Development of a Potentiometric Nitrate Ion Microsensor Improved Using Conductive Polymer Doped with Carbon Nanotubes as a Transducing Layer †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
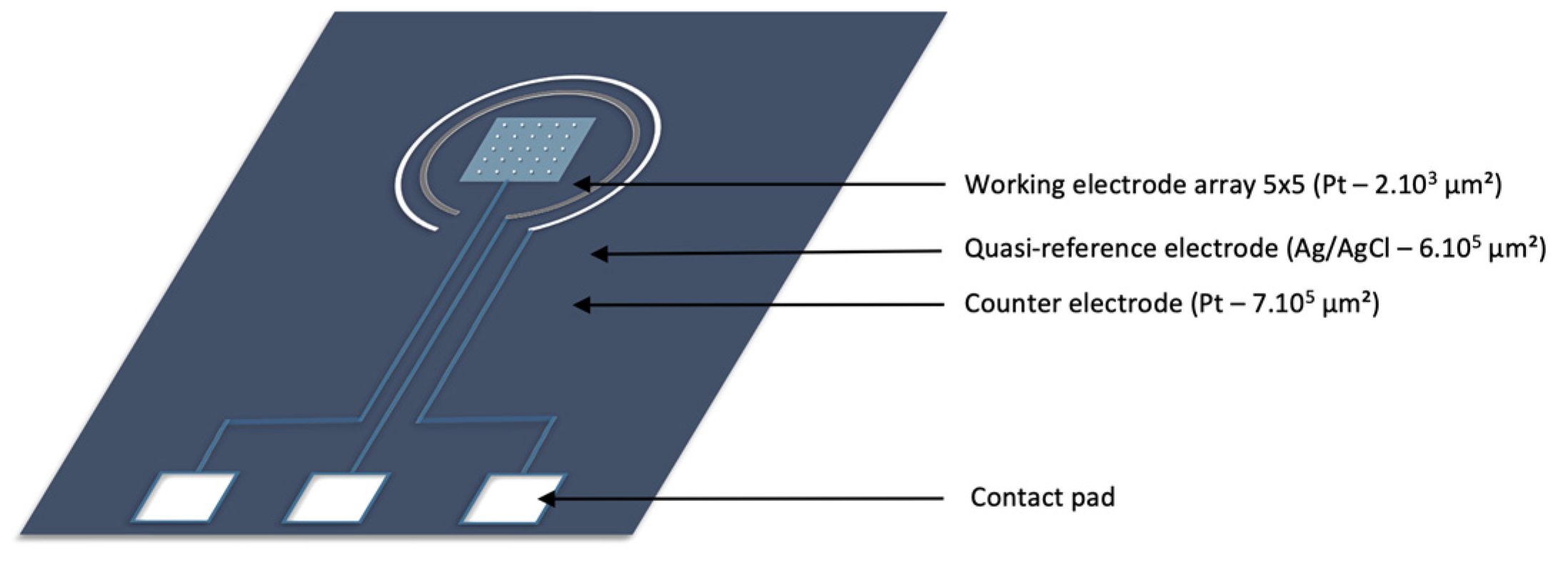
2.1. Microsensor Geometry
2.2. Working Microelectrode Array Functionalization
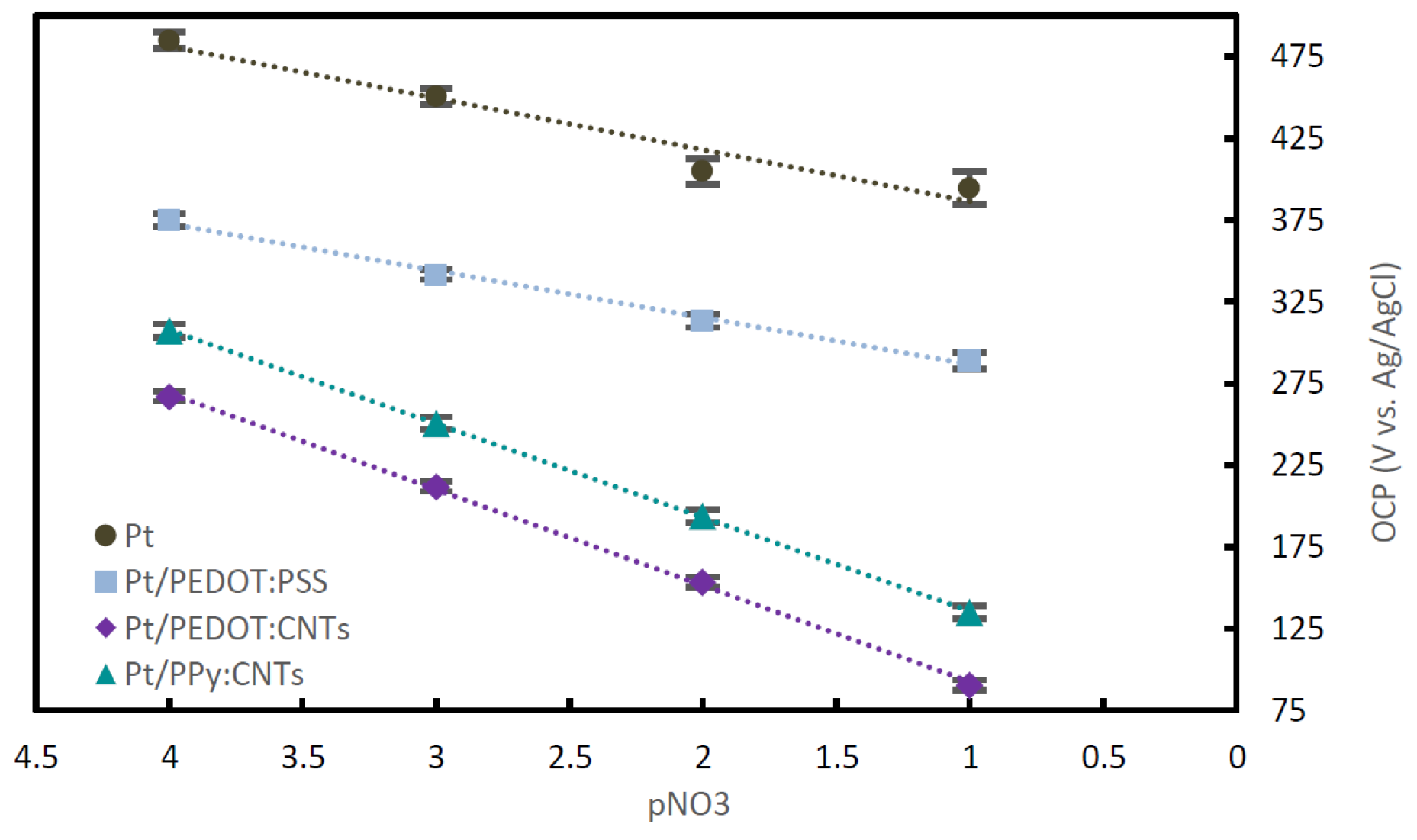
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christophe, C.; Belaïdi, F.S.; Launay, J.; Gros, P.; Questel, E.; Temple-Boyer, P. Elaboration of integrated microelectrodes for the detection of antioxidant species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 177, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, X.; Quin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Single-piece SC-ISE with polymer-carbon nanotube composites. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbioli, M.; Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; De Rooij, N.F. Potential Drifts of SC-ISE due to zero-current ion fluxes through the sensor membrane. Electroanalysis 2007, 12, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
