Intelligent Firefighting Technology for Drone Swarms with Multi-Sensor Integrated Path Planning: YOLOv8 Algorithm-Driven Fire Source Identification and Precision Deployment Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Research Methodology
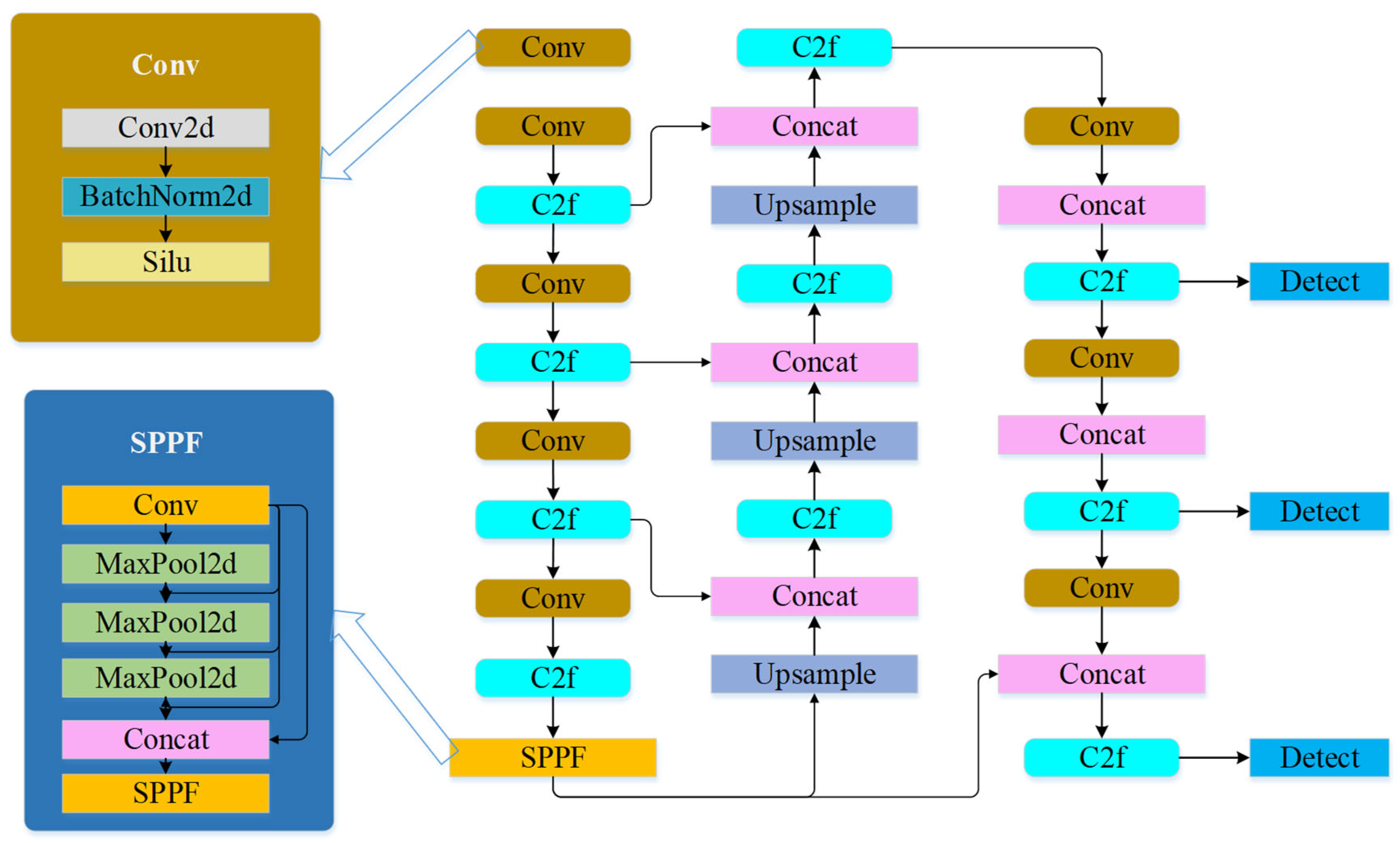
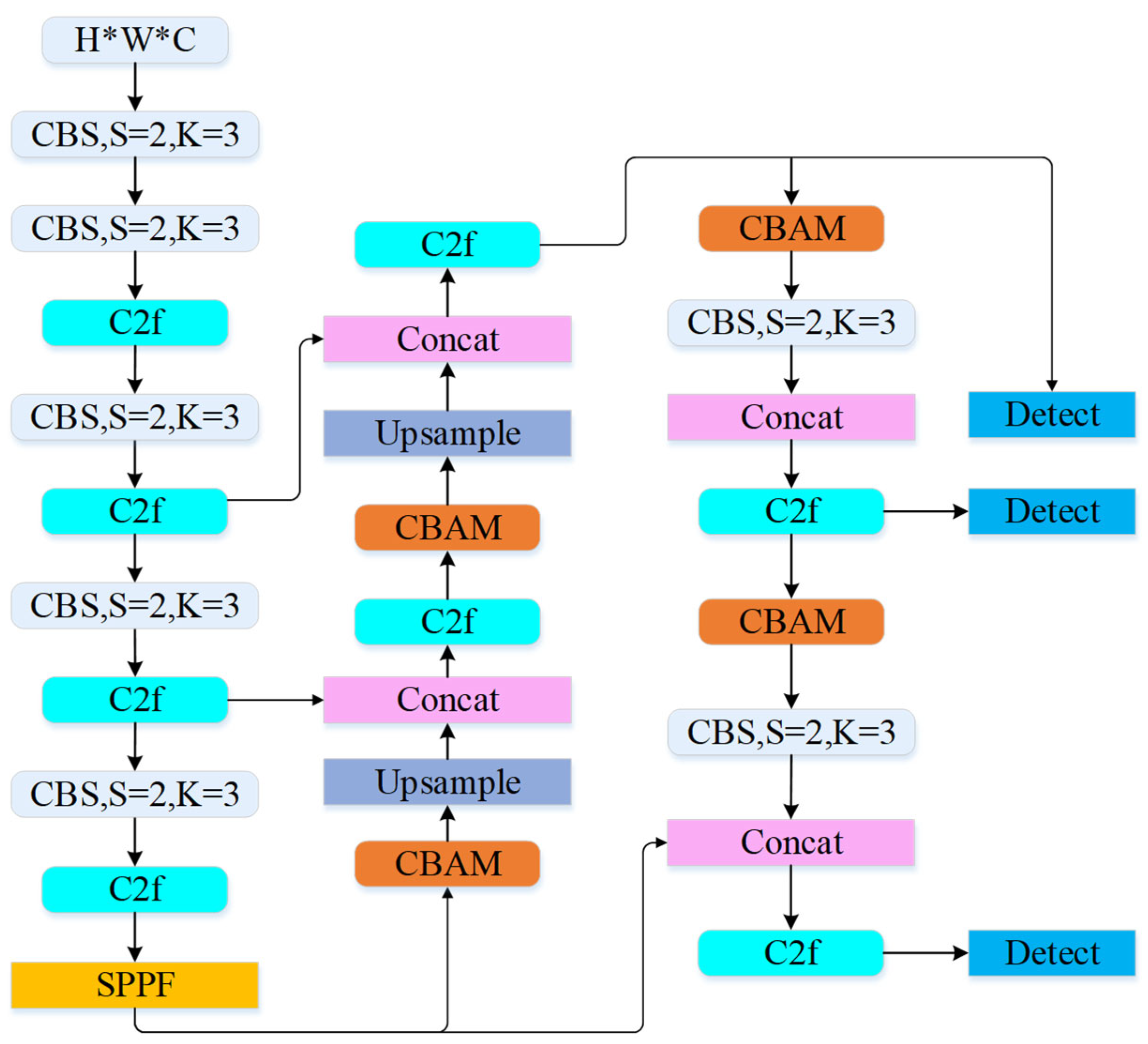
3.1. Fire Source Identification Method
3.2. Multi-Sensor Data Fusion
| Algorithm 1: IAO Algorithm Pseudo-Code |
| 1. Initialize the flight tasks and the positions of individuals . Set the maximum number of iterations () and the learning rate (). |
| 2. For each individual, gather information and update the position: |
| 3. Evaluate and filter the collected information. Adjust the position based on a random condition: |
| , then |
| 4. Perform information analysis and organization, adjusting positions using |
| , then |
| 5. Once the iteration is complete, output the optimal path and terminate the process. |
| Algorithm 2: CFOA Algorithm Pseudo-Code |
| 1. Initialize the fish swarm position: Randomly distribute in the search space. Set the maximum number of iterations and the capture rate . |
| 2. Exploration phase: Update the capture rate using the formula: |
| 3. Fitness calculation: Compute the fitness of each individual and update the fish swarm position using Equation (12). |
| 4. Independent search phase: Perform the independent search phase using the formula in Equation (13). |
| 5. Group fishing phase: Calculate the centroid of the fish swarm , and update the positions. |
| 6. Development phase: Update the position of each individual: |
