Abstract
Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) air-to-ground (AG) communication plays a critical role in the evolving space–air–ground integrated network of the upcoming sixth-generation cellular network (6G). The integration of massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems has become essential for ensuring optimal performing communication technologies. This article presents a novel dual-driven learning-based network for millimeter-wave (mm-wave) massive MIMO symbol detection of UAV AG communications. Our main contribution is that the proposed approach combines a data-driven symbol-correction network with a model-driven orthogonal approximate message passing network (OAMP-Net). Through joint training, the dual-driven network reduces symbol detection errors propagated through each iteration of the model-driven OAMP-Net. The numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the dual-driven detector over the conventional minimum mean square error (MMSE), orthogonal approximate message passing (OAMP), and OAMP-Net detectors at various noise powers and channel estimation errors. The dual-driven MIMO detector exhibits a 2–3 dB lower signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) requirement compared to the MMSE and OAMP-Net detectors to achieve a bit error rate (BER) of when the channel estimation error is −30 dB. Moreover, the dual-driven MIMO detector exhibits an increased tolerance to channel estimation errors by 2–3 dB to achieve a BER of .
1. Introduction
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have attracted significant attention in both military and industrial applications, ranging from reconnaissance and attacks to communications, delivery, and search operations, due to their affordability, versatility, and accessibility [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Space–air–ground integrated networks (SAGINs) have emerged as a prominent research topic in the development of the sixth-generation cellular network (6G) [7], where UAVs and millimeter-wave (mm-wave) massive multiple-input–multiple-output (MIMO) systems are expected to play crucial roles [8,9]. The unique characteristics of UAVs, such as their high maneuverability and potential for unmanned operations, necessitate advancements in communication technologies, leading to an increased interest from researchers, companies, and organizations [10,11,12,13]. Recognizing the importance of UAVs, the third-generation partnership project (3GPP) has proposed the new radio (NR) support for UAVs as a specialized category of user equipment (UE) [14,15], highlighting the urgent need for research on UAV communication systems [16].
UAV communications encompass various modes, including air-to-ground (AG) communications, air-to-air (AA) communications, and UAV-assisted communications. In the context of UAV AG communication, researchers such as Lin et al. [17] and Luo et al. [18] have explored tensor-based joint channel estimation and symbol detection in UAV-assisted communication systems. Khawaja et al. have summarized channel models for UAV AG communications [19], while Khuwaja et al. have provided a comprehensive survey on channel modeling for UAV communications [20]. As MIMO technology is expected to be employed in UAV communication systems, MIMO symbol detection has become crucial; although, limited research has been conducted in this area.
MIMO detection is a crucial process in wireless communication systems that employ multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver. In MIMO systems, multiple spatial streams are transmitted simultaneously using different antenna configurations, allowing for increased data rates, improved reliability, and enhanced spectral efficiency. The goal of MIMO detection is to estimate the transmitted symbols or bits at the receiver by efficiently recovering the original data from the received signals affected by noise, interference, and channel impairments. This process involves solving the detection problem, where the receiver must determine the transmitted symbols based on the received signals and knowledge of the channel. Thus, the application of MIMO detection is necessary in any scenario where multiple antennas are employed at both the transmitter and receiver in UAV AG communications.
Regarding MIMO detection, maximum likelihood (ML) detection exhibits an optimal performance but suffers from a prohibitively high complexity [21]. Linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) detectors can reduce the complexity to an acceptable level but fail to match the performance of ML detection [22]. Donoho et al. introduced the iterative approximate message passing (AMP) algorithm for MIMO detection, which has been proven to be Bayes-optimal for independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) sub-Gaussian channels [23]. Ma and Ping proposed orthogonal AMP (OAMP) for channel estimation, which outperforms AMP, particularly for ill-conditioned matrices [24]. By unfolding the structure of the OAMP algorithm and adding some trainable parameters, He et al. introduced OAMP-Net [25] and OAMP-Net2 [26] for MIMO detection. Zhou et al. proposed conjugate gradient OAMP-Net (CG-OAMP-Net) for MIMO detection to reduce the complexity of OAMP [27]. Khani et al. introduced MMNnet for channel estimation, which exhibits superior performance and has a lower computational complexity for realistic channels [28]. These approaches represent model-driven channel estimators or MIMO detectors, which learn through traditional iterative structures, but the propagation of detection errors over the iterations may lead to divergence. Deep learning techniques, such as neural networks (NNs), have also been proposed for MIMO detection [29,30,31]. However, these data-driven models are highly dependent on the size and quality of the training dataset and are often treated as black boxes due to their end-to-end training approach.
Inspired by the aforementioned approaches, Zheng et al. investigated hybrid-driven channel estimation in intelligent reflecting-surface-aided millimeter-wave communications with infinite-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) [32]. Li et al. proposed a dual-driven learning-based channel estimator for massive MIMO systems with one-bit ADCs [33]. In summary, model-driven networks can learn from traditional iterative structures, which are sensitive to MIMO detection errors, while data-driven networks can operate as black boxes. This motivates us to explore a combination of model-driven and data-driven networks to reduce detection errors and ensure a good MIMO detection performance.
