Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of Al-6063 to Steel Alloy UNS S32304 †
Abstract
1. Introduction
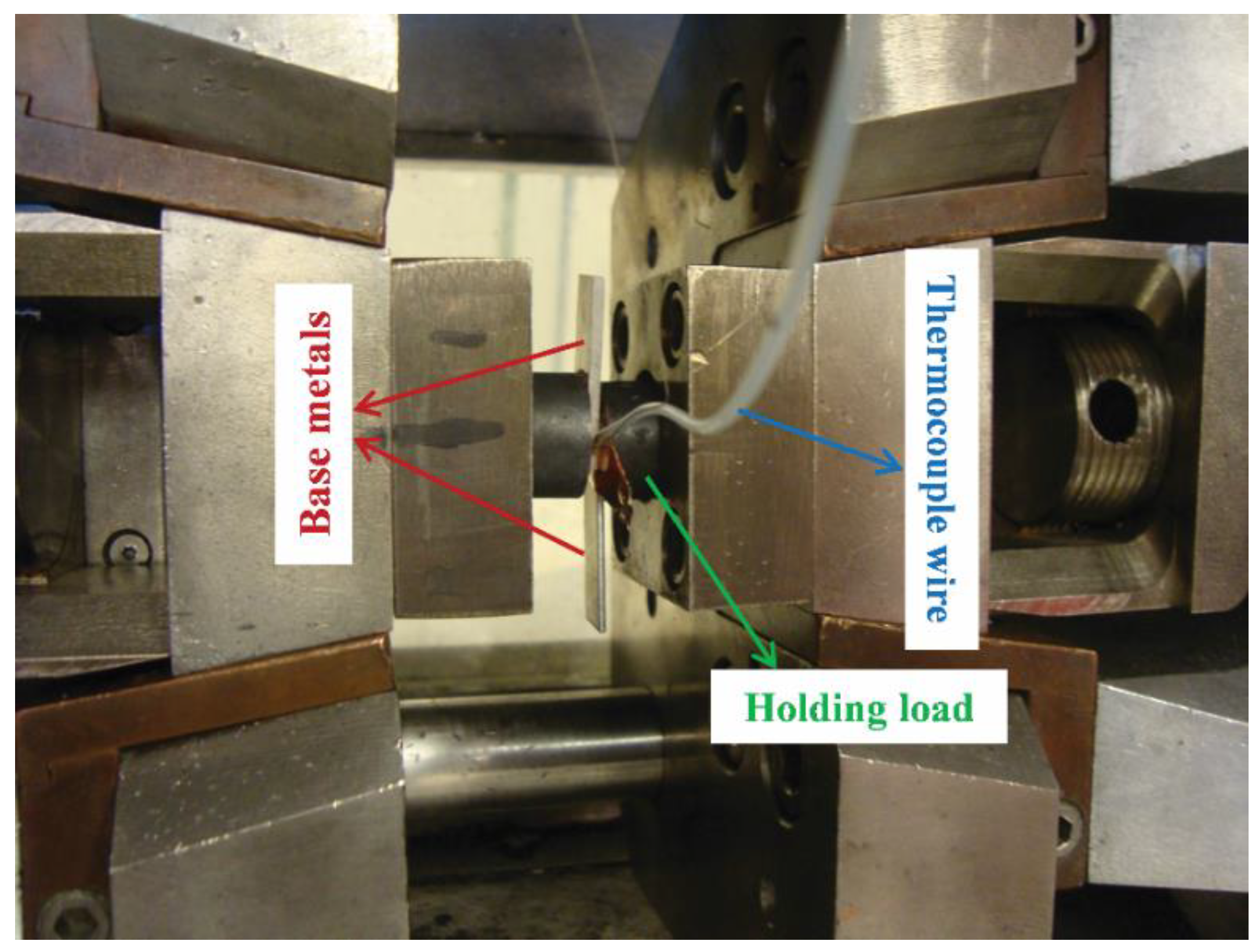
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
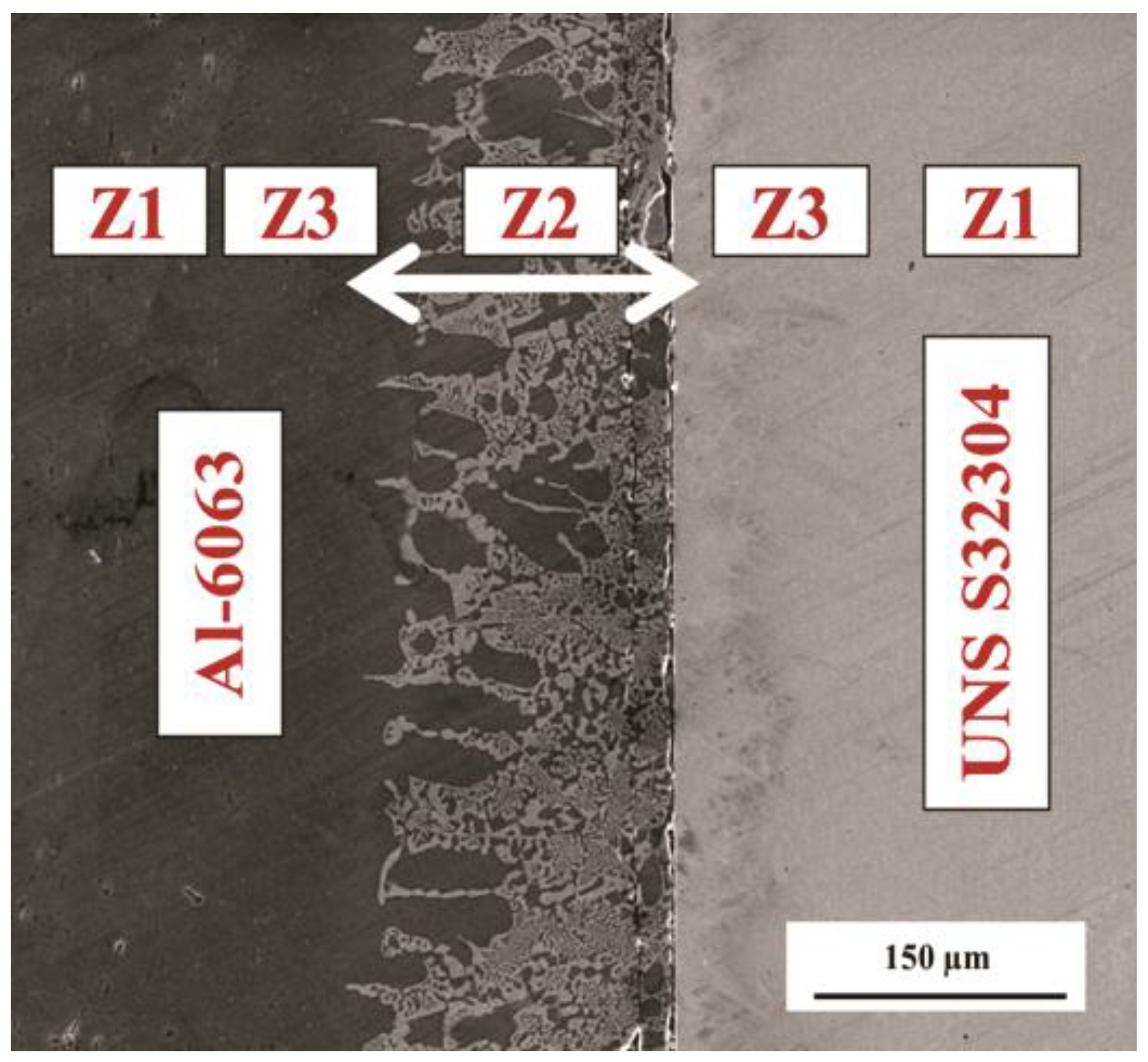
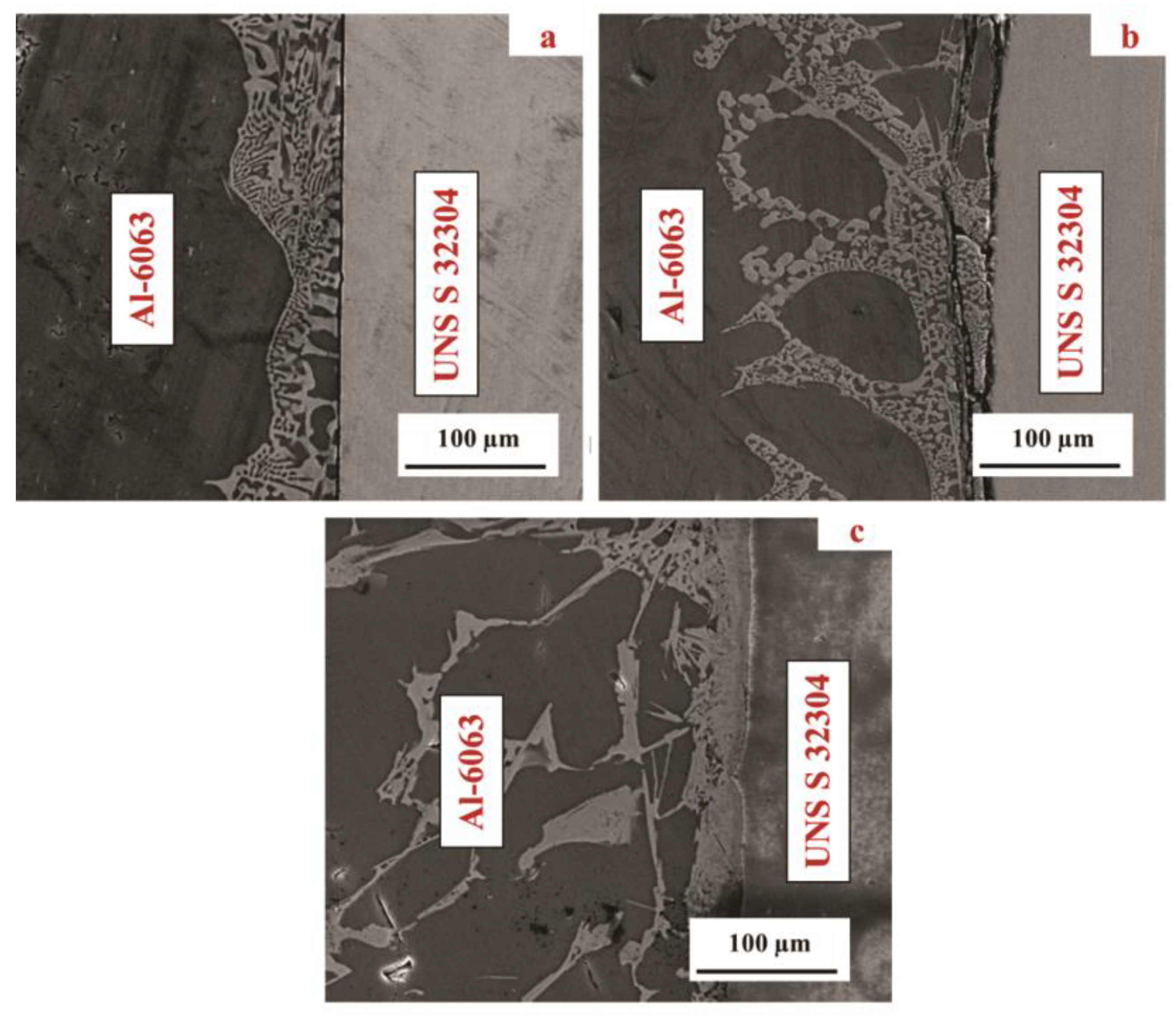
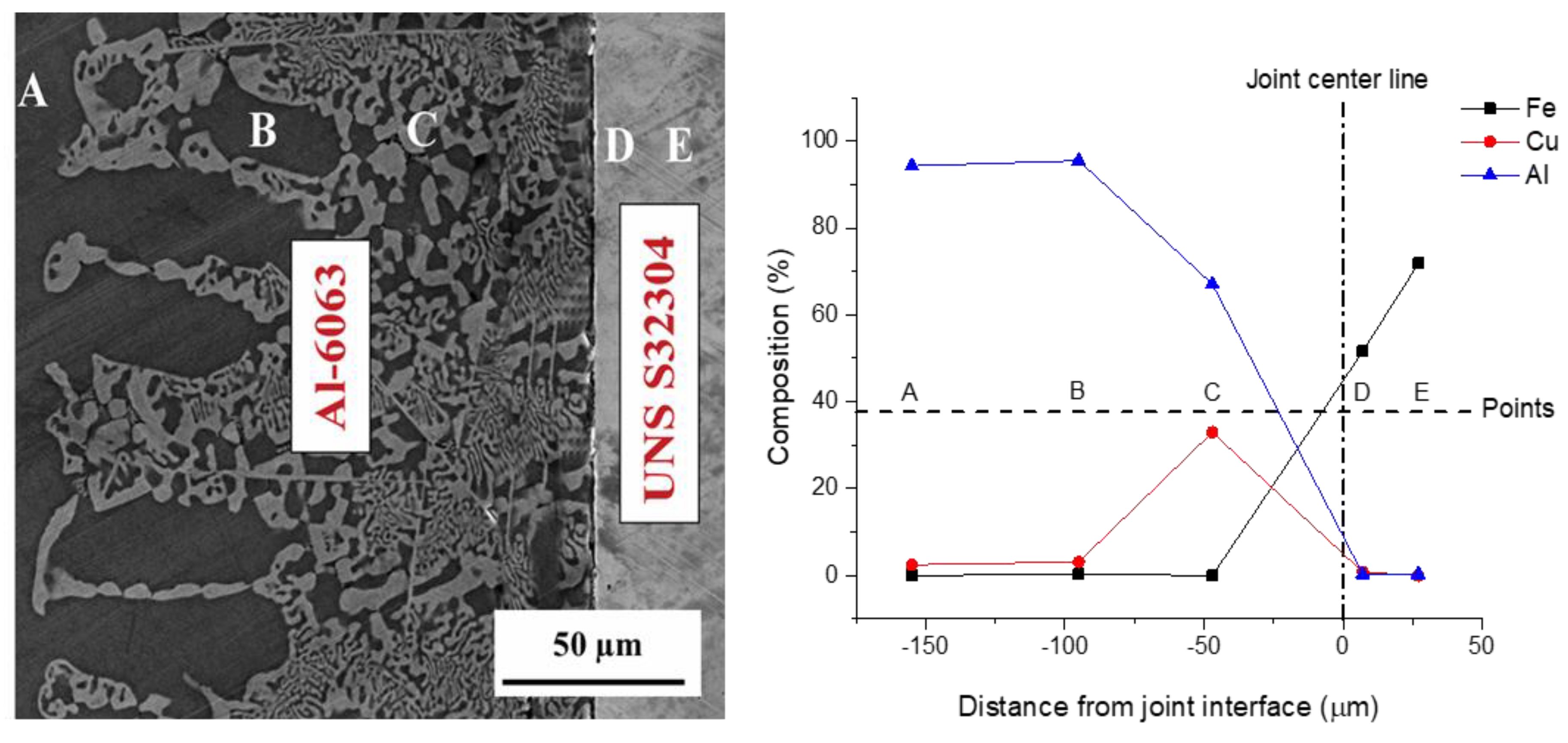
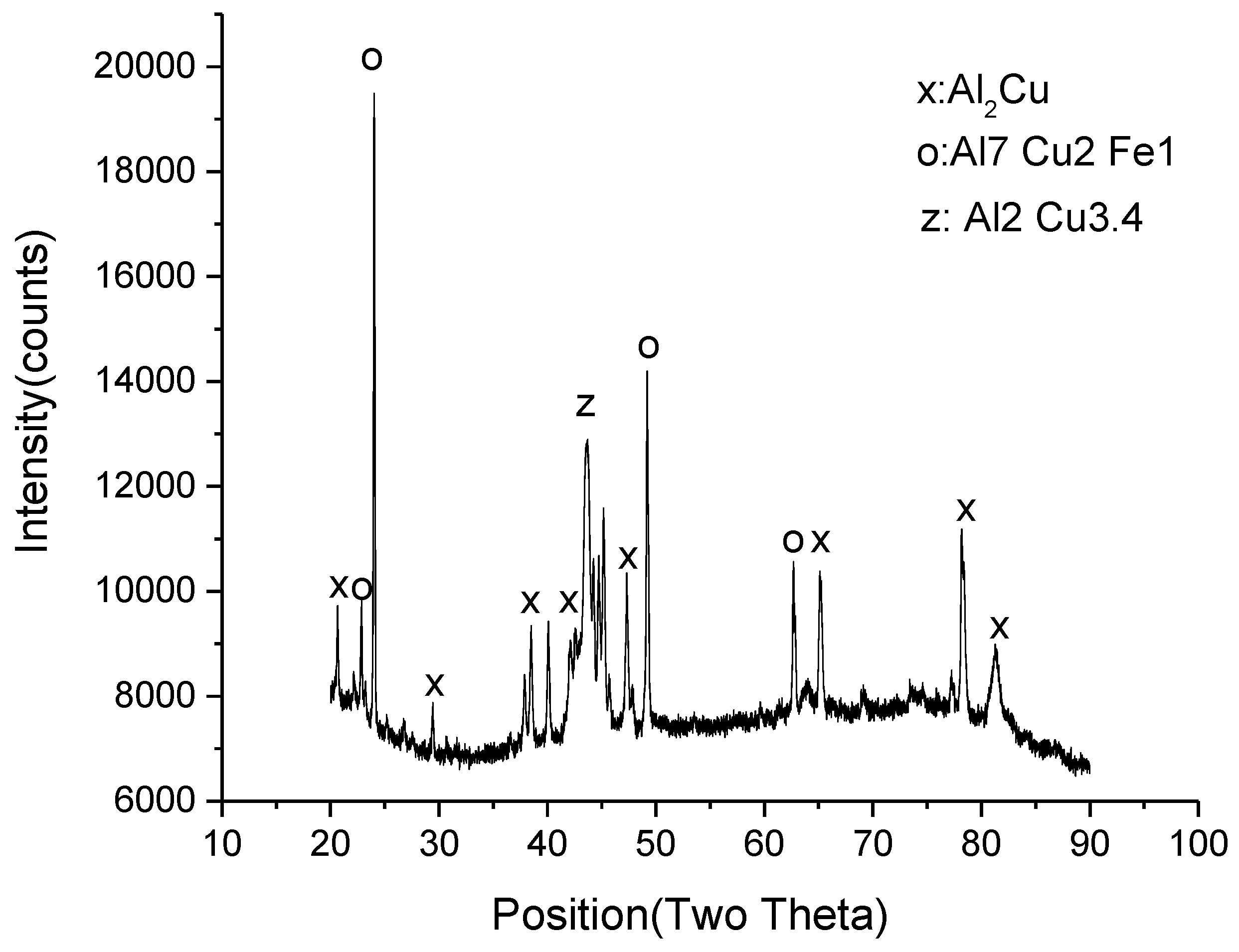
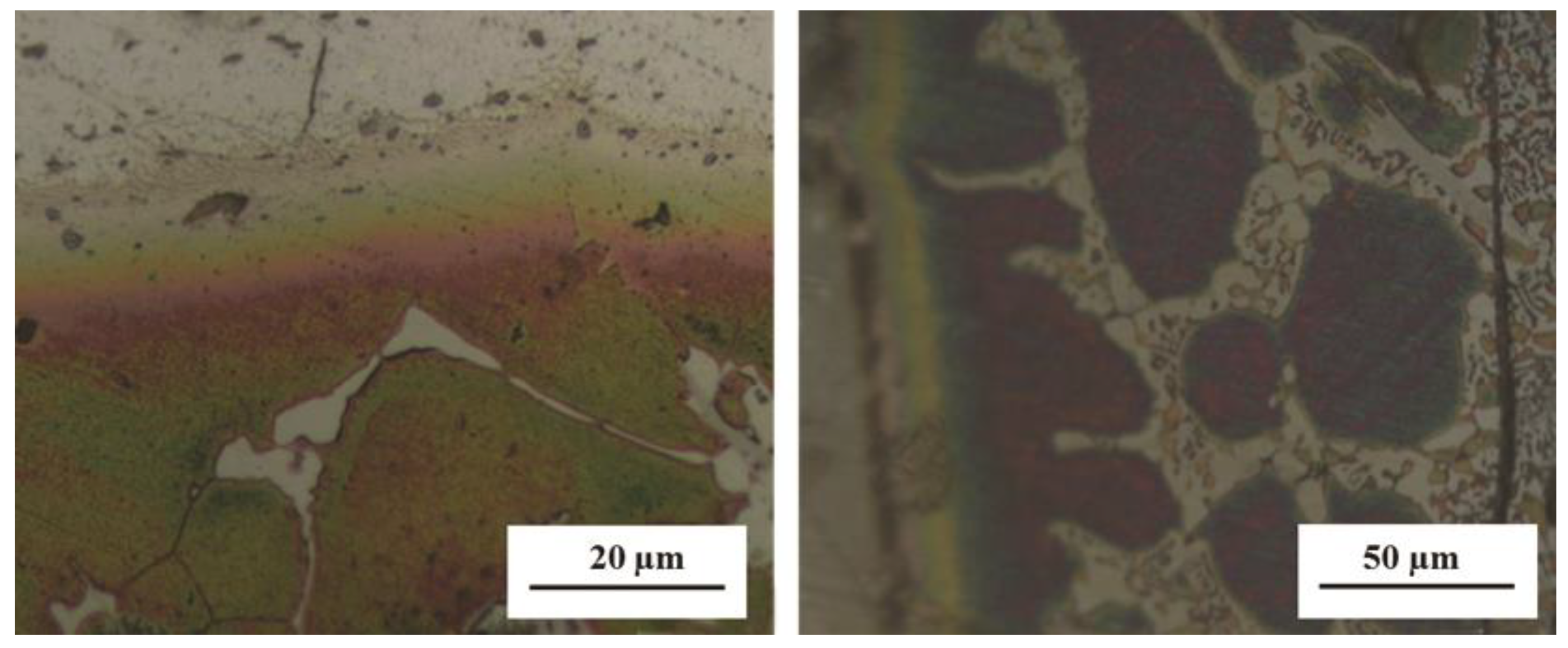
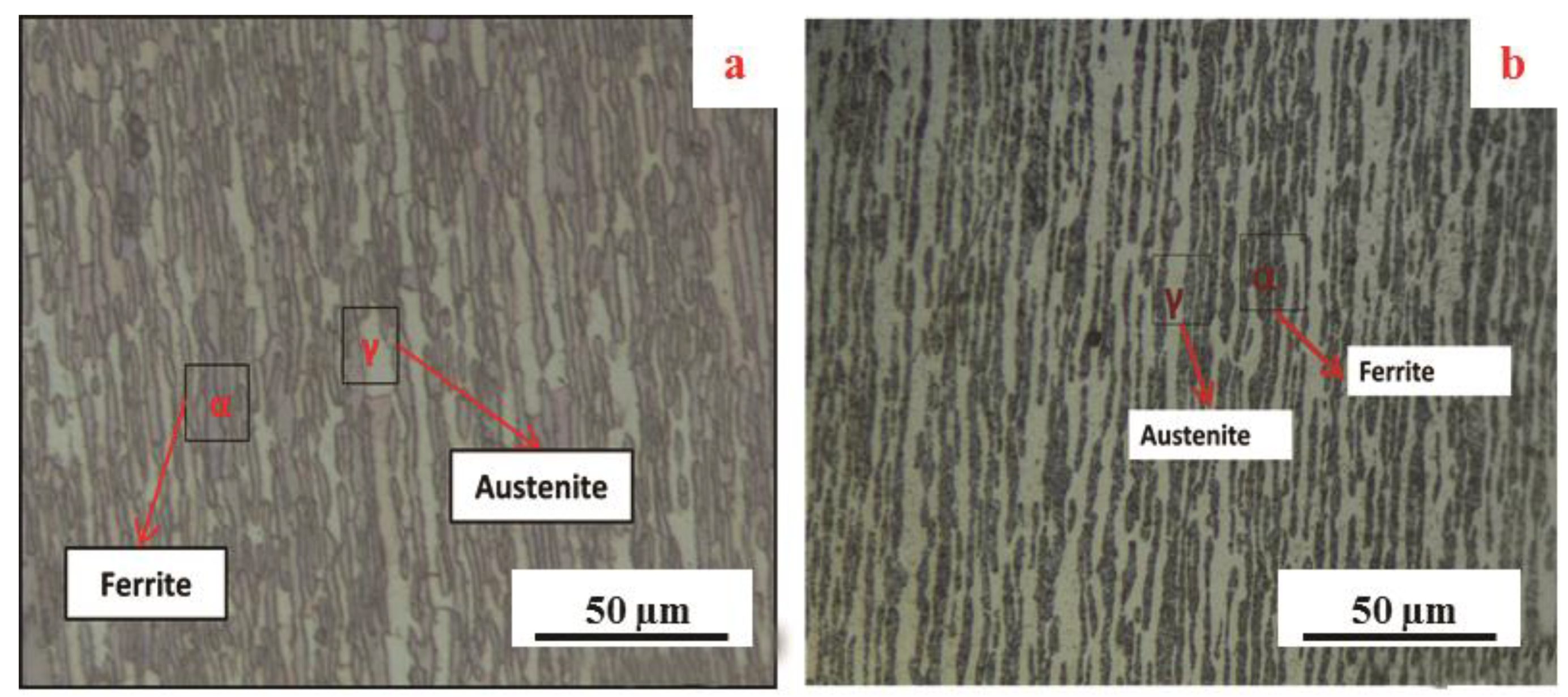
3.1. Microstructural Development in Joints
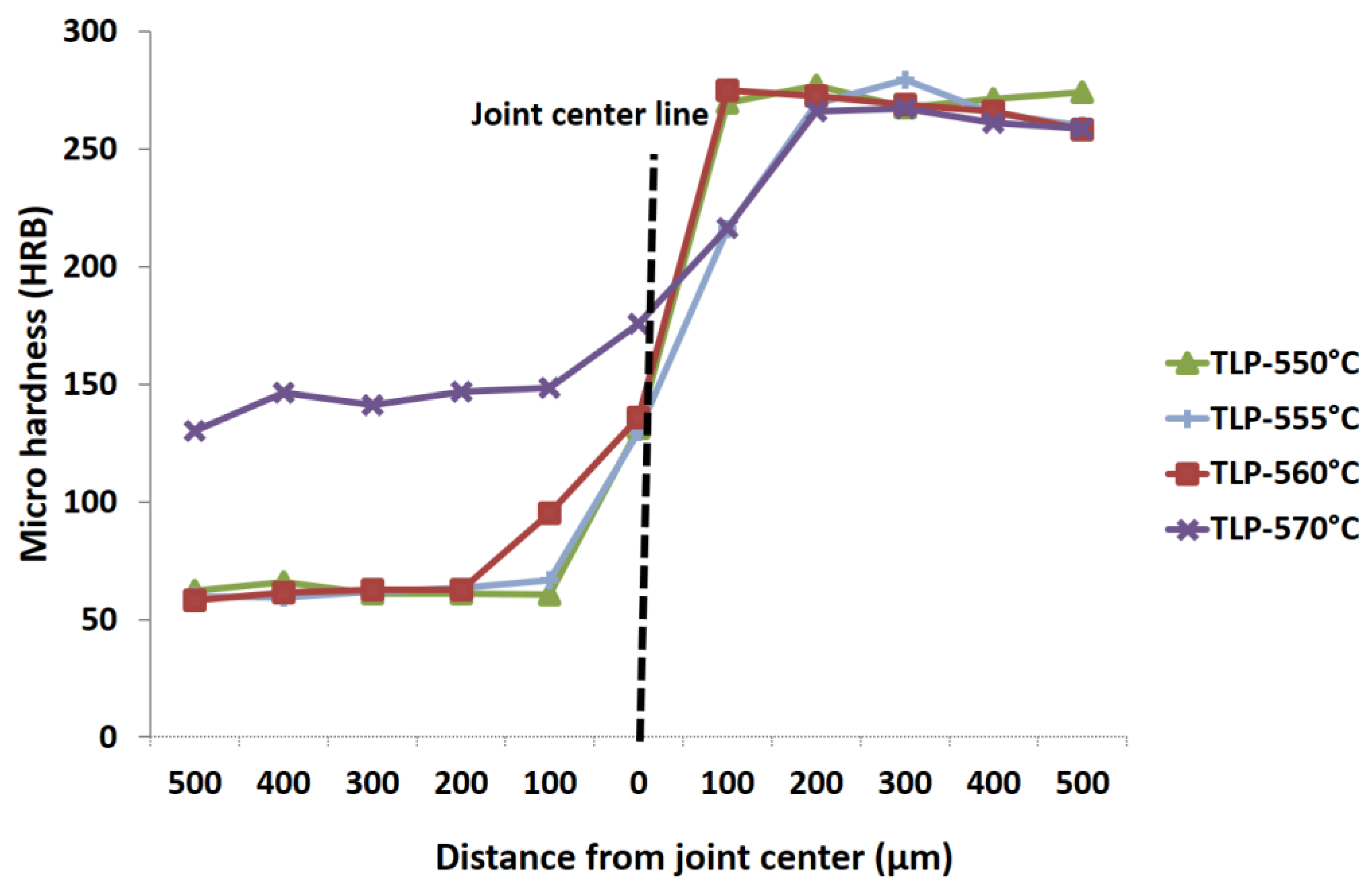
