Impact Analysis of Time Synchronization Error in Airborne Target Tracking Using a Heterogeneous Sensor Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
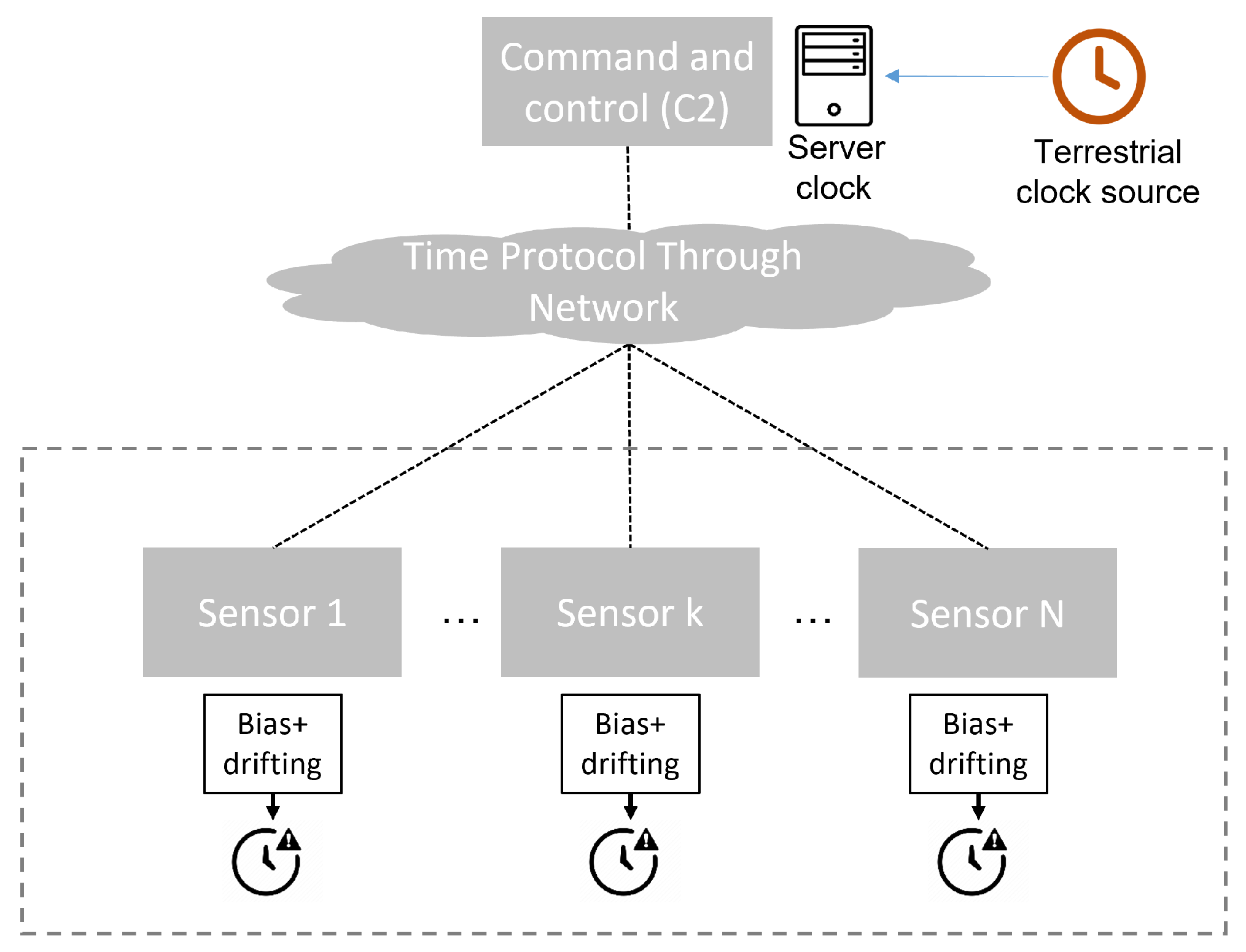
2. Preliminaries