In this article, we propose a dual-driven learning-based MIMO detector designed for use in mm-wave massive MIMO systems for UAV AG communications. We unfold the architecture of the model-driven OAMP-Net network and insert a data-driven symbol correction network. This data-driven network corrects detection errors, while in the model-driven network, the propagation of errors is reduced during each iteration due to the corrected symbols, ensuring the convergence and good performance of the OAMP-Net network. The key contributions of this article are as follows:
- 1.
- We introduce a dual-driven learning-based network for massive MIMO symbol detection in UAV AG communications. The use of a data-driven network reduces detection errors, and the model-driven component is an OAMP-Net network. We design an iterative algorithm for the dual-driven network to enable joint parameter updates in both the data-driven and model-driven modules during each iteration.
- 2.
- We develop the structure of the symbol correction network, which contains fully connected layers with nonlinear activation functions to minimize detection errors.
To sum up, the main contribution of this article is a dual-driven MIMO detector created by inserting a data-driven neural network into the model-driven OAMP-Net network. Our main hypothesis is that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector will outperform the model-driven OAMP-Net and some other traditional MIMO detectors as it has the advantages of both the data-driven and model-driven networks. This hypothesis is verified in this article, which is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the system model, the MIMO detection problem, and the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector. The simulation settings of the test experiments, the results of the chosen tests to verify the detector’s performance, and discussions on whether the hypothesis is verified are presented in Section 3. Section 4 concludes this article.
2. Methods
In this section, we provide a detailed description of the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method. We begin by presenting a brief overview of the UAV AG communication scenario in urban areas. Subsequently, we introduce the mathematical formulation of the communication system. Building upon this mathematical expression, we outline the MIMO symbol detection problem. Finally, we provide a comprehensive explanation of the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method.
UAV AG Communication Scenario: We start by providing an overview of the UAV AG communication scenario, specifically focusing on an urban area. This setting involves UAVs acting as communication nodes, transmitting and receiving signals from ground base stations. UAVs’ high maneuverability enables them to establish wireless links with ground stations (GSs), facilitating efficient communication in urban environments.
Expression of the Communication System: We present a mathematical formulation that characterizes this UAV AG communication system, which includes wireless channel modeling.
MIMO Symbol Detection Problem: Based on the mathematical formulation, we identify the MIMO symbol detection problem.
Proposed Dual-Driven Learning-Based MIMO Symbol Detection Method: Here, we provide a comprehensive description of the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection technique. This approach combines both model-driven and data-driven networks to enhance the detection accuracy. We delve into the architecture and working principles of the dual-driven network, highlighting the integration of the model-driven OAMP-Net and the data-driven symbol correction network. We elaborate on how the algorithm updates the parameters of both modules simultaneously in each iteration, ensuring effective collaboration between the model-driven and data-driven components.
By following this structure, we aim to provide a detailed understanding of the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method, contextualizing them within the UAV AG communication scenario.
2.1. System Model
As shown in Figure 1, we consider a millimeter-wave massive MIMO system designed for UAV AG communications. In this system, the GS acts as the receiver and is equipped with receiving (Rx) antennas. UAVs are considered as transmitters, and each UAV is equipped with a single transmitting (Tx) antenna.
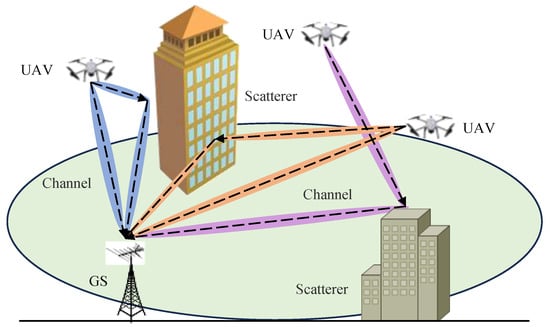
Figure 1.
A typical UAV AG propagation scenario in an urban area. UAVs transmit signals which the GS then receives. Some scatterers are present in the propagation environment. There may be line-of-sight (LOS) paths or non-light-of-sight (NLOS) paths for UAVs in different locations.
As depicted in Figure 2, the uncoded bits for the n-th transmitter () are individually modulated into transmitted symbols, denoted as for the n-th transmitter () and the k-th subcarrier (). Here, represents the total number of subcarriers for each UAV. The symbols belong to the finite set of constellation points denoted as , which can be defined using quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) or phase shift keying (PSK) schemes, following standard practices. All UAVs share the same , and is randomly selected from . For simplicity, we assume that represents the symbol transmitted to the antenna of each UAV, without considering the specific processes of the inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) or cyclic prefix (CP) insertion in the time domain. The transmitted symbols propagate through the wireless channel . The received signal vector for the k-th subcarrier is given as
where , , and is the complex Gaussian noise vector with as the noise variance.
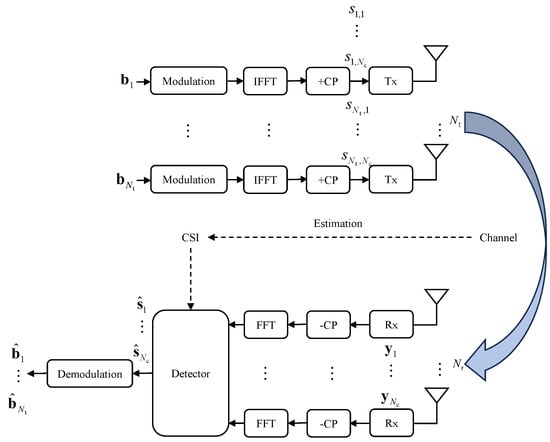
Figure 2.
