Highlights
This section summarizes the core contributions and practical value of the research on the Knowledge-Enhanced Graph of Thoughts (K-EGoT) framework for automated safety modeling of high-altitude solar drones, focusing on key experimental results and their significance for both academic research and industrial applications.
What are the main findings?
- The proposed K-EGoT framework, when applied to a 7B-parameter model (Qwen2-7B-Instruct), achieves a Safety Extension Score (SES) of 92.7 in high-altitude solar drone safety modeling, significantly outperforming standard Graph of Thoughts (GoT) prompting (84.7) and other fine-tuning baselines (e.g., SFT + DPO-Behavioral with 89.4).
- The “Safety Rationale”—a verifiable link between LLM-generated model extensions and expert-curated safety principles—is the core driver of K-EGoT’s performance; removing it leads to a 7.6-point drop in total SES and a 14.2-point drop in Rationale Quality (Srat) in ablation tests.
What are the implications of the main findings?
- For specialized safety-critical domains like high-altitude solar drones, aligning LLM reasoning with expert logic (via rationale-centric optimization) is more impactful than general-purpose prompting or behavioral-only fine-tuning, enabling smaller models to outperform larger generic models in domain-specific tasks.
- K-EGoT provides an auditable and reliable solution for early-stage automated safety modeling, addressing the inefficiency of manual expert analysis and the opaqueness of traditional LLM applications, which can reduce late-stage design modification costs and accelerate drone development cycles.
Abstract
As the application of high-altitude solar drones expands, ensuring their safety is paramount. Traditional safety modeling, which relies on manual expert analysis, struggles to keep pace with rapid development cycles. While Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a path to automation, state-of-the-art reasoning frameworks like Graph of Thoughts (GoT) are too generic, lacking the domain-specific knowledge required for effective application. To address this gap, we introduce K-EGoT, a framework that grounds LLM reasoning in a verifiable, domain-specific knowledge base. Our method introduces a “Safety Rationale”—a mandatory, auditable link between LLM-generated model extensions and expert-curated safety principles. We then train a specialized model using a novel “thought process alignment” strategy, applying Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) to the quality of these rationales to ensure the model’sreasoning aligns with expert logic. On a high-fidelity dataset for the flight control–energy coupling problem, our 7B K-EGoT model achieved a Safety Extension Score (SES) of 92.7, significantly outperforming the 84.7 score from standard GoT prompting. Our work delivers a reliable and auditable solution for automated safety modeling for this critical class of drones.
1. Introduction
High-altitude solar drones, often referred to as High-Altitude Long-Endurance (HALE) drones, are platforms designed for long-endurance missions in the stratosphere. As shown in Figure 1, their most notable physical characteristic is a very high aspect ratio, meaning the wings are morphologically extremely long and narrow, to accommodate large-area photovoltaic solar arrays. This morphology allows them to fly and charge via solar power during the day, while relying on batteries for continued flight overnight. As the application of these drones expands, stringent safety assurance becomes paramount. Unlike conventional drones, high-altitude solar drones must perpetually consider energy constraints during operation. Therefore, the principal safety risk is not isolated to individual components but emerges from the profound and intricate, dynamic interplay between the Flight Control System (FCS) and the Energy Management System (EMS)—the flight control–energy coupling. If system defects are not identified in the preliminary design stages, they can precipitate catastrophic failures, incurring remediation costs that are orders of magnitude greater than their initial prevention. While established safety analysis methodologies exist, such as Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) [1] and Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) [2], their conventional application has a fundamental limitation. These techniques are typically executed as post-design validation activities, divorced from the formative stages of system architecture. This methodological gap means that safety considerations are not integrated into the design blueprint from its inception, often leading to the late discovery of design-induced vulnerabilities that necessitate costly and disruptive modifications. To address this shortcoming, modern systems engineering advocates for the adoption of Safety Modeling at the genesis of the design process. Specifically, SysML-based safety modeling provides a structured, model-driven framework to conduct a comprehensive and holistic analysis of the system. By formally capturing safety requirements and constraints within the system model itself, this approach aims to ensure that reliability is “designed in” rather than “inspected in,” thereby enhancing dependable future operation. However, the practical application of this paradigm remains a significant challenge, as the process of identifying relevant hazards and translating them into the formal semantics of a SysML model continues to be a labor-intensive endeavor, heavily reliant on the extensive experience of senior safety engineers and demanding a substantial investment of time.
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) offers a promising avenue for automating this complex modeling process. However, high-quality modeling cannot be achieved through generic models or simple prompt engineering. Advanced reasoning frameworks like Graph of Thoughts (GoT) [3] are too general-purpose and lack the domain-specific grounding necessary for this nuanced safety field. Similarly, optimization techniques like Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), when focused only on the final output (a practice known as “behavioral alignment”), can produce a correct result without ensuring the underlying reasoning is sound. For high-altitude solar drones, where an AI merely guessing the right answer is unacceptable. This limitation is critical. Our work is built upon these powerful frameworks, but our contribution is a fundamental paradigm shift from “behavioral imitation” to “thought process alignment”. Unlike conventional methods that often merely fine-tune on expert data to mimic correct answers, our Knowledge-Enhanced Graph of Thoughts (K-EGoT) framework directly addresses the untrustworthy “black box” problem. We introduce the “Safety Rationale”—a verifiable, traceable reasoning step that makes the model’s logic both transparent and fully auditable. The core innovation lies in how we use this: we shift the optimization target of DPO from the final output (behavior) directly to the quality of the reasoning process itself, compelling the model to truly internalize deep expert logic, not just superficial spurious correlations.


Figure 1.
Typical High-Altitude Solar Drones. Reproduced from [4].
We conducted a comprehensive experimental evaluation on a specially constructed dataset centered on real-world operational scenarios of high-altitude solar drones. The results show that our K-EGoT framework, leveraging dynamic exploration to solve complex coupled problems, significantly outperforms standard and fixed fine-tuning. This result strongly demonstrates that our “thought process alignment” is a more crucial and effective integration of knowledge than simple behavioral alignment or general-purpose reasoning alone.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- We propose a method to enhance the Graph of Thoughts (GoT) framework by introducing a “Safety Rationale,” enabling the deep coupling of general-purpose LLM reasoning with a verifiable, domain-specific drone safety knowledge base.
- We demonstrate that using the “Safety Rationale” as the basis for Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) allows for aligning the model’s reasoning process with expert logic, a more robust approach than conventional behavioral alignment.
- We construct and release a high-quality evaluation dataset for the flight control–energy coupling safety problem, including a domain knowledge base, which provides a valuable resource for future research. The dataset’s reliability is supported by a high inter-rater reliability score (Fleiss’ Kappa = 0.82).
- Through comprehensive experiments, we provide empirical evidence that our knowledge-enhancement approach on a 7B model surpasses standard fine-tuning and prompting baselines on the same model, underscoring the value of verifiable reasoning over general capabilities in the domain of drone safety modeling.
The paper is organized as follows:
Introduction: The core position of safety in the context of the expansion of high-altitude solar UAV applications is described. It is pointed out that the traditional safety modeling relying on artificial expert analysis is difficult to keep up with the pace of rapid development, and the existing large language model (LLM) reasoning framework (such as graph of thoughts, got) is too universal due to the lack of domain knowledge; It is clear that the purpose of this study is to propose a K-EGoT framework to fill the above gaps, and briefly introduce the organizational logic of the subsequent chapters of the paper.
Background and related work: review the existing safety analysis methods (such as fault tree analysis, FTA; Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) is mainly used for post design verification, breaking away from the limitations of early system architecture, combing the evolution of LLM reasoning paradigm from chain of thought (COT) to tree of thoughts (TOT) and got. At the same time, it points out that the current LLM application in processing structured forms such as SysML state machine diagram and the lack of verifiability traceability required for UAV certification, which paves the way for the proposal of K-EGoT framework.
Intelligent safety modeling method: the core content of the K-EGoT framework is introduced in detail, including two core stages—“domain expert model training” (cultivating the basic LLM as domain experts through supervision and fine-tuning and direct preference optimization) and “dynamic safety extension reasoning” (performing safety extension tasks with the trained expert model as the core); This paper expounds the system construction process of UAV safety knowledge base (source extraction, classification and structure, de duplication conflict resolution, formalization), and explains the specific implementation of framework training and reasoning pipeline, such as the construction of mixed length thinking chain data set and the two-stage optimization based on “safety reasoning basis”.
Experiments and analysis: design experiments to verify the effectiveness of the K-EGoT framework. First, explain the experimental settings (build a high reliability data set with expert annotations, with Fleiss’ kappa of 0.82; Design two kinds of baselines: word class and fine-tuning; Based on qwen2-7b-instrument); Then answer the research questions through three kinds of experiments: performance comparison experiment verifies that K-EGoTt (SES 92.7) is significantly better than the baseline; Ablation Experiment quantifies the contribution of got reasoning, reasoning basis alignment, and dynamic reasoning; qualitative case analysis verifies the quality of safety extension and points out the limitations of conflict handling standards.
Discussion: discuss the research enlightenment, and emphasize the effectiveness of the combination of general reasoning framework and domain knowledge base for the professional field, as well as the key significance of verifying the reasoning process (not just the result) for UAV safety; Analyze the threat of effectiveness (the effectiveness of the structure is mitigated by the consistency of experts, the internal effectiveness is controlled by the unified model and configuration, and the external effectiveness is dealt with by proposing the road map of cross domain promotion); At the same time, it explains the value of K-EGoTt in automating early safety analysis, reducing costs and accelerating the development cycle.
Conclusion: summarize the core contribution of the paper, that is, put forward the K-EGoT framework to solve the problem of automatic safety modeling of high altitude solar UAV and verify its advantages; Acknowledge current limitations (e.g., difficulties in handling implicit priority conflict criteria); Pointed out the future research direction (development of priority arbitration mechanism, integration of formal verification tools); Finally, the author’s contribution, financial support, data availability and other information are supplemented, and the Appendix A details the knowledge base safety standards.
