Decentralized Learning and Model Averaging Based Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an AMC method using decentralized learning and residual network (ResNet) towards drone communication systems. This novel framework can achieve good classification performance and improve training efficiency while protecting data privacy.
- We compare the classification accuracy of support vector machine (SVM)-based CentAMC method and deep neural network (DNN)-based CentAMC method using dataset RadioML 2016.10a, and improve that DL-based AMC performs better than ML-based AMC.
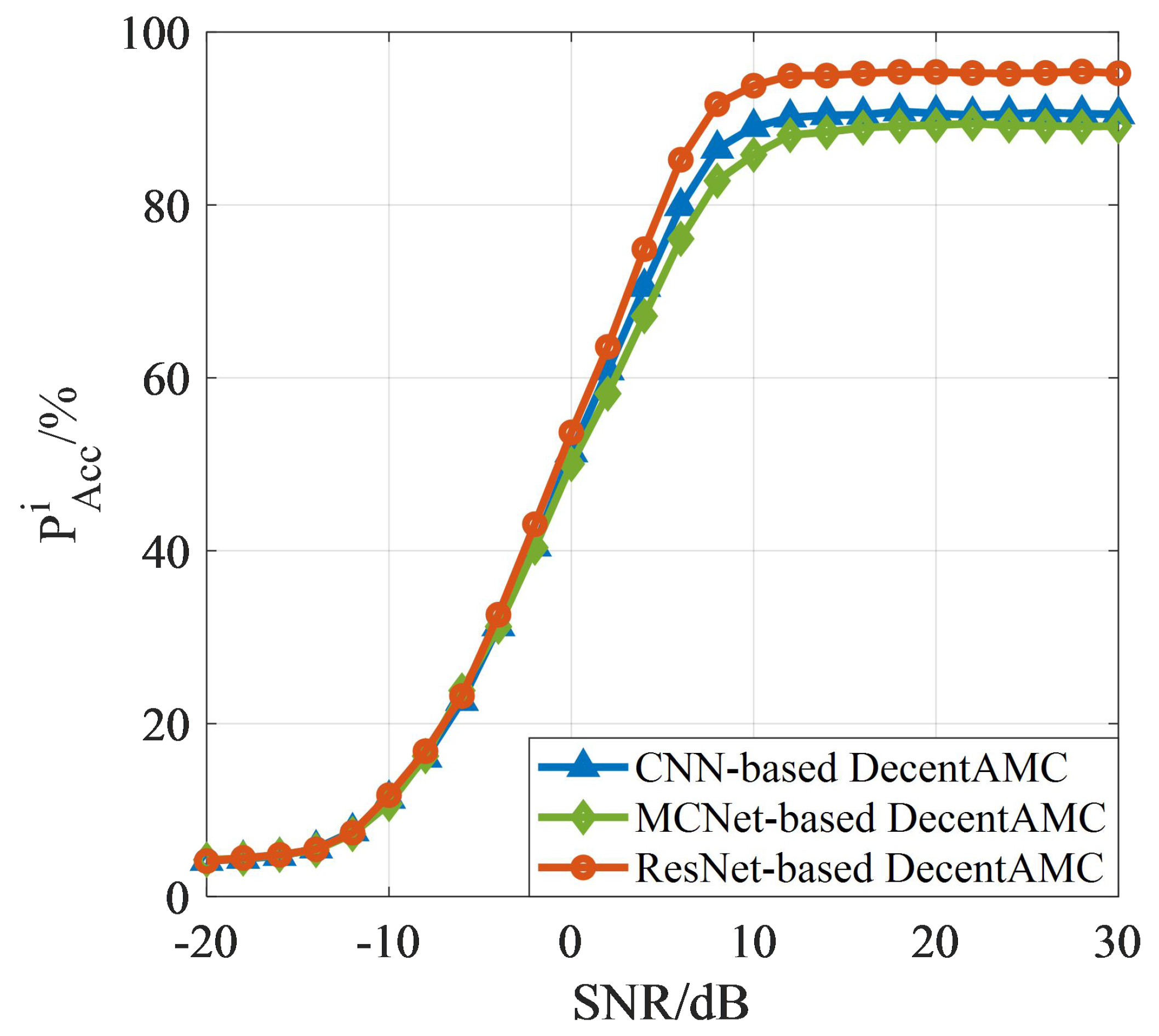
- We compare classification accuracy of different DNN-based AMC methods using dataset RadioML 2018.01a. The proposed ResNet-based DecentAMC method performs better than current DNN-based DecentAMC method.