A block diagram illustrating a MIMO system for UAV AG communications. The detector relies on the estimated channel state information (CSI) to operate.
To enhance understanding, the definitions of key notations used in this article are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Definitions of key notations in this article.
2.2. The MIMO Signal Detection Problem
The MIMO signal detection problem involves estimating the transmitted symbol of in relation to the known received signal vector and channel matrix . This detection is formulated as
However, solving the optimization problem in Equation (2) using the optimal ML detector is computationally challenging due to the finite alphabet constraint . The ML detector exhibits a prohibitively high complexity, and thus various other detectors with different complexities and characteristics have been explored.
In the MIMO signal detection problem, it is typically assumed that the wireless channel for the k-th subcarrier () is known through perfect channel estimation. The impact of imperfect channel estimation will also be discussed in the following Results and Discussion section.
2.3. Dual-Driven Learning-Based MIMO Signal Detection
Our proposed approach is a dual-driven learning framework for MIMO signal detection. This framework leverages the architecture of the model-driven OAMP-Net network and incorporates a data-driven symbol correction network. By integrating this component, we aim to enhance the performance and convergence of the OAMP-Net network.
As shown in Figure 3, we unfold the architecture of the model-driven OAMP-Net network and introduce a data-driven symbol correction network within the framework. The data-driven symbol correction network is trained extensively to reduce the errors associated with the estimated symbols passed through each iteration of the OAMP-Net network. This correction mechanism ensures an improved performance and convergence of the OAMP-Net network.
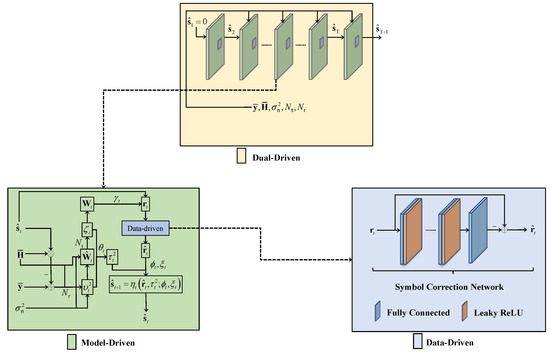
Figure 3.
Structure of the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection network.
By combining the strengths of both the model-driven and data-driven approaches, our dual-driven learning framework provides a novel solution for MIMO signal detection. This allows for the efficient utilization of the OAMP-Net network while leveraging the capabilities of the data-driven symbol correction network to refine the estimated symbols in each iteration.
We can rewrite Equation (1) in a real-valued form, since both the OAMP-Net and the symbol correction network operate in the real-valued domain:
We can drop the subscript k in Equation (3) for brevity since the dual-driven learning-based MIMO detector operates equally across all subcarriers. Equation (3) can be expressed as
To detect symbols with a known , , and noise variance , the OAMP algorithm iteratively passes information between a linear estimator (LE) and a nonlinear estimator (NLE) [24]:
Equations (5) and (6) represent the LE and NLE in the OAMP algorithm. and are the LE and NLE’s outputs, representing the information exchanged in each iteration; t and are the iteration indexes; is the decorrelated matrix; and is the nonlinear divergence-free estimator [24]. The LE and NLE error vectors, and , are defined as and . The error variance estimators and of and are defined as and , respectively [24]. and denote the expectation function and the norm, respectively. According to the OAMP algorithm [24], can be calculated as follows:
where denotes the trace of matrix . In our implementation, we incorporate a smoothing technique to update by using a convex combination of the previous estimate and the newly calculated estimate based on Equation (7): . Additionally, to prevent stability issues, we set the final value for each iteration to , where returns the maximum value and is set to . This ensures that the value of does not become too small, maintaining calculation stability.
As mentioned earlier, the matrix is the decorrelated matrix, which satisfies to ensure that and are uncorrelated. Here, denotes the identity matrix. In the OAMP algorithm, , where is the decorrelated coefficient given by = and is the LMMSE matrix defined as [24].
The error variance estimator can be calculated as follows [24]:
In OAMP-Net, there are four trainable variables denoted as , which are optimized to enhance the detection performance in each LE and NLE iteration [26]. The calculation of in Equation (7) remains the same in both the OAMP algorithm and the OAMP-Net network. Equation (5) in the OAMP-Net network can be rewritten as follows [25,26]:
The error variance estimator of in the OAMP-Net network is calculated as [25,26]
The NLE estimator in the OAMP-Net network, denoted as , can be represented by [25,26]
Equations (9)–(11) represent key processes in each iteration of the model-driven OAMP-Net. Now, let us introduce the data-driven symbol correction network.
The calculations of in Equation (9) and in Equation (10) are modified versions of Equations (5) and (8), respectively, where trainable variables are introduced. Notably, when and , the calculations remain the same as in the OAMP algorithm and the OAMP-Net network. These trainable variables, and , control the update step sizes of and . Consequently, they can influence the convergence of the LE estimator and the overall detection performance. In Equation (11), we observe that and serve as the prior mean and variance of , respectively. To ensure the convergence and optimal performance of the OAMP-Net detector, it is necessary to minimize estimation errors in the LE estimator, which are essentially calculations of . Therefore, prior to passing to the NLE estimator, we insert a data-driven neural network to correct the values of . This data-driven symbol correction network maps the estimated to a corrected version, , which is closer to the true value.
