A Deep Learning Approach of Intrusion Detection and Tracking with UAV-Based 360° Camera and 3-Axis Gimbal
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- An intrusion target detection system based on the multi-rotor UAV was designed and implemented, and the related work of hardware selection, software architecture design, and target detection algorithm implementation was completed. Field flight tests were carried out based on this UAV system.
- (2)
- In order to solve the problem of the limited viewing angle of UAVs for detecting intrusion targets, this research proposes a method that combines 360° panoramic images and 3-axis gimbal image tracking to improve the search and discovery range of intrusion targets.
- (3)
- Based on a field flight test, 3043 flight images taken by a 360° panoramic camera and a 3-axis gimbal in various environments were collected, and an intrusion data set was produced. Considering the applicability of the YOLO model in intrusion target detection, this paper proposes an improved YOLOv5s-360ID model based on the original YOLOv5-s model.
- (4)
- The YOLOv5s-360ID model uses the K-Means++ clustering algorithm to regain the anchor box that matches the small target detection task. At the same time, this research also improves the bounding box regression loss function of the original YOLOv5-s model.
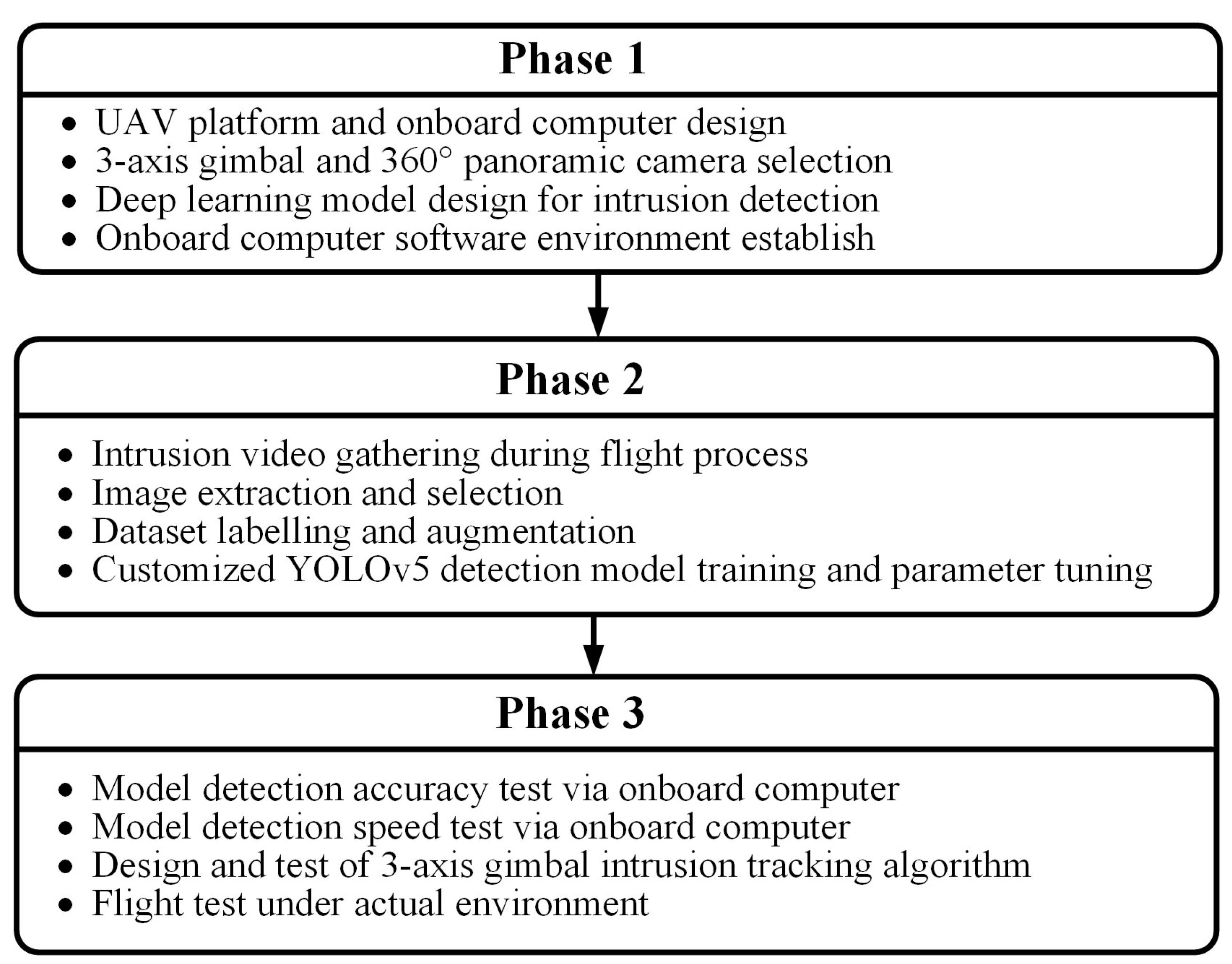
2. Materials and Methods
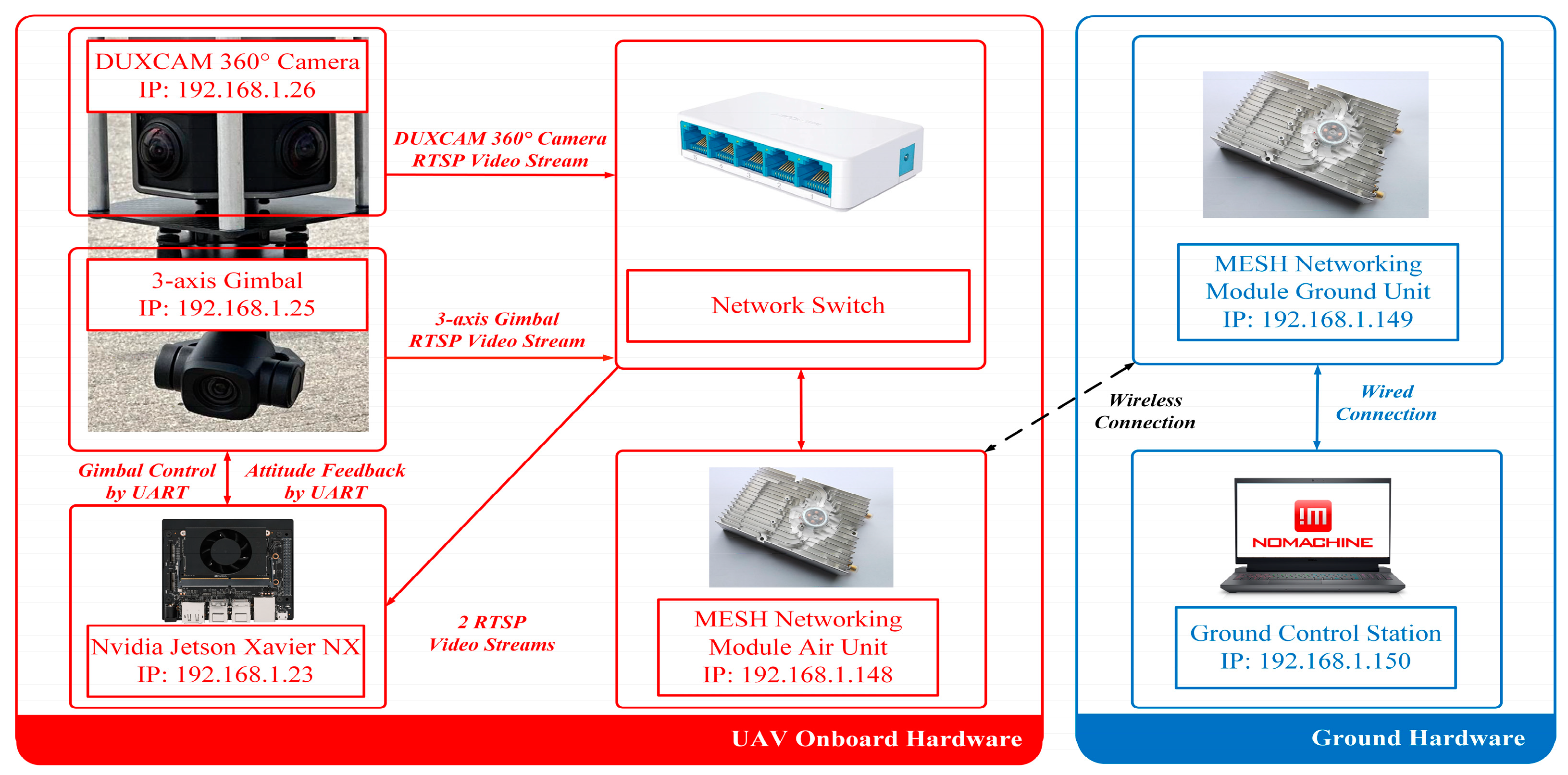
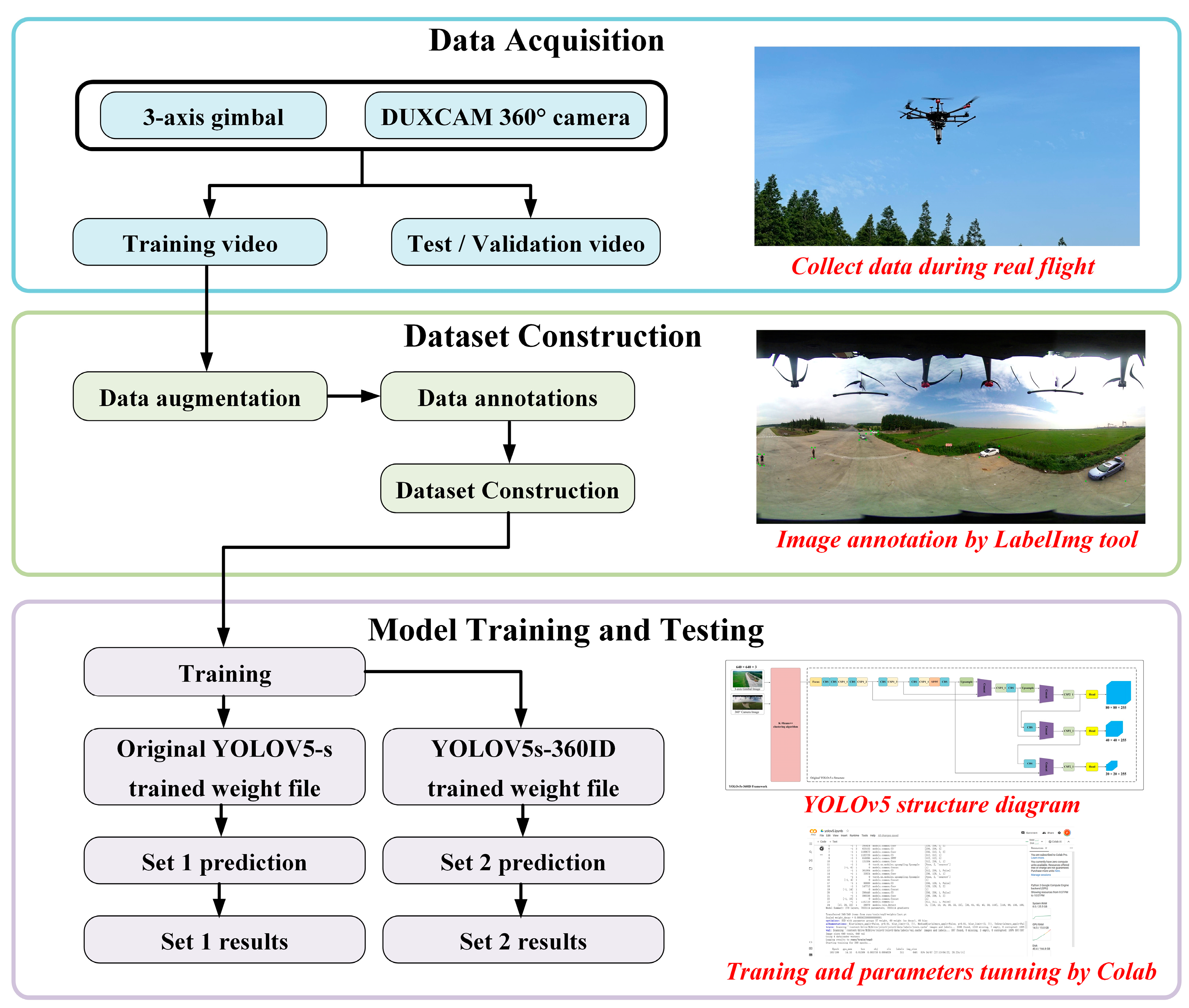
2.1. Hardware Design
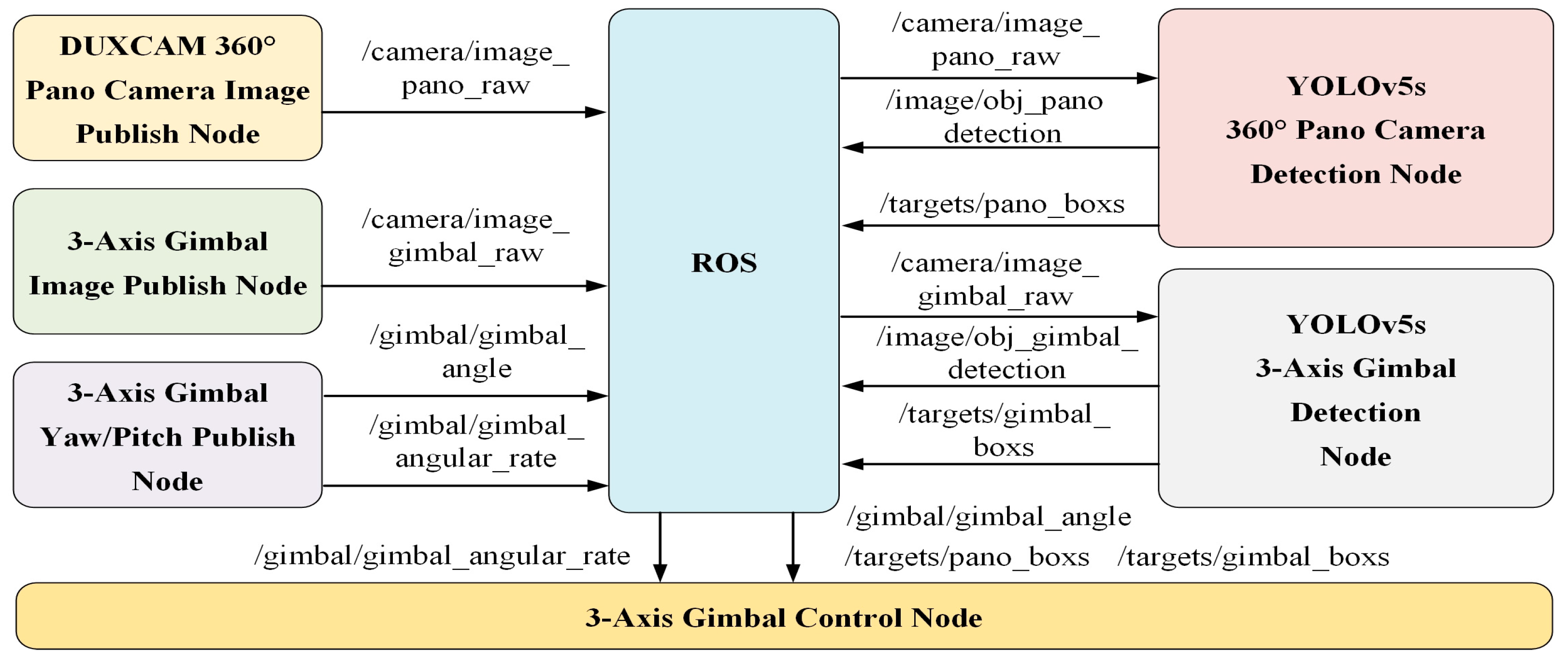
2.2. Software Design
2.2.1. Intrusion Detection Model Implementation
