Digital Skills Framework in Higher Education †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Digital Skills Proficiency: Influencing Factors
1.2. Digital Skills as Graduate Attributes in the Curriculum Framework
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Digital Skills Instrument (DSI)
2.2. Expert Judgment Content Validation
2.3. Pilot Study
3. Results
3.1. Content Validation by Expert Judgment
3.2. Pilot Study
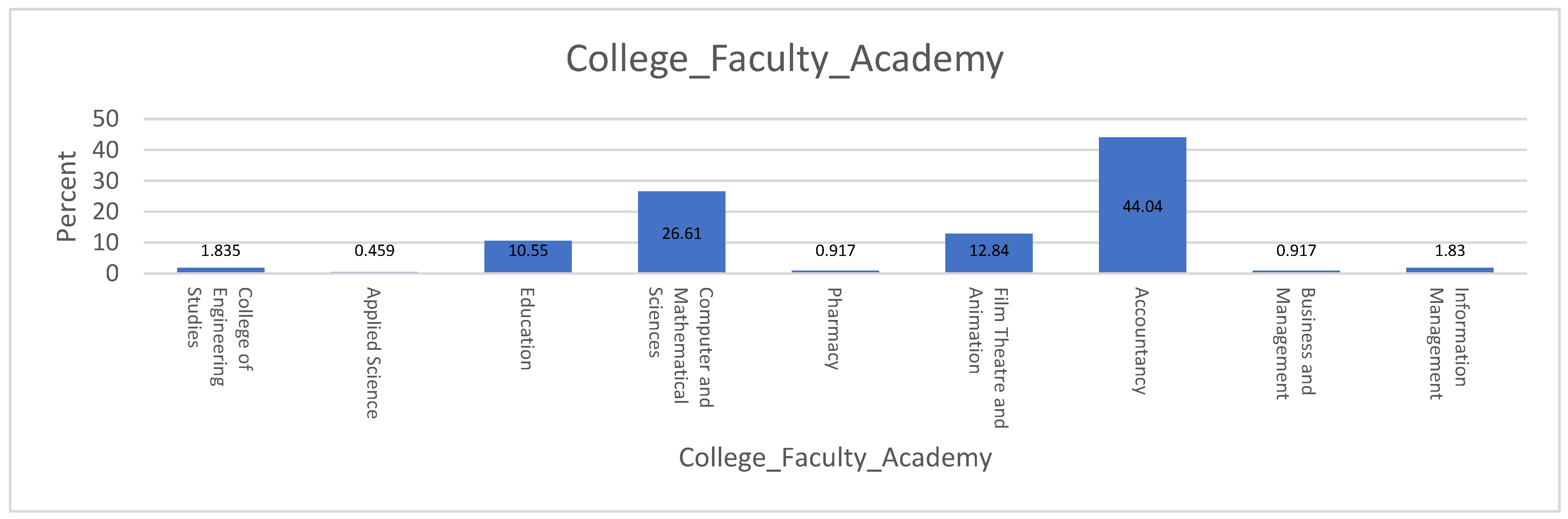
Distribution of Respondents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewi, R.S.; Hasanah, U.; Zuhri, M. Analysis Study of Factors Affecting Students’ Digital Literacy Competency. Ilkogr. Online 2021, 20, 424–431. [Google Scholar]
- Vodă, A.I.; Cautisanu, C.; Grădinaru, C.; Tănăsescu, C.; de Moraes, G.H.S.M. Exploring Digital Literacy Skills in Social Sciences and Humanities Students. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deursen, A.J.A.M.; Helsper, E.J.; Eynon, R. Measuring Digital Skills. From Digital Skills to Tangible Outcomes Project Report. 2014. Available online: https://www.oii.ox.ac.uk/research/projects/?id=112 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Sivarajah, U.; Kamal, M.M.; Irani, Z.; Weerakkody, V. Critical analysis of Big Data challenges and analytical methods. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Platform for Shaping the Future of the New Economy and Society. Schools of the Future: Defining New Models of Education for the Fourth Industrial Revolution; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO. A Global Framework of Reference on Digital Literacy Skills for Indicators 4.4.2; Information Paper No. 51; UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2018; Available online: http://uis.unesco.org/sites/default/files/documents/ip51-global-framework-reference-digital-literacy-skills-2018-en.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Malaysian Qualifications Agency. Malaysian Qualification Framework (MQF), 2nd ed.; Malaysian Qualification Agency: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar-Pérez, J.; Cuervo-Martínez, Á. Content Validity and expert judgement: An approach to its use. Av. Med. 2008, 6, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Van Laar, E.; Van Deursen, A.J.; Van Dijk, J.A.; De Haan, J. The relation between 21st-century skills and digital skills: A systematic literature review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 72, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienlin, T.; Johannes, N. The impact of digital technology use on adolescent well-being. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 22, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belshaw, D.A. What Is’ Digital Literacy’? A Pragmatic Investigation. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bozkurt, A.; Tu, C.H. Digital identity formation: Socially being real and present on digital networks. Educ. Media Int. 2016, 53, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Component | Number of Items |