| 7. Termination: If the maximum number of iterations is reached, output the optimal path and terminate. |
3.3. Experimental Data
4. Results Analysis
4.1. Fire Source Detection Accuracy Evaluation
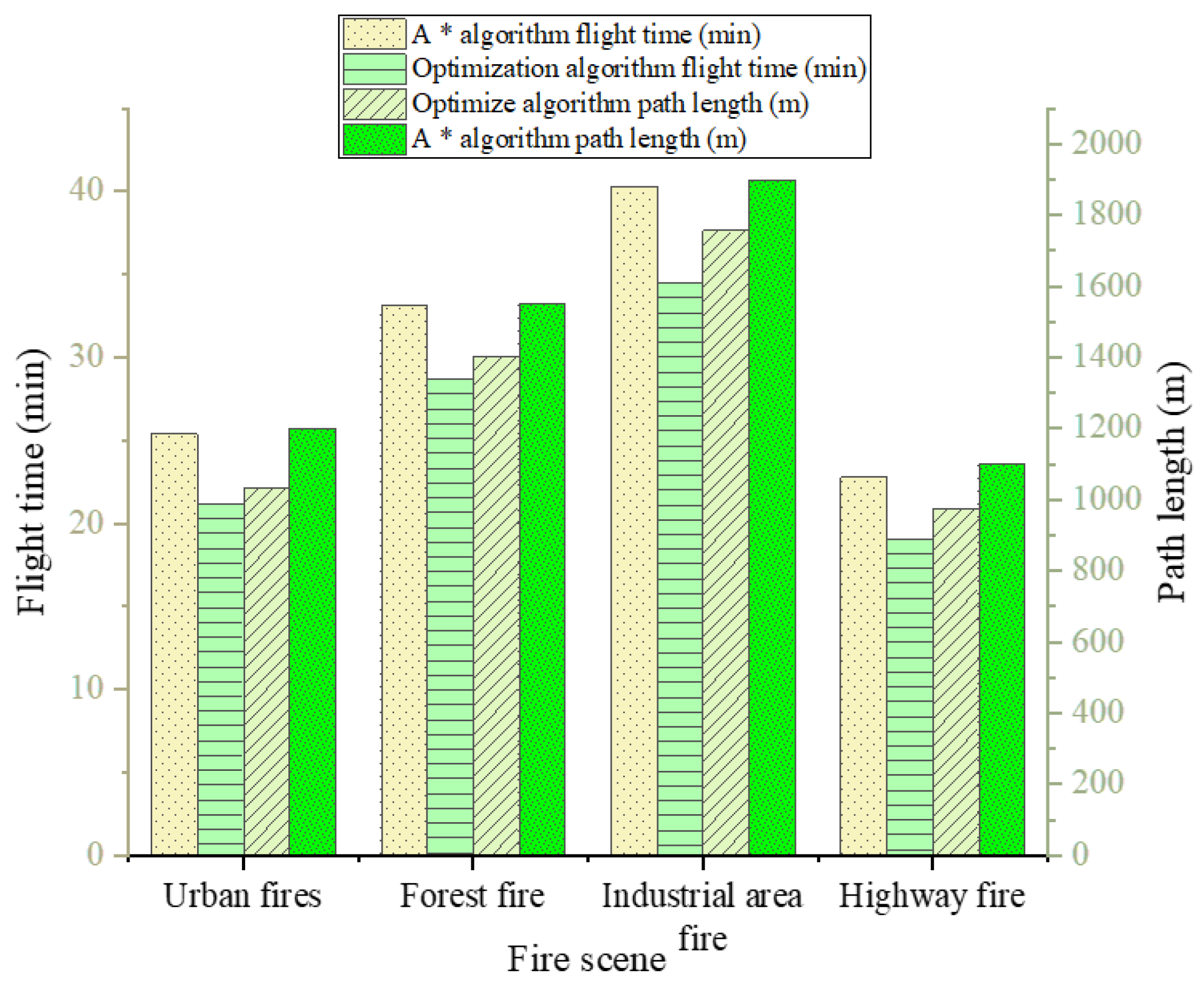
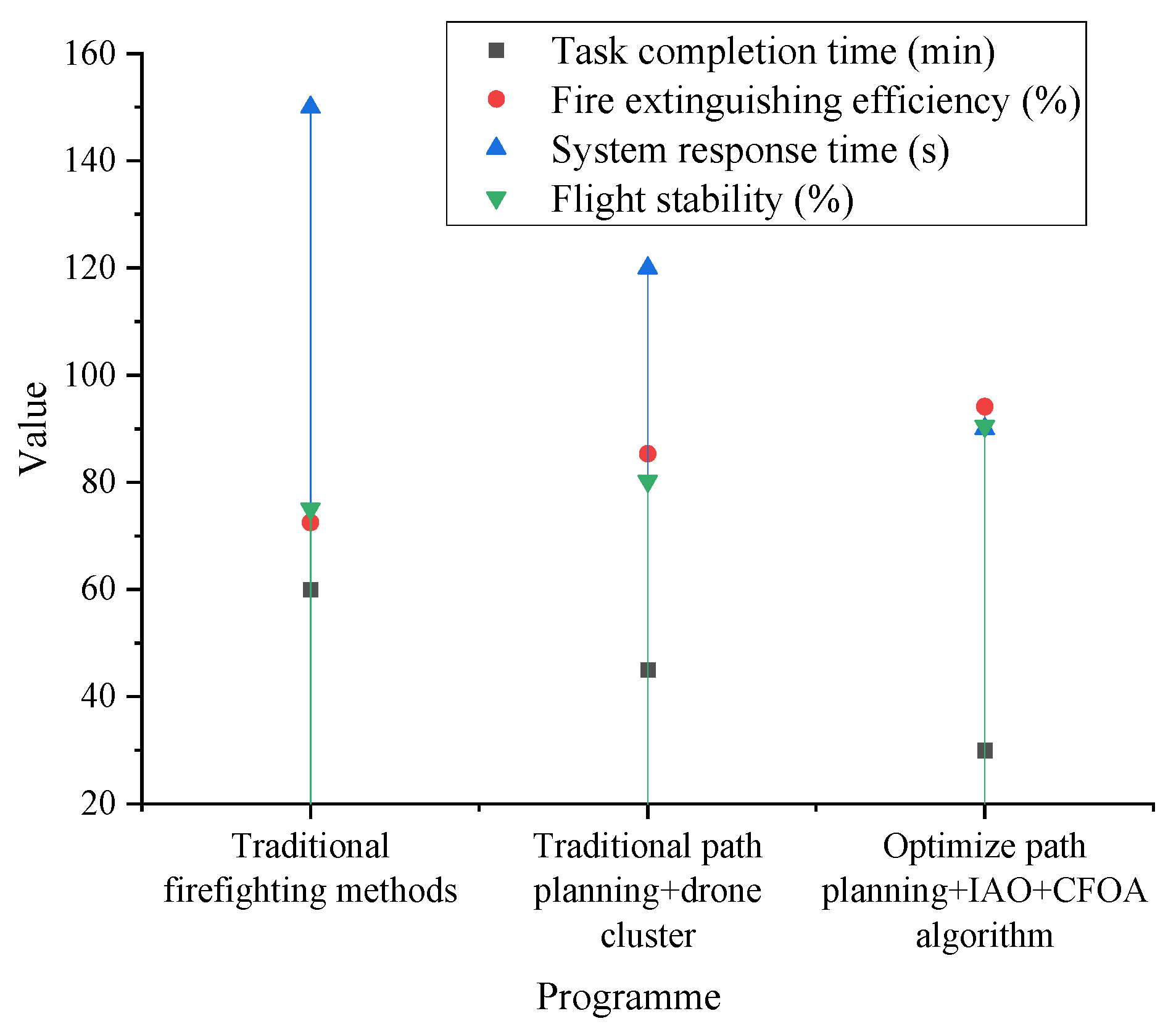
4.2. Path Planning Efficiency Evaluation
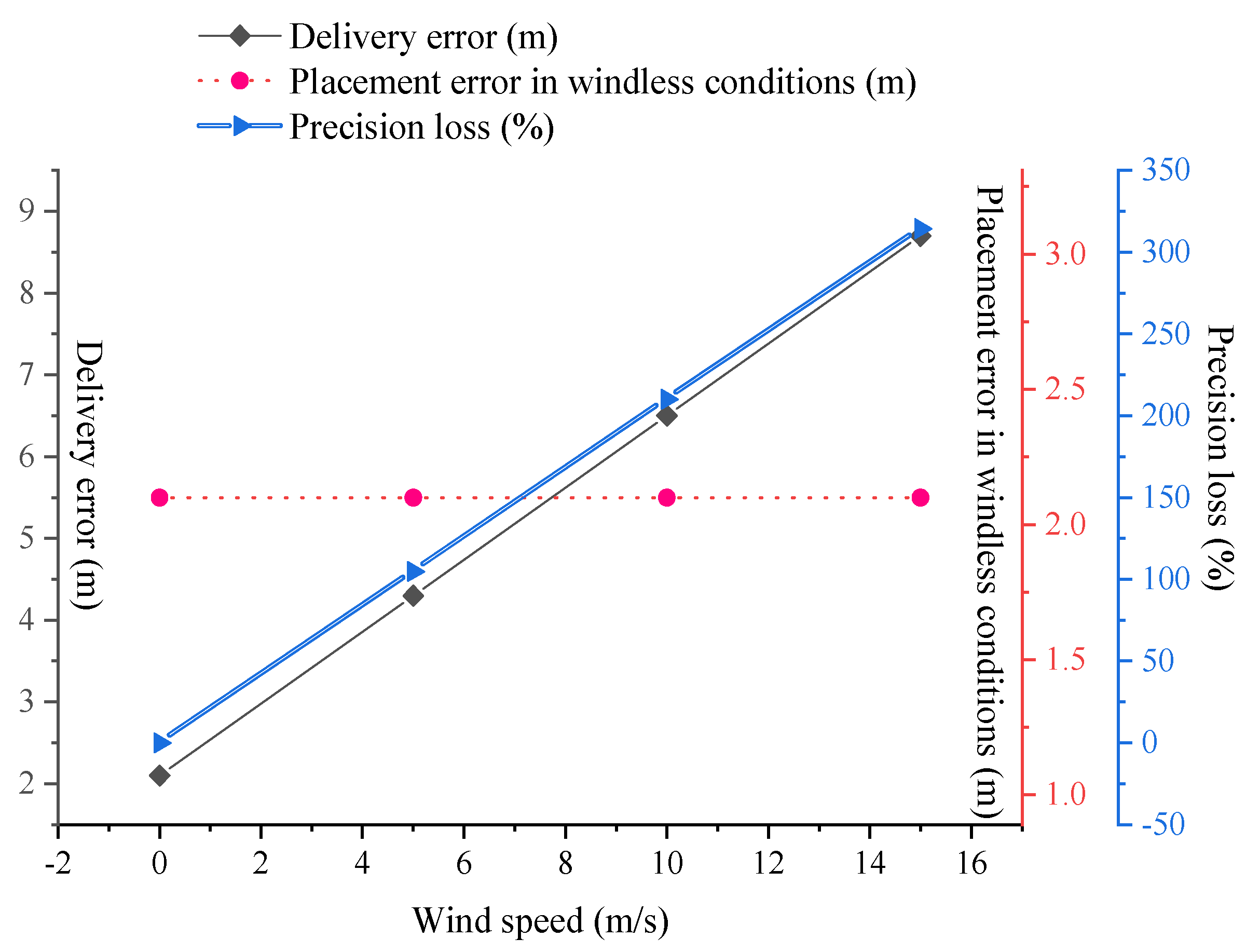
4.3. Fire Suppression Material Deployment Accuracy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saydirasulovich, S.N.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Djuraev, O.; Abdusalomov, A.; Cho, Y.-I. An improved wildfire smoke detection based on YOLOv8 and UAV images. Sensors 2023, 23, 8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titu, M.F.S.; Pavel, M.A.; Michael GK, O.; Babar, H.; Aman, U.; Khan, R. Real-Time Fire Detection: Integrating Lightweight Deep Learning Models on Drones with Edge Computing. Drones 2024, 8, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.; Zhou, S.; Liu, L.; Pan, W. Tiny-Object Detection Based on Optimized YOLO-CSQ for Accurate Drone Detection in Wildfire Scenarios. Drones 2024, 8, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamta, I.; Demir, B.E. Development of a deep learning-based surveillance system for forest fire detection and monitoring using UAV. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Duan, B.; Guan, R.; Yang, G.; Zhen, Z. LUFFD-YOLO: A Lightweight Model for UAV Remote Sensing Forest Fire Detection Based on Attention Mechanism and Multi-Level Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tao, F.; Gao, Z.; Li, J. FGYOLO: An Integrated