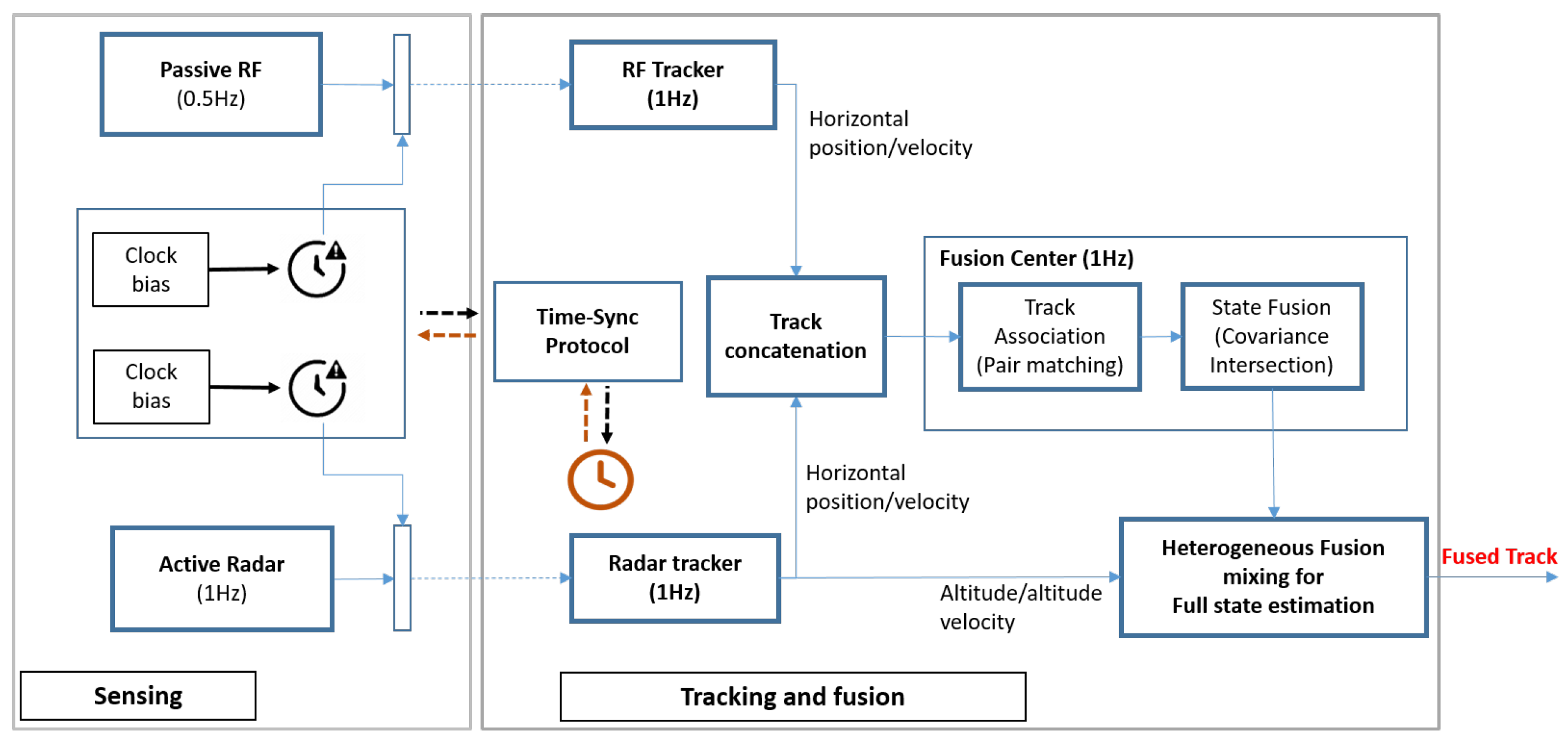
3. Target Tracking System
3.1. Sensor Model
3.2. Local Tracker
3.2.1. Measurement-to-Track Association and Filtering
3.2.2. Track Update with Time Alignment
3.3. Track Fusion
4. Impact Analysis
