A Study on Difficulties Encountered and Perception by English as Second Language (ESL) Learners in Malaysian University Examination Test (MUET) †
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Malaysian University English Test
1.2. Perception and Difficulties Encountered by Students as the Second Language Learner
2. Problem Statement
3. Purpose and Objectives of the Study
4. Research Questions
- What are the challenges faced by ESL students in MUET?
- 1.1
- Challenges in terms of readiness;
- 1.2
- Challenges in terms of knowledge in varied vocabularies;
- 1.3
- Challenges in terms of time constraints in answering questions.
- What are the perceptions of ESL learners toward MUET?
5. Significance of the Study
6. Literature Review
6.1. The Use of MUET for University Entry and Graduation Purpose
6.2. Research Related to the Scope of Study
7. Methods
7.1. Population and Sample
7.2. Instrument
7.3. Pilot Interview and Saturation of Study
7.4. Data Collection Procedure
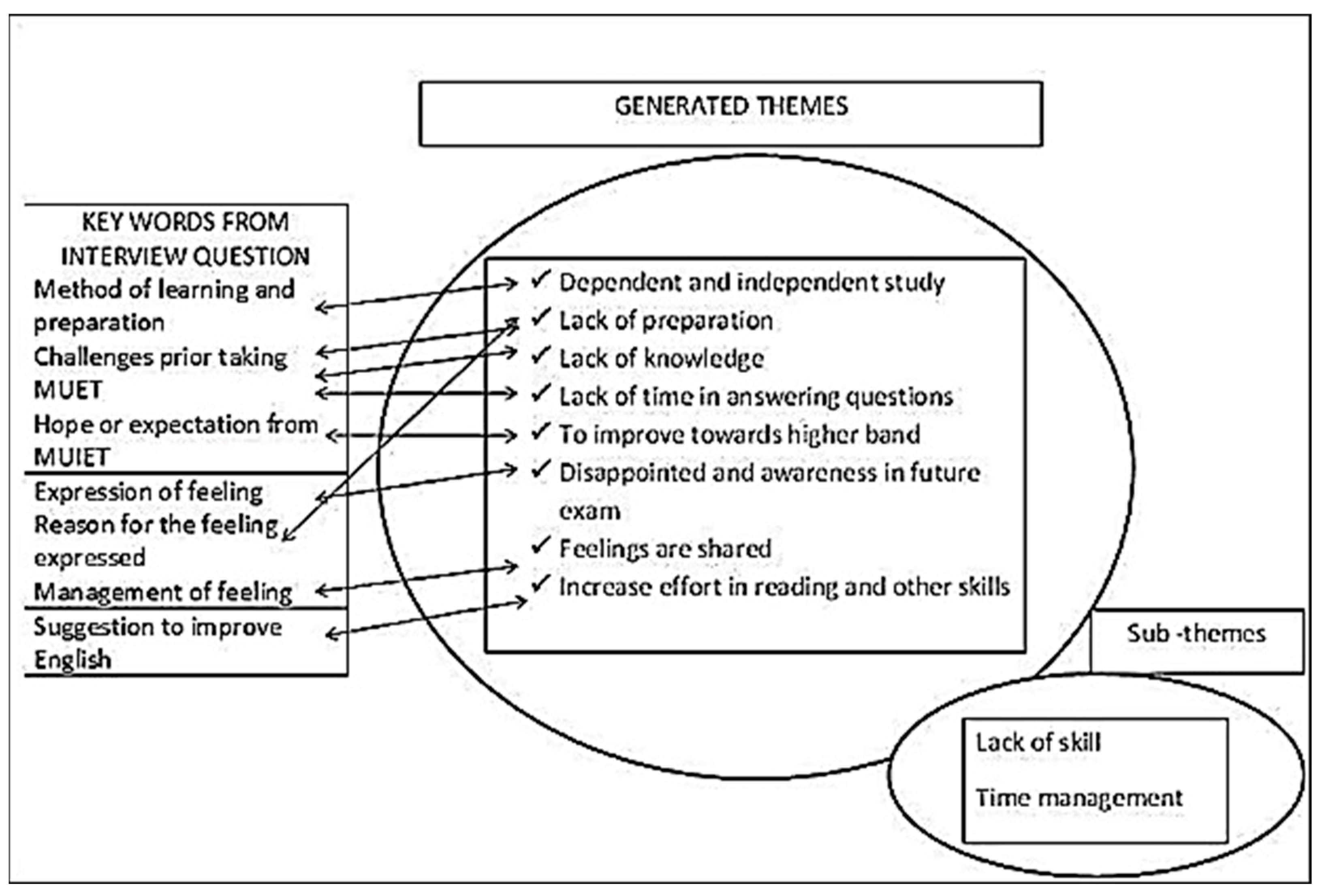
7.5. Data Analysis Procedure (DCR) Steps
7.6. Credibility and Trustworthiness
8. Result and Discussion
- Research question 1: What are the challenges faced by ESL students in MUET?
Attending class and taking notes from the internet and YouTube (some channels) that provide teaching MUET for all the skills, so I just see the format and how to prepare and do the exercises.
