Characterization of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel by Cold Rolled and Machining vs. DMLS Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
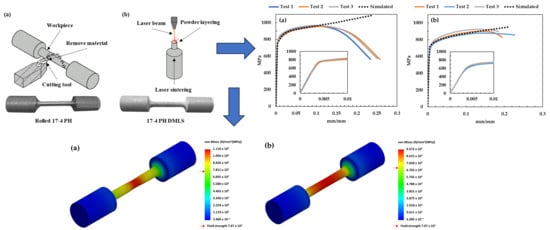
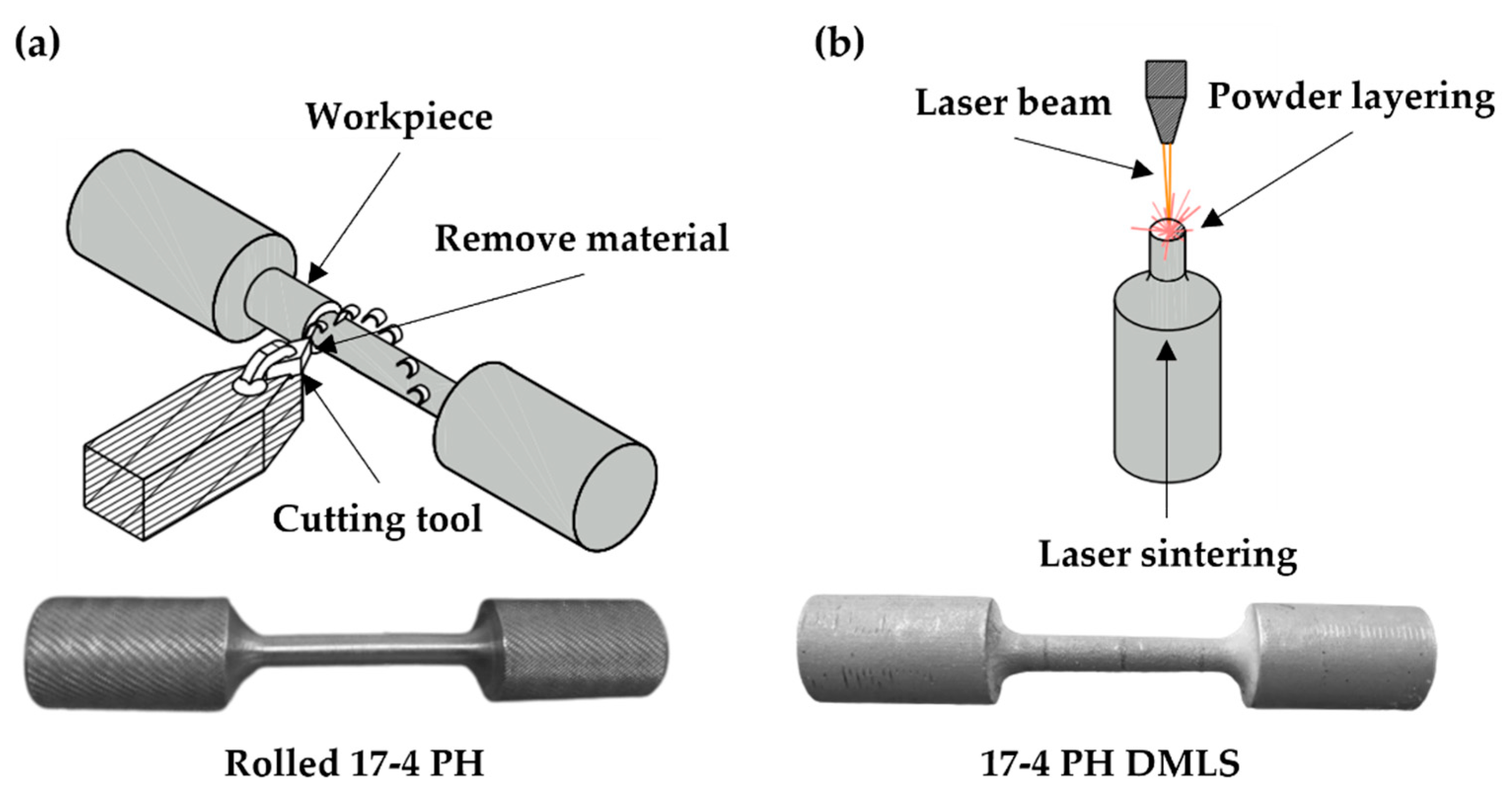
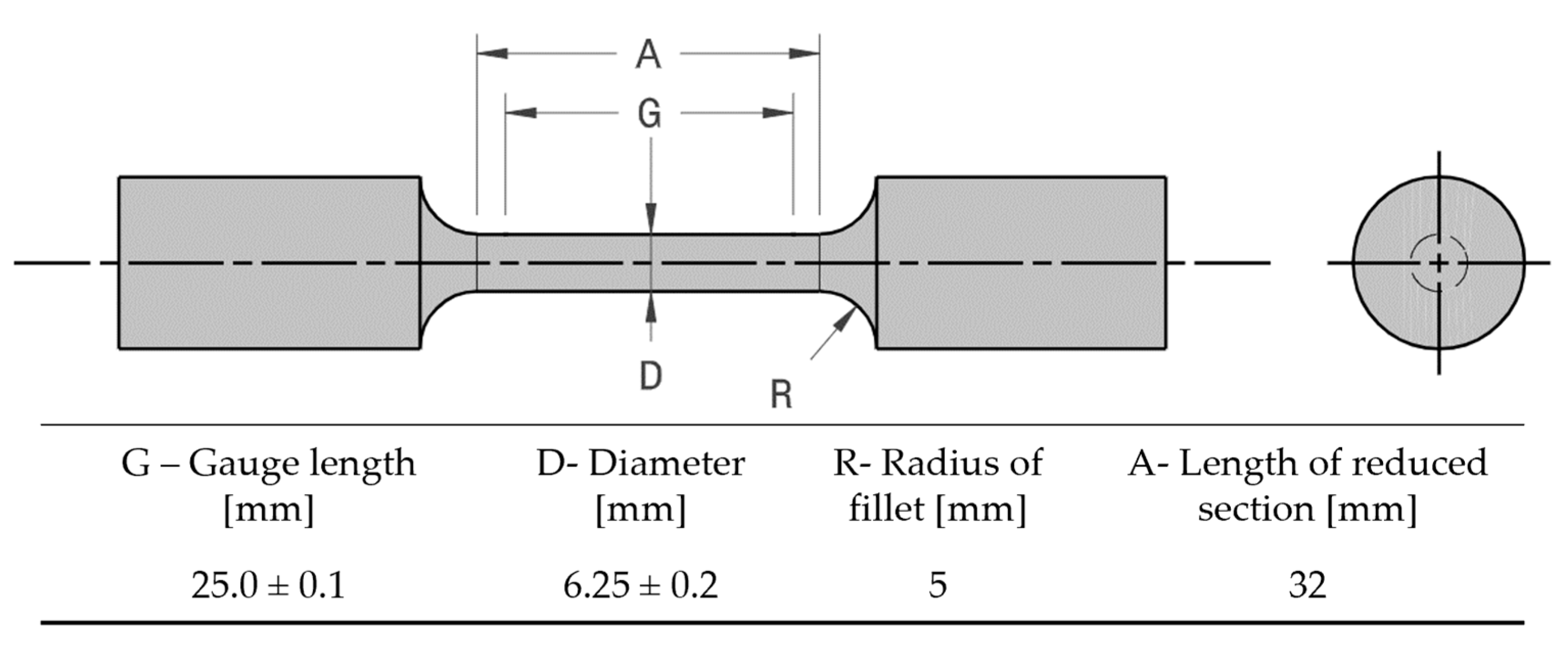
2. Materials and Methods
Experimental Procedure
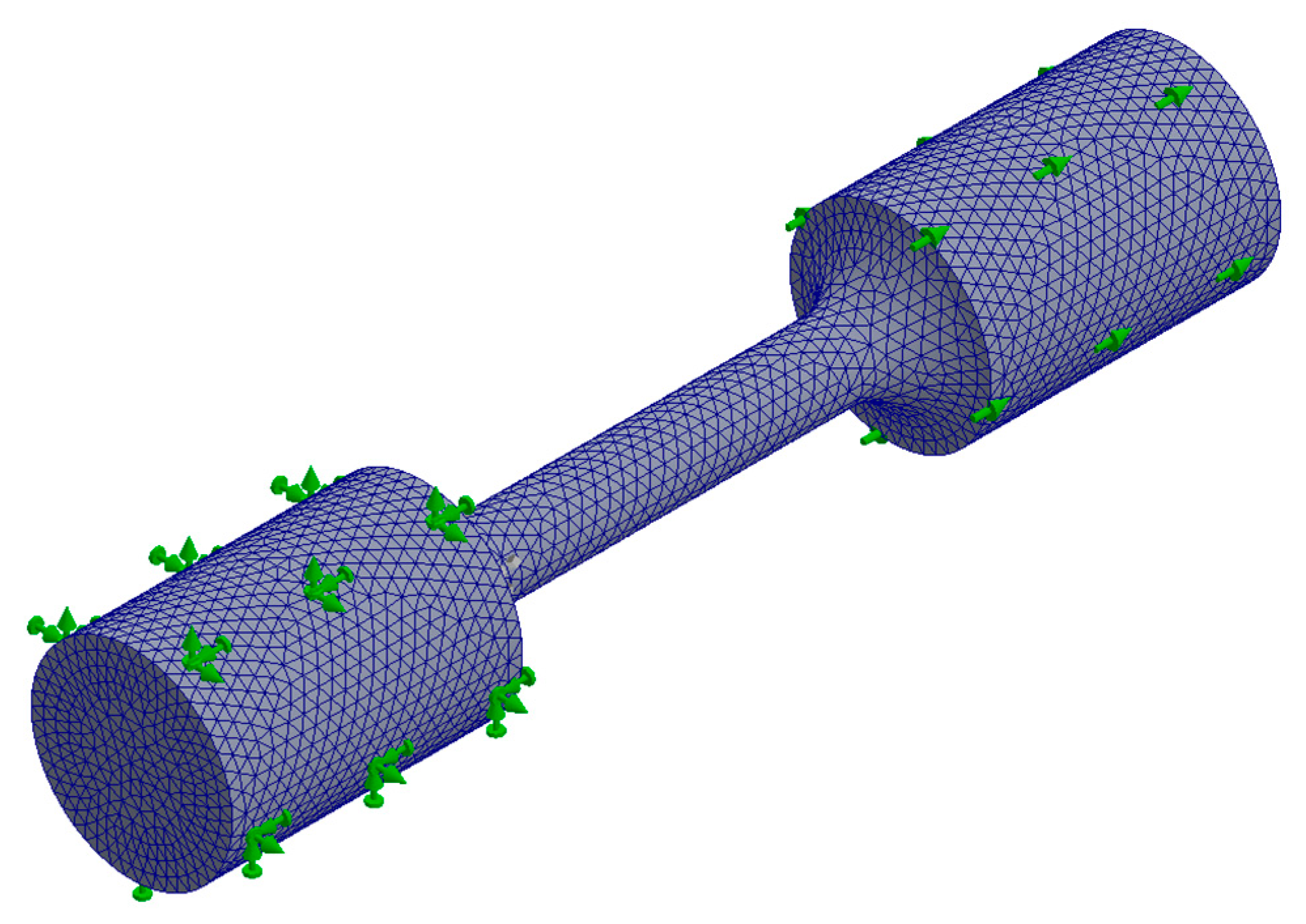