4.1. Influence on Local Tracking and Association
4.1.1. Influence on Measurement-to-Track Association and Filtering
4.1.2. Influence on Track Update with Time Alignment
4.2. Impact on Track-to-Track Association
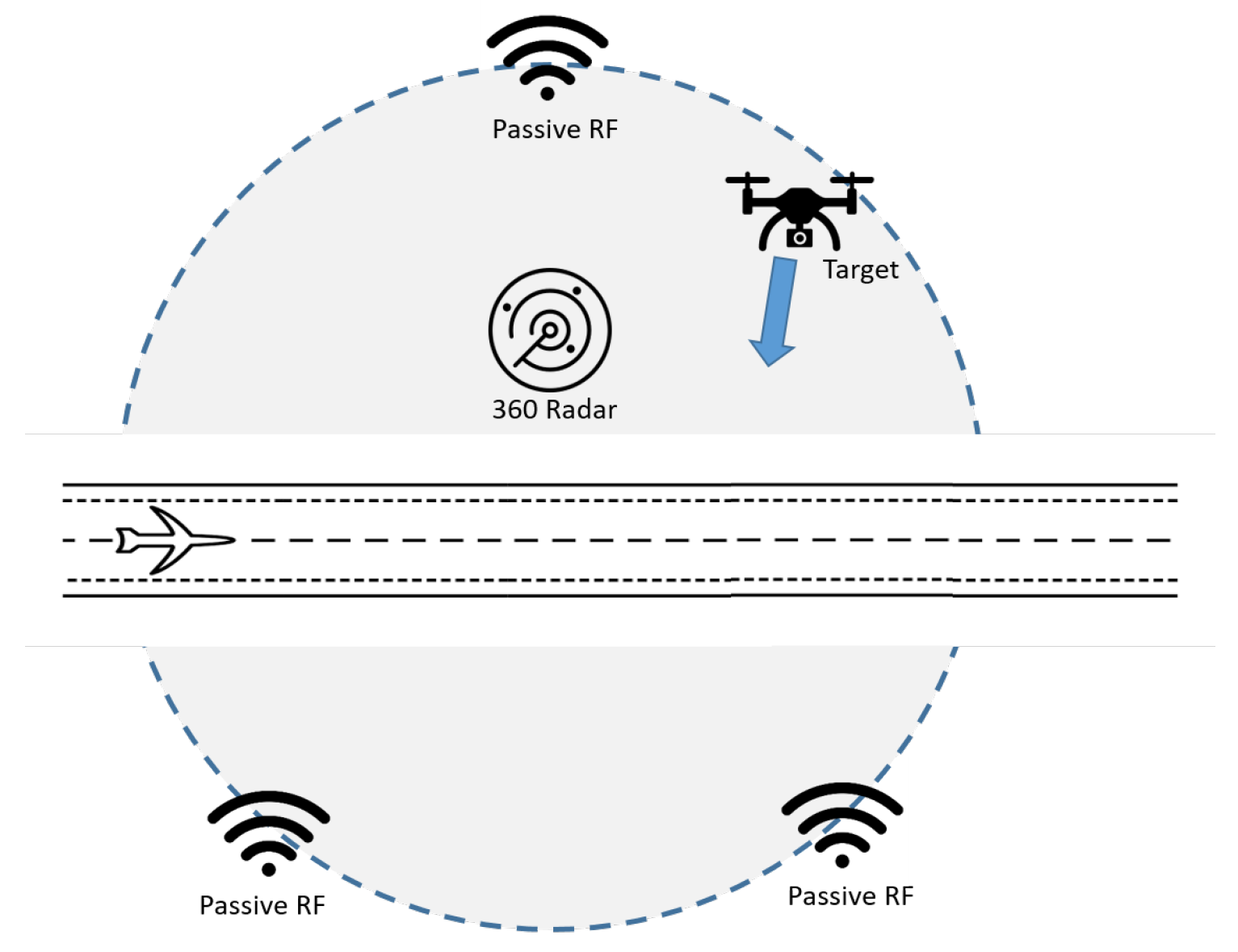
