Translational Research in Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Cell Therapy †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Day 1 Lectures
2.1. Prenatal Diagnosis and Intrauterine Assessment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr. Suresh, MediScan System, Chennai
- Overlapping phenotypic features
- Lack of precise molecular diagnosis of many diseases
- Variability in the manifestation of skeletal findings
- Lack of a systematic approach
- The inability of the ultrasound to provide an integrated view.
2.2. Radiological Assessment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Basilar Impression
Dr Sridhar Gibikote, Professor and Head, Department of Radiology Christian Medical College, Vellore
- Ø Category I—Thin and gracile bones
- Ø Category II—Short and thick limbs
- Ø Category III—Cystic changes
2.3. Osteogenesis Imperfecta—A Combined Phenomic and Genomic Approach
Dr. David Sillence, Genetic Medicine, Children’s Hospital, Westmead, Australia
2.4. Molecular Diagnosis and Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr. Hitesh Shah, Pediatric Orthopedics, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal
2.5. Current Surgical Management of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr. James Fernandez, Sheffield Children’s Hospital, United Kingdom
2.6. Clinical Assessment and Management of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr. Eva Åström Astrid Lindgren Children’s Hospital at Karolinska University Hospital and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
2.7. Medical Management of OI: Action of Bisphosphonate Treatment
Dr. Eva Åström, Astrid Lindgren Children’s Hospital at Karolinska University Hospital and Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden
2.8. Update on Therapy of Osteogenesis Imperfecta 2019
Dr. David Sillence, Genetic Medicine, Children’s Hospital, Westmead, Australia
2.9. Quality of Life in Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr Claire Hill, Physiotherapist, Sheffield Children’s Hospital, United Kingdom
2.10. Importance of Physiotherapy in the Treatment of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr Claire Hill Physiotherapist, Sheffield Children’s Hospital, United Kingdom