In terms of readiness, I think I am not ready I can’t prepare all the things and push myself to do three papers listening writing and reading.
For me I think…aaaa I have enough knowledge, but I think I don’t have quite enough knowledge, but the grammar and vocabularies don’t think to have enough knowledge because if take reading and writing I always forget the meaning of the words and also, I forget the vocabulary and grammar.
Not enough time for answering the question for reading and listening.
I can’t real the apa…aaaa the audio what the audio said sometimes it’s fast for me so I can’t catch the audio.
Reading is long passage sometimes words more too hard I don’t the passage is talking and the topic about not in Malaysia the words lah difficult to understand.
Speaking sometimes we get two times, and the duration is 2 min to get the point and to elaborate and when we lack vocabulary, we don’t know how to describe and know what to talk but we can’t talk in front of the examiner.
- Research question 2: What are the perceptions of ESL students toward MUET?
We can learn more skills and we can use them for the next life in working I hope MUET can improve my English. the expectation in terms of band I hope I can get Band 3 or four to finish my studies and my future studies.
I hope I can get a minimum of Band 3 and do well in listening because I have very bad listening skills. In the hall, I can’t hear the voice clearly and it’s too quick to catch up on what they want to say in the audio.
To get Band 3 and above.
Because to enter university I need Band 3 so I am sad because I think I can’t further study in degree.
When I see my result...yes. I feel disappointed.
Because I know I am not prepared for the exam and do not have enough time and mistakes is from me and I accept it and I know I can take it again.
Because I know I am not prepared for the exam and do not have enough time and mistakes is from me and I accept it and I know I can take it again.
The reason for sharing because between parents because later they want to know the result because they know I am taking the result. I share it with my parents and friends and the friend’s result is better than mine, so I feel disappointed.Share with my friends because they asked if they don’t ask, I will keep it to myself.
Discuss with my mom and share with mom why fail and listen to their advice and not get stressed. Other than that, I tried to correct my mistakes to overcome so I promise myself.
Mmm more reading to get a new word or new, new…more reading to get new word …more exercises to know the sentence the meaning of the sentence and more speak to others.Anything else? (interviewer)Mmm more hear a lot of English songs(No. 38: I#2)
Read articles and journals to improve my knowledge and get to know the situation in Malaysia or oversea. We can watch movies to gain knowledge from that we can hear and read subtitles so want to improve in speaking and reading especially.
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunt, A.; Beglar, D.A. Framework for developing EFL reading vocabulary. Read. For. Lang. 2005, 17, 23–59. [Google Scholar]
- The Star Online. Young and Jobless. Available online: https://www.thestar.com.my/business/business-news/2017/03/27/young-and-jobless/ (accessed on 8 January 2022).
- Maros, M.; Salehuddin, K.; Hua, T.K. Everyone People Must Have A Best Friend. Interference of Malay Structures in English Written Discourse. In Proceedings of the TLEiA Conference. Teaching and Learning of English: Towards an Asian Perspective, Penang, Malaysia, 8–20 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jalaluddin, N.H.; Norsimah, M.A.; Kesumawati, A.B. The mastery of english language among lower secondary school students in Malaysia: A linguistic analysis. Euro. J. Soc. Sci. 2008, 7, 106–119. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, S.H.; Wong, B.E. Assessing Oral Skills of Pre-tertiary Students: The Nature of the Communicative Act. In Proceedings of the International Conference on English Instruction and Assessment, Chiayi, Taiwan, 24–25 April 2004; pp. 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Malaysian Examinations Council, Regulations, Test Specifications, Test Format and Sample Questions. Available online: https://www.mpm.edu.my/en/muet/regulations-test-specifications-test-format-and-sample-questions (accessed on 22 May 2022).