5. Simulation Study
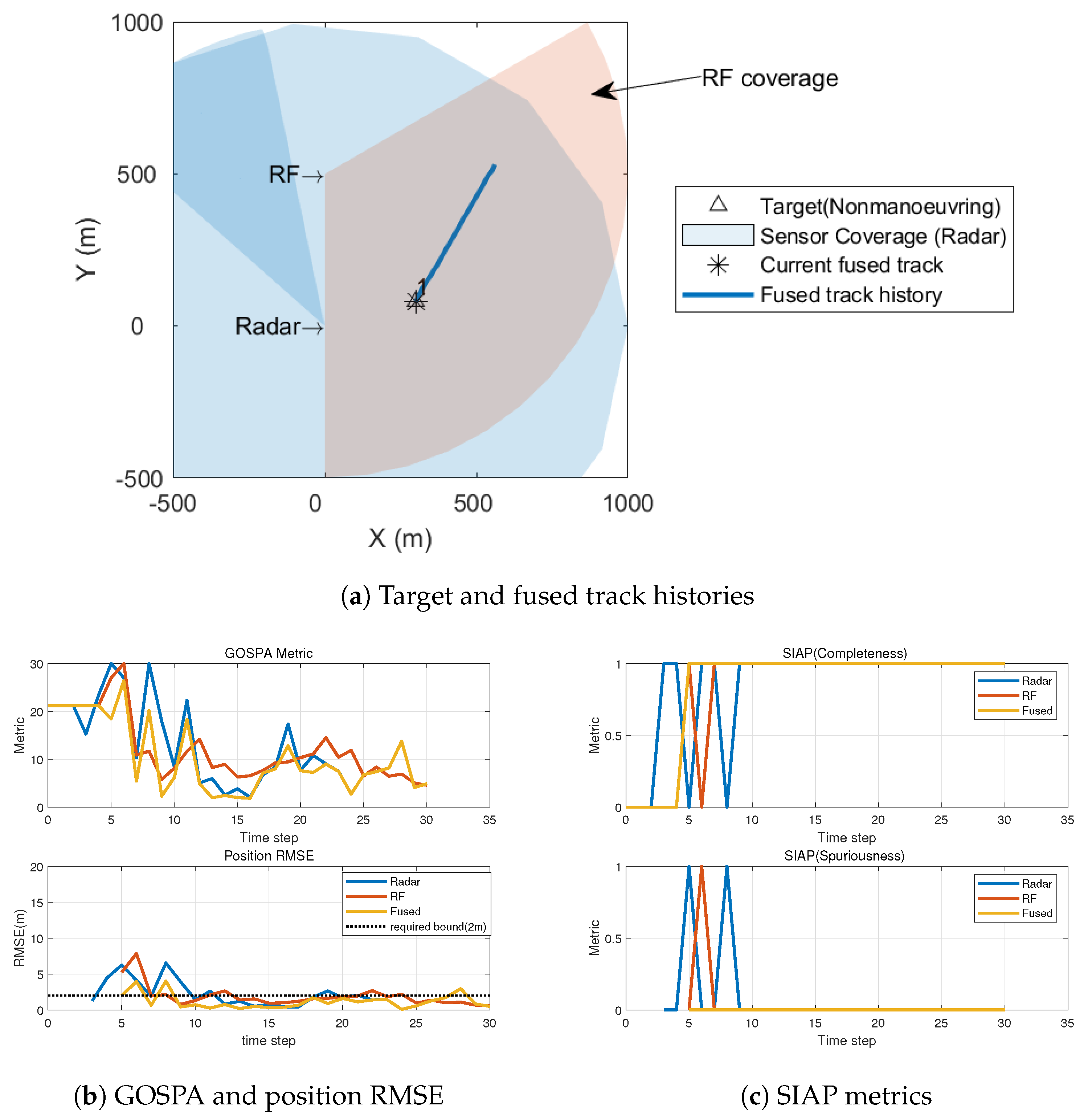
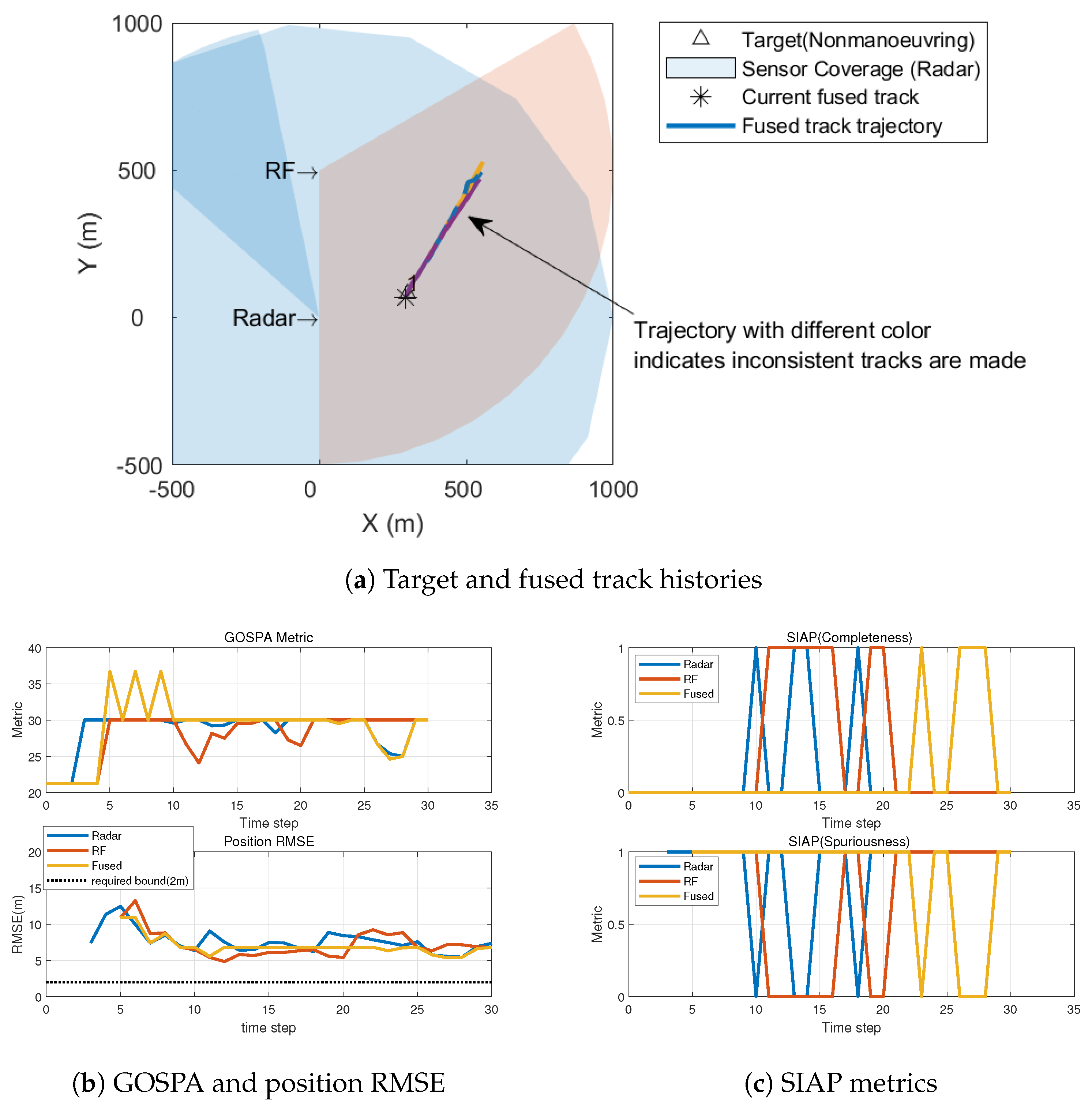
5.1. Comparison between Synchronized and Unsynchronized Sensor Networks
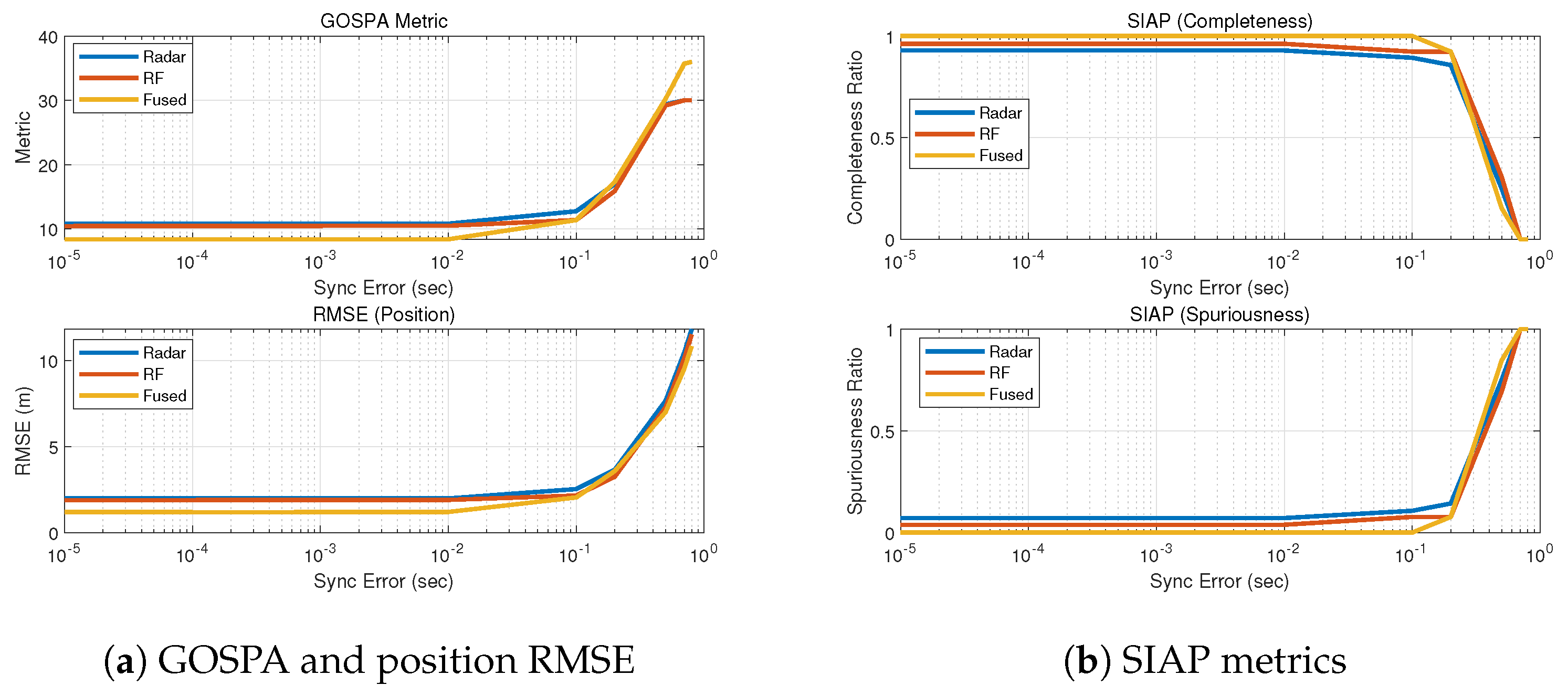
