Enhancing Mission Planning of Large-Scale UAV Swarms with Ensemble Predictive Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- By leveraging the greedy search, we propose a UAV swarm target assignment algorithm suitable for large-scale missions. This algorithm demonstrates a balanced combination of solving efficiency and effectiveness in large-scale missions.
- (2)
- We propose a machine learning-based approach to predict trajectory length, aiming to ensure the efficiency of the mission planning algorithm during replanning and, consequently, enhance mission success rates.
2. Problem Formulation
3. Methodology
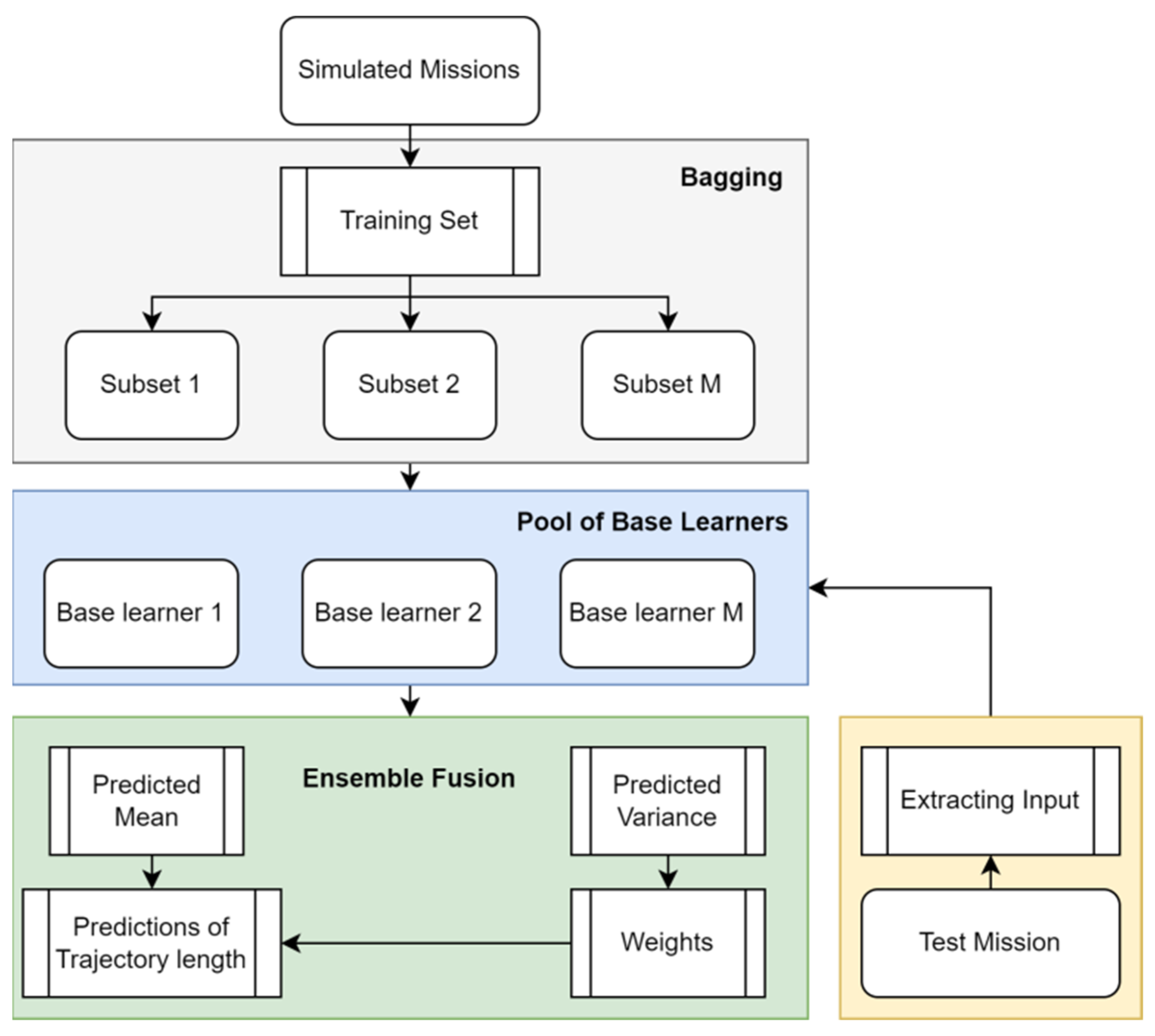
3.1. Ensemble Predictive Model of Trajectory Length
3.1.1. Feature Extraction
3.1.2. Ensemble of GPR
3.2. Greedy Target Assignment
4. Experiments and Analysis
4.1. Performance Analysis of GTA
- (1)
- GA_P, stands for GA with penalty function as the constraint handling technique.