In the symbol correction network, we treat the errors of the LE estimator outputs as residual noise. By training the symbol correction network, it can reconstruct the residual noise. The input vector of the symbol correction network is from each iteration, and the output is the reconstructed residual noise of the same size as . Our implementation employs an -layer symbol correction network [34]. The first layers are fully connected layers with the leaky rectified linear unit (ReLU) function, which helps to extract noise characteristics. The final layer is a fully connected layer without the leaky ReLU function, serving as the output layer to reconstruct the residual noise. Finally, the noise-cleaned is obtained by subtracting the reconstructed noise from the input :
where represents the function expression of the symbol correction network with network parameters . Table 2 presents the hyperparameters of the data-driven symbol correction network.

Table 2.
Hyperparameters of the data-driven symbol correction network.
In our method, we use a symbol correction network with , indicating that there are two fully connected layers with the leaky ReLU function and an fully connected output layer without the leaky ReLU function. The slope of the leak in every leaky ReLU function is set to 0.3.
For the l-th layer () in the symbol correction network, the output vector is computed as follows: . Here, , , and represent the weight matrix, the input vector, and the bias term of the l-th layer, respectively.
In the first layer, the input vector is , which has the same size as . We set and , resulting in .
In the second layer, the input vector is , and we set and , resulting in .
In the final layer, the input vector is , and we set and , resulting in .
The element in the p-th row and the q-th column of is denoted as , and the j-th element of is denoted as . Therefore, the set of parameters in the symbol correction network is denoted as . During initialization, we set and .
After inserting the data-driven symbol correction network, the LE and NLE in our dual-driven MIMO detector can be expressed as follows:
In this formulation, the data-driven symbol correction network is inserted into the OAMP-Net network. The trainable variables of both the OAMP-Net and the symbol correction network are updated simultaneously in each iteration. Here, denotes the total number of iterations. The normalized mean square error (NMSE) of and is used as the loss function:
Here, and represent the jth samples in the training set, respectively, and denotes the batch size.
3. Numerical Results and Discussion
This section presents our experimental results and the corresponding discussions.
We begin by providing a comprehensive introduction to the simulation settings, including the methodology for setting the experiment parameters and generating the experimental data. Subsequently, we present and analyze the experimental results.
To verify the hypothesis that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector outperforms the OAMP-Net and some other detectors, we chose the bit error rate (BER) as the evaluation metric to assess performance. The reason why BER was chosen as the evaluation metric instead of the symbol error rate (SER) is that we considered the role of demodulation; the symbol estimation error does not completely lead to the bit estimation error, while the bits truly determine the quality of the communications, as stated in [25,26,27,29,30].
According to Equation (4), we find that the MIMO detection process is affected by channel and noise . Thus, we compare the BERs of the dual-driven MIMO detector and other detectors under different noise powers and channel estimation errors. To test the convergence of the proposed dual-driven detector, we compare the BERs of the dual-driven detector and the OAMP-Net with different layers with different learning rates.
3.1. Simulation Settings
We conducted several simulation experiments to validate the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method. The simulation settings used in these experiments are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Simulation settings.
In our setup, there are UAVs, each equipped with a single transmitting antenna. The GS has receiving antennas. The receiving antennas are dual-polarized and arranged in a uniform planar array (UPA) with an antenna spacing of /2 between adjacent elements.
For the propagation scenario, we consider an urban environment where the main scatterers are buildings, trees, and moving vehicles. The GS is located at a height of 25 m, while the heights of the UAVs are randomly and uniformly distributed between 1 m and 100 m. We assume that all UAVs are moving in a straight line at a speed of 30 km/h.
The UAV communication system operates in the millimeter-wave frequency band with a center frequency of 73 GHz. The frequency band has a width of 100 MHz. We use a total of 1024 subcarriers, with a spacing of 60 kHz between adjacent subcarriers.
The channel matrix for () and () is generated based on the 3GPP TR 38.901 V16.1.0 [14] and 3GPP TR 36.777 V15.0.0 [15] specifications. We employ a 4QAM modulation scheme. Although the constellation set contains only four constellation points, we can generate any number of training sample combinations with complex Gaussian noise vector . Here, the superscript j denotes the j-th sample combination in the dataset. The dataset consists of 16,000 training samples, 2000 validation samples, and 2000 testing samples. We use a mini-batch size of 100.
To optimize the entire dual-driven network and minimize the loss function, we employ the adaptive moment estimation (Adam) optimizer. The Adam optimizer utilizes a variable learning rate of , , and .
3.2. Baselines
To evaluate the performance of the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector, we selected several commonly used methods as baselines. These baselines include a linear detector known as the MMSE detector and model-driven detectors such as the OAMP algorithm and the OAMP-Net network. Descriptions of these baselines are presented in the following section.
Linear detector: MMSE detector [22]. The MMSE detector estimates the transmitted signal, denoted as , using the following equation:
where represents the estimated result of .