5.2. Performance under Increasing Synchronization Errors
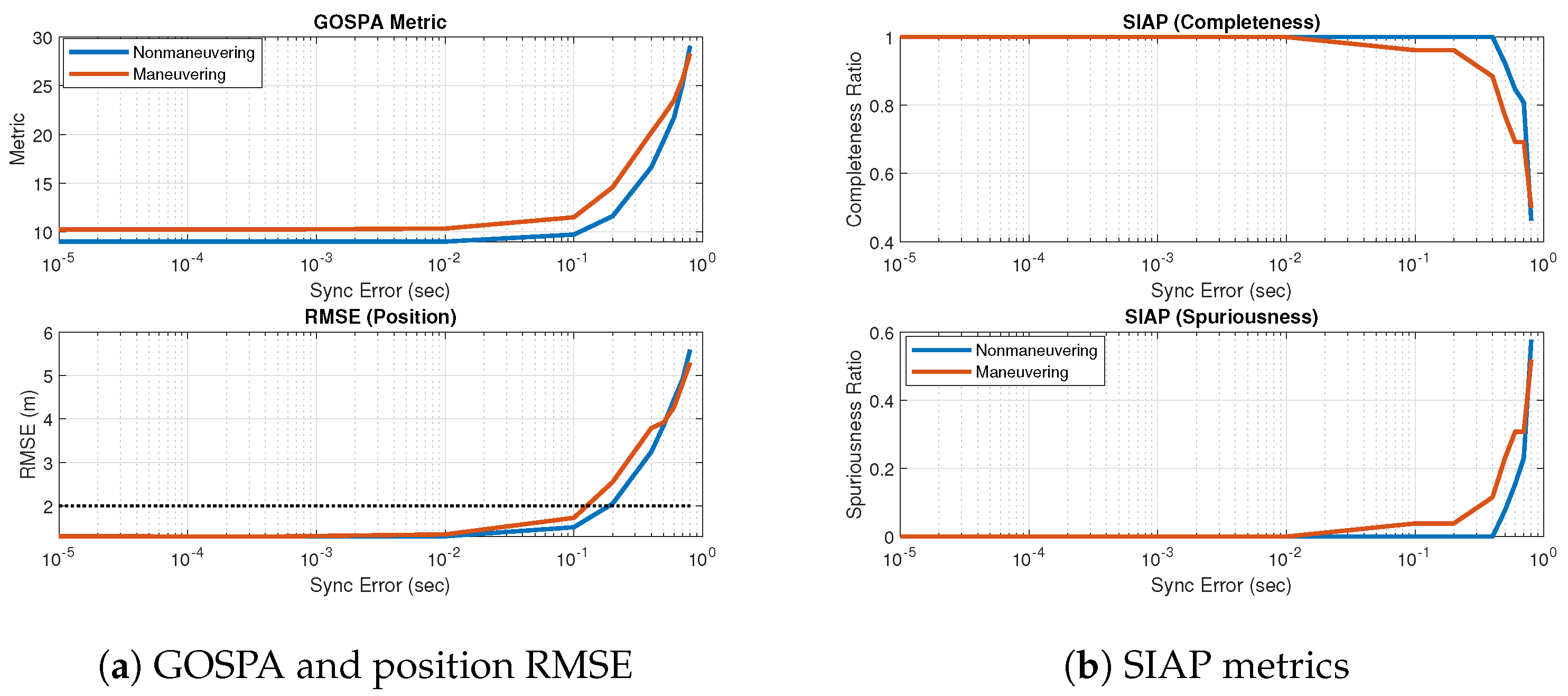
5.3. Performance When the Target Is Maneuvering
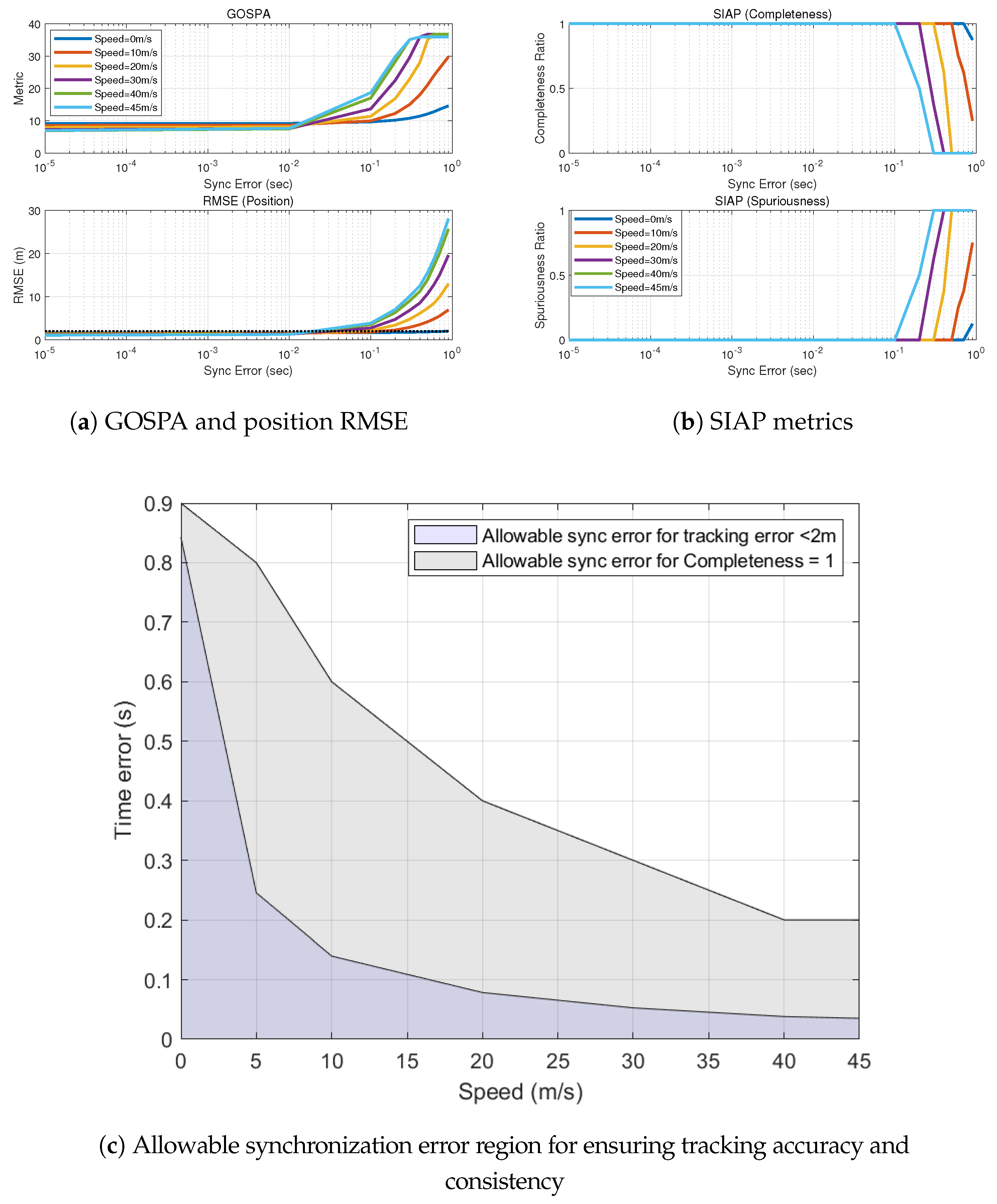
5.4. Performance under Speed Variations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hallie, D. Gatwick’s December Drone Closure Cost Airlines $64.5 million. Fortune. 2019. Available online: https://fortune.com/2019/01/22/gatwick-drone-closure-cost/ (accessed on 4 March 2024).