Feature Enhancement Lightweight Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Forest Fire Detection Framework Based on YOLOv8n. Forests 2024, 15, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, L.; Robert TL, K. An improved fire and smoke detection method based on YOLOv8n for smart factories. Sensors 2024, 24, 4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choutri, K.; Lagha, M.; Meshoul, S.; Batouche, M.; Bouzidi, F.; Charef, W. Fire detection and geo-localization using uav’s aerial images and yolo-based models. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, P. A wildfire smoke detection based on improved YOLOv8. Int. J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2024, 25, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandouzi, M.; Berrahal, M.; Grari, M.; Boukabous, M.; Moussaoui, O.; Azizi, M.; Ghoumid, K.; Elmiad, A.K. Semantic segmentation and thermal imaging for forest fires detection and monitoring by drones. Bull. Electr. Eng. Inform. 2024, 13, 2784–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaat, F.M.; ZainEldin, H. An improved fire detection approach based on YOLO-v8 for smart cities. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 20939–20954. [Google Scholar]
- Alsamurai, M.Q.F.; Çevik, Ü.M. Detection of Animals and humans in forest fires using Yolov8. J. Electr. Syst. 2024, 20, 831–843. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Shao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, J. Precision-Boosted Forest Fire Target Detection via Enhanced YOLOv8 Model. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Duan, J.