Anti-Listerial Effect of 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic Acid Esters Synthesized by Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microorganism
2.2. Materials
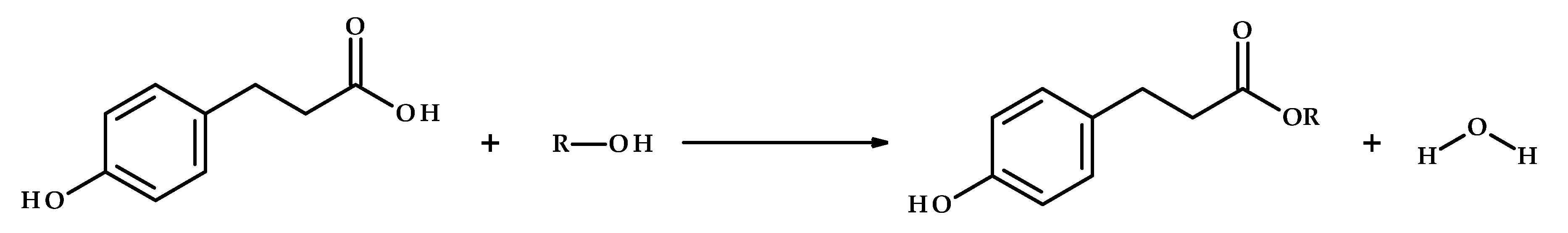
2.3. Esters Synthesis, Purification, and Identification
- Ethyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 1.23 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 2.59 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.12 (2H, q, J = 6.6 Hz), 5.18 (1H, s), 6.70–6.80 (2H, m), 7.00–7.10 (2H, m).
- Butyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.91 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 1.34 (2H, m), 1.58 (2H, m), 2.59 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.07 (2H, t, J = 6.6 Hz), 4.99 (1H, s), 6.70–6.79 (2H, m), 7.02–7.10 (2H, m).
- Hexyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.89 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 1.29 (6H, m), 1.60 (2H, m), 2.59 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.06 (2H, t, J = 6.6 Hz), 4.98 (1H, s), 6.70–6.80 (2H, m), 7.00–7.12 (2H, m).
- Octyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.88 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 1.28 (10H, m), 1.60 (2H, m), 2.59 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.05 (2H, t, J = 6.6 Hz), 4.97 (1H, s), 6.70–6.78 (2H, m), 7.02–7.10 (2H, m).
- Decyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 0.88 (3H, t, J = 7.3 Hz), 1.26 (14H, m), 1.61 (2H, m), 2.58 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 2.88 (2H, t, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.05 (2H, t, J = 6.6 Hz), 4.86 (1H, s), 6.70–6.78 (2H, m), 7.01–7.11 (2H, m).
2.4. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration
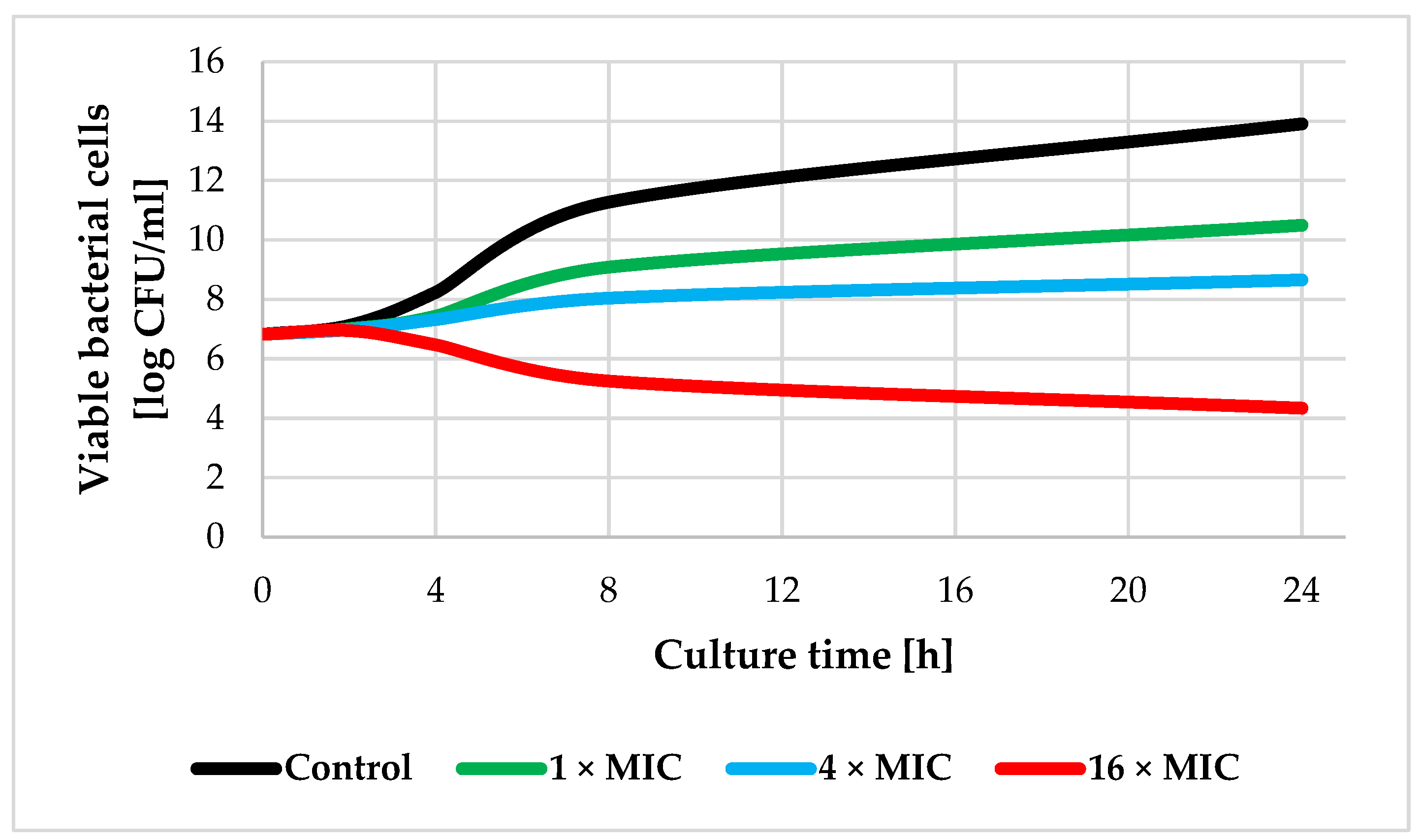
2.5. Time-Kill Assay
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuch, A.; Goc, A.; Belkiewicz, K.; Filipello, V.; Ronkiewicz, P.; Gołębiewska, A.; Wróbel, I.; Kiedrowska, M.; Waśko, I.; Hryniewicz, W.; et al. Molecular diversity and antimicrobial susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from invasive infections in Poland (1997–2013). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allerberger, F.; Wagner, M. Listeriosis: A resurgent foodborne infection. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Listeriosis—Annual Epidemiological Report for 2017. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/listeriosis-annual-epidemiological-report-2017.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Anastas, P.T.; Zimmerman, J.B. The United Nations sustainability goals: How can sustainable chemistry contribute? Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 13, 150–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieniuk, B.; Wołoszynowska, M.; Białecka-Florjańczyk, E.; Fabiszewska, A. Synthesis of Industrially Useful Phenolic Compounds Esters by Means of Biocatalysts Obtained Along with Waste Fish Oil Utilization. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standards. ISO 20776–1. Clinical laboratory Testing and In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems–Susceptibility Testing of Infectious Agents and Evaluation of Performance of Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test Devices–Part 1: Reference Method for Testing the In Vitro Activity of Antimicrobial Agents against Rapidly Growing Aerobic Bacteria Involved in Infectious Diseases; International Organization for Standards: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.G.; Bian, L.Q.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, R.R.; Shao, S.Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.W.; Dang, Y.L.; Ding, Y.; Sun, H. Multifunctional alkyl ferulate esters as potential food additives: Antibacterial activity and mode of action against Listeria monocytogenes and its application on American sturgeon caviar preservation. Food Control 2019, 96, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konate, K.; Hilou, A.; Mavoungou, J.F.; Lepengue, A.N.; Souza, A.; Barro, N.; Datte, J.Y.; M’Bachti, B.; Nacoulma, O.G. Antimicrobial activity of polyphenol-rich fractions from Sida alba L. (Malvaceae) against co-trimoxazol-resistant bacteria strains. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2012, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compound | MIC [mM] | MBC [mM] |
|---|---|---|
| 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic acid | 16 | 32 |
| Ethyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate | 8 | 16 |
| Butyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate | 2 | 4 |
| Hexyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate | 0.5 | 1 |
| Octyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate | 0.0625 | 0.25 |
| Decyl 4-hydroxyphenylpropanoate | 0.25 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zieniuk, B.; Białecka-Florjańczyk, E.; Fabiszewska, A. Anti-Listerial Effect of 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic Acid Esters Synthesized by Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Proceedings 2021, 70, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07700
Zieniuk B, Białecka-Florjańczyk E, Fabiszewska A. Anti-Listerial Effect of 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic Acid Esters Synthesized by Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07700
Chicago/Turabian StyleZieniuk, Bartłomiej, Ewa Białecka-Florjańczyk, and Agata Fabiszewska. 2021. "Anti-Listerial Effect of 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic Acid Esters Synthesized by Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07700
APA StyleZieniuk, B., Białecka-Florjańczyk, E., & Fabiszewska, A. (2021). Anti-Listerial Effect of 4-Hydroxyphenylpropanoic Acid Esters Synthesized by Lipase-Catalyzed Esterification. Proceedings, 70(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07700







