Test for the Production and Assay of the Proteolytic Activities of Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea Isolated from Algerian Hypersaline Environments †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materiel and Methods
2.1. Samples and Strain Isolation
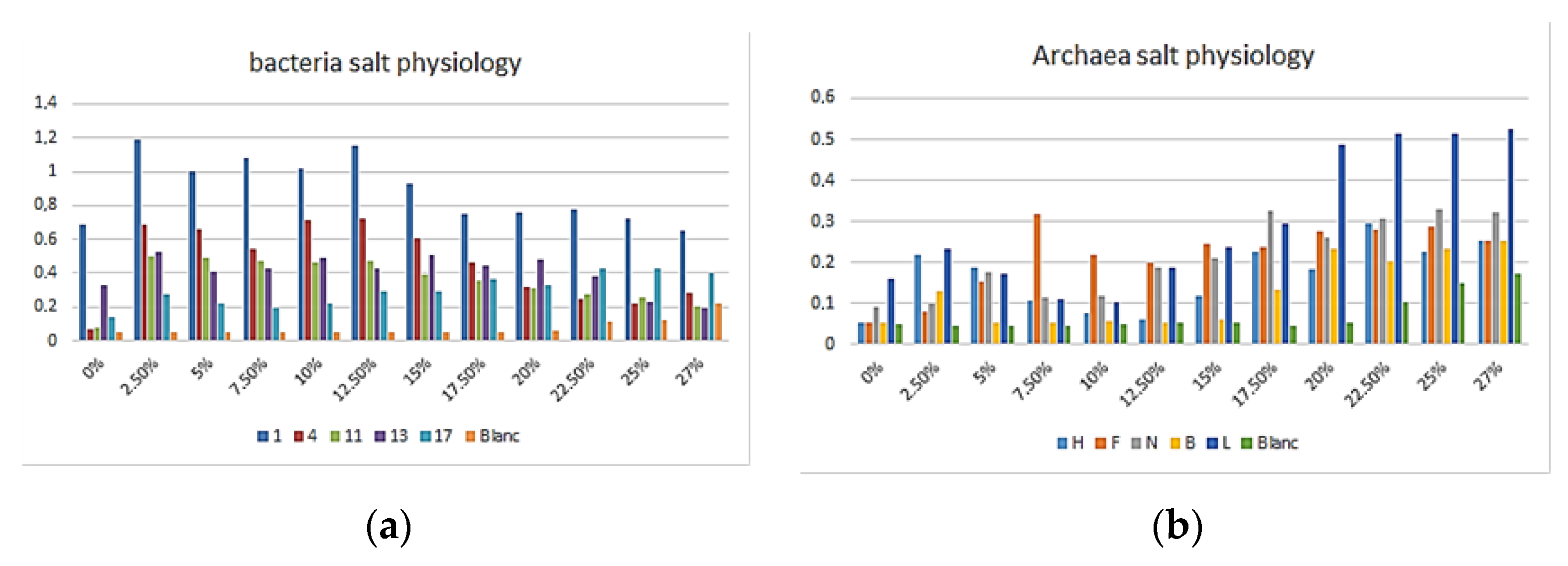
2.2. Morphology and Physiology
2.3. DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Gene Amplification and Strain Identification
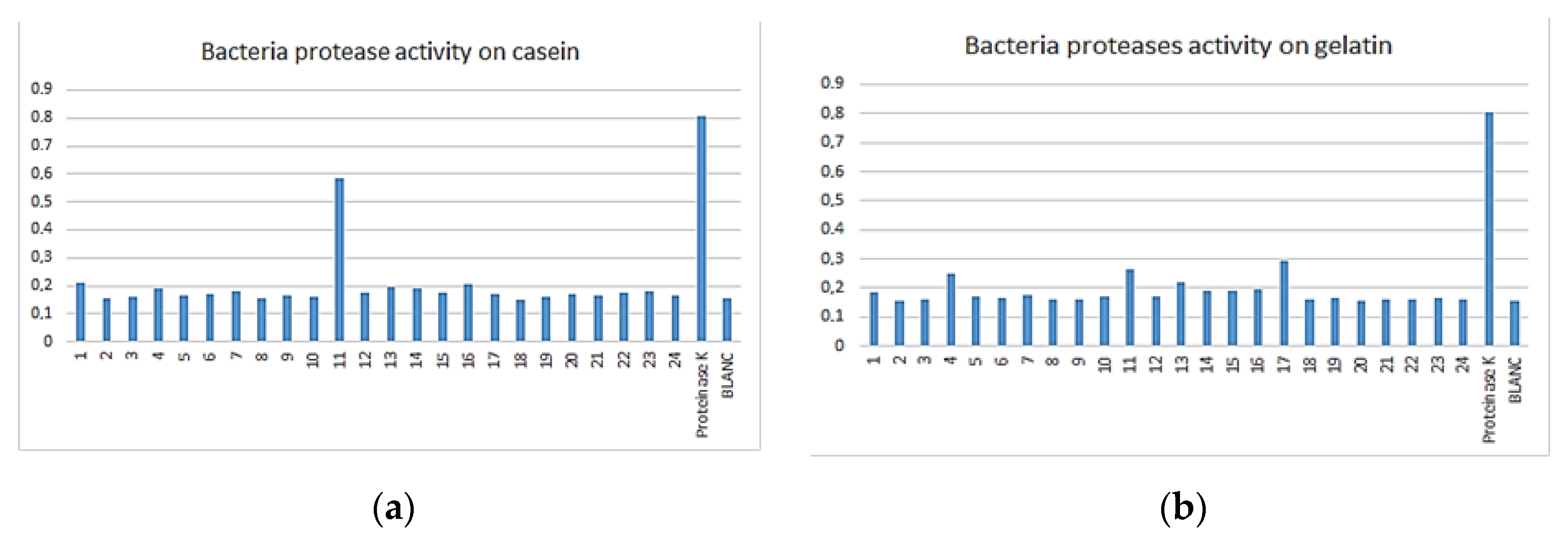
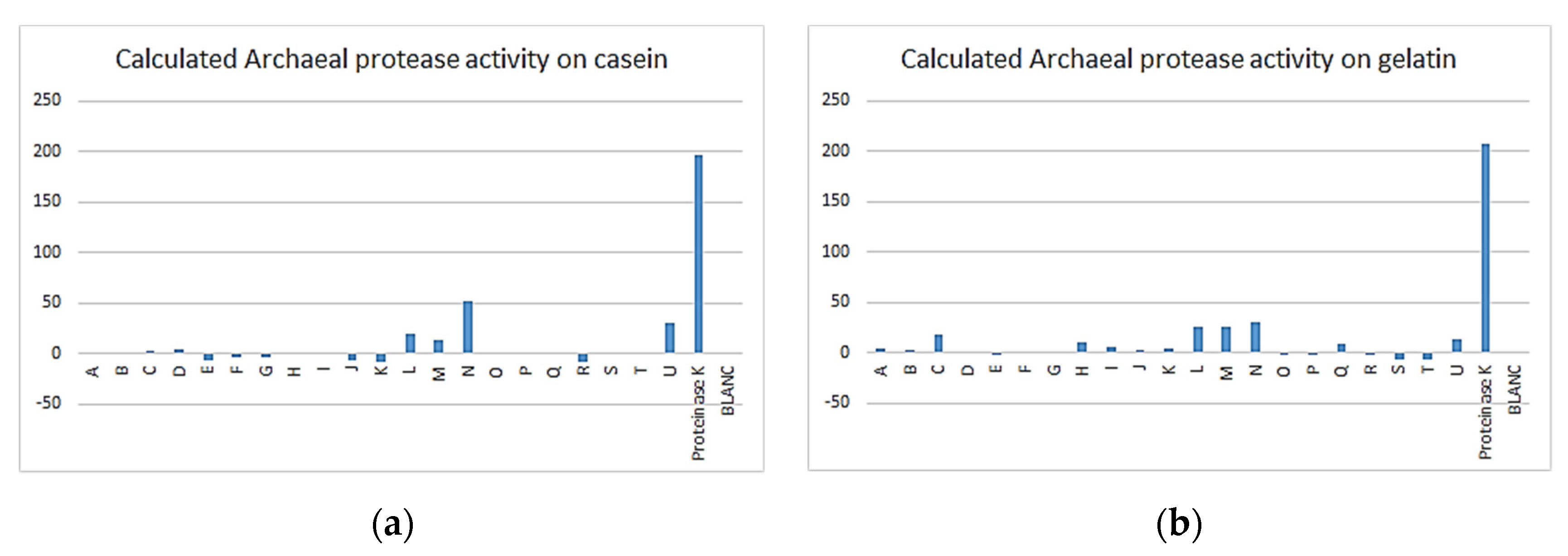
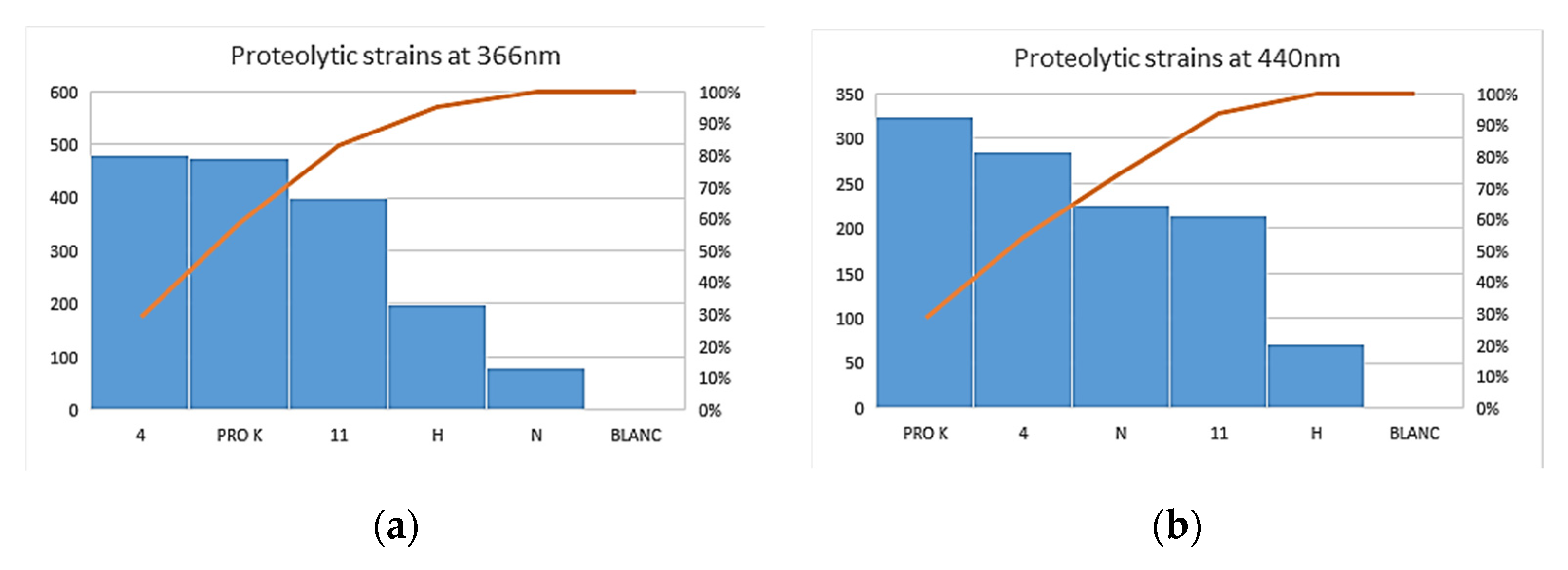
2.4. Enzymatic Assay
3. Results
3.1. Morphology and Physiology
3.2. Identification by 16S rRNA Gene Analysis