3. Simulation Configuration
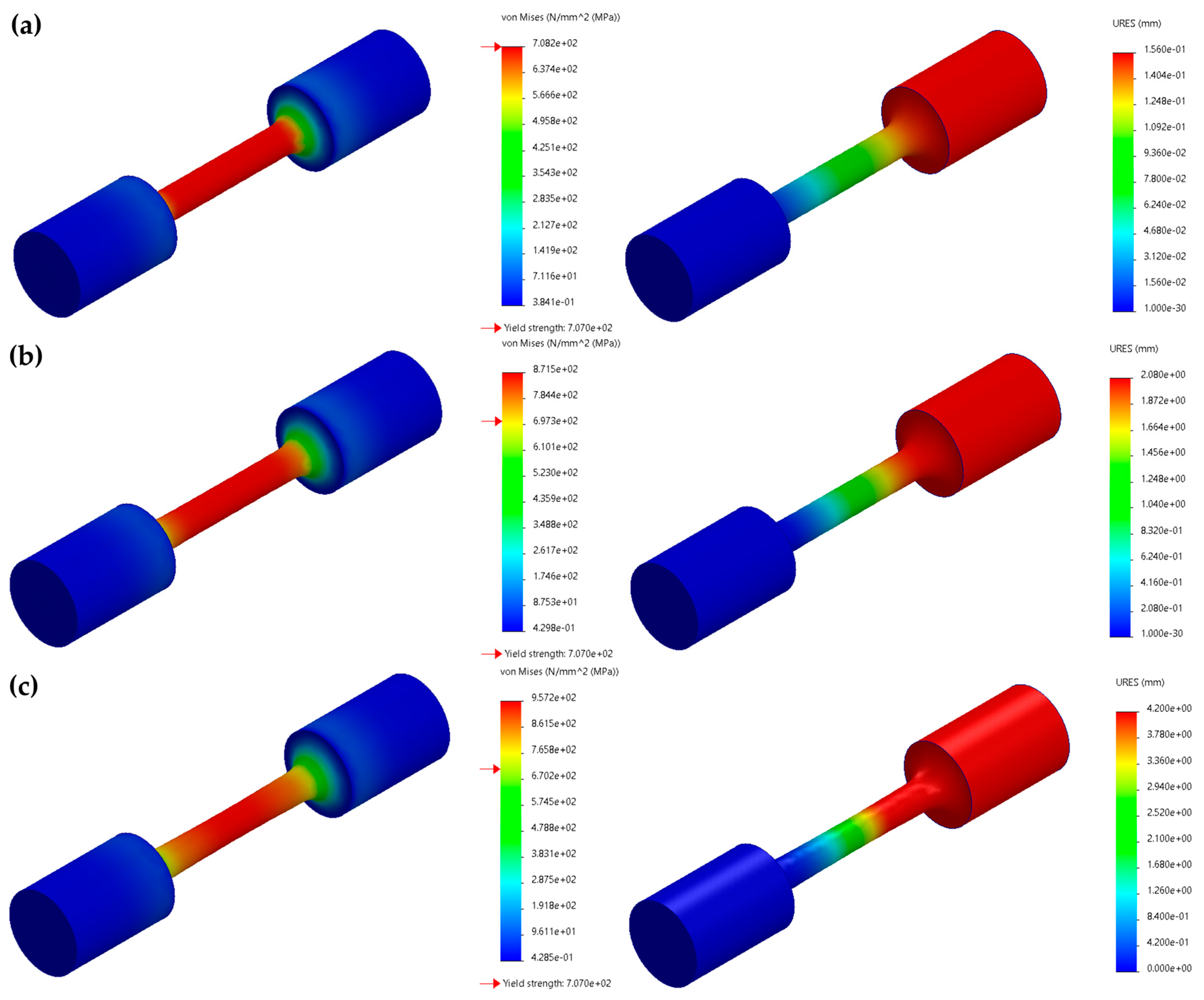
Numerical Simulation by Finite Element Method
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Microstructural Characterization
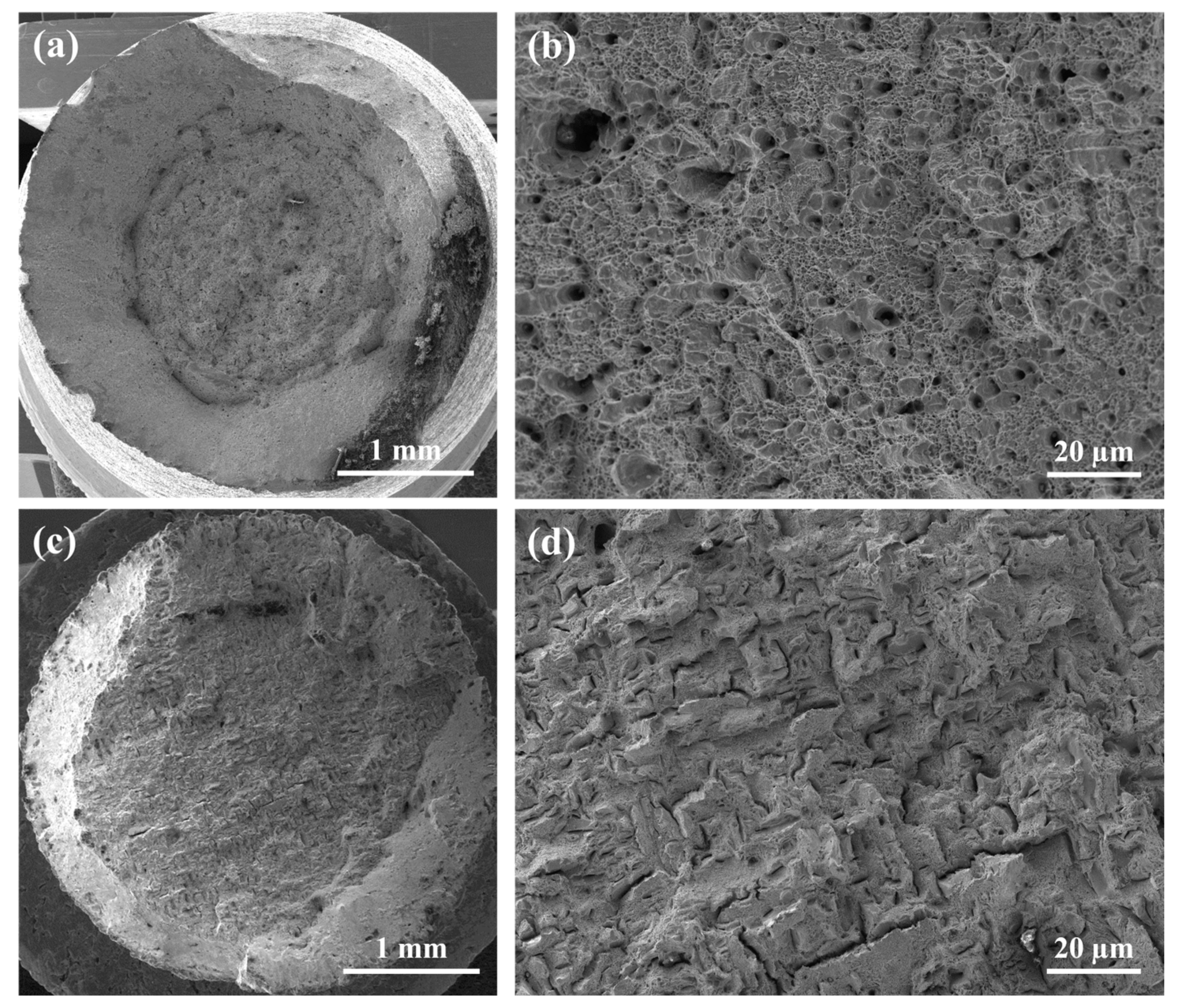
4.2. Experimental Characterization of Mechanical Properties
5. Conclusions
- The rolled 17-4 PH stainless steel microstructure showed the typical martensitic structure for the longitudinal and transversal cross-sections. The microstructure for 17-4 PH DMLS stainless steel reveals the layers or levels of melting of the steel powder due to the laser process, characterized by complex directional columnar structures parallel to the DMLS build direction.