2.11. Fetal Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr Cecilia Götherström, Department of Clinical Science, Intervention & Technology Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
2.12. The Long and Winding Road to Cell Therapy for Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr Edwin M. Horwitz, Professor of Pediatrics, Co-Director, Center for Pediatric Cellular Therapies, Member, Immunology and Molecular Pathogenesis Program, Emory University
2.13. BOOST TO BRITTLE BONES—A Collaborative Project between CMC Vellore and Karolinska University
Dr Vrisha Madhuri, Pediatric Orthopedics Department, Christian Medical College and Hospital, Vellore India
2.14. Role of DEXA in Osteogenesis Imperfecta Assessment
Dr Thomas V. Paul, Department of Endocrinology, CMC Vellore
3. Day 2 Lectures: Regulatory and Ethical Aspects of Cell Therapy Clinical Trials
3.1. The Need for Dialogue—Between Regulators, Investigators, and Industry
Prof. Alok Srivastava, Head, Center for Stem Cell Research, CMC Vellore
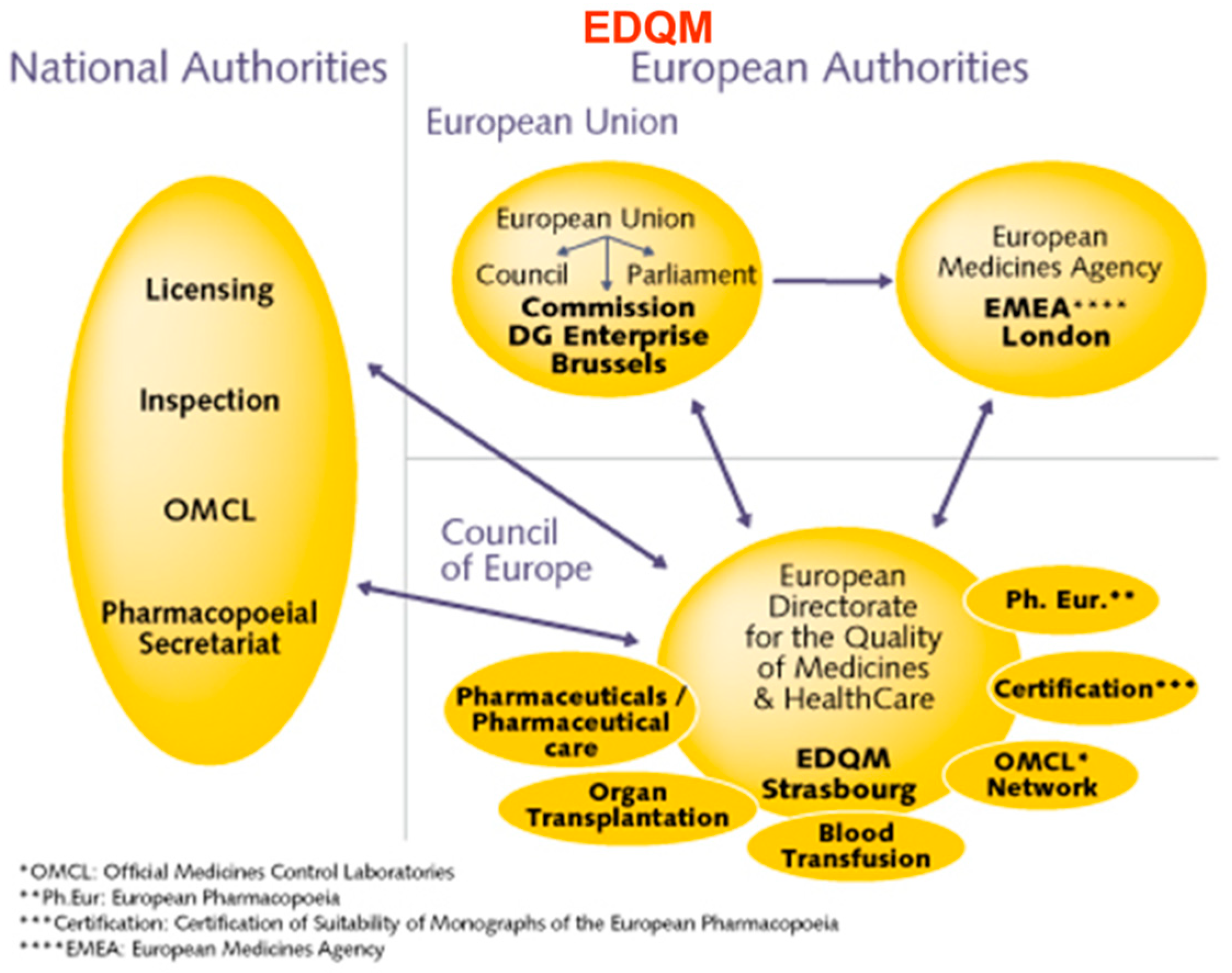
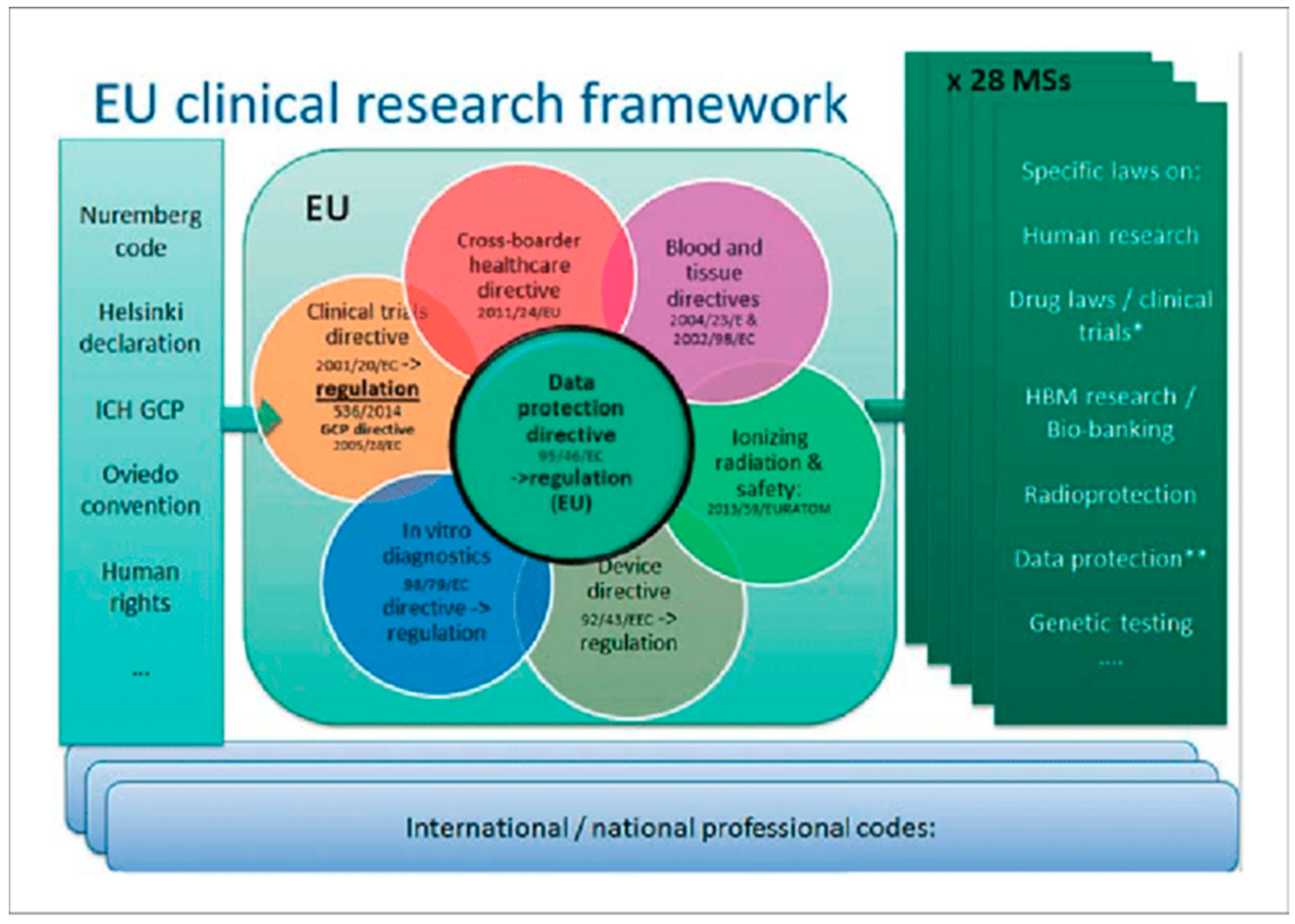
3.2. Current Challenges in the Regulation of Production and Distribution of Innovative Cell Therapy Products in Europe