- (2)
- PSO_P, stands for PSO with penalty function as the constraint handling technique.
- (3)
- GA_AP, stands for GA with adaptive penalty function [23] as the constraint handling technique.
- (4)
- PSO_AP, stands for PSO with adaptive penalty function [23] as the constraint handling technique.
- (5)
- GA_RH, stands for GA with a repair heuristic [24] as the constraint handling technique.
- (6)
- PSO_RH, stands for PSO with a repair heuristic [24] as the constraint handling technique.
4.2. Performance Analysis of Ensemble Predictive Model
4.2.1. Validation from a Regression Perspective
- (1)
- SGP, stands for single GPR model.
- (2)
- EnGP_SB, stands for the single best base learner in the ensemble.
- (3)
- EnGP_AG, stands for ensemble GPR with averaging fusion method.
- (4)
- EnGP_SW, stands for ensemble GPR with a static weighting scheme. The specific weighting of base learners is derived from the training errors.
- (5)
- EnGP_DS, stands for ensemble GPR with a dynamic selection scheme [26].
4.2.2. Validation from a Mission Planning Perspective
4.3. Simulation Platform for Visualization
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, D. UAV Swarm Search Path Planning Method Based on Probability of Containment. Drones 2024, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, D. A Path-Planning Method for UAV Swarm under Multiple Environmental Threats. Drones 2024, 8, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C. Task Assignment of UAV Swarms Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Drones 2023, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Anavatti, S.G.; Garratt, M.A. Multiobjective mission route planning problem: A neural network-based forecasting model for mission planning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 22, 430–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, L.T.; Michalewicz, Z.; Parkinson, E.; Abello, M.B. Adaptation in dynamic environments: A case study in mission planning. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2011, 16, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Défago, X. Solving Simultaneous Target Assignment and Path Planning Efficiently with Time-Independent Execution. Artif. Intell. 2023, 321, 103946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babel, L. Coordinated Target Assignment and UAV Path Planning with Timing Constraints. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2019, 94, 857–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Er, M.J. Cooperative path planning with priority target assignment and collision avoidance guidance for rescue unmanned surface vehicles in a complex ocean environment. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.; Salmon, J. An agent-based modeling approach for simulating the impact of small unmanned aircraft systems on future battlefields. J. Déf. Model. Simul. Appl. Methodol. Technol. 2022, 19, 481–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J. Artificial intelligence & future warfare: Implications for international security. Def. Secur. Anal. 2019, 35, 147–169. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, R.; McLain, T.; Goodrich, M.; Anderson, E. Coordinated target assignment and intercept for unmanned air vehicles. IEEE Trans. Robot. Autom. 2002, 18, 911–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stirling, W.C.; Goodrich, M.A. Conditional preferences for social systems. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics. e-Systems and e-Man for Cybernetics in Cyberspace (Cat.No.01CH37236), Tucson, AZ, USA, 7–10 October 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein, D. Finding the k Shortest Paths. SIAM J. Comput. 