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Background
Ensuring the safety of high-altitude solar drones is a task of paramount importance, given their deployment in long-endurance missions lasting weeks or even months in the stratosphere. These platforms operate under extreme environmental fluctuations and rely on advanced autonomous decision-making in the absence of continuous human supervision. Therefore, achieving endogenous safety—building reliability into the system from the very beginning of its design—is the foremost challenge to guarantee their operational success. To realize this goal, a structured and formal approach is indispensable, making the Systems Modeling Language (SysML) a critical tool [5]. As the de facto standard for model-driven engineering in complex aerospace systems, SysML provides a rich set of graphical notations to rigorously specify, analyze, and document the intricate behaviors of these drones, ensuring design consistency and facilitating early verification. However, applying SysML to effectively model the safety of high-altitude solar drones presents a formidable challenge. The primary difficulty does not lie in the language itself, but in formally capturing the system’s most critical and complex risk: the profound flight control–energy coupling. The maneuvering decisions of the Flight Control System (FCS) are fundamentally constrained by the real-time status of the Energy Management System (EMS), such as the battery’s State of Charge (SOC) and available solar power. Conversely, the EMS’s ability to harvest and manage energy is directly influenced by the aircraft’s attitude and trajectory, which are determined by the FCS. Manually using SysML constructs, such as the State Machine Diagram, to exhaustively identify and model all hazardous interactions within this tightly coupled decision space is a daunting task, fraught with the risk of overlooking latent safety constraints.
2.2. Related Work
2.2.1. Traditional and Model-Based Safety Analysis
Formal safety analysis of avionics systems is a mature discipline governed by rigorous standards and methodologies. Foundational techniques include Functional Hazard Analysis (FHA) [6], Fault Tree Analysis, and Failure Mode and Effect Analysis. Mandated by key aerospace safety standards like ARP-4761 [7], these methods are essential for identifying and mitigating risks. To bridge the gap of these techniques being disconnected from design models, the field of model-based safety analysis has emerged, aiming to integrate safety considerations directly into design models using mechanisms like SysML Profiles [8]. Researchers have successfully used profiles to embed safety information in models [9,10] and support hazard analysis [11].
Limitations: While these model-based approaches create a semantic link between safety and design artifacts, the link is not generative. The safety expert must still manually interpret standards, identify relevant constraints, and translate them into the model using the profile’s stereotypes and tags. The framework does not proactively propose safety extensions or reason about the completeness of the analysis, remaining a passive documentation tool that still heavily relies on manual expert effort.
2.2.2. Defect Detection of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
UAV flight data anomaly detection faces three challenges: the diversity of anomaly types leads to insufficient coverage of a single model, the scarcity of labeled data limits the supervised learning performance, and sensor noise interferes with the accuracy of the model. Existing research has improved the detection range through hybrid models and multi model fusion. For example, the CA-1DCL-EF model achieved an accuracy of 94.22% in detecting bias and drift anomalies [12,13]. Using unsupervised and semi supervised learning to reduce dependence on annotated data, the STARE model achieved an F1 score of 89.34% on the ALFA dataset, while the VAE model achieved an accuracy of 92.31% on imbalanced datasets [14,15]. At the same time, data preprocessing and feature engineering are introduced to enhance the anti noise ability. The combination of Savitzky Golay filtering and DCNN-AE achieves an F1 score of 99.89%, and the feature selection based on MIC reduces the noise false detection rate by 8% [16,17].
Limitations: The above research focuses on anomaly detection and response during the operation phase of unmanned aerial vehicles, but fails to advance safety considerations to the modeling and design phase of the system. This paradigm essentially relies on algorithms to identify abnormal patterns that have occurred or are developing from sensor data streams, but cannot fundamentally prevent or avoid inherent risks caused by platform design flaws, inaccurate control system modeling, or improper component selection. Therefore, integrating “design safety” with “operational safety” and embedding robustness and fault tolerance through safety checks and other means in the modeling stage is a key direction to improve the overall safety of unmanned aerial vehicle systems from the source, and is also an important gap in the existing research system.
2.2.3. LLM Applications in Software Engineering: Testing and Safety
The advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) [18] has opened new avenues for automating knowledge-intensive tasks in software engineering, including software testing [19,20] and deriving safety requirements from specifications [21].
Limitations: Despite their potential, these applications typically operate on natural language specifications or source code. They are not directly equipped to handle the structured, graphical formalism of SysML state machine diagrams. Furthermore, they often lack the rigorous, verifiable traceability required for the certification of drone systems, as their reasoning process is opaque and not explicitly grounded in an accepted safety standard or knowledge base.
2.2.4. Evolution and Limitations of LLM Reasoning Paradigms
To enhance complex task performance, LLM reasoning strategies have evolved from linear Chain of Thought (CoT) [22] to more complex, multi-path structures like Tree of Thoughts (ToT) [23] and Graph of Thoughts (GoT). These frameworks improve general problem-solving by allowing for exploration, evaluation, and aggregation of different reasoning paths. Concepts like self-refinement [24] and self-evaluation [25] are often employed within these structures to improve intermediate results.
Limitations: These powerful paradigms are still general-purpose frameworks. Their self-evaluation capabilities rely on generic heuristics derived from the model’s pre-trained knowledge, which is insufficient for domains requiring deep specialization, such as drone safety. Despite its multi-path exploration, ToT’s heuristic-based node evaluation can prematurely prune globally optimal paths in the absence of domain knowledge. For instance, in an energy management scenario, a seemingly “inefficient” decision like a precautionary descent might be the safest long-term strategy, a nuance that a general-purpose heuristic is unlikely to capture. This creates a clear research gap: the need for a mechanism to ground these flexible reasoning structures in a verifiable, domain-specific knowledge base.
3. Intelligent Safety Modeling Method
3.1. Overall Architecture: The Knowledge-Enhanced Graph of Thoughts (K-EGoT) Framework
To address the challenge of formally and explicitly injecting implicit safety design criteria into early-stage design models for high-altitude solar drones, this paper proposes an innovative Knowledge-Enhanced Graph of Thoughts (K-EGoT) framework. As shown in Figure 2, this framework aims to deeply integrate the powerful generative reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) with the profound expert knowledge of the drone safety domain, thereby achieving automated and trustworthy safety extension of SysML state machine diagrams.
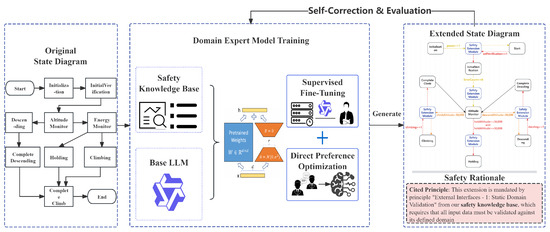
Figure 2.
Overall Architecture of the K-EGoT framework, illustrating the two-phase process: (1) training a domain-expert model by aligning it with a safety knowledge base, and (2) using the expert model in a dynamic reasoning loop to extend an initial SysML diagram.
The implementation of this framework involves two core phases, clearly embodying the design philosophy of “first train the expert, then let the expert work”.
In Phase 1: Domain Expert Model Training, our goal is to cultivate a general-purpose Base Large Language Model (Base LLM) into a domain expert well-versed in the safety of high-altitude solar drone flight control–energy coupling. This phase begins with two key inputs: our constructed Drone Safety Knowledge Base and a Base LLM (e.g., Qwen2-7B). Subsequently, we adopt a Two-Phase Optimization Strategy: first, we perform basic capability alignment using domain datasets through Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT); then, through Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), evaluated based on the quality of the “Safety Rationale,” we achieve a robust alignment with expert reasoning processes. The final output of this phase is a deeply domain-specialized Domain Expert Model.
In Phase 2: Dynamic Safety Extension Reasoning, we use the trained Domain Expert Model as the core “execution engine” to perform specific safety extension tasks within a structured graph that possesses dynamic self-correction and intelligent exploration capabilities. This phase takes an Initial SysML State Machine Diagram as input. Our execution engine begins its work, with a core internal workflow that loops through generating an extension plan and safety rationale, followed by self-correction and evaluation based on the knowledge base. This loop iterates through Dynamic Exploration & Optimization until an optimal solution is found. Finally, this phase outputs two key products: an extended safety state machine diagram with endogenous safety semantics, and a corresponding Traceable Safety Rationale.
3.2. Knowledge Base Curation
The foundation of our knowledge-enhancement approach is a verifiable, domain-specific knowledge base. The quality and structure of this knowledge are critical for grounding the LLM’s reasoning. We developed a systematic methodology to curate this knowledge base, transforming broad safety standards into a structured format composed of formalized objects with unique IDs and defined fields.
The curation process involved four key stages:
- Source Identification and Extraction: Our process began with identifying authoritative sources, including general aerospace safety standards (e.g., ARP-4761) and internal design documentation for high-altitude solar drones. A team of three domain experts systematically reviewed these documents to extract atomic safety principles, requirements, and failure mode descriptions relevant to software design.
- Classification and Structuring: The extracted raw principles were then classified into a structured hierarchy. We developed a five-category taxonomy corresponding to key aspects of the system’s design: (1) External Interfaces, (2) Functional Logic, (3) Functional Hierarchy, (4) States and Modes, and (5) Flight Control–Energy Coupling. Each principle was assigned to one or more categories.
- De-duplication and Conflict Resolution: Principles extracted from different sources often had semantic overlaps. Experts collaboratively reviewed the classified principles to merge duplicates and rephrase them into a canonical form. Potential conflicts between principles (e.g., a safety principle requiring power-off of a component versus a functional principle requiring it to be on) were resolved by establishing explicit priority rules and context-dependent applicability notes.
