Expeditious Low-Cost SfM Photogrammetry and a TLS Survey for the Structural Analysis of Illasi Castle (Italy)
Abstract
1. Introduction
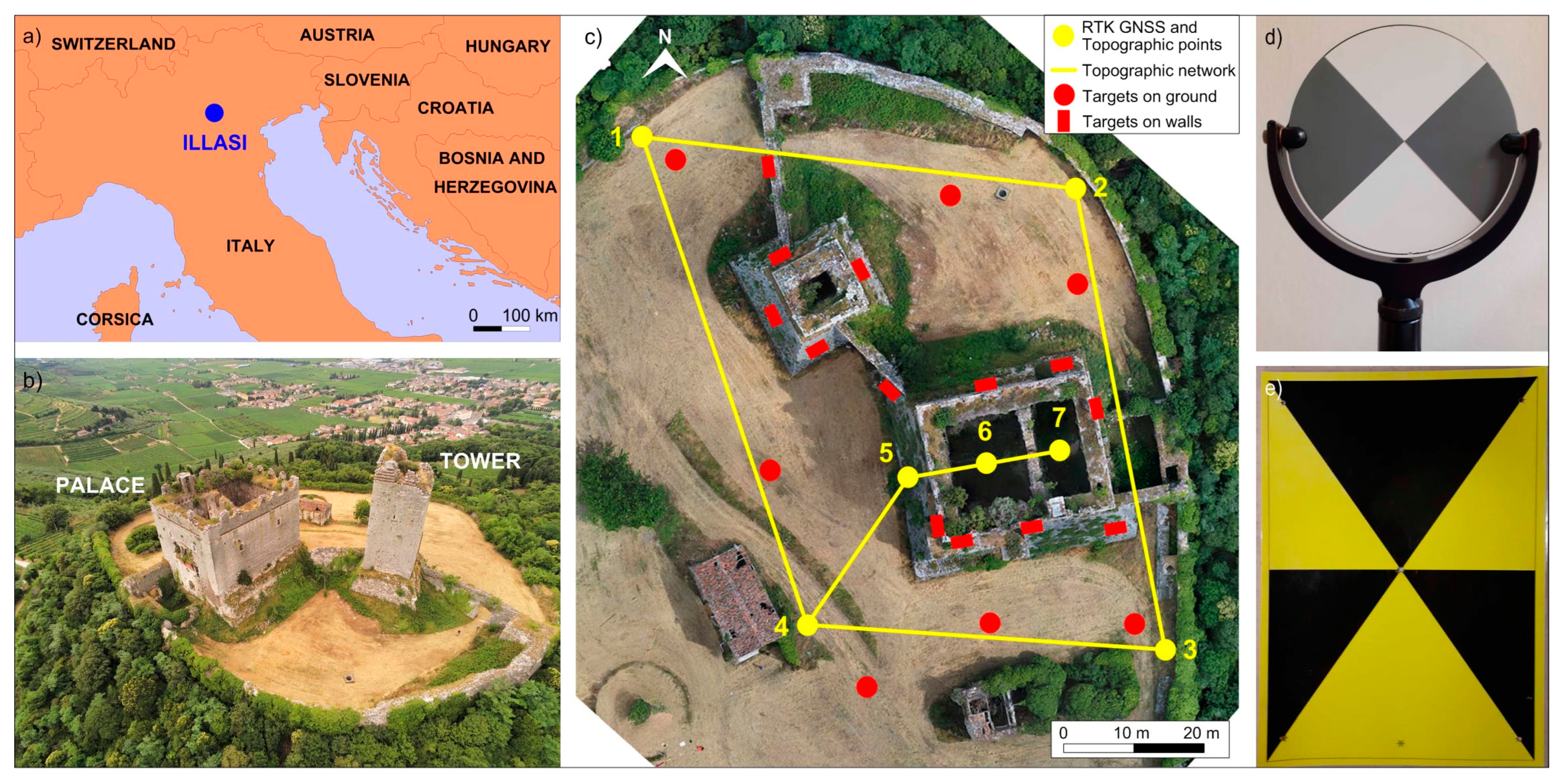
2. Illasi Castle
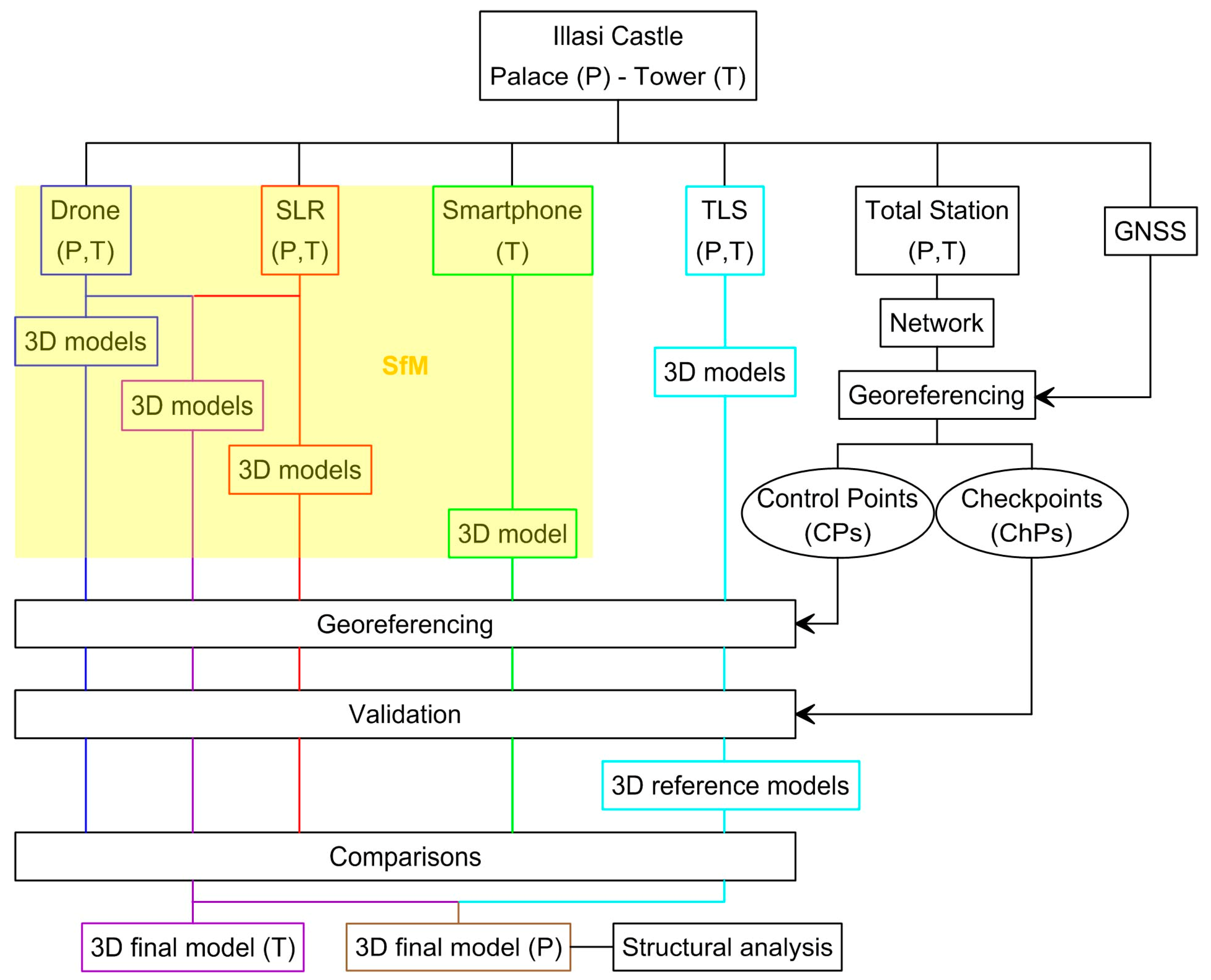
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Surveys
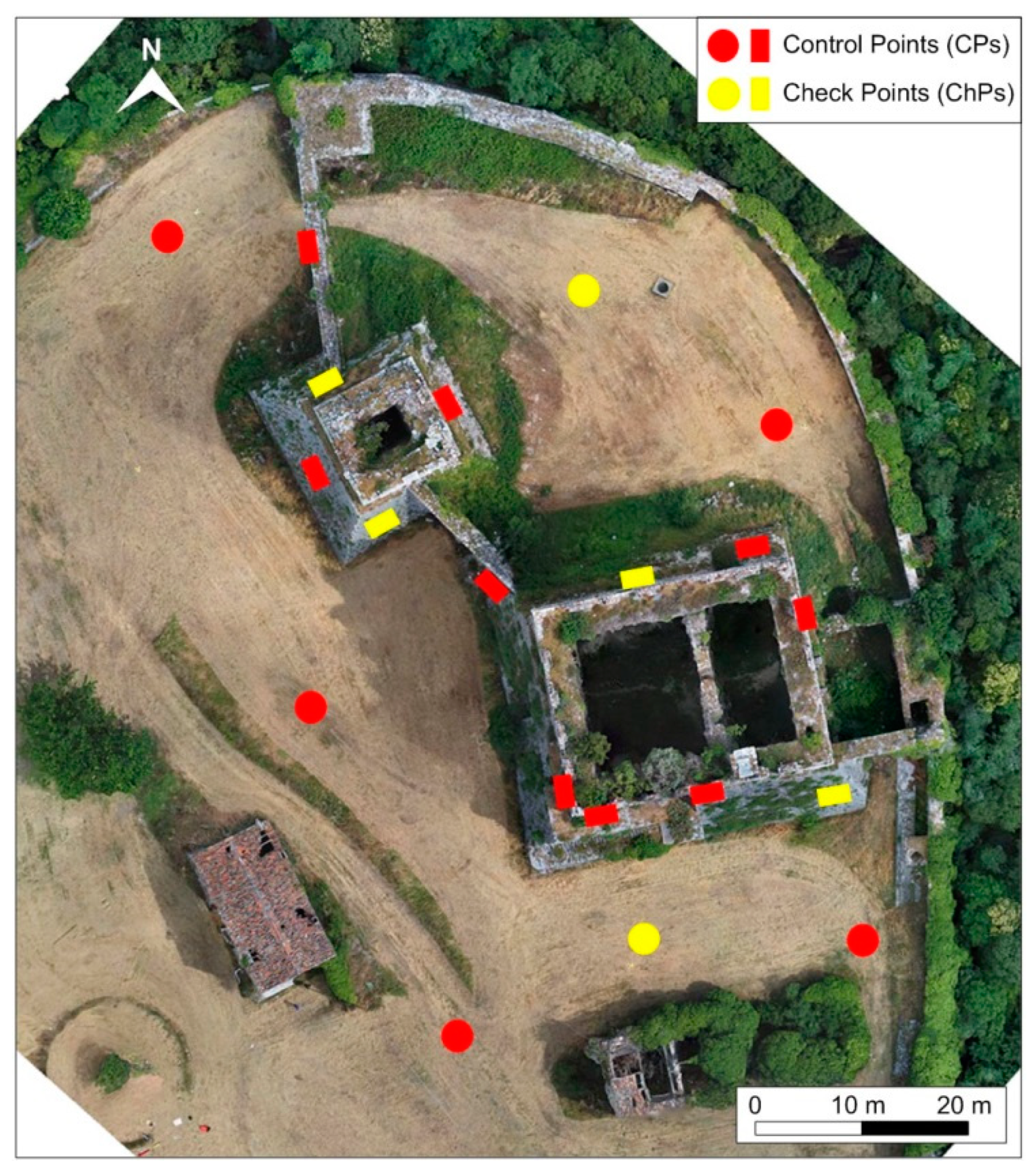
3.1.1. RTK GNSS and Topographic Measurements of the Reference Network
3.1.2. 3D Photogrammetric Survey by Drone
3.1.3. Ground-Based Photogrammetric Acquisitions
3.1.4. TLS Acquisitions
3.2. 3D Data Processing
4. Results and Discussion
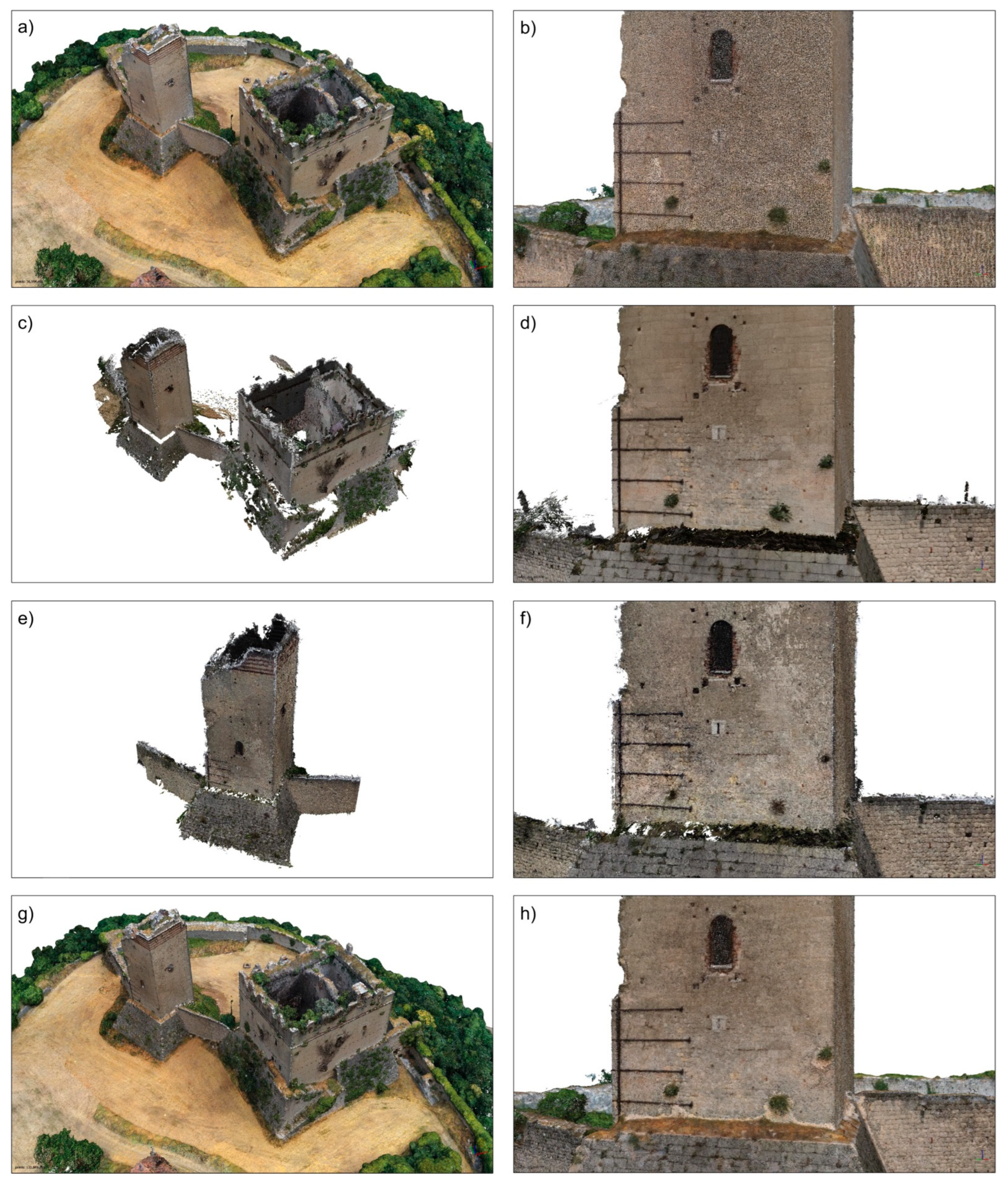
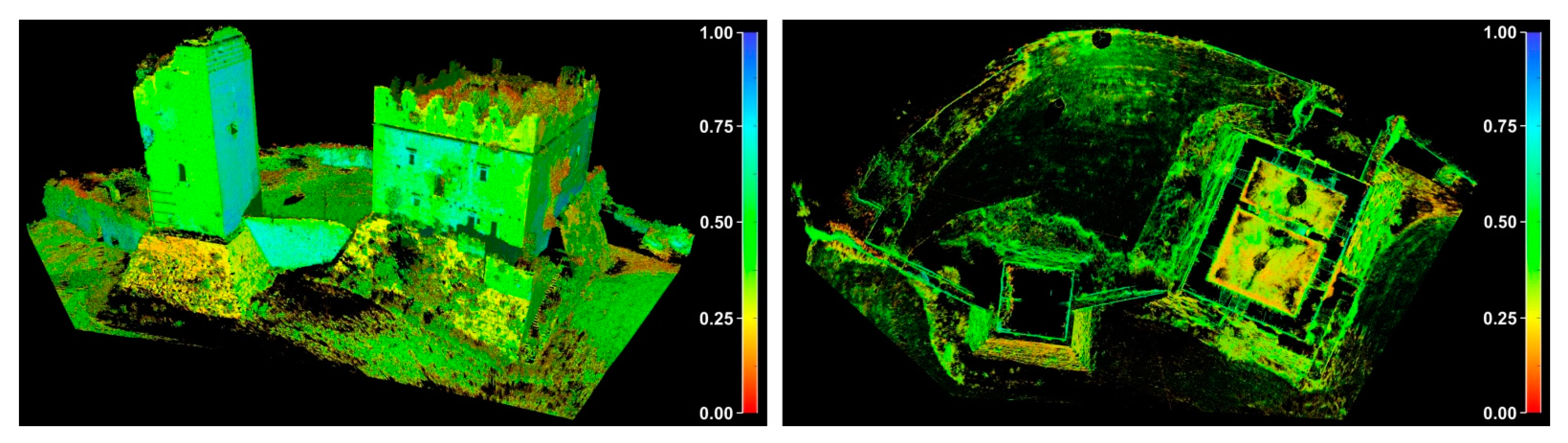
4.1. Processing of the Point Clouds
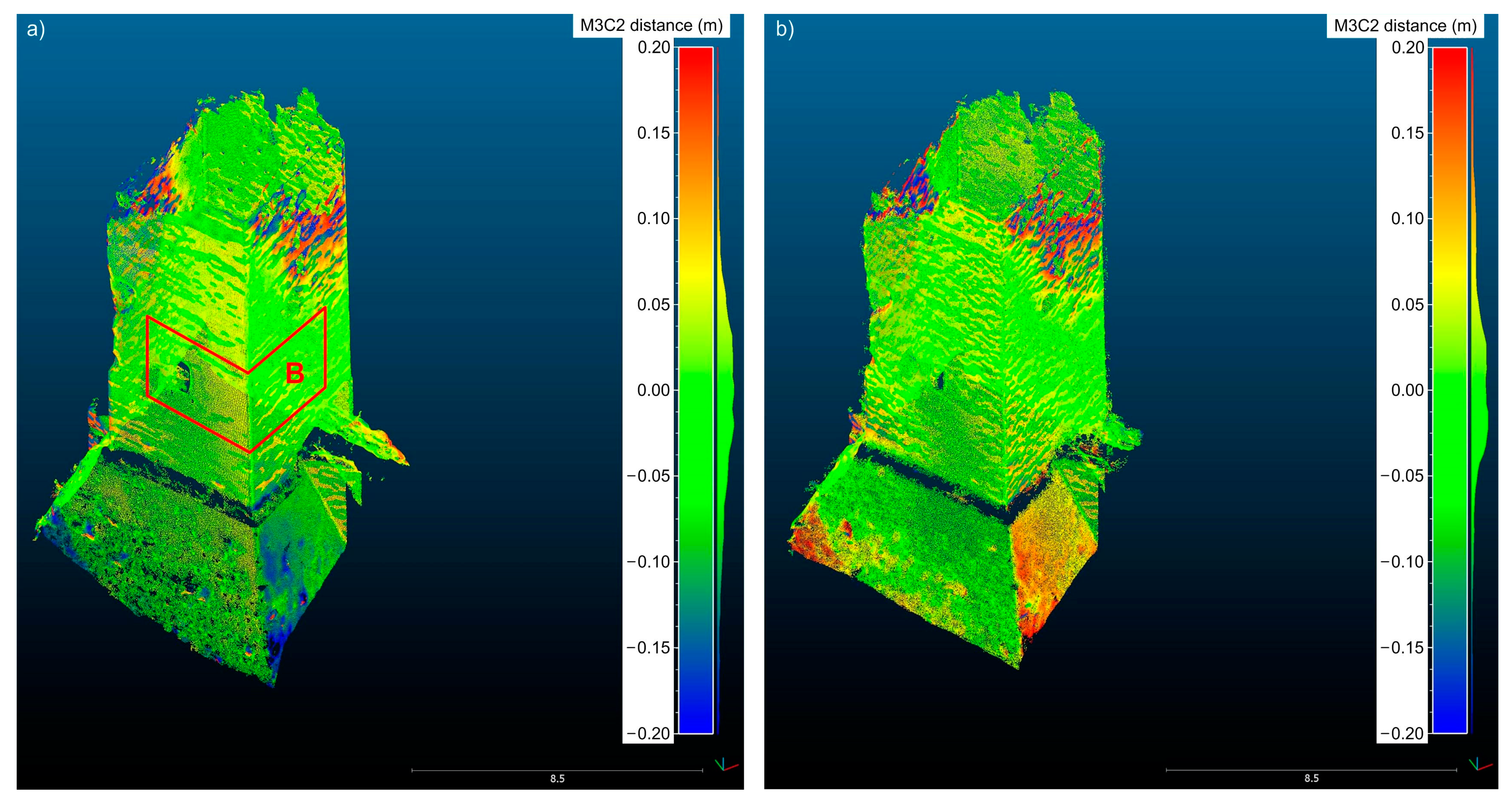
4.2. Comparisons between Point Clouds
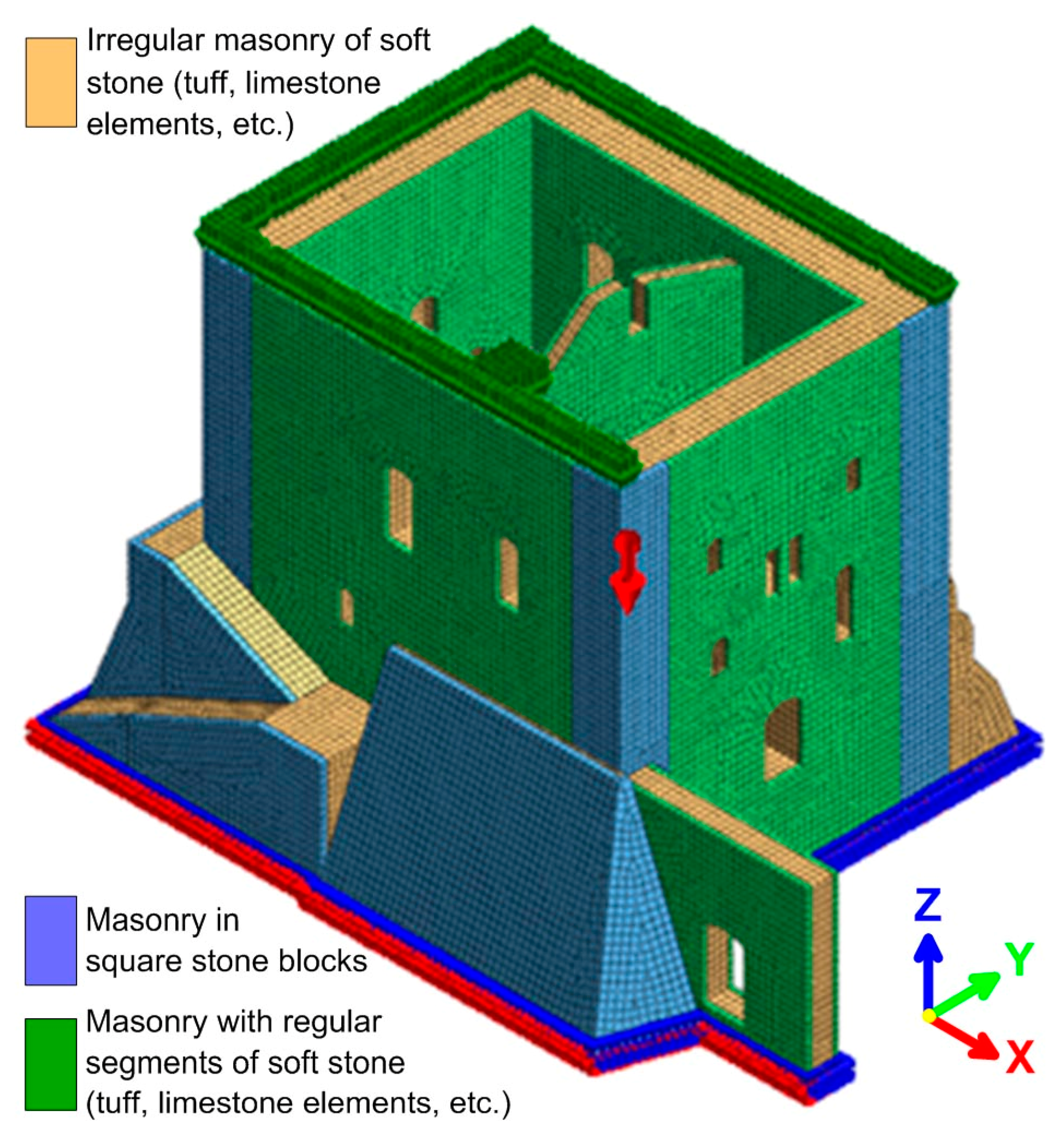
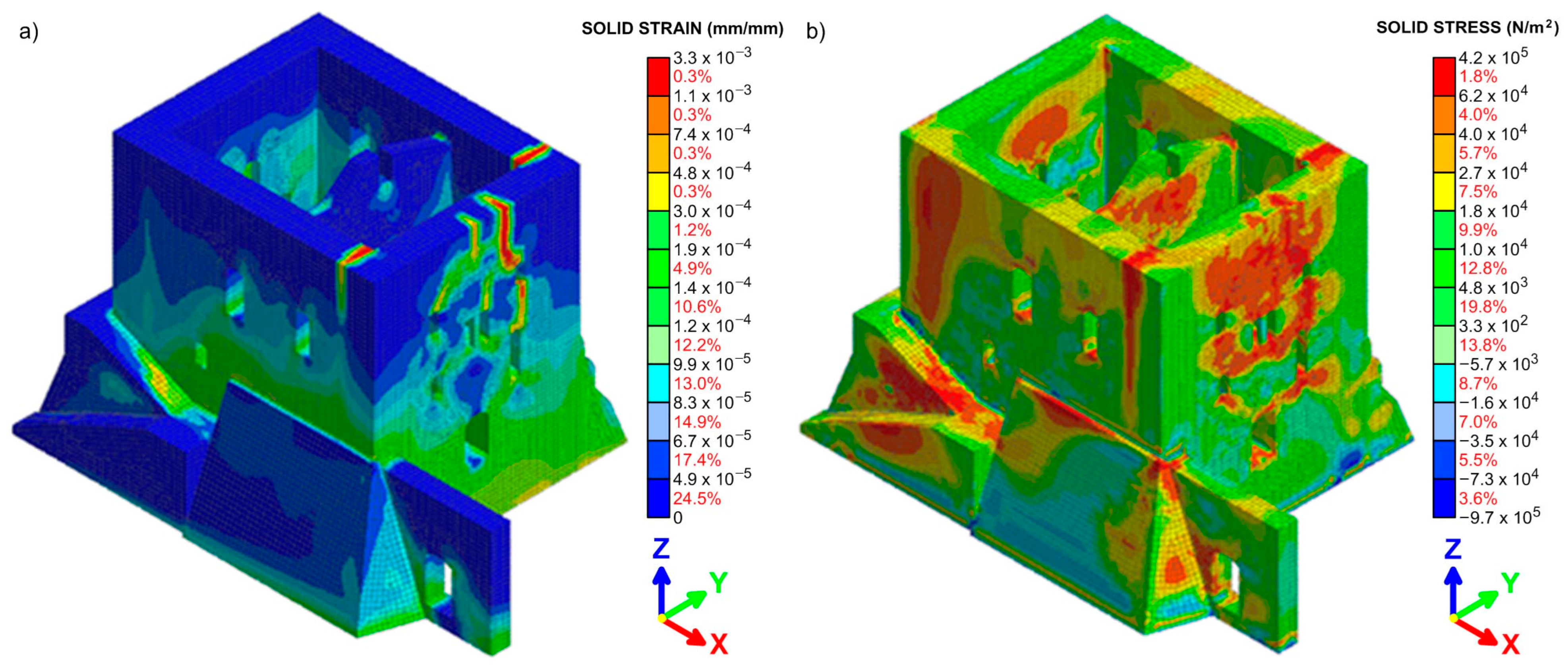
4.3. Structural Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grussenmeyer, P.; Landes, T.; Voegtle, T.; Ringle, K. Comparison methods of terrestrial laser scanning, photogrammetry and tacheometry data for recording of cultural heritage buildings. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Beijing, China, 3–11 July 2008; pp. 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Fabris, M.; Boatto, G.; Achilli, V. 3D Laser scanning surveys in the modelling of cultural heritage. In Recent Advances in Non-Destructive Inspection; Meola, C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Fabris, M.; Achilli, V.; Artese, G.; Bragagnolo, D.; Menin, A. High resolution survey of Phaistos Palace (Crete) by TLS and terrestrial photogrammetry. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012; Volume XXXIX-B5, pp. 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moropoulou, A.; Labropoulos, K.; Delegou, E.T.; Karoglou, M.; Bakolas, A. Non-destructive techniques as a tool for the protection of built cultural heritage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 48, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagati, C.; Lo Turco, M. From structure from motion to historical building information modeling: Populating a semantic-aware library of architectural elements. J. Electron. Imaging 2017, 26, 011007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoš, K.; Pukanská, K.; Repáň, P.; Kseňak, L.; Sabová, J. Modelling the Surface of Racing Vessel’s Hull by Laser Scanning and Digital Photogrammetry. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaggi, I.; Bitelli, G.; Serantoni, E.; Wieser, A. Point cloud dataset and FEM for a complex geometry: The San Luzi bell tower case study. In Proceedings of the GEORES 2019—2nd International Conference of Geomatics and Restoration, Milan, Italy, 8–10 May 2019; Volume XLII-2/W11, pp. 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plata, A.R.M.d.l.; Franco, P.A.C.; Franco, J.C.; Gibello Bravo, V. Protocol Development for Point Clouds, Triangulated Meshes and Parametric Model Acquisition and Integration in an HBIM Workflow for Change Control and Management in a UNESCO’s World Heritage Site. Sensors 2021, 21, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanseverino, A.; Messina, B.; Limongiello, M.; Guida, C.G. An HBIM Methodology for the Accurate and Georeferenced Reconstruction of Urban Contexts Surveyed by UAV: The Case of the Castle of Charles V. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrett, B.E.; Vernon, C.A.; Beckstrand, H.; Pollei, M.; Markert, K.; Franke, K.W.; Hedengren, J.D. Large-Scale Reality Modeling of a University Campus Using Combined UAV and Terrestrial Photogrammetry for Historical Preservation and Practical Use. Drones 2021, 5, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, L.; Shen, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, R. Tridimensional Reconstruction Applied to Cultural Heritage with the Use of Camera-Equipped UAV and Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10413–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitelli, G.; Dellapasqua, M.; Girelli, V.; Sanchini, E.; Tini, M. 3D geomatics techniques for an integrated approach to Cultural Heritage knowledge: The case of San Michele in Acerboli’s church in Santarcangelo di Romagna. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Florence, Italy, 22–24 May 2017; Volume XLII-5/W1, pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monego, M.; Menin, A.; Fabris, M.; Achilli, V. 3D survey of Sarno Baths (Pompeii) by integrated geomatic methodologies. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 40, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Achilli, V.; Fabris, M.; Menin, A.; Monego, M.; Tessari, G.; Floris, M. Combining Sentinel-1 Interferometry and Ground-Based Geomatics Techniques for Monitoring Buildings Affected by Mass Movements. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betti, M.; Bonora, V.; Galano, L.; Pellis, E.; Tucci, G.; Vignoli, A. An Integrated Geometric and Material Survey for the Conservation of Heritage Masonry Structures. Heritage 2021, 4, 585–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, G.; Betti, M.; Facchini, L.; Orlando, M. Non-destructive characterization of stone columns by dynamic test: Application to the lower colonnade of the Dome of the Siena Cathedral. Eng. Struct. 2012, 45, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysandrou, V.; Agapiou, A. Comparison of documentation techniques for the restoration and rehabilitation of cultural heritage monuments: The example of Pyrgos ‘Troulli’ medieval tower in Cyprus. In Proceedings of the Third International Euro-Mediterranean Conference, EuroMed 2010, Lemessos, Cyprus, 8–13 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Solla, M.; Gonçalves, L.M.S.; Gonçalves, G.; Francisco, C.; Puente, I.; Providência, P.; Gaspar, F.; Rodrigues, H. A Building Information Modeling Approach to Integrate Geomatic Data for the Documentation and Preservation of Cultural Heritage. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieraccini, M.; Dei, D.; Betti, M.; Bartoli, G.; Tucci, G.; Guardini, N. Dynamic identification of historic masonry towers through an expeditious and no-contact approach: Application to the “Torre del Mangia” in Siena (Italy). J. Cult. Herit. 2014, 15, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Neumann, I. Finite Element Analysis based on A Parametric Model by Approximating Point Clouds. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, H.; Gong, J. Low-Cost and Efficient Indoor 3D Reconstruction through Annotated Hierarchical Structure-from-Motion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, N.-J.; Wu, Y.-C. AR-Based 3D Virtual Reconstruction of Brick Details. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, G.; Bartoli, G.; Betti, M.; Bonora, V.; Korumaz, M.; Korumaz, A.G. Advanced procedure for documenting and assessment of Cultural Heritage: From Laser Scanning to Finite Element. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 364, 012085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiassi, B.; Vermeltfoort, A.; Lourenço, P. Masonry Mechanical Properties. In Numerical Modelling of Masonry and Historical Structures—From Theory to Application, 1st ed.; Ghiassi, B., Milani, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK; Elsevier: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 239–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hinks, T.; Carr, H.; Truong-Hong, L.; Laefer, D.F. Point Cloud Data Conversion into Solid Models via Point-Based Voxelization. J. Surv. Eng. 2013, 139, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzetti, L.; Banfi, F.; Brumana, R.; Gusmeroli, G.; Oreni, D.; Previtali, M.; Schiantarelli, G. BIM from laser clouds and finite element analysis: Combining structural analysis and geometric complexity. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Ávila, Spain, 25–27 February 2015; Volume XL-5/W4, pp. 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, G.; D’Altri, A.M.; Bitelli, G.; Selvaggi, I.; Lambertini, A. From Laser Scanning to Finite Element Analysis of Complex Buildings by Using a Semi-Automatic Procedure. Sensors 2015, 15, 18360–18380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Aparicio, L.J.; Villarino, A.; García-Gago, J.; González-Aguilera, D. Photogrammetric, Geometrical, and Numerical Strategies to Evaluate Initial and Current Conditions in Historical Constructions: A Test Case in the Church of San Lorenzo (Zamora, Spain). Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassier, M.; Hardy, G.; Bejarano-Urrego, L.; Drougkas, A.; Verstrynge, E.; Van Balen, K.; Vergauwen, M. Semi-automated Creation of Accurate FE Meshes of Heritage Masonry Walls from Point Cloud Data. In Structural Analysis of Historical Constructions: An Interdisciplinary Approach; RILEM Bookseries, 18; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rissolo, D.; Hess, M.R.; Huchim Herrera, J.; Lo, E.; Petrovic, V.; Amador, F.E.; Kuester, F. Comprehensive digital documentation and preliminary structural assessment of Satunsat: A unique Maya architectural labyrinth at Oxkintok, Yucatan, Mexico. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Ávila, Spain, 1–5 September 2019; Volume XLII-2/W15, pp. 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, N.; Coïsson, E.; Diotri, F.; Ferrari, L.; Mikolajewska, S.; Morra di Cella, U.; Roncella, R.; Zerbi, A. History, Geometry, Structure: Interdisciplinary analysis of a historical bridge. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Milan, Italy, 8–10 May 2019; Volume XLII-2/W11, pp. 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.R. TLS-FEM integrated structural deformation analysis on the Beamless Hall at Nanjing, China. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Beijing, China, 28 August–1 September 2021; Volume XLVI-M-1-2021, pp. 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, X. Structure monitoring and deformation analysis of tunnel structure. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State Archive of Verona. Private Archive of Pompei Family, (ASVr, Pompei), section XXVI, 68, section XXVII, 71, section XXVII, 73.