- Diffraction XRD patterns for rolled 17-4 PH stainless steel present ferritic (α) and austenitic (γ) phases. The XRD patterns for 17-4 PH DMLS stainless steel show the presence of both ferritic (α) or martensitic and austenitic (γ) phases.
- The mechanical properties obtained from the simple tension test decreased by 17% for the elastic modulus, 7.8% for the yield strength, and 7% ultimate strength for 17-4 PH DMLS compared with rolled 17-4 PH stainless steel.
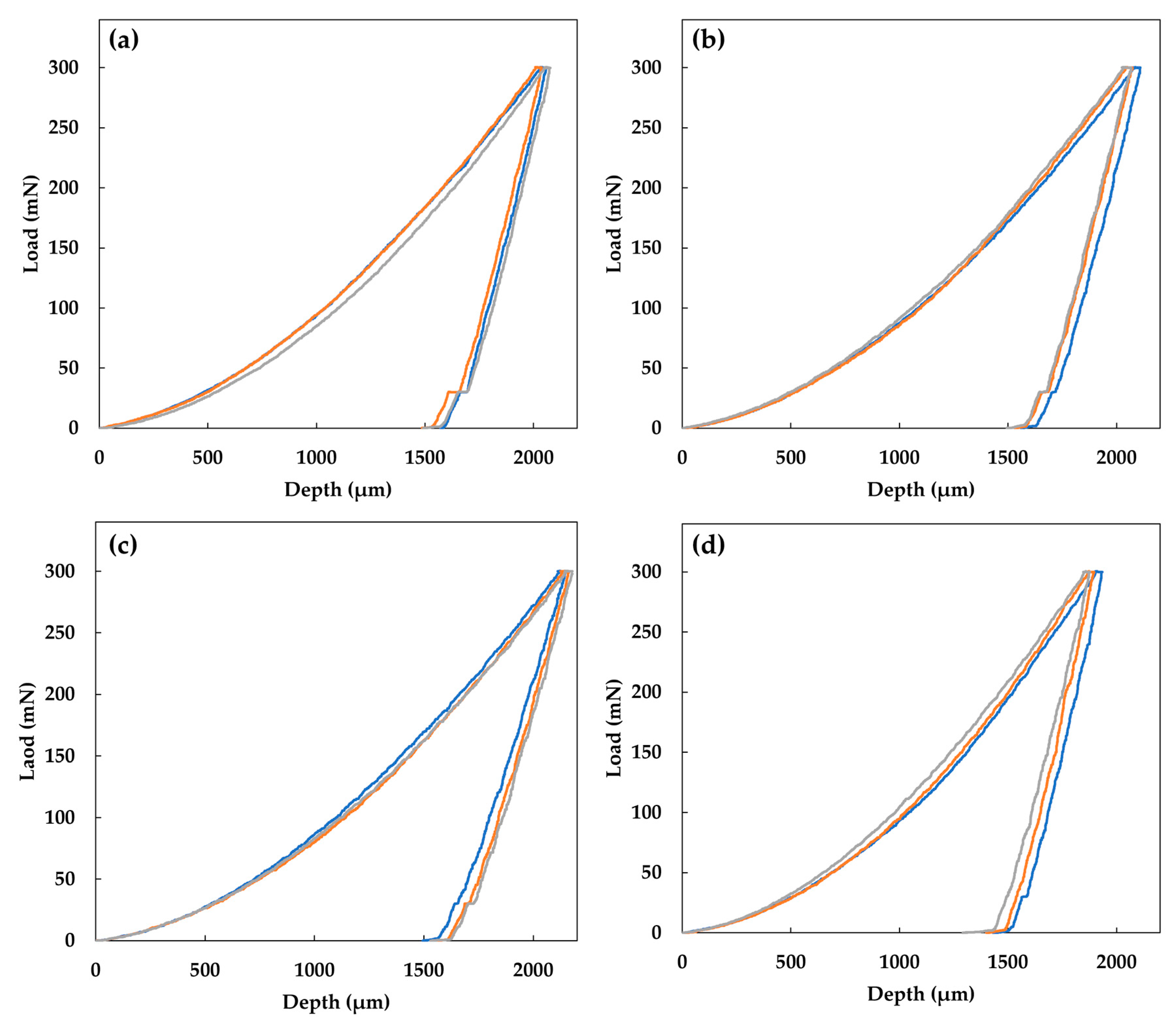
- The nanoindentation results of mechanical properties analyzed for rolled 17-4 PH showed similar values for the longitudinal and transversal cross-sections. Meanwhile, the properties of 17-4 PH DMLS stainless steel samples presented an anisotropic behavior with a variation in the elastic modulus as result of the superposition of the DMLS layers.
- According to the experimental and simulated tests, the DMLS 17-4 PH compared with rolled 17-4 PH stainless steel samples decreased the yield strength by ~8% and the ultimate strength by ~11%. This mechanical behavior could be attributed to defects in the DMLS process, such as defects due to unfused voids and porosity.