3.3. Channel Estimation Errors
In order to detect symbols, all detectors require knowledge of the channel information. In the proposed dual-driven MIMO detection algorithm presented in Algorithm 1, the channel matrix is crucial prior information. While some MIMO symbol detection methods assume perfect channel estimation with known channel state information (CSI), it is important to acknowledge that channel estimation errors are inevitable in practical scenarios. To evaluate the robustness of the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector against channel estimation errors, we include channel estimation errors by adding complex Gaussian noise to the accurate channel matrix. Specifically, we modify the accurate channel matrix by introducing the estimated channel matrix as follows:
where represents the complex Gaussian noise vector with as the noise variance. In our numerical simulations, in (17) will replace in (1). To quantify the channel estimation error, we utilize the mean squared error (MSE) between and . In our implementation, all data sample combinations in the training dataset are generated under the condition of a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of 20 dB and an MSE of −30 dB.
| Algorithm 1 The proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection algorithm |
|
3.4. BER versus SNR
To verify whether the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector will outperform the baselines at different noise powers, we conducted the following test by setting the SNR to between 0 dB and 25 dB using a channel estimation MSE of −30 dB and seven layers in the dual-driven network. Figure 4 presents the results of the dual-driven MIMO detector, MMSE MIMO detector, OAMP detector, and OAMP-Net detector using testing data samples generated at various SNRs, with a channel estimation MSE of −30 dB. From the figure, it is evident that the proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method outperforms the other three MIMO detectors at all SNRs from high-SNR to low-SNR regions. In particular, the dual-driven detector exhibits significant performance advantages over the other three detectors at higher SNRs. The MMSE and OAMP-Net detectors’ performances appear to be similar.
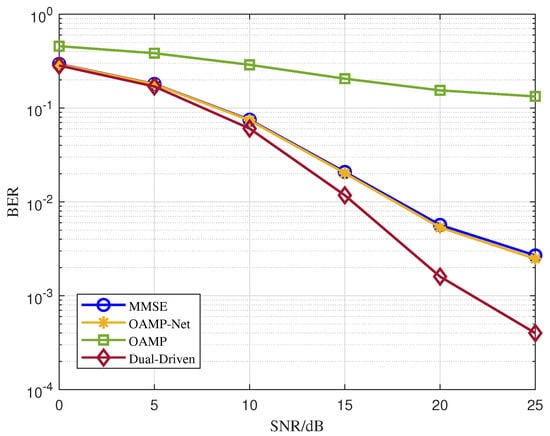
Figure 4.
BER versus SNR for the dual-driven MIMO detector and three other detectors when the channel estimation MSE = −30 dB.
Since the only difference between the dual-driven MIMO detector and the OAMP-Net detector is the inserted data-driven symbol correction network, as shown in Figure 3, we can conclude that the increased performance of the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector is completely caused by detection error correction in the symbol correction network. For example, when the SNR is 20 dB and the channel estimation MSE is −30 dB, the dual-driven MIMO detector can achieve a BER of , while OAMP-Net can only achieve a BER of . To achieve the target BER of , the dual-driven MIMO detector requires a BNR of 15.1 dB, while the MMSE and OAMP-Net detectors require SNRs of 17.7 dB and 17.6 dB, respectively. This implies that the dual-driven MIMO detector achieves the same BER, with an SNR reduction of 2–3 dB compared to the other two detectors. Moreover, the proposed dual-driven detector achieves a BER of at a BNR of around 22.5 dB, while the other three detectors fail to reach this level. Notably, the OAMP detector exhibits a poor performance and is highly sensitive to the channel matrix structure and noise, leading to performance degradations.
Considering that the training data samples were generated at an SNR of 20 dB and the testing data samples were generated at different SNRs, the results demonstrate that the data-driven component of the proposed dual-driven detector effectively corrects symbols and exhibits robustness to noise.
To sum up, this test verifies the hypothesis that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detection outperforms the OAMP-Net, OAMP, and MMSE detectors at different noise powers.
3.5. BER versus MSE
To verify whether the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector can outperform the baselines at different channel estimation errors, we conducted a test, setting the channel estimation MSE at between −40 dB and −26 dB at an SNR of 20 dB and with seven layers in the dual-driven network. Figure 5 illustrates the results obtained from the dual-driven MIMO, MMSE MIMO, OAMP, and OAMP-Net detectors using testing data samples generated at various MSEs while maintaining an SNR of 20 dB. The findings presented in Figure 5 align with those depicted in Figure 4.
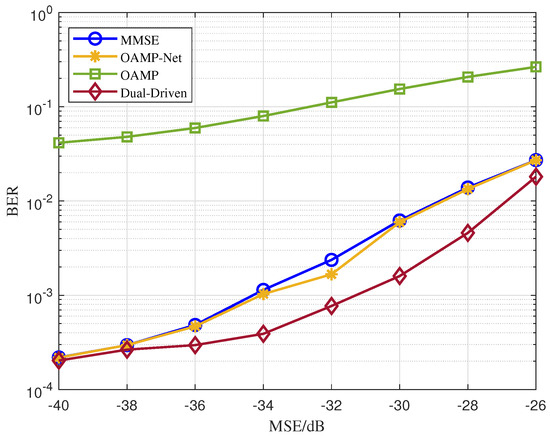
Figure 5.