- Formalization: Finally, each curated principle was formalized into a machine-readable object with a unique ID, a concise natural-language description, and structured fields (e.g., Hazard, Context, Mitigation Guideline). This formalization is crucial for enabling the automated verification of the metric, as discussed in Section 4.2.
This rigorous curation process ensures that our knowledge base is not merely a collection of text but a structured and verifiable foundation for our K-EGoT framework. To facilitate a systematic failure mode analysis, the knowledge base is organized into five core categories: External Interfaces, Functional Logic, Functional Hierarchy, States and Modes, and the critical Flight Control–Energy Coupling. Each category contains specific tables of analysis criteria, with some classifications featuring finer subdivisions. For instance, the “Functional Logic” category is further detailed from four perspectives, including control computation and processing logic, whereas “Functional Hierarchy” is analyzed in terms of serial and parallel relationships. This hierarchical structure thereby forms a comprehensive and structured knowledge system designed to guide and validate the AI model’s reasoning process. The detailed safety criteria organized by this methodology are provided in the Appendix A and Appendix B. These criteria form the core of our knowledge base, providing verifiable “factual evidence” for subsequent intelligent reasoning. For the complete, structured list of these criteria, categorized as described, please refer to Appendix A (Safety Criteria Knowledge Base).
3.3. K-EGoT Training and Reasoning Pipeline
Having established a domain knowledge base, the K-EGoT framework “activates” this knowledge through an advanced training and reasoning pipeline, enabling it to dynamically guide and optimize the safety modeling process.
3.3.1. Phase 1: Base Model Training Based on Thought Process Alignment
The first phase of the K-EGoT framework is to train a base model with an “expert-level” safety mindset. This phase aims to make the model not only imitate correct outputs but also understand and reproduce the intrinsic logic that safety experts use in their decision-making.
Dataset Construction for High-Altitude Solar Drone Safety Scenarios: To train the LLM to master the specific safety logic of high-altitude solar drones, we created an extended state machine diagram dataset. This dataset is composed of both long and short Chains of Thought (CoT), which provide the foundational reasoning paths for the subsequent “Graph of Thoughts” exploration.
The long-chain data was generated first. We used the Deepseek-R1 model, providing it with specific scenarios for high-altitude solar drones (e.g., “Design a state transition for a drone from daytime charging cruise to nighttime energy-saving mode, considering the risk of power fluctuations due to cloud cover”). This process created a dataset featuring detailed, step-by-step reasoning and explicit “Safety Rationales”.
Separately, the short-chain data was created using DeepSeek-V3 as a rewriter. This model compressed the lengthy reasoning processes from the long-chain data into concise versions that retained the core logic. By mixing these short reasoning chains with the original long ones during supervised fine-tuning, the model learns both comprehensive reasoning patterns and efficient reasoning shortcuts. This enables it to generate logically rigorous yet concise reasoning. Figure 3 illustrates this rewriting process, where a rewriter model is prompted to compress a detailed, lengthy chain of thought (“Long Instruction”) into a concise version (“Short Instruction”) that retains the core logic.
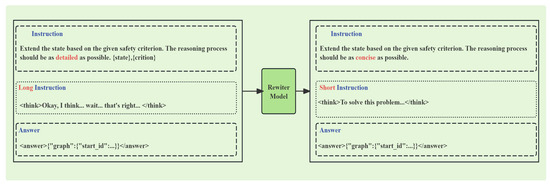
Figure 3.
Creation of mixed-length Chain of Thought for state machine diagram extension.
When rewriting the Chains of Thought generated by DeepSeek-R1, the prompt template used is shown in Appendix B, which includes explicit constraints such as retaining key steps and prioritizing professional terminology (e.g., SOC, MPPT).
For each data point in dataset , the rewriter model is used to convert the long Chain of Thought trajectory into a shorter one , formally expressed as (1):
represents the “input scene prompt” corresponding to the i-th data point, which triggers the initial task description for the model to generate the inference trajectory. Using these rewritten short CoT trajectories, a short reasoning chain dataset is constructed. Finally, the long and short datasets are randomly merged to create a new mixed dataset . The equation is (2).
Figure 4 provides an example of the final data structure, contrasting the “long think” tag in the long-CoT dataset (left) with the “short think” tag in the short-CoT dataset (right).
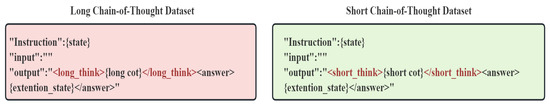
Figure 4.
Example of long and short Chain of Thought datasets.
Two-Phase Model Optimization based on “Safety Rationale”: (1) Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) Cold-Start Phase: The LLM is fine-tuned using the mixed dataset to stimulate its reasoning capabilities for the high-altitude solar drone flight control and energy management domain. The optimization objective for Mixture SFT, denoted as M, can be formulated as follows (3)–(5):
represents the target output corresponding to the i-th data point, and represents the input scene prompt for the i-th data point. This mixed approach ensures the model learns both the comprehensive flight control–energy coupling reasoning patterns from the long Chains of Thought and the efficient reasoning methods demonstrated by the short ones.
(2) Thought Process Alignment Phase based on Direct Preference Optimization (DPO): After the SFT cold-start, the DPO training phase begins. The core of this phase is to achieve thought process alignment. The positive and negative sample pairs we construct are judged not only by the correctness of the final model code but, more importantly, by the logicality and completeness of the accompanying “Safety Rationale”. For example:
- Positive Sample (): The extension plan is correct, and its “Safety Rationale” clearly references knowledge base criteria with a complete logical chain.
- Negative Sample (): The extension plan may be coincidentally correct, but its “Safety Rationale” is logically confused, far-fetched, or fails to cite the most relevant criteria.
The optimization objective function for DPO can be expressed as (6):
where denotes the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) loss function, where represents the learnable parameters of the domain expert model. A smaller loss value indicates that the model is more inclined to generate outputs preferred by experts. is the DPO training dataset, composed of “input-positive/negative sample pairs” for the safety modeling scenario of high-altitude solar-powered unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). x stands for a single input sample in this dataset. is the set of positive samples corresponding to input x; positive samples must satisfy the criteria of “correct SysML extension scheme, complete logical safety basis, and citation of knowledge base standards”. is the set of negative samples corresponding to input x; negative samples are characterized by “even if the extension scheme is coincidentally correct, the safety basis still has logical confusion or fails to cite key knowledge base standards”. and respectively represent the probabilities that the model, with parameters , generates a positive sample and a negative sample given input x. Through the cross-entropy loss, the formula forces the model to maximize the “proportion of probabilities for generating positive samples”: the numerator is the sum of generation probabilities of all positive samples, while the denominator is the sum of generation probabilities of both positive and negative samples. The logarithm of this ratio is taken, a negative sign is added, and then the sum is calculated by iterating over all input samples in . Ultimately, this aligns the model"s reasoning process with the expert’s safety logic.
In this way, we deeply integrate the domain knowledge of flight control–energy coupling into the DPO training process, strengthening the model’s safety awareness and making it more inclined to generate extension plans that comply with the safety specifications for high-altitude solar drones.
3.3.2. Phase 2: Dynamic Safety Extension Reasoning Based on K-EGoT
Once a deeply domain-aligned expert model is available, the second phase of K-EGoT—dynamic reasoning—begins. This phase uses the trained model as an “execution engine” to perform the actual state machine diagram safety extension within a structured, self-correcting graph. The process, which achieves efficient and reliable exploration of complex safety problems through structured node interactions and dynamic parameter adjustments, is formally described in Algorithm 1.
The reasoning process of K-EGoT consists of three types of logical nodes that work together to form an iterative self-optimization loop:
- Answering Node: This node is executed by our trained expert model, . It receives the current SysML model fragment and an aggregated prompt from its parent node . It then generates a set of candidate extensions, where each candidate consists of a new model fragment and a corresponding, knowledge-base-traceable “Safety Rationale” . This stochastic generation process can be formalized as sampling from the expert model"s probability distribution, conditioned on the input and controlled by a dynamic exploration factor . The equation is (7):
- Evaluation Node: This node is also executed by our expert model. It receives an output pair from an Answering Node and performs a domain-specific evaluation. Its task is to assess the quality of the “Safety Rationale” against the domain knowledge base . The evaluation yields a normalized score and a meta-rationale, the “Evaluation Rationale” . The score is a function of the rationale’s logical coherence and its grounding in the knowledge base. The equation is (8):where is a weighting factor.
- Aggregate Rationale Node: This node is responsible for synthesizing information to guide future reasoning steps. It fuses the prompt that led to the current solution with the generated rationale and the evaluation rationale . The function in the formula serves as the “aggregation mechanism”, it systematically combines the input elements (, , and ) to identify their respective strengths and weaknesses. Through this integration, produces a more precise and informative aggregated prompt , which then embeds corrective instructions or refined guidance for the subsequent layer of Answering Nodes. In essence, ensures that prior reasoning (encoded in ), newly generated insights (), and evaluative feedback () are harmonized into a cohesive and improved prompt, enabling more effective reasoning in later stages. The equation is (9):
| Algorithm 1 K-EGoT Dynamic Safety Extension Reasoning |
|
Dynamic Control of Exploration and Exploitation: One of the most critical mechanisms of the K-EGoT framework is the use of the score produced by the Evaluation Node to dynamically control the generation Exploration Factor () of subsequent nodes, thereby achieving an intelligent balance between the breadth (exploration) and depth (exploitation) of the search.
- High Score → Low Exploration Factor (Exploitation): If an extension plan receives a high score, indicating a credible reasoning path, the framework reduces the exploration factor to encourage more deterministic, high-fidelity refinement along that path.
- Low Score → High Exploration Factor (Exploration): If a plan scores poorly, suggesting a flawed path, the framework increases the exploration factor to promote diversity and encourage the model to escape local minima by exploring novel solutions.