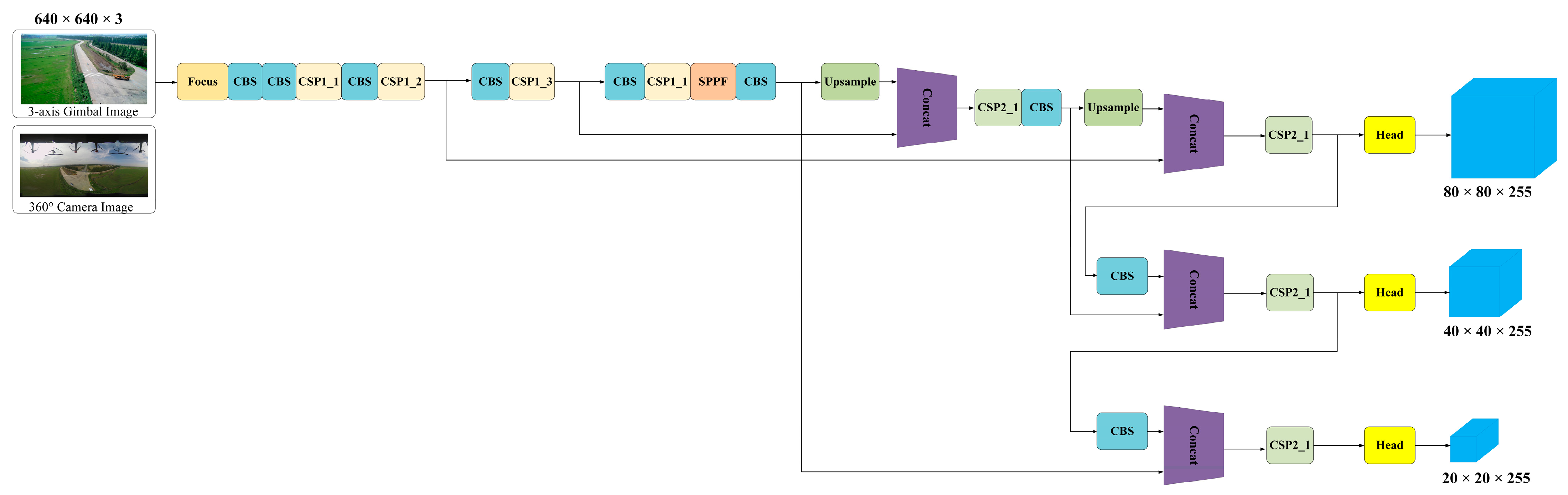
2.2.2. YOLOv5-s Detection Algorithm
2.2.3. The Improved Detection Algorithm YOLOv5s-360ID
2.2.4. Anchor Box Improvement Optimization in YOLOv5s-360ID
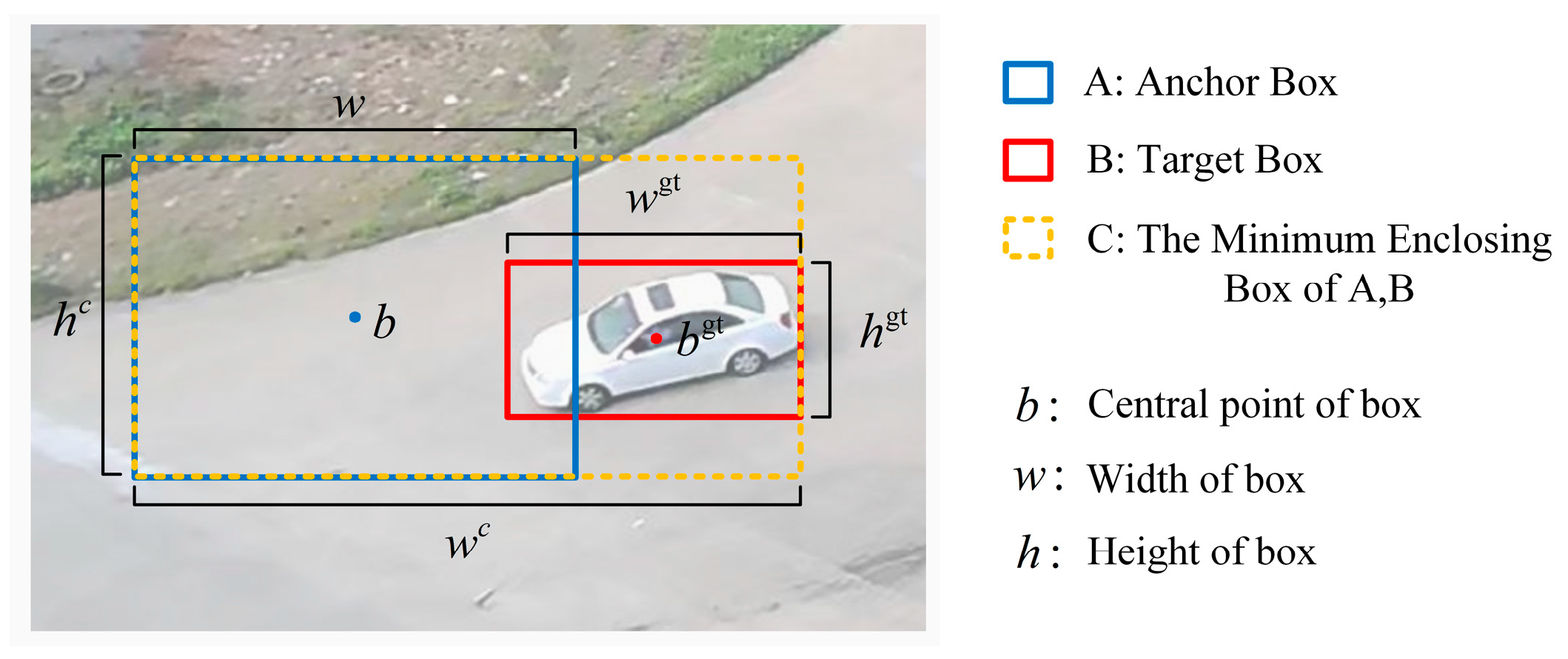
2.2.5. Improvement of Bounding Box Regression Loss Function in YOLOv5s-360ID
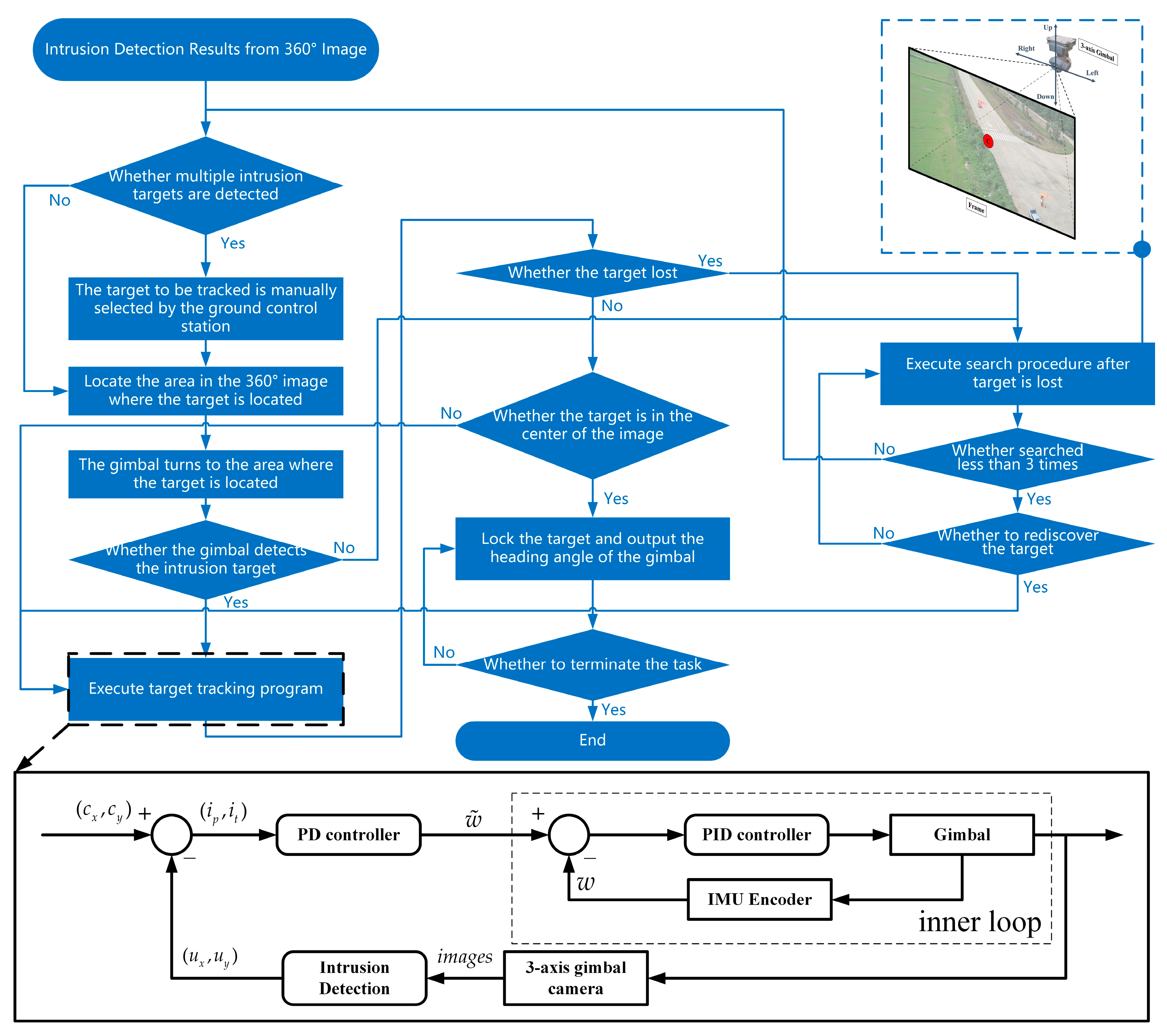
2.2.6. Target Tracking Algorithm
3. Results
3.1. Intrusion Detection Model Experiment
3.2. Field Flight Test
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, B.; Ma, R.; Hao, Q. Development of UAV-based target tracking and recognition systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 3409–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Xu, H.; Fang, X.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, G. Quantitative Assessment Framework for Non-Structural Bird’s Nest Risk Information of Transmission Tower in High-Resolution UAV Images. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 5013712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, P.; Pramanik, A. Deep learning techniques—R-CNN to mask R-CNN: A survey. In Computational Intelligence in Pattern Recognition. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 657–668. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Las Condes, Chile, 11–18 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhao, W.; Sun, Q. Study of object detection based on Faster R-CNN. In Proceedings of the 2017 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), Jinan, China, 20–22 October 2017; pp. 6233–6236. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, T.; Wu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Research and application of intelligent intrusion detection system with accuracy analysis methodology. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2018, 88, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, L.; Bhardwaj, B.; Lu, P.; Bridgelall, R. Railroad track condition monitoring using inertial sensors and digital signal processing: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 19, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Video analytics for railroad safety research: An artificial intelligence approach. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, G.; Bo, Y.; Yu, J.; Liang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ou, K. Railway intrusion detection based on refined spatial and temporal features for UAV surveillance scene. Measurement 2023, 211, 112602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Lv, X.; Lian, X.; Wang, G. YOLOv4_Drone: UAV image target detection based on an improved YOLOv4 algorithm. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2021, 93, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Li, H.; Li, Z. Panoramic shot device of 720-degree VR for hexacopter UAV based on 3-axis gimbal. Electron. Res. 2019, 55, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S. Detection, localization, and tracking of multiple MAVs with panoramic stereo camera networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1226–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humpe, A. Bridge inspection with an off-the-shelf 360° camera drone. Drones 2020, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baculi, J.E.; Ippolito, C.A. Towards an Autonomous sUAS Operating in UTM TCL4+ and STEReO Fire Scenario. In Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum, virtual event, 11–15 & 19–21 January 2021; p. 1471. [Google Scholar]
- Shvorov, S.; Lysenko, V.; Pasichnyk, N.; Opryshko, O.; Komarchuk, D.; Rosamakha, Y.; Rudenskyi, A.; Lukin, V.; Martsyfei, A. The method of determining the amount of yield based on the results of remote sensing obtained using UAV on the example of wheat. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 15th International Conference on Advanced Trends in Radioelectronics, Telecommunications and Computer Engineering (TCSET), Lviv-Slavske, Ukraine, 25–29 February 2020; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Ai, J. Deep Learning Approach to Drogue Detection for Fixed-Wing UAV Autonomous Aerial Refueling with Visual Camera. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Warsaw, Poland, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 827–834. [Google Scholar]
- Ijaz, H.; Ahmad, R.; Ahmed, R.; Ahmad, W.; Kai, Y.; Jun, W. A UAV assisted edge framework for real-time disaster management. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1001013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koubaa, A.; Ammar, A.; Abdelkader, M.; Alhabashi, Y.; Ghouti, L. AERO: AI-Enabled Remote Sensing Observation with Onboard Edge Computing in UAVs. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Jeon, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y. Swarm Reconnaissance Drone System for Real-Time Object Detection Over a Large Area. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 23505–23516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, X.; Wan, Y.; Wang, J.; Lyu, H. An Improved YOLOv5 Method for Small Object Detection in UAV Capture Scenes. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 14365–14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.Z. Improved YOLOV5-Based UAV Pavement Crack Detection. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 15901–15909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, J. EIoU: An improved vehicle detection algorithm based on vehiclenet neural network. J. Phys. Conf. Series. 2021, 1924, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.-Z.; Zheng, Y.-F. Research on application of improved YOLO V3 algorithm in road target detection. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1654, 012060. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y. Road infrared target detection with I-YOLO. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, H.; Ramirez-Serrano, A.; Guan, L.; Gao, Y. Image object extraction based on semantic detection and improved K-means algorithm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 171129–171139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Zhou, S.; Qi, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, C. Improved YOLOv5s for Small Ship Detection with Optical Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 8002205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Shao, F.; Yang, L.; Luo, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Object Detection Based on an Improved YOLOv7 Model for Unmanned Aerial-Vehicle Patrol Tasks in Controlled Areas. Electronics 2023, 12, 4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Real-time visual tracking of moving targets using a low-cost unmanned aerial vehicle with a 3-axis stabilized gimbal system. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Lee, D.; Park, W.; Byun, W.; Huh, S.; Nam, W. Autonomous Control of UAV for Proximity Tracking of Ground Vehicles with AprilTag and Feedforward Control. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), Warsaw, Poland, 6–9 June 2023; pp. 349–353. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J. Tracking Strategy of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Tracking Moving Target. Int. J. Control. Autom. Syst. 2021, 19, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Goadrich, M. The relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC curves. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; pp. 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A probabilistic interpretation of precision, recall and F-score, with implication for evaluation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Retrieval, Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 21–23 March 2005; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.J.; Kim, J.J. A deep learning framework performance evaluation to use yolo in nvidia jetson platform. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kashiyama, T.; Maeda, H.; Omata, H.; Sekimoto, Y. Real-time citywide reconstruction of traffic flow from moving cameras on lightweight edge devices. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X. Foreign Objects Identification of Transmission Line Based on Improved YOLOv7. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 51997–52008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao HY, M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.M.; Romero-González, J.A. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
