Kumquat (Fortunella margarita): A Good Alternative for the Ingestion of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
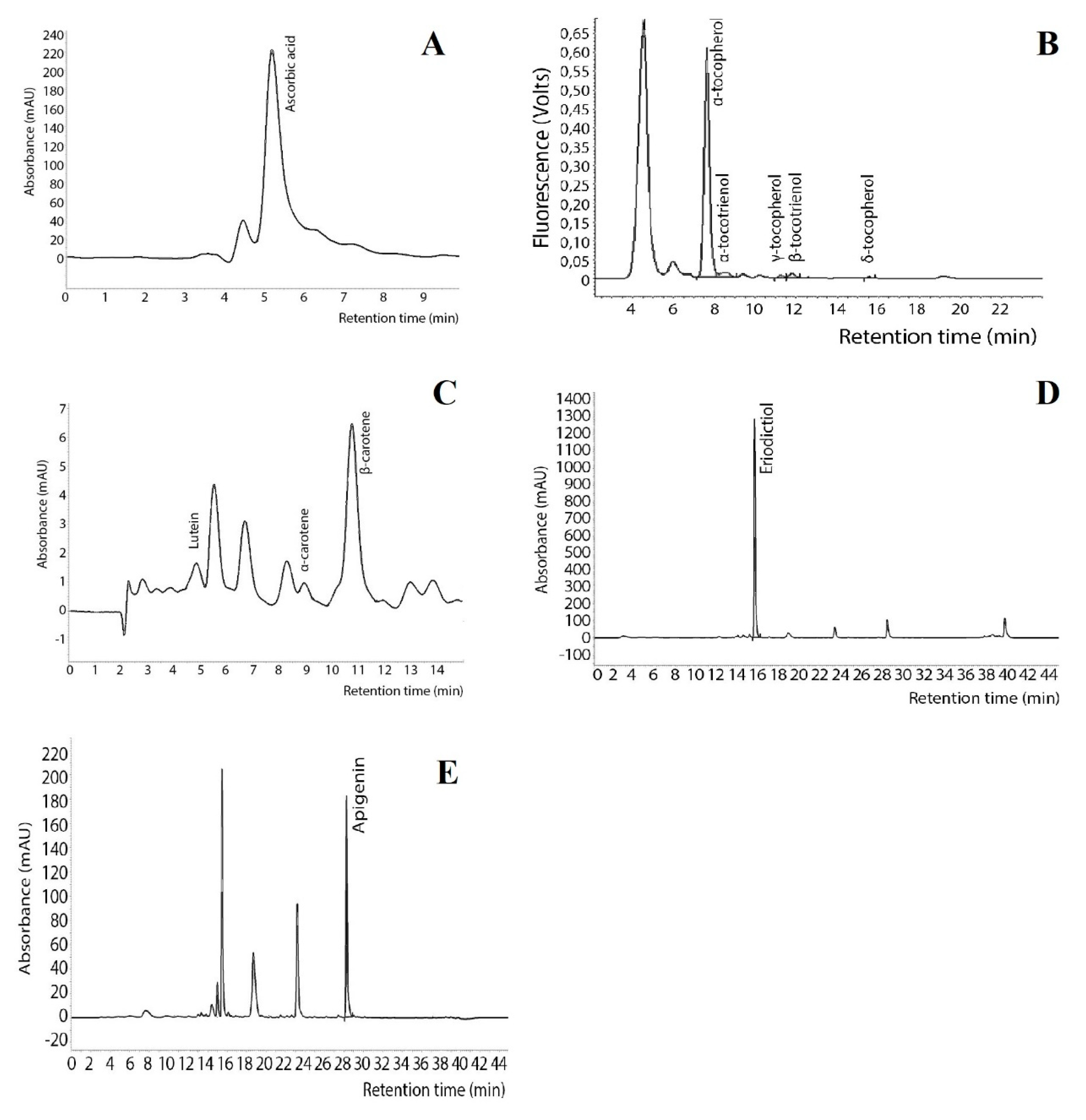
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA. Food Composition Databases. National Nutrient Database for Standard. 2017. Available online: https://ndb.nal.usda.gov/ndb/search (accessed on 15 March 2020).
- Donadio, L.C.; Mourão-Filho, F.A.A.; Moreira, C.S.; Centros de origem, distribuição geográfica das plantas cítricas e histórico na citricultura no Brasil. (Eds.). Citros; Campinas: Instituto Agronômico e Fundag; pp. 1–18.