Dr. Gudmund Hedenskog, QP, Vecura, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
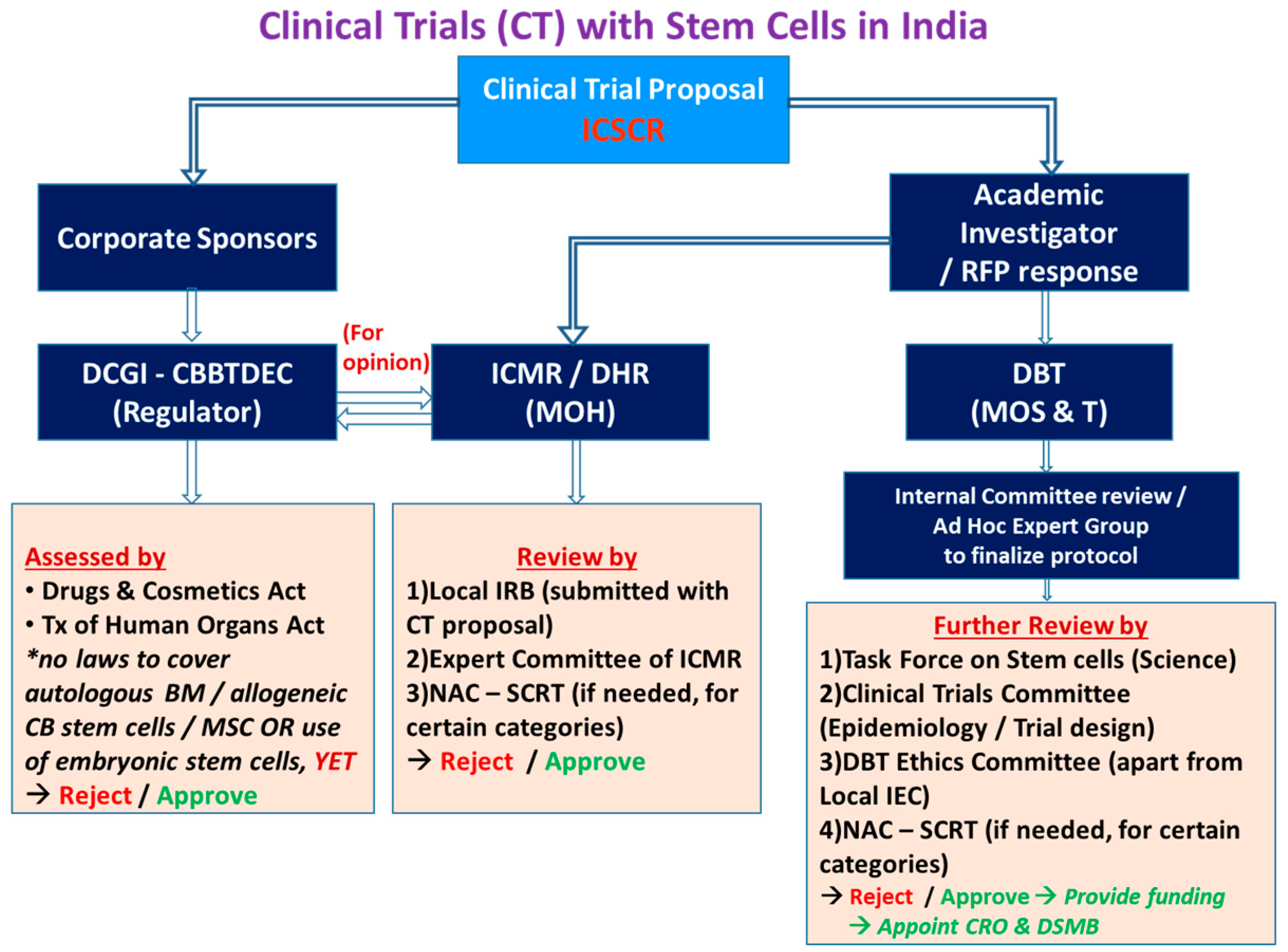
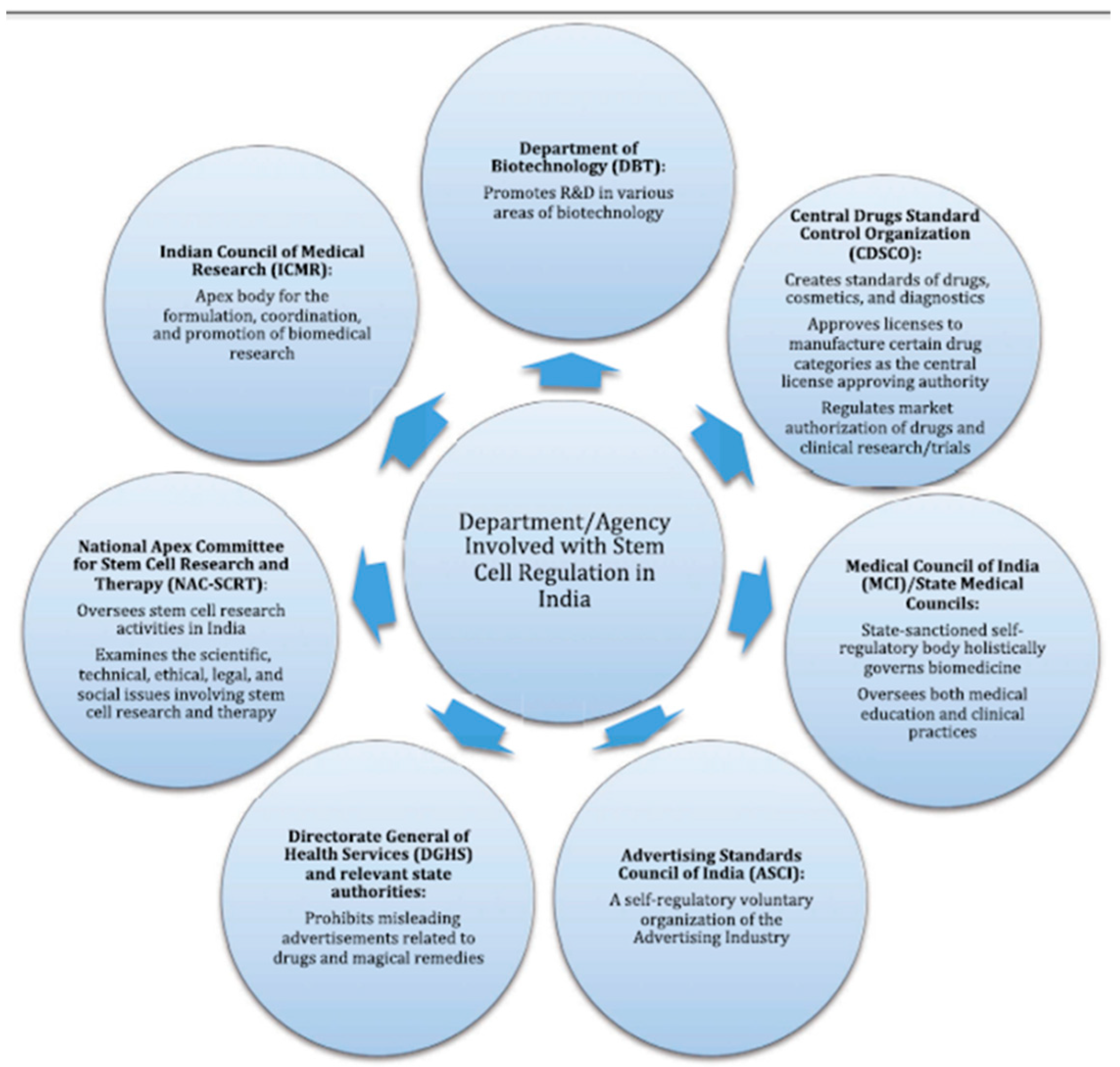
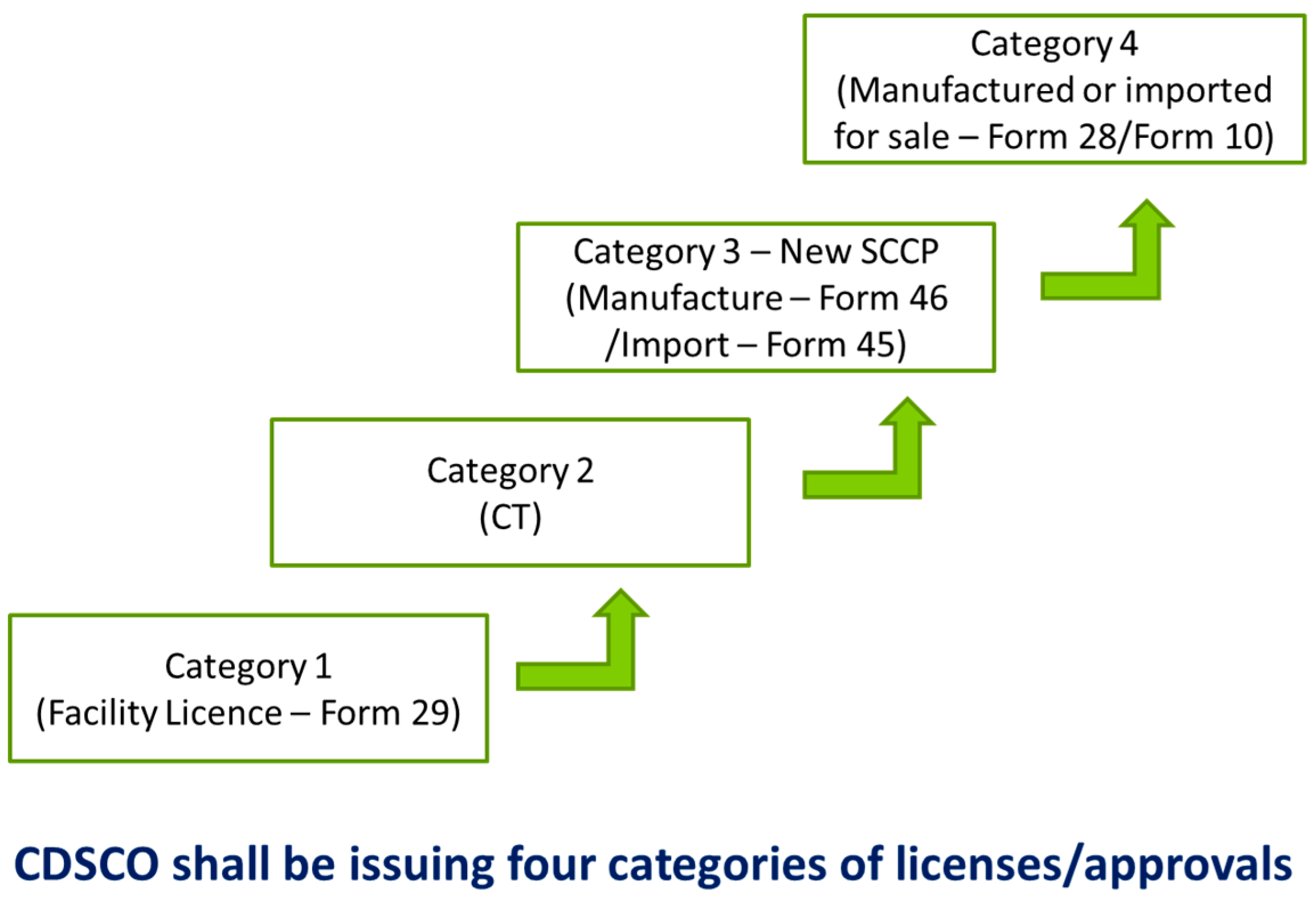
3.3. Cell Therapy—Regulatory Changes in India’s Landscape: Emerging Concepts
Dr Velu Nair, Lt Gen, Hemato-Oncology & Bone Marrow Transplant, Comprehensive Blood & Cancer Center (CBCC), India
3.4. Regulation of Cell-Based Therapies: Commercial Perspective (India)
Dr. Pawan Gupta, Stempeutics, Bangalore
3.5. Regulation of ATMPs in Europe
Vera Franzen, Regulatory Affairs Consultant at Vera Franzén Consulting AB
3.6. Manufacture and Quality Assurance of Stem Cell Products
Dr. Lilian Walther-Jallow, Department of Clinical Science, Intervention & Technology Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
3.7. Reconstitution of Cell Therapy Products
Annika Goos, Department of Clinical Science, Intervention & Technology, Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
3.8. Putting the Cell into Cell Therapy
Dr Edwin M Horowitz, Emory University, USA
3.9. Regulatory Requirements to Conduct a New Cell-Scaffold Product Clinical Trial in India: Challenges and Implementation.
