lower surface roughness and cutting force values along with a higher MRR) in dry milling of different processed Mg-Gd-Y-Er alloys was determined using the TOPSIS, which is based on the Taguchi experimental design. The conclusions are summarized below.
- ❖
- According to the TOPSIS, the optimal conditions for the as-cast and the age-hardened samples (225 °C for 8 h) were achieved in experimental run 7. The best run for the T4-treated and the age-hardened samples (200 °C for 16 h) was determined to be run 9. Furthermore, after subjecting the as-cast and the age-hardened samples to 225 °C for 8 h, experiment 9 was shown to be the second best.
- ❖
- The TOPSIS converts the many objectives listed into a single response system and is evaluated using the closeness coefficient. The highest closeness coefficient value is achieved using a spindle speed ranging from 1000 to 1500 rpm, a feed rate of 150 mm/min, and a depth of cut between 0.5 mm and 1 mm.
- ❖
- The ANOVA result indicates that the depth of cut and the spindle speed are the most influential factors in both the as-cast and the T4-treated samples. The feed rate was the most crucial factor while analyzing the age-hardened samples. Additionally, the second most influential factor was the feed rate in the as-cast and the T4-treated samples.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R.A.; methodology, A.R.A. and S.S.; validation, S.S. and A.U.; formal analysis, S.S. and A.U.; investigation, A.R.A. and S.S.; resources, S.S.; data curation, A.U.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S. and A.U.; writing—review and editing, A.U., S.S. and A.R.A.; supervision, A.R.A.; funding acquisition, A.R.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be shared upon request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Baral, S.K.; Thawre, M.M.; Sunil, B.R.; Dumpala, R. A review on developing high-performance ZE41 magnesium alloy by using bulk deformation and surface modification methods. J. Magnes. Alloys 2023, 11, 776–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshith, M.; Seenuvasaperumal, P. Review on the effect of different processing techniques on the microstructure and mechanical behaviour of AZ31 Magnesium alloy. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1692–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiger, M.P.; Pietak, A.M.; Huadmai, J.; Dias, G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: A review. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 1728–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Yao, C.; Huang, X. Effect of cutting parameters on machinability characteristics in milling of magnesium alloy with carbide tool. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2016, 8, 168781401662839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobivel, K.; Sekar, K.V. Influence of cutting parameters on end milling of magnesium alloy AZ31B. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafapour, A.; Mohammadi, M.; Ebrahimpour, A. The Influence of Milling Parameters on Surface Properties in Milled AZ91C Magnesium Alloy. IJMSE 2021, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, N.; Batra, U.; Kumar, K. Experimental Investigation and Optimization of Wire Electrical Discharge Machining for Surface Characteristics and Corrosion Rate of Biodegradable Mg Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 4117–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirita, B.; Grigoras, C.; Tampu, C.; Herghelegiu, E. Analysis of cutting forces and surface quality during face milling of a magnesium alloy. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 591, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtowicz, N.; Danis, I.; Monies, F.; Lamesle, P.; Chieragati, R. The Influence of Cutting Conditions on Surface Integrity of a Wrought Magnesium Alloy. Procedia Eng. 2013, 63, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, A.; Nancharaiah, T.; Dumpala, R.; Sunil, B.R. Role of heat treatment on machining characteristics and surface roughness of AZ91 Mg alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Li, L.; Guo, G.; Zhu, X.; Meng, Y.; Chen, M. Milling machinability analysis of GW63K rare-earth magnesium alloys based on the concept of clean cutting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 9380–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, G.; Gupta, M.K.; Chen, M. Wear behavior of different coated tools in MQL-assisted milling of magnesium-based rare-earth alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 27, 1665–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, S.; Senthilkumar, V.; Asokan, P.; Arulkirubakaran, D. Effect of cryogenic cooling on machinability and surface quality of bio-degradable ZK60 Mg alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouini, N.; Ruslan, M.S.M.; Ghani, J.A.; Haron, C.H.C. Sustainable High-Speed Milling of Magnesium Alloy AZ91D in Dry and Cryogenic Conditions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, D.; Ren, J. Optimization of process parameters for surface roughness and microhardness in dry milling of magnesium alloy using Taguchi with grey relational analysis. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsana, S.; Radadia, N.; Sheth, M.; Sheth, N.; Savsani, V.; Prasad, N.E.; Ramprabhu, T. Machining parameter optimization for EDM machining of Mg–RE–Zn–Zr alloy using multi-objective Passing Vehicle Search algorithm. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Katyal, P.; Kumar, K. Effect of End Milling Process Parameters and Corrosion Behaviour of ZE41A Magnesium Alloy using Taguchi Based GRA. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Katyal, P.; Mandhania, S. Grey relational analysis based multiresponse optimization for WEDM of ZE41A magnesium alloy. Int. J. Lightweight Mater. Manuf. 2022, 5, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suneesh, E.; Sivapragash, M. Multi-response optimisation of micro-milling performance while machining a novel magnesium alloy and its alumina composites. Measurement 2021, 168, 108345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Du, B.; Liu, K.; Du, W. Microstructure and mechanical performance of Mg-Gd-Y-Nd-Zr alloys prepared via pre-annealing, hot extrusion and ageing. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantzsche, K.; Bohlen, J.; Wendt, J.; Kainer, K.U.; Yi, S.B.; Letzig, D. Effect of rare earth additions on microstructure and texture development of magnesium alloy sheets. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, N.; Barnett, M.R. The origin of “rare earth” texture development in extruded Mg-based alloys and its effect on tensile ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekumalla, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Almajid, A.; Gupta, M. Mechanical Properties of Magnesium-Rare Earth Alloy Systems: A Review. Metals 2014, 5, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, W.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, N. Enhanced strength and ductility of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys by secondary extrusion. J. Magnes. Alloys 2013, 1, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Qin, G.; Ren, Y.; Pei, W.; Chen, D.; Guo, Y. The maximum solubility of Y in α-Mg and composition ranges of Mg24Y5−x and Mg2Y1−x intermetallic phases in Mg–Y binary system. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M. Recent developments in high-strength Mg-RE-based alloys: Focusing on Mg-Gd and Mg-Y systems. J. Magnes. Alloys 2018, 6, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, N.; Lei, C. Study on solution and aging heat treatment of a super high strength cast Mg-7.8Gd-2.7Y-2.0Ag-0.4Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 849, 143523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Al-Samman, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg –2Gd –3Y –0.6Zr alloy upon conventional and hydrostatic extrusion. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ding, W.; Lindemann, J.; Leyens, C. Mechanical properties of the hot-rolled Mg–12Gd–3Y magnesium alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 118, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, W.; Song, X.; Zhang, P.; Ding, W.; Korsunsky, A. Influence of heat treatment on fatigue behaviour of high-strength Mg–10Gd–3Y alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6053–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, V.; Ceschini, L.; Morri, A.; Apelian, D. Influence of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Rare Earth-Rich Magnesium Alloy. Int. J. Met. 2017, 11, 382–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Fu, P.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W. Development of high strength sand cast Mg–Gd–Zn alloy by co-precipitation of the prismatic β′ and β1 phases. Mater. Charact. 2019, 153, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varatharajulu, M.; Duraiselvam, M.; Pradeep, G.K.; Jagadeesh, B. Tool temperature thermographic study on end milling magnesium AZ31 using carbide tool. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 295, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, G.; Muthu, S.; Devadasan, S.R. Prediction of surface roughness of end milling operation using genetic algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 77, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.S.K.; Rao, P.V. Selection of an optimal parametric combination for achieving a better surface finish in dry milling using genetic algorithms. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 28, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narooei, K.D.; Ramli, R. Optimal Selection of Cutting Parameters for Surface Roughness in Milling Machining of AA6061-T6. Int. J. Eng. 2022, 35, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahshoor, M.; Guo, Y.B. Surface integrity of biodegradable orthopedic magnesium–calcium alloy by high-speed dry face milling. Prod. Eng. 2011, 5, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premnath, A.A.; Alwarsamy, T.; Rajmohan, T. Experimental Investigation and Optimization of Process Parameters in Milling of Hybrid Metal Matrix Composites. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2012, 27, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).