- Koller, O.L.; Soprano, E. Principais cultivares cítricos. In Citricultura Catarinense, 1st ed.; Epagri: Florianópolis, Brazil, 2013; pp. 57–119. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaroto, J.; Raiher, A.P. Determinantes da renda e pobreza dos agricultores do Vale do Ribeira. Agric. Policy Rev. 2013, 22, 5–25. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Ku, Y.H. Quantitation of bioactive compounds in citrus fruits cultivated in Taiwan. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirra, M.; Palma, A.; D’aquino, S.; Angioni, A.; Minello, E.V.; Melis, M.; Cabras, P. Influence of postharvest hot water treatment on nutritional and functional properties of kumquat (Fortunella japonica Lour. Swingle Cv. Ovale) fruit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.R.; Diniz, A.B. Composição química da laranja kinkan e de frutas cítricas. DEMETRA Food Nutr. Health 2015, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, M.H.; Yang, K.M.; Huang, T.C.; Wu, M.L. Traditional small-size citrus from Taiwan: Essential oils, bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity. Medicines 2017, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Murthy, K.C.; Etlinger, M.; Mantur, S.M.; Patil, B.S. Radical scavenging capacities and inhibition of human prostate (LNCaP) cell proliferation by Fortunella margarita. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz. Normas Analíticas do Instituto Adolfo Lutz: Métodos Químicos e Físicos para Análises de Alimentos, 4th ed; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: Brasília, Brasil, 2005; Volume 1, 1018p. [Google Scholar]
- Official Methods of Analysis. Official Methods of Analysis of the AOAC International, 19th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, F.M.; Ribeiro, S.M.R.; Della Lucia, C.M.; Pinheiro-Sant’ana, H.M.; Stringheta, P.C. Optimization of methodology to analyze ascorbic and dehydroascorbic acid in vegetables. Quím. Nova 2009, 32, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro-Sant’ana, H.M.; Guinazi, M.; Da Silva Oliveira, D.; Della Lucia, C.M.; De Lazzari Reis, B.; Brandão, S.C.C. Method for simultaneous analysis of eight vitamin E isomers in various foods by high performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 8496–8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. Assessment of the provitamin A contents of foods—The Brazilian experience. J. Food Compos. Anal. 1996, 9, 196–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, L.; Seitz, L.M.; Rooney, W.L.; Rooney, L.W. Flavonid composition of red sorghum genotypes. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illescas, J.L.; Bacho, O.; Ferrer, S. Análisis de los principales frutos tropicales comercializados. Distrib. Y Consumo 2007, 95, 33–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ramful, D.; Tarnus, E.; Aruoma, O.I.; Bourdon, E.; Bahorun, T. Polyphenol composition, vitamin C content and antioxidant capacity of Mauritian citrus fruit pulps. Food Res. Int. 2011, 7, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, M.A.L.; Guidolin Canniatti-Brazaca, S. Quantificação de vitamina C e capacidade antioxidante de variedades cítricas. Ciência E Tecnol. De Aliment. 2010, 30, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.P.; Schroder, E.C.; Souza, E.L.S.; Scivittaro, W.B.; Castro, L.A.S.; Rocha, P.S.G. Laranjeiras sem acidez. Pelotas: Embrapa Clima Temperado. Embrapa Clima Temperado Documentos 2010, 298, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Kawaii, S.; Tomono, Y.; Katase, E.; Ogawa, K.; Yano, M. Quantitation of flavonoid constituents in Citrus fruits. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1999, 47, 3565–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.M.; López, B.G.C.; Diniz, S.N.; Antunes, A.A.; Garcia, D.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Marcucci, M.C. Quantification of flavonoids in brazilian orange peels and industrial orange juice processing wastes. Agric. Sci. 2017, 8, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.N.; Ho, C.T. Phenolic compounds and biological activities of small-size citrus: Kumquat and calamondin. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, M.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N.; Ashraf, M. Variations of antioxidant characteristics and mineral contents in pulp and peel of different apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) cultivars from Pakistan. Molecules 2012, 17, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Centesimal Composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture 1 (g·100 g−1) | Lipids 1 (g·100 g−1) | Total Ash 1 (g·100 g−1) | Protein 1 (g·100 g−1) | Carbohydrates 1 (g·100 g−1) |
| 76.79 ± 0.98 | 1.18 ± 0.06 | 3.66 ± 0.18 | 7.38 ± 0.39 | 5.23 ± 0.30 |
| Total fiber 2 (g·100 g−1) | Insoluble fiber 2 (g·100 g−1) | Soluble fiber 2 (g·100 g−1) | TEV 3 (kcal·100 g−1) | |
| 5.31 ± 0.06 | 3.28 ± 0.15 | 2.03 ± 0.09 | 61.06 | |
| Chemical Elements | Concentration (mg·100 g−1) |
|---|---|
| Phosphor | 16.94 ± 0.23 |
| Potassium | 163.16 ± 3.29 |
| Calcium | 64.99 ± 1.41 |
| Magnesium | 16.71 ± 0.40 |
| Sulfur | 13.92 ± 0.23 |
| Copper | 0.07 ± 0.01 |
| Iron | 0.30 ± 0.06 |
| Zinc | 0.09 ± 0.00 |
| Manganese | 0.10 ± 0.00 |
| Sodium | 2.63 ± 0.00 |
| Chrome | 0.01 ± 0.33 |
| Cadmium | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Aluminum | 0.57 ± 0.33 |
| Nickel | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Lead | 0.00 ± 0.00 |
| Components | Concentration |
|---|---|
| Vitamin C (mg·100 g−1) | |
| Ascorbic acid | 2.32 ± 44.24 |
| Vitamin E (µg·100 g−1) | |
| α-tocopherol | 569.00 ± 10.20 |
| α-tocotrienol | 35.76 ± 4.03 |
| β-tocopherol | nd |
| β-tocotrienol | 66.89 ± 39.93 |
| γ-tocopherol | 4.22 ± 0.13 |
| γ-tocotrienol | nd |
| δ-tocopherol | nd |
| δ-tocotrienol | nd |
| Total Vitamin E | 675.87 ± 54.29 |
| Carotenoids (µg·100 g−1) | - |
| α-carotene | 661.81 ± 22.76 |
| β-carotene | 447.74 ± 19.90 |
| Lutein | 173.60 ± 33.61 |
| Sum of carotenoids | 1283.15 |
| Vitamin A value (RAE 100 g−1) 1 | 129.77 |
| 3-desoxyanthocianidins (µg·100 g−1) | |
| Luteolinidin | nd |
| Apigeninidin | nd |
| 5-methoxy-luteolinidin | nd |
| 7-methoxy-apigeninidin | nd |
| Flavones (µg·100 g−1) | |
| Apigenin | 38,157.30 ± 531.00 |
| Luteolin | nd |
| Sum of flavones | 38,157.30 ± 531.00 |
| Flavanones (µg·100 g−1) | |
| Eriodictiol | 36,880.95 ±384.02 |
| Naringenin | nd |
| Sum of flavanones | 36,880.95 ± 384.02 |
| Total phenolics (mg GAE·100 g−1) | 98.55 ±1.93 |
| Antioxidant capacity (%) | 62.01 ± 3.41 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, C.S.e.; Anunciação, P.C.; Lucia, C.M.D.; Dôres, R.G.R.d.; Milagres, R.C.R.d.M.; Sant’Ana, H.M.P. Kumquat (Fortunella margarita): A Good Alternative for the Ingestion of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds. Proceedings 2021, 70, 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07590
Souza CSe, Anunciação PC, Lucia CMD, Dôres RGRd, Milagres RCRdM, Sant’Ana HMP. Kumquat (Fortunella margarita): A Good Alternative for the Ingestion of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds. Proceedings. 2021; 70(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07590
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Clarice Silva e, Pamella Cristine Anunciação, Ceres Mattos Della Lucia, Rosana Gonçalves Rodrigues das Dôres, Regina Célia Rodrigues de Miranda Milagres, and Helena Maria Pinheiro Sant’Ana. 2021. "Kumquat (Fortunella margarita): A Good Alternative for the Ingestion of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds" Proceedings 70, no. 1: 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07590
APA StyleSouza, C. S. e., Anunciação, P. C., Lucia, C. M. D., Dôres, R. G. R. d., Milagres, R. C. R. d. M., & Sant’Ana, H. M. P. (2021). Kumquat (Fortunella margarita): A Good Alternative for the Ingestion of Nutrients and Bioactive Compounds. Proceedings, 70(1), 105. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods_2020-07590





