An Efficient Adjacent Frame Fusion Mechanism for Airborne Visual Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an efficient mechanism for adjacent frame fusion, consisting of two modules that entail minimal parameter increment and impose negligible computational overhead. Our mechanism is designed to be plug-and-play, ensuring ease of implementation. It has been validated on two datasets, NPS [18] and FL-Drone [7], demonstrating significantly enhanced effects.
- We propose a feature alignment fusion module, which distinguishes itself from intricate alignment techniques such as optical flow estimation and deformable convolution. Instead, this module utilizes local similarity calculation to align the features of adjacent frames with those of key frames and subsequently use them for feature fusion. Simultaneously, a comprehensive ablation study was conducted to substantiate the effectiveness of the proposed feature alignment fusion module.
- We propose a background subtraction module, drawing inspiration from the background subtraction technique in moving object detection. This module subtracts the background features of the adjacent frames from the foreground features of the key frame to enhance the target features and enhance the model’s accuracy.
2. Related Works
2.1. Small Object Detection
2.2. Video Object Detection
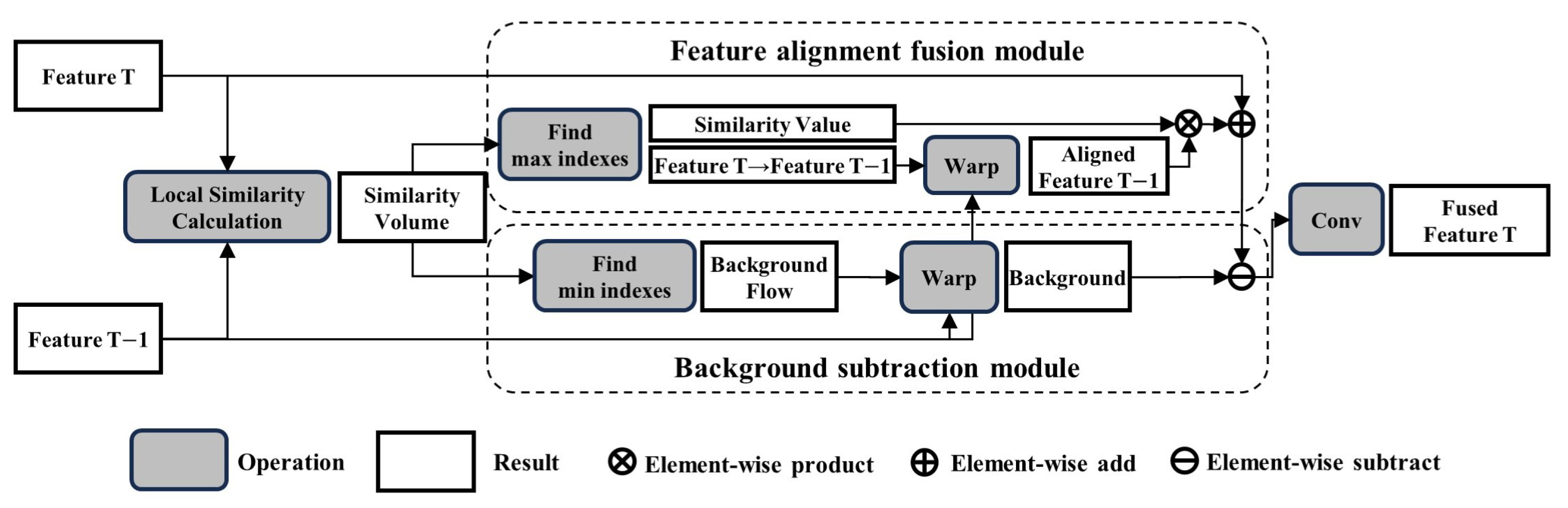
3. Proposed Method
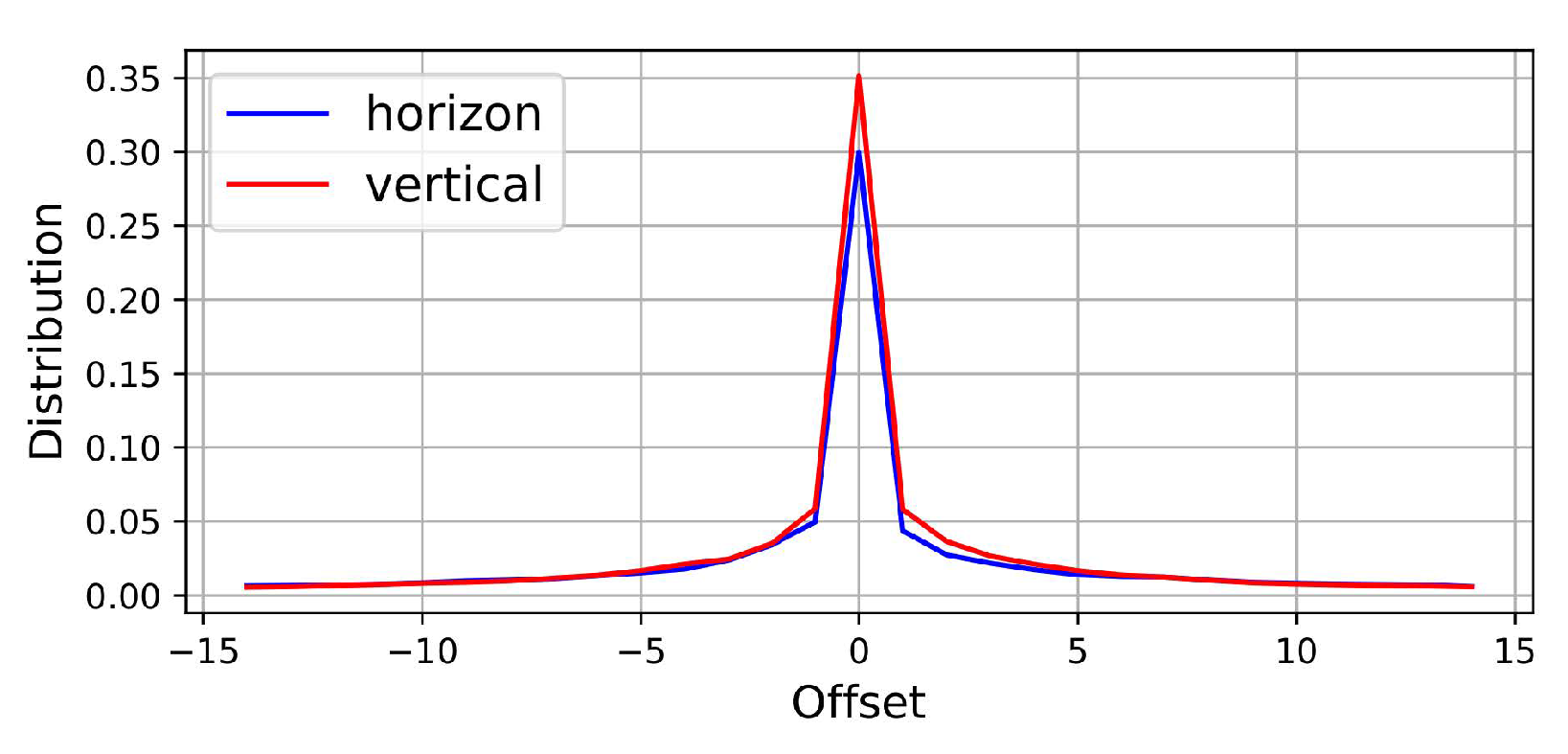
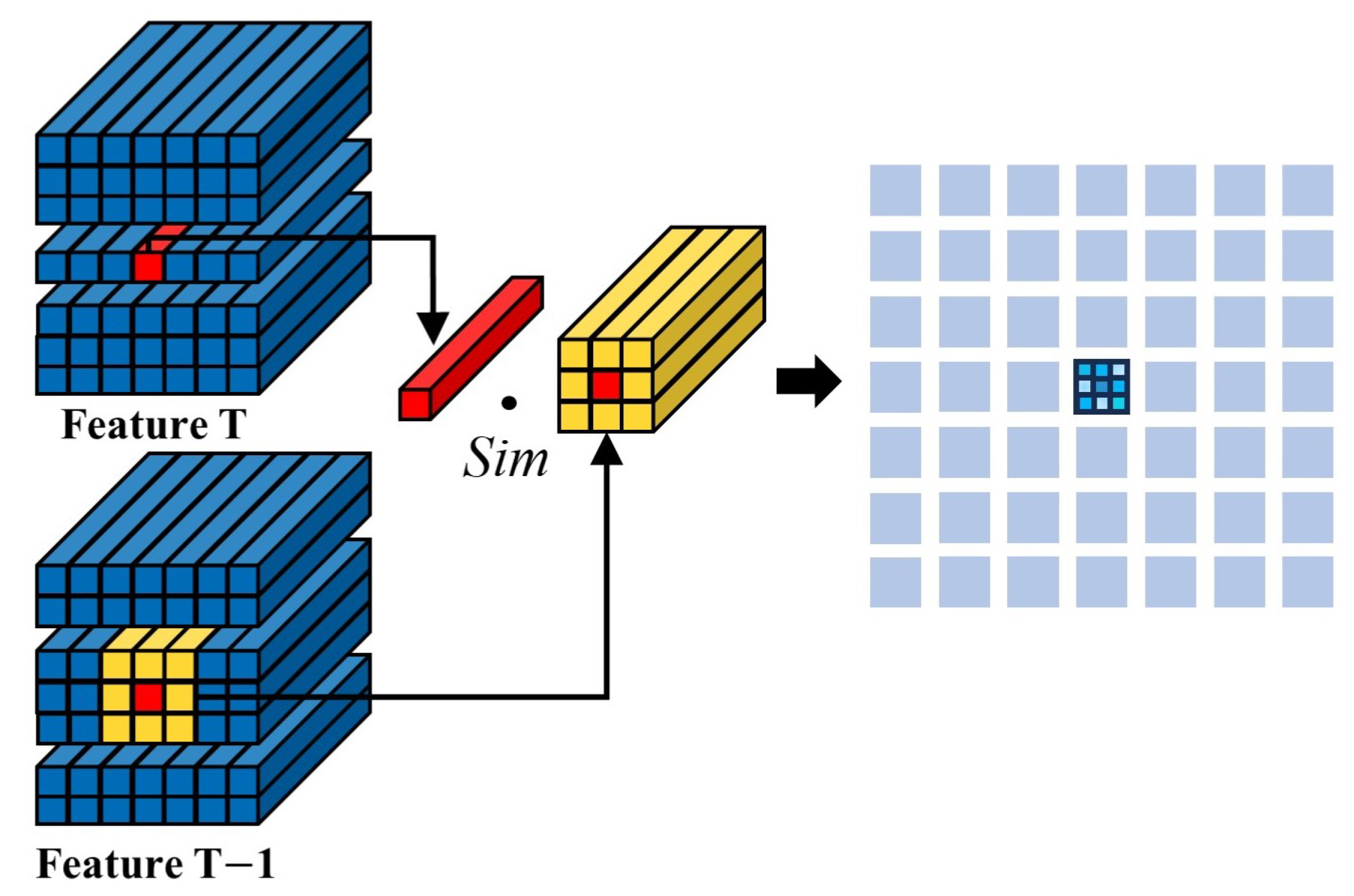
3.1. Local Similarity Calculation
3.2. Feature Alignment Fusion Module
3.3. Background Subtraction Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Comparison with State of the Art
4.3. Ablation Experiments and Analysis
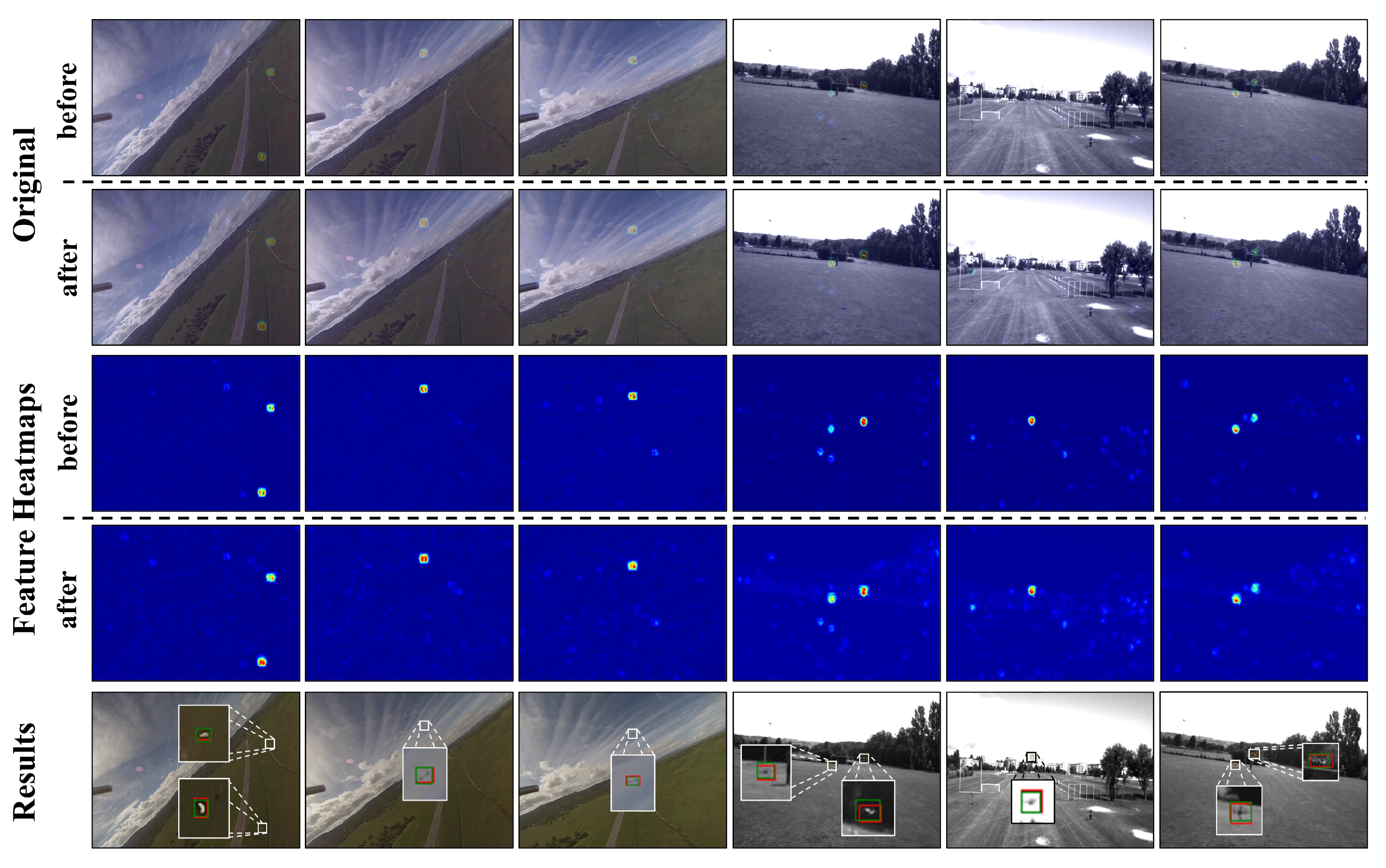
4.4. Visualization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quamar, M.M.; Al-Ramadan, B.; Khan, K.; Shafiullah, M.; El Ferik, S. Advancements and Applications of Drone-Integrated Geographic Information System Technology & mdash: A Review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Peng, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liu, W. A Novel Dual Mixing Attention Network for UAV-Based Vehicle Re-Identification. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Dosari, K.; Hunaiti, Z.; Balachandran, W. Systematic Review on Civilian Drones in Safety and Security Applications. Drones 2023, 7, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, S.; Swarnkar, R.; Srinivas, S.; Namwade, G. Application of Drone in Agriculture. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2019, 8, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raivi, A.M.; Huda, S.M.A.; Alam, M.M.; Moh, S. Drone Routing for Drone-Based Delivery Systems: A Review of Trajectory Planning, Charging, and Security. Sensors 2023, 23, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanalian, M.; Abdelkefi, A. Classifications, applications, and design challenges of drones: A review. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2017, 91, 99–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozantsev, A.; Lepetit, V.; Fua, P. Detecting Flying Objects Using a Single Moving Camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, R.H.; Marandi, A. Security Threats Analysis of the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle System. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2021—2021 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 29 November–2 December 2021; pp. 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Agrawal, A.; Goyal, A.; Luong, N.C.; Niyato, D.; Yu, F.R.; Guizani, M. Fast, Reliable, and Secure Drone Communication: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutorials 2021, 23, 2802–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Luo, H. An Improved Yolov5 for Multi-Rotor UAV Detection. Electronics 2022, 11, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, K.; Ouyang, Q.; Li, N. Real-Time Small Drones Detection Based on Pruned YOLOv4. Sensors 2021, 21, 3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerzel, D. Eye movements and visible persistence explain the mislocalization of the final position of a moving target. Vis. Res. 2000, 40, 3703–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nijhawan, R. Visual prediction: Psychophysics and neurophysiology of compensation for time delays. Behav. Brain Sci. 2008, 31, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Guo, D.; Fu, Y. A Real-Time and Lightweight Method for Tiny Airborne Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 3016–3025. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.W.; Sultani, W.; Shah, M. Dogfight: Detecting Drones From Drones Videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 7067–7076. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhi, X.; Han, H.; Jiang, S.; Shi, T.; Gong, J.; Zhang, W. Enhancing UAV Detection in Surveillance Camera Videos through Spatiotemporal Information and Optical Flow. Sensors 2023, 23, 6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangam, T.; Dave, I.R.; Sultani, W.; Shah, M. TransVisDrone: Spatio-Temporal Transformer for Vision-based Drone-to-Drone Detection in Aerial Videos. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 6006–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, D.H.; Chung, T.; Kolsch, M.; Wachs, J.; Bouman, C. Multi-target detection and tracking from a single camera in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 4992–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisantal, M.; Wojna, Z.; Murawski, J.; Naruniec, J.; Cho, K. Augmentation for small object detection. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.07296. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Dong, J. RRNet: A Hybrid Detector for Object Detection in Drone-Captured Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zoph, B.; Cubuk, E.D.; Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.Y.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Learning Data Augmentation Strategies for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 566–583. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F. FSSD: Feature Fusion Single Shot Multibox Detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00960. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.Y.; Liu, W.; Ranga, A.; Tyagi, A.; Berg, A.C. DSSD: Deconvolutional Single Shot Detector. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1701.06659. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Mazur, N.; Liu, Y.; Malaviya, D. Small Object Detection Method Based on Adaptive Spatial Parallel Convolution and Fast Multi-Scale Fusion. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Bai, K.; Sun, Y. Centered Multi-Task Generative Adversarial Network for Small Object Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtrai, L.; Pham, M.T.; Lefèvre, S. Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images Based on Super-Resolution with Auxiliary Generative Adversarial Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, M.; Ghanem, B. SOD-MTGAN: Small Object Detection via Multi-Task Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transformer Prediction Head for Object Detection on Drone-Captured Scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–27 October 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Min, X.; Hu, R.; Long, Y.; Luo, H.; Yi, J. FasterX: Real-Time Object Detection Based on Edge GPUs for UAV Applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.03157. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Khorrami, P.; Paine, T.L.; Ramachandran, P.; Babaeizadeh, M.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Huang, T.S. Seq-NMS for Video Object Detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1602.08465. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.; Li, H.; Yan, J.; Zeng, X.; Yang, B.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; et al. T-CNN: Tubelets with Convolutional Neural Networks for Object Detection From Videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 28, 2896–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feichtenhofer, C.; Pinz, A.; Zisserman, A. Detect to Track and Track to Detect. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Yuan, L.; Wei, Y. Flow-Guided Feature Aggregation for Video Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wang, L. Memory Enhanced Global-Local Aggregation for Video Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; NanoCode012; Kwon, Y.; Tao, X.; Fang, J.; imyhxy; Michael, K.; et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v6.1-TensorRT, TensorFlow Edge TPU and OpenVINO Export and Inference. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/6222936 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Liu, Z.; Ning, J.; Cao, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Hu, H. Video Swin Transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3202–3211. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Fan, B.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xiang, S.; Prinet, V.; Pan, C. Progressive Sparse Local Attention for Video Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; van der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. FlowNet: Learning Optical Flow with Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ilg, E.; Mayer, N.; Saikia, T.; Keuper, M.