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y. Real-time fire detection algorithms running on small embedded devices based on MobileNetV3 and YOLOv4. Fire Ecol. 2023, 19, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Y.; Fan, D.; Di, F. A lightweight fire detection algorithm for small targets based on YOLOv5s. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 14104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, P.; Walambe, R.; Mandaokar, S.; Chandel, P.; Kotecha, K.; Ghinea, G. Gas detection and identification using multimodal artificial intelligence based sensor fusion. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2021, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.A.; Omri, M.; Abdel-Khalek, S.; Ali, E.S.; Alotaibi, M.F. Optimal path planning for drones based on swarm intelligence algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10133–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Bedeer, E.; Nguyen, H.H.; Barton, R.; Henry, J. UAV trajectory planning in wireless sensor networks for energy consumption minimization by deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 9540–9554. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Han, G.; Qi, X.; Du, J.; Xu, T.; Martinez-Garcia, M. Energy-optimal data collection for unmanned aerial vehicle-aided industrial wireless sensor network-based agricultural monitoring system: A clustering compressed sampling approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 4411–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C.; Dong, X. Risk prediction and credibility detection of network public opinion using blockchain technology. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 187, 122177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnai, M.; Losè, M.T.; Satler, M.; Avizzano, C.A. Towards Autonomous Firefighting UAVs: Online Planners for Obstacle Avoidance and Payload Delivery. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2024, 110, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, J. Objective multi-criteria decision-making for optimal firefighter protective clothing size selection. Int. J. Occup. Saf. Ergon. 2024, 30, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.; Chen, S.F.; Hsu, Y.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Hua, K.L. Forest fire segmentation via temporal transformer from aerial images. Forests 2023, 14, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, F.; Mason, F.; Pase, F.; Chiariotti, F.; Testolin, A.; Zanella, A.; Zorzi, M. Distributed reinforcement learning for flexible and efficient UAV swarm control. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 955–969. [Google Scholar]
- Soderlund, A.; Kumar, M. Estimating the spread of wildland fires via evidence-based information fusion. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2022, 31, 511–526. [Google Scholar]
- Yunusov, N.; Islam, B.M.S.; Abdusalomov, A.; Kim, W. Robust Forest Fire Detection Method for Surveillance Systems Based on You Only Look Once Version 8 and Transfer Learning Approaches. Processes 2024, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, T. FFYOLO: A Lightweight Forest Fire Detection Model Based on YOLOv8. Fire 2024, 7, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Luo, L. Aircraft Target Detection on Airport Surface Based on Improved YOLOX. Comput. Simul. 