2. AMC Description and Signal Model
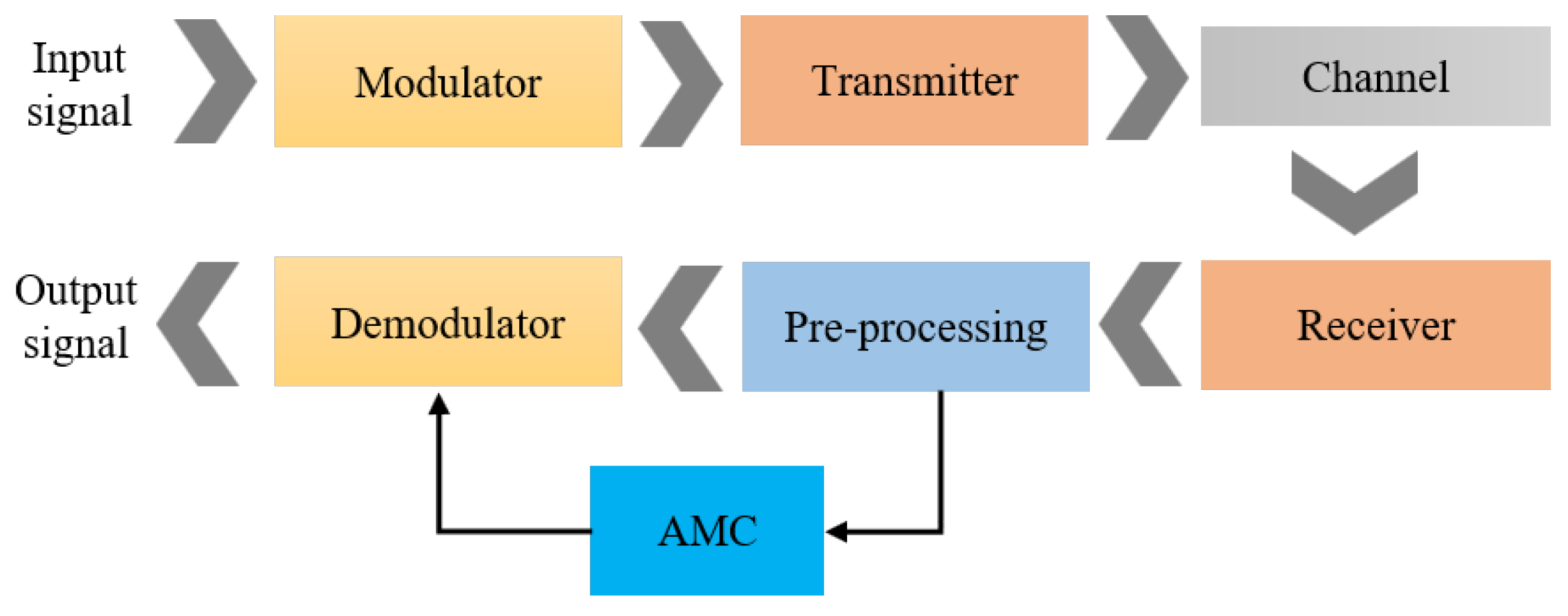
2.1. AMC Description
2.2. Signal Model
3. ML-Based AMC and DL-Based AMC
3.1. Classic AMC Method Based on Artificial Features and ML
3.2. Modern AMC Method Based on Deep Features and DL
4. Our Proposed AMC Method
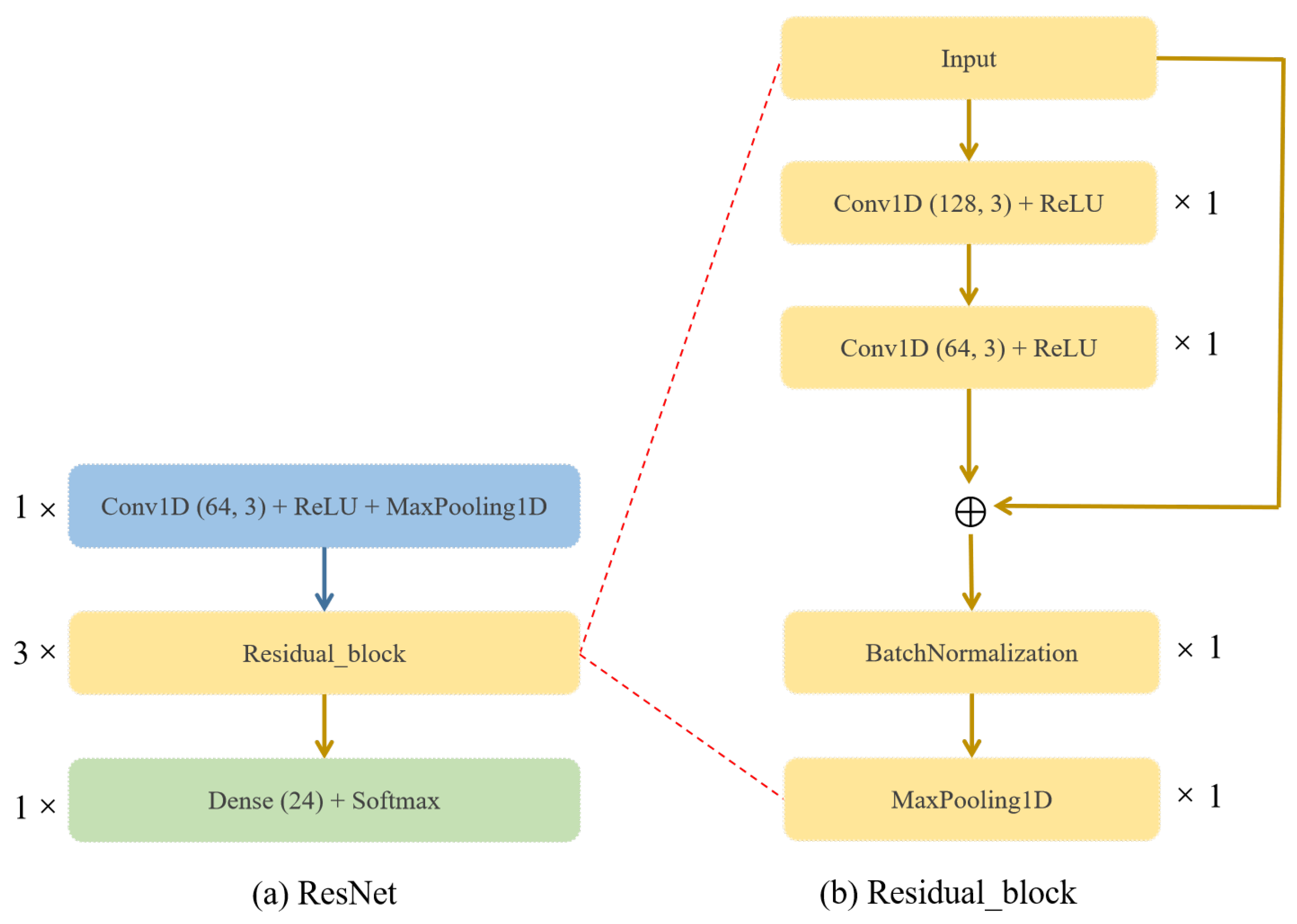
4.1. System Model of DecentAMC
4.1.1. Broadcasting Initial Comprehensive Model
4.1.2. Training, Updating and Uploading Local Model
4.1.3. Local Models Aggregation
4.1.4. Global Model Downloading
| Algorithm 1 Algorithm statement of the proposed ResNet-based DecentAMC method. |
Input: IQ samples and corresponding labels. Output: . CS sets initial parameters and builds initial global model (i.e., ResNet) and then send this model to all local devices.