|---|---|
| Information literacy | 11 |
| Computer and technology literacy | 4 |
| Visual literacy | 3 |
| Digital communication/collaboration skills | 4 |
| Total | 22 |
| Expert | Field of Expertise | Research/Teaching Experience (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Language testing (social sciences) | 18 |
| 2 | Measurement and evaluation (social sciences) | 20 |
| 3 | Digital literacy (science and technology) | 21 |
| 4 | Artificial intelligence (science and technology) | 15 |
| 5 | Instructional communication and new media (social sciences) | 16 |
| 6 | Psychometric assessment (social sciences) | 25 |
| 7 | Pharmacy (health science) | 20 |
| 8 | Law and criminal justice (social sciences) | 21 |
| Category | Scale | Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Sufficiency The items within the same dimension should suffice to measure this dimension. | 4 | The item is sufficient to measure the dimension |
| 3 | The item measures some aspects of the dimension but does not represent the full dimension | |
| 2 | A few items must be added to fully assess the dimension | |
| 1 | The item is insufficient to measure the dimension | |
| Clarity The items can be understood easily. (i.e., syntax and semantics are appropriate). | 4 | The item is sufficient to measure the dimension |
| 3 | The item measures some aspects of the dimension but does not represent the full dimension | |
| 2 | A few items must be added to fully assess the dimension | |
| 1 | The item is insufficient to measure the dimension | |
| Coherence The items are logically related to the dimension or indicator they are measuring. | 4 | The item is sufficient to measure the dimension |
| 3 | The item measures some aspects of the dimension but does not represent the full dimension | |
| 2 | A few items must be added to fully assess the dimension | |
| 1 | The item is insufficient to measure the dimension | |
| Relevance The items are essential or important. (i.e., they must be included). | 4 | The item is sufficient to measure the dimension |
| 3 | The item measures some aspects of the dimension but does not represent the full dimension | |
| 2 | A few items must be added to fully assess the dimension | |
| 1 | The item is insufficient to measure the dimension |
| Category | Cronbach’s Alpha | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sufficiency | 0.915 | 3.56 | 0.446 |
| Clarity | 0.944 | 3.40 | 0.532 |
| Coherence | 0.941 | 3.55 | 0.530 |
| Relevance | 0.934 | 3.52 | 0.529 |
| Construct | Characteristics | Characteristics | Cronbach’s Alpha | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Skills | C1—Information Literacy | Sufficiency | 0.924 | |
| Clarity | 0.961 | |||
| Coherence | 0.949 | 0.94 | ||
| Relevance | 0.926 | |||
| C2—Computer and Technology Literacy | Sufficiency | 0.966 | ||
| Clarity | 0.860 | |||
| Coherence | 0.934 | 0.93 | ||