This self-adaptive mechanism is governed by an exploration factor update rule that adjusts for the next iteration based on the best score, , achieved in the current iteration. We model this relationship using a shifted sigmoid function, ensuring smooth transitions between exploration and exploitation. The equation is (10):
where is the logistic sigmoid function; is a scaling factor controlling the sharpness of the transition; is a predefined score threshold that demarcates “good” from “poor” solutions; is the minimum threshold for exploring factors, at which point the model prioritizes generating schemes based on validated safety logic to reduce randomness; is the maximum threshold for exploring factors, at which point the model will generate more diverse candidate solutions to cover potential undiscovered risks.
4. Experiments and Analysis
To rigorously evaluate our proposed K-EGoT framework, we designed a comprehensive set of experiments aimed at answering the following three research questions:
- Research Question 1 (Overall Effectiveness): How does the overall performance of our K-EGoT framework compare to current state-of-the-art prompting strategies and standard fine-tuning methods on the safety model extension task?
- Research Question 2 (Component Contribution): How much do the key components of the K-EGoT framework (GoT reasoning paradigm, rationale-based alignment, dynamic reasoning strategy) individually contribute to its overall performance?
- Research Question 3 (Generation Quality): What is the practical quality and interpretability of the safety extensions and “Safety Rationales” generated by the K-EGoT framework?
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Dataset Curation Process
For a rigorous evaluation, we constructed a domain-specific dataset centered on the complex operational scenarios of “high-altitude solar drones”. The curation process involved three stages:
Initial Draft Generation: We began by generating 200 initial functional state machine diagrams. We used the DeepSeek-V3 model with scenario-based prompts (e.g., “Design a state machine for a drone transitioning from daytime charging cruise to nighttime energy-saving mode, considering potential cloud cover”.). These drafts served as a baseline for expert annotation.
Expert Annotation and Rationale Formulation: We assembled a team of three drone safety experts with 2.5, 7, and 11 years of industry experience, respectively. Each initial diagram was independently annotated by two experts. The annotation task was governed by a strict guideline: (1) Correct any functional errors in the diagram. (2) Extend the diagram by adding states, transitions, and guards to cover all relevant safety criteria from our knowledge base (Section 3.2). (3) For each modification, write a detailed “Safety Rationale” that explicitly cites the relevant Knowledge Base principle ID, explains the potential risk, and details how the modification mitigates it.
Adjudication and Reliability Assessment: To ensure consistency, a third, senior expert reviewed cases where the two primary annotators disagreed and made a final adjudication. To quantify the consistency of our expert annotations, we calculated the Inter-Rater Reliability (IRR) on a subset of 50 diagrams independently annotated by all three experts. Using Fleiss’ Kappa for multiple raters on the categorical task of identifying required safety extensions, we achieved a Kappa value of 0.82, indicating substantial agreement. This high level of agreement mitigates concerns about the subjectivity of the ground truth and confirms the reliability of our evaluation dataset. The final dataset comprises triplets of (Original Diagram, Expert-Extended Diagram, Safety Rationale).
4.1.2. Baselines
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of our K-EGoT framework, we designed a hierarchical set of baseline methods. All methods, including the prompting-based baselines, were executed on the same Qwen2-7B-Instruct base model to ensure a fair comparison of the approaches themselves, rather than the underlying model scale. The parameters of the Qwen2-7B-Instruction model are shown in the Table 1.

Table 1.
Qwen2-7B Model Architecture and Core Parameters.
Group 1: Prompting-Based Baselines. This group explores the upper limits of pure prompting engineering on the base model.
- Chain of Thought (CoT): The model is provided with a few examples showing a linear, step-by-step reasoning process.
- Tree of Thought (ToT): The model is prompted to generate multiple possible extensions at each step, perform self-evaluation, and select the best one to continue.
- Graph of Thought (GoT): The model is guided by the state-of-the-art GoT prompting strategy to merge and refine reasoning paths.
Group 2: Fine-Tuning Baselines. This group evaluates different fine-tuning strategies on the same base model.
- Standard SFT: The model is fine-tuned on our dataset using standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) without the “Safety Rationale”.
- SFT + DPO-Behavioral: After SFT, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is applied. The preference pairs are constructed solely based on whether the final generated model code is correct (behavioral alignment).
- K-EGoT (Our Method): Our complete method, which fine-tunes the model using our rationale-centric, two-phase optimization strategy.
4.1.3. Implementation Details
All experiments used the Qwen2-7B-Instruct as the base model. During model training, we used bf16 mixed precision. Key hyperparameters were set as follows: the learning rate was set to 1.0 × 10−4 with a cosine annealing schedule; the per-device training batch size was 1, with an 8-step gradient accumulation, resulting in an effective batch size of 8. All models were trained for 3.0 epochs. All experiments were conducted on a server equipped with three NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 (24 GB VRAM) GPUs.
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
We designed a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes both automated quantitative analysis and qualitative expert assessment. The evaluation formula is (11)
The weighting in Equation (11) is set based on engineering priorities in safety-critical domains, established in consultation with domain experts. Correctness () is assigned the highest weight (0.5) as the functional and structural accuracy of the final safety model is the foremost requirement; an incorrect model is unacceptable regardless of its rationale. Rationale Quality () is given the next highest weight (0.3) as it reflects the core research objective: ensuring the model’s reasoning process is auditable and aligned with expert logic, which is critical for trustworthy AI in safety engineering. Structural Integrity () is weighted at 0.2, treating it as a foundational criterion. While syntactical validity (e.g., valid JSON) is essential for automation, it is considered a less complex task and thus carries less weight than the semantic correctness of the model and the logical soundness of its reasoning. The calculation methods for each sub-metric are as follows:
- A. Correctness (): This metric (12) aims to measure the structural similarity of the generated safety state machine diagram to the expert-annotated ideal diagram, calculated by computing the F1-score of graph elements (: is the F1 score of the state element : is the F1 score of the transition element.).This weighting reflects the consensus of domain experts that in SysML state machines, the critical safety logic (e.g., guards, triggers, and constraints like the flight control–energy coupling) is primarily embedded within the transitions (0.6) rather than the states (0.4), making them more critical to evaluate correctly.
- B. Rationale Quality (): This metric (13) quantifies the logicality and traceability of the “Safety Rationale”. It is composed of two sub-metrics:The 0.7 weight for emphasizes our study’s focus on objective, auditable traceability, a “hard metric” essential for safety certification (aligning with standards like ARP-4761). Coherence (0.3), a “soft metric” assessing logical fluency, is considered supplementary, as our goal is verifiable reasoning, not just plausible-sounding text. is a hard metric calculated by parsing the ‘Safety Rationale’ to extract cited knowledge base principle IDs. We then perform an exact match check against our knowledge base to verify if the cited ID exists and is relevant to the problem context. The score is the proportion of correctly cited principles. ‘Coherence’ is evaluated by an LLM-based judge.
- C. Structural Integrity (): This metric (14) evaluates the basic technical quality of the generated output (e.g., valid JSON format, schema adherence).where is a validity metric for generating output in JSON format, is an indicator of the degree of compliance of the generated output with a predefined schema (data structure specification), is an effective indicator of the connectivity between elements in the generated state machine and other structures.
Expert Evaluation
We invited the same three experts who participated in the dataset curation to conduct a blind evaluation of the extended models. They rated them on a scale of 1–5 across three key dimensions. Higher scores indicate superior model performance.
- Safety Coverage (): Does the extension cover all critical flight control–energy coupling risks?
- Rationale Trustworthiness (): Is the model’s reasoning process reliable and trustworthy?
- Engineering Practicality (): Is the extended model overly complex? Is it feasible for application in actual engineering practice?
4.3. Results
4.3.1. Research Question 1: Overall Effectiveness Analysis
To answer Research Question 1, we conducted a comprehensive comparison of our proposed K-EGoT framework against all baseline methods. The main experimental results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of different methods on the safety extension task. All methods use the Qwen2-7B-Instruct base model.
The results reveal a clear hierarchy of performance. Our K-EGoT framework achieved the highest score across all automated and expert evaluation metrics, with a total SES score of 92.7. This score underscores a significant improvement over both prompting-based and standard fine-tuning approaches. A key observation is the strong correlation between our core automated metric, Rationale Quality (), and the expert-rated Rationale Trustworthiness (). K-EGoT’s top score in (88.4) is mirrored by its top score in (4.7), providing strong evidence that our methodology of aligning the reasoning process produces genuinely more trustworthy and verifiable outputs.
The fine-tuning baselines (Group 2) uniformly and substantially outperform the prompting-based baselines (Group 1), even when the most advanced GoT prompting is used. For instance, even a Standard SFT model (Total SES 88.0) is more effective than the GoT-prompted model (Total SES 84.7). This highlights that for highly specialized and structured tasks, injecting domain knowledge through fine-tuning is far more critical than relying on the general-purpose reasoning of a prompted model. While GoT is the strongest of the prompting methods, its relatively low score (74.0) indicates a struggle to produce domain-aligned, verifiable reasoning steps, a gap that only fine-tuning appears to bridge effectively. Finally, comparing SFT + DPO-Behavioral (89.4) with K-EGoT (92.7) demonstrates the incremental but crucial value of our rationale-centric alignment over simple behavioral alignment.