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Brox, T. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of Optical Flow Estimation with Deep Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Teed, Z.; Deng, J. RAFT: Recurrent All-Pairs Field Transforms for Optical Flow. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 402–419. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J. LSTFE-Net: Long Short-Term Feature Enhancement Network for Video Small Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 14613–14622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Su, D.; Liu, C.; Jin, L.; Sun, X.; Peng, X. Deformable Non-Local Network for Video Super-Resolution. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 177734–177744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Zhou, S.; Xu, X.; Loy, C.C. BasicVSR++: Improving Video Super-Resolution with Enhanced Propagation and Alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5972–5981. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Piccardi, M. Background subtraction techniques: A review. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37583), Hague, The Netherlands, 10–13 October 2004; Volume 4, pp. 3099–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. FCOS: A simple and strong anchor-free object detector. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 44, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]


| Method | AP-FL | AP-NPS | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCOS [46] | 62.4 | 83.7 | 28 |
| Mask-RCNN [47] | 68.9 | 89.5 | 29 |
| YOLOv5-tph [28] | 67.2 | 92.5 | 27 |
| Dogfight [15] | 72.0 | 89.1 | 2 |
| Transvisdrone (f ) [17] | 71.7 | 94.0 | 30 |
| Transvisdrone (f ) [17] | 72.6 | 94.9 | 30 |
| Ours | 73.2 | 94.0 | 45 |
| Method | Resolution | AP | P | R | F1 | Param. (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 1280 | 68.5 | 73.5 | 66.6 | 69.9 | 46.10 | 430.6 | 51 |
| Ours | 480 | 67.8 | 66.5 | 68.3 | 67.4 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 133 |
| 640 | 68.5 | 69.5 | 67.6 | 68.5 | 46.17 | 108.5 | 113 | |
