Antimicrobial Activity of Aqueous Plant Extracts as Potential Natural Additives †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Microorganisms
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
2.4. Phenolic Fingerprinting and Quantification, and Statistical Analysis
2.5. Antimicrobial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
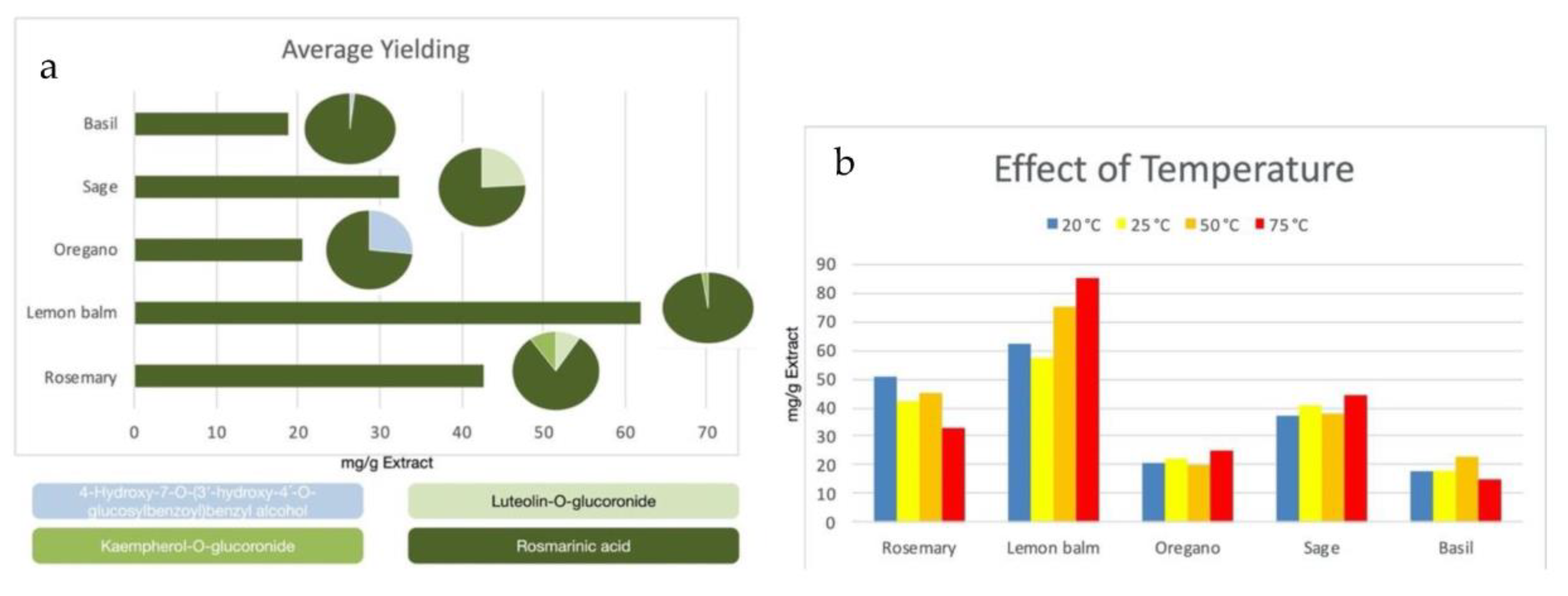
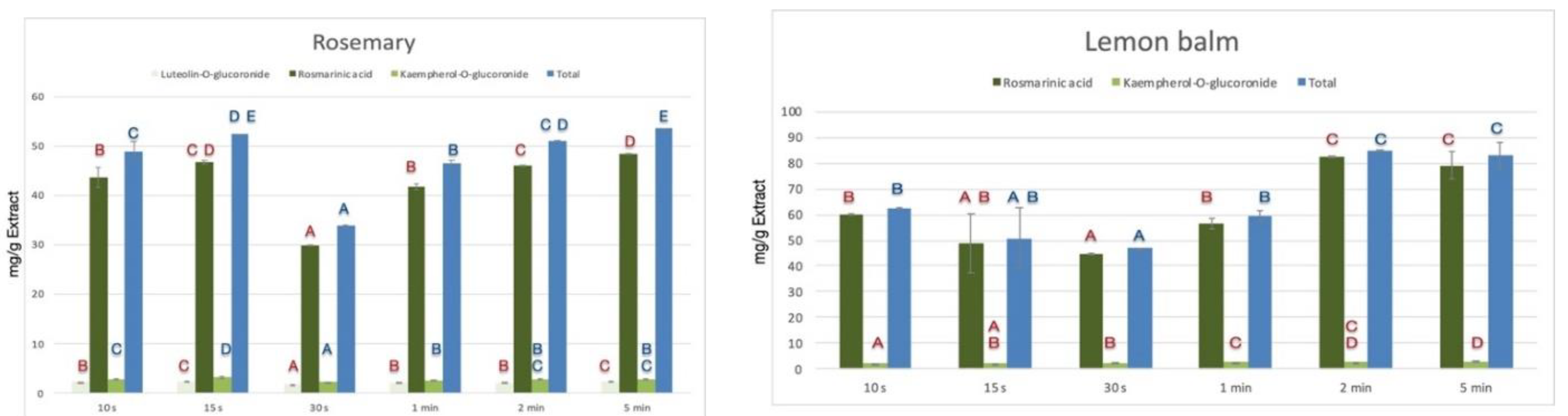
3.1. Extraction Optimization Studies
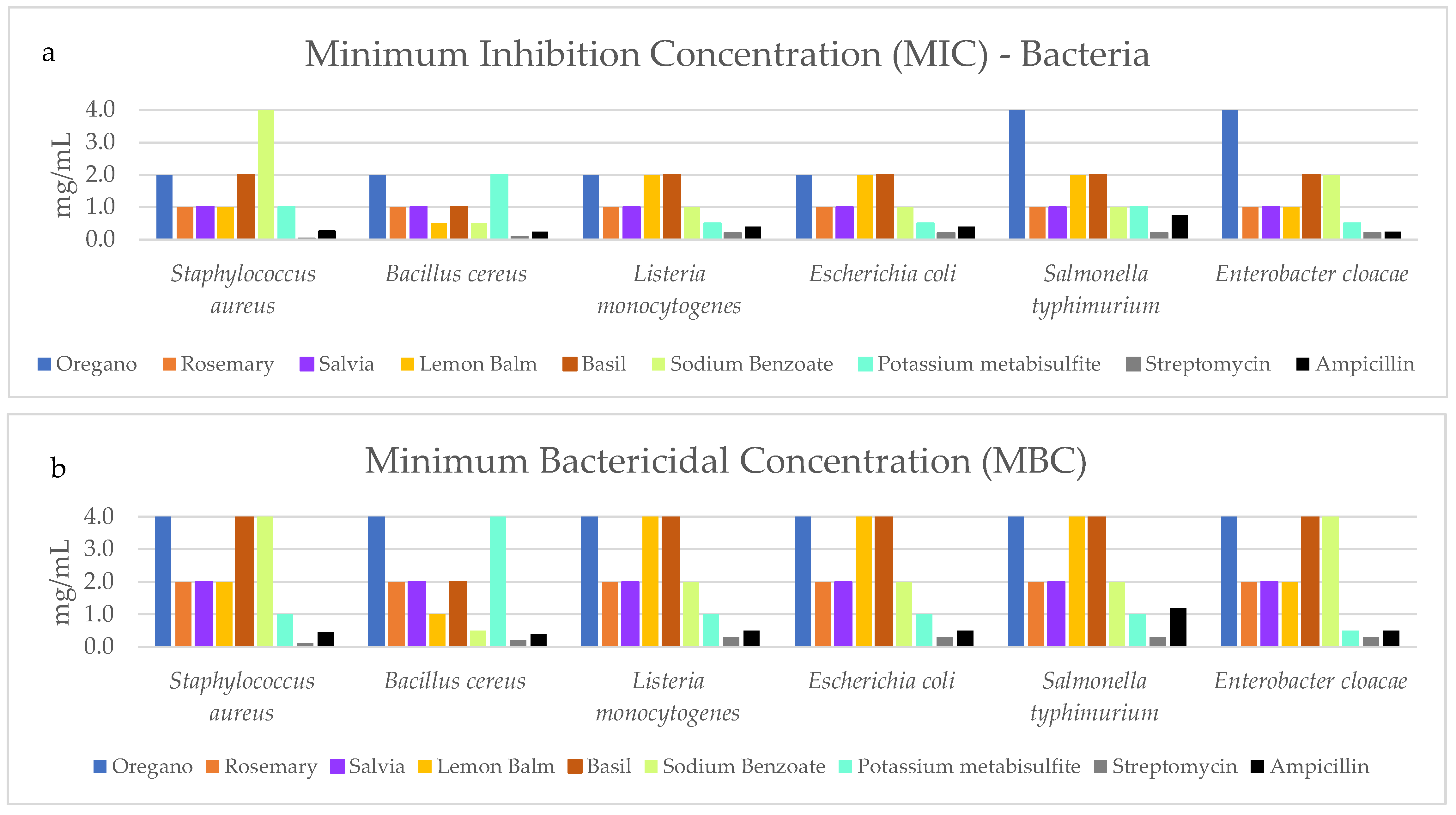
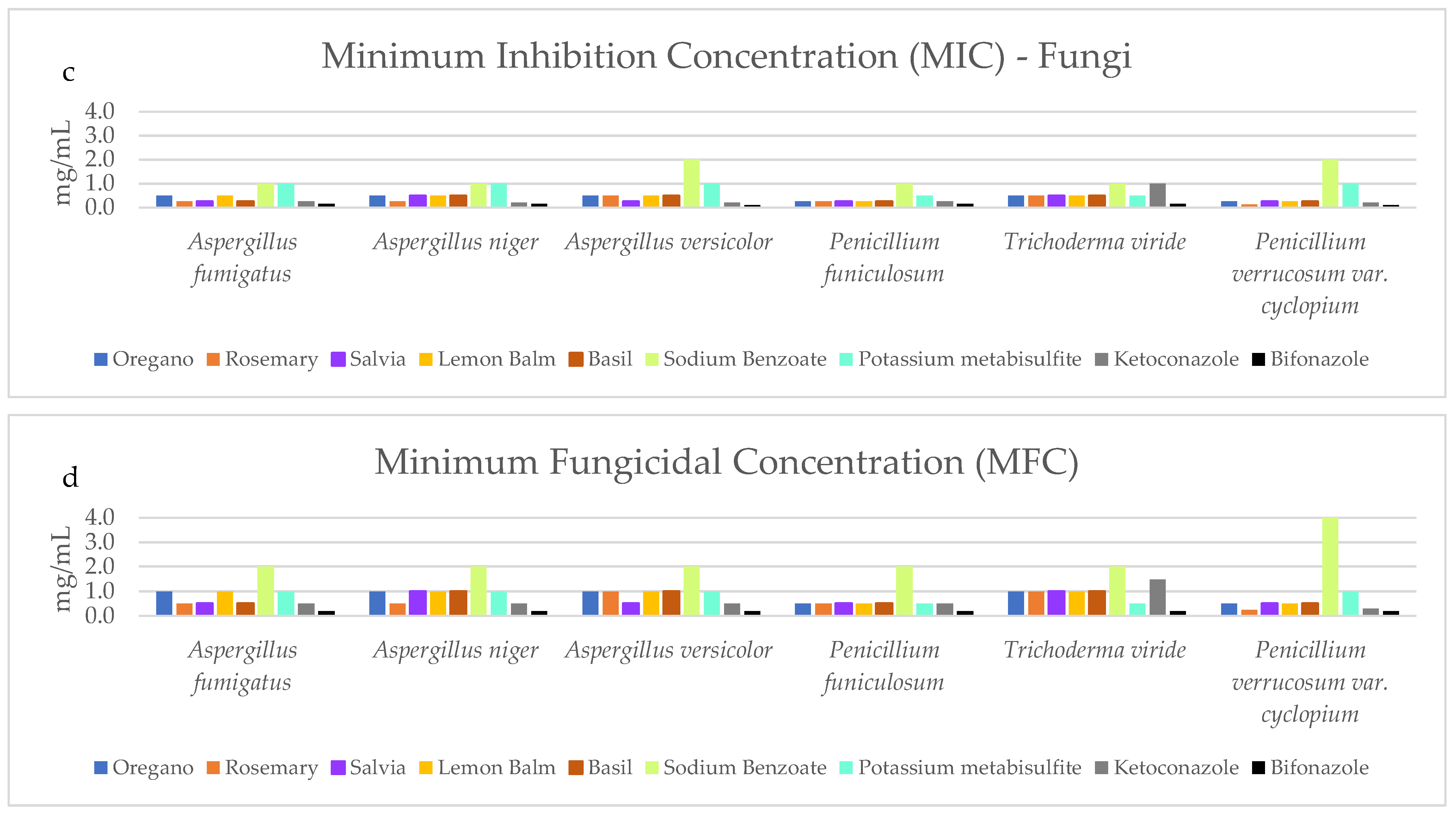
3.2. Antimicrobial Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carocho, M.; Morales, P.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Natural food additives: Quo vadis? Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, N.; Albuquerque, B.R.; Pereira, C.; Corrêa, R.C.G.; Lopes, C.B.; Calhelha, R.C.; Alves, M.J.; Berros, L.