Abstract
Parkinson’s disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. Patients with PD experience motor disturbances, postural instability, gait disturbances, and balance disorders, causing a high risk of falls. Virtual reality (VR), as one physiotherapy intervention, can be an option to prevent the prevalence of accidental falls. In this literature review, the authors selected five papers to examine the effectiveness of VR in reducing fall risk in PD and its limitations. The results show a decrease in the risk of falling in PD, which was assessed using several parameters.
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease. Pathologically, PD is defined as reduced dopamine due to the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) and the presence of Lewy bodies. Lewy bodies are a collection of insoluble alpha-synuclein proteins [1]. In PD, the damage to the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra is more than 60%, and the level of the neurotransmitter dopamine is reduced from the physiological minimum. When dopamine levels decrease, the subthalamic nucleus will overstimulate the globus pallidus internus (GPi) to compensate. Then, the GPi will over-inhibit the thalamus. Both will cause under-stimulation of the motor cortex [2].
PD is the most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s, affecting 2–3% of the population over 65 years [3,4]. Based on data from the Central Statistics Agency of Indonesia in 2015, as many as 200,000 out of 20 million elderlies, or around 0.01%, experienced PD. The number is expected to increase by approximately 75,000 annually [5]. Along with life expectancy, the incidence of PD will increase [2].
Parkinson’s disease is diagnosed by the typical symptoms of PD based on the physical and neurological examination findings. In addition, supporting examinations such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and brain ultrasounds are used as diagnostic tools. Symptoms experienced by PD patients include both motor and non-motor symptoms. These motor symptoms include resting tremors, bradykinesia, rigidity, loss of coordination, gait disturbances, balance disorders, and postural instability. Non-motor symptoms include sensory disturbances, sleep behavior disorders, autonomic disorders, and behavioral problems [6,7,8].
Motor impairment in PD patients may lead to an increased risk of falls, two to threefold compared to healthy elderly populations [6,7]. As many as 45–68% of patients with PD experience frequent falls each year, and two-thirds experience repeated falls, resulting in injury, activity limitations, a decreased quality of life, and even death [9]. Furthermore, 20–30% of the elderly with a high disability due to falls lose their freedom to carry out activities of daily life. Thus, preventing falls among the elderly is essential to avoid impacting quality of life [10].
Previous studies examined the effectiveness of various physiotherapy strategies in improving motor function and reducing the risk of falls for patients with PD. Treatment can be tailored to the individual needs, including treadmill training, overground walking, cycling, cueing techniques, cognitive movement strategies, and balance exercises [6,11]. In addition, virtual reality is believed to be an option.
Virtual reality (VR) is a computer software application in the form of a visual simulation that imitates an environment or the real world, where users can interact through actual actions. VR is distinguished based on the user’s level of immersion or realism. The level of immersion or realism is measured by the sensory and motor range connected to the VR environment [12]. VR is divided into three types: immersive, semi-immersive, and non-immersive. In the rehabilitation of PD patients, VR is used for walking exercises and proprioceptive, vestibular, and cognitive training [7]. VR can improve balance and functional capacity, reduce risk, increase self-confidence, and improve the quality of life of PD patients [13]. Therefore, this literature review will examine the effectiveness of VR in reducing the risk of falls in PD patients and explain its advantages and limitations, as well as the type and doses used.
2. Methods
This study is a literature review carried out from January to May 2022 through PubMed, Scopus, and ProQuest databases. The literature search strategy used to find articles uses the PICO framework. The keywords used in the literature search were Parkinson’s OR Parkinson’s disease OR Parkinsonism OR Paralysis Agitans OR Shaking palsy AND Virtual reality OR Virtual realities OR VR AND falls. Furthermore, the articles were critically appraised using an appraisal instrument called JBI Critical Appraisal Tools. Meanwhile, we synthesized data using a simplified approach.
3. Results
The data collection used the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematics Review and Meta-Analysis) method (Figure 1). The critical appraisal assessment was conducted on seven published journals, showing that two journals did not meet the inclusion criteria. Five journals were obtained for which data synthesis would be carried out. Table 1 shows the articles that were included and excluded after critical appraisal.