for do: All LDs download the latest global model weight . for do: All LDs train and update local model weight. end for All LDs upload local model parameter to CS. CS updates global model parameter by model aggregation . end for return |
5. Simulation Results and Discussions
5.1. Dataset Description
5.1.1. RadioML 2016.10a
5.1.2. RadioML 2018.01a
5.2. Comparative AMC Methods
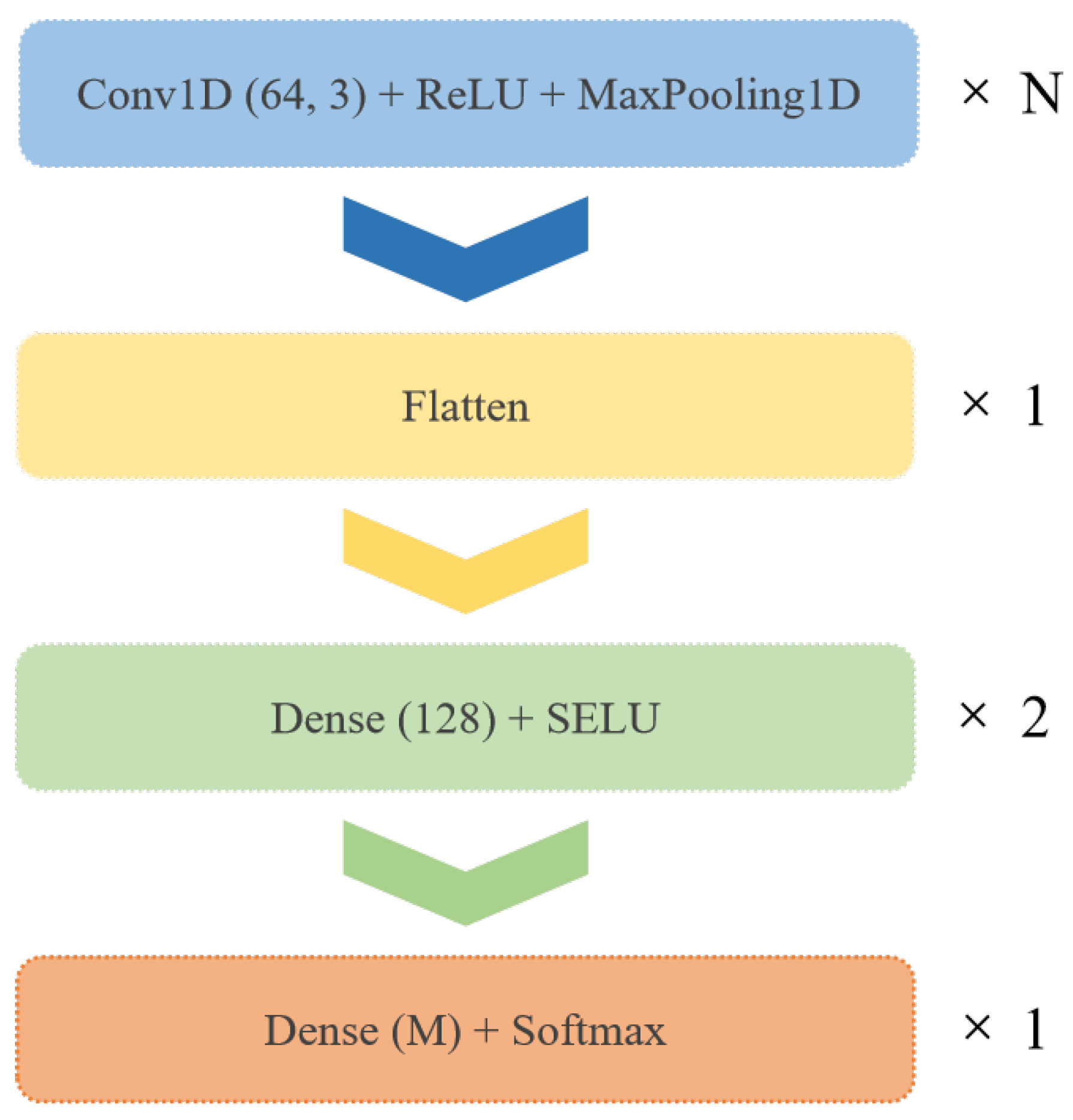
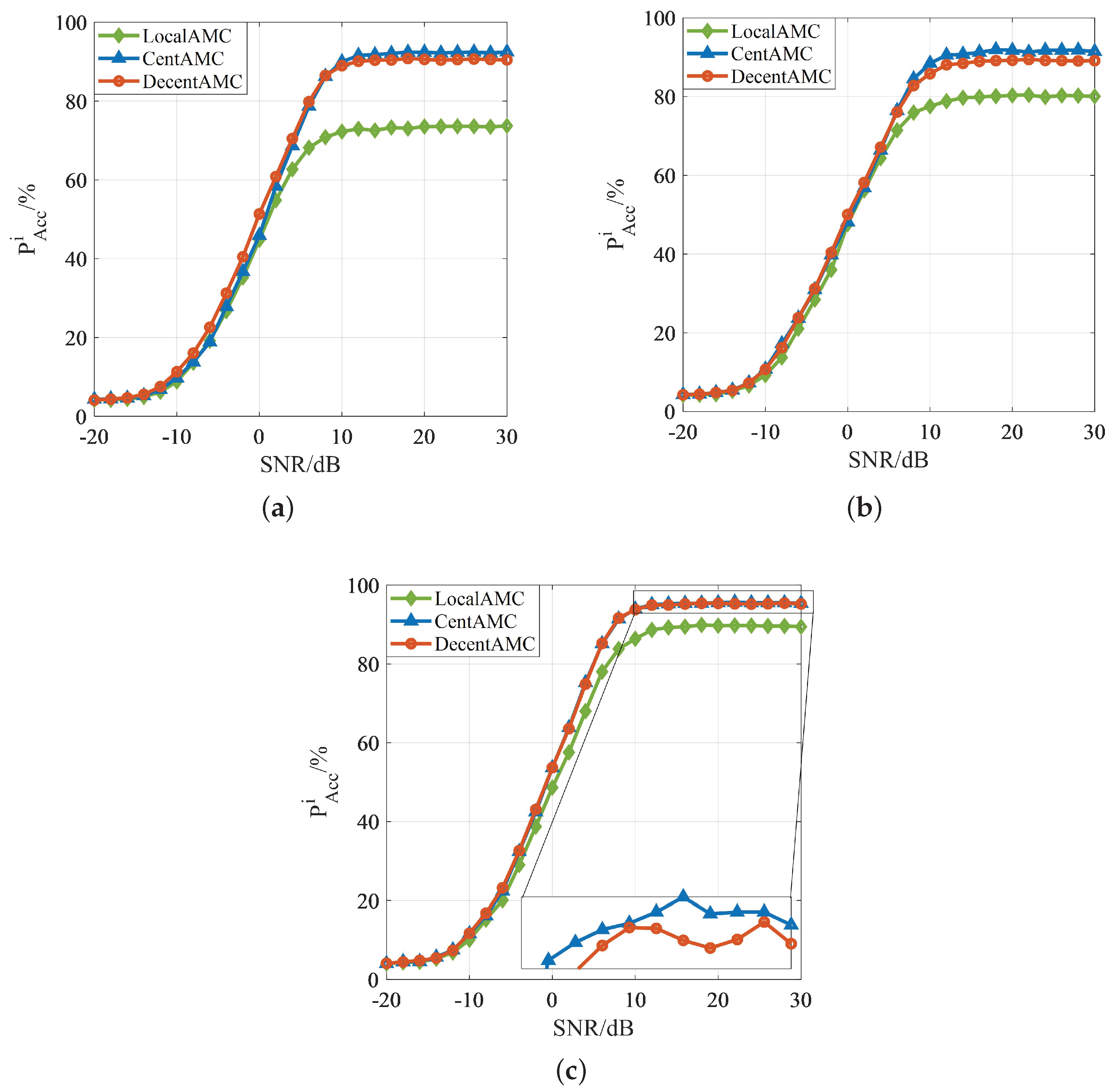
5.2.1. AMC Method Based on Local Framework
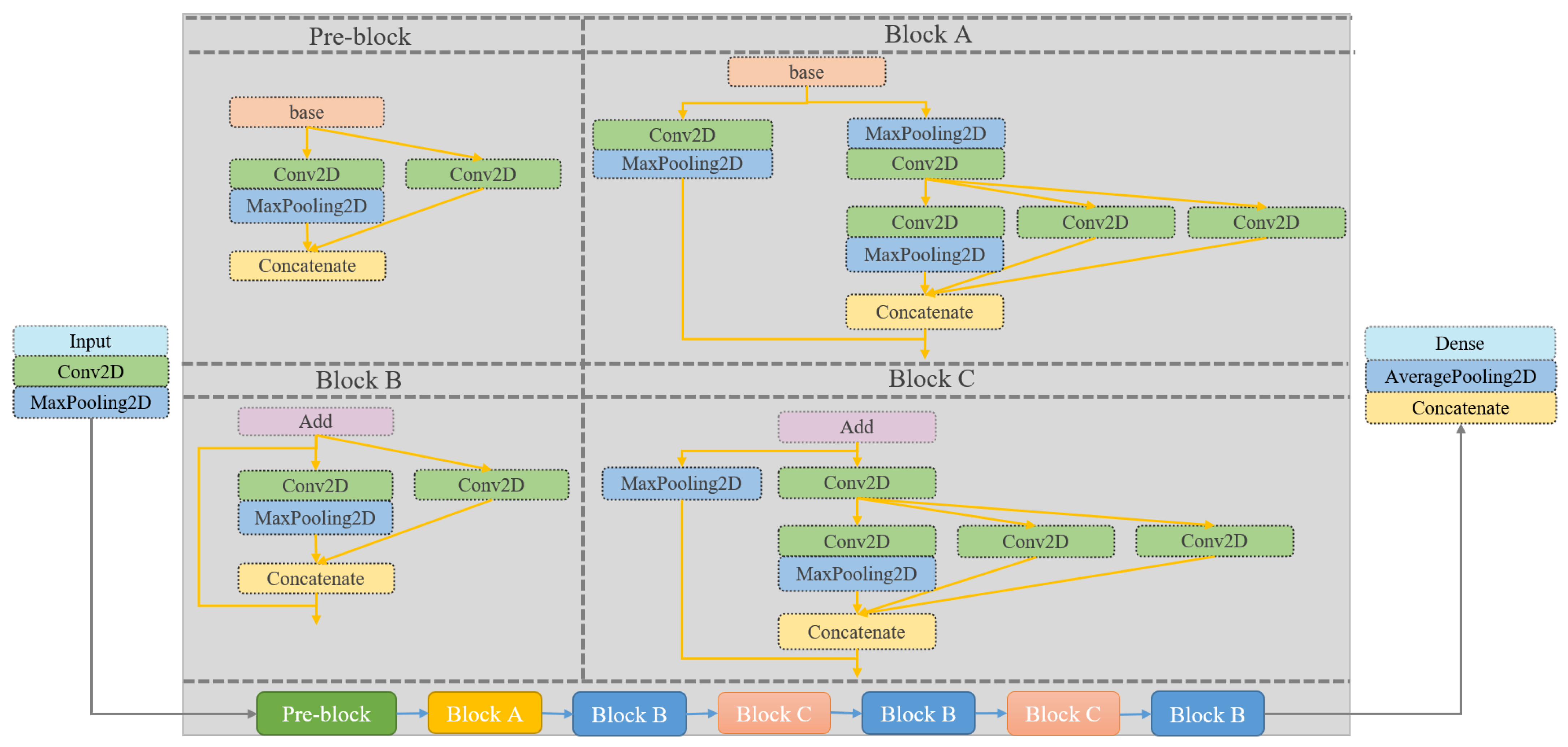
5.2.2. AMC Method Based on Centralized Framework
5.3. Classification Performance: ML vs. DL
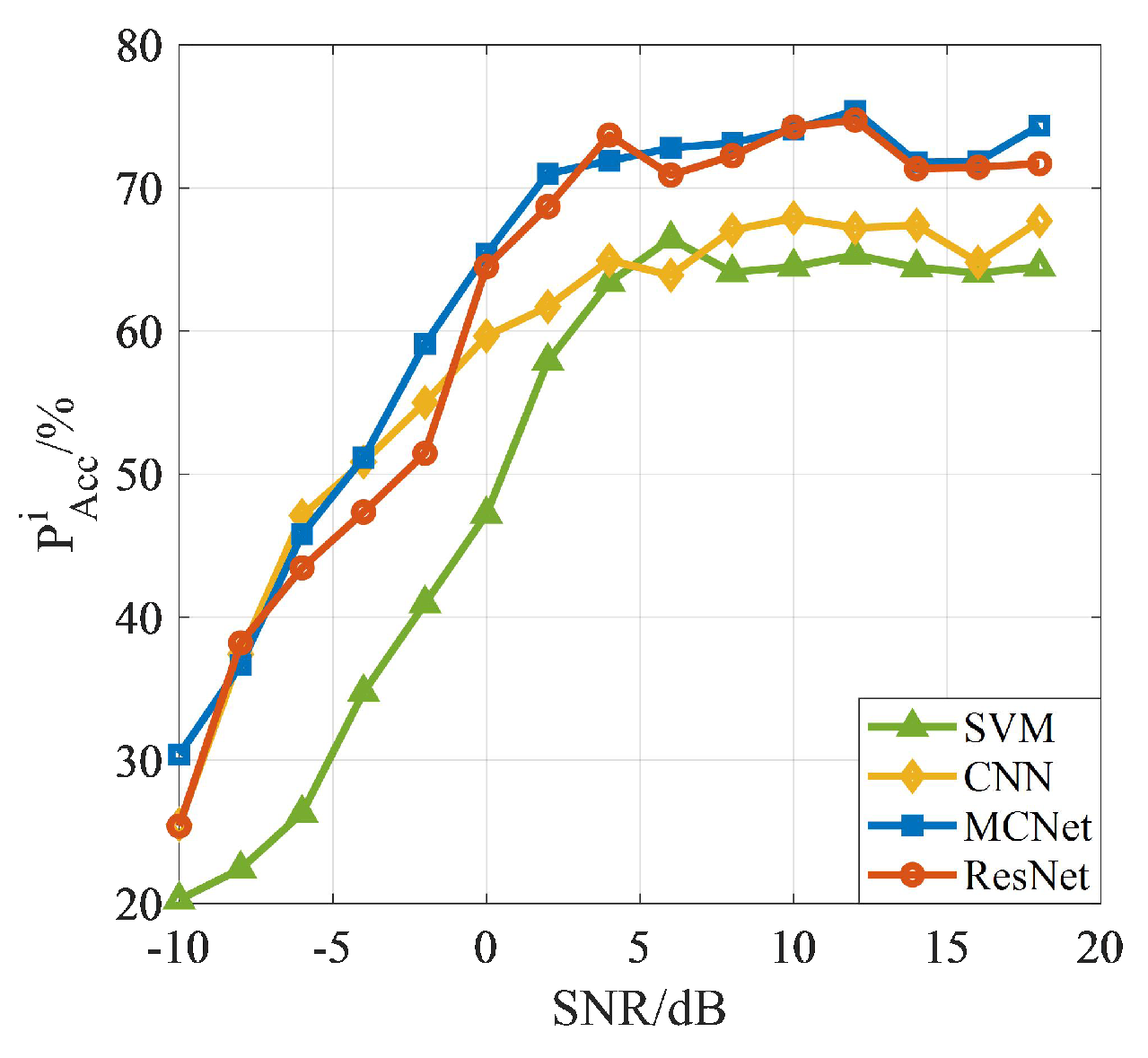
5.4. Classification Performance: Different AMC Methods Based on CNN, MCNet and Proposed ResNet
The Correct Classification Probability under Different SNR
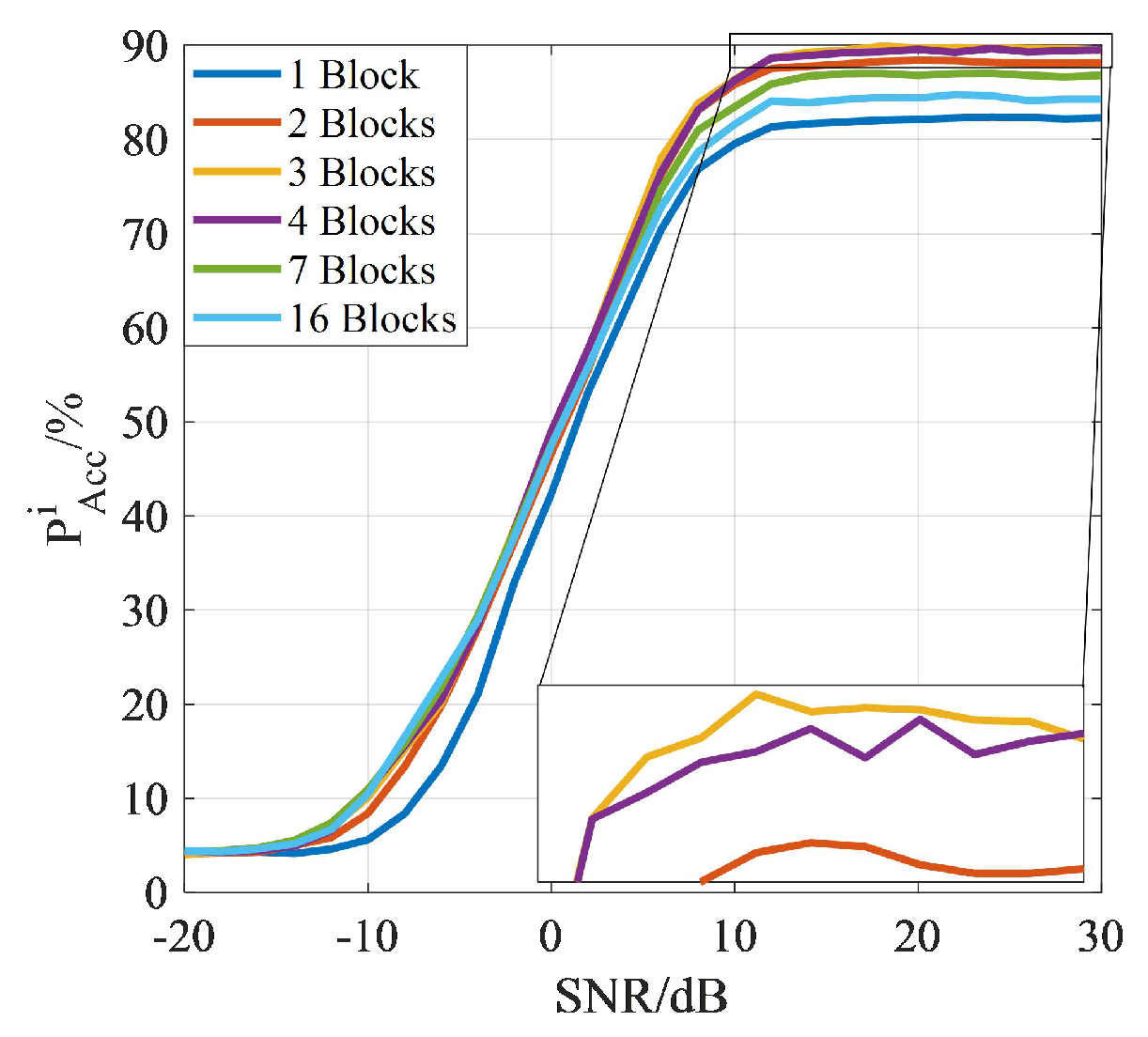
5.5. Communication Overhead: ResNet-Based AMC Methods vs. Comparative AMC Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qi, P.; Zhou, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z. FedBKD: Heterogenous federated learning via bidirectional knowledge distillation for modulation classification in IoT-edge system. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 17, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Liu, Y.; Gui, G.; Fu, X.; Dong, H.; Adebisi, B.; Gacanin, H.; Sari, H. A lightweight decentralized learning-based automatic modulation classification method for resource-constrained edge devices. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 9, 24708–24720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.B.; Liu, G.W.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, Z.C.; Hua, L.J.; Lin, Y. Multi-signal modulation classification using sliding window detection and complex convolutional network in frequency domain. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 19438–19449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Gu, H.