3.2. Micro-Hardness Evaluation
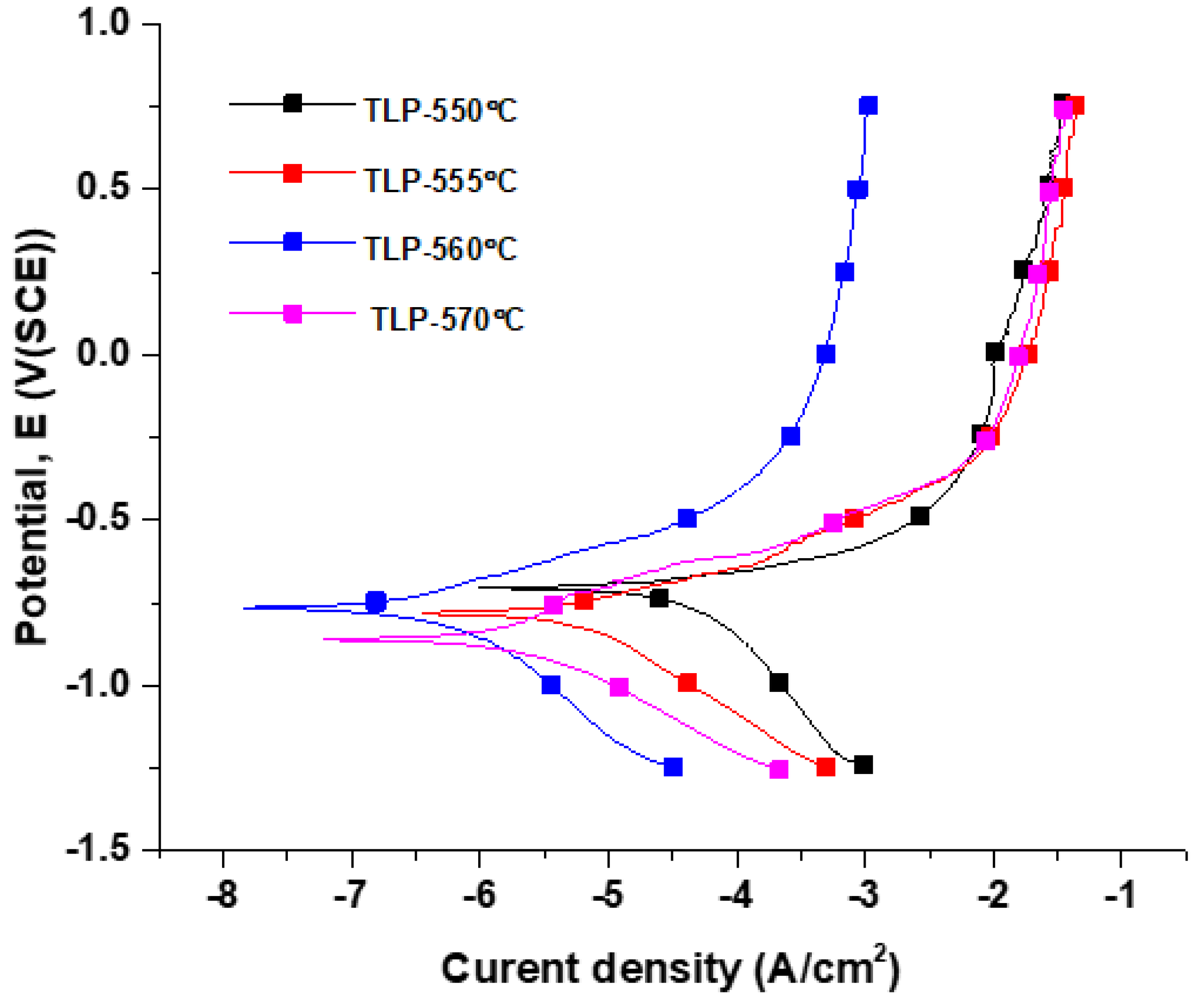
3.3. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
- The resultant area of TLP bonding consisted of three distinct zones including base metal, reaction zone and diffusion affected zone. Cu diffused into the Al alloy and formed an eutectic phase. However, no reaction was observed on the UNS S32304 side.
- As the bonding temperature increased from 550 °C to 570 °C, the thickness of the reaction zone increased by over 100%.
