Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide with Noble Metals Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Sensing †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
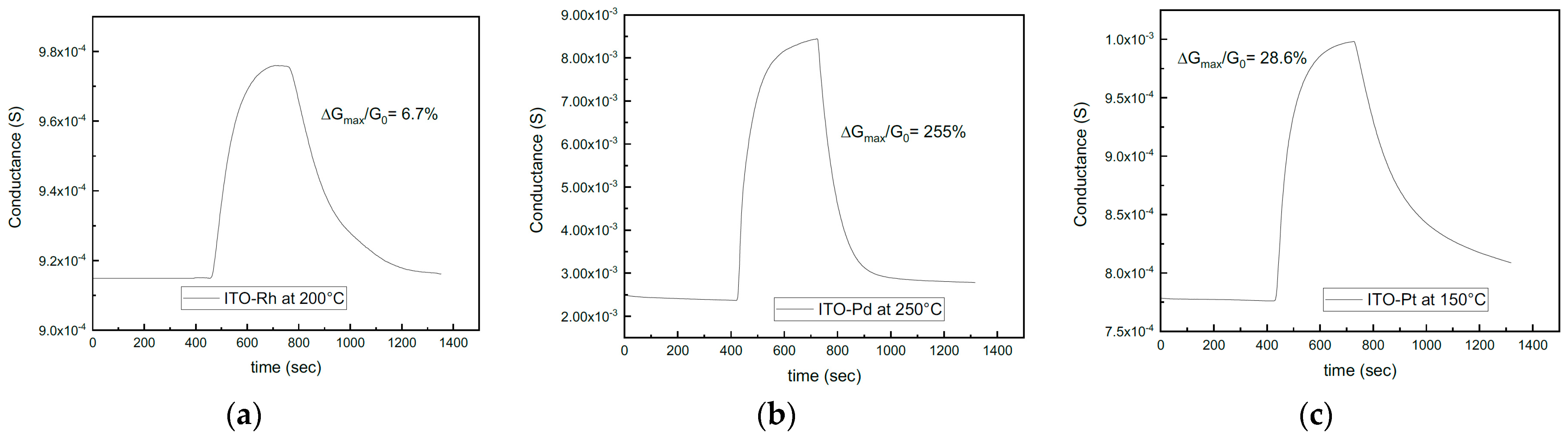
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ball, M.; Wietschel, M. The future of hydrogen–opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttner, W.J.; Post, M.B.; Burgess, R.; Rivkin, C. An overview of hydrogen safety sensors and requirements. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 2462–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Q.; Lin, C.L.; Yu, X.B.; Wang, T.H. Room-temperature hydrogen storage characteristics of ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.S.; Park, J.Y.; Choi, S.-W.; Kim, H.S.; Na, H.G.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, H.W. Significant enhancement of the sensing characteristics of In2O3 nanowires by functionalization with Pt nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 415502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadek, A.Z.; Choopun, S.; Wlodarski, W.; Ippolito, S.J.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Characterization of ZnO nanobelt-based gas sensor for H2, NO2, and hydrocarbon sensing. IEEE. Sens. J. 2007, 7, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedi, F.; Miglietta, M.L.; Polichetti, T.; Ricciardella, F.; Massera, E.; Ninno, D.; Di Francia, G. A study on the physicochemical properties of hydroalcoholic solutions to improve the direct exfoliation of natural graphite down to few-layers graphene. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 035601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmadi, I.; Nugroho, F.A.A.; Langhammer, C. High-performance nanostructured palladium- based hydrogen sensors—Current limitations and strategies for their mitigation. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3306–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfano, B.; Miglietta, M.L.; Massera, E.; Arroyo, P.; Lozano, J.; Polichetti, T. Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide with Noble Metals Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Sensing. Proceedings 2024, 97, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097113
Alfano B, Miglietta ML, Massera E, Arroyo P, Lozano J, Polichetti T. Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide with Noble Metals Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Sensing. Proceedings. 2024; 97(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097113
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfano, Brigida, Maria Lucia Miglietta, Ettore Massera, Patricia Arroyo, Jesus Lozano, and Tiziana Polichetti. 2024. "Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide with Noble Metals Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Sensing" Proceedings 97, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097113
APA StyleAlfano, B., Miglietta, M. L., Massera, E., Arroyo, P., Lozano, J., & Polichetti, T. (2024). Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide with Noble Metals Nanoparticles in Hydrogen Sensing. Proceedings, 97(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097113