1998, 28, 652–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddula, T.; Minai, A.A.; Polycarpou, M.M. Multi-Target Assignment and Path Planning for Groups of UAVs. In Recent Developments in Cooperative Control and Optimization; Butenko, S., Murphey, R., Pardalos, P.M., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Eun, Y.; Bang, H. Cooperative Task Assignment/Path Planning of Multiple Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Using Genetic Al-gorithm. J. Aircr. 2009, 46, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.T.; Kamel, M.A. Cooperative Task Assignment and Trajectory Planning of Unmanned Systems Via HFLC and PSO. Unmanned Syst. 2019, 7, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, A.T.; Kamel, M.A.; Jardin, P.T.; Givigi, S.N. Task assignment/trajectory planning for unmanned vehicles via HFLC and PSO. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Miami, FL, USA, 13–16 June 2017; pp. 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Qie, H.; Shi, D.; Shen, T.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Joint Optimization of Multi-UAV Target Assignment and Path Planning Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 146264–146272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Kumar, N. Path planning techniques for unmanned aerial vehicles: A review, solutions, and challenges. Comput. Commun. 2020, 149, 270–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalil, T.; Nasreen, S. A survey of feature selection and feature extraction techniques in machine learning. In Proceedings of the Science and Information Conference (SAI), London, UK, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Lv, H.; Chen, N. A Survey on ensemble learning under the era of deep learning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 5545–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganaie, M.A.; Hu, M.; Malik, A.K.; Tanveer, M.; Suganthan, P.N. Ensemble deep learning: A review. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrag, A.; Messalti, S. Adaptive GA-based reconfiguration of photovoltaic array combating partial shading conditions. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 30, 1145–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salcedo-Sanz, S. A survey of repair methods used as constraint handling techniques in evolutionary algorithms. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2009, 3, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demšar, J. Statistical comparisons of classifiers over multiple data sets. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2006, 7, 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wang, W.; Meng, G.; Meng, T.; Song, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Mao, Z. Selective Feature Bagging of one-class classifiers for novelty detection in high-dimensional data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| # of Mission | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| S_1 | 30 | 10 | 10 |
| S_2 | 30 | 15 | 10 |
| S_3 | 30 | 20 | 10 |
| S_4 | 30 | 25 | 10 |
| S_5 | 30 | 30 | 10 |
| M_1 | 60 | 20 | 15 |
| M_2 | 60 | 30 | 15 |
| M_3 | 60 | 40 | 15 |
| M_4 | 60 | 50 | 15 |
| M_5 | 60 | 60 | 15 |
| L_1 | 100 | 20 | 20 |
| L_2 | 100 | 40 | 20 |
| L_3 | 100 | 60 | 20 |
| L_4 | 100 | 80 | 20 |
| L_5 | 100 | 100 | 20 |
| GA_P | PSO_P | GA_AP | PSO_AP | GA_RH | PSO_RH | GTA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S_1 | −15.9623 | −15.2346 | −16.5111 | −15.7414 | −16.1472 | −15.3825 | −14.9387 |
| S_2 | −16.7131 | −15.5826 | −16.3602 | −15.2327 | −16.0523 | −15.9094 | −15.7745 |
| S_3 | −16.2092 | −15.0937 | −16.5651 | −15.3886 | −16.0423 | −15.6635 | −15.8704 |
| S_4 | −15.8224 | −15.0747 | −16.3782 | −15.3046 | −16.7391 | −16.1253 | −15.4985 |
| S_5 | −15.5172 | −14.5837 | −15.8661 | −15.2165 | −15.3773 | −15.0106 | −15.3234 |
| M_1 | −24.1685 | −23.4417 | −24.7343 | −24.0426 | −25.2892 | −24.3974 | −25.6881 |