BER versus MSE for the dual-driven MIMO detector and the other three detectors when SNR = 20 dB.
The proposed dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection method outperforms the other three MIMO detectors at a channel estimation MSE ranging from −40 dB to −26 dB. Both the MMSE and the OAMP-Net detectors exhibit similar performances, while the OAMP detector demonstrates the poorest performance among the four detectors.
We have demonstrated that the dual-driven detector’s performance improvement can mainly be attributed to the symbol correction network in Section 3.4. When the SNR is 20 dB and the channel estimation MSE is −28 dB, the dual-driven MIMO detector can achieve a BER of , while the OAMP-Net can only achieve a BER of . To achieve the target BER of , the dual-driven MIMO detector requires a channel estimation MSE of −31.2 dB, whereas the MMSE and the OAMP-Net detectors necessitate channel estimation MSEs of −34.2 dB and −34 dB, respectively. This indicates that the dual-driven MIMO detector requires a increased channel estimation MSE by 2–3 dB to achieve the same BER as the other two detectors.
Considering that the training data samples were generated with a channel estimation MSE of −30 dB and the testing data samples were generated with varying channel estimation MSEs, the results demonstrate the effective performance of the proposed dual-driven detector in mitigating the impact of channel estimation errors.
To sum up, this test verifies the hypothesis that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector outperforms the OAMP-Net, the OAMP, and the MMSE detectors at different channel estimation errors.
3.6. BER versus Layers
To verify whether the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector will outperform the OAMP-Net detector with different network layers, we conducted the tests using a channel estimation MSE of −30 dB and an SNR of 20 dB. In this context, the number of layers corresponds to the number of iterations, denoted as T.
A performance comparison between the dual-driven detector and the OAMP-Net detector is shown in Figure 6 as the number of layers ranges from 1 to 7. We can see that the performance of OAMP-Net hardly improves, while the performance of the dual-driven detector improves with increasing network layers, which means the detection error can effectively be reduced iteratively in the dual-driven network.
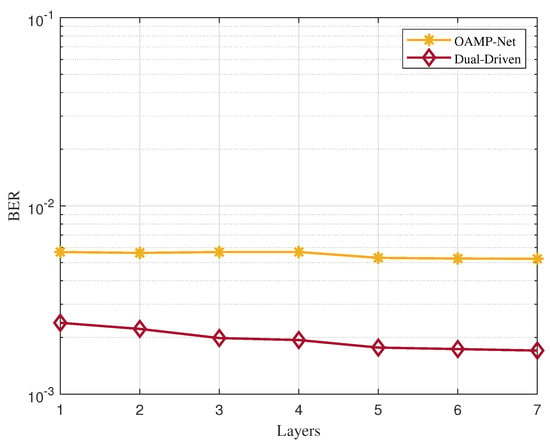
Figure 6.
BER versus layers for the dual-driven MIMO detector and OAMP-Net when the SNR = 20 dB and the MSE = −30 dB.
Figure 7 depicts the results for the dual-driven MIMO detector with varying numbers of layers and different learning rates for the Adam optimizer, maintaining an SNR of 20 dB and a channel estimation MSE of −30 dB. It is evident that as the number of layers increases, the BER generally decreases across all three different learning rates. However, when the learning rate is set to 0.00001, the BER with seven layers is actually higher than that with six layers. This discrepancy could be attributed to overfitting. Consequently, in our implementation, we choose to set T to seven as a suitable number of layers. Different learning rates control the convergence speed. It is noticeable that the differences among the three learning rates (0.01, 0.0005, and 0.00001) are not significant. Therefore, we opted for a variable learning rate approach. Specifically, we set the learning rate to 0.001 initially until convergence and then adjusted it to 0.005 or 0.0001 to prevent overfitting.
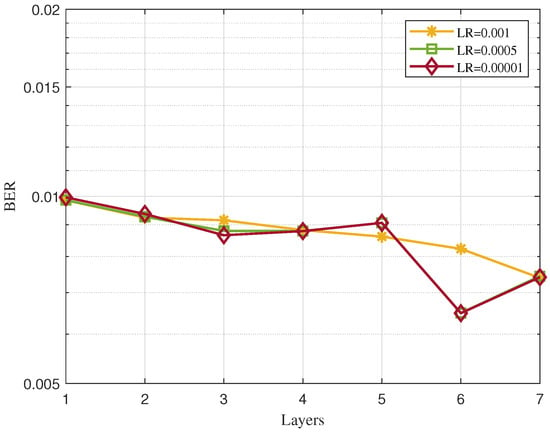
Figure 7.
BER versus layers using different learning rates for the dual-driven MIMO detector when the SNR = 20 dB and the MSE = −30 dB.
To sum up, this test verifies the hypothesis the that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector outperforms the OAMP-Net with different layers. With different layers and different learning rates, the proposed dual-driven detector can converge well and maintain stability.
3.7. Computational Complexity
The complexity of online deployment of the dual-driven MIMO detector is related to two aspects: (i) fully connected layers in the symbol correction network with a computational complexity of and (ii) OAMP-Net with a computational complexity of [25]. and are the input and output sizes in the lth layer, respectively. According to Table 2, the computational complexity of the symbol correction network is . can range from hundreds to thousands in the massive access case or the ultra MIMO case. Since is a constant when the dual-driven network is stable, the overall complexity of the dual-driven MIMO detector is , which is same as OAMP-Net.