Dr Annie John, Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute of Medical Sciences, Kerala
3.10. Fetal Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Dr Cecilia Götherström, Department of Clinical Science, Intervention & Technology Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
3.11. Conduct of Cell/Cell Scaffold Clinical Trials: Roadblocks and Challenges
Dr. Vrisha Madhuri, Prof. Pediatric Orthopedics, Adjunct Scientist, CSCR, CMC Vellore
3.12. Clinical Concerns (GCP) and Regulatory Strategies for Implementation: European Standards
Lilian Walther- Jallow, Department of Clinical Science, Intervention & Technology Karolinska Institutet, Sweden
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
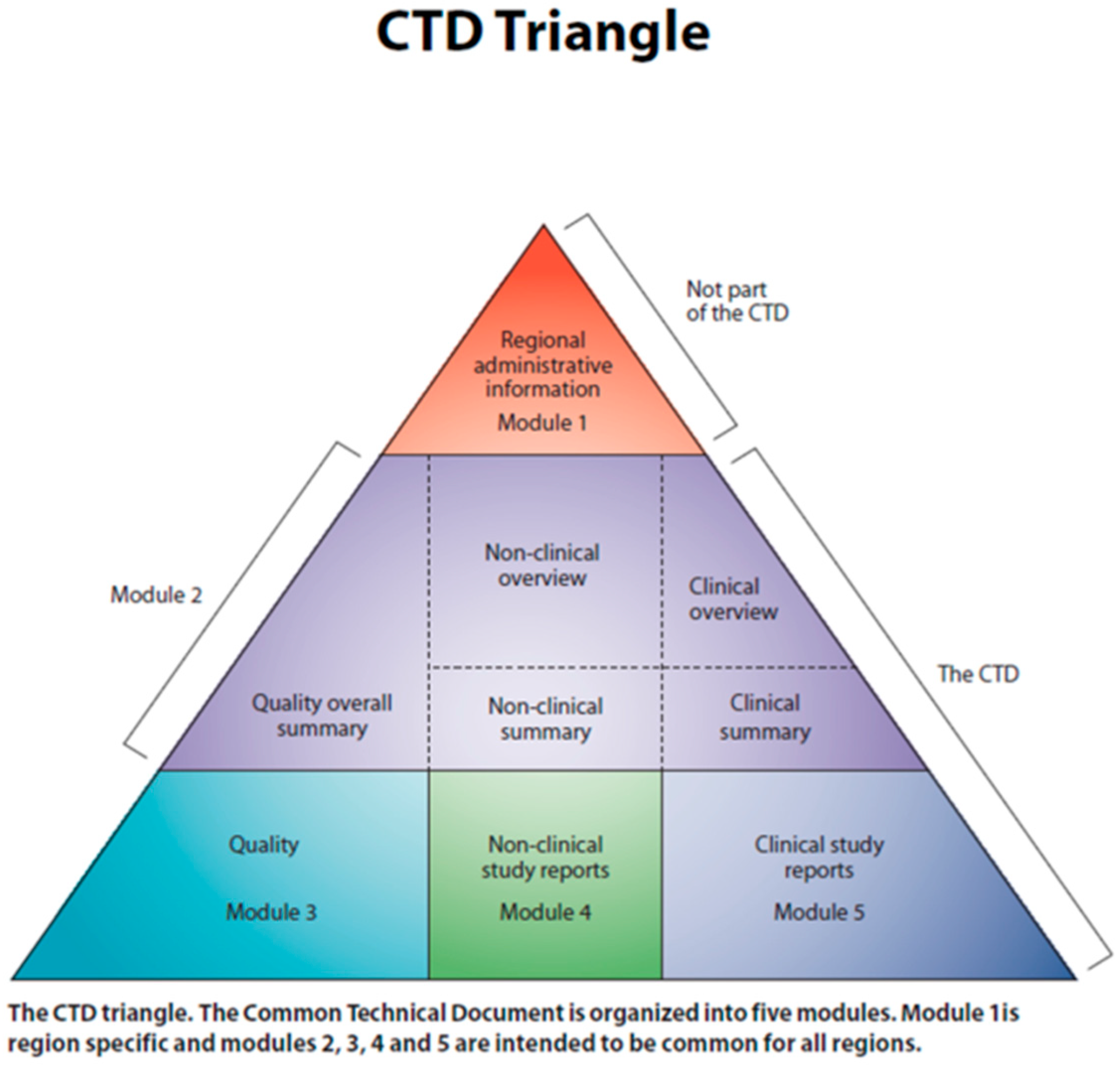
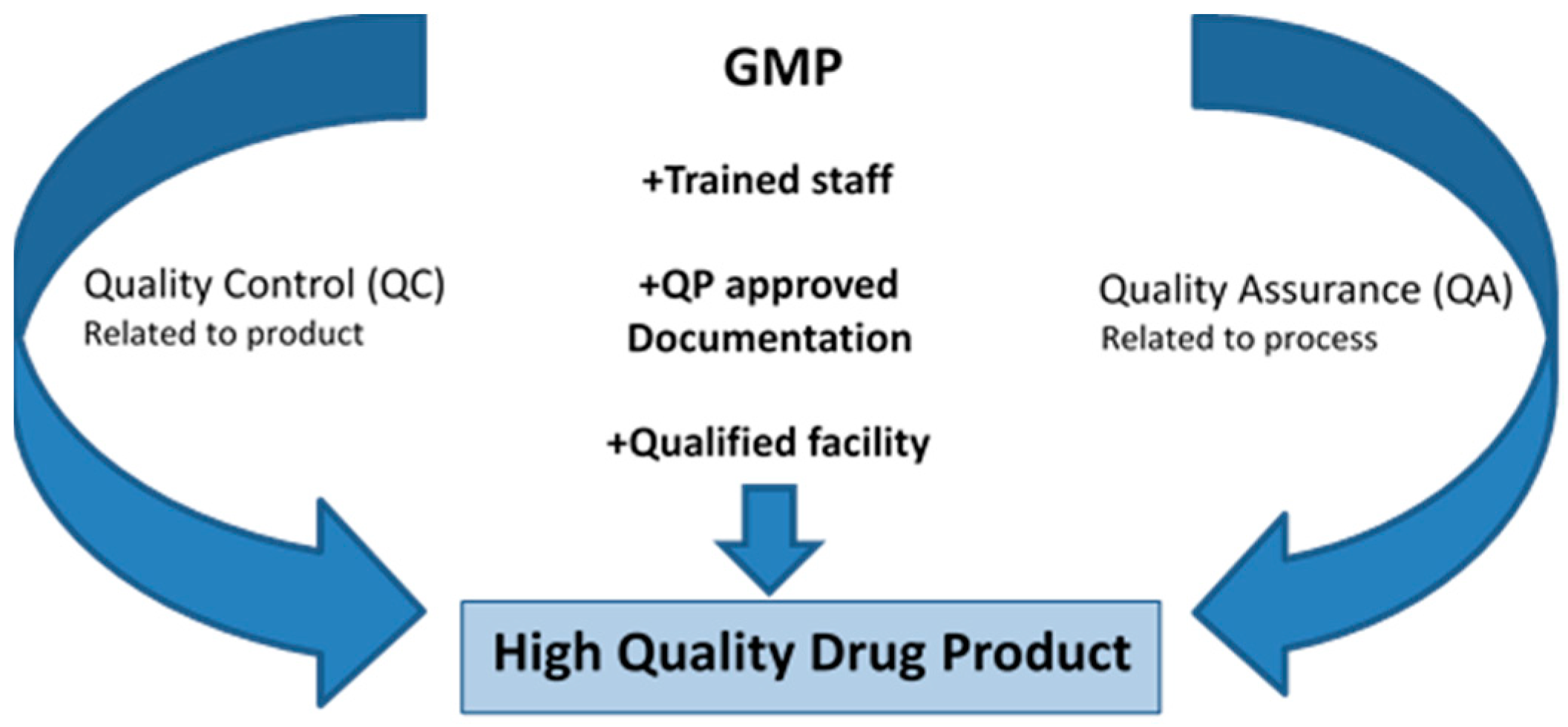
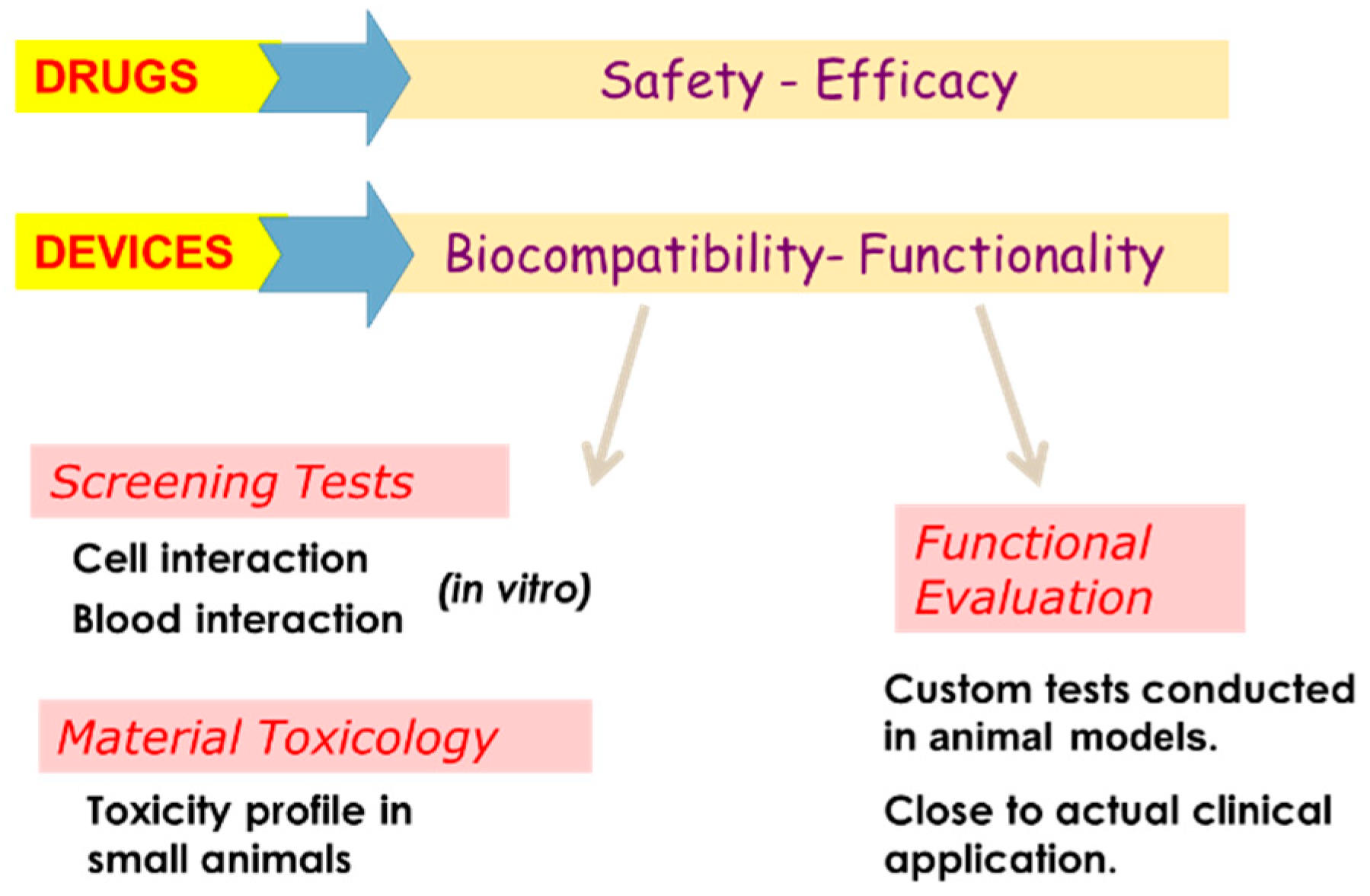
| Syndrome Name | Equivalent Numerical Type | Subtypes |
|---|---|---|
| Classic Non-deforming OI (with Blue Sclerae) | 1 | 2 |
| Common variable OI (with normal sclerae) | 4 | 10 |
| OI with calcification in interosseous membranes | 5 | 1 |
| Progressively Deforming OI with normal sclerae | 3 | 18 |
| Perinatally Lethal OI | 2 | 5 |
| Modes of Inheritance | Number |
|---|---|
| Autosomal Dominant | 4(+3) |
| Autosomal Recessive | 16 |
| X-linked | 2 |
| Mosaicism (Somatic plus germinal cell) | - |
| Chromosomal microdeletion- Includes 7q, 17q, Tetrasomy 9p | A number reported |
| Polygenic | Unknown but likely |
| Type of Mutation | Genomic Sequence Variants |
|---|---|
| Nonsense | Premature stop codons |
| Missense | Single nucleotide substitutions |
| Splicing mutations | In-frame and frameshift deletions |
| Insertions/deletions | Frameshift or in-frame sequence variation |
| Gene | Protein | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Genes encoding Type 1 collagens and post translational modifications | ||
| COL1A1 | Collagen 1 alpha 1 chain | Structural polypeptide |
| COL1A2 | Collagen 1 alpha 2 chain | Structural polypeptide |
| CRTAP | Cartilage associated protein | Prolyl 3—hydrolation |
| LEPRE1 | Leucine proline-enriched proteoglycan (leprecan) 1 | Prolyl 3’- hydrolation |
| PPIB | Peptidylprolyl isomerase B | Prolyl 3’- hydrolation |
| P4HB | Prolyl 4-hydrolase, beta-subunit Procollagen lysyl hydrolase 2 | Prolyl 4’- hydrolation Lysylhydrolation |
| PLOD2 | ||
| SERPINH1 | Serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade H, member 1 | Collagen specific ER chaperone (Colligin/HSP) |
| SERPINF1 | Serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade F, member 1 | PEDF involved in osteoblast/osteoclast homeostasis |