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Gui, G.; Gacanin, H. Deep complex-valued convolutional neural network for drone recognition based on RF fingerprinting. Drones 2022, 6, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, O.A.; Abdi, A.; Bar-Ness, Y.; Su, W. Survey of automatic modulation classification techniques: Classical approaches and new trends. IET Commun. 2007, 1, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.; Hu, F.; Hao, Q. Deep learning for intelligent wireless networks: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 2585–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldemerdash, Y.A.; Dobre, O.A.; Öner, M. Signal identification for multiple-antenna wireless systems: Achievements and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1524–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobre, O.A. Signal identification for emerging intelligent radios: Classical problems and new challenges. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2015, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Nandi, A. Automatic Modulation Classification: Principles, Algorithms and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Polydoros, A. Digital modulation classification: The BPSK versus QPSK case. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 October 1988; pp. 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotou, P.; Anastasopoulos, A.; Polydoros, A. Likelihood ratio tests for modulation classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2000; pp. 670–674. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Dai, R.; Huang, J.; Yao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ning, F.; Feng, Z. Automatic modulation classification using gated recurrent residual network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7795–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Huang, S.; Zhang, R.; Feng, Z.; Liu, L. Multitask-learning-based deep neural network for automatic modulation classification. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 2192–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gui, G.; Wang, Y.; Gacanin, H.; Adachi, F. Automatic modulation classification based on decentralized learning and ensemble learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 7942–7946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, A.K.; Azzouz, E.E. Algorithms for automatic modulation recognition of communication signals. IEEE Trans. Commun. 