The K-EGoT framework achieved a score of 92.7 on the safety Extended Score (SES), demonstrating significant advantages over traditional GoT methods with a score of 84.7. This achievement represents a significant advancement in AI inference methods in safety critical areas. This study has achieved a significant shift from general heuristic reasoning to domain knowledge based verifiable reasoning, and its innovation is mainly reflected in three aspects: firstly, the framework achieves deep alignment at the level of thinking processes by introducing a “safety basis” mechanism. Unlike behavior alignment methods that only focus on the final output, K-EGoT requires each decision to be traceable to specific principles in the knowledge base. For example, when analyzing the coupling relationship between flight control and energy management, professional guidelines such as “Flight Control Energy Coupling-1” are explicitly referenced to ensure transparency and verifiability of the inference process. Secondly, the innovative dynamic exploration mechanism effectively balances the complex relationship between safety constraints and task requirements. The system can make intelligent adjustments based on real-time operating conditions, such as automatically limiting climb operations when the battery state of charge (SOC) is low at night, ensuring both flight safety and feasibility of task execution. Thirdly, this study provides the first automated safety modeling solution with complete auditing capabilities for the field of solar unmanned aerial vehicles. Practice has shown that this solution can improve expert analysis efficiency by more than 10 percentage points, while fully meeting the strict requirements of aviation standards such as ARP-4761 for system safety, establishing a new benchmark for the development of autonomous system safety engineering.
Answer to Research Question 1: The experimental results show that the K-EGoT framework is comprehensively and significantly superior to all baseline methods. The data clearly indicates that for this specialized task, fine-tuning focused on the reasoning process is substantially more effective than general-purpose prompting or simple behavioral fine-tuning on the same base model.
4.3.2. Research Question 2: Component Contribution Analysis
The ablation study results, presented in Table 3, allow for a deeper analysis of each component’s contribution to the framework’s success. The findings decisively reveal the specific role each innovation plays.

Table 3.
Ablation study results.
- The necessity of the GoT reasoning paradigm: Removing the non-linear GoT structure and reverting to a linear reasoning chain (w/o GoT Reasoning) results in a significant performance drop, particularly in Rationale Quality (). This indicates that for complex safety problems where multiple, interacting criteria must be considered simultaneously, the ability to explore, merge, and refine parallel lines of thought is crucial for developing a comprehensive and logical safety case.
- The core value of “Safety Rationale” alignment: Removing rationale-based alignment (w/o Rationale Alignment) causes the most substantial performance degradation, with the total SES score dropping by 7.6 points and the score plummeting by 14.2 points. This irrefutably proves that using the “Safety Rationale” as the target for DPO is the core driver of our framework’s performance. This method compels the model to internalize the expert’s verifiable reasoning process, bridging the gap between simply generating a syntactically correct model and generating a trustworthy, defensible one.
- The effectiveness of the dynamic reasoning strategy: Removing the dynamic, self-correcting reasoning loop (w/o Dynamic Reasoning) leads to a smaller but still notable performance decrease. This component acts as a fine-tuning mechanism for the reasoning process itself. Its function is to intelligently manage the trade-off between exploring a wide range of potential hazards (exploration) and perfecting the most promising safety mitigation strategy (exploitation). Its contribution, while not as foundational as rationale alignment, is key to achieving the highest level of stability and quality in the final generated model.
Answer to Research Question 2: The ablation study systematically demonstrates that the contribution of each component in the K-EGoT framework is positive and significant. Rationale-based alignment is the most critical factor, followed by the GoT reasoning structure, with the dynamic reasoning strategy providing a final layer of optimization.
4.3.3. Research Question 3: Qualitative and Failure Case Analysis
To answer Research Question 3, we qualitatively analyze the practical quality and interpretability of the results through a specific case study. We chose a typical “High-Altitude Solar Drone Altitude and Energy Coordinated Control System” as our case. The core task of this system is to maximize energy efficiency for long-endurance missions while meeting mission requirements.
The original functional state diagram, as shown in Figure 5, This state diagram presents the drone’s altitude control process through the logic of “state nodes + transition conditions”: Starting from the Start node, when Power == 1, it enters the Initialization state, and when SelfVeri == 1, it enters the InitialVerification state with ErrorCount = 0; then it enters the Altitude Monitor state. If Climb == 1, it enters the Energy Monitor state. When Energy == 1, it enters the Climbing state, and when Altitude == 1, it enters the Complete Climb state. If Climb == 0, it enters the Descending state, and when Altitude == 1, it enters the Complete Descending state. If Energy == 0, it enters the Holding state. Finally, the Complete Climb, Complete Descending, and Holding states all lead to the End node. This diagram originally describes the basic altitude control logic but ignores energy constraints. For example, it may enter the high-power-consuming Climbing state even when the battery is low, posing a safety hazard.
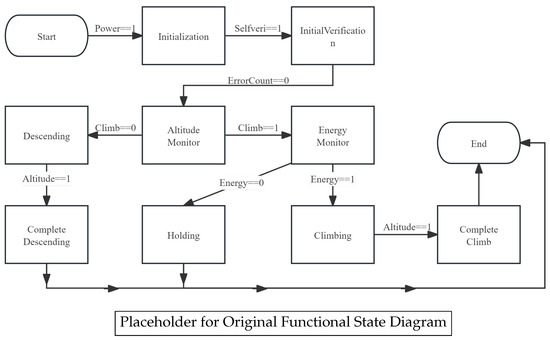
Figure 5.
Original functional state diagram, which lacks energy-aware safety constraints.
Our K-EGoT framework takes this original diagram and the relevant safety criteria from our knowledge base as input and automatically generates the safety-extended state diagram shown in Figure 6. The extended functional state diagram consists of two parts: the upper Input_Validation sub-diagram validates sensor data through Static Data Validation and Dynamic Data Validation, triggering Fault Diagnosis and Fault Handling in case of failures; the lower main process starts from Start, proceeds through Initialization, Initial Verification, and Altitude Monitor, then uses Power Arbiter as a safety safeguard to distinguish between Daylight Climbing and Night Climbing, managing the climbing process through Time judgment. It retains the Descending, Complete Descending, and Holding processes while adding an Emergency Mode, with all processes ultimately leading to End. Overall, it satisfies safety criteria through multiple dimensions including input validation, energy arbitration, time-divided climbing, and emergency mode.
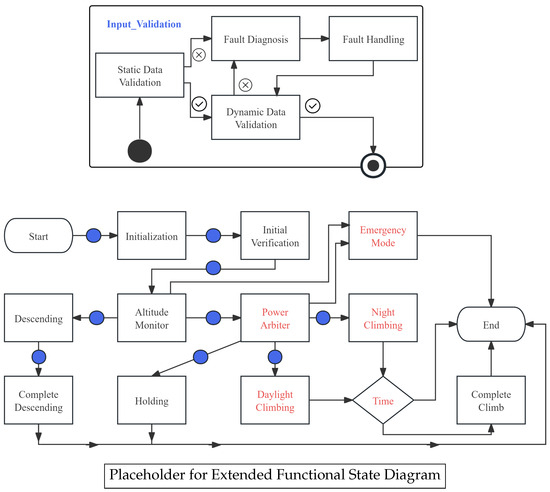
Figure 6.
Extended functional state diagram generated by K-EGoT, incorporating safety mitigations (The blue junctions represent the sub state graph Input_Validation).
More importantly, while generating this extension, K-EGoT produces a clear “Safety Rationale,” for example:
Risk: The original model’s logic is incomplete as it decouples flight maneuvers from energy availability. This could permit the drone to enter a high-power ‘Climbing’ state during nighttime, risking a complete energy depletion and subsequent loss of control. Cited Principle: This modification is driven by the core principle “Flight Control–Energy Coupling-1: Degradation of Maneuverability under Energy Constraints”. This principle mandates that the flight control system must degrade its maneuvering capabilities based on the current battery State of Charge (SOC). Applied Extension: A mandatory ‘EnergyMonitor’ guard state has been inserted before the ‘Climbing’ state. Any transition to ‘Climbing’ is now contingent on this guard verifying that the current ‘Battery_SOC’ is above a predefined safety threshold. Outcome: The extension explicitly models the critical flight control–energy coupling, ensuring the drone prioritizes survival over mission objectives in energy-scarce situations.
This “Safety Rationale” clearly articulates the necessity of the extension, the cited principle, the specific modification, and the achieved safety outcome. This demonstrates that K-EGoT can not only generate structurally correct models but also provide a traceable, interpretable reasoning process for its decisions, which is of extremely high value in practical engineering applications.
However, our approach is not without limitations. A notable failure case occurred when two safety criteria had a subtle, context-dependent priority. For instance, a criterion mandating minimal control surface movement for energy saving (from Appendix A.5) conflicted with one requiring rapid attitude adjustment to maximize solar exposure (from Appendix A.2). The model correctly identified both but struggled to generate a state that optimally arbitrated between them, instead proposing an overly conservative solution that prioritized energy saving at the expense of mission objectives. This highlights a current limitation in reasoning about implicit priority hierarchies, which often requires a deeper, qualitative understanding of the mission phase.
Answer to Research Question 3: The case study and failure analysis demonstrate that K-EGoT generates high-quality, interpretable, and traceable safety extensions. While it successfully handles explicit safety criteria, its primary limitation lies in arbitrating between conflicting criteria with implicit, context-dependent priorities.
4.3.4. Research Question 4: Computational Efficiency Analysis
While our primary goal is to maximize the quality and trustworthiness of the safety model, it is important to quantify the computational cost required to achieve this. We evaluated all methods on the same hardware (3 NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 GPUs) and measured four key efficiency metrics:
- Total Training Time (hours): This measures the one-time, upfront cost required to produce a usable specialist model. This is critical for assessing the engineering effort needed for deployment.
- Average Inference Latency (seconds): This measures the total time required to generate one complete safety-extended diagram from an initial diagram, averaged over the 200-diagram test set. This represents the “thinking time” of the model.
- Average Inference Calls: This measures the average number of times the LLM must be queried to produce one complete output. This represents the complexity of the reasoning process.
- Average Inference Tokens: This measures the average total number of tokens processed by the LLM during a complete inference task. This metric is a proxy for the total amount of computational work performed and directly correlates with API costs in a production environment.