- Although voids and intermetallic compounds (Al2Cu) were found at the interface, a TLP joint was produced successfully at 570 °C.
- Employing Cu foil as an interlayer suppressed the formation of Fe–Al intermetallics.
- Hardness was increased on the Al-6063 side as a result of Cu diffusion. However, changes in hardness for the UNS S32304 steel was negligible.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinsen, K.; Hu, S.J.; Carlson, B.E. Joining of dissimilar materials. CIRP Ann. 2015, 64, 679–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.I.; Khan, T.I.; Roven, H.J. Transient liquid phase bonding of AA-6063 to UNS S32304 using Cu interlayer. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-C.; Pinkerton, A.J.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Mistry, A.T. Gap-free fibre laser welding of Zn-coated steel on Al alloy for light-weight automotive applications. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, T.; Naito, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nose, T.; Murayama, G.; Saita, K.; Oikawa, H. Dissimilar metal joining technologies for steel sheet and aluminum alloy sheet in auto body. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2013, 103, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, K.; Shrestha, M.; Martikainen, J. Trends in Joining Dissimilar Metals by Welding. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 440, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, G.; Peyre, P.; Deschaux Beaume, F.; Stuart, D.; Fras, G. Galvanised steel to aluminium joining by laser and GTAW processes. Mater. Charact. 2008, 59, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.W.; Gao, M.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, G.; Zeng, X.Y. Interface properties and thermodynamic analysis of laser–arc hybrid welded Al/steel joint. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 18, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findik, F. Recent developments in explosive welding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prawoto, Y. Synergy of erosion and galvanic effects of dissimilar steel welding: Field failure analysis case study and laboratory test results. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2013, 25, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralimohan, C.H.; Haribabu, S.; Reddy, Y.H.; Muthupandi, V.; Sivaprasad, K. Evaluation of Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Materials by Friction Welding. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissimilar Materials Joining. Available online: https://ewi.org/dissimilar-materials-joining/ (accessed on 6 May 2018).