| M_2 | −24.6015 | −23.8827 | −25.1373 | −24.4866 | −25.7102 | −24.8914 | −26.8931 |
| M_3 | −25.2245 | −24.2966 | −25.7833 | −24.0057 | −26.7611 | −25.5544 | −26.0242 |
| M_4 | −23.0195 | −22.1907 | −23.5654 | −22.8206 | −25.0142 | −24.1473 | −25.7831 |
| M_5 | −25.9614 | −25.0367 | −26.3012 | −25.3416 | −26.0073 | −25.6855 | −28.5541 |
| L_1 | −31.2375 | −30.5017 | −31.6904 | −31.1256 | −33.2262 | −32.3853 | −36.8371 |
| L_2 | −33.7554 | −32.3676 | −33.3085 | −31.6317 | −34.8702 | −33.9603 | −36.5741 |
| L_3 | −33.0467 | −33.3195 | −33.1916 | −33.6214 | −35.0252 | −34.1583 | −37.2971 |
| L_4 | −32.3204 | −31.4027 | −32.6735 | −32.0906 | −34.4342 | −34.0273 | −36.9001 |
| L_5 | −30.0897 | −30.3606 | −30.6465 | −30.9244 | −32.7052 | −32.0043 | −35.5631 |
| Ave value | −24.433 | −23.491 | −24.580 | −23.798 | −25.293 | −24.620 | −26.235 |
| Ave ranking | 4.20 | 6.53 | 3.13 | 5.73 | 2.13 | 3.87 | 2.40 |
| GA_P | PSO_P | GA_AP | PSO_AP | GA_RH | PSO_RH | GTA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 2.72 | 2.45 | 3.19 | 2.88 | 26.90 | 24.75 | 0.15 |
| Medium | 3.46 | 3.04 | 3.70 | 3.26 | 46.44 | 41.08 | 0.24 |
| Large | 5.53 | 5.17 | 5.62 | 5.43 | 73.22 | 70.37 | 0.36 |
| SGP | EnGP_SB | EnGP_AG | EnGP_SW | EnGP_DS | EnGP_DW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 0.056 | 0.048 | 0.044 | 0.031 | 0.021 | 0.025 |
| M | 0.092 | 0.082 | 0.088 | 0.080 | 0.067 | 0.064 |
| L | 0.115 | 0.095 | 0.092 | 0.094 | 0.071 | 0.073 |
| Total | 0.088 | 0.079 | 0.075 | 0.071 | 0.056 | 0.057 |
| # of Mission | GTA | GA_RH | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ED | LR | SVR | EnGP | Oracle | ED | LR | SVR | EnGP | Oracle | |
| 1 | −33.166 | −35.214 | −35.601 | −36.540 | −36.837 | −31.202 | −31.588 | −31.588 | −32.017 | −33.226 |
| 2 | −33.047 | −35.333 | −34.807 | −36.190 | −36.574 | −31.409 | −31.872 | −32.018 | −32.667 | −34.870 |
| 3 | −33.601 | −35.239 | −35.239 | −37.067 | −37.297 | −31.184 | −33.443 | −32.670 | −33.904 | −35.025 |
| 4 | −34.007 | −35.287 | −35.607 | −36.453 | −36.900 | −30.150 | −33.672 | −33.672 | −34.709 | −34.434 |
| 5 | −32.910 | −34.270 | −34.989 | −35.971 | −35.563 | −30.022 | −30.584 | −30.823 | −31.284 | −32.705 |
| 6 | −33.759 | −35.920 | −36.495 | −38.004 | −38.620 | −33.294 | −34.025 | −34.025 | −34.025 | −34.928 |
| 7 | −35.029 | −35.029 | −37.558 | −39.205 | −39.744 | −32.004 | −32.402 | −33.827 | −35.769 | −35.769 |
| 8 | −34.448 | −36.290 | −36.843 | −37.550 | −38.013 | −30.982 | −31.109 | −33.004 | −33.004 | −33.658 |
| 9 | −35.901 | −37.282 | −37.828 | −37.828 | −39.226 | −32.183 | −34.229 | −34.772 | −35.928 | −35.440 |
| 10 | −38.776 | −40.189 | −41.537 | −42.000 | −41.537 | −32.374 | −33.493 | −34.021 | −35.299 | −37.251 |
| Ave. value | −34.464 | −36.005 | −36.650 | −37.681 | −38.031 | −31.480 | −32.642 | −33.042 | −33.861 | −34.731 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, G.; Zhou, M.; Meng, T.; Wang, B. Enhancing Mission Planning of Large-Scale UAV Swarms with Ensemble Predictive Model. Drones 2024, 8, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8080362
Meng G, Zhou M, Meng T, Wang B. Enhancing Mission Planning of Large-Scale UAV Swarms with Ensemble Predictive Model. Drones. 2024; 8(8):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8080362
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Guanglei, Mingzhe Zhou, Tiankuo Meng, and Biao Wang. 2024. "Enhancing Mission Planning of Large-Scale UAV Swarms with Ensemble Predictive Model" Drones 8, no. 8: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8080362
APA StyleMeng, G., Zhou, M., Meng, T., & Wang, B. (2024). Enhancing Mission Planning of Large-Scale UAV Swarms with Ensemble Predictive Model. Drones, 8(8), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8080362