3.3. Enzymatic Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moreno, M.D.L.; Pérez, D.; García, M.T.; Mellado, E. Halophilic Bacteria as a Source of Novel Hydrolytic Enzymes. Life 2013, 3, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grégoire, P.; Fardeau, M.; Gauasco, S.; Bouanane, A.; Michotey, V.; Bonin, P.; Dubourg, K.; Cambard, J.; Ollivier, B. Les micro-organismes de l’extrême. Press. Therm. Climat. 2009, 146, 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Galinski, E.A.; Grant, W.D.; Oren, A.; Ventosa, A. Halophiles 2010: Life in Saline Environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6971–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coêlho, D.F.; Saturnino, T.P.; Fernandes, F.F.; Mazzola, P.G.; Silveira, E.; Tambourgi, E.B. Azocasein Substrate for Determination of Proteolytic Activity: Reexamining a Traditional Method Using Bromelain Samples. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri, H.; Askari, M.; Sarikhan, S. Purification and characterization of an extracellular haloalkaline serine protease from the moderately halophilic bacterium, Bacillus iranensis (X5B). Extremophiles 2015, 20, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttall, S.; Bath, C.; Pfeiffer, M.; Santos, F.; Eichler, J.; Mcalpine, T. The Halohandbook. Media, March, 1–144. 2008. Available online: http://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&btnG=Search&q=intitle:The+Halohandbook#0 (accessed on 24 April 2017).