| FKBP10 | FK506 binding protein 10 | Type I procollagen chaperone C terminal cleavage, Type I procollagens |
| BMP1 | Bone morphogenetic protein 1 | Calcium flux in ER disturbs collagen folding |
| TMEM38B | Transmembrane protein 38B/TRIC | |
| Genes encoding transcriptional regulator | ||
| CREB3L1 | OASIS | Unfolded Protein Response |
| MBTPS2 | Membrane-bound transcription factor peptidase, Site-2 | Regulated intra-membrane proteolysis |
| FAM46A | Family with sequence similarity, Member A | Nucleotidyltransferase fold protein |
| Genes encoding signaling processes | ||
| LRP5 | LDL-receptor related protein 5 | WNT-β-catenin signalling pathway |
| WNT-1 | Wingless-type MMTV integration site family, member 1 | WNT-β-catenin signalling pathway |
| Genes encoding processes of Osteogenesis | ||
| PLS3 | Plastin 3 | Bone Cell migration |
| IFITM5 | Interferon-Induced-Transmembrane protein 5 | Modulator of bone formation Osteoblast specific transcription factor |
| SP7/OSX | SP7 transcription factor (Osterix) | |
| Genes encoding matrix proteins or modifications | ||
| XYLT2 | Xylosyltransferase 2 | Tetrasaccharide linkage to proteoglycan core proteins |
| SEC24D | SEC24-related gene family, member D | Component of COP II machinery and transport of proteins through ER |
| SPARC | Secreted protein, Acidic, Cysteine-Rich | Osteonectin |
| Disorder—Gene | Mode of Inheritance | MIM of Condition | Gene Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| OI type 1—COLIA1 | AD | 16200 | Collagen alpha 1 (I) |
| 166240 | |||
| OI type 1—COLIA2 | AD | 166200 | Collagen alpha 2 (I) |
| 166240 |
| Disorder—Gene | Mode of Inheritance | MIM of Condition |
|---|---|---|
| OI type 4—COLIA1 | AD | 166220 |
| OI type 4—COLIA2 | AD | 166220 |
| OI type 4—WNT1 | AD | 615220 |
| OI type 4—CRTAP | AR | 610854 |
| OI type 4—PPIB | AR | 259440 |
| OI type 4—SP7 | AR | 606633 |
| OI type 4—PLOD2 | AR | 609220 |
| OI type 4—FKBP10 | AR | 610968 |
| OI type 4—PLS3 | XL | 300912 |
| OI type 4—MBTPS2 | XL | 605927 |
| Disorder—Gene | OMIM | Mode of Inheritance | MIM of Condition | Gene Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OI type 2—COL1A1 | AD | 166210 | Collagen alpha 1(I) | |
| OI type 2—COL1A2 | AD, AR | 166210, 259400 | Collagen alpha 2(I) | |
| OI type 2—CRTAP | VII | AR | 610854 | Cartilage- associated protein |
| OI type 2—P3H1/LEPRE 1 | VIII | AR | 610915 | Prolyl-3 hydroxyl/LEPRE1 |
| OI type 2—PIPB | IX | AR | 259440 | Cyclophilin B |