- The fracture morphology of the surface of rolled 17-4 PH stainless steel presented the typical cone shape fracture, showing a ductile fracture mode that is characterized by the presence of large quantities of fine dimples. The fracture surface of 17-4 PH DMLS stainless steel samples showed elongated defects in the fracture surfaces associated with partially fragile fracture mode and some defects due to unfused voids. Also, the laser sintering process causes a decrease in strength and plasticity, resulting in the material’s brittle behavior.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirmahdi, E. Defects in Turbine Impeller Blades with Non-destructive Testing: Modeling, Ultrasonic Waves, Defect Analysis. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. C. 2021, 102, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Rajabi, M.; Yousefi, M.; Sadegh, M.; Kerahroodi, A. Failure Analysis of a 17-4PH Stainless Steel Part in an Exhaust Fastener. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2021, 21, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamovic, D.; Ristic, B.; Zivic, F. Review of Existing Biomaterials-Method of Material Selection for Specific Applications in Orthopedics. In Biomaterials in Clinical Practice; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 47–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.L.S.; Dlegel, O.; Xu, X. Bonding integrity of hybrid 18Ni300-17-4 PH steel using the laser powder bed fusion process for the fabrication of plastic injection mould inserts. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 4963–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, R.; Ma, Y.; Wu, D. Nonlinear sealing force of a seawater balance valve used in an 11,000-meter manned submersible. Front. Mech. Eng. 2023, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vunnam, S.; Saboo, A.; Sudbrack, C.; Starr, T. Effect of powder chemical composition on the as-built microstructure of 17-4 PH stainless steel processed by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 30, 100876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Chi, C.T.; Wang, W.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, M.S.; Chen, X.G.; Chen, Z.H.; Cheng, X.P.; Xie, Y.J. The effects of fabrication atmosphere condition on the microstructural and mechanical properties of laser direct manufactured stainless steel 17-4 PH. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabooni, S.; Chabok, A.; Feng, S.C.; Blaauw, H.; Pijper, T.C.; Yang, H.J.; Pei, Y.T. Laser powder bed fusion of 17–4 PH stainless steel: A comparative study on the effect of heat treatment on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.; Jalalahmadi, B.; Ashtekar, A.; Jiang, Y. Cyclic deformation and fatigue behavior of additively manufactured 17–4PH stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, I.; Eshkabilov, S.; Azarmi, F.; Sevostianov, I.; Tangpong, X.W. Investigation on elastic properties and unconventional plasticity of 316L stainless steel processed by selective laser melting technology. Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 7, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luecke, W.E.; Slotwinski, J.A. Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel Made by Additive Manufacturing. J. Res. Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. 2014, 119, 398–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon, S.M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, T.B.; Lee, S.H.; Jun, T.S.; Son, Y.; Choi, K. Normalizing Effect of Heat Treatment Processing on 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Manufactured by Powder Bed Fusion. Metals 2022, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KC, S.; Nezhadfar, P.D.; Phillips, C.; Kennedy, M.S.; Shamsaei, N.; Jackson, R.L. Tribological behavior of 17–4PH stainless steel fabricated by traditional manufacturing and laser-based additive manufacturing methods. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, T.; Karagoz, T.; Kurama, S.; Sezer, P.; Yazici, O.F.; Ozkok, R. Laser metal deposition of 17–4 PH stainless steel: Geometrical, microstructural, and mechanical properties investigation for structural applications. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 41, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Cashell, K.A.; Anguilano, L. Post-fire Structural Properties of Hot-Rolled and Cold-Rolled Duplex Stainless Steel Reinforcing Bar. Fire Technol. 2022, 58, 2283–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, L.; Li, L.; Yue, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, C. Finite element simulation for straightedge lineal roll forming process of high frequency welding pipe. Int. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2023, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, I.; Das, P.; Bhattacharjee, D.; Datta, S. In Search of the Attributes Responsible for Sliver Formation in Cold Rolled Steel Sheets. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D. 2017, 98, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.I.; Na, L.I.; Xing, P.; Xiang, L.U.; Ji, L.I. Fatigue Property of Hot Rolled and Cold Rolled Strips. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2013, 20, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, P.; Aggarwal, S.; Banthia, N.; Singh, U.S.; Kalia, A.; Pesin, A. A comprehensive review on incremental deformation in rolling processes. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2022, 69, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzehi, S.; Mirzadeh, H. Cold unidirectional/cross-rolling of austenitic stainless steels: A review. Arch. Civ. Mech. 2022, 22, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikumapayi, O.M.; Akinlabi, E.T.; Onu, P.; Abolusoro, O.P. Rolling operation in metal forming: Process and principles—A brief study. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 26, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Leu, M.C. Additive manufacturing: Technology, applications and research needs. Front. Mech. Eng. 2013, 8, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoward, J.E.; Gupta, N.; Lehmhus, D. Additive Manufacturing of Composites and Complex Materials. JOM 2018, 70, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everton, S.K.; Hirsch, M.; Stravroulakis, P.; Leach, R.K.; Clare, A.T. Review of in-situ process monitoring and in-situ metrology for metal additive manufacturing. Mater. Des. 2016, 95, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.S.; Shukla, M.; Kumar, A. 3D thermal simulation of powder bed fusion additive manufacturing of stainless steel. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2023, 17, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Basu, D.; Meyer, J.L.L.; Larson, E.; Kuo, R.; Beuth, J.; Rollett, A. Study of Powder Gas Entrapment and Its Effects on Porosity in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Parts Fabricated in Laser Powder Bed Fusion. JOM 2021, 73, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, T.A.M.; Sahlaoui, H.; Mabrouki, T.; Sallem, H.; Rech, J. Selective Laser Melting of Stainless-Steel: A Review of Process, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Post-Processing treatments. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2023, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatões, D.; Alves, R.; Alves, B.; Vieira, M.T. Selective Laser Melting and Mechanical Properties of Stainless Steels. Materials 2022, 15, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Du, W.; Bai, P.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, X. Microstructure and Properties of Porous 17-4PH Stainless Steel Prepared by Selective Laser Melting. Trans. Indian. Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadfar, P.D.; Gradl, P.R.; Shao, S.; Shamsaei, N. Microstructure and Deformation Behavior of Additively Manufactured 17–4 Stainless Steel: Laser Powder Bed Fusion vs. Laser Powder Directed Energy Deposition. JOM 2022, 74, 1136–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akessa, A.D.; Tucho, W.M.; Lemu, H.G.; Grønsund, J. Investigations of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH ss Printed Using a MarkForged Metal, X. Materials 2022, 15, 6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, H.K.; Pal, D.; Patil, N.; Starr, T.L.; Stucker, B.E. Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of 17-4 Precipitation Hardenable Steel Processed by Selective Laser Melting. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 4421–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.C.; Morales, M.A.; Cole, D.P.; Shumeyko, C.M.; Riddick, J.C. Mechanical Behavior of 17-4 PH stainless steel processed by atomic diffusion additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 114, 2103–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadollahi, A.; Shamsaei, N.; Thompson, S.M.; Elwany, A.; Bian, L. Mechanical and microstructural properties of selective laser melted 17-4 PH stainless steel. In Proceedings of the ASME international mechanical engineering congress and exposition. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, Houston, TX, USA, 13–19 November 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, I.; Garciandía, F.; Zubiri, F.; Zapirain, F.; Esnaola, A. Study of mechanical properties of AISI 316 stainless steel processed by “selective laser melting”, following different manufacturing strategies. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 51, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwanpreecha, C.; Seensattayawong, P.; Vadhanakovint, V.; Manonukul, A. Influence of Specimen Layout on 17-4PH (AISI 630) Alloys Fabricated by Low-Cost Additive Manufacturing. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. 2021, 52, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedziora, S.; Decker, T.; Museyibov, E.; Morbach, J.; Hohmann, S.; Huwer, A.; Wahl, M. Strength Properties of 316L and 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Produced with Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2022, 15, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Elwany, A.; Yadollahi, A.; Thompson, S.M.; Bian, L.; Shamsaei, N. Mechanical properties and microstructural characterization of selective laser melted17-4 PH stainless steel. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2017, 23, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkindi, T.; Alyammahi, M.; Susantyoko, R.A.; Atatreh, S. The effect of varying specimens’ printing angles to the bed surface on the tensile strength of 3D-printed 17-4PH stainless-steels via metal FFF additive manufacturing. MRS Commun. 2021, 11, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakshah, M.G.; Eslami, A.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Berenjkoub, A. Effect of Heat Treatment on Corrosion, Fatigue, and Corrosion Fatigue Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 32, 6610–6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadfar, P.D.; Shrestha, R.; Phan, N.; Shamsaei, N. Fatigue behavior of additively manufactured 17-4 PH stainless steel: Synergistic effects of surface roughness and heat treatment. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 124, 188–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, D.; Vogel, L.; Fischer, A. The effects of sintering temperature and hold time on densification, mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics of binder jet 3D printed 17-4 PH stainless steel. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, H.; Lewis, B.; Styman, P. Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties of Precipitation-Hardened Martensitic Steel 17-4PH using Small and Shear Punch Testing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 4206–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Du, W.; Yao, D. Influence of powder particle size distribution on microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel fabricated by selective laser Melting. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 25, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, Z.; Tseng, C.; Hwang, K. Microstructures, Mechanical Properties, and Fracture Behaviors of Metal-Injection Molded 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2015, 21, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguste, P.; Mauduit, A.; Fouquet, L.; Pillot, S. Study on 17-4 PH stainless steel produced by selective laser melting. Sci. Bull. B Chem. Mater. Sci. UPB. 2018, 80, 197–210. [Google Scholar]
- El Moghazi, S.N.; Wolfe, T.; Ivey, D.G.; Henein, H. Plasma transfer arc additive manufacturing of 17-4 PH: Assessment of defects. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, I.K.; Selvaraj, N.; Kumar, A. Parametric investigation and characterization of 17-4 PH stainless steel parts fabricated by selective laser melting. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2023, 30, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikeya, I.; Selvraj, N.; Kumar, A. A Review on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of L-PBF 17-4PH and 15-5PH SS. In Recent Advances in Manufacturing Processes and Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Zhao, X.; Li, S.; Han, C.; Wei, Q.; Wen, S.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y. Differences in microstructure and properties between selective laser melting and traditional manufacturing for fabrication of metal parts: A review. Front. Mech. Eng. 2015, 10, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porro, M.; Zhang, B.; Parmar, A.; Shin, Y. Data Driven Modeling of Mechanical Properties for 17 4 PH Stainless Steel Built by Additive Manufacturing. Integr. Mater. Manuf. Innov. 2022, 11, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promsuwan, P.; Tongsri, R.; Kowitwarangkul, P.; Ninpetch, P.; Threrujirapapong, T. Investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steels fabricated by materials extrusion additive manufacturing. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 45, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wie, J.; London, T.; Griffiths, D.; Bhamji, I.; Oancea, V. Estimates of the mechanical properties of laser powder bed fusion Ti-6Al-4V parts using finite element models. Mater. Des. 2019, 169, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A370-03a; Standard Test Methods and Definitions for Mechanical Testing of Steel Products. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PN, USA, 2017.