3.8. Engineering Benefits
The use of a dual-driven MIMO detector in practical applications provides several engineering benefits.
Enhanced Performance: The dual-driven MIMO detector leverages the power of deep learning and neural networks to achieve improved performance compared to traditional model-driven MIMO detectors or linear MIMO detectors. By capturing complex nonlinear relationships between the correct symbols and the received symbols, dual-driven MIMO detectors can achieve higher accuracy and robustness in MIMO detection. This leads to enhanced system performance in terms of data rates, reliability, and overall communication quality.
Adaptability to Various Channel Conditions: A dual-driven MIMO detector can adapt to different channel conditions, including varying noise powers and channel estimation errors. Through the training process, the dual-driven MIMO detector learns to extract relevant features from the received signals and detect MIMO symbols effectively. This adaptability makes the dual-driven MIMO detector applicable for a wide range of practical wireless communication environments.
Flexibility and Scalability: The dual-driven MIMO detector offers flexibility and scalability in terms of system configuration and deployment. It can be adapted to different MIMO system setups, including varying numbers of antennas, spatial streams, and modulation schemes. The neural network architecture of the dual-driven MIMO detector can be customized and optimized to accommodate specific system requirements, making it suitable for a wide range of practical MIMO communication scenarios.
Real-Time and Near-Real-Time Processing: The dual-driven MIMO detector can be implemented efficiently to enable real-time or near-real-time processing, depending on the hardware and computational resources available. By leveraging parallel computing, hardware acceleration techniques, and optimization algorithms, dual-driven MIMO detectors may be suitable for time-critical applications.
These engineering benefits make the dual-driven MIMO detector a better choice.
However, the limitation of the dual-driven MIMO detector is that the off-line training process needs to accumulate data and be trained, which means the dual-driven MIMO detector needs extra storage and computing resources.
4. Conclusions
In this article, we present a novel dual-driven learning-based network for massive MIMO detection in UAV AG communications. The proposed network consists of two components: a data-driven network with three fully connected layers that corrects symbol estimation errors to minimize detection errors, and a model-driven OAMP-Net, which performs MIMO detection through iterative processes. The main contribution of this paper is that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector is a novel combination of a data-driven symbol correction network and the model-driven OAMP-Net. The entire dual-driven network is trained simultaneously to optimize its performance. Our main hypothesis was that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector will outperform the model-driven OAMP-Net and other traditional MIMO detectors since it has the advantages of both the data-driven network and the model-driven network.
We analyze the network structure of the dual-driven network and the dual-driven learning-based MIMO symbol detection algorithm in detail. To verify the hypothesis that the proposed dual-driven MIMO detector will outperform OAMP-Net and some other detectors at different noise powers and different channel estimation errors, we carry out extensive test simulations. Through these simulations, we demonstrate that the dual-driven learning detector exhibits significant performance improvements compared to the MMSE, OAMP, and OAMP-Net detectors across a wide range of SNRs (0 dB to 25 dB) and MSEs (−40 dB to −26 dB). When the SNR is 20 dB and the MSE is −30 dB, the dual-driven MIMO detector can achieve a BER of , while the OAMP-Net can only achieve a BER of . Since the only difference between the dual-driven MIMO detector and the OAMP-Net detector is the inserted data-driven symbol correction network, we can verify our hypothesis. In addition, with different layers and different learning rates, the proposed dual-driven detector converges well and maintains stability.
The proposed dual-driven MIMO detector provides several engineering benefits: enhanced performance, adaptability to various channel conditions, good flexibility and scalability, and near-real-time processing ability.