2024, 41, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Catargiu, C.; Cleju, N.; Ciocoiu, I.B. A Comparative Performance Evaluation of YOLO-Type Detectors on a New Open Fire and Smoke Dataset. Sensors 2024, 24, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yan, H.; Shi, L. Multi-scale coupled attention for visual object detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11191. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, S.; Rony, J.H.; Uddin, J.; Samad, A. Real-Time Obstacle Detection with YOLOv8 in a WSN Using UAV Aerial Photography. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aibin, M.; Li, Y.; Sharma, R.; Ling, J.; Ye, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Coria, L.; Huang, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Advancing Forest Fire Risk Evaluation: An Integrated Framework for Visualizing Area-Specific Forest Fire Risks Using UAV Imagery, Object Detection and Color Mapping Techniques. Drones 2024, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves LA, O.; Ghali, R.; Akhloufi, M.A. YOLO-Based Models for Smoke and Wildfire Detection in Ground and Aerial Images. Fire 2024, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Duan, R.; Yang, F.; Xu, L. Low Complexity Forest Fire Detection Based on Improved YOLOv8 Network. Forests 2024, 15, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Piao, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, B. An Improved Forest Smoke Detection Model Based on YOLOv8. Forests 2024, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, R.; Akhloufi, M.A.; Mseddi, W.S. Deep learning and transformer approaches for UAV-based wildfire detection and segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Hassan, B.; Khan, S.; Ahmed, R.; Abuassba, A. DeepFire: A novel dataset and deep transfer learning benchmark for forest fire detection. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 5358359. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Muminov, A. Forest fire smoke detection based on deep learning approaches and unmanned aerial vehicle images. Sensors 2023, 23, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özel, B.; Alam, M.S.; Khan, M.U. Review of Modern Forest Fire Detection Techniques: Innovations in Image Processing and Deep Learning. Information 2024, 15, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7240-8:2014; Fire Detection and Alarm Systems—Part 8: Point-Type Fire Detectors Using a Carbon Monoxide Sensor in Combination with a Heat Sensor. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.



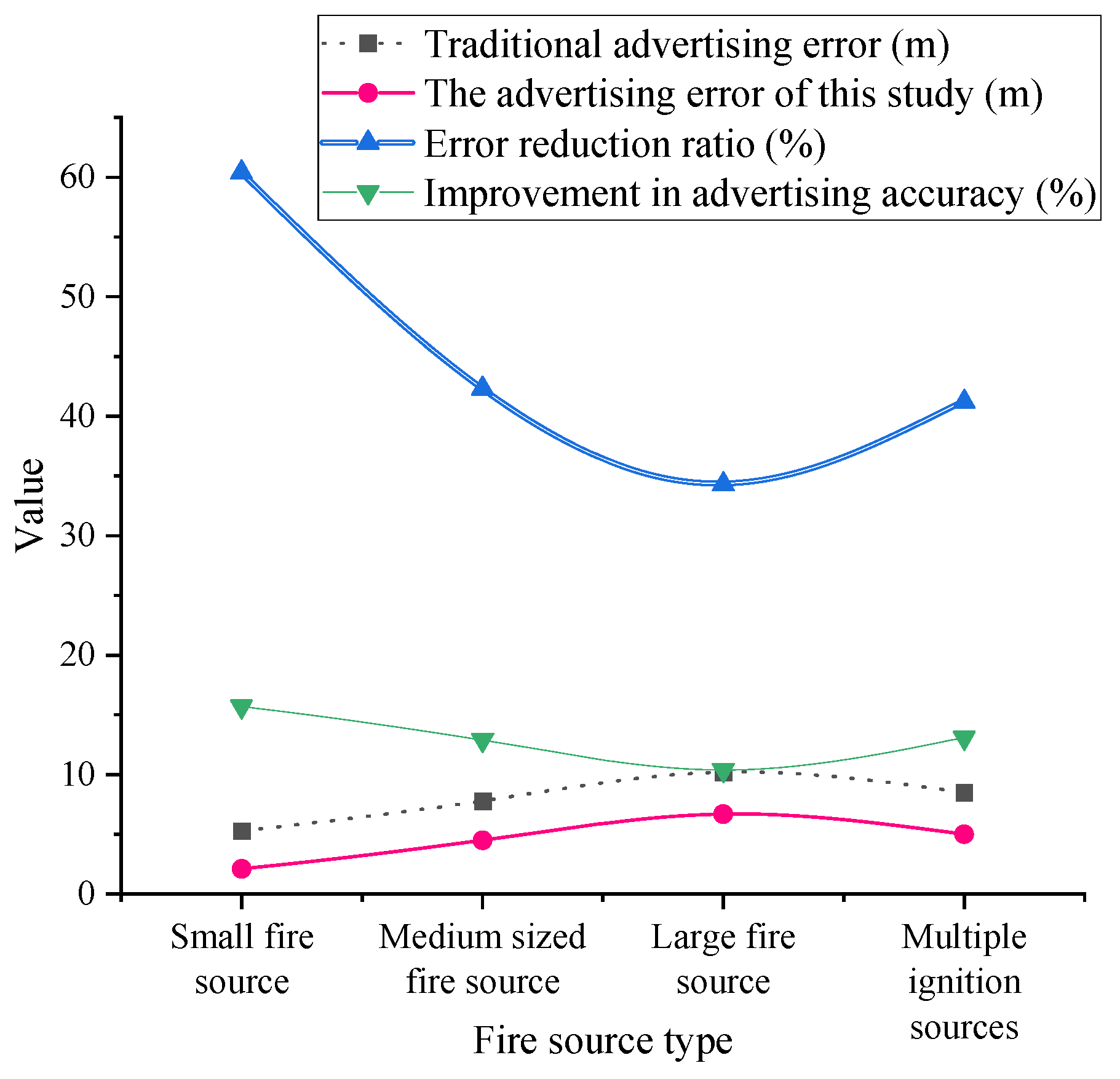
| Fire Source Type | Criteria | YOLOv8 Accuracy | Optimized Accuracy | False Detection Rate Decrease |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small Fire Source | Flame area < 1 m2, Heat radiation < 50 kW/m2 82.3% | 82.3% | 94.6% | 12.7% |
| Medium Fire Source | 1 m2 ≤ area < 5 m2, 50–200 kW/m2 | 88.1% | 96.2% | 9.5% |