| 800 | 72.9 | 73.4 | 71.0 | 72.2 | 46.17 | 169.5 | 90 | |
| 1280 | 73.2 | 73.5 | 72.3 | 72.9 | 46.17 | 433.9 | 45 |
| Method | AP | P | R | F1 | Param. (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 59.5 | 64.9 | 62.0 | 63.4 | 46.10 | 60.5 | 147 |
| Align and directly add | 63.0 | 65.6 | 61.7 | 63.6 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 139 |
| Align and weighted add | 65.0 | 65.3 | 64.8 | 65.0 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 137 |
| Subtraction | 61.7 | 64.0 | 57.1 | 60.3 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 138 |
| Both | 67.8 | 66.5 | 68.3 | 67.4 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 133 |
| Method | AP | P | R | F1 | Param. (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3 | 67.8 | 66.5 | 68.3 | 67.4 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 133 |
| P4 | 58.9 | 66.7 | 58.6 | 62.4 | 46.37 | 61.0 | 132 |
| P5 | 61.4 | 67.4 | 63.9 | 65.6 | 46.37 | 61.0 | 131 |
| Method | AP | P | R | F1 | Param. (M) | GFLOPs | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 3 | 67.8 | 66.5 | 68.3 | 67.4 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 133 |
| K = 5 | 66.4 | 64.7 | 69.8 | 67.2 | 46.17 | 61.0 | 124 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, Z.; Peng, Y.; Liu, W.; Yin, W.; Hao, H.; Han, B.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, D. An Efficient Adjacent Frame Fusion Mechanism for Airborne Visual Object Detection. Drones 2024, 8, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8040144
Ye Z, Peng Y, Liu W, Yin W, Hao H, Han B, Zhu Y, Xiao D. An Efficient Adjacent Frame Fusion Mechanism for Airborne Visual Object Detection. Drones. 2024; 8(4):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8040144
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Zecong, Yueping Peng, Wenchao Liu, Wenji Yin, Hexiang Hao, Baixuan Han, Yanfei Zhu, and Dong Xiao. 2024. "An Efficient Adjacent Frame Fusion Mechanism for Airborne Visual Object Detection" Drones 8, no. 4: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8040144
APA StyleYe, Z., Peng, Y., Liu, W., Yin, W., Hao, H., Han, B., Zhu, Y., & Xiao, D. (2024). An Efficient Adjacent Frame Fusion Mechanism for Airborne Visual Object Detection. Drones, 8(4), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8040144