- Wu, Y.W.; Chen, M.C. Writing Strategies and Writing Difficulties among College Students of Differing English Proficiency. In Proceedings of the 24th ROC-TEFL, Taipei, Taiwan, 5–6 May 2007; pp. 176–189. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, G. Beyond “Bad Writing”: Teaching English Composition to Chinese ESL Students. In Proceeding of the 44th Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication, San Diego, CA, USA, 31 March–3 April 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D. Use of standardized tests as university graduation requirement. Engl. Teach. Anseonggun 2004, 59, 251–266. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.C.; Newfields, T. Tertiary EFL proficiency graduation requirements in Taiwan: A study of washback on learning. Electron. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 2012, 9, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, R.M. High-Stakes Testing: Coping with Collateral Damage; Routledge: New York, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.C. Learner washback variability in standardized exit tests. TESL-EJ 2014, 18, n2. [Google Scholar]
- Stecher, B.M. Consequences of Large-scale, High Stakes Testing on School and Classroom Practice. In Making Sense of Test-Based Account; Hamilton, L.S., Stecher, B.M., Klein, S.P., Eds.; Rand Corporation: Santa Monica, CA, USA, 2002; pp. 79–100. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, H.Y. Stakes, Needs and Washback: An Investigation of the English Benchmark Policy for Graduation and EFL Education at Two Technological Universities in Taiwan; Unpublished. Unpublished Ph.D. Dissertation, National Taiwan Normal University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, Y. Does the university entrance examination motivate learners? A case study of learner interviews. Akita Engl. Stud. 2001, 3, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.K. Language policy in Malaysia: Reversing direction. Lang. Pol. 2005, 4, 241–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Nordin, R. A case for reconstruction of the pedagogy of the Malaysian University English Test (MUET) through thematic units instruction. J. Inst. Res. South East Asia 2006, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar]
- Othman, J.; Nordin, A.B. MUET as a predictor of academic achievement in ESL teacher education. GEMA Online J. Lang. Stud. 2013, 13, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Archvadze, E. The Problems of First Language Interference in the Process of Teaching Second Languages; Tsereteli State University: Kutaisi, GA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Che Musa, N.; Koo, L.Y.; Azman, H. Exploring English language learning and teaching in Malaysia. GEMA Online J. Lang. Stud. 2012, 12, 35–51. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshan, A.; Karimi, E. The interference of first language and second language acquisition. Theory Pract. Lang. Stud. 2015, 5, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekova, B. Language interference and methods of its overcoming in foreign language teaching. Trakia J. Scie. 2010, 8, 320–324. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, M.; Zaidi, S.M.; Mahmood, K. Self-Esteem & academic performance among university students. J. Educ. Prac. 2015, 6, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Lee, A.R. L2 learners’ anxiety, self-confidence and oral performance. In Proceedings of the 10th Conference of Pan-Pacific Association of Applied Linguistics, Edinburgh, UK, 4–5 August 2005; pp. 107–208. [Google Scholar]
- Rethinasamy, S.; Chuah, M.K. The Malaysian University English Test (MUET) and its use for placement purposes: A predictive validity study. Electron. J. Foreign Lang. Teach. 2011, 8, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yunus, M.; Chien, H.C. The use of mind mapping strategy in Malaysian University English Test (MUET) Writing. Creat. Educ. 2016, 7, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crouch, M.; McKenzie, H. The logic of small samples in interview-based qualitative research. Soc. Sci. Inform. 2006, 45, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W. Educational Research: Planning, Conducting and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research; Pearson: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Patton, M.Q. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Montoya, M. Preparing for interview research: The interview protocol refinement framework. Qual. Rep. 2016, 21, 811–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.A.; Schattner, P.; Mazza, D. Doing a pilot study: Why is it essential? Malays. Fam. Physician 2006, 1, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Charmaz, K. Constructing Grounded Theory: A Practical Guide through Qualitative Analysis; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Seidman, I. Interviewing as Qualitative Research: A Guide Researchers in Education and the Social Sciences, 4th ed.; Teachers College Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Merriam, S.B.; Tisdell, E.J. Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation, 4th ed.; Jossey-Bass: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bazeley, P. Analysing qualitative data: More than ‘identifying themes’. Malay. J. Qual. Res. 2009, 2, 6–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, N. Investigating the Washback Effect of the MUET as a University Entry Test on Students in Malaysia. Doctoral Dissertation, University of York, York, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kuen, Y.L.; Embi, M.A. MUET preparation language learning strategies. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2012, 3, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abdul Rahim, H.; Hayazi, M.Y. Penggunaan Alat Bantu Mengajar (ABM) Di Kalangan Guru- Guru Teknikal Di Sekolah Menengah Teknik Daerah Johor Bahru, Johor; Universiti Teknologi Malaysia: Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
| (Total Number of Agreements/Total Number of Responses) × 100% | |
|---|---|
| Inter-rater 1: | (8/9) × 100 = 88% |
| Inter-rater 2: | (8/9) × 100 = 88% |
| Average: | (16/18) × 100 = 88% |
| Research Questions | Interview Questions | Major Themes |
|---|---|---|
| Research Question: 1: What Are The Challenges Faced By The ESL Students in MUET? |
|
|
| ||
| Research Question 2: What Are the Perceptions by The Esl Students Toward Muet? |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karnine, S.M.B.B.V.K.S.V.; Preece, A.S.D.; Ahmad, I.B.S.; Muhammad, S.S.B. A Study on Difficulties Encountered and Perception by English as Second Language (ESL) Learners in Malaysian University Examination Test (MUET). Proceedings 2022, 82, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082053
Karnine SMBBVKSV, Preece ASD, Ahmad IBS, Muhammad SSB. A Study on Difficulties Encountered and Perception by English as Second Language (ESL) Learners in Malaysian University Examination Test (MUET). Proceedings. 2022; 82(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082053
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarnine, Seeni Mehraj Begam Bt V. K. S. Vyzul, Abdul Shakour Duncan Preece, Ismail Bin Sheikh Ahmad, and Siti Salmiah Binti Muhammad. 2022. "A Study on Difficulties Encountered and Perception by English as Second Language (ESL) Learners in Malaysian University Examination Test (MUET)" Proceedings 82, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082053
APA StyleKarnine, S. M. B. B. V. K. S. V., Preece, A. S. D., Ahmad, I. B. S., & Muhammad, S. S. B. (2022). A Study on Difficulties Encountered and Perception by English as Second Language (ESL) Learners in Malaysian University Examination Test (MUET). Proceedings, 82(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2022082053