The results of this efficiency comparison are presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Computational efficiency comparison. All fine-tuning models were trained on the same devices. All inference metrics are averaged over the 200-diagram test set.
The data in Table 4 reveals the computational trade-offs made by our framework. Training Cost Analysis: The prompting-based baselines (Group 1) require no training time, which is their primary advantage. The fine-tuning methods (Group 2) require a one-time training cost. Our K-EGoT (18.25 h) and the SFT + DPO-Behavioral (16.93 h) methods require more than double the training time of Standard SFT (7.12 h). This is an expected result, as they both involve a more complex two-stage training process (SFT + DPO). Considering the improvement of model performance, this one-time training cost is also acceptable.
Inference Cost Analysis: The inference metrics clearly show the cost of “thinking like an expert”. The single-pass methods (CoT, Standard SFT, SFT + DPO) are the fastest, with latencies around 10-14 s, requiring only 1 inference call. In contrast, our K-EGoT framework is by far the most computationally intensive, taking an average of 266.38 s to process a single diagram. This high latency is a direct and deliberate consequence of its design. It is caused by the 18.62 average inference calls, which are necessary to execute the dynamic reasoning loop described in Algorithm 1. These calls represent the framework iteratively generating solutions, evaluating them against the knowledge base, and refining its strategy. The high token count (6012.80) reflects the generation of not just the final model, but also the verifiable “Safety Rationales” and “Evaluation Rationales” at each step.
Answer to Research Question 4: The K-EGoT framework demonstrates a clear and deliberate engineering trade-off. It exchanges significantly higher one-time training costs and per-inference computational costs (latency, calls, and tokens) for the substantial gains in model quality, verifiability, and trustworthiness documented in Table 2 and Table 3. For a safety-critical, non-real-time task like automated design-stage safety modeling, where correctness and auditable reasoning are paramount. Additional training and reasoning costs are acceptable.
5. Discussion
Our research demonstrates that enhancing advanced reasoning frameworks like GoT with a verifiable knowledge base is a highly effective strategy for specialized domains. The results show that a smaller model (7B parameters), when deeply aligned with expert reasoning patterns, can significantly outperform prompting-based approaches on the same hardware. The core insight is that for drone systems, verifying the process of reasoning via the “Safety Rationale” is more crucial than just verifying the final product. This approach turns the opaque reasoning of LLMs into a transparent, auditable trail, a critical step towards building trustworthy AI for safety engineering. Our work provides a new tool for engineers to automate early-stage safety analysis, potentially reducing costs and helping teams find critical design flaws much earlier in the development lifecycle.
The practical value of the K-EGoT framework is mainly reflected in three aspects: firstly, it addresses the limitations of traditional safety analysis as a post design verification activity, facilitates the integration of safety considerations from the initial stage of the design blueprint, and can help reduce the likelihood of high-cost design rework in the later stage. Secondly, the audit trajectory generated by the safety basis mechanism aligns with the strict transparency requirements of aviation safety certification, supporting the feasibility of AI assisted safety engineering for application in the regulated aerospace field. Finally, the success of the framework on the 7B model indicates that professional safety modeling does not necessarily require a large-scale foundational model, which has particular relevance for engineering teams with limited computing resources. Case studies have shown that the system can automatically identify key safety constraints such as “prohibit climbing during low battery at night” and generate engineer verifiable decision basis through structured knowledge referencing.
Construct Validity: A potential threat is the subjectivity of our “golden standard” expert-annotated dataset. To mitigate this, we employed a rigorous curation process involving multiple experts and adjudication. We quantitatively demonstrated the reliability of this process by reporting a high Inter-Rater Reliability score (Fleiss’ Kappa = 0.82), which confirms a substantial agreement among our experts and provides a strong defense against claims of excessive subjectivity.
Internal Validity: The superior performance of our method could be attributed to implementation details rather than the approach itself. We controlled for this by using the exact same base model (Qwen2-7B) and training configuration for all fine-tuning baselines, ensuring that the only significant variable was the fine-tuning strategy itself.
External Validity: Our study is specific to the domain of high-altitude solar drones. To address this, we propose a concrete Generalization Roadmap rather than making broad claims. We believe the K-EGoT philosophy is transferable. For the autonomous driving domain, for instance, a transfer would involve: (1) curating a knowledge base from standards like ISO 26262 [26]; (2) creating a preference dataset focused on critical decision points (e.g., intersection negotiation scenarios); and (3) fine-tuning an expert model for that domain using our rationale-centric alignment method. This constitutes a core direction for our future work.
Although the current achievements are significant, research has also revealed several directions that require further investigation: the primary challenge is to develop more refined priority arbitration mechanisms to address implicit context related priority issues between safety criteria, such as conflicts between energy conservation and task objectives. Secondly, it is necessary to integrate the framework output with the formal validation tool chain and prove the safety attributes of the generated model through mathematical methods—this is a necessary step for industrial applications. In terms of cross domain promotion, the methodology of this framework can be adapted to fields such as autonomous driving, but it needs to reconstruct the knowledge base based on standards such as ISO 26262 and re align the domains. From the perspective of system evolution, it is possible to explore the extension of modeling from the design phase to runtime safety monitoring, and build a safety assurance system that covers the entire lifecycle of unmanned aerial vehicles. Finally, developing effective human-machine collaboration interfaces that enable evidence to efficiently support engineers in reviewing and refining AI generated models will be important for achieving human-machine collaborative safety engineering.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented K-EGoT, a method to enhance the Graph of Thoughts reasoning framework with a domain-specific knowledge base. K-EGoT framework proposed in this study notably improves the automation level of high-altitude solar unmanned aerial vehicle safety modeling by integrating domain expertise with the reasoning ability of large language models. The experimental results show that the K-EGoT model with 7B parameters achieves a SES Score of 92.7 points, which is considerably higher than the standard GoT prompt method (84.7 points). This improvement is primarily attributed to the innovative introduction of the “Safety Rationale” mechanism, which establishes a traceable connection between the reasoning process of LLM and the knowledge base verified by experts. The ablation study further indicated that the alignment strategy based on safety criteria contributed the most (improving SES by 7.6 points), followed by GoT inference structure (5.2 points) and dynamic inference strategy (3.1 points). This knowledge enhancement method addresses a key challenge of the lack of domain foundation in the application of general reasoning frameworks in the field of professional safety.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.S. and X.L.; methodology, Q.S.; software, Y.R.; validation, Q.S., B.F. and Y.R.; formal analysis, Q.S. and X.L.; investigation, C.H.; resources, Y.Y.; data curation, Q.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Q.S., B.F. and Y.R.; writing—review and editing, Q.S.; visualization, B.F.; supervision, C.H.; project administration, Y.Y.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is supported by the National Key R&D Program (Grant #2022YFB4501904).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The source code, knowledge base, and datasets generated and analyzed during this study are openly available in the K-EGoT repository on GitHub (version 1.0.0)at the following location: https://github.com/suqingran777/K-EGoT (accessed on 4 November 2025).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. The authors also acknowledge the use of artificial intelligence (AI) tools solely for optimizing the English expression of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Safety Criteria Knowledge Base
This appendix contains the detailed safety criteria curated for our knowledge base, as described in the main text.
Appendix A.1. External Interface Failure Mode Analysis Criteria

Table A1.
Data analysis criteria for external interface failure modes of high-altitude solar drones.
Table A1.
Data analysis criteria for external interface failure modes of high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | Static Data Domain Verification: For both continuous (e.g., battery voltage, control surface angle) and discrete (e.g., operating mode enumeration) interface data, check the correctness of handling under conditions of “normal/abnormal equivalence classes, boundary values, max/min values, undefined values, and precision,” ensuring that the flight control and energy management systems comprehensively validate all input data domains. |
| 2 | Dynamic Data Characteristics Verification: For the temporal behavior of interface data, check the correctness of handling dynamic anomalies such as “multi-cycle data stuck-at, rate-of-change overrun, and numerical jumps,” which is crucial for the timely detection of energy system (e.g., sudden power drop) or sensor failures. |
| 3 | Data Handling Verification in Critical Events: For critical events such as “power-on initialization and power-loss restart,” check the correctness of handling critical interface data (e.g., fault counts, energy state SOC) for initial values, safe values, and default values, ensuring the system can reliably enter a predetermined safe state. |
| 4 | Data Consistency Verification under Multiple Policies/States: For cases where a single interface data has multiple fault handling strategies or different requirements in different flight modes, check the consistency and correctness of its safe value and initial value settings to avoid safety hazards caused by conflicts between flight control and energy policies. |
| 5 | Data Behavior Verification during State Transitions: Check whether the “value, value range, and update frequency” of relevant functional interface data change as expected when the drone transitions between critical operating states (e.g., from “daytime charging cruise” to “nighttime energy-saving”), ensuring smooth and safe state transitions. |
| 6 | (Flight Control–Energy Coupling) Comprehensive Verification of Energy State Interface: Comprehensively check the key output interfaces of the Energy Management System (EMS) (e.g., comprehensive available power, expected endurance), analyze the accuracy of its allocation under parallel multitasking (communication, flight control), and verify whether its data update frequency and range meet the minimum safety requirements of the flight control system in energy-saving flight modes. |
Appendix A.2. Functional Logic Failure Mode Analysis Criteria

Table A2.
Control computation analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A2.