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. By-products of camu-camu [Myrciaria dúbia (Kunth) McVaugh] as promising sources of bioactive high added-value food ingredients: Functionalization of yogurts. Molecules 2020, 25, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso, F.S.; Caleja, C.; Calhelha, R.C.; Pires, T.C.S.; Alves, M.J.; Barros, L.; Genena, A.K.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Characterization and application of pomegranate epicarp extracts as functional ingredients in a typical Brazilian pastry product. Molecules 2020, 25, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soković, M.; Glamočlija, J.; Marin, P.D.; Brkić, D.; Griensven, J.L.D. Antibacterial effects of the essential oils of commonly consumed medicinal herbs using an in vitro model. Molecules 2010, 15, 7532–7546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, G.D.A.R.; Oliveira, A.E.; Conceição, E.C.; leles, M.I.G. Mutiresponse optimization of na extraction procedure of carnosol and rosmarinic and carnosic acids from rosemary. Food Chem. 2016, 211, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sik, B.; Hanczné, E.L.; Kapcsándi, V.; Ajtony, Z. Conventional and nonconventional extraction techniques for optimal extraction processes of rosmarinic acid and six Lamiaceae plants as determined by HPLC-DAD measurement. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 184, 113173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pedrosa, M.C.; Ueda, J.M.; Heleno, S.; Melgar, B.; Ivanov, M.; Soković, M.; Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R.; Barros, L. Antimicrobial Activity of Aqueous Plant Extracts as Potential Natural Additives. Proceedings 2021, 70, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07595
Pedrosa MC, Ueda JM, Heleno S, Melgar B, Ivanov M, Soković M, Carocho M, Ferreira ICFR, Barros L. Antimicrobial Activity of Aqueous Plant Extracts as Potential Natural Additives. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07595
Chicago/Turabian StylePedrosa, Mariana C., Jonata M. Ueda, Sandrina Heleno, Bruno Melgar, Marija Ivanov, Marina Soković, Marcio Carocho, Isabel C. F. R. Ferreira, and Lillian Barros. 2021. "Antimicrobial Activity of Aqueous Plant Extracts as Potential Natural Additives" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07595
APA StylePedrosa, M. C., Ueda, J. M., Heleno, S., Melgar, B., Ivanov, M., Soković, M., Carocho, M., Ferreira, I. C. F. R., & Barros, L. (2021). Antimicrobial Activity of Aqueous Plant Extracts as Potential Natural Additives. Proceedings, 70(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07595