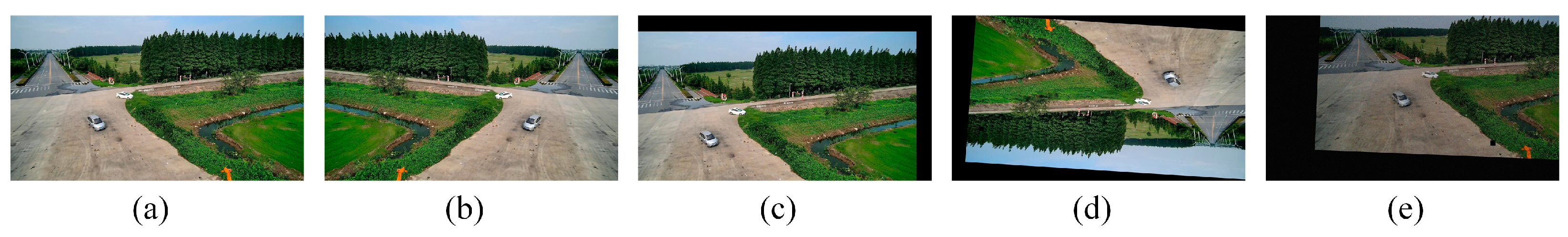
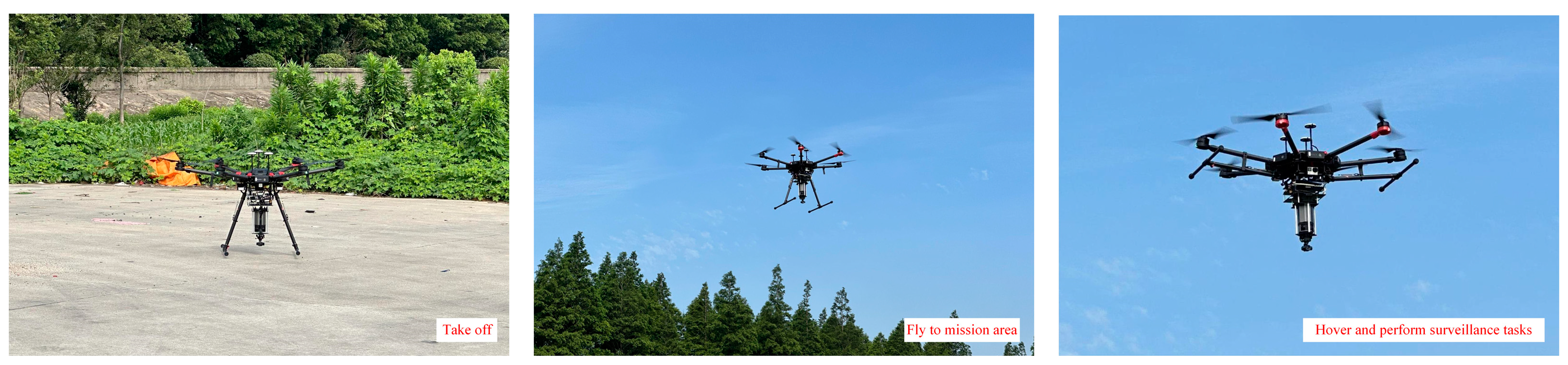
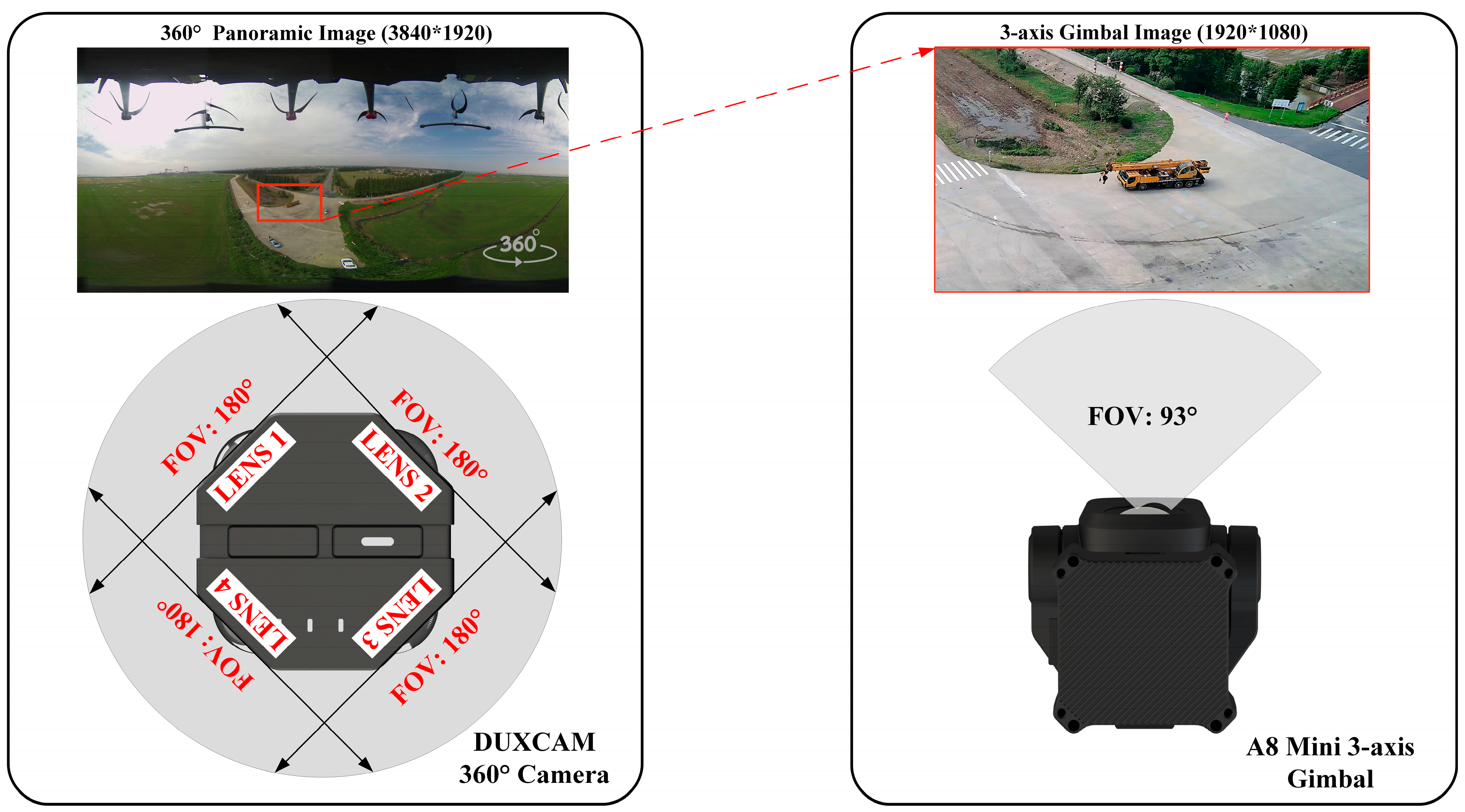
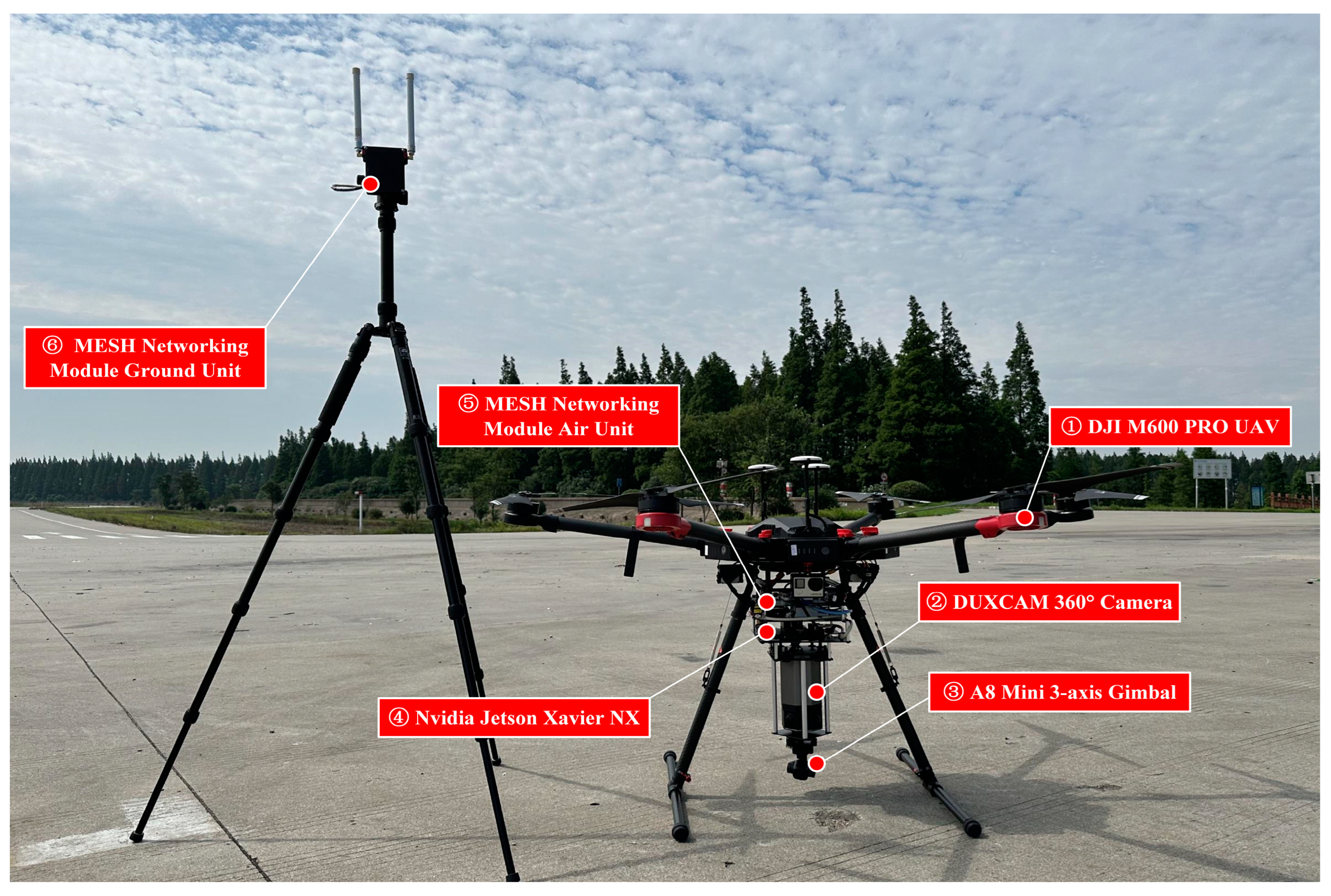






| Specifications | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| DJI M600 PRO UAV | Dimensions | 1668 × 1518 × 727 mm |
| Max Take-Off Weight | 15.5 kg | |
| Max Forward Speed | 65 km/h | |
| Max Ascent Speed | 5 m/s | |
| Max Descent Speed | 3 m/s | |
| Max Angular Velocity | Pitch: 300°/s Yaw: 150°/s | |
| Max Endurance Time | 16 min | |
| Max Remote Control Distance | 5 km | |
| A8 Mini 3-axis Gimbal | Dimensions | 55 × 55 × 70 mm |
| Photo Size | 1920 × 1080 | |
| Lens | FOV: 93° | |
| Focal Length | 21 mm | |
| Angular Vibration Range | ±0.01° | |
| Controllable Range | Pitch: −135°~+45° Yaw: −30°~30° | |
| DUXCAM 360° Camera | Dimensions | 80 × 80 × 160 mm |
| Photo Size | 3840 × 1920 | |
| Lens | 4 × F2.0 fisheye lens FOV: 360° |
| Specifications | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Jetson Xavier NX | AI Performance | 21 TOPS |
| CPU Max Frequency | 1.9 GHz | |
| GPU Max Frequency | 1100 MHz | |
| Memory | 16 GB | |
| DL Accelerator | 2× NVDLA | |
| USB | 1× USB 3.2 Gen2 (10 Gbps) 3× USB 2.0 | |
| Power | 10 W~20 W | |
| Mechanical | 103 × 90.5 × 34 mm |
| Image | Personnel | Vehicle | Crane | Truck | Bicycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 360° panoramic images | 3810 | 5463 | 257 | 432 | 341 |