1998, 46, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Graphic constellations and DBN based automatic modulation classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 4–7 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Guo, S.; Jia, C. Recognition of digital modulation signals based on wavelet amplitude difference. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 26–28 August 2016; pp. 627–630. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, W. Measurement of spectral correlation. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1986, 34, 1111–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.A.; Spooner, C.M. Cyclic spectral analysis for signal detection and modulation recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), San Diego, CA, USA, 23–26 October 1988; pp. 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Song, T.; Hu, J.; Yang, J.; Gui, G. Deep learning-inspired message passing algorithm for efficient resource allocation in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Y.-C.; Niyato, D. Intelligent sharing for LTE and WiFi systems in unlicensed bands: A deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 2793–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Xia, W.; Gui, G. Fast beamforming design via deep learning. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, T.; Hoydis, J. An introduction to deep learning for the physical layer. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2017, 3, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Tu, Y.; Dou, Z. An improved neural network pruning technology for automatic modulation classification in edge devices. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 5703–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chai, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z. Automatic Modulation Classification Using Compressive Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 79636–79643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gan, C.; Sun, S.; Wang, M. Automatic modulation classification using convolutional neural network with features fusion of SPWVD and BJD. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Netw. 2019, 5, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Gui, G. LightAMC: Lightweight automatic modulation classification via deep learning and compressive sensing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3491–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Chen, P.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. Automatic modulation classification: A deep learning enabled approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2018, 67, 10760–10772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Shih, W.-T.; Guo, J.; Wen, C.-K.; Jin, S. Lightweight convolutional neural networks for CSI feedback in massive MIMO. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 2624–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, S.; Li, Z. Automatic modulation classification based on deep residual networks with multimodal information. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, H.E.; Pal, A. Parallel and distributed machine learning algorithms for scalable big data analytics. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2020, 108, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bajwa, W.U. ByRDiE: Byzantine-resilient distributed coordinate descent for decentralized learning. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Netw. 2019, 5, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Adebisi, B.; Gacanin, H.; Gui, G. Distributed learning for automatic modulation classification in edge devices. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2020, 9, 2177–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Gui, G.; Wang, Y.; Ohtsuki, T.; Adebisi, B.; Gacanin, H.; Adachi, F. Lightweight network and model aggregation for automatic modulation classification in wireless communications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 29 March–1 April 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Swami, A.; Sadler, B.M. Hierarchical digital modulation classification using cumulants. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2000, 48, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh-The, T.; Hua, C.; Pham, Q.; Kim, D. MCNet: An efficient CNN architecture for robust automatic modulation classification. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2020, 24, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.; Hall, K.; Mann, G. Distributed training strategies for the structured perceptron. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2 June 2010; pp. 456–464. [Google Scholar]
- Oshea, T.J.; West, N. Radio machine learning dataset generation with GNU radio. In Proceedings of the GNU Radio Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 6 September 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- O’shea, T.J.; Roy, T.; Clancy, T.C. Over-the-air deep learning based radio signal classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Choromanska, A.E.; LeCun, Y. Deep learning with elastic averaging SGD. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]

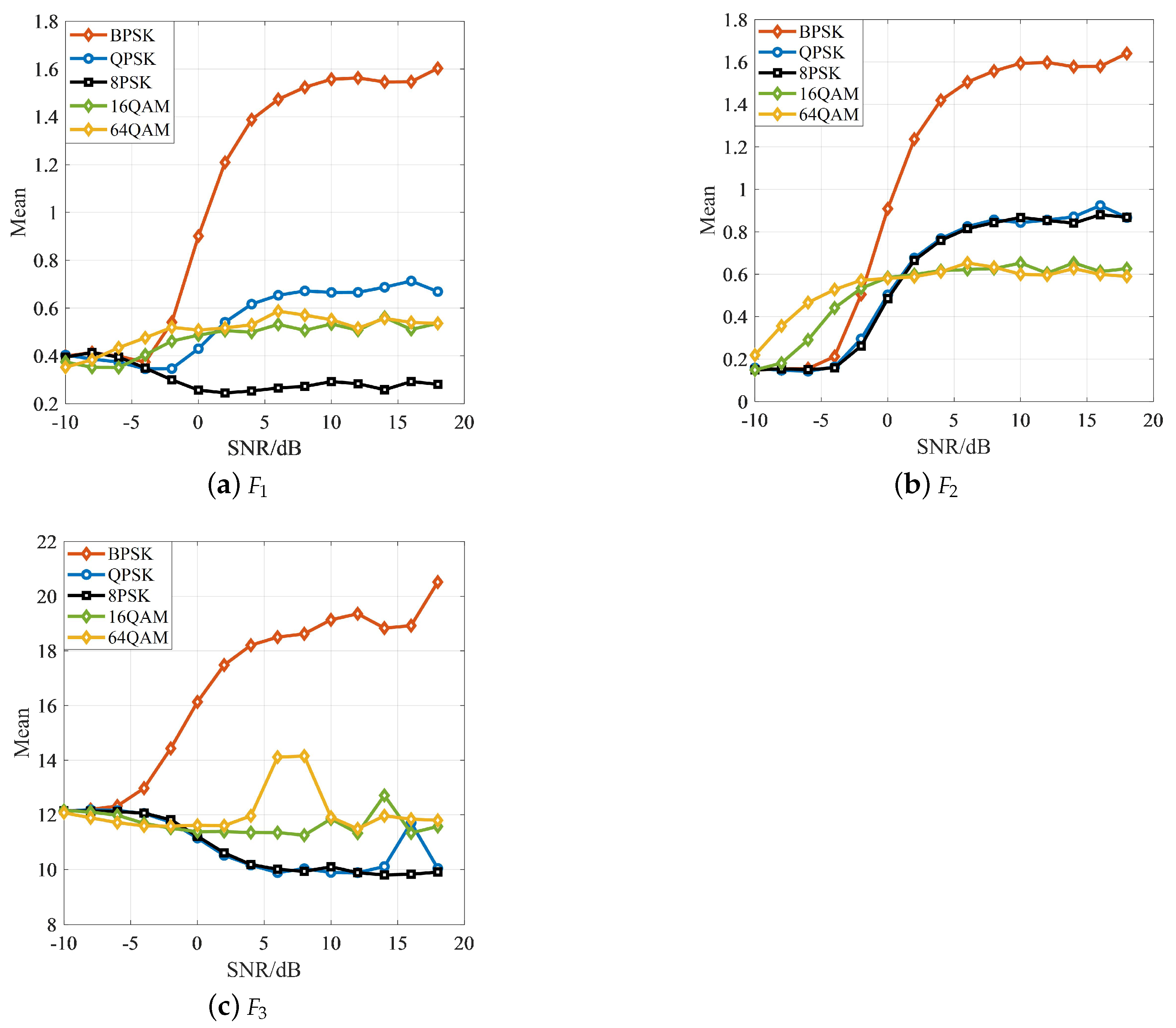
| Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|
| The received band signal | |
| h | Channel coefficient |
| Frequency offset | |
| Carrier phase offset | |
| k-th symbol generated | |
| m of | m-th modulation scheme |
| Additive Gaussian noise | |
| K | The number of signal symbols |
| BPSK | E | E | |||||
| QPSK | 0 | E | 0 | 0 | |||
| 8PSK | 0 | E | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 16QAM | 0 | E | 0 | 0 | |||
| 64QAM | 0 | E | 0 | 0 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Device | GeForce GTX 2080Ti |
| Dataset | DeepSig RadioML (version 2018.01A) |
| Batch size of training | 50 |
| Batch size of testing | 20 |
| Epoch | 100 |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Environment | Keras 2.2.4 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| (a) Classification Accuracy of CNN-Based AMC Methods | ||||
| Method (CNN-Based) | ||||
| LocalAMC | 44.79% | 72.26% | 73.55% | 73.72% |
| CentAMC | 45.91% | 89.96% | 92.41% | 92.49% |
