Improved Dissolution Rate of Oxcarbazepine by Centrifugal Spinning: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Implications †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
2.1. Material
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Preparation of Microfiber
2.2.2. Percentage Yield Calculation
2.3. Determination of Drug Content and Entrapment Efficiency of Microfibers
2.4. Disintegration Time
2.5. Morphology
2.6. X-ray Diffraction Studies
2.7. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
2.8. Thermal Characterization Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.9. In Vitro Dissolution Studies
2.10. Preparation and Characterization of Suitable Dosage Form
2.11. In Vivo Dissolution Studies (Salivary Method)
2.12. In Vivo/Pharmacokinetic Studies
2.13. Stability Studies (Aged Sample)
3. Results
3.1. Percentage Yield, Drug Loading and Disintegration Time
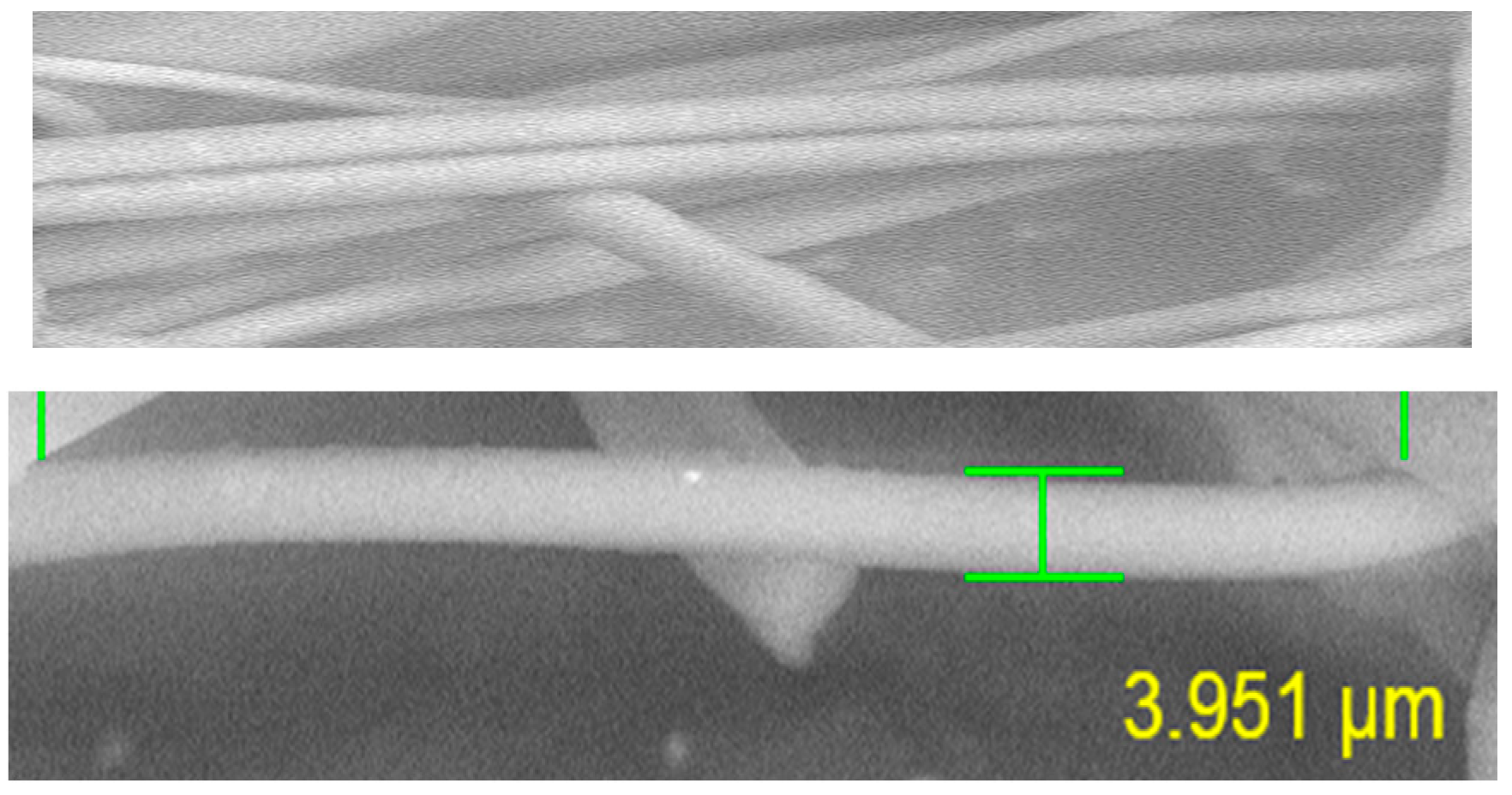
3.2. Morphology
3.3. In Vitro Dissolution Rate Studies
3.4. X-ray Diffraction
3.5. ATR-FTIR Spectrophotometry
3.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.7. Characterization of Tablet Dosage Form
3.8. In Vivo Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OXC | Oxcarbazepine |
| BCS | Biopharmaceutical classification system |
| API | Active pharmaceutical ingredient |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| USP | United states Pharmacopeia |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| DSC | Differential scanning calorimeter |
| CS | Centrifugal spinning |
| PVA | Poly vinyl alcohol |
| PVP | Poly vinyl pyrrolidone |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| DLE | Drug loading efficiency |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| tmax, | Time to reach maximum concentration |
| Cmax | Maximum concentration |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| CMS | Centrifugal melt spinning |
References
- De Mohac, L.M.; Keating, A.V.; Pina, M.D.F.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T. Engineering of Nanofibrous Amorphous and Crystalline Solid Dispersions for Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, P.; Sebe, I.; Stiedl, B.; Kállai-Szabó, B.; Zelkó, R. Tracking of crystalline-amorphous transition of carvedilol in rotary spun microfibers and their formulation to orodispersible tablets for in vitro dissolution enhancement. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2015, 115, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dahan, A.; Miller, J.M.; Amidon, G.L. Prediction of Solubility and Permeability Class Membership: Provisional BCS Classification of the World’s Top Oral Drugs. AAPS J. 2009, 11, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, N.K.; Bhattacharya, A.; Pushkar, S.; Mishra, A. Biopharmaceutical classification system: A strategic tool for oral drug delivery technology. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 3, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Patel, N.; Lin, S. Solubility and dissolution enhancement strategies: Current understanding and recent trends. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marano, S.; Barker, S.A.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Missaghi, S.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Craig, D.Q. Development of micro-fibrous solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drugs in sucrose using temperature-controlled centrifugal spinning. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 103, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, P.-C.; Khetarpal, V.K.; Cariola, C.M.; Rowlings, C.E. Formulation studies of a poorly water-soluble drug in solid dispersions to improve bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 118, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, R.Y.; Zhang, G.Z.; Zhang, H.C.; Qu, J.-P. Recent Advances in Centrifugal Spinning Preparation of Nanofibers. J. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1015, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Centrifugal Spinning: An Alternative Approach to Fabricate Nanofibers at High Speed and Low Cost. Polym. Rev. 2014, 54, 677–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghoraibi, I.; AlOmari, S. Different Methods for Nanofiber Design and Fabrication; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Zhou, Y.; Shan, W.-G.; Shen, J. Mechanistic study on rapid fabrication of fibrous films via centrifugal melt spinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Yang, B. Highly porous fibers prepared by centrifugal spinning. Mater. Des. 2017, 114, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almetwally, A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; Elshakankery, M.; Kasem, M.H. Technology of nano-fibers: Production techniques and properties—Critical review. J. Text. Assoc. 2017, 78, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kanawung, K.; Panitchanapan, K.; Puangmalee, S.-O.; Utok, W.; Kreua-Ongarjnukool, N.; Rangkupan, R.; Meechaisue, C.; Supaphol, P. Preparation and Characterization of Polycaprolactone/Diclofenac Sodium and Poly(vinyl alcohol)/Tetracycline Hydrochloride Fiber Mats and Their Release of the Model Drugs. Polym. J. 2007, 39, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, H.; Liu, T.