| Relevance | 0.950 | |||
| C3—Visual Literacy | Sufficiency | 0.855 | ||
| Clarity | 0.732 | |||
| Coherence | 0.812 | 0.82 | ||
| Relevance | 0.902 | |||
| C4–Digital Communication/ Collaboration Skill | Sufficiency | 0.736 | ||
| Clarity | 0.650 | |||
| Coherence | 0.823 | 0.76 | ||
| Relevance | 0.837 |
| Component | Item | Scale Mean If Item Deleted | Scale Variance If Item Deleted | Corrected Item-Total Correlation | Cronbach’s Alpha If Item Deleted | Cronbach’s Alpha Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1-Information Literacy | C1.1 | 110.49 | 235.726 | 0.687 | 0.966 | 0.957 |
| C1.2 | 110.52 | 235.264 | 0.738 | 0.966 | ||
| C1.3 | 110.42 | 235.904 | 0.754 | 0.966 | ||
| C1.4 | 110.60 | 232.683 | 0.804 | 0.965 | ||
| C1.5 | 110.57 | 232.689 | 0.794 | 0.965 | ||
| C1.6 | 110.71 | 234.522 | 0.736 | 0.966 | ||
| C1.7 | 110.76 | 232.793 | 0.758 | 0.965 | ||
| C1.8 | 110.69 | 233.006 | 0.790 | 0.965 | ||
| C1.9 | 110.80 | 231.848 | 0.780 | 0.965 | ||
| C1.10 | 110.59 | 234.732 | 0.717 | 0.966 | ||
| C1.11 | 110.72 | 232.590 | 0.749 | 0.966 | ||
| C1.12 | 111.07 | 235.193 | 0.607 | 0.967 | ||
| C2-Computer and Technology Literacy | C2.1 | 110.51 | 233.928 | 0.747 | 0.966 | 0.895 |
| C2.2 | 110.99 | 232.968 | 0.620 | 0.967 | ||
| C2.3 | 110.69 | 233.790 | 0.741 | 0.966 | ||
| C2.4 | 110.76 | 233.300 | 0.736 | 0.966 | ||
| C2.5 | 11.13 | 234.324 | 0.572 | 0.967 | ||
| C3-Digital Communication/Collaboration Skill | C3.1 | 110.69 | 232.702 | 0.746 | 0.966 | 0.919 |
| C3.2 | 110.67 | 233.016 | 0.718 | 0.966 | ||
| C3.3 | 110.89 | 231.938 | 0.692 | 0.966 | ||
| C3.4 | 110.61 | 234.082 | 0.701 | 0.966 | ||
| C4-Digital Identity and Well-Being | C4.1 | 110.31 | 236.879 | 0.616 | 0.966 | 0.847 |
| C4.2 | 110.63 | 233.745 | 0.654 | 0.966 | ||
| C4.3 | 110.40 | 235.882 | 0.629 | 0.966 | ||
| C5-Digital Ethics | C5.1 | 110.39 | 234.846 | 0.688 | 0.966 | 0.942 |
| C5.2 | 110.59 | 233.691 | 0.714 | 0.966 | ||
| C5.3 | 110.44 | 235.408 | 0.674 | 0.966 | ||
| C5.4 | 110.43 | 235.167 | 0.665 | 0.966 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aris, S.R.S.; Teoh, S.H.; Deni, S.M.; Nadzri, F.A.; Dalim, S.F. Digital Skills Framework in Higher Education. Proceedings 2022, 82, 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082061
Aris SRS, Teoh SH, Deni SM, Nadzri FA, Dalim SF. Digital Skills Framework in Higher Education. Proceedings. 2022; 82(1):61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082061
Chicago/Turabian StyleAris, Sharipah Ruzaina Syed, Sian Hoon Teoh, Sayang Mohd Deni, Fazyudi Ahmad Nadzri, and Siti Fairuz Dalim. 2022. "Digital Skills Framework in Higher Education" Proceedings 82, no. 1: 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082061
APA StyleAris, S. R. S., Teoh, S. H., Deni, S. M., Nadzri, F. A., & Dalim, S. F. (2022). Digital Skills Framework in Higher Education. Proceedings, 82(1), 61. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082061