- Kaleem, Z.; Rehmani, M.H. Amateur Drone Monitoring: State-of-the-Art Architectures, Key Enabling Technologies, and Future Research Directions. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2018, 25, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingali, G.; Tunali, G.; Carlbom, I. Audio-visual tracking for natural interactivity. In Proceedings of the Seventh ACM iInternational Conference on Multimedia (Part 1), Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–5 November 1999; pp. 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Azari, M.M.; Sallouha, H.; Chiumento, A.; Rajendran, S.; Vinogradov, E.; Pollin, S. Key Technologies and System Trade-offs for Detection and Localization of Amateur Drones. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaempchen, N.; Dietmayer, K. Data synchronization strategies for multi-sensor fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Shanghai, China, 12–15 October 2003; Volume 85, pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, D.D. NextGen Network Synchronization; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, P.H. Global Positioning System (GPS) time dissemination for real-time applications. Real-Time Syst. 1997, 12, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakakis, E.; Tange, K.; Reusch, N.; Zaballa, E.O.; Fafoutis, X.; Schoeberl, M.; Dragoni, N. Fault-tolerant Clock Synchronization using Precise Time Protocol Multi-Domain Aggregation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 24th International Symposium on Real-Time Distributed Computing (ISORC), Daegu, Republic of Korea, 1–3 June 2021; pp. 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, O.; Iturbe, X.; Val, I. Tackling the Challenges of the Integration of Wired and Wireless TSN with a Technology Proof-of-Concept. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 18, 7361–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Akos, D.; Dennis, J. Time Source Options for Alternate Positioning Navigation and Timing (APNT); Technical Report; Federal Aviation Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Lévesque, M.; Tipper, D. A survey of clock synchronization over packet-switched networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 2926–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D. Internet time synchronization: The network time protocol. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1991, 39, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1588–2019—IEEE Standard for a Precision Clock Synchronization Protocol for Networked Measurement and Control Systems; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–499. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shao, L.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, P. Estimation of Clock Skew for Time Synchronization Based on Two-Way Message Exchange Mechanism in Industrial Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4755–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Wu, N.; Shen, Y.; Win, M.Z. Cooperative Network Synchronization: Asymptotic Analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, I.; Kushwaha, M.; Kusy, B.; Volgyesi, P.; Simon, G.; Koutsoukos, X.; Ledeczi, A. Time synchronization for multi-modal target tracking in heterogeneous sensor networks. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Networked Distributed Systems for Intelligent Sensing and Control, Kalamata, Greece, 30 June 2007; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Behrendt, K.; Fodero, K. The Perfect Time: An Examination of Time- Synchronization Techniques. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual Western Protective Relay Conference, Spokane, WA, USA, 21–24 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kehrer, S.; Kleineberg, O.; Heffernan, D. A comparison of fault-tolerance concepts for IEEE 802.1 Time Sensitive Networks (TSN). In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Emerging Technology and Factory Automation (ETFA), Barcelona, Spain, 16–19 September 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goward, D. What Happened to GPS in Denver? GPS World, 21 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Hernandez, I.; Walter, T.; Neish, A.; O’Driscoll, C. Independent time synchronization for resilient gnss receivers. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 21–24 January 2020; pp. 964–978. [Google Scholar]
- Christ, R.D.; Wernli Sr, R.L. The ROV Manual: A User Guide for Remotely Operated Vehicles; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Chen, K.; Su, A. Incorporating delayed measurements in an improved high-degree cubature Kalman filter for the nonlinear state estimation of chemical processes. ISA Trans. 2019, 86, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosov, A. Tracking a Maneuvering Object by Indirect Observations with Random Delays. Drones 2023, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosov, A.V. Observation-Based Filtering of State of a Nonlinear Dynamical System with Random Delays. Autom. Remote Control 2023, 84, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhmacher, D.; Vo, B.T.; Vo, B.N. A consistent metric for performance evaluation of multi-object filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2008, 56, 3447–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Votruba, P.; Nisley, R.; Rothrock, R.; Zombro, B. Single Integrated Air Picture (SIAP) Metrics Implementation; Technical Report; Single Integrated Air Picture System Engineering Task Force: Arlington, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Liu, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; He, T. Time Synchronization based on Cross-Technology Communication for IoT Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023, 10, 19753–19764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Kim, S. Irregular situations in real-world intelligent systems. Adv. Comput. 2024, 134, 253–283. [Google Scholar]