- Torbati, A.M.; Miranda, R.M.; Quintino, L.; Williams, S.; Yapp, D. Optimization procedures for GMAW of bimetal pipes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Doi, Y.; Yanagisawa, A.; Konuma, S. Resistance Spot Welding of Mild Steel to Al-Mg Alloy. Q. J. Jpn. Weld. Soc. 2005, 23, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J. Recent development in aluminium for automotive applications. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, J.; Al-Samman, T. Superior light metals by texture engineering: Optimized aluminum and magnesium alloys for automotive applications. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 818–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, D.; Han, L.; Liu, D. Interfacial microstructure and mechanical property of resistance spot welded joint of high strength steel and aluminium alloy with 4047 AlSi12 interlayer. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Sheng, G.; Luo, J.; Li, J. Microstructural characteristics of joint region during diffusion-brazing of magnesium alloy and stainless steel using pure copper interlayer. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elthalabawy, W.M.; Khan, T.I. Microstructural development of diffusion-brazed austenitic stainless steel to magnesium alloy using a nickel interlayer. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, T.; Koba, M.; Nambu, S.; Inoue, J.; Koseki, T. Reactive Transient Liquid Phase Bonding between AZ31 Magnesium Alloy and Low Carbon Steel. Mater. Trans. 2011, 52, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, L.H.; Ishak, M. Review of Research Progress on Aluminum–Steel Dissimilar Welding. Mater. Manuf. Processes 2014, 29, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Shi, H.; Zhang, K.; Tu, Y.; Iwamato, C.; Satonaka, S. Interfacial characterization of joint between mild steel and aluminum alloy welded by resistance spot welding. Mater. Charact. 2010, 61, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meco, S.; Pardal, G.; Ganguly, S.; Williams, S.; McPherson, N. Application of laser in seam welding of dissimilar steel to aluminium joints for thick structural components. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 67, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, A.; Shabadi, R.; Deschamps, A.; Surey, M.; Mattei, S.; Grevey, D.; Cicala, E. Dissimilar material joining using laser (aluminum to steel using zinc-based filler wire). Opt. Lasers Eng. 2007, 39, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yan, Q.; Gao, W.; Huang, J. Investigation of laser welding on butt joints of Al/steel dissimilar materials. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri-David, A. Study of metallurgic and mechanical properties of laser welded heterogeneous joints between DP600 galvanised steel and aluminium 6082. Mater. Des. 2014, 54, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, Y.; Feng, T. Microstructure characteristics in the interface zone of Ti/Al diffusion bonding. Mater. Lett. 2002, 56, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaiah, P.; Suresh, A.; Tagore, G.R.N. Mechanical properties of friction welded 6063 aluminum alloy and austenitic stainless steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5512–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarian, M.; Khodabandeh, A.; Manafi, S. Evaluation of diffusion welding of 6061 aluminum and AZ31 magnesium alloys without using an interlayer. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Kovacevic, R. Joining of Al 6061 alloy to AISI 1018 steel by combined effects of fusion and solid state welding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2004, 44, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Haghshenas, M.; Gerlich, A.P. Role of welding parameters on interfacial bonding in dissimilar steel/aluminum friction stir welds. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2015, 18, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaki, M.M.; Wati, J.N.; Idris, J. Transient liquid phase diffusion brazing of stainless steel 304. Weld. J. 2013, 92, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Zhao, X.; Song, M.; Fing, J.; Yang, B. Diffusion bonding of Ti-6 Al-4 V to QAl 10-3-1.5 with Ni/Cu interlayers. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2006, 22, 817–820. [Google Scholar]
- Na, H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, B.; Kang, C. Effect of brazing conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of duplex stainless steels to Cr−Cu alloy with Cu− base insert metal. Met. Mater. Int. 2007, 13, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-F.; Si, N.-C.; Chen, J. Contact reactive brazing of Al alloy/Cu/stainless steel joints and dissolution behaviors of interlayer. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orio, R.L.D. Electromigration Modeling and Simulation; Technical University of Vienna: Vienna, Austria, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, A.; Mishin, Y. Atomic mechanisms of grain boundary diffusion: Low versus high temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 3155–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padron, T.; Khan, T.I.; Kabir, M.J. Modelling the transient liquid phase bonding behaviour of a duplex stainless steel using copper interlayers. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 385, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, G.A.; Krauss, G.; Kennedy, R.L. Tool Steels, 5th ed.; ASM International: Geauga, OH, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, D.L.; Totemeier, T.C. 22-Mechanical properties of metals and alloys. In Smithells Metals Reference Book, 2nd ed.; Gale, W.F., Totemeir, T.C., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, U.K, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, T.I.; Kabir, M.J.; Bulpett, R. Effect of transient liquid-phase bonding variables on the properties of a micro-duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 372, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, M.I.; Roven, H.J.; Khan, T.I.; Iveland, T. Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of Al-6063 to Steel Alloy UNS S32304. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2018, 2, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2030058
Saleh MI, Roven HJ, Khan TI, Iveland T. Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of Al-6063 to Steel Alloy UNS S32304. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing. 2018; 2(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2030058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Mohamed I., Hans J. Roven, Tahir I. Khan, and Terje Iveland. 2018. "Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of Al-6063 to Steel Alloy UNS S32304" Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing 2, no. 3: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2030058
APA StyleSaleh, M. I., Roven, H. J., Khan, T. I., & Iveland, T. (2018). Transient Liquid Phase Bonding of Al-6063 to Steel Alloy UNS S32304. Journal of Manufacturing and Materials Processing, 2(3), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmmp2030058