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Electrospinning of ibuprofen-loaded composite nanofibers for improving the performances of transdermal patches. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 13, 3855–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samprasit, W.; Akkaramongkolporn, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Rojanarata, T.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Opanasopit, P. Fast releasing oral electrospun PVP/CD nanofiber mats of taste-masked meloxicam. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 487, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasekh, M.; Karavasili, C.; Soong, Y.L.; Bouropoulos, N.; Morris, M.; Armitage, D.; Li, X.; Fatouros, D.G.; Ahmad, Z. Electro spun PVP-indomethacin constituents for transdermal dressings and drug delivery devices. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illangakoon, U.E.; Gill, H.; Shearman, G.C.; Parhizkar, M.; Mahalingam, S.; Chatterton, N.P.; Williams, G.R. Fast dissolving paracetamol/caffeine nanofibers prepared by electrospinning. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zheng, N.; Wang, X.; Ivone, R.; Shan, W.-G.; Shen, J. Rapid Preparation of Spherical Granules via the Melt Centrifugal Atomization Technique. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Craig, D. Recent developments in micro- and nanofabrication techniques for the preparation of amorphous pharmaceutical dosage forms. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Elger, C.E. Oxcarbazepine (Trileptal). An effective and well tolerated new drug as first choice in treatment of focal seizures. Der Nervenarzt 2000, 71, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, S.; Barker, S.A.; Raimi-Abraham, B.T.; Missaghi, S.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A.; Aliev, A.E.; Craig, D.Q.M. Microfibrous Solid Dispersions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs Produced via Centrifugal Spinning: Unexpected Dissolution Behavior on Recrystallization. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1666–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douroumis, D.; Fahr, A. Enhanced dissolution of Oxcarbazepine microcrystals using a static mixer process. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 59, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusban, F.; Perrie, Y.; Mohammed, A.R. Formulation of multiarticulate systems as lyophilized orally disintegrating tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, P.; De Marco, I. The Use of Poly(N-vinyl pyrrolidone) in the Delivery of Drugs: A Review. Polymers 2020, 12, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattama Donghuntong, N.S. Wanchai Chongcharoen, effect of saccharides on the structural integrity of centrifugal spinning sucrose fiber. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 2018, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Muzaffar, K. Nayik, G.A.; Kumar, P. Stickiness Problem Associated with Spray Drying of Sugar and Acid Rich Foods: A Mini Review. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015, 2015, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ashok Kumar, S.; Ansari, M.Z.A.; Manjunatham, K.G.; Murtuza, S.A. An experimental study on viscosity of water soluble polymers used in pre compressed pressboards insulation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
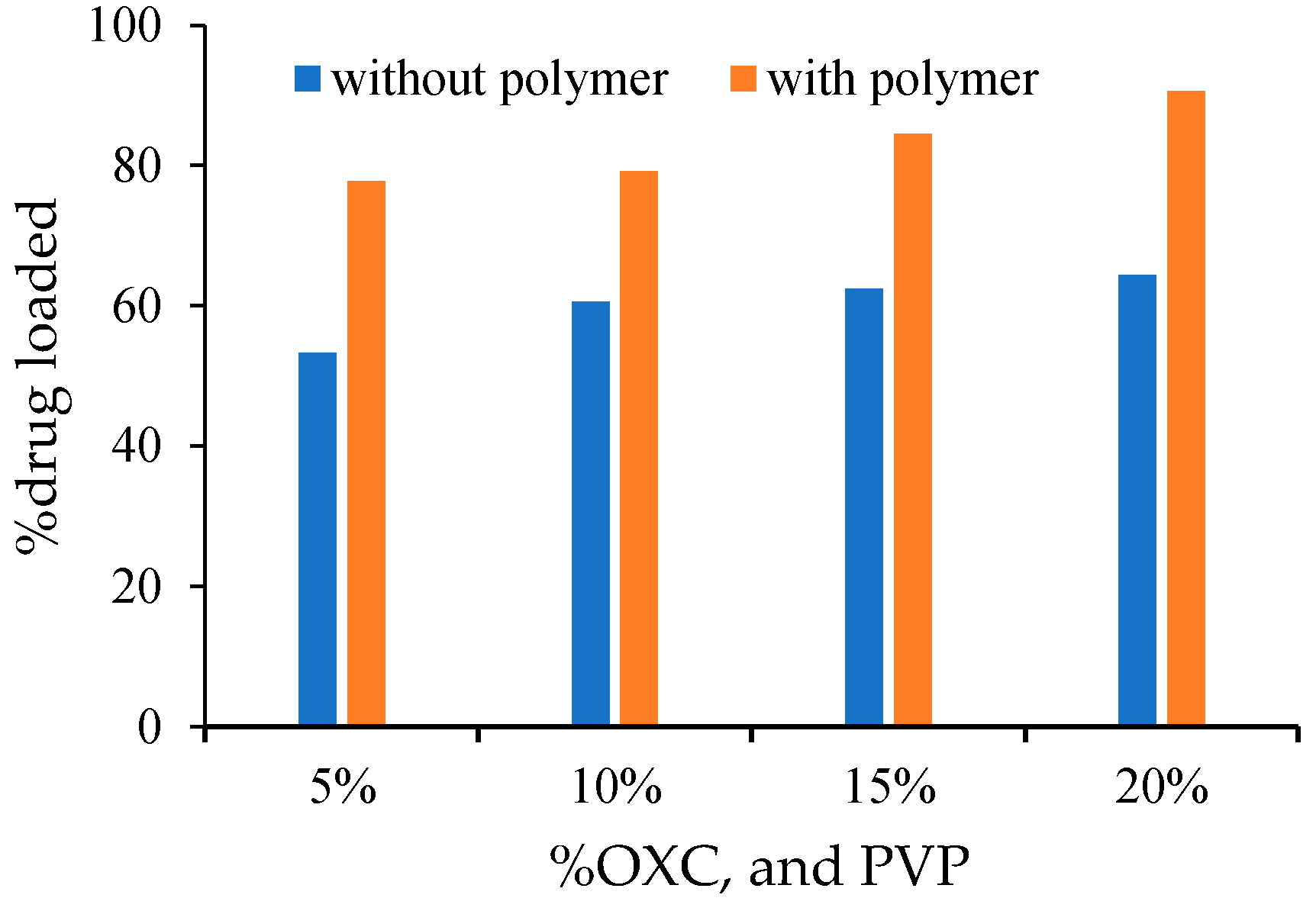



| Formulation | OXC % | Sucrose % | Polymer | %Age Yield | %Age OXC Loaded |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank | 0 | 100 | 0 | 92 | |
| DS5 | 5 | 95 | 0 | 54 | 53.2 |
| DS10 | 10 | 90 | 0 | 51 | 60.6 |
| DS15 | 15 | 85 | 0 | 44.2 | 62 |
| DS20 | 20 | 80 | 00 | 37.8 | 63.8 |
| DS30 | 30 | 70 | 0 | 18 | 34.2 |
| DSP5 | 20 | 75 | 5 | 74 | 77.72 |
| DSP10 | 20 | 70 | 10 | 78 | 79.17 |
| DSP15 | 20 | 65 | 15 | 80 | 84.52 |
| DSP20 | 20 | 60 | 20 | 88 | 90.60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, A.; Nasir, S.; Hussain, F.; Abbas, N.; Bukhari, N.I.; Arshad, M.S.; Mudassir, J.; Latif, S.; Ali, A. Improved Dissolution Rate of Oxcarbazepine by Centrifugal Spinning: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Implications. Proceedings 2021, 78, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08702
Hussain A, Nasir S, Hussain F, Abbas N, Bukhari NI, Arshad MS, Mudassir J, Latif S, Ali A. Improved Dissolution Rate of Oxcarbazepine by Centrifugal Spinning: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Implications. Proceedings. 2021; 78(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08702
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Amjad, Sidra Nasir, Fahad Hussain, Nasir Abbas, Nadeem Irfan Bukhari, Muhammad Sohail Arshad, Jahanzeb Mudassir, Sumera Latif, and Abid Ali. 2021. "Improved Dissolution Rate of Oxcarbazepine by Centrifugal Spinning: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Implications" Proceedings 78, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08702
APA StyleHussain, A., Nasir, S., Hussain, F., Abbas, N., Bukhari, N. I., Arshad, M. S., Mudassir, J., Latif, S., & Ali, A. (2021). Improved Dissolution Rate of Oxcarbazepine by Centrifugal Spinning: In-Vitro and In-Vivo Implications. Proceedings, 78(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECP2020-08702