- Zarick, R.; Hagen, M.; Bartoš, R. The impact of network latency on the synchronization of real-world IEEE 1588–2008 devices. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Precision Clock Synchronization for Measurement, Control and Communication, Portsmouth, NH, USA, 27 September–1 October 2010; pp. 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsel, F.; Anastasiia, K.; Gonzalo, F. Open-Source LiDAR Time Synchronization System by Mimicking GNSS-clock. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Precision Clock Synchronization for Measurement, Control and Communication (ISPCS), Vienna, Austria, 2–6 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- McCall, D. Breaking Down Sources of Dynamic Time Error for Chains of Networked Devices using Monte Carlo Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Precision Clock Synchronization for Measurement, Control, and Communication (ISPCS), Vienna, Austria, 2–6 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Schüngel, M.; Dietrich, S.; Ginthör, D.; Chen, S.P.; Kuhn, M. Analysis of time synchronization for converged wired and wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Vienna, Austria, 8–1 September 2020; Volume 1, pp. 198–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Track association and fusion with heterogeneous local trackers. In Proceedings of the 2007 46th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, New Orleans, LA, USA, 12–14 December 2007; pp. 2675–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Bar-Shalom, Y.; Tian, X. Heterogeneous track-to-track fusion. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information Fusion, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–8 July 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Roecker, J.; Theisen, D. Multiple sensor tracking architecture comparison. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2014, 29, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, M.; Chang, K.C.; Arulampalam, S.; Yan, Y. Heterogeneous track-to-track fusion in 3-D using IRST sensor and air MTI radar. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 3062–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaranta, C.; Balzarotti, G. Technique for radar and infrared search and track data fusion. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 046401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Truong, H.; Ravindranathan, M.; Nguyen, A.; Han, R.; Vu, T. Cost-Effective and Passive RF-Based Drone Presence Detection and Characterization. GetMobile Mob. Comp. Comm. 2018, 21, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeywickrama, S.; Jayasinghe, L.; Fu, H.; Nissanka, S.; Yuen, C. RF-based Direction Finding of UAVs Using DNN. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communication Systems (ICCS), Chengdu, China, 19–21 December 2018; pp. 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüßler, D.; Shoykhetbrod, A.; Gütgemann, S.; Küter, A.; Welp, B.; Pohl, N.; Krebs, C. Detection of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) in urban environments. In Emerging Imaging and Sensing Technologies for Security and Defence III; and Unmanned Sensors, Systems, and Countermeasures, Proceedings of the SPIE SECURITY + DEFENCE, Berlin, Germany, 10–13 September 2018; Buller, G.S., Hollins, R.C., Lamb, R.A., Mueller, M., Eds.; International Society for Optics and Photonics, SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10799, p. 107990R. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Daum, F.; Huang, J. The Probabilistic Data Association Filter: Estimation in the presence of measurement origin uncertainty. IEEE Control Syst. 2009, 29, 82–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Distributed joint probabilistic data association filter with hybrid fusion strategy. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2019, 69, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Shin, H.S.; Tsourdos, A. Information-theoretic joint probabilistic data association filter. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2020, 66, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Shalom, Y.; Chen, H. IMM estimator with out-of-sequence measurements. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2005, 41, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntzinger, M.M.; Aeberhard, M.; Schröder, F.; Sarholz, F.; Dietmayer, K. Tracking in a cluttered environment with out-of-sequence measurements. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Vehicular Electronics and Safety (ICVES), Pune, India, 11–12 November 2009; pp. 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzka, S.; Altendorfer, R. A comparison of track-to-track fusion algorithms for automotive sensor fusion. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 20–22 August 2008; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MathWorks. Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox; MathWorks: Natick, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
| Sensors | Radar | RF |
|---|---|---|
| Detection update rate | 1 Hz | 0.5 Hz |
| Azimuth resolution (Deg) | 3 | 5 |
| Range resolution (m) | 5 | 5 |
| Elevation resolution (Deg) | 3 | - |
| Location (m) | (0,0,0) | (0,500,0) |
| Detection range (m) | 1000 | 1000 |
| Radar Tracker | RF Tracker | |
|---|---|---|
| Update rate | 1 Hz | 1 Hz |
| Filter | 3D-CV-EKF [41] | 2D-CV-EKF [41] |
| Association threshold, b | 30 | 30 |
| M/N logic parameters for track maintenance | ||
| M/N logic parameters for track deletion |
| Ideal, | Synchronized, ms | Unsynchronized ( s) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radar | RF | Fused | Radar | RF | Fused | Radar | RF | Fused | |
| RMSE | 1.9819 | 1.549 | 0.7815 | 1.982 | 1.892 | 1.186 | 7.662 | 7.279 | 7.0064 |
| GOSPA | 10.811 | 9.276 | 6.857 | 11.278 | 10.468 | 8.371 | 29.362 | 29.195 | 30.230 |
| (%) | 100 | 100 | 100 | 92.86 | 96.15 | 100 | 25.00 | 30.77 | 15.38 |
| (%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.14 | 3.85 | 0 | 75.00 | 69.23 | 84.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Yuan, Z.; Petrunin, I.; Shin, H. Impact Analysis of Time Synchronization Error in Airborne Target Tracking Using a Heterogeneous Sensor Network. Drones 2024, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8050167
Lee S, Yuan Z, Petrunin I, Shin H. Impact Analysis of Time Synchronization Error in Airborne Target Tracking Using a Heterogeneous Sensor Network. Drones. 2024; 8(5):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8050167
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seokwon, Zongjian Yuan, Ivan Petrunin, and Hyosang Shin. 2024. "Impact Analysis of Time Synchronization Error in Airborne Target Tracking Using a Heterogeneous Sensor Network" Drones 8, no. 5: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8050167
APA StyleLee, S., Yuan, Z., Petrunin, I., & Shin, H. (2024). Impact Analysis of Time Synchronization Error in Airborne Target Tracking Using a Heterogeneous Sensor Network. Drones, 8(5), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8050167