This article lays a solid foundation for the advancement of UAV AG communications in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.L. and S.Z.; methodology, H.L.; validation, H.L. and S.Z.; formal analysis, H.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, H.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.H., F.Z. and H.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Please contact the authors for data requests.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MIMO | Multiple-Input Multiple-Output |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| AG | Air-to-Ground |
| 6G | Sixth-Generation Cellular Network |
| mm-wave | millimeter-wave |
| OAMP-Net | Orthogonal Approximate Message Passing Network |
| MMSE | Minimum Mean Square Error |
| OAMP | Orthogonal Approximate Message Passing |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| SER | Symbol Error Rate |
| SAGIN | Space–Air–Ground Integrated Network |
| 3GPP | Third-Generation Partnership Project |
| NR | New Radio |
| UE | User Equipment |
| AA | Air-to-Air |
| LMMSE | Linear Minimum Mean Square Error |
| AMP | Approximate Message Passing |
| CG-OAMP-Net | Conjugate Gradient OAMP-Net |
| NN | Neural Network |
| ADC | Analog-to-Digital Converter |
| GS | Ground Station |
| LOS | Line Of Sight |
| NLOS | Non-Line Of Sight |
| Rx | Receiving |
| Tx | Transmitting |
| CSI | Channel State Information |
| QAM | Quadrature Amplitude Modulation |
| PSK | Phase Shift Keying |
| IFFT | Inverse Fast Fourier Transform |
| CP | Cyclic Prefix |
| LE | Linear Estimator |
| NLE | Nonlinear Estimater |
| NMSE | Normalized Mean Square Error |
| BER | Bit Error Rate |
| UPA | Uniform Planar Array |
| Adam | Adaptive Moment estimation |
References
- Liu, W.; Zhang, T.; Huang, S.; Li, K. A hybrid optimization framework for UAV reconnaissance mission planning. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 173, 108653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.P.; Noura, H.; Salman, O.; Chehab, A. Security analysis of drones systems: Attacks, limitations, and recommendations. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, Y. UAV communications for 5G and beyond: Recent advances and future trends. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 6, 2241–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, W.C.; Li, Y.; Shang, J.; Urban, T.L. Impact of drone delivery on sustainability and cost: Realizing the UAV potential through vehicle routing optimization. Appl. Energy 2019, 242, 1164–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, E.T.; Alqefari, S.S.; Koubaa, A. Lsar: Multi-uav collaboration for search and rescue missions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 55817–55832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouamri, M.A.; Alkanhel, R.; Gueguen, C.; Alohali, M.A.; Ghoneim, S.S. Modeling and analysis of uav-assisted mobile network with imperfect beam alignment. CMC-Comput. Mater. Contin. 2023, 74, 453–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Fadlullah, Z.M.; Kato, N. Space-air-ground integrated network: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2714–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W. Research challenges and opportunities of UAV millimeter-wave communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2019, 26, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraci, G.; Garcia-Rodriguez, A.; Azari, M.M.; Lozano, A.; Mezzavilla, M.; Chatzinotas, S.; Chen, Y.; Rangan, S.; Di Renzo, M. What will the future of UAV cellular communications be? A flight from 5G to 6G. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2022, 24, 1304–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, R.; Lim, T.J. Wireless communications with unmanned aerial vehicles: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, R. Accessing from the sky: A tutorial on UAV communications for 5G and beyond. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 2327–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, M.; Saad, W.; Bennis, M.; Debbah, M. Mobile unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for energy-efficient Internet of Things communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2017, 16, 7574–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, F.; Ding, G.; Zhang, T.; Jia, W.; Nallanathan, A. Integrating communications and control for UAV systems: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 67519–67527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3GPP. Study on Channel Model for Frequencies from 0.5 to 100 GHz (Release 17); TR 38.901 V17.1.0; 3GPP, Technical Report; 3GPP Mobile Competence Centre: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP. Study on Enhanced LTE Support for Aerial Vehicles (Release 15); TR 36.777 V15.0.0; 3GPP, Technical Report; 3GPP Mobile Competence Centre: Sophia Antipolis, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, L.; Jain, R.; Vaszkun, G. Survey of important issues in UAV communication networks. IEEE Commun. Tutor. 2015, 18, 1123–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pan, X.; Luo, X.; Cheng, Y. Joint Channel Estimation and Symbol Detection for UAV-Assisted Systems Using Tensor Framework. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Nanjing, China, 11–14 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, L. A robust tensor-based receiver for joint channel estimation and symbol detection in UAV assisted communication systems. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 21st International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Tianjin, China, 13–16 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khawaja, W.; Guvenc, I.; Matolak, D.W.; Fiebig, U.C.; Schneckenburger, N. A survey of air-to-ground propagation channel modeling for unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 2361–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuwaja, A.A.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, N.; Alouini, M.S.; Dobbins, P. A survey of channel modeling for UAV communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2804–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damen, M.O.; El Gamal, H.; Caire, G. On maximum-likelihood detection and the search for the closest lattice point. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2003, 49, 2389–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.L.; Rainbolt, B.J. MMSE detection of multicarrier CDMA. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2000, 18, 2356–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Maleki, A.; Montanari, A. Message-passing algorithms for compressed sensing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18914–18919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Ping, L. Orthogonal amp. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2020–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wen, C.K.; Jin, S.; Li, G.Y. A model-driven deep learning network for MIMO detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–29 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Wen, C.K.; Jin, S.; Li, G.Y. Model-driven deep learning for MIMO detection. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Syu, C.W.; Wen, C.K.; Zhang, J.; Jin, S. Model-driven deep learning-based MIMO-OFDM detector: Design, simulation, and experimental results. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 5193–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khani, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Hoydis, J.; Fleming, P. Adaptive neural signal detection for massive MIMO. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 5635–5648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Li, G.Y.; Juang, B.H. Power of deep learning for channel estimation and signal detection in OFDM systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 7, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, N.; Diskin, T.; Wiesel, A. Deep MIMO detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–29 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Takabe, S.; Imanishi, M.; Wadayama, T.; Hayakawa, R.; Hayashi, K. Trainable projected gradient detector for massive overloaded MIMO channels: Data-driven tuning approach. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 93326–93338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wu, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, W.; Jing, X. Hybrid Driven Learning for Channel Estimation in Intelligent Reflecting Surface Aided Millimeter Wave Communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, S.; Zheng, S.; Jiang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Dual-Driven Learning for Channel Estimation of Massive MIMO Systems with One-Bit ADCs. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Basha, S.S.; Dubey, S.R.; Pulabaigari, V.; Mukherjee, S. Impact of fully connected layers on performance of convolutional neural networks for image classification. Neurocomputing 2020, 378, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).