- Saggioro, F.; Varanini, G.M. Il castello di Illasi. Storia e archeologia. In Archaeologica; Bretschneider, G., Ed.; università degli studi di padova: Rome, Italy, 2009; Volume 151, p. 300. ISBN 9788876892370. [Google Scholar]
- Saggioro, F.; Mancassola, N. Il castello di Illasi (VR): Dati archeologici sull’insediamento medioevale. In Paesaggi, Comunità, Villaggi Medievali; Fondazione Centro Italiano di Studi sull’Alto Medioevo: Spoleto (Perugia), Italy, 2012; pp. 639–644. ISBN 9788879883474. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz-Ablanedo, E.; Chandler, J.H.; Rodríguez-Pérez, J.R.; Ordóñez, C. Accuracy of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) and SfM Photogrammetry Survey as a Function of the Number and Location of Ground Control Points Used. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-González, E.; Agüera-Vega, F.; Carvajal-Ramírez, F.; Martínez-Carricondo, P. UAV Photogrammetry Accuracy Assessment for Corridor Mapping Based on the Number and Distribution of Ground Control Points. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CloudCompare (Version 2.12 Alpha). Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Lague, D.; Brodu, N.; Leroux, J. Accurate 3D comparison of complex topography with terrestrial laser scanner: Application to the Rangitikei canyon (N-Z). ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A. Accuracy Assessment of Cultural Heritage Models Extracting 3D Point Cloud Geometric Features with RPAS SfM-MVS and TLS Techniques. Drones 2021, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monego, M.; Fabris, M.; Menin, A.; Achilli, V. 3-D Survey applied to industrial archaeology by tls methodology. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Florence, Italy, 22–24 May 2017; Volume XLII-5/W1, pp. 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monego, M.; Achilli, V.; Fabris, M.; Menin, A. 3-D Survey of Rocky Structures: The Dolomitic Spire of the Gusela del Vescovà. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1246, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyano, J.; Nieto-Julián, J.E.; Bienvenido-Huertas, D.; Marín-García, D. Validation of Close-Range Photogrammetry for Architectural and Archaeological Heritage: Analysis of Point Density and 3D Mesh Geometry. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrini, R.; Clementi, F.; Lucidi, A.; Giannetti, S.; Santoni, A. From TLS to FE analysis: Points cloud exploitation for structural behaviour definition. The San Ciriaco’s Bell Tower. In Proceedings of the International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Ávila, Spain, 1–5 September 2019; Volume XLII-2/W15, pp. 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Villiers, W.I. Computational and Experimental Modelling of Masonry Walling towards Performance-Based Standardisation of Alternative Masonry Units for Low-Income Housing. Dissertation Presented for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Engineering in the Faculty of Engineering, at Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa. 2019. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/268883067.pdf (accessed on 6 September 2022).




| Processing Time | Operation | Drone (h, m) | SLR (h, m) | Smartphone (m) | Drone + SLR (d, h, m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tie points (sparse cloud) | Matching: | 0, 31 | 0, 51 | 3 | 0, 1, 16 |
| Alignment: | 0, 4 | 0, 14 | 2 | 0, 0, 23 | |
| Dense cloud | Depth map generation: | 4, 57 | 1, 38 | 14 | 0, 5, 34 |
| Dense cloud generation: | 19, 16 | 2, 48 | 15 | 2, 17, 10 | |
| 3D model (mesh) | Reconstruction: | 0, 19 | 0, 44 | 22 | 0, 1, 2 |
| Texturing: | 0, 4 | 0, 36 | 6 | 0, 1, 7 |
| 3D Model | N. CPs | N. ChPs | RMSE (cm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPs | ChPs | |||
| Drone | 14 | 6 | 1.4 | 1.1 |
| SLR | 9 | 4 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Drone + SLR | 14 | 6 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| Smartphone | 5 | - | 1.9 | - |
| Mean Distance (cm) | Standard Deviation (cm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Available Data | ||
| TLS and Drone | 0.9 | 10.1 |
| TLS and SLR | –0.5 | 9.6 |
| TLS and Drone + SLR | 0.6 | 9.6 |
| TLS and Smartphone | –1.5 | 10.9 |
| Smartphone and SLR | 1.5 | 11.9 |
| Area A | ||
| TLS and Drone | 0.2 | 2.4 |
| TLS and SLR | –0.3 | 1.8 |
| TLS and Drone + SLR | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| Area B | ||
| TLS and Drone | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| TLS and SLR | 0.2 | 2.7 |
| TLS and Drone + SLR | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| TLS and Smartphone | –0.1 | 4.7 |
| Smartphone and SLR | –0.1 | 7.1 |
| Internal Palace | ||
| TLS and Drone + SLR | 1.1 | 7.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabris, M.; Fontana Granotto, P.; Monego, M. Expeditious Low-Cost SfM Photogrammetry and a TLS Survey for the Structural Analysis of Illasi Castle (Italy). Drones 2023, 7, 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7020101
Fabris M, Fontana Granotto P, Monego M. Expeditious Low-Cost SfM Photogrammetry and a TLS Survey for the Structural Analysis of Illasi Castle (Italy). Drones. 2023; 7(2):101. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7020101
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabris, Massimo, Pietro Fontana Granotto, and Michele Monego. 2023. "Expeditious Low-Cost SfM Photogrammetry and a TLS Survey for the Structural Analysis of Illasi Castle (Italy)" Drones 7, no. 2: 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7020101
APA StyleFabris, M., Fontana Granotto, P., & Monego, M. (2023). Expeditious Low-Cost SfM Photogrammetry and a TLS Survey for the Structural Analysis of Illasi Castle (Italy). Drones, 7(2), 101. https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7020101