| Large Fire Source | area ≥ 5 m2, Heat radiation ≥ 200 kW/m2 | 91.4% | 97.8% | 5.2% |
| Multi-fire Source | 3 independent fire points present simultaneously | 76.5% | 92.1% | 15.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, B.; Yu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Lai, R.; Lv, J.; Zhou, B. Intelligent Firefighting Technology for Drone Swarms with Multi-Sensor Integrated Path Planning: YOLOv8 Algorithm-Driven Fire Source Identification and Precision Deployment Strategy. Drones 2025, 9, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9050348
Yu B, Yu S, Zhao Y, Wang J, Lai R, Lv J, Zhou B. Intelligent Firefighting Technology for Drone Swarms with Multi-Sensor Integrated Path Planning: YOLOv8 Algorithm-Driven Fire Source Identification and Precision Deployment Strategy. Drones. 2025; 9(5):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9050348
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Bingxin, Shengze Yu, Yuandi Zhao, Jin Wang, Ran Lai, Jisong Lv, and Botao Zhou. 2025. "Intelligent Firefighting Technology for Drone Swarms with Multi-Sensor Integrated Path Planning: YOLOv8 Algorithm-Driven Fire Source Identification and Precision Deployment Strategy" Drones 9, no. 5: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9050348
APA StyleYu, B., Yu, S., Zhao, Y., Wang, J., Lai, R., Lv, J., & Zhou, B. (2025). Intelligent Firefighting Technology for Drone Swarms with Multi-Sensor Integrated Path Planning: YOLOv8 Algorithm-Driven Fire Source Identification and Precision Deployment Strategy. Drones, 9(5), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones9050348