- Dammak, D.F.; Smaoui, S.M.; Ghanmi, F.; Boujelben, I.; Maalej, S. Characterization of halo-alkaline and thermostable protease from Halorubrum ezzemoulense strain ETR14 isolated from Sfax solar saltern in Tunisia. J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cojoc, R.; Merciu, S.; Popescu, G.; Dumitru, L.; Enache, M.; Kamekura, M.; Enache, M. Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes of halophilic bacteria isolated from a subterranean rock salt crystal. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 14, 4658–4664. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, C.; González, C. Method for Simultaneous Detection of Proteinase and Esterase Activities in Extremely Halophilic Bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 1972, 24, 516–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomri, M.A.; Rico-Díaz, A.; Escuder-Rodríguez, J.-J.; Khaldi, T.E.M.; González-Siso, M.-I.; Kharroub, K. Production and Characterization of an Extracellular Acid Protease from Thermophilic Brevibacillus sp. OA30 Isolated from an Algerian Hot Spring. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siroosi, M.; Amoozegar, M.A.; Khajeh, K.; Fazeli, M.; Rezaei, M.H. Purification and characterization of a novel extracellular halophilic and organic solvent-tolerant amylopullulanase from the haloarchaeon, Halorubrum sp. strain Ha25. Extremophiles 2014, 18, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galkiewicz, J.P.; Kellogg, C.A. Cross-Kingdom Amplification Using Bacteria-Specific Primers: Complications for Studies of Coral Microbial Ecology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 7828–7831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guendouze, A.; Plener, L.; Bzdrenga, J.; Jacquet, P.; Rémy, B.; Elias, M.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Daudé, D.; Chabrière, E. Effect of Quorum Quenching Lactonase in Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Comparison with Quorum Sensing Inhibitors. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brock, F.M.; Forsberg, C.W.; Buchanan-Smith, J.G. Proteolytic activity of rumen microorganisms and effects of proteinase inhibitors. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1982, 44, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuprom, J.; Bovornreungroj, P.; Ahmad, M.; Kantachote, D.; Dueramae, S. Approach toward enhancement of halophilic protease production by Halobacterium sp. strain LBU50301 using statistical design response surface methodology. Biotechnol. Rep. 2016, 10, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanekar, P.P.; Kanekar, S.P.; Kelkar, A.S.; Dhakephalkar, P.K. Halophiles—Taxonomy, Diversity, Physiology and Applications. In Microorganisms in Environmental Management: Microbes and Environment; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 9789400722, pp. 1–819. [Google Scholar]
- De la Halba, R.R.; Sánchez-porro, C.; Marquez, M.C.; Ventosa, A. Extremophiles Halophiles. In Extremophiles Handbook; Horikochi, K., Ed.; Springer Science+Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Karray, F.; Ben Abdallah, M.; Kallel, N.; Hamza, M.; Fakhfakh, M.; Sayadi, S. Extracellular hydrolytic enzymes produced by halophilic bacteria and archaea isolated from hypersaline lake. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 45, 1297–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gram | Cell form | Protease | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Cocci | Rod | Coccobacilli | Casein | Gelatin | |
| Bacteria | 8 | 16 | 3 | 16 | 5 | 16 | 23 |
| Archaea | 1 | 17 | 12 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 21 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benmebarek, H.; Escuder-Rodríguez, J.-J.; González-Siso, M.-I.; Karroub, K. Test for the Production and Assay of the Proteolytic Activities of Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea Isolated from Algerian Hypersaline Environments. Proceedings 2020, 66, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066012
Benmebarek H, Escuder-Rodríguez J-J, González-Siso M-I, Karroub K. Test for the Production and Assay of the Proteolytic Activities of Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea Isolated from Algerian Hypersaline Environments. Proceedings. 2020; 66(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066012
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenmebarek, Hania, Juan-José Escuder-Rodríguez, María-Isabel González-Siso, and Karima Karroub. 2020. "Test for the Production and Assay of the Proteolytic Activities of Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea Isolated from Algerian Hypersaline Environments" Proceedings 66, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066012
APA StyleBenmebarek, H., Escuder-Rodríguez, J.-J., González-Siso, M.-I., & Karroub, K. (2020). Test for the Production and Assay of the Proteolytic Activities of Halophilic Bacteria and Archaea Isolated from Algerian Hypersaline Environments. Proceedings, 66(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2020066012