| Disorder—Gene | OMIM | Mode of Inheritance | MIM of Condition | Orphanet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OI type 3—COLIA1 | III | AD, AR | 259420 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—COLIA2 | VI | AD, AR | 216812 | |
| OI type 3—SEPINF1 | VII | AR | 613982 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—CRTAP | VIII | AR | 610682 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—P3H1/LEPRE1 | IX | AR | 610915 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—PIPB | X | AR | 259440 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—SERPINH1 | XI | AR | 613848 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—FKBP10 | XII | AR | 610968 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—SP7/OSX | XIII | AR | 606633 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—TMEM38B | XIV | AR | 615066 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—BMP1 | XV | AR | 112264 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—WNT1 | XVI | AD, AR | 615220 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—CREB3L1 | XVII | AR | 616229 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—SPARC | XVIII | AR | 616507 | 216812 |
| OI type 3—FAM24A | AR | 617952 | 216812 | |
| OI type 3—PLOD2 * | AR | 609220 | 216812 | |
| OI type 3—MBTPS2 | XLR | 300294 | 216820 | |
| OI type 3—SEC24D ** | AR | 616294 | 216812 |
| Disorder—Gene | Mode of Inheritance | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis X-linked | XL | PLS3 |
| Osteoporosis X-linked | XL | MBTPS2 |
| Osteoporosis—Autosomal dominant | AD | WNT1 |
| Osteoporosis—autosomal dominant | AD | LRP5 |
| Osteoporosis—pseudoglioma | AR | LRP5 |
| Osteoporosis, cataracts, and retinal dysplasia (spondylo-ocular) | AR | XYLT2 |
| OI with congenital joint contractures type 1(Bruck syndrome) | AR | FKBP10 |
| OI with congenital joint contractures type 2(Bruck syndrome) | AR | PLOD2 |
| Osteoporosis with radiolucent lesions of the mandible—Gnathodiaphyseal Dysplasia | AD | ANO5 |
| Osteogenesis Imperfecta with craniosynostosis (Cole–Carpenter) | AD | P4HB |
| Osteogenesis Imperfecta with craniosynostosis (Cole–Carpenter Like) | AR | SEC24D |
| Singleton–Merten syndrome type 1 | AD | IFIH1 |
| Singleton–Merten syndrome type 2 | AD | DDX58 |
| Short Stature, Bone fragility, DD and Immunodeficiency | AR | NBAS * |