| DecentAMC | 51.36% | 89.00% | 90.60% | 90.47% |
| (b) Classification Accuracy MCNet-Based AMC Methods | ||||
| Method (MCNet-Based) | ||||
| LocalAMC | 47.62% | 77.56% | 80.31% | 80.06% |
| CentAMC | 48.17% | 88.45% | 91.74% | 91.46% |
| DecentAMC | 50.04% | 85.82% | 89.23% | 89.13% |
| (c) Classification Accuracy ResNet-Based AMC Methods | ||||
| Method (ResNet-Based) | ||||
| LocalAMC | 48.65% | 86.38% | 89.72% | 89.45% |
| CentAMC | 53.63% | 93.92% | 95.54% | 95.41% |
| DecentAMC (proposed) | 53.69% | 93.80% | 95.39% | 95.24% |
| DecentAMC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 51.36% | 89.00% | 90.60% | 90.47% |
| MCNet | 50.04% | 85.82% | 89.23% | 89.13% |
| DecentAMC | 53.69% | 93.80% | 95.39% | 95.24% |
| (proposed) | (3.65%↑, 2.09%↑) | (7.98%↑, 4.80%↑) | (6.16%↑, 4.79%↑) | (6.11%↑, 4.77%↑) |
| Network Structure | |
|---|---|
| CNN | 678 Kb |
| MCNet | 637 Kb |
| ResNet | 649 Kb |
| Network Structure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 0 Kb | 17,188,992 Kb | 1,635,336 Kb (90.49%↓) |
| MCNet | 0 Kb | 17,188,500 Kb | 1,536,444 Kb (91.06%↓) |
| ResNet | 0 Kb | 17,188,644 Kb | 1,565,388 Kb (90.89%↓) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, X.; Gui, G. Decentralized Learning and Model Averaging Based Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems. Drones 2023, 7, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7060391
Ma M, Xu Y, Wang Z, Fu X, Gui G. Decentralized Learning and Model Averaging Based Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems. Drones. 2023; 7(6):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7060391
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Min, Yunhe Xu, Zhi Wang, Xue Fu, and Guan Gui. 2023. "Decentralized Learning and Model Averaging Based Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems" Drones 7, no. 6: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7060391
APA StyleMa, M., Xu, Y., Wang, Z., Fu, X., & Gui, G. (2023). Decentralized Learning and Model Averaging Based Automatic Modulation Classification in Drone Communication Systems. Drones, 7(6), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7060391