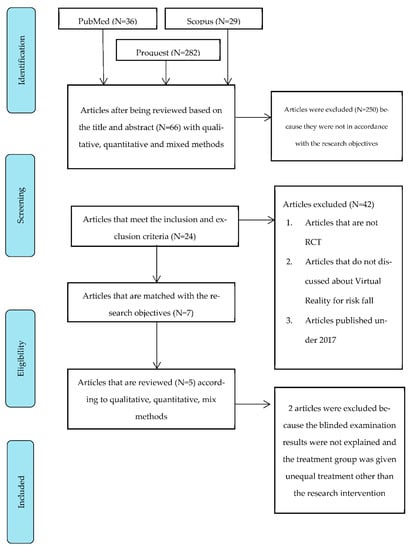
Figure 1.
PRISMA Flow Diagram.

Table 1.
Articles of inclusion and exclusion.
The article by Van der Kolk et al. was excluded as the outcome, and the procedure for intervention was not described. The report by Kashif et al. was excluded because the treatment group was given unequal treatment rather than the research intervention.
All inclusion articles have a randomized controlled trial (RCT) study design with a level of evidence 1B, which is the highest level of study after a systematic review. The research locations are mostly in European countries, namely, Italy and Belgium. Bekkers et al.’s research took place in Belgium, Feng et al.’s study in China, and the other three articles in Italy.
Each article has varied numbers and types of participants. The participants’ demographics ranged in age from 60 to 90 years, while the stage of PD assessed by Hoehn and Yahr ranged from stage II to IV. Stages II-IV show symptoms of mild to moderate PD.
The VR interventions in the five articles used different types, namely, immersive, and non-immersive types. The doses given in the studies also varied, between 6 and 12 weeks with 3–5 x/sessions and a duration of 40–50 min per session. Table 2 shows the methods and dosages of the interventions given.

Table 2.
Intervention and Dose.
The assessment of the risk of falling in PD used different parameters, including the number of falls, the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), the Timed Up and Go Test (TUGT), and the Mini-Balance Evaluation System Test (Mini-BEST). Table 3 shows the assessment parameters used by each article.

Table 3.
Parameters.
The articles reviewed were filtered by the differences in the provision of interventions in the treatment groups and the control groups, as well as by the research results and research methods used, as seen in Table 4.

Table 4.
Article Screening.
4. Discussion
PD is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects dopaminergic function and several neurotransmission systems, one of which is the cholinergic system [14]. The cholinergic system plays a vital role in controlling attention and discriminating stimuli. Thus, dysfunction of the cholinergic system can increase the risk of falling. It can be assessed through the activity of short-latency afferent inhibition (SAI), which is a picture of sensorimotor interactions through stimulation of the peripheral nerves. Peripheral nerve stimulation activates cholinergic neurons, so the inhibitory response to cortical activity can be assessed. The more significant the inhibition of SAI, the better the performance of the complex walk [15,16,17]. SAI results are predictors of changes in dual-task gait regardless of cognitive status and can be used as a parameter to assess fall risk [18]. It can be measured using transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), a neurophysiological tool to examine the integrity of the corticomotor pathway in various diseases associated with motor dysfunction [19].
In this literature review, the authors found that providing exercise through VR effectively reduced the risk of falling in PD. A study conducted by Pelosin et al. showed a significant reduction in the risk of falling, as seen by a decrease in the number of falls and the average results of short-latency afferent inhibition (SAI). In contrast, in the control group, there was no change in the mean SAI results and the number of falls [17].
The findings align with the results of a study by Severiano et al. that showed the use of VR in rehabilitation to reduce the risk of falls in PD patients is compelling. VR can train brain responses and behavior through the complex motor–cognitive interactions created during exercise. Complex motor–cognitive interactions can increase neuroplasticity and better motor learning compared to repetitive motor tasks without variation [7]. The mechanism of plasticity in the learning process in PD patients is dependent on external feedback. The visual feedback through the device will allow patients to sense their position and direction of movement. The feedback will improve a patient’s behavior, maintain enthusiasm, and provide an excellent emotional experience to motivate them to continue practicing.
In addition, VR can also improve the patient’s cognition through the preparation of a different environment at each stage of the game so that with many experiments, patients can acquire skills in the VR world and apply them in the real world. VR games also improve the patient’s posture stability by increasing the vestibular organs’ interaction ability and practicing static and dynamic postural control [20].