Control computation analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | State-Dependent Control Law Computation Verification: For the control law computation of the drone in different flight modes (e.g., daytime charging cruise, nighttime energy-saving) and energy states, check if it can correctly load and execute the corresponding control gains and computation logic based on the current energy state (e.g., battery SOC, available power) and flight phase. |
| 2 | Multi-Source Input Data Fusion Computation Verification: For flight control and energy management functions that rely on multi-source sensor inputs (e.g., GPS, IMU, light, voltage), check the correctness of the fusion algorithm’s handling under various sensor data combinations (normal, abnormal, boundary values) to prevent erroneous computation of flight attitude or energy strategy due to a single sensor failure. |
| 3 | Algorithm Critical Condition Handling Verification: Check for division-by-zero risks in the drone’s flight control or energy management algorithms (e.g., when calculating remaining flight time or attitude adjustment amount), especially under critical conditions where sensor data may be momentarily zero, ensuring the algorithm’s robustness. |
| 4 | Real-time Performance and Timeout Handling Verification: Check the computation process of critical functions like flight control laws or energy allocation strategies. Analyze whether the system can switch to a predefined safe flight or power-saving mode in the event of a timeout (failure to return a result within the specified deadline), avoiding flight instability due to computation delays. |

Table A3.
Processing logic analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A3.
Processing logic analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | Energy-Constrained Function Entry Logic Verification: Check the execution condition handling logic for high-energy-consumption functions (e.g., rapid climb, high-power communication). Analyze whether it completely includes a check on the current available energy. Focus on whether the function can be correctly interrupted or suspended when the execution condition changes from “met” to “not met” under critical energy conditions. |
| 2 | Logical Consistency Verification across Multiple Flight Modes: For the same function that can be executed in different operating states (e.g., “daytime charging cruise” and “nighttime energy-saving altitude-hold”), check if its internal processing logic is correctly adapted and switched according to the current flight mode, preventing the execution of incorrect or sub-optimal logic branches after a state transition. |
| 3 | Power Allocation and Task Priority Logic Verification: Check the logical judgment conditions and branches for power allocation in the Energy Management System (EMS). Analyze whether the decision logic ensures the absolute priority of the highest safety-level functions, such as flight control, when both the flight control system and mission payloads (e.g., communication, reconnaissance) request power simultaneously. Also, check for logical loopholes that could result in no branch being satisfied. |
| 4 | Cross-System Fault Handling Logic Verification: Check the completeness of the fault handling logic. Analyze whether the flight control system’s logic can correctly receive a fault reported by the energy system (e.g., BMS) and switch to the corresponding safe flight mode (e.g., reduce altitude, return to base), preventing fault propagation and escalation between systems. |
| 5 | Redundant System Switching Logic Verification: For redundant components in the flight control or energy system (e.g., dual-redundant flight control computers, backup battery packs), check the trigger conditions of their switching logic. Analyze whether this logic considers not only the failure of the primary component but also the energy consumption of the switching operation itself, avoiding unnecessary or high-risk switching at low battery levels. |
| 6 | Autonomous Task Replanning Logic Verification: Check the processing logic of the onboard task planner. Analyze whether its replanning logic can be correctly triggered when the perceived energy state (e.g., actual sunlight is much lower than expected) deviates significantly from the planning baseline, and generate a new, energy-feasible flight path or task sequence. |

Table A4.
Task timing analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A4.
Task timing analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | Energy-Constrained Task Duration Verification: For high-power-consumption tasks (e.g., sustained large-angle maneuvers, payload at full power), check if their execution duration is dynamically limited by the current energy reserve. Analyze whether the task can be safely terminated early when the energy is about to be depleted. |
| 2 | Energy-State-Dependent Task Trigger Time Verification: For tasks that depend on specific energy conditions (e.g., data downlink executed only when there is sufficient daylight), analyze whether their trigger time could be activated during the wrong energy window due to delays or premature misjudgments by sensors (e.g., light sensors). |
| 3 | Timing Protection Verification in Critical Flight Phases: For critical flight phases such as takeoff, landing, and crossing jet streams, check if the flight control task’s timing has the highest priority. Analyze if there is a risk of it being delayed by prolonged occupation by other non-critical tasks (e.g., system self-checks, data organization). |
| 4 | Timing Coordination Verification for Energy Mode Switching: Check the task timing during the drone’s transition from “daytime charging” mode to “nighttime energy-saving” mode. Analyze if improper switching timing could lead to high-power-consumption tasks not being terminated in time, thereby excessively consuming nighttime reserve energy. |
| 5 | Cumulative Timing Error Verification in Long-Endurance Flights: For missions lasting several days or weeks, check for non-negligible cumulative timing errors in the task scheduler that relies on an internal clock. Analyze whether this error could cause the drone’s energy acquisition strategy (e.g., attitude adjustment for maximum sunlight) to deviate from the actual day-night cycle, thus reducing overall energy efficiency. |

Table A5.
Redundancy switching analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A5.
Redundancy switching analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | Synchronized Switching Verification of Flight Control and Energy State: When the primary flight control computer switches to the backup, check if the new primary computer can instantly and accurately synchronize the latest state from the Energy Management System (e.g., current battery SOC, power budget), preventing it from making erroneous flight decisions based on outdated energy information. |
| 2 | Impact Verification of Energy System Redundancy Switching on Flight Control Stability: When the system switches between primary and backup power sources (e.g., different battery packs), check for instantaneous voltage drops or spikes on the power bus. Analyze whether such electrical transients could impact the stability of the flight control computer or actuators. |
| 3 | Redundancy Strategy Consistency Verification under Cross-System Faults: When a flight control system redundant unit (e.g., IMU, GPS) fails and switches, check if the Energy Management System can maintain normal power support to the new primary unit. Conversely, when an energy system redundant unit (e.g., BMS) fails and switches, check if the flight control system can correctly identify and adjust the flight strategy to adapt to potentially changed power baselines. |
| 4 | Seamless Control and Timing Verification during Switching: Check the control authority handover process between the primary and backup flight controllers. Analyze if it is completed within the specified timing to ensure seamless control of the flight attitude. Also, check if the switching operation itself could trigger a transient peak power demand that exceeds the energy system’s supply capability. |
| 5 | Redundancy Health Management and Switching Decision Verification in Long-Endurance Flights: For long-endurance missions, check the health monitoring logic for redundant units in both the flight control and energy systems. Analyze whether its switching decisions comprehensively consider the slow degradation trend of component performance and the energy plan for the remaining mission time to make optimal switching timing decisions. |
Appendix A.3. Functional Hierarchy Failure Mode Analysis Criteria

Table A6.
Serial relationship analysis criteria for drone functions.
Table A6.
Serial relationship analysis criteria for drone functions.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | (Error Propagation from Energy Assessment to Flight Decision) For the serial function chain “Energy State Assessment -> Flight Strategy Decision,” check if the output data from the preceding energy assessment function (e.g., an incorrect battery SOC estimate) causes the subsequent flight control decision function to execute a dangerous flight maneuver (e.g., choosing to climb when the battery is low). |
| 2 | (Impact of Serial Execution Timing Delays) Check if the prolonged execution time of a preceding energy management function (e.g., BMS self-test) delays the startup of a subsequent critical flight control function, thereby missing the optimal maneuver window or causing flight instability. |
| 3 | (Loss of Intermediate State Conditions) In the multi-step serial process of “Energy mode switch -> payload power adjustment -> flight control gain adjustment,” check if the completion flag of a preceding function is accidentally lost after its execution, preventing the subsequent function from being correctly triggered. |
| 4 | (Inconsistent Data Formats and Units) Check for conversion errors between the power data output by the Energy Management System (unit: Watts) and the input expected by the flight control system (unit: thrust percentage). Analyze if such inconsistencies could lead to severe overshoot or undershoot of flight control commands. |
| 5 | (Serial Impact of Flight State on Energy Perception) Check if a specific flight maneuver (e.g., a steep bank turn causing the solar panel to be shaded by the wing) serially affects the accuracy of a subsequent energy perception function, leading to erroneous energy assessment and flight decisions. |
| 6 | (Cumulative Decision Risk in Long-Endurance Flights) Check if minor energy estimation biases in a series of “perceive-decide” cycles accumulate over time, ultimately causing the flight control system to make an incorrect long-term planning decision that leads to mission failure near the end of the mission. |

Table A7.
Parallel relationship analysis criteria for drone functions.
Table A7.
Parallel relationship analysis criteria for drone functions.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | (Power Competition between Flight Control and Mission Payloads) For the parallel execution of flight control functions and mission payload functions (e.g., high-power communication, reconnaissance pods), check if the energy allocation strategy can effectively manage power competition, preventing undervoltage in the critical flight control system due to total power requests exceeding the energy system’s supply capacity. |
| 2 | (Conflicting Access to Shared Resources by Parallel Functions) Check if concurrently executing flight control algorithms and energy optimization algorithms perform read/write operations on the same shared data area (e.g., flight state parameters, environmental parameters). Analyze for risks of data conflicts or inconsistencies due to the absence of lock protection. |
| 3 | (Concurrent Command Conflicts for Mutually Exclusive Actuators) Check for the risk of multiple parallel functions (e.g., flight control attitude adjustment and energy system solar panel angle adjustment) sending control commands to the same actuator simultaneously. Analyze if the system’s command arbitration mechanism can effectively prevent the concurrent execution of mutually exclusive actions. |
| 4 | (Thermal Management Conflicts in Parallel Tasks) When high-load flight control computation tasks and energy charge/discharge management tasks execute in parallel, check if the total heat generated exceeds the cooling capacity of the onboard equipment. Analyze if the increased fan power consumption by the thermal management system to cool down affects the available power for the flight control system. |
| 5 | (Parallel Competition for Data Bus Bandwidth) Check for bus bandwidth competition between the high-frequency sensor data stream of the flight control system, the dense state updates of the energy system, and the large-bandwidth data downlink of the mission payload. Analyze if high bus load could lead to delays or data loss in flight control commands. |
| 6 | (Parallel Fault Diagnosis and Decision Arbitration) When the fault diagnosis modules of the flight control system and the energy system run in parallel, check if the overall safety management function can correctly arbitrate when both report faults simultaneously (e.g., IMU failure and battery over-temperature), and enter the safest flight and energy mode. |
Appendix A.4. State/Mode Failure Mode Analysis Criteria

Table A8.