- Leo, P.; D’Ostuni, S.; Perulli, P.; Sastre, M.A.C.; Fernández-Abia, A.I.; Barreiro, J. Analysis of microstructure and defects in 17-4 PH stainless steel sample manufactured by Selective Laser Melting. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 41, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aripin, M.A.; Sajuri, Z.; Jamadon, N.H.; Baghdadi, A.H.; Syarif, J.; Mohamed, I.F.; Aziz, A.M. Effects of Build Orientations on Microstructure Evolution, Porosity Formation, and Mechanical Performance of Selective Laser Melted 17-4 PH Stainless Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. Nanoindentation, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mazeran, P.-E.; Beyaoui, M.; Bigerelle, M.; Guigon, M. Determination of mechanical properties by nanoindentation in the case of viscous materials. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 103, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, L.A.; Dong, H.; Li, X.-Y.; Pindeo, C.E.; Tschiptschin, P.A. Scratch test of active screen low temperature plasma nitrided AISI 410 martensitic stainless steel. Wear 2017, 376–377, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, V.; Giannella, V.; Caiazzo, F.; Sepe, R. Influence of position and building orientation on the static properties of LPBF specimens in 17-4 PH stainless steel. Forces Mech. 2022, 8, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
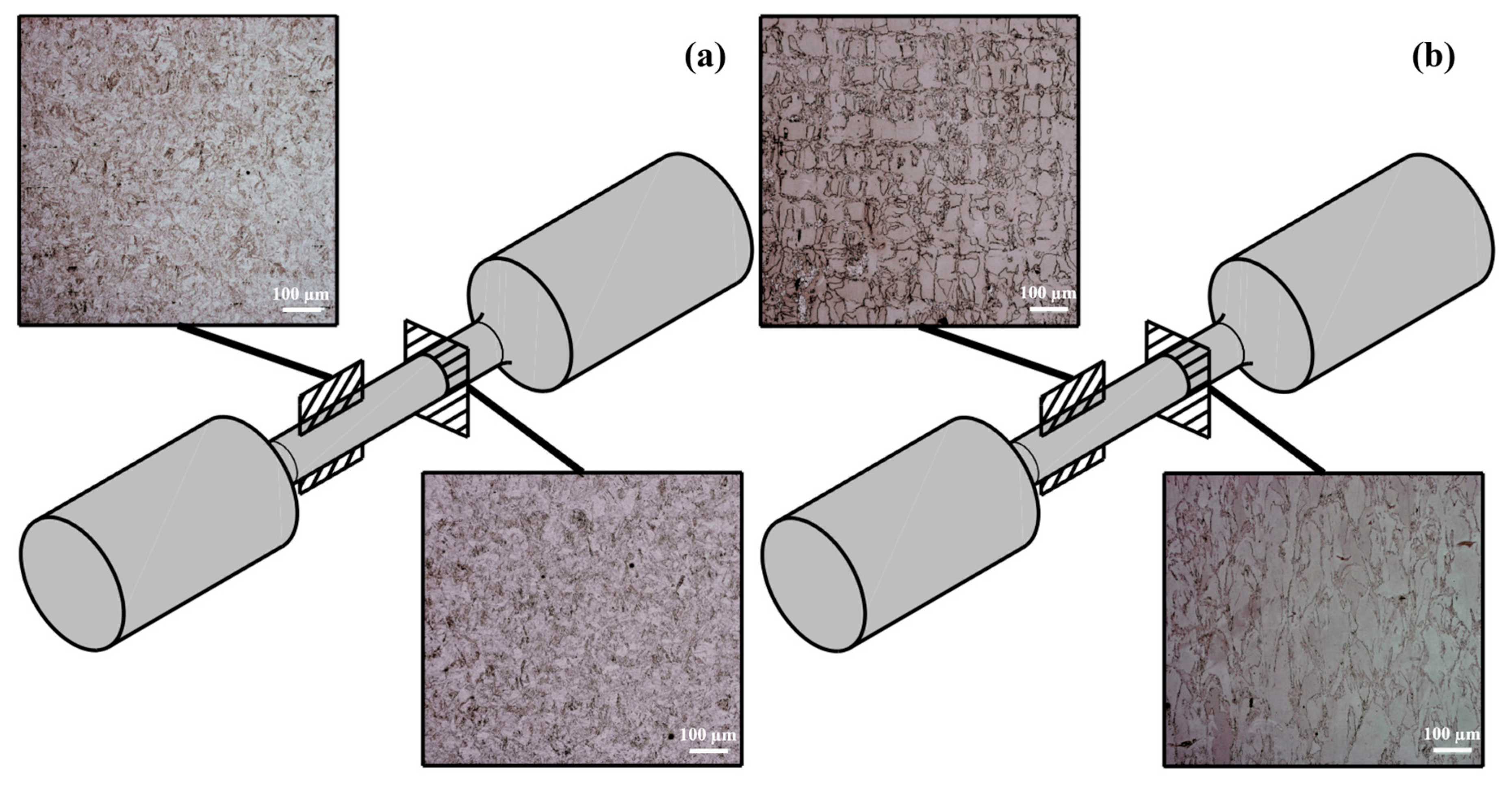
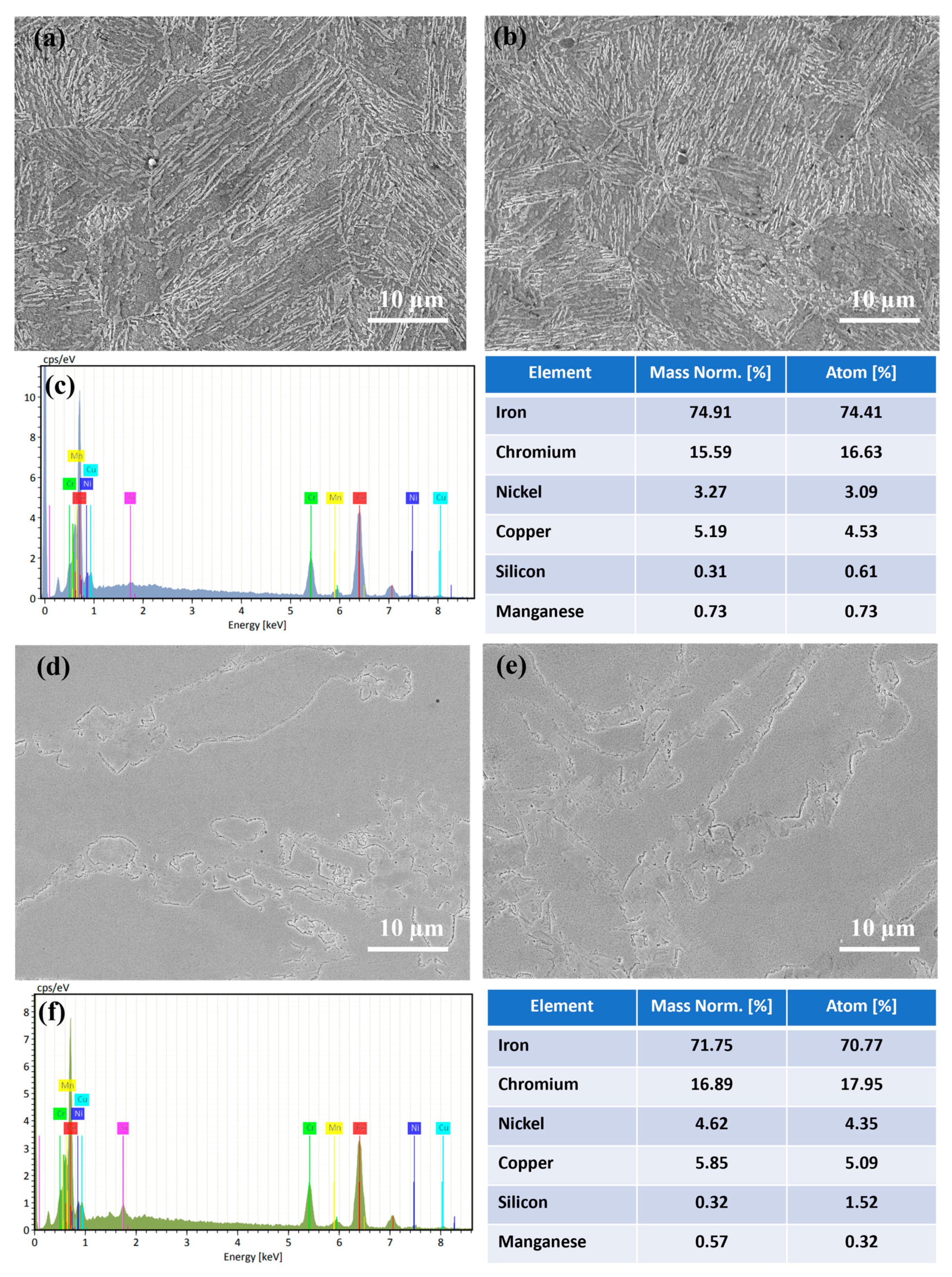

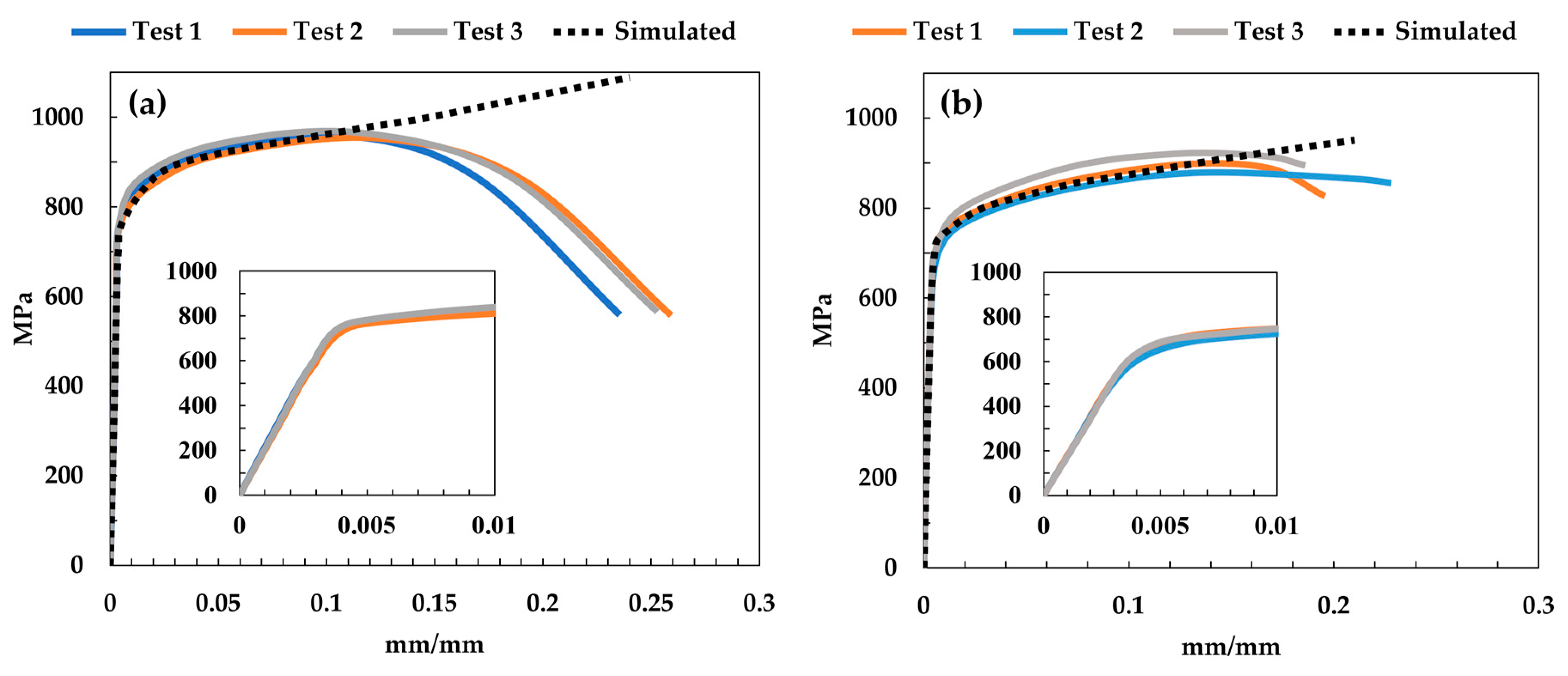

| Element | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mn | Nb | C | Si | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolled 17-4 PH | 15–17.5 | 3–5 | 3–5 | 1 | 0.15–0.45 | 0.07 | 1 | Bal. |
| 17-4 PH DMLS | 15–17.5 | 3–5 | 3–5 | 1 | 0.15–0.45 | 0.07 | 1 | Bal. |
| Property | Rolled 17-4 PH | 17-4 PH DMLS |
|---|---|---|
| Elastic modulus (E) GPa | 200 ± 1.8 | 166 ± 4.1 |
| Yield strength YS ( MPa | 767 ± 6.4 | 707 ± 13.3 |
| Ultimate strength UTS ( MPa | 965 ± 9.2 | 897 ± 22.9 |
| Elongation % | 21.2 ± 0.7 | 16.8 ± 0.4 |
| Hardness (HV0.1) | 298 ± 3.8 | 312 ± 8.76 |
| Sample | Depth (nm) | E (GPa) | H (GPa) | S (N/m) | Ke (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rolled 17-4 PH-L | 2056 ± 18.87 | 187 ± 14.8 | 2.93 ± 0.09 | 147.3 ± 2.2 | 22.38 ± 28.30 |
| Rolled 17-4 PH-T | 2083 ± 21.79 | 189 ± 12.4 | 2.91 ± 0.13 | 145.9 ± 1.7 | 22.23 ± 29.62 |
| 17-4 PH DMLS-L | 2128 ± 21.79 | 144 ± 16.1 | 2.84 ± 0.26 | 142.5 ± 5.1 | 25.08 ± 30.56 |
| 17-4 PH DMLS-T | 1901 ± 29.56 | 171 ± 13.3 | 3.01 ± 0.13 | 159.8 ± 2.2 | 28.50 ± 38.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-Garibaldi, P.; Alvarez-Vera, M.; Beltrán-Fernández, J.A.; Carrera-Espinoza, R.; Hdz-García, H.M.; Díaz-Guillen, J.C.; Muñoz-Arroyo, R.; Ortega, J.A.; Molenda, P. Characterization of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel by Cold Rolled and Machining vs. DMLS Additive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8020048
Moreno-Garibaldi P, Alvarez-Vera M, Beltrán-Fernández JA, Carrera-Espinoza R, Hdz-García HM, Díaz-Guillen JC, Muñoz-Arroyo R, Ortega JA, Molenda P. Characterization of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel by Cold Rolled and Machining vs. DMLS Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2024; 8(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-Garibaldi, Pablo, Melvyn Alvarez-Vera, Juan Alfonso Beltrán-Fernández, Rafael Carrera-Espinoza, Héctor Manuel Hdz-García, J. C. Díaz-Guillen, Rita Muñoz-Arroyo, Javier A. Ortega, and Paul Molenda. 2024. "Characterization of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel by Cold Rolled and Machining vs. DMLS Additive Manufacturing" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 8, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8020048
APA StyleMoreno-Garibaldi, P., Alvarez-Vera, M., Beltrán-Fernández, J. A., Carrera-Espinoza, R., Hdz-García, H. M., Díaz-Guillen, J. C., Muñoz-Arroyo, R., Ortega, J. A., & Molenda, P. (2024). Characterization of Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel by Cold Rolled and Machining vs. DMLS Additive Manufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 8(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp8020048