Components such as vision, proprioception, and the vestibular system influence balance. Thus, VR can stimulate sensorimotor and cognitive so that balance can be maintained. The research shows that freezing of gait (FOG) and walking disorders can be treated by providing interventions that combine cognitive and motor tasks. Practice with VR will train patients to focus on obstacles that will cause tripping [21]. These five articles show that the minimum effective dose for VR training is 6–12 weeks, with 3 to 5 weekly sessions for a duration of 45–50 min per session, focusing on balance training and walking exercises [17,20,21,22,23].
All PD patients studied in the five articles had mild to moderate stages, namely, Hoehn and Yahr, II-IV. According to the study by Pazzaglia et al. and Gandolfi et al., PD patients with severe balance or cognitive disorders were a limitation to using VR. PD patients with severe symptoms or stages are not recommended to use VR because it is unsafe for patients [22,23]. The use of VR in mild to moderate stages of PD can improve the mechanism of neuroplasticity so that there is an improvement in motor disorders through motor relearning. Neuroplasticity and connectivity can occur at corticocortical and thalamocortical levels, including the tissues associated with the basal ganglia pathway. Taking advantage of this neuroplasticity mechanism in severe PD is difficult, as severe balance and cognition disorders can affect the learning process. Although VR has been shown to reduce the risk of falling through improved balance and gait, it is unclear whether there is a reduction in progression in PD [6].
Although the five articles reviewed showed promising results in reducing the risk of falling in PD patients, the article by Gandolfi et al. comparing VR intervention with sensory integration balance training (SIBT) showed better and more maintainable BBS scores after one month of follow-up in the SIBT treatment group than in the VR group. This result is suspected as Nintendo Wii Fit’s VR workouts focus on balance exercises that include weight-shifting exercises, symmetrical footwork, and controlled movement close to stability limits in high repetitions. Meanwhile, the exercise provided focused less on postural control caused by destabilization. Therefore, the comparison between the effect of VR and SIBT interventions in reducing the risk of falling in PD should be studied further in subsequent studies [22].
5. Conclusions
This literature review recommends that VR interventions reduce the risk of falling in PD. The VR exercises can be immersive or non-immersive, with games that focus on balance training and walking activities tailored to the needs of each patient. Supervision by a physiotherapist is essential to keep the patient safe during training sessions. Although proven effective, VR has limitations in PD patients with balance disorders and severe cognitive impairment because it will be dangerous for the patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.A.D. and V.R.P.; methodology, F.A.D. and V.R.P.; software, V.R.P.; validation, F.A.D., R.P. and A.D.P.; formal analysis, F.A.D.; resources, V.R.P.; data curation, V.R.P.; writing—original draft preparation, V.R.P.; writing—review and editing, F.A.D.; project administration, M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Simon, D.K.; Tanner, C.M.; Brundin, P. Parkinson Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunawan, G.; Dalhar, M.; Kurniawan, S.N. Parkinson Dan Terapi Stem Sel. Malang Neurol. J. 2017, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Balestrino, R.; Schapira, A.H.V. Parkinson Disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poewe, W.; Seppi, K.; Tanner, C.M.; Halliday, G.M.; Brundin, P.; Volkmann, J.; Schrag, A.E.; Lang, A.E. Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahyu, A. Klasifikasi Penyakit Parkinson Menggunakan Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Berdasarkan Ekstraksi Fitur Multifractal Detrended Fluctuation Analysis (MFDFA) Pada Sinyal Gait. Available online: https://repository.its.ac.id/42195/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Calabrò, R.S.; Naro, A.; Cimino, V.; Buda, A.; Paladina, G.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Manuli, A.; Milardi, D.; Bramanti, P.; Bramanti, A. Improving Motor Performance in Parkinson’s Disease: A Preliminary Study on the Promising Use of the Computer Assisted Virtual Reality Environment (CAREN). Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, C.G.; Allen, N.E.; Nackaerts, E.; Paul, S.S.; Nieuwboer, A.; Gilat, M. Virtual Reality in Research and Rehabilitation of Gait and Balance in Parkinson Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis, Motor Symptoms and Non-Motor Features; Future Medicine: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, C.G.; Paul, S.S.; Nieuwboer, A. Prevention of Falls in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of Fall Risk Factors and the Role of Physical Interventions. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2014, 4, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryani, U. Hubungan Tingkat Kemandirian Dalam Aktivitas Sehari-Hari Dengan Resiko Jatuh Pada Lansia Di PTSW Sabai Nan Aluih Sicincin Kabupaten Padang Pariaman. Kepemimp. Dan Pengur. Sekol. 2018, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Giardini, M.; Nardone, A.; Godi, M.; Guglielmetti, S.; Arcolin, I.; Pisano, F.; Schieppati, M. Instrumental or Physical-Exercise Rehabilitation of Balance Improves Both Balance and Gait in Parkinson’s Disease. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 5614242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wong, S.S.L.; Lai, F.H.Y. The Effect of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation on Balance in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Electronics 2021, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severiano, M.I.R.; Zeigelboim, B.S.; Teive, H.A.G.; Santos, G.J.B.; Fonseca, V.R. Effect of Virtual Reality in Parkinson’s Disease: A Prospective Observational Study TT-Efeito Da Realidade Virtual Na Doença de Parkinson: Estudo Observacional Prospectivo. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2018, 76, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Nardone, R.; Brigo, F.; Versace, V.; Höller, Y.; Tezzon, F.; Saltuari, L.; Trinka, E.; Sebastianelli, L. Cortical Afferent Inhibition Abnormalities Reveal Cholinergic Dysfunction in Parkinson’s Disease: A Reappraisal. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Di Lenola, D.; Abagnale, C.; Ferrandes, F.; Sebastianelli, G.; Casillo, F.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Serrao, M.; Evangelista, M.; Schoenen, J.; et al. Short-Latency Afferent Inhibition and Somato-Sensory Evoked Potentials during the Migraine Cycle: Surrogate Markers of a Cycling Cholinergic Thalamo-Cortical Drive? J. Headache Pain 2020, 21, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, Y.; Zomorrodi, R.; Backhouse, F.; Cash, R.F.H.; Barr, M.S.; Rajji, T.K.; Chen, R.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Blumberger, D.M. Reduced Prefrontal Short-Latency Afferent Inhibition in Older Adults and Its Relation to Executive Function: A TMS-EEG Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosin, E.; Cerulli, C.; Ogliastro, C.; Lagravinese, G.; Mori, L.; Bonassi, G.; Mirelman, A.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Abbruzzese, G.; Marchese, R.; et al. A Multimodal Training Modulates Short Afferent Inhibition and Improves Complex Walking in a Cohort of Faller Older Adults with an Increased Prevalence of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2020, 75, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosin, E.; Ogliastro, C.; Lagravinese, G.; Bonassi, G.; Mirelman, A.; Hausdorff, J.M.; Abbruzzese, G.; Avanzino, L. Attentional Control of Gait and Falls: Is Cholinergic Dysfunction a Common Substrate in the Elderly and Parkinson’s Disease? Front. Aging Neurosci. 2016, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groppa, S.; Oliviero, A.; Eisen, A.; Quartarone, A.; Cohen, L.G.; Mall, V.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Mima, T.; Rossi, S.; Thickbroom, G.W.; et al. A Practical Guide to Diagnostic Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: Report of an IFCN Committee. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 153, 853–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Li, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Gan, L.; Shang, X.; Wu, Z. Virtual Reality Rehabilitation versus Conventional Physical Therapy for Improving Balance and Gait in Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 4186–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekkers, E.M.J.; Mirelman, A.; Alcock, L.; Rochester, L.; Nieuwhof, F.; Bloem, B.R.; Pelosin, E.; Avanzino, L.; Cereatti, A.; Della Croce, U.; et al. Do Patients With Parkinson’s Disease With Freezing of Gait Respond Differently Than Those Without to Treadmill Training Augmented by Virtual Reality? Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2020, 34, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, M.; Geroin, C.; Dimitrova, E.; Boldrini, P.; Waldner, A.; Bonadiman, S.; Picelli, A.; Regazzo, S.; Stirbu, E.; Primon, D.; et al. Virtual Reality Telerehabilitation for Postural Instability in Parkinson’s Disease: A Multicenter, Single-Blind, Randomized, Controlled Trial. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 7962826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazzaglia, C.; Imbimbo, I.; Tranchita, E.; Minganti, C.; Ricciardi, D.; Lo Monaco, R.; Parisi, A.; Padua, L. Comparison of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation and Conventional Rehabilitation in Parkinson’s Disease: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Physiotherapy 2020, 106, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).