| 3-axis gimbal images | 1330 | 4330 | 226 | 386 | 311 |
| Model | Epoch | Batch Size | Learning Rate | Input Shape | Trainset/Validation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original YOLOv5-s | 200 | 32 | 0.005 | 640 × 640 | 9:1 |
| YOLOv5s-360ID | 200 | 32 | 0.005 | 640 × 640 | 9:1 |
| Model | mAP@50 | AP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel | Vehicle | Crane | Truck | Bicycle | ||
| Original YOLOv5-s | 72.4% | 81.6% | 86.1% | 93.1% | 64.2% | 37% |
| YOLOv5s-360ID | 75.2% | 82.7% | 88.8% | 96.5% | 66.8% | 41.2% |
| Model | FPS |
|---|---|
| Original YOLOv5-s | 33 |
| YOLOv5s-360ID | 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Ai, J. A Deep Learning Approach of Intrusion Detection and Tracking with UAV-Based 360° Camera and 3-Axis Gimbal. Drones 2024, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020068
Xu Y, Liu Y, Li H, Wang L, Ai J. A Deep Learning Approach of Intrusion Detection and Tracking with UAV-Based 360° Camera and 3-Axis Gimbal. Drones. 2024; 8(2):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020068
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yao, Yunxiao Liu, Han Li, Liangxiu Wang, and Jianliang Ai. 2024. "A Deep Learning Approach of Intrusion Detection and Tracking with UAV-Based 360° Camera and 3-Axis Gimbal" Drones 8, no. 2: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020068
APA StyleXu, Y., Liu, Y., Li, H., Wang, L., & Ai, J. (2024). A Deep Learning Approach of Intrusion Detection and Tracking with UAV-Based 360° Camera and 3-Axis Gimbal. Drones, 8(2), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones8020068