Operating state analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A8.
Operating state analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | (Completeness of Core Flight Modes) Check if the drone’s software state machine completely defines the core operating states covering its entire mission profile, including “Daytime Charging Cruise,” “Nighttime Energy-Saving Altitude-Hold,” “Emergency Energy Mode,” and “Safe Return-to-Home,” and analyze for undefined system states that could leave the software in an indeterminate state. |
| 2 | (Robustness of State Entry Conditions) Check the conditions for entering critical operating states (e.g., “Nighttime Energy-Saving”). Analyze if they rely solely on a single sensor (e.g., light sensor) and if there is a risk of flight control and energy strategies being incorrectly triggered due to transient sensor noise or failure. |
| 3 | (State Recovery after Power Loss and Restart) For accidental power loss and restart that may occur during long-endurance missions, check the software’s state recovery logic after restart. Analyze if it can correctly assess the current energy state and flight environment and recover to the safest operating state, rather than simply reverting to the state before the power loss. |
| 4 | (Consistency of Functions and Interfaces within a State) In a specific operating state (e.g., “Emergency Energy Mode”), check if the behavior of all functions and the value ranges of all interfaces are consistent with the state’s definition. For example, in this state, can the flight control system correctly prohibit high-energy maneuvers, and is the mission payload placed in its lowest power consumption mode? |

Table A9.
State scenario analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A9.
State scenario analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | (Smoothness of Day-Night Mode Switching) Check the transition process from “Daytime Charging Cruise” to “Nighttime Energy-Saving” state. Analyze if this process incorporates hysteresis comparison or filtering mechanisms to prevent frequent “chattering” of energy and flight control strategies between the two states due to transient factors like cloud cover. |
| 2 | (Priority of Emergency State Transition) Check the trigger logic for transitioning to the “Emergency Energy” mode. Analyze if this transition has the highest priority, capable of interrupting any ongoing non-critical tasks and forcing the flight control system to execute the most energy-efficient survival flight strategy. |
| 3 | (Mutual Exclusivity of Multiple Transition Conditions) For a state (e.g., “Cruise”) that can transition to multiple next states (e.g., “Climbing,” “Descending,” “Evasive Maneuver”), check if these transition conditions are designed with strict mutual exclusivity based on flight control commands and energy state to prevent uncertain behavior when multiple transition conditions are met simultaneously. |
| 4 | (Functional Coordination during State Transitions) During a state transition, check if the execution order and timing of different functions (e.g., flight control gain adjustment, energy allocation table switching, mission payload on/off) are precisely coordinated to prevent transient system instability due to incorrect execution order. |
| 5 | (Safety of Recovery from a Fault State) Check the transition logic for recovering from a fault state (e.g., “Battery Over-Temperature Protection”) to a normal operating state. Analyze if it includes a “post-recovery observation period” to confirm that the fault has been genuinely cleared, avoiding rapid “enter fault—recover normal” cycles near the fault threshold. |
Appendix A.5. Flight Control–Energy Coupling Failure Mode Analysis Criteria

Table A10.
Flight control–energy coupling failure mode analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
Table A10.
Flight control–energy coupling failure mode analysis criteria for high-altitude solar drones.
| No. | Analysis Criterion |
|---|---|
| 1 | (Degradation of Maneuverability under Energy Constraints) In an energy-constrained state (e.g., nighttime flight, crossing Earth’s shadow), check if the flight control system can correctly execute a maneuverability degradation strategy. Analyze whether the system, upon receiving a high-energy command (e.g., rapid climb to evade a stratospheric jet stream), can autonomously decide to reject the command or execute a more energy-efficient alternative maneuver based on the current battery SOC (State of Charge) and power budget. |
| 2 | (Impact of Solar Power Fluctuations on Attitude Stability) In scenarios with rapidly changing solar irradiance (e.g., a drone entering and exiting clouds in the stratosphere), check if the Energy Management System’s Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm causes transient fluctuations in the power bus voltage. Analyze if this electrical disturbance could impact the attitude stability of the flight control by affecting the actuator servo system. |
| 3 | (Power Priority Management for Mission and Flight Control) Check the arbitration logic of the energy allocation strategy. Analyze if the system, during insufficient energy income, can decisively and correctly cut or reduce power to lower-priority mission payloads (e.g., HD video transmission) when high-priority flight control tasks (e.g., attitude hold) and payloads simultaneously request power, to ensure the absolute power supply safety of the flight control system. |
| 4 | (Cross-System Impact of Local Energy System Failures) Analyze if a local failure in the energy system (e.g., a single solar panel failing due to a space debris impact) could mislead the flight control system’s long-term route planning through an incorrect energy state assessment. For example, making an erroneous and overly conservative return-to-base decision due to underestimating future energy harvesting capabilities. |
| 5 | (Coupling of Thermal Management, Flight Control, and Energy in Extreme Temperatures) Under the vast day-night temperature differences in near-space, check the behavior of the onboard thermal management system. Analyze if the high power consumption from activating heaters to keep batteries warm during the extremely cold night reduces the power margin available for the flight control system, thereby affecting the drone’s maneuverability at night. |
| 6 | (Coupled Failure of Navigation Drift and Energy Optimization in Long-Endurance Flights) During missions lasting several weeks, check if the cumulative position drift of the flight control system’s navigation unit (e.g., IMU) causes a deviation in the solar position calculation within the Energy Management System. This could lead to errors in the drone’s autonomous “solar maximization” attitude tracking, ultimately reducing the energy acquisition efficiency over the entire mission period. |
Appendix B. Prompt in K-EGoT
The rewrite prompt is shown in Figure A1.

Figure A1.
Prompt for Chain of Thought rewriting.
References
- Vesely, W.E.; Goldberg, F.F.; Roberts, N.H.; Haasl, D.F. Fault Tree Handbook (NUREG-0492); U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 1981.
- Schneider, H. Failure Mode and Effect Analysis: FMEA from Theory to Execution; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Besta, M.; Blach, N.; Kubicek, A.; Gerstenberger, R.; Podstawski, M.; Gianinazzi, L.; Gajda, J.; Lehmann, T.; Niewiadomski, H.; Nyczyk, P.; et al. Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 17682–17690. [Google Scholar]
- Gosnold. France Debates Its Near-Space Policy. 10 January 2023. Available online: https://satelliteobservation.net/2023/01/10/france-debates-its-near-space-policy/ (accessed on 11 August 2025).
- Wilson, P.; Mantooth, H.A. Modeling Approaches. In Model-Based Engineering for Complex Electronic Systems; Newnes: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, P.J.; Kelly, T.P. Functional hazard analysis for highly integrated aerospace systems. In Proceedings of the IEE Certification of Ground/Air Systems Seminar (Ref. No. 1998/255), London, UK, 18 March 1998; pp. 4/1–4/6. [Google Scholar]
- S-18 Aircraft and Systems Development and Safety Assessment Committee. Guidelines and Methods for Conducting the Safety Assessment Process on Civil Airborne Systems and Equipment; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Object Management Group. A UML Profile for MARTE, Beta 1; Technical Report ptc/07-08-04; Object Management Group: Needham, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, G.; Sakamoto, T.; Kotoku, T. A Profile and tool for modelling safety information with design information in SysML. Softw. Syst. Model. 2014, 15, 813–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, D.P.; Hirata, C.; Nadjm-Tehrani, S. A STAMP-based ontology approach to support safety and security analyses. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2019, 47, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.; Roth, M.; Lindemann, U. The hazard analysis Profile: Linking safety analysis and SysML. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual IEEE Systems Conference (SysCon), Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 April 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Zhu, C. Data-driven multivariate regression-based anomaly detection and recovery of unmanned aerial vehicle flight data. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2024, 11, 176–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Peng, Y.; Peng, X. Multivariate regression-based fault detection and recovery of UAV flight data. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 3527–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Nan, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Robust spatio-temporal autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection of unmanned aerial vehicle with flight data. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 3526014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.; Chung, S. Deep learning-based anomaly detection for individual drone vehicles performing swarm missions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, A.; An, X. Deeply integrated autoencoder-based anomaly detection and critical parameter dentification for unmanned aerial vehicle actuators. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 24905–24920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, A.; Liao, Z. Spatio-temporal correlation-based multiple regression for anomaly detection and recovery of unmanned erial vehicle flight data. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 60, 102440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Xia, X. Automated Unit Test Refactoring. In Proceedings of the ACM on Software Engineering, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 27 April–3 May 2025; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2025; Volume 2, pp. 713–733. [Google Scholar]
- Altmayer Pizzorno, J.; Berger, E.D. CoverUp: Effective High Coverage Test Generation for Python. In Proceedings of the ACM on Software Engineering, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 27 April–3 May 2025; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2025; Volume 2, pp. 2897–2919. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, X.; Wang, S.; Zou, H.; Liu, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L. Incorporating Verification Standards for Security Requirements Generation from Functional Specifications. In Proceedings of the ACM on Software Engineering, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 27 April–3 May 2025; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2025; Volume 2, pp. 1710–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D. Chain of Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 24824–24837. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Yu, D.; Zhao, J.; Shafran, I.; Griffiths, T.; Cao, Y.; Narasimhan, K. Tree of thoughts: Deliberate problem solving with large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 11809–11822. [Google Scholar]
- Madaan, A.; Tandon, N.; Gupta, P.; Hallinan, S.; Gao, L.; Wiegreffe, S.; Alon, U.; Dziri, N.; Prabhumoye, S.; Yang, Y.; et al. Self-refine: Iterative refinement with self-feedback. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 46534–46594. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Kawaguchi, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.X.; Kan, M.Y.; He, J.; Xie, M. Self-evaluation guided beam search for reasoning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 41618–41650. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 26262; Road Vehicles—Functional Safety. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).