| OI Type | INCDS 2014 | Genes | Mutations |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 1 | COL1A1, COL1A2 COL1A1, COL1A2, CRTAP, LEPRE1, PPIB COL1A1, COL1A2, CRTAP, LEPRE1, PPIB, FKBP10, SERPINF1, SERPINH1, SP7/OSX, BMP1, TMEM38B, WNT1, CREB3L1, SPARC, PLOD2, P4HB, SEC24D COL1A1, COL1A2, WNT1, CRTAP, PPIB, SP7, PLOD2, FKBP10, PLS3, MBTPS2 IFITM5 SERPINF1 CRTAP LEPRE1 PPIB SERPINH1 FKBP10 SP7/OSX TMEM38B BMP1 WNT1 CREB3L1 SPARC FAM46A PLOD2 P4HB SEC24D PLS3 MBTPS2 LRP5 XYLT2 | Nonsense, frameshift, split-site Missense, multiexon deletion Various Various. Normally these are gly Insertion cryptic initiationSite:- c.-14C>T Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various AR Various, both heterozygous and homozygous Various AR Various AR AR Various AR Heterozygous AR X-Linked hemizygous, and heterozygous X-Linked hemizygous AR (but AD gain of function) AR (usually Spondylo-ocular) |
| II | 2 | ||
| III | 3 | ||
| IV | 4 | ||
| V | 5 | ||
| VI | 6 | ||
| VII | 7 | ||
| VIII | 8 | ||
| IX | 9 | ||
| X | 10 | ||
| XI | 11 | ||
| XII | 12 | ||
| XIII | 13 | ||
| XIV | 14 | ||
| XV | 15 | ||
| XVI | 16 | ||
| XVII | 17 | ||
| XVIII | 18 |
| Disorder | Mode of Inheritance | Gene | Gene Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Progeria (Hutchinson-Gilford) | AD | LMNA | Lamin A/C |
| Mandibulo-Acral Dysplasia A | AR | LMNA | Lamin A/C |
| Mandibulo-Acral Dysplasia B | AR | ZMPSTE24 | Zinc metalloproteinase2 |
| Wrinkly skin syndrome | AR | ATP6VOA2 | H+ ATPase |
| Gerodermaosteodysplasticum | AR | GORAB | GORAB |
| Cutis Laxa with ProgeroidFeatures | AR | PYCR1 | Pyrroline-5-carboxylatereductase1 |
| Wiedemann–Rautenstrauch | AR | ||
| Werner Syndrome | AR | RECQL2 | WRN (DNA helicase) |
| Metageria (Acrogeria, Gottrontype) | AR |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madhuri, V.; Ramesh, S.; Raymond, R.; Selina, A.; Loganathan, L. Translational Research in Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Cell Therapy. Proceedings 2021, 72, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2021072003
Madhuri V, Ramesh S, Raymond R, Selina A, Loganathan L. Translational Research in Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Cell Therapy. Proceedings. 2021; 72(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2021072003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadhuri, Vrisha, Sowmya Ramesh, Renita Raymond, Agnes Selina, and Lakshmi Loganathan. 2021. "Translational Research in Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Cell Therapy" Proceedings 72, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2021072003
APA StyleMadhuri, V., Ramesh, S., Raymond, R., Selina, A., & Loganathan, L. (2021). Translational Research in Osteogenesis Imperfecta and Cell Therapy. Proceedings, 72(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2021072003