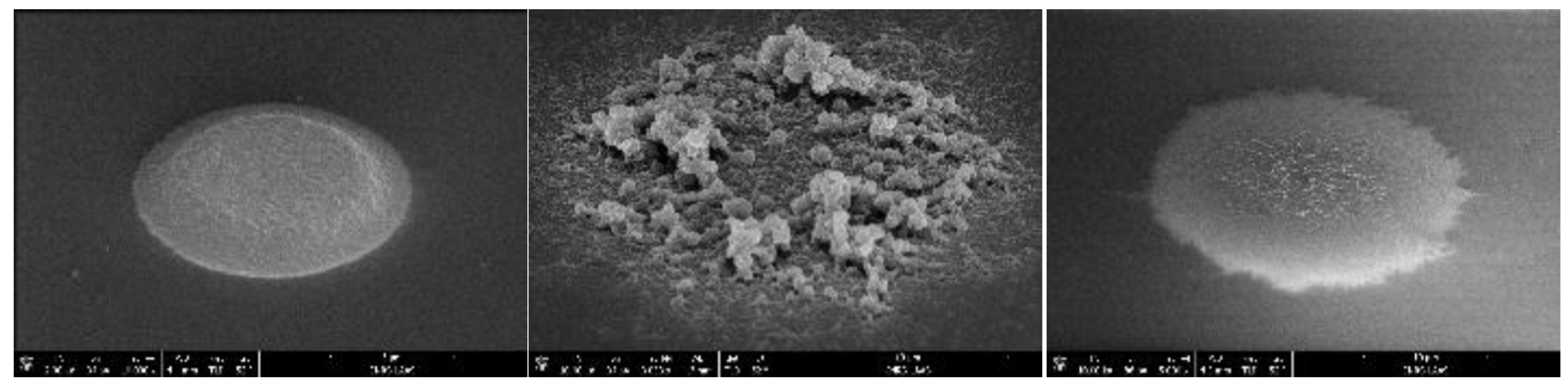

| Composite | Monomer | Dopant |
|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:PSS | EDOT 10 mM | NaPSS 34 mM |
| PEDOT:DWCNTs | EDOT 10 mM | DWCNTs 1 mg/mL |
| PPy:DWCNTs | Py 150 mM | DWCNTs 1 mg/mL |
| Transducing Layer | Sensitivity Slope | Limit of Detection | Long-Term Drift |
|---|---|---|---|
| Without | 40.1 mV/pNO3 | 1.10−4 M | n/a |
| PEDOT:PSS | 28.7 mV/pNO3 | 1.10−4 M | n/a |
| PEDOT:DWCNTs | 57.3 mV/pNO3 | 1.10−5 M | ±0.1 mV/h |
| PPy:DWCNTs | 57.4 mV/pNO3 | 1.10−5 M | ±0.05 mV/h |
| Transducing Layer | Interfering Ion | Log (K) |
|---|---|---|
| PEDOT:DWCNTs | Cl− HCO3− SO42− | 2.65 2.8 4.1 |
| PPy:DWCNTs | Cl− HCO3− SO42− | 2.2 2.8 3.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bene, C.; Flahaut, E.; Legnani, M.; Temple-Boyer, P.; Launay, J. Development of a Potentiometric Nitrate Ion Microsensor Improved Using Conductive Polymer Doped with Carbon Nanotubes as a Transducing Layer. Proceedings 2024, 97, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097111
Bene C, Flahaut E, Legnani M, Temple-Boyer P, Launay J. Development of a Potentiometric Nitrate Ion Microsensor Improved Using Conductive Polymer Doped with Carbon Nanotubes as a Transducing Layer. Proceedings. 2024; 97(1):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097111
Chicago/Turabian StyleBene, Camille, Emmanuel Flahaut, Morgan Legnani, Pierre Temple-Boyer, and Jérôme Launay. 2024. "Development of a Potentiometric Nitrate Ion Microsensor Improved Using Conductive Polymer Doped with Carbon Nanotubes as a Transducing Layer" Proceedings 97, no. 1: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097111
APA StyleBene, C., Flahaut, E., Legnani, M., Temple-Boyer, P., & Launay, J. (2024). Development of a Potentiometric Nitrate Ion Microsensor Improved Using Conductive Polymer Doped with Carbon Nanotubes as a Transducing Layer. Proceedings